The Effects of Inoculation with Rhizosphere Phosphate-Solubilizing Bacteria on the Growth and Physiology of Reaumuria soongorica Seedlings Under NaCl Stress
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Materials
2.1.1. Overview of the Study Area and Soil Sample Collection
2.1.2. Testing Material
2.2. Determination Indexes and Methods
2.2.1. Isolation and Identification of Phosphate-Solubilizing Bacteria
2.2.2. Functional Characteristics of Phosphate-Solubilizing Bacteria
2.2.3. Pot Experiments
2.3. Data Statistics and Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Determination of Phosphorus-Solubilizing Capacity of Phosphate-Solubilizing Bacteria
3.1.1. Phosphate-Solubilizing Ability of Different Strains
3.1.2. Growth Dynamics of Phosphate-Solubilizing Bacteria During Phosphate-Solubilizing Process
3.2. Effect of Phosphate-Solubilizing Bacteria on Growth of R. soongorica
3.3. Effect of Phosphate-Solubilizing Bacteria on Antioxidant Enzyme Activity of R. soongorica Seedlings
3.4. Effect of Phosphate-Solubilizing Bacteria on Osmotic Adjustment Substance of R. soongorica Seedlings
3.5. Effects of Phosphate-Solubilizing Bacteria on Phosphorus Content in Leaves and Rhizosphere Soil of R. soongorica Seedlings
3.6. Comprehensive Evaluation of Effects of Different Phosphate-Solubilizing Bacteria on Salt Tolerance of R. soongorica Seedlings Under NaCl Stress
4. Discussion
4.1. Functional Characteristics of Rhizosphere Phosphorus-Solubilizing Bacteria
4.2. Effects of Phosphate-Solubilizing Bacteria on Growth and Physiological Characteristics of R. soongorica Seedlings Under NaCl Stress
4.3. Effects of Rhizosphere Phosphate-Solubilizing Bacteria on Phosphorus Content of R. soongorica Seedlings Under NaCl Stress
4.4. Comprehensive Evaluation of Effect of Rhizosphere Phosphate-Solubilizing Bacteria on Salt Tolerance of R. soongorica Seedlings Under NaCl Stress
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Su, T.; Wang, X.; Ning, S.; Sheng, J.; Jiang, P.; Gao, S.; Yang, Q.; Zhou, Z.; Cui, H.; Li, Z. Enhancing Soil Salinity Evaluation Accuracy in Arid Regions: An Integrated Spatiotemporal Data Fusion and AI Model Approach for Arable Lands. Land 2024, 13, 1837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potestio, S.; Giannelli, G.; Degola, F.; Vamerali, T.; Fragni, R.; Cocconi, E.; Sandei, L.; Visioli, G. Salt stress mitigation and improvement in fruit nutritional characteristics of tomato plants: New opportunities from the exploitation of a halotorelant Agrobacterium strain. Plant Stress 2024, 13, 100558. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Ping, Y.; Li, K.; Qi, D.-D.; Song, F.-Q. Label-free quantitative proteomics of arbuscular mycorrhizal Elaeagnus angustifolia seedlings provides insights into salt-stress tolerance mechanisms. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 13, 1098260. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Huqail, A.A.; Aref, N.M.A.; Khan, F.; Sobhy, S.E.; Hafez, E.E.; Khalifa, A.M.; Saad-Allah, K.M. Azolla filiculoides extract improved salt tolerance in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) is associated with prompting osmostasis, antioxidant potential and stress-interrelated genes. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 11100. [Google Scholar]
- Banzouzi Bouzika, V.J.; Chong, P.-f.; Jia, X.-y.; Lu, W.-t.; Tin, Y.-l. Effects of foliar-spraying nitric oxide on the carbon metabolism enzymes activities and nutrients in leaves and roots of Reaumuria soongorica (pall.) maxim seedlings under NaCl stress. Plant Stress 2022, 5, 100096. [Google Scholar]
- Teles, E.A.P.; Xavier, J.F.; Arcênio, F.S.; Amaya, R.L.; Gonçalves, J.V.S.; Rouws, L.F.M.; Zonta, E.; Coelho, I.S. Characterization and evaluation of potential halotolerant phosphate solubilizing bacteria from Salicornia fruticosa rhizosphere. Front. Plant Sci. 2024, 14, 1324056. [Google Scholar]
- Bakki, M.; Banane, B.; Marhane, O.; Esmaeel, Q.; Hatimi, A.; Barka, E.A.; Azim, K.; Bouizgarne, B. Phosphate solubilizing Pseudomonas and Bacillus combined with rock phosphates promoting tomato growth and reducing bacterial canker disease. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1289466. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, Y.; Yuan, J.; Wang, G.; Hu, Z.; Luo, W.; Zhao, X.; Guo, Y.; Ji, X.; Hu, W.; Li, M. Phosphate-solubilizing bacteria improve the antioxidant enzyme activity of Potamogeton crispus L. and enhance the remediation effect on Cd-contaminated sediment. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 470, 134305. [Google Scholar]
- Saranya, K.; Sundaramanickam, A.; Manupoori, S.; Kanth, S.V. Screening of multi-faceted phosphate-solubilising bacterium from seagrass meadow and their plant growth promotion under saline stress condition. Microbiol. Res. 2022, 261, 127080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Yang, W.; Kou, J.; Li, Q.; Liu, J.; Chi, L.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Q.; Yu, Y. Impacts of phosphate-solubilizing bacterium strain MWP-1 on vegetation growth, soil characteristics, and microbial communities in the Muli coal mining area, China. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1500070. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Qin, Q.; Pan, J.; Sun, L.; Sun, Y.; Xue, Y.; Song, K. Transcriptome analysis in roots and leaves of wheat seedlings in response to low-phosphorus stress. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 19802. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y. Effects of High Salt Stress on Soil Carbon, Nitrogen, and Phosphorus Metabolism and Its Microbiological Mechanism; Northwest Agriculture and Forestry University: Xi’an, China, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.J. Effect of Low Phosphorus on Light Energy Utilization of Sorghum Bicolor ‘Dochna’ Under Salt Stress; Shandong Normal University: Jinan, China, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Ibeas, M.A.; Salinas-Grenet, H.; Johnson, N.R.; Pérez-Díaz, J.; Vidal, E.A.; Alvarez, J.M.; Estevez, J.M. Filling the gaps on root hair development under salt stress and phosphate starvation using current evidence coupled with a meta-analysis approach. Plant Physiol. 2024, 196, 2140–2149. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhao, L.; Su, R.; He, H. Effects of soil salt stress on phosphorus utilization of Medicago sativa. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2019, 38, 414–422. [Google Scholar]
- He, F.-L.; Bao, A.-K.; Wang, S.-M.; Jin, H.-X. NaCl stimulates growth and alleviates drought stress in the salt-secreting xerophyte Reaumuria soongorica. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2019, 162, 433–443. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Chong, P.; Yan, S.; Liu, Z.; Bao, X.; Tan, B. Transcriptome and Proteome Association Analysis to Screen Candidate Genes Related to Salt Tolerance in Reaumuria soongorica Leaves under Salt Stress. Plants 2023, 12, 3542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, S.; Chong, P.; Zhao, M.; Liu, H. Physiological response and proteomics analysis of Reaumuria soongorica under salt stress. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 2539. [Google Scholar]
- Shan, L.; Yang, C.; Li, Y.; Duan, Y.; Geng, D.; Li, Z.; Zhang, R.; Duan, G.; Васильевич, Ж.А. Effects of drought stress on root physiological traits and root biomass allocation of Reaumuria soongorica. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2015, 35, 155–159. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.; Zhao, J.; Yang, J.; Xie, J.; Sun, Z. Feature Selection and Regression Models for Multisource Data-Based Soil Salinity Prediction: A Case Study of Minqin Oasis in Arid China. Land 2024, 13, 877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, S.; Shao, M.; Ding, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Su, C. The Process of Soil Carbon Sequestration in Different Ecological Zones of Qingtu Lake in the Arid–Semi-Arid Region of Western China. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 2122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Q.; Tang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Shao, Y.; Wu, W.; Wang, J.; Ding, X.; Han, X.; Bilal, M. Isolation and characterization of phosphate-solubilizing bacteria from rhizosphere of poplar on road verge and their antagonistic potential against various phytopathogens. BMC Microbiol. 2023, 23, 221. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Chong, P.; Liu, Z.; Bao, X.; Tan, B. Exogenous hydrogen sulfide improves salt stress tolerance of Reaumuria soongorica seedlings by regulating active oxygen metabolism. PeerJ 2023, 11, e15881. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, J.F. Plant Physiology Experiment Instruction; Higher Education Press: Beijing, China, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Bao, S.D. Soil Agrochemical Analysis; China Agriculture Press: Beijing, China, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Janati, W.; Mikou, K.; El Ghadraoui, L.; Errachidi, F. Growth stimulation of two legumes (Vicia faba and Pisum sativum) using phosphate-solubilizing bacteria inoculation. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1212702. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, L.; Cai, B. Phosphate-Solubilizing Bacteria: Advances in Their Physiology, Molecular Mechanisms and Microbial Community Effects. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 2904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.L.; Wang, D.L.; Zhou, Q.; Zhang, T.; Li, M.Y. Screening and growth-promoting characteristics of phosphate-solubilizing strains from the rhizosphere of Phragmites australis in saline-alkali soil. Jiangsu J. Agric. 2024, 40, 64–74. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Shi, M.; Cao, Z.; Lu, Q.; Yang, T.; Fan, Y.; Wei, Z. Effect of organic acids production and bacterial community on the possible mechanism of phosphorus solubilization during composting with enriched phosphate-solubilizing bacteria inoculation. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 247, 190–199. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Luo, Y.H.; Ke, Z.B.; Zhong, C.; Chen, Y.J. Isolation, identification, and characteristics of phosphate-solubilizing bacteria from mangrove soil. China Environ. Sci. 2020, 40, 2664–2673. [Google Scholar]
- Khourchi, S.; Elhaissoufi, W.; Ibnyasser, A.; Haddine, M.; Ghani, R.; Zeroual, Y.; Delaplace, P.; Bargaz, A. Integrated use of polyphosphate and P-solubilizing bacteria enhanced P use efficiency and growth performance of durum wheat. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1211397. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, Y.; Narayanan, M.; Shi, X.; Chen, X.; Li, Z.; Ma, Y. Phosphate-solubilizing bacteria: Their agroecological function and optimistic application for enhancing agro-productivity. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 901, 166468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nurrahma, A.H.I.; Harsonowati, W.; Putri, H.H.; Iqbal, R. Current Research Trends in Endophytic Fungi Modulating Plant Adaptation to Climate Change-associated Soil Salinity Stress. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2024, 24, 6446–6466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wael, D.; El-Amier, Y.; Saber, W.I.A.; Elsayed, A. Plant-associated halotolerant bacteria improving growth of Vicia faba L. Mariout-2 under salinity conditions. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 16737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahimi Chegeni, A.; Fatehi, F.; Ebrahimi, A.; Maleki, M. Phosphate-Solubilizing Bacteria Modulated Salinity Stress in the Presence of Phosphorous through Improving Growth, Biochemical Properties, and Gene Expression of Chickpea (Cicer arientnum L.). J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2023, 23, 4450–4462. [Google Scholar]
- AbuQamar, S.F.; El-Saadony, M.T.; Saad, A.M.; Desoky, E.-S.M.; Elrys, A.S.; El-Mageed, T.A.A.; Semida, W.M.; Abdelkhalik, A.; Mosa, W.F.A.; Al Kafaas, S.S.; et al. Halotolerant plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria improve soil fertility and plant salinity tolerance for sustainable agriculture—A review. Plant Stress 2024, 12, 100482. [Google Scholar]
- Siddika, A.; Rashid, A.A.; Khan, S.N.; Khatun, A.; Karim, M.M.; Prasad, P.V.V.; Hasanuzzaman, M. Harnessing plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria, Bacillus subtilis and B. aryabhattai to combat salt stress in rice: A study on the regulation of antioxidant defense, ion homeostasis, and photosynthetic parameters. Front. Plant Sci. 2024, 15, 1419764. [Google Scholar]
- Su, R.; Zhang, Z.; Chang, C.; Peng, Q.; Cheng, X.; Pang, J.; He, H.; Lambers, H. Interactive effects of phosphorus fertilization and salinity on plant growth, phosphorus and sodium status, and tartrate exudation by roots of two alfalfa cultivars. Ann. Bot. 2022, 129, 53–64. [Google Scholar]
- Koczorski, P.; Furtado, B.U.; Baum, C.; Weih, M.; Ingvarsson, P.; Hulisz, P.; Hrynkiewicz, K. Large effect of phosphate-solubilizing bacteria on the growth and gene expression of Salix spp. at low phosphorus levels. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1218617. [Google Scholar]
- Khosravi, M.; Heydari, M.; Alikhani, A.H. Mitigating negative impacts of drought on oak seedlings performances through plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria. J. Environ. Manag. 2025, 375, 124163. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, S.; Chong, P.F.; Zhao, M. Effect of salt stress on the photosynthetic characteristics and endogenous hormones, and: A comprehensive evaluation of salt tolerance in Reaumuria soongorica seedlings. Plant Signal. Behav. 2022, 17, 2031782. [Google Scholar]
- Gan, H.H.; Gong, S.; Liu, H.; Chu, J.M. Evaluation of salt tolerance of seedlings of three afforestation tree species in China and screening of indicators. For. Sci. Res. 2024, 37, 156–168. [Google Scholar]

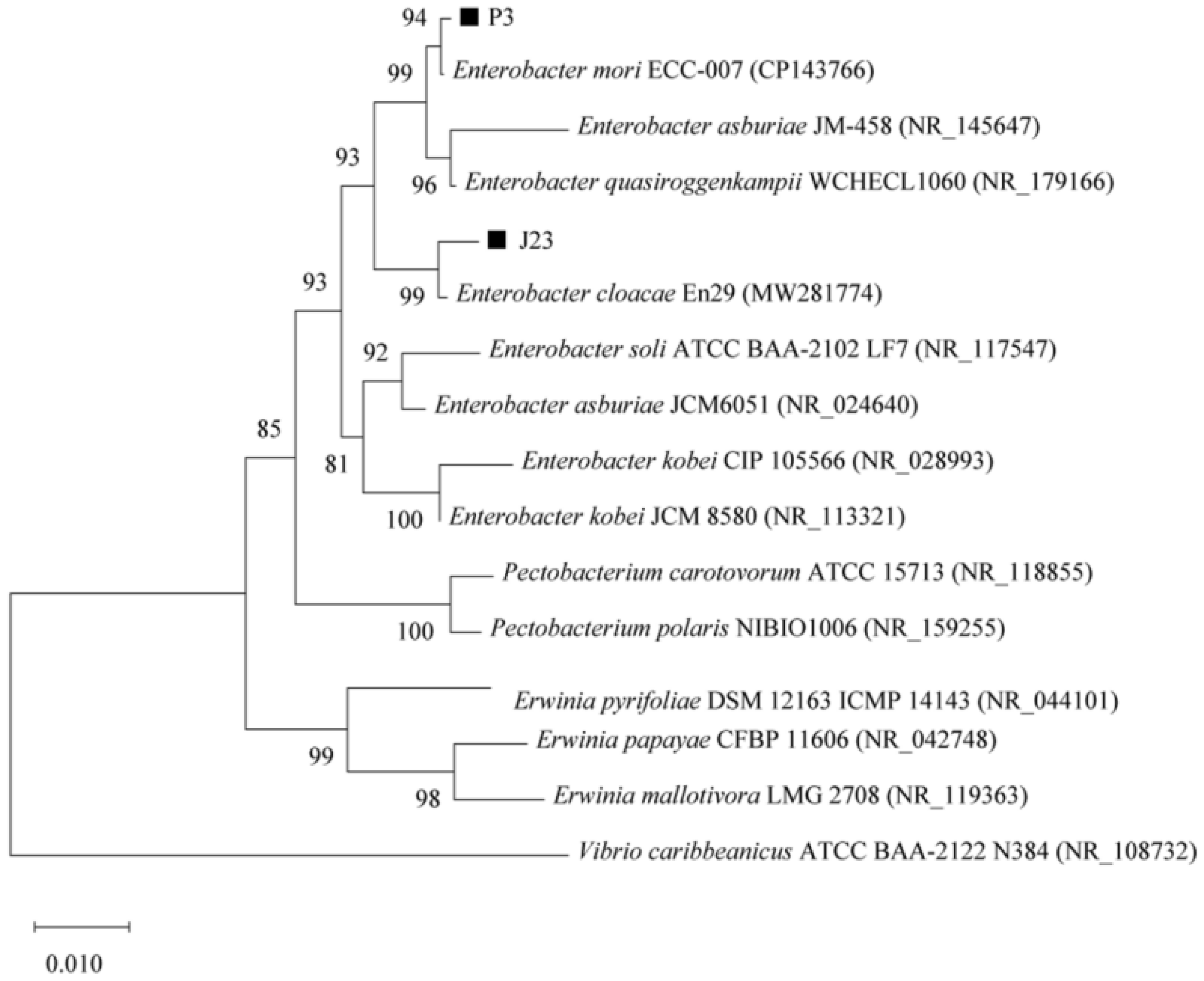
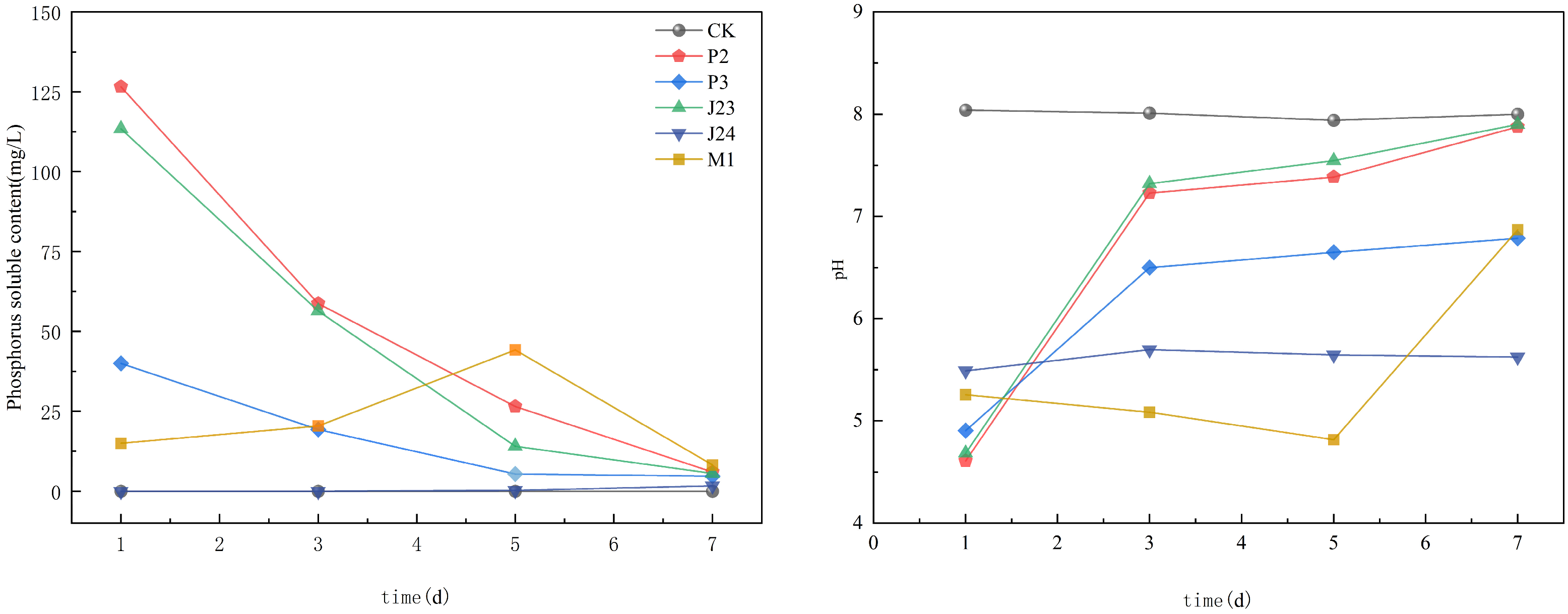
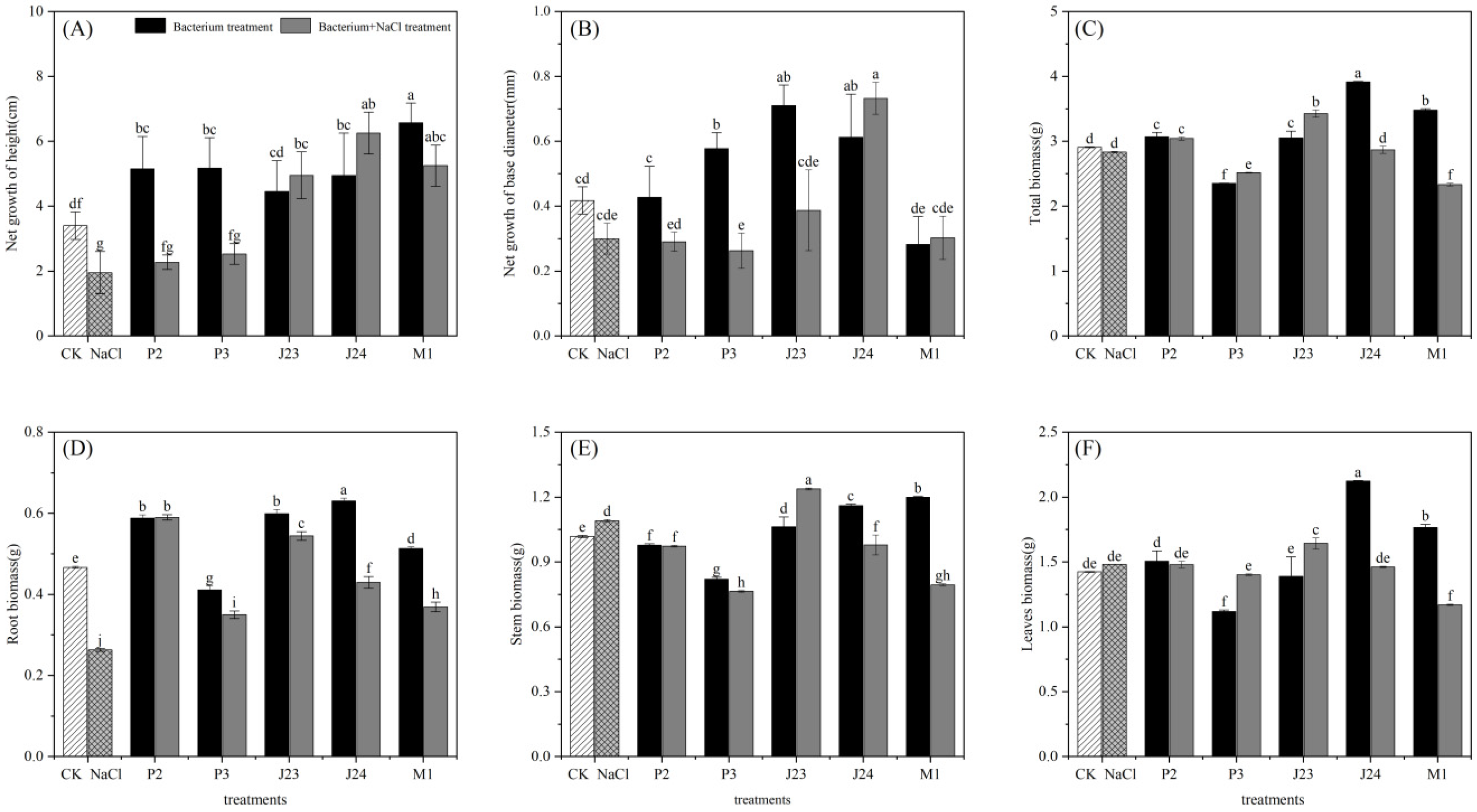
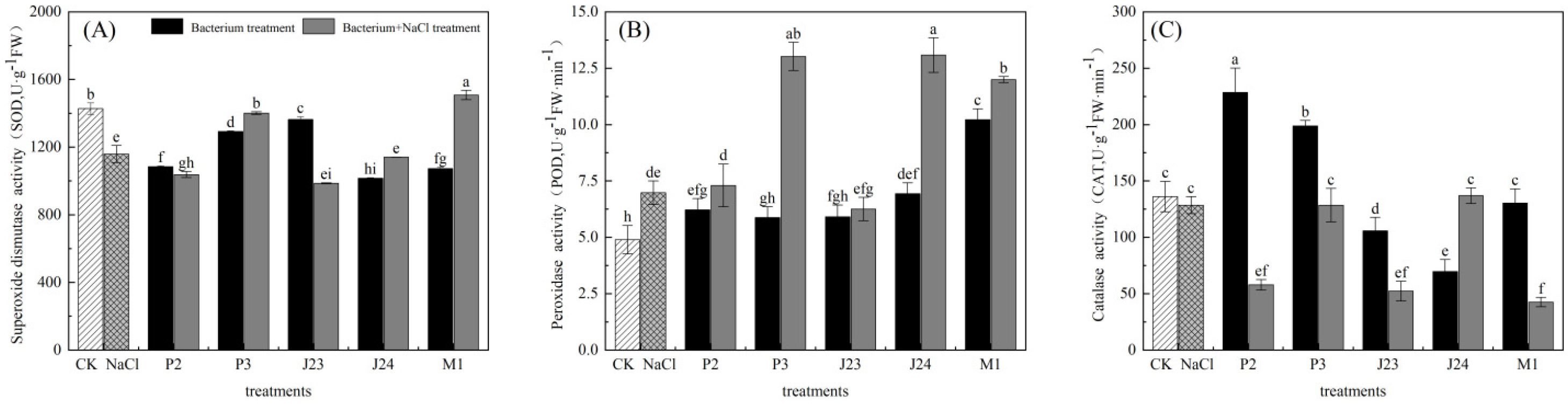
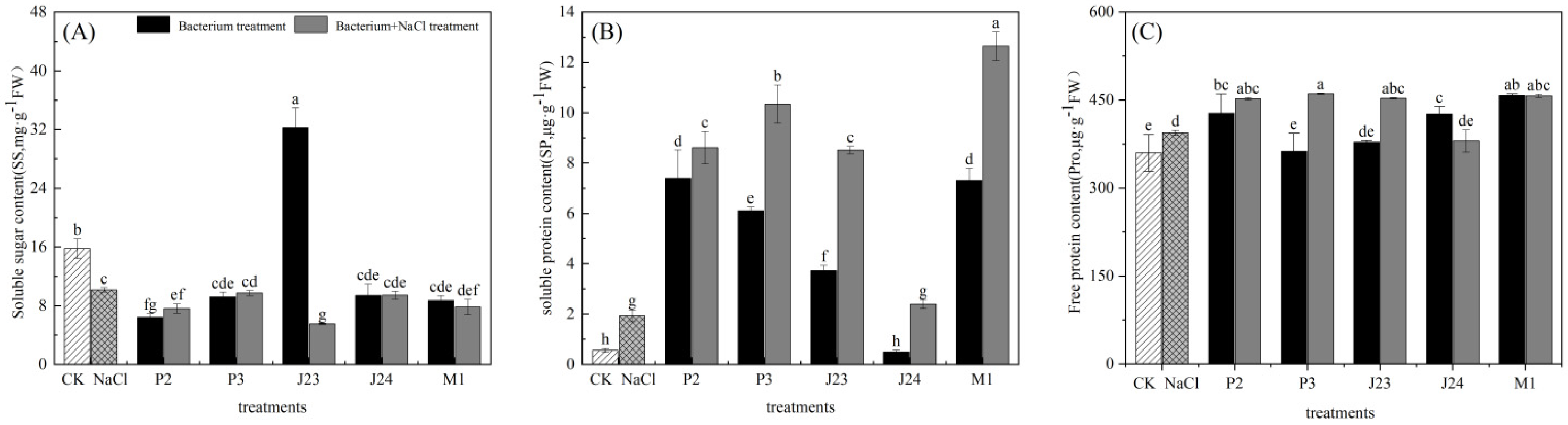
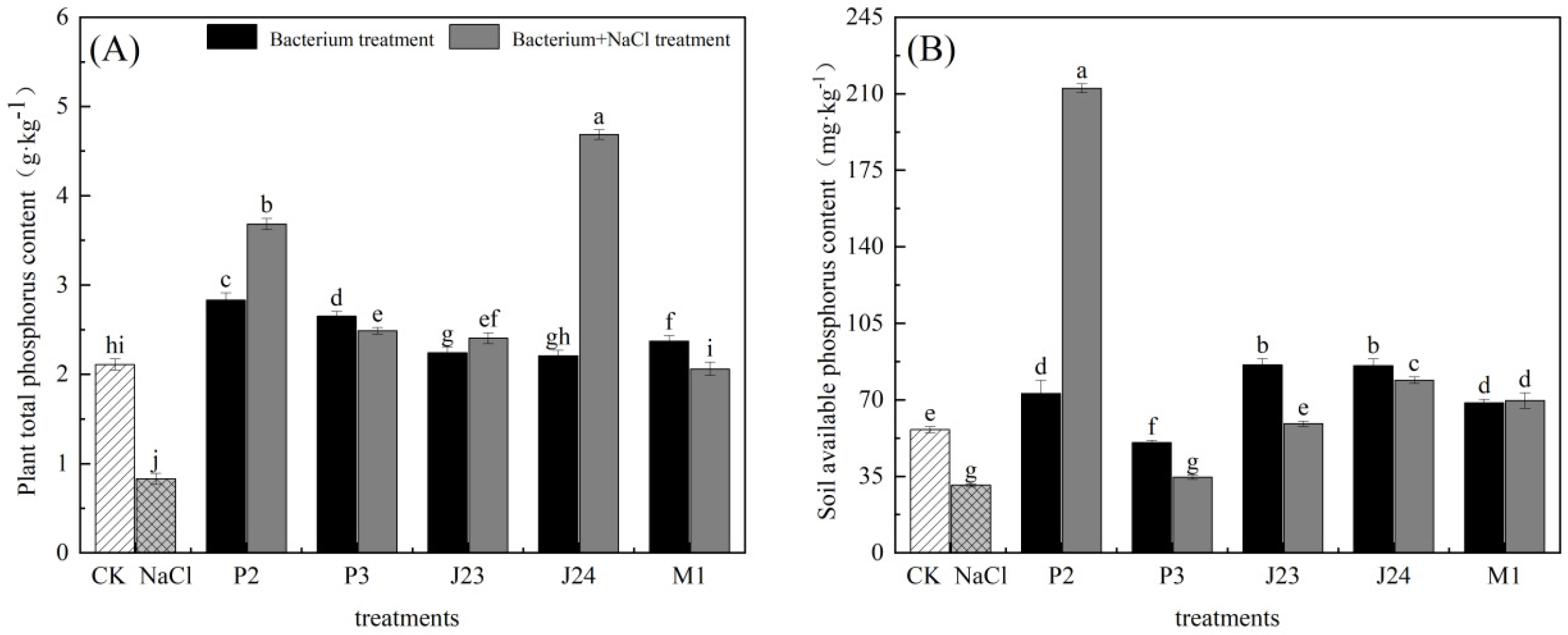
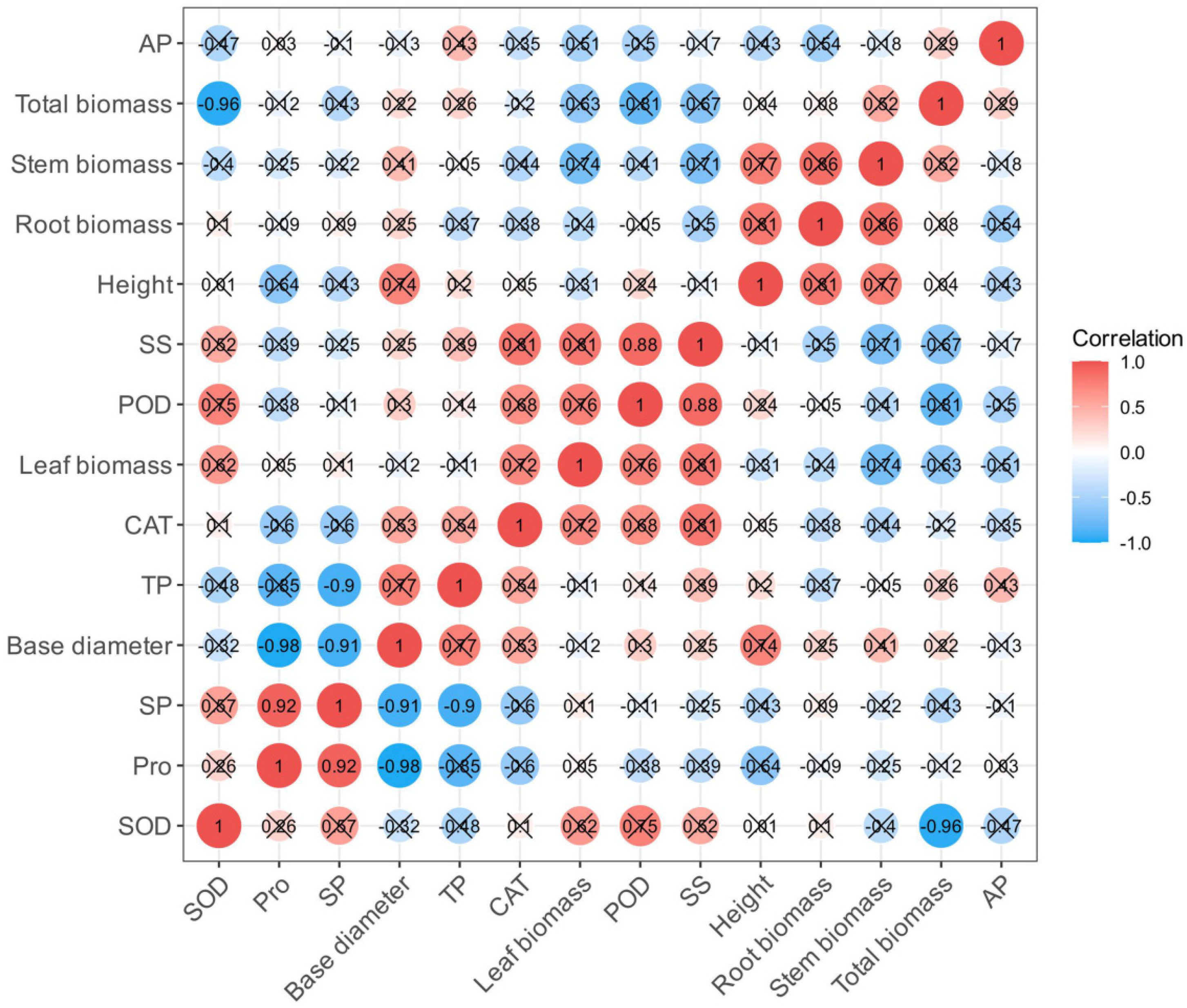
| Bacterial Strain Number | Name of the Bacterial Strain | Colony Diameter, D (cm) | Diameter of Dissolved Phosphorus Ring, d (cm) | Solubilizing Index, SI(D + d/D) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| P2 | Bacillus pumilus | 0.53 ± 0.01 c | 1.35 ± 0.04 b | 3.55 ± 0.01 a |
| P3 | Enterobacter mori | 0.74 ± 0.01 a | 1.14 ± 0.00 c | 2.53 ± 0.02 b |
| J23 | Enterobacter cloacae | 0.62 ± 0.05 b | 1.44 ± 0.00 a | 3.33 ± 0.20 a |
| J24 | Bacillus safensis | 0.39 ± 0.02 d | 0.42 ± 0.03 e | 2.08 ± 0.00 c |
| M1 | Bacillus megaterium | 0.51 ± 0.00 c | 0.89 ± 0.02 d | 2.75 ± 0.01 b |
| Bacterial Strain Number | Name of the Bacterial Strain | pH |
|---|---|---|
| P2 | Bacillus pumilus | −0.965 ** |
| P3 | Enterobacter mori | −0.952 ** |
| J23 | Enterobacter cloacae | −0.945 ** |
| J24 | Bacillus safensis | 0.177 |
| M1 | Bacillus megaterium | −0.728 * |
| Variable | Principal Component 1 | Principal Component 2 | Principal Component 3 | Principal Component 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Net growth of height | 0.006 | 0.110 | −0.420 | −0.351 |
| Net growth of ground diameter | 0.036 | 0.191 | −0.126 | −0.150 |
| Total biomass | 0.157 | 0.003 | −0.053 | 0.178 |
| Root biomass | 0.149 | −0.042 | 0.146 | −0.140 |
| Stem biomass | 0.150 | 0.006 | −0.197 | 0.070 |
| Leaf biomass | 0.137 | 0.028 | −0.006 | 0.458 |
| Superoxide dismutase activity, SOD | −0.157 | −0.031 | −0.067 | −0.084 |
| Catalase activity, CAT | −0.048 | 0.160 | 0.120 | 0.459 |
| Peroxidase activity, POD | −0.136 | 0.108 | −0.004 | 0.029 |
| Free protein content, Pro | −0.023 | −0.198 | 0.032 | 0.189 |
| Soluble sugar content, SS | −0.110 | 0.115 | 0.243 | 0.141 |
| Soluble protein content, SP | −0.069 | −0.184 | −0.044 | −0.025 |
| Plant total phosphorus content, TP | 0.053 | 0.167 | 0.241 | −0.177 |
| Soil available phosphorus content, AP | 0.074 | −0.033 | 0.406 | −0.442 |
| Eigenvalue | 6.232 | 4.885 | 1.789 | 1.094 |
| Contribution/% | 44.515 | 34.894 | 12.778 | 7.812 |
| Cumulative contribution/% | 44.515 | 79.409 | 92.188 | 100.000 |
| Bacterial Strain Number | Name of the Bacterial Strain | D-Value | Rank |
|---|---|---|---|
| P2 | Bacillus pumilus | 0.522 | 2 |
| P3 | Enterobacter mori | 0.231 | 4 |
| J23 | Enterobacter cloacae | 0.518 | 3 |
| J24 | Bacillus safensis | 0.651 | 1 |
| M1 | Bacillus megaterium | 0.022 | 5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, X.; Chong, P.; Bao, X.; Zhang, F. The Effects of Inoculation with Rhizosphere Phosphate-Solubilizing Bacteria on the Growth and Physiology of Reaumuria soongorica Seedlings Under NaCl Stress. Forests 2025, 16, 591. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16040591
Wang X, Chong P, Bao X, Zhang F. The Effects of Inoculation with Rhizosphere Phosphate-Solubilizing Bacteria on the Growth and Physiology of Reaumuria soongorica Seedlings Under NaCl Stress. Forests. 2025; 16(4):591. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16040591
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Xueying, Peifang Chong, Xinguang Bao, and Feng Zhang. 2025. "The Effects of Inoculation with Rhizosphere Phosphate-Solubilizing Bacteria on the Growth and Physiology of Reaumuria soongorica Seedlings Under NaCl Stress" Forests 16, no. 4: 591. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16040591
APA StyleWang, X., Chong, P., Bao, X., & Zhang, F. (2025). The Effects of Inoculation with Rhizosphere Phosphate-Solubilizing Bacteria on the Growth and Physiology of Reaumuria soongorica Seedlings Under NaCl Stress. Forests, 16(4), 591. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16040591






