Priority Effect of Endophyte Community in Newly Fallen Leaves of Quercus acutissima Carruth. on Litter Decomposition and Saprotrophic Microbial Community
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Site and Litter Collection
2.2. Field Experiment Design for Litter Decomposition
2.3. Extracellular Enzyme Activity, Carbon Dioxide Release, and Remaining Mass
2.4. DNA Extraction, PCR Amplification, and NovaSeq Sequencing
2.5. Leaf Litter Extracellular Enzyme Stoichiometry (EES)
2.6. Leaf Litter Organic Matter Quality
2.7. Statistical Analysis
2.7.1. Microbial Diversity
2.7.2. Microbial Community Assembly
2.7.3. Co-Occurrence Network Analysis
2.7.4. LEfSe Analysis
2.7.5. Source Tracking Analysis
2.7.6. Structural Equation Modeling (SEM)
3. Results
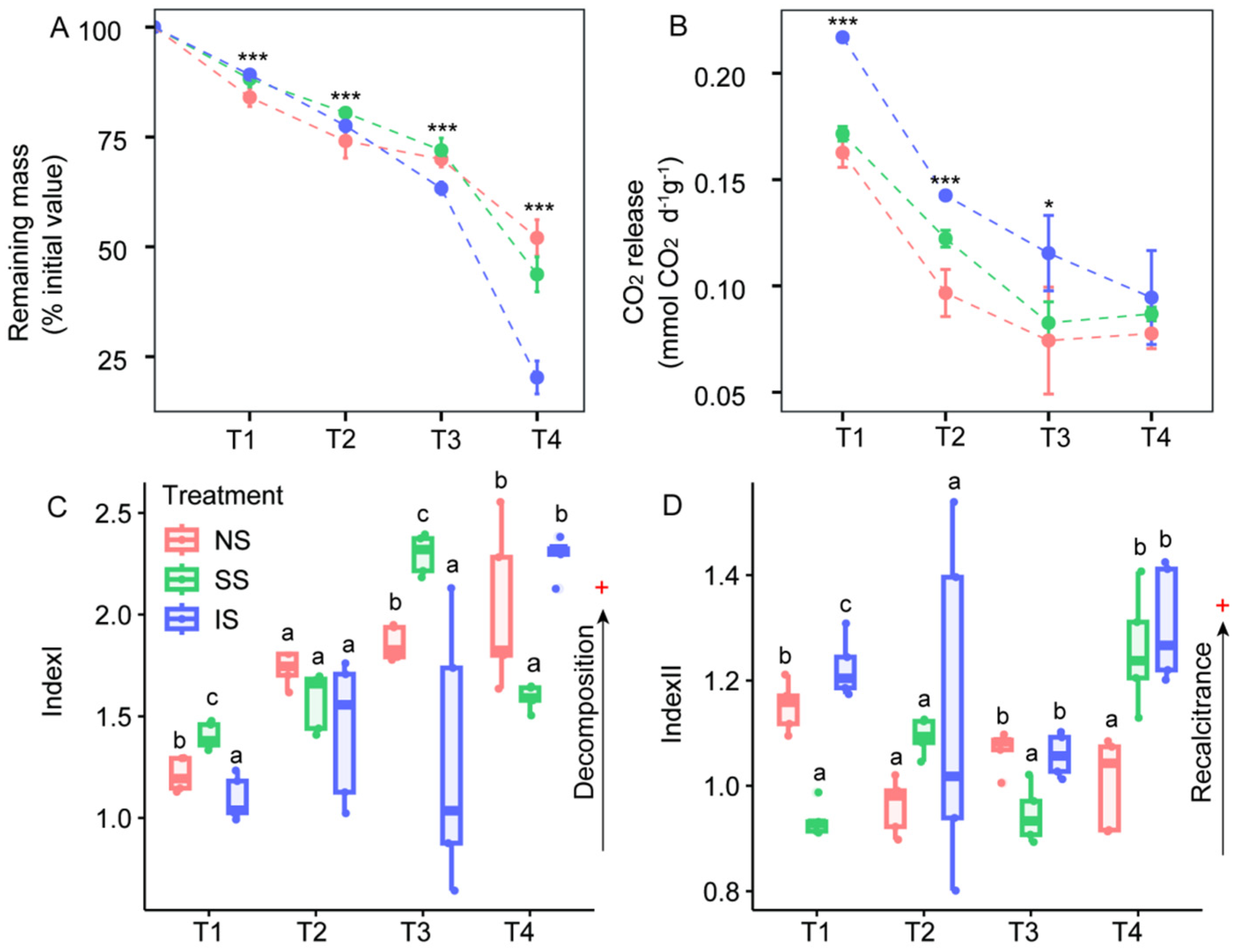
3.1. Remaining Mass, CO2 Release and Organic Matter Quality
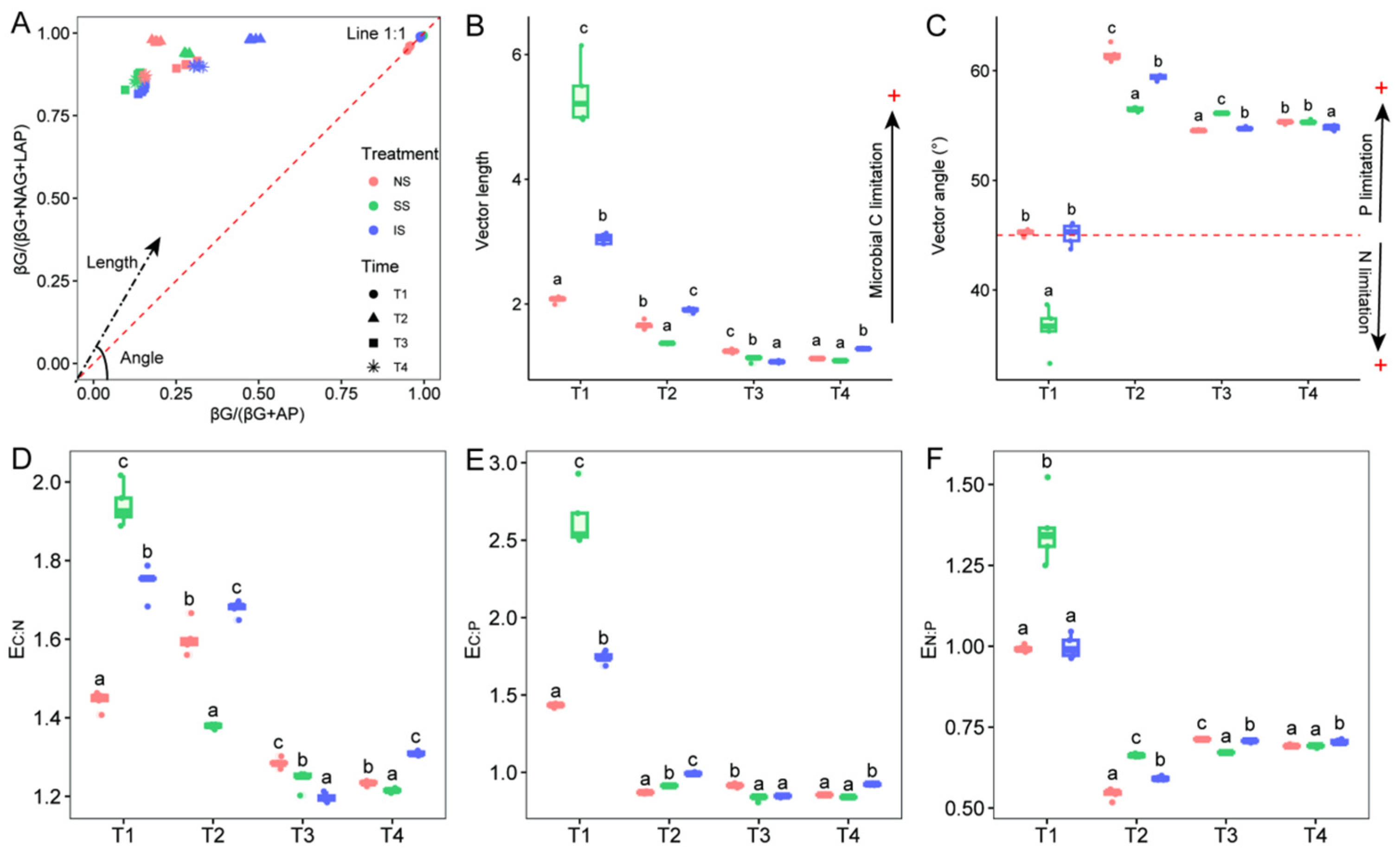
3.2. Extracellular Enzyme Activity and Stoichiometry
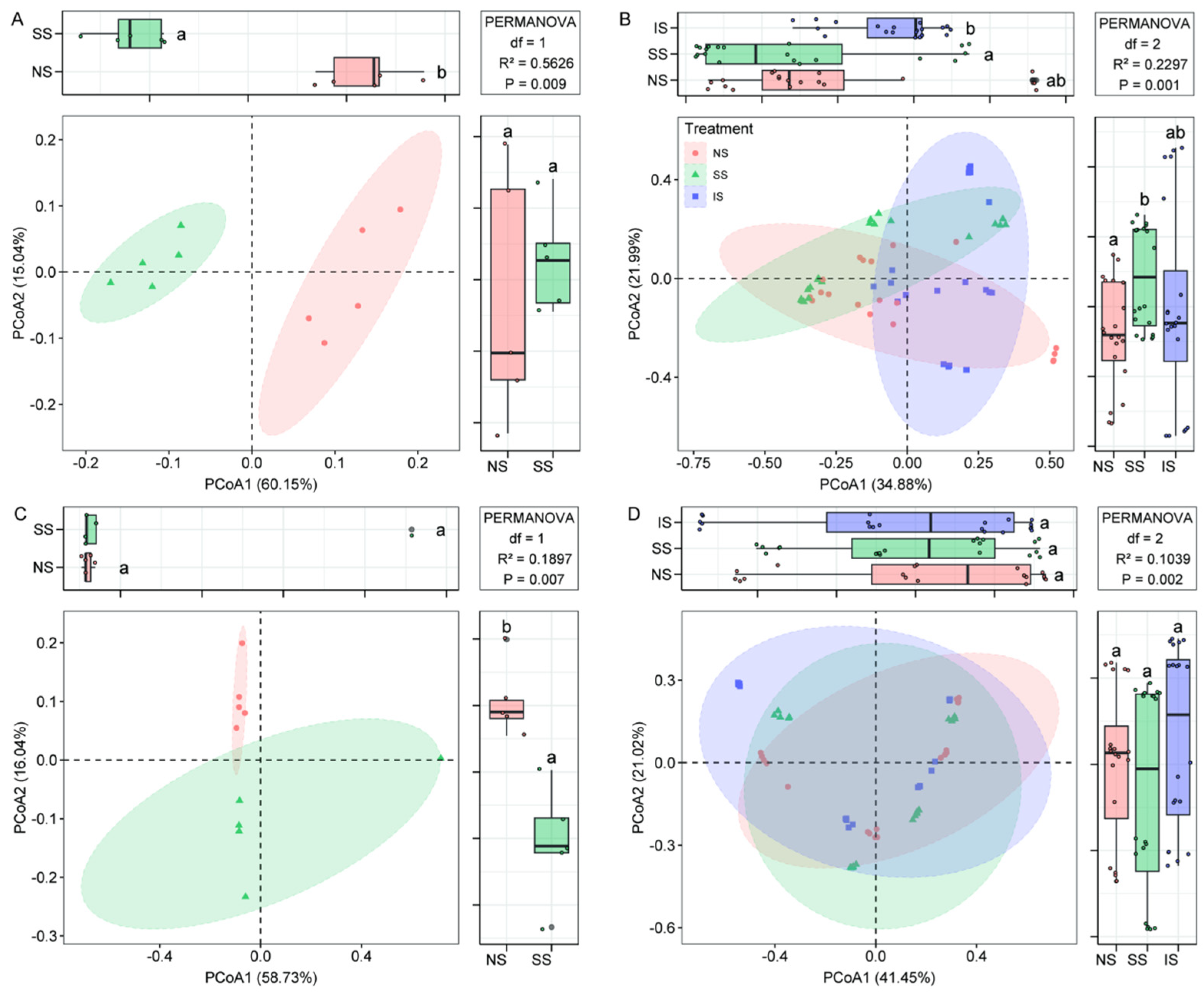
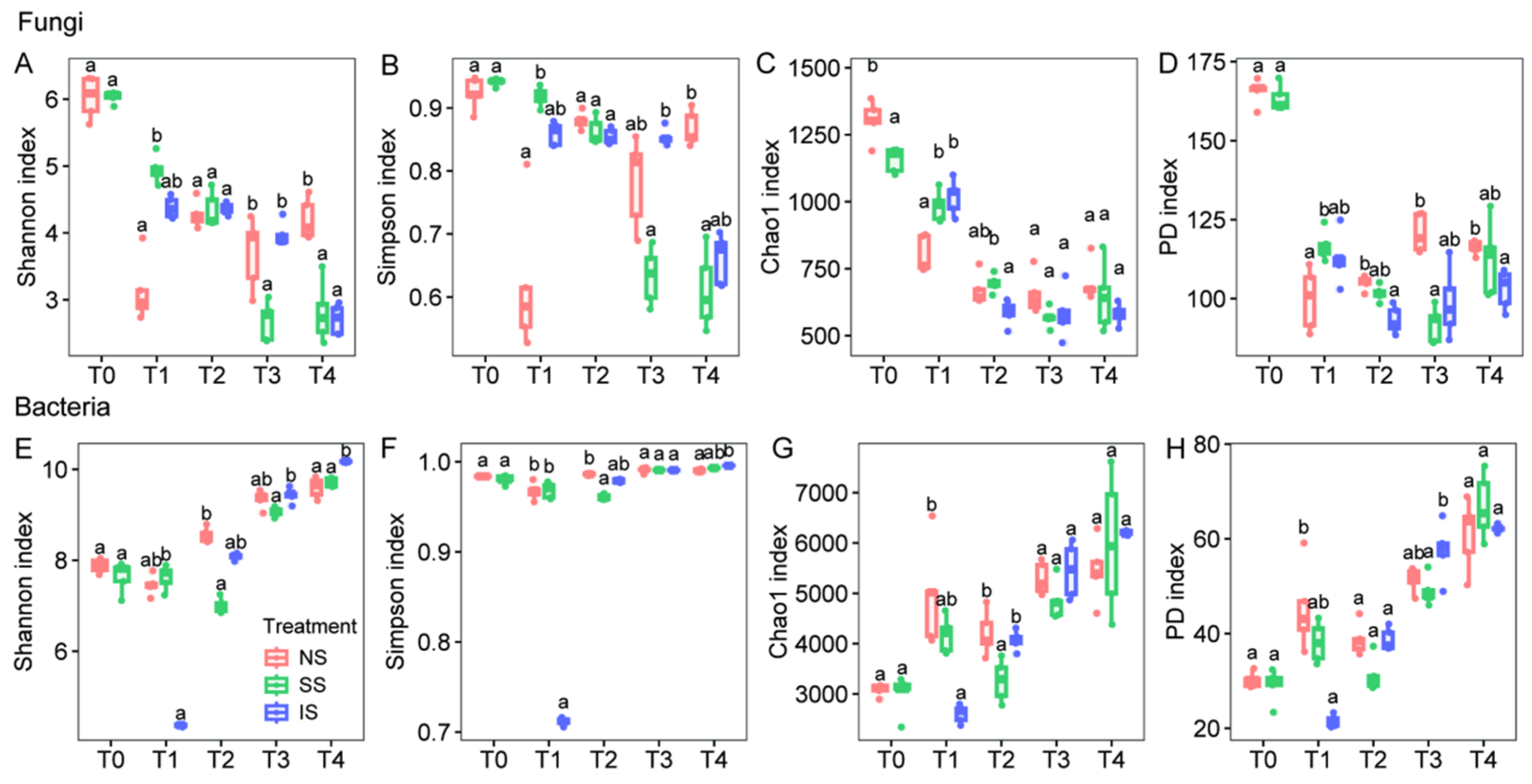
3.3. Microbial Community Structure and Diversity
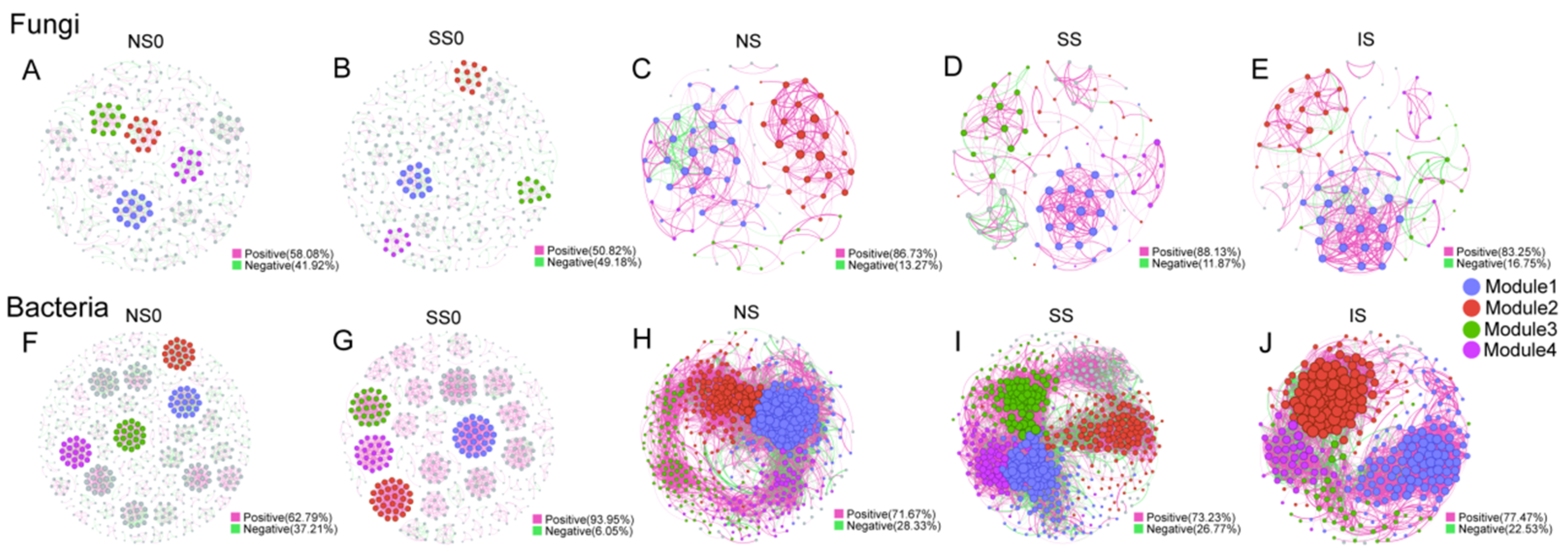
3.4. Co-Occurrence Network Analysis
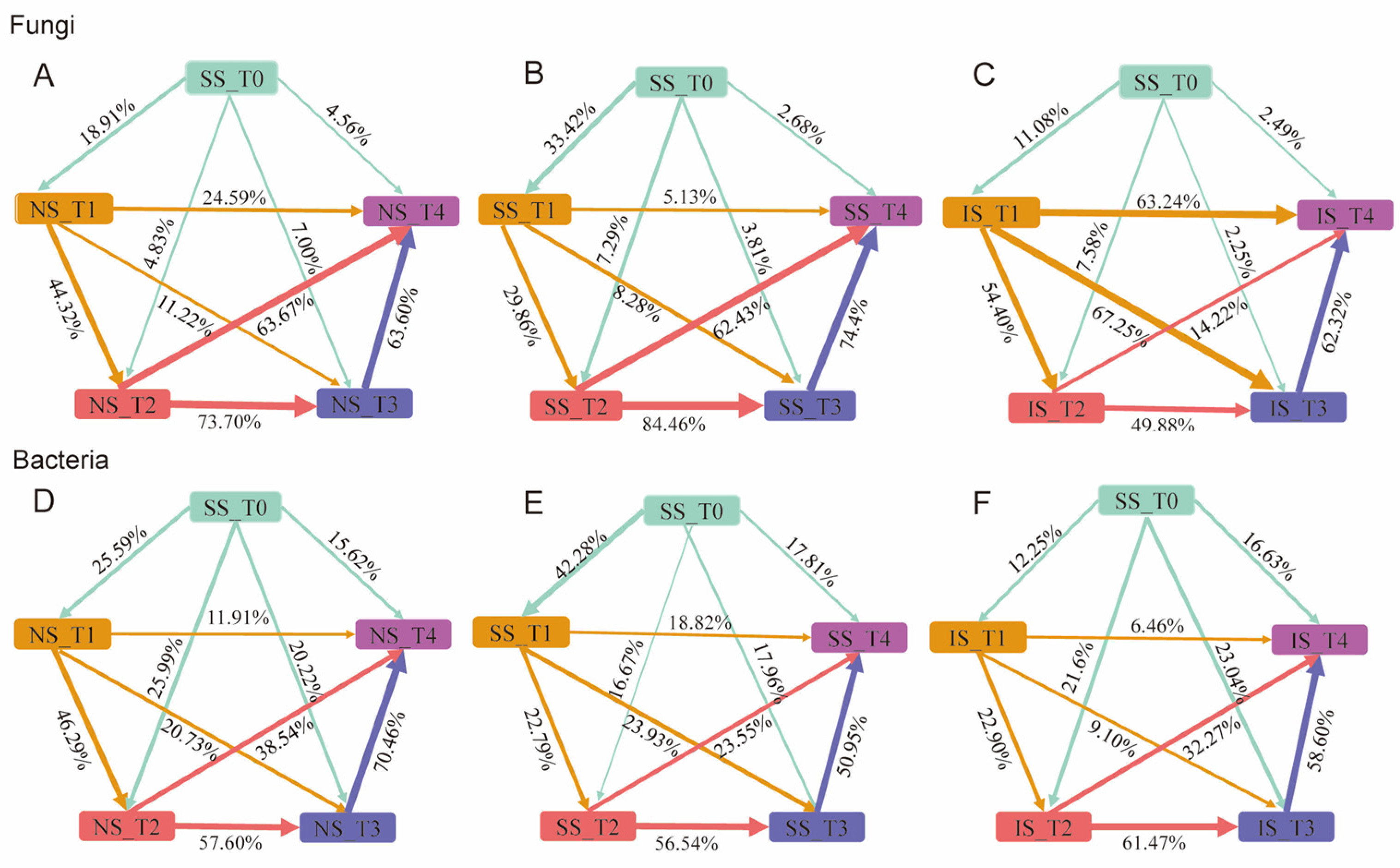
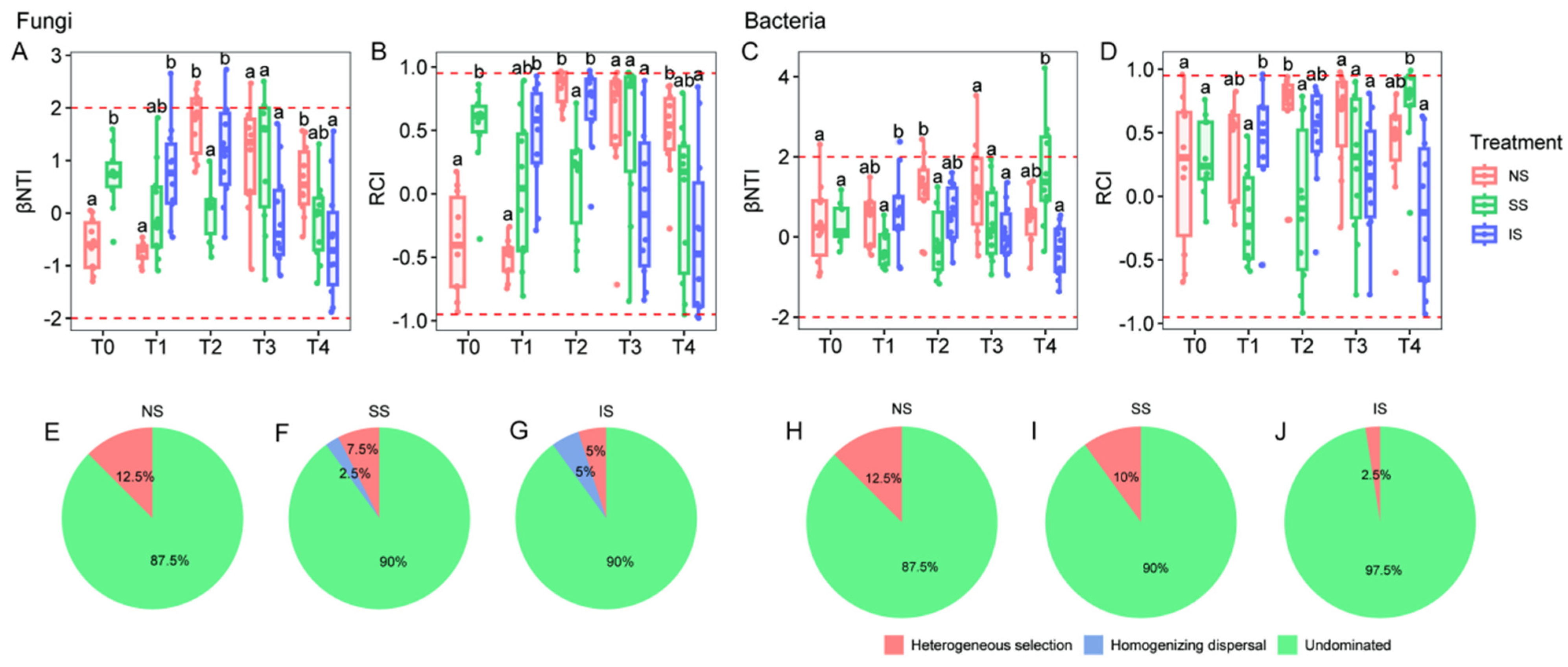
3.5. Community Assembly
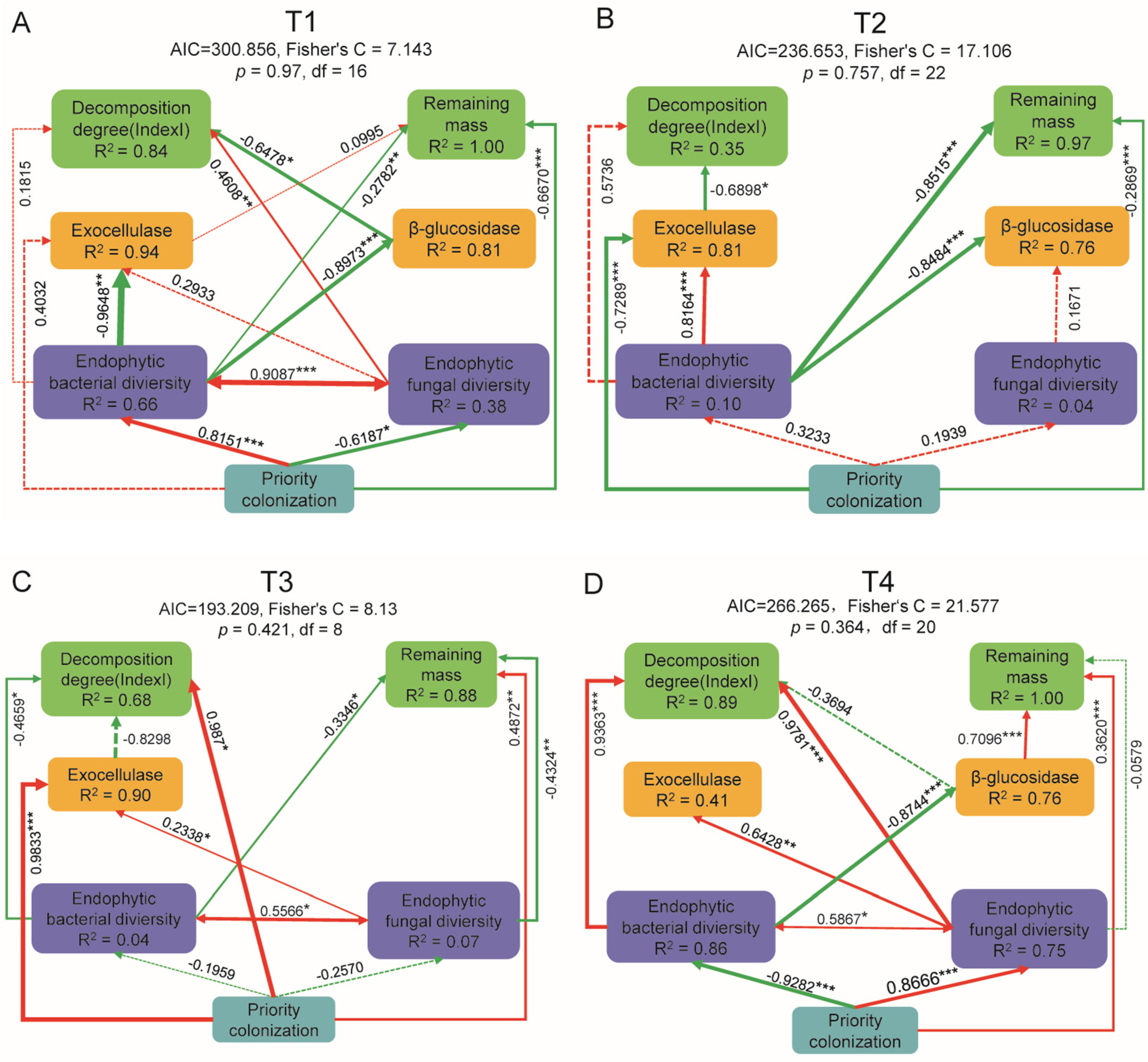
3.6. Relationship of Endophytes to Decomposition Function
4. Discussion
4.1. Litter Decomposition
4.2. Microbial Diversity
4.3. Microbial Co-Occurrence Network and Community Assembly
4.4. Enduring Effect of Endophytic Microbe on Litter Decomposition
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ball, B.A.; Carrillo, Y.; Molina, M. The influence of litter composition across the litter-soil interface on mass loss, nitrogen dynamics and the decomposer community. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2014, 69, 71–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rachmawati, S.; Yulistyarini, T.; Hairiah, K. Decomposition of tree litter: Interaction between inherent quality and environment. Biodiversitas 2019, 20, 1946–1952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Siegrist, J.A.; McCulley, R.L.; Bush, L.P.; Phillips, T.D. Alkaloids may not be responsible for endophyte-associated reductions in tall fescue decomposition rates. Funct. Ecol. 2010, 24, 460–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolfe, E.R.; Ballhorn, D.J. Do foliar endophytes matter in litter decomposition? Microorganisms 2020, 8, 446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Zheng, Y.; Xu, G.; Guo, Q.; Tan, J.; Ding, G. Fungal diversity within the phyllosphere of Pinus massoniana and the possible involvement of phyllospheric fungi in litter decomposition. Fungal Biol. 2021, 125, 785–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, H.; Li, L.; Dai, C. The potential application of the endophyte Phomopsis liquidambari to the ecological remediation of long-term cropping soil. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2013, 67, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; He, X.; Ma, T.; Han, G.; Xiang, C. Priority colonization of Cinnamomum camphora litter by endophytes affects decomposition rate, fungal community and microbial activities under field conditions. Pedobiologia 2015, 58, 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustonen, K.; Mykrä, H.; Louhi, P.; Markkola, A.; Tolkkinen, M.; Huusko, A.; Alioravainen, N.; Lehtinen, S.; Muotka, T. Sediments and flow have mainly independent effects on multitrophic stream communities and ecosystem functions. Ecol. Appl. 2016, 26, 2116–2129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bell-Dereske, L.; Gao, X.; Masiello, C.A.; Sinsabaugh, R.L.; Emery, S.M.; Rudgers, J.A. Plant–fungal symbiosis affects litter decomposition during primary succession. Oikos 2017, 126, 801–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, K.; Cao, W.; Hu, L.; Fu, W.; Gong, J.; Kang, N.; Dai, C. Symbiotic fungal endophyte Phomopsis liquidambari-rice system promotes nitrogen transformation by influencing below-ground straw decomposition in paddy soil. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2019, 126, 191–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolfe, E.R.; Younginger, B.S.; LeRoy, C.J. Fungal endophyte-infected leaf litter alters in-stream microbial communities and negatively influences aquatic fungal sporulation. Oikos 2019, 128, 405–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korkama-Rajala, T.; Müller, M.M.; Pennanen, T. Decomposition and fungi of needle litter from slow- and fast-growing Norway spruce (Picea abies) clones. Microb. Ecol. 2008, 56, 76–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grimmett, I.J.; Smith, K.A.; Bärlocher, F. Tar-spot infection delays fungal colonization and decomposition of maple leaves. Freshw. Sci. 2012, 31, 1088–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omacini, M.; Semmartin, M.; Pérez, L.I.; Gundel, P.E. Grass–endophyte symbiosis: A neglected aboveground interaction with multiple belowground consequences. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2012, 61, 273–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gundel, P.E.; Helander, M.; Garibaldi, L.A.; Vázquez-de-Aldana, B.R.; Zabalgogeazcoa, I.; Saikkonen, K. Role of foliar fungal endophytes in litter decomposition among species and population origins. Fungal Ecol. 2016, 21, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gundel, P.E.; Helander, M.; Garibaldi, L.A.; Vázquez-de-Aldana, B.R.; Zabalgogeazcoa, I.; Saikkonen, K. Direct and indirect effects of the fungal endophyte Epichloë uncinatum on litter decomposition of the host grass, Schedonorus pratensis. Plant Ecol. 2017, 218, 1107–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, M.; Chai, Q.; Li, X.; Yao, X.; Li, C.; Christensen, M.J.; Nan, Z. An asexual Epichloë endophyte modifies the nutrient stoichiometry of wild barley (Hordeum brevisubulatum) under salt stress. Plant Soil 2015, 387, 153–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, M.; Wang, Y.; Wang, H.; Bao, G.; Li, X. Effects of Epichloë endophytes on litter decomposition -- depending on different host species. Plant Soil 2022, 471, 715–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šnajdr, J.; Cajthaml, T.; Valášková, V.; Merhautová, V.; Petránková, M.; Spetz, P.; Leppänen, K.; Baldrian, P. Transformation of Quercus petraea litter: Successive changes in litter chemistry are reflected in differential enzyme activity and changes in the microbial community composition. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2011, 75, 291–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerreiro, M.A.; Brachmann, A.; Begerow, D.; Peršoh, D. Transient leaf endophytes are the most active fungi in 1-year-old beech leaf litter. Fungal Divers. 2018, 89, 237–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Jin, Y.; Yao, X.; Wei, X.K.; Li, X.; Li, C.; White, J.F.; Nan, Z. Gene analysis reveals that leaf litter from Epichloë endophyte-infected perennial ryegrass alters diversity and abundance of soil microbes involved in nitrification and denitrification. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2021, 154, 108123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buyer, J.S.; Zuberer, D.A.; Nichols, K.A.; Franzluebbers, A.J. Soil microbial community function, structure, and glomalin in response to tall fescue endophyte infection. Plant Soil 2011, 339, 401–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suryanarayanan, T.S. Endophyte research: Going beyond isolation and metabolite documentation. Fungal Ecol. 2013, 6, 561–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szink, I.; Davis, E.L.; Ricks, K.D.; Koide, R.T. New evidence for broad trophic status of leaf endophytic fungi of Quercus gambelii. Fungal Ecol. 2016, 22, 2–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Promputtha, I.; McKenzie, E.H.; Tennakoon, D.S.; Lumyong, S.; Hyde, K.D. Succession and natural occurrence of saprobic fungi on leaves of Magnolia liliifera in a tropical forest. Cryptogam. Mycol. 2017, 38, 213–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osono, T. Role of phyllosphere fungi of forest trees in the development of decomposer fungal communities and decomposition processes of leaf litter. Can. J. Microbiol. 2006, 52, 701–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koide, R.; Osono, T.; Takeda, H. Colonization and lignin decomposition of Camellia japonica leaf litter by endophytic fungi. Mycoscience 2005, 46, 280–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukasawa, Y.; Osono, T.; Takeda, H. Effects of attack of saprobic fungi on twig litter decomposition by endophytic fungi. Ecol. Res. 2009, 24, 1067–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Jin, Y.; Hou, F.; Bowatte, S. Soil microbial and chemical responses to foliar Epichloë fungal infection in Lolium perenne, Hordeum brevisubulatum and Achnatherum inebrians. Fungal Ecol. 2021, 53, 101091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Han, G.; Lin, Y.; Tian, X.; Xiang, C.; Tian, Q.; Wang, F.; He, Z. Diversity and decomposition potential of endophytes in leaves of a Cinnamomum Camphora plantation in China. Ecol. Res. 2012, 27, 273–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojas, X.; Guo, J.; Leff, J.W.; McNear, D.H., Jr.; Fierer, N.; McCulley, R.L. Infection with a shoot-specific fungal endophyte (Epichloë) alters tall fescue soil microbial communities. Microb. Ecol. 2016, 72, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, Y.; Wei, X.; White, J.F.; Chen, T.; Li, X.; Chen, Z.; Li, C. Soil fungal and bacterial communities are altered by incorporation of leaf litter containing a fungal endophyte. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2022, 73, e13240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukami, T.; Dickie, I.A.; Wilkie, J.P.; Paulus, B.C.; Park, D.; Roberts, A.; Buchanan, P.K.; Allen, R.B. Assembly history dictates ecosystem functioning: Evidence from wood decomposer communities. Ecol. Lett. 2010, 13, 675–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dickie, I.A.; Fukami, T.; Wilkie, J.P.; Allen, R.B.; Buchanan, P.K. Do assembly history effects attenuate from species to ecosystem properties? A field test with wood-inhabiting fungi. Ecol. Lett. 2012, 15, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agnihotri, S.; Dutt, D.; Tyagi, C.H.; Kumar, A.; Upadhyaya, J.S. Production and biochemical characterization of a novel cellulose-poor alkali-thermo-tolerant xylanase from Coprinellus disseminatus SW-1 NTCC 1165. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2010, 26, 1349–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinsabaugh, R.L.; Antibus, R.K.; Linkins, A.E.; McClaugherty, C.A.; Rayburn, L.; Repert, D.; Weiland, T. Wood decomposition: Nitrogen and phosphorus dynamics in relation to extracellular enzyme activity. Ecology 1993, 74, 1586–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wang, J.; Wang, H.; Tang, Y. Isolation, purification, and partial characterization of acid phosphatase from sweet potato leaves. Food Sci. 2015, 36, 152–157. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.; Cai, X.; Luo, X.; Wang, S.; Guo, A.; Hou, J.; Wu, R. Molecular cloning and characterization of leucine aminopeptidase gene from Taenia Pisiformis. Exp. Parasitol. 2018, 186, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papa, S.; Pellegrino, A.; Fioretto, A. Microbial activity and quality changes during decomposition of Quercus ilex leaf litter in three Mediterranean woods. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2008, 40, 401–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Li, H.; Sun, Y.; Shao, K.; Wang, X.; Ma, X.; Hu, A.; Zhang, H.; Fan, J. How habitat heterogeneity shapes bacterial and protistan communities in temperate coastal areas near estuaries. Environ. Microbiol. 2022, 24, 1775–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinsabaugh, R.L.; Shah, J.J.F. Ecoenzymatic stoichiometry and ecological theory. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Evol. Syst. 2012, 43, 313–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moorhead, D.L.; Sinsabaugh, R.L.; Hill, B.H.; Weintraub, M.N. Vector analysis of ecoenzyme activities reveal constraints on coupled C, N and P dynamics. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2016, 93, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Wu, Z.; Zong, Y.; Li, W.; Chen, F.; Wang, G.G.; Li, J.; Fang, X. Mixing with coniferous tree species alleviates rhizosphere soil phosphorus limitation of broad-leaved trees in subtropical plantations. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2022, 175, 108853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abay, P.; Gong, L.; Luo, Y.; Zhu, H.; Ding, Z. Soil extracellular enzyme stoichiometry reveals the nutrient limitations in soil microbial metabolism under different carbon input manipulations. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 913, 169793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Duan, C.; Wang, X.; Zhang, X.; Ju, W.; Chen, H.; Yue, S.; Wang, Y.; Li, S.; et al. Ecoenzymatic stoichiometry reveals microbial phosphorus limitation decreases the nitrogen cycling potential of soils in semi-arid agricultural ecosystems. Soil Tillage Res. 2020, 197, 104463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margenot, A.J.; Calderón, F.J.; Bowles, T.M.; Parikh, S.J.; Jackson, L.E. Soil organic matter functional group composition in relation to organic carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus fractions in organically managed tomato fields. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2015, 79, 772–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veum, K.S.; Goyne, K.W.; Kremer, R.J.; Miles, R.J.; Sudduth, K.A. Biological indicators of soil quality and soil organic matter characteristics in an agricultural management continuum. Biogeochemistry 2014, 117, 81–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oksanen, J.; Blanchet, F.G.; Friendly, M.; Kindt, R.; Legendre, P.; McGlinn, D.; Minchin, P.R.; O’Hara, R.B.; Simpson, G.L.; Solymos, P.; et al. Vegan: Community Ecology Package (Version 2.5-7). 2020. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=vegan (accessed on 5 August 2024).
- Stegen, J.C.; Lin, X.; Fredrickson, J.K.; Chen, X.; Kennedy, D.W.; Murray, C.J.; Rockhold, M.L.; Konopka, A. Quantifying community assembly processes and identifying features that impose them. ISME J. 2013, 7, 2069–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xun, W.; Li, W.; Xiong, W.; Ren, Y.; Liu, Y.; Miao, Y.; Xu, Z.; Zhang, N.; Shen, Q.; Zhang, R. Diversity-triggered deterministic bacterial assembly constrains community functions. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 3833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Deng, Y.; Feng, K.; Cai, W.; Li, S.; Yin, H.; Xu, M.; Ning, D.; Qu, Y. Deterministic assembly and diversity gradient altered the biofilm community performances of bioreactors. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 1315–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stegen, J.C.; Lin, X.; Fredrickson, J.K.; Konopka, A.E. Estimating and mapping ecological processes influencing microbial community assembly. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Yang, T.; Bao, Y.; He, P.; Yang, K.; Mei, X.; Wei, Z.; Xu, Y.; Shen, Q.; Banerjee, S. Network analysis and subsequent culturing reveal keystone taxa involved in microbial litter decomposition dynamics. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2021, 157, 108230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastian, M.; Heymann, S.; Jacomy, M. Gephi: An open source software for exploring and manipulating networks. In Proceedings of the International AAAI Conference on Web and Social Media, San Jose, CA, USA, 17–29 May 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guimerà, R.; Amaral, L.A.N. Functional cartography of complex metabolic networks. Nature 2005, 433, 895–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, S.; Ma, Q.; Marsden, K.A.; Chadwick, D.R.; Luo, Y.; Kuzyakov, Y.; Wu, L.; Jones, D.L. Microbial community succession in soil is mainly driven by carbon and nitrogen contents rather than phosphorus and sulphur contents. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2023, 180, 109019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segata, N.; Izard, J.; Waldron, L.; Gevers, D.; Miropolsky, L.; Garrett, W.S.; Huttenhower, C. Metagenomic biomarker discovery and explanation. Genome Biol. 2011, 12, R60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Li, H.; Yao, T.; Su, M.; Ran, F.; Han, B.; Li, J.; Lan, X.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, X.; et al. Microbial inoculation influences bacterial community succession and physicochemical characteristics during pig manure composting with corn straw. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 289, 121653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, T.; Li, C.; Song, F. Differences in microbial community and metabolites in litter layer of plantation and original Korean pine forests in north temperate zone. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shenhav, L.; Thompson, M.; Joseph, T.A.; Briscoe, L.; Furman, O.; Bogumil, D.; Mizrahi, I.; Pe’er, I.; Halperin, E. FEAST: Fast expectation-maximization for microbial source tracking. Nat. Methods 2019, 16, 627–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Ren, K.; Yan, X.; Tsyganov, A.N.; Mazei, Y.; Smirnov, A.; Mazei, N.; Zhang, Y.; Rensing, C.; Yang, J. Linking biodiversity and ecological function through extensive microeukaryotic movement across different habitats in six urban parks. iMeta 2023, 2, e103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Delgado-Baquerizo, M.; Fanin, N.; Chen, X.; Zhou, Y.; Du, G.; Hu, F.; Jiang, L.; Hu, S.; Liu, M. Nutrient-induced acidification modulates soil biodiversity-function relationships. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 2858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Omacini, M.; Chneton, E.J.; Ghersa, C.M.; Otero, P. Do foliar endophytes affect grass litter decomposition? A microcosm approach using Lolium multiflorum. Oikos 2004, 104, 581–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudgers, J.A.; Caly, K. Endophyte symbiosis with tall fescue: How strong are the impacts on communities and ecosystems? Fung. Biol. Rev. 2007, 21, 107–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Li, X.; Gao, Y.; Ren, A. Plant endophytes and arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi alter the decomposition of Achnatherum sibiricum litter. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2022, 180, 104616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sariyildiz, T.; Anderson, J.M. Variation in the chemical composition of green leaves and leaf litters from three deciduous tree species growing on different soil types. Forest Ecol. Manag. 2005, 210, 303–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Mamuti, M.; Liu, H.; Shu, Y.; Hu, S.; Wang, X.; Li, B.; Xu, L. Effects of nutrient additions on litter decomposition regulated by phosphorus-induced changes in litter chemistry in a subtropical forest, China. Forest Ecol. Manag. 2017, 400, 123–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, D.; Wang, M.; Zheng, Y.; Lv, M.; Zhu, G.; Zhong, Q.; Cheng, D. Leaf litter phosphorus regulates the soil meso- and micro-faunal contribution to home-field advantage effects on litter decomposition along elevation gradients. Catena 2021, 207, 105673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tie, L.; Hu, J.; Peñuelas, J.; Sardans, J.; Wei, S.; Liu, X.; Zhou, S.; Huang, C. The amounts and ratio of nitrogen and phosphorus addition drive the rate of litter decomposition in a subtropical forest. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 833, 155163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodenhausen, N.; Horton, M.W.; Bergelson, J. Bacterial communities associated with the leaves and the roots of Arabidopsis thaliana. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e56329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, H.; Ye, R.; Pang, L.; Jiang, H.; Tian, K.; Gao, Y.; Ji, Y.; Wang, P.; Yang, J.; Zou, X.; et al. Endophytic bacterium Bacillus cereus affects host litter decomposition by regulating soil microbial structure and phosphate mineralization. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2023, 192, 105092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richter, A.; Blei, F.; Hu, G.; Schwitalla, J.W.; Lozano-Andrade, C.N.; Xie, J.; Jarmusch, S.A.; Wibowo, M.; Kjeldgaard, B.; Surabhi, S.; et al. Enhanced surface colonisation and competition during bacterial adaptation to a fungus. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 4486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagg, C.; Schlaeppi, K.; Banerjee, S.; Kuramae, E.E.; van der Heijden, M.G.A. Fungal-bacterial diversity and microbiome complexity predict ecosystem functioning. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 4841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chase, J.M. Stochastic community assembly causes higher biodiversity in more productive environments. Science 2010, 328, 1388–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dini-Andreote, F.; Stegen, J.C.; van Elsas, J.D.; Salles, J.F. Disentangling mechanisms that mediate the balance between stochastic and deterministic processes in microbial succession. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, E1326–E1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McEnany, J.; Good, B.H. Predicting the first steps of evolution in randomly assembled communities. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 8495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, L.A.; Gusmão, L.F.P. Communities of saprobic fungi on leaf litter of Vismia guianensis in remnants of the Brazilian Atlantic Forest. J. For. Res. 2017, 28, 163–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L. Diversity and Molecular Systematics of Aquatic Fungi in the Karst Plateau Wetlands of Guizhou. Doctoral Dissertation, Guizhou University, Guiyang, China, 2020. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Y.; Veisenhorn, P.; Guo, X.; Wang, D.; Yang, T.; Shi, Y.; Zhang, H.; Chu, H. Effect of long-term fertilization on bacterial communities in wheat endosphere. Pedosphere 2021, 31, 538–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.A.; Karim, A.; Mishra, P.; Dubowski, J.J.; Yousuf, A.; Sarmin, S.; Khan, M.M.R. Microbial synergistic interactions enhanced power generation in co-culture driven microbial fuel cell. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 738, 140138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarsan, S.; Pandiyan, A.; Rodhe, A.V.; Jagavati, S. Synergistic interactions among microbial communities. In Microbes in Microbial Communities; Singh, R.P., Manchanda, G., Bhattacharjee, K., Panosyan, H., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2021; pp. 1–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, P.Y.; Nguyen, T.H.; Sanchez, J.M.; DeFelice, B.C.; Huang, K.C. Resource competition predicts assembly of gut bacterial communities in vitro. Nat. Microbiol. 2024, 9, 1036–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Ma, Q.; Jin, M.; Huang, L.; Hui, D.; Sardans, J.; Peñuelas, J.; O’Connor, P.; Zhu, Y.; Yang, X.; et al. From grasslands to genes: Exploring the major microbial drivers of antibiotic-resistance in microhabitats under persistent overgraving. Microbiome 2024, 12, 245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, D.; Lin, Y.; He, Z.; He, X.; Kong, X. Priority Effect of Endophyte Community in Newly Fallen Leaves of Quercus acutissima Carruth. on Litter Decomposition and Saprotrophic Microbial Community. Forests 2025, 16, 249. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16020249
Yang D, Lin Y, He Z, He X, Kong X. Priority Effect of Endophyte Community in Newly Fallen Leaves of Quercus acutissima Carruth. on Litter Decomposition and Saprotrophic Microbial Community. Forests. 2025; 16(2):249. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16020249
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Dongmei, Yonghui Lin, Zaihua He, Xingbing He, and Xiangshi Kong. 2025. "Priority Effect of Endophyte Community in Newly Fallen Leaves of Quercus acutissima Carruth. on Litter Decomposition and Saprotrophic Microbial Community" Forests 16, no. 2: 249. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16020249
APA StyleYang, D., Lin, Y., He, Z., He, X., & Kong, X. (2025). Priority Effect of Endophyte Community in Newly Fallen Leaves of Quercus acutissima Carruth. on Litter Decomposition and Saprotrophic Microbial Community. Forests, 16(2), 249. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16020249





