Salt-Stress-Induced Ion Transport Contributes to K+/Na+ Homeostasis in Roots of Ping’ou Hybrid Hazelnut
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Test Materials and Hydroponic Culture
2.2. Salt Treatment and Sampling
2.3. Ion Concentration Analysis
2.4. Non-Invasive Micro-Test Technology
2.5. Measurements of Ion Flux under Salt Stress
2.6. Measurements of Ion Flux under Transport Inhibitor (Pharmacological Experiments)
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. NaCl-Induced Ion Cncentration
3.2. NaCl-Induced Ion Fluxes
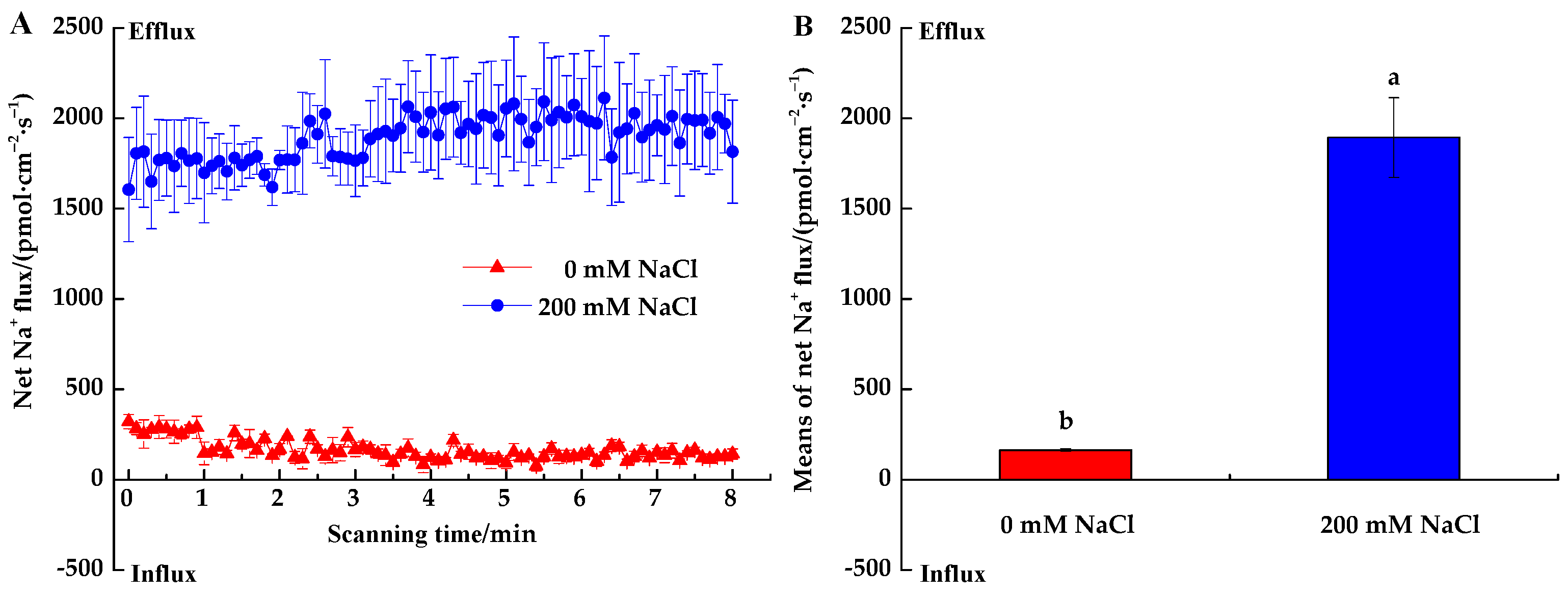
3.2.1. Na+ Fluxes
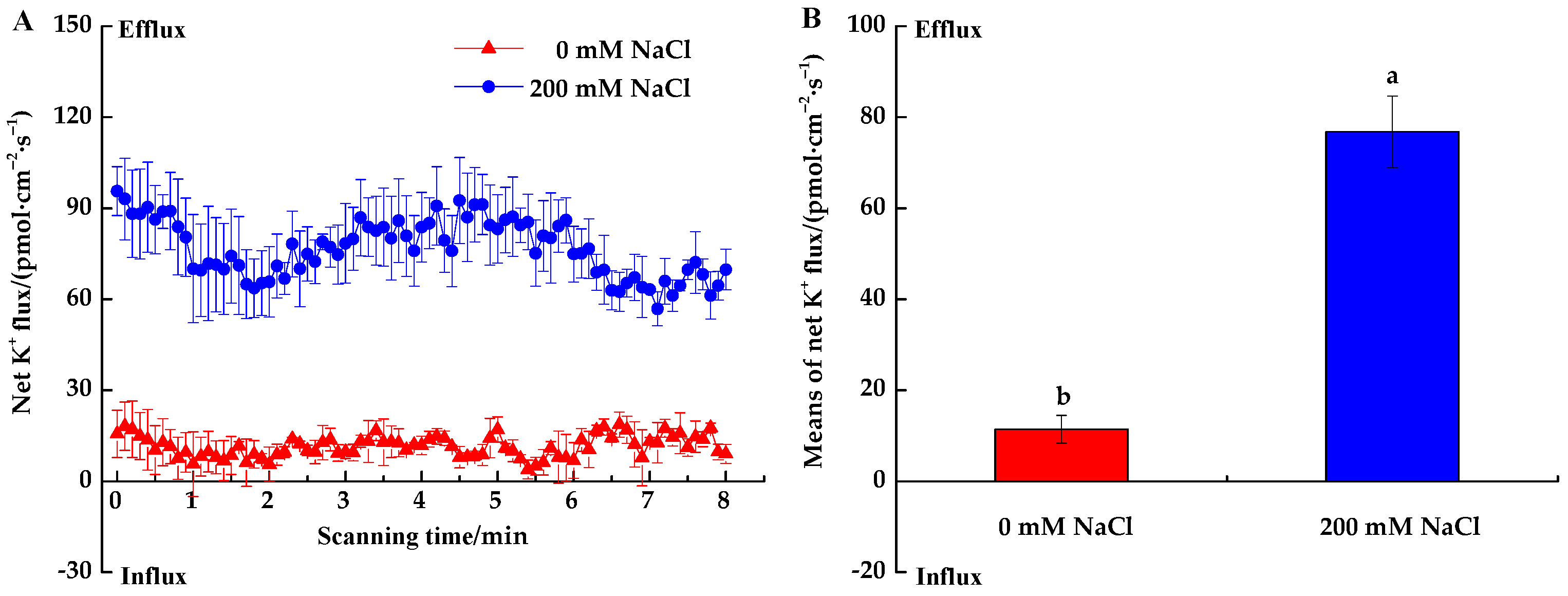
3.2.2. K+ Fluxes
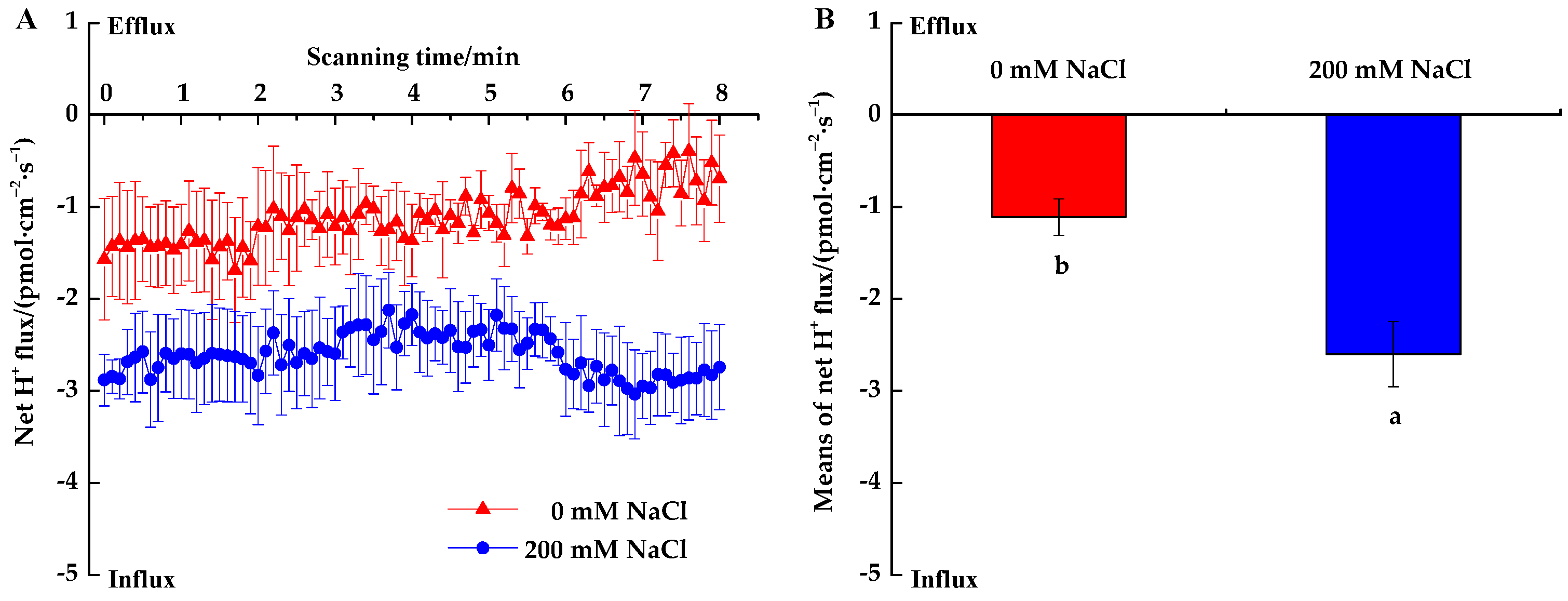
3.2.3. H+ Fluxes
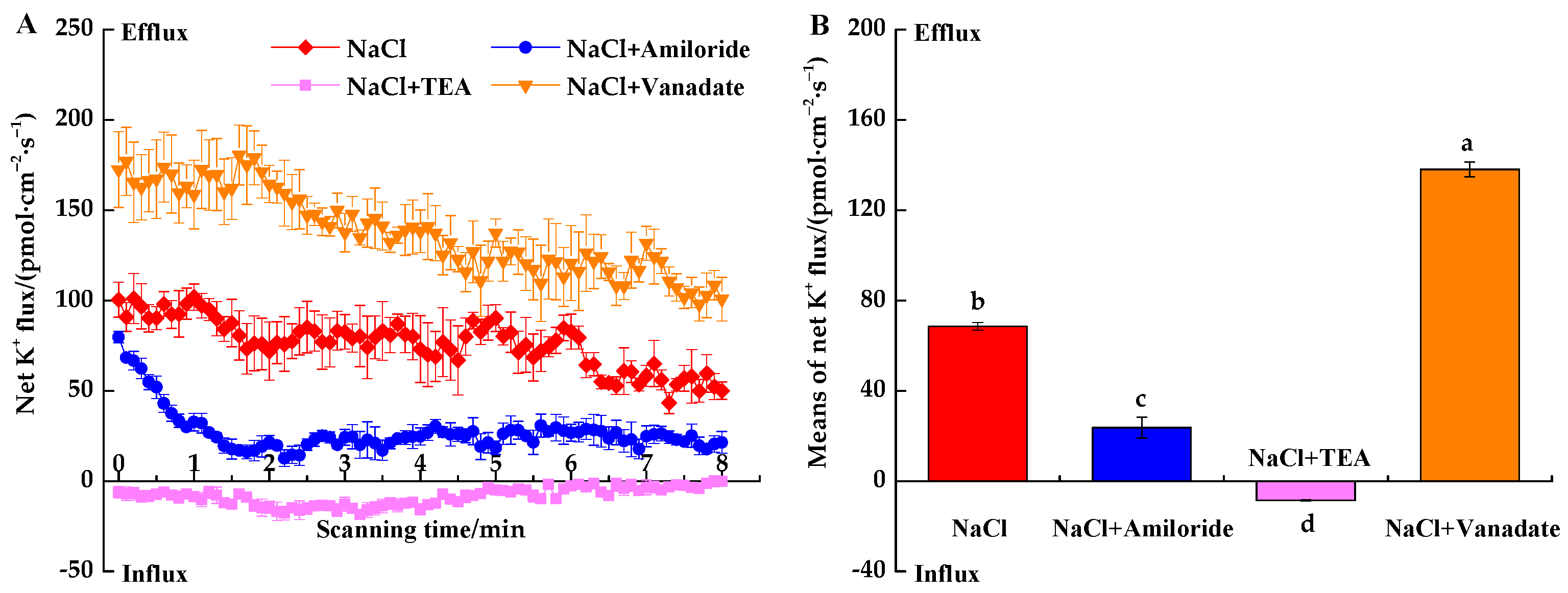
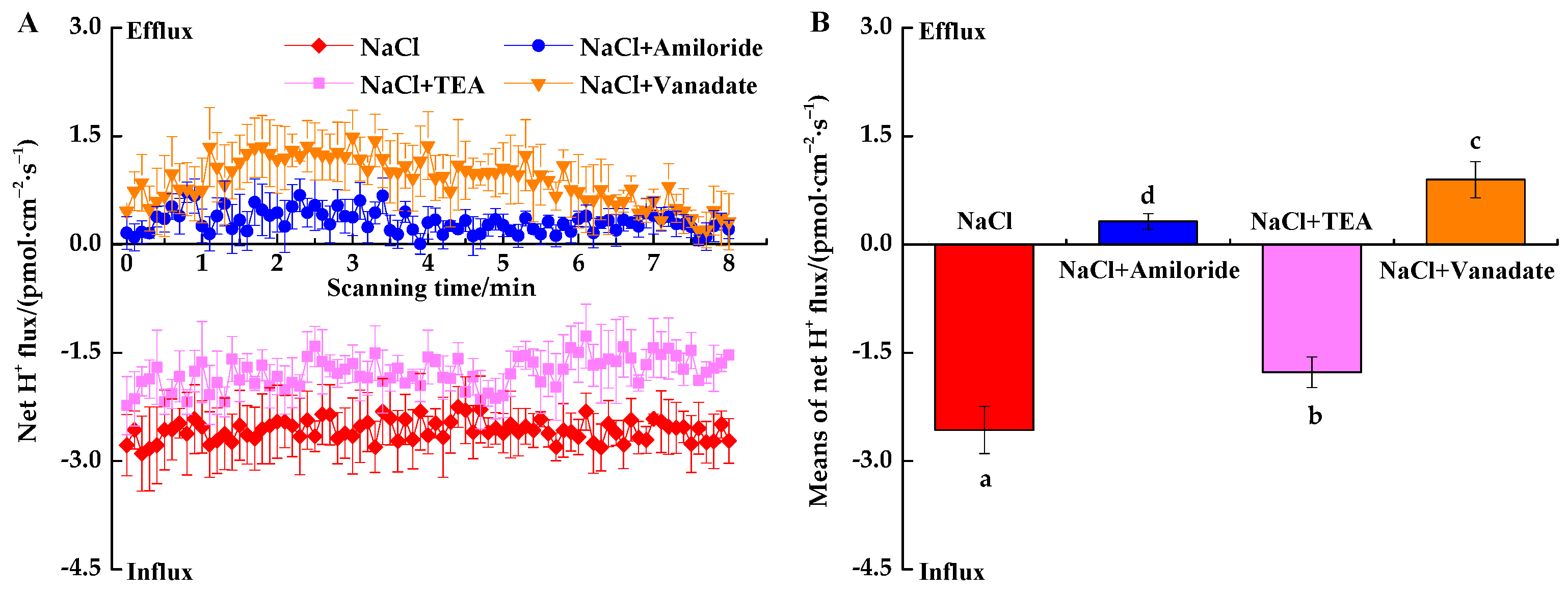
3.3. Effects of Transport Inhibitors on Ion Fluxes under NaCl Stress
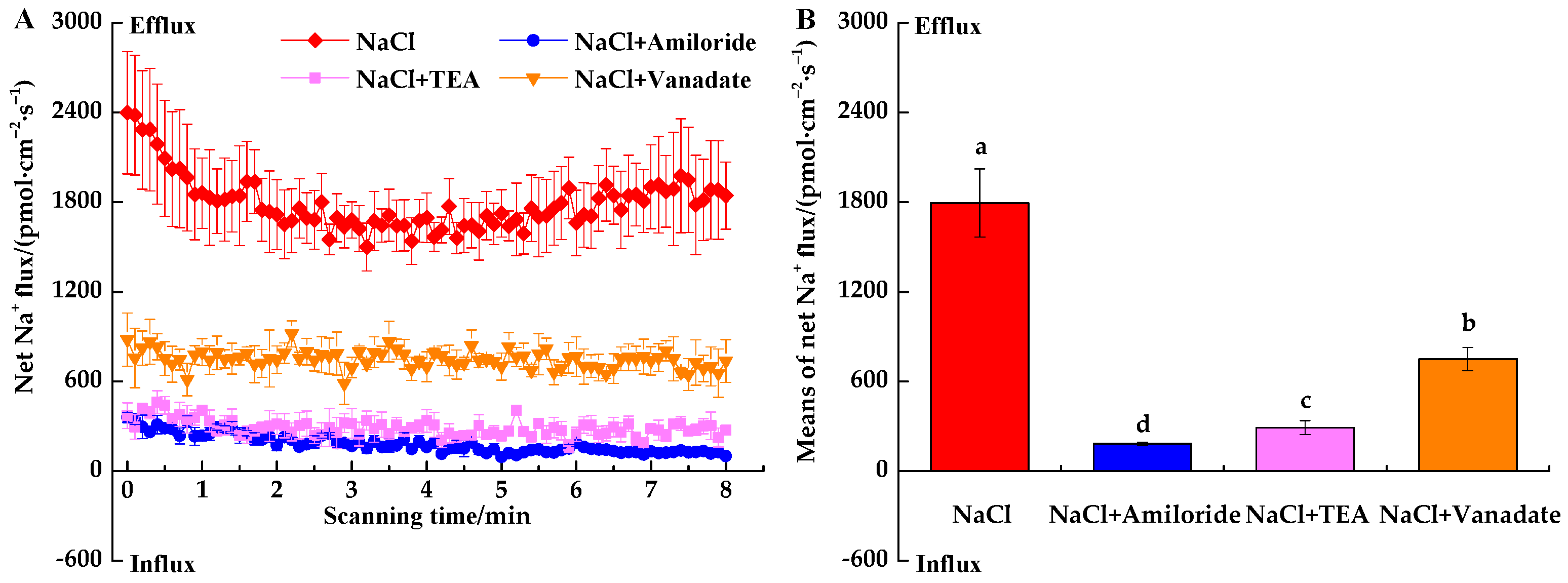
3.3.1. Inhibitor-Induced Na+ Fluxes under NaCl Stress
3.3.2. Inhibitor-Induced K+ Fluxes under NaCl Stress
3.3.3. Inhibitor-Induced H+ Fluxes under NaCl Stress
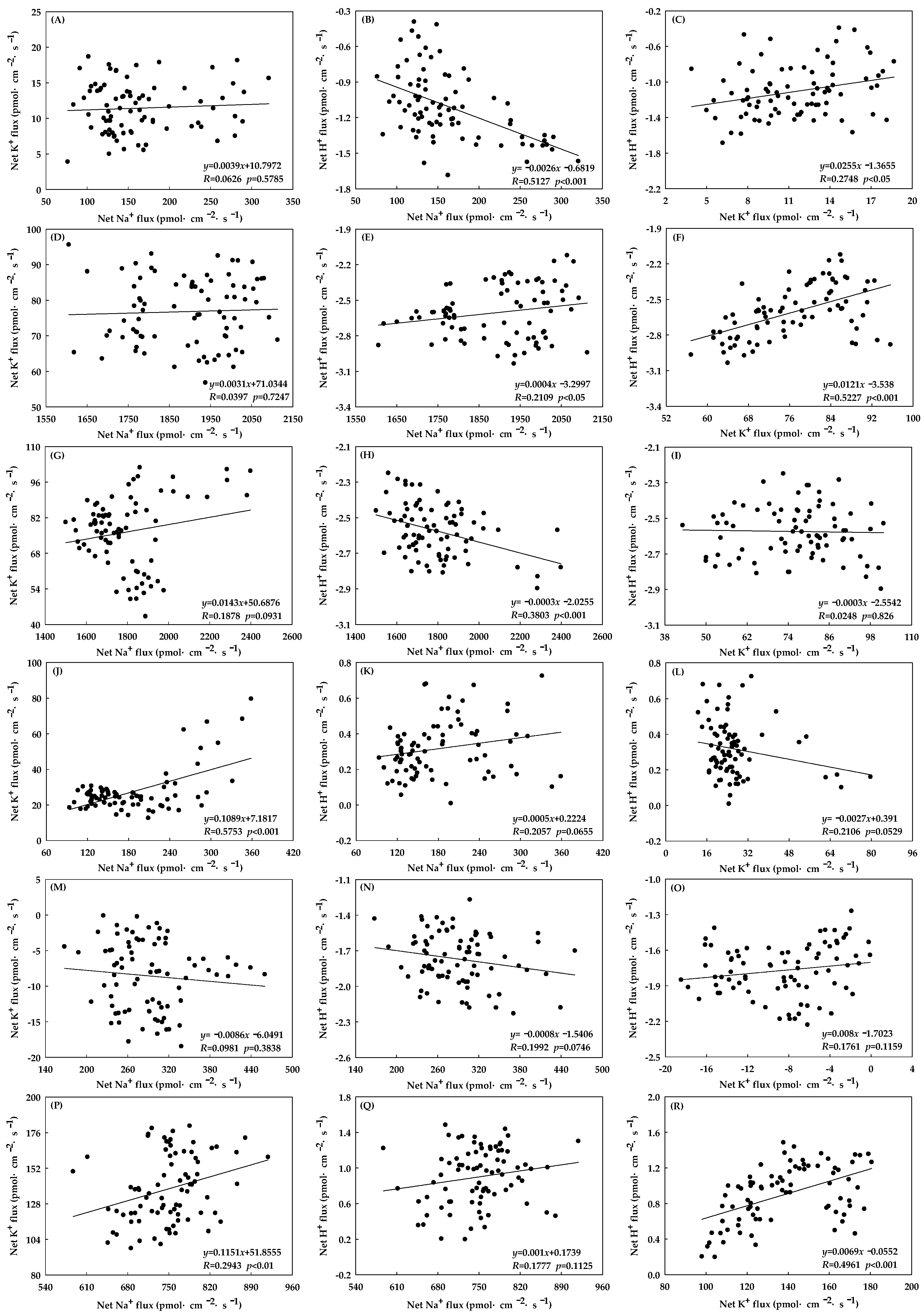
3.4. Relationships among Na+, K+ and H+ Fluxes
4. Discussion
4.1. Salinity Effects on Root Ion Concentration and Ratio
4.2. Salinity Effects on Root Na+, K+ and H+ Fluxes
4.3. Responses of Ion Fluxes to Inhibitors under NaCl Stress
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Munns, R.; Tester, M. Mechanisms of salinity tolerance. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2008, 59, 651–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.Y.; Liu, Y.Q.; Duan, H.R.; Yin, X.X.; Cui, Y.N.; Chai, W.W.; Song, X.; Flowers, T.J.; Wang, S.M. SsHKT1 1 is coordinated with SsSOS1 and SsNHX1 to regulate Na+ homeostasis in Suaeda salsa under saline conditions. Plant Soil 2020, 449, 117–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.Q.; Zhang, H.L.; Shabala, S.; Li, H.Y.; Yang, X.Y.; Zhuang, H.X. Tissue tolerance mechanisms conferring salinity tolerance in a halophytic perennial species Nitraria sibirica pall. Tree Physiol. 2021, 41, 1264–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, J.K. Abiotic stress signaling and responses in plants. Cell 2016, 167, 313–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ismail, A.M.; Horie, T. Genomics, physiology, and molecular breeding approaches for improving salt tolerance. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2017, 68, 405–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acosta-Motos, J.R.; Ortuño, M.F.; Bernal-Vicente, A.; Diaz-Vivancos, P.; Sanchez-Blanco, M.J.; Hernandez, J.A. Plant responses to salt stress: Adaptive mechanisms. Agronomy 2017, 7, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.Q.; Guo, Y. Elucidating the molecular mechanisms mediating plant salt-stress responses. New Phytol. 2018, 217, 523–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.Z.; Zhang, H.; Song, C.P.; Zhu, J.K.; Shabala, S. Mechanisms of plant responses and adaptation to soil salinity. Innovation 2020, 1, 100017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponce, K.S.; Meng, L.; Guo, L.; Leng, Y.; Ye, G. Advances in sensing, response and regulation mechanism of salt tolerance in rice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raddatz, N.; de los Ríos, L.M.; Lindahl, M.; Quintero, F.J.; Pardo, J.M. Coordinated transport of nitrate, potassium, and sodium. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EI Mahi, H.; Hormaeche, J.P.; De, L.A.; Villalta, I.; Espartero, J.; Arjona, F.G.; Fernández, J.L.; Bundó, M.; Mendoza, I.; Mieulet, D.; et al. A critical role of sodium flux via the plasma membrane Na+/H+ exchanger SOS1 in the salt tolerance of rice. Plant Physiol. 2019, 180, 1046–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demidchik, V.; Maathuis, F.J.M. Physiological roles of nonselective cation channels in plants: From salt stress to signaling and development. New Phytol. 2007, 175, 387–404. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.H.; Zhang, X.C.; Giraldo, J.P.; Shabala, S. It is not all about sodium: Revealing tissue specificity and signalling roles of potassium in plant responses to salt stress. Plant Soil 2018, 431, 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Jegadeeson, V.; Kumari, K.; Pulipati, S.; Parida, A.; Venkataraman, G. Expression of wild rice Porteresia coarctata PcNHX1 antiporter gene (PcNHX1) in tobacco controlled by PcNHX1 promoter (PcNHX1p) confers Na+-specific hypocotyl elongation and stem-specific Na+ accumulation in transgenic tobacco. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2019, 139, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shabala, L.; Cuin, T.A.; Newman, I.A.; Shabala, S. Salinity-induced ion flux patterns from the excised roots of Arabidopsis sos mutants. Planta 2005, 222, 1041–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubio, F.; Nieves-Cordones, M.; Horie, T.; Shabala, S. Doing ‘business as usual’ comes with a cost: Evaluating energy cost of maintaining plant intracellular K+ homeostasis under saline conditions. New Phytol. 2019, 225, 1097–1104. [Google Scholar]
- Shabala, S. Ionic and osmotic components of salt stress specifically modulate net ion fluxes from bean leaf mesophyll. Plant Cell Environ. 2000, 23, 825–837. [Google Scholar]
- Maathuis, F.J.M.; Amtmann, A. K+ nutrition and Na+ toxicity: The basis of cellular K+/Na+ ratios. Ann. Bot. 1999, 84, 123–133. [Google Scholar]
- Köster, P.; Wallrad, L.; Edel, K.H.; Faisal, M.; Alatar, A.A.; Kudla, J. The battle of two ions: Ca2+ signalling against Na+ stress. Plant Biol. 2019, 21, 39–48. [Google Scholar]
- Munns, R.; Day, D.A.; Fricke, W.; Watt, M.; Arsova, B.; Barkla, B.J.; Bose, J.; Byrt, C.S.; Chen, Z.H.; Foster, K.Y.; et al. Energy costs of salt tolerance in crop plants. New Phytol. 2020, 225, 1072–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabala, S.; Chen, G.; Chen, Z.H.; Pottosin, I. The energy cost of the tonoplast futile sodium leak. New Phytol. 2019, 225, 1105–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lang, T.; Li, N.Y.; Lu, Y.J.; Sun, H.M.; Shen, Z.D.; Jing, X.S.; Zhao, R.; Shen, X.; Chen, S.L. Extracellular ATP, hydrogen peroxide, calcium and nitric oxide mediate root ion fluxes in Bruguiera gymnorrhiza subjected to salt stress. J. Beijing For. Univ. 2014, 36, 16–22. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Z.M.; Mao, G.L.; Xu, X.; Wang, S.; Zheng, R.; Yang, S.J. Effect of salt stress and inhibitor on uptake and transportation of Na+ and K+ in the root of Ningxia Lycium barbarum L. Agric. Res. Arid Areas 2017, 35, 140–145. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Kang, H.X.; Wu, G.Q.; Wei, M.; Li, S.J. The role of Na+/H+ antiporter in response of plant to abiotic stress. Plant Physiol. J. 2022, 58, 511–523. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Shabala, S.; Newman, I.A. Salinity effects on the activity of plasma membrane H+ and Ca2+ transporters in bean leaf mesophyll: Masking role of the cell wall. Ann. Bot. 2000, 85, 681–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silvestri, C.; Bacchetta, L.; Bellincontro, A.; Cristofori, V. Advances in cultivar choice, hazelnut orchard management and nuts storage for enhancing product quality and safety: An overview. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2021, 101, 27–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Wang, L.J.; Zhao, T.T. High genetic variability and complex population structure of the native Chinese hazelnut. Braz. J. Bot. 2018, 41, 687–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, D.; Shi, Y.J.; Song, F.H.; Mahmut, A.; Song, Z.J.; Ling, J.X.; Zuo, C. Evaluation of fruit economic traits of Corylus heterophylla × C. avellane. J. Northeast Forest. Univ. 2020, 48, 45–49. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhuang, Q.W.; Wu, S.X.; Yang, Y.; Niu, Y.X.; Yan, Y.Y. Spatiotemporal characteristics of different degree of salinized cultivated land in Xinjiang in recent ten years. J. Univ. Chin. Acad. Sci. 2021, 38, 341–349. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Morton, M.J.L.; Awlia, M.; Al-Tamimi, N.; Saade, S.; Pailles, Y.; Negrao, S.; Tester, M. Salt stress under the scalpel-dissecting the genetics of salt tolerance. Plant J. 2019, 97, 148–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, D.; Shi, Y.J.; Song, F.H.; Li, J.C. Effects of salt stress on growth, photosynthetic and fluorescence characteristics, and root architecture of Corylus heterophylla × C. avellan seedlings. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2019, 30, 3376–3384. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Luo, D.; Shi, Y.J.; Song, F.H. Physiological responses of seedlings of Ping’ou hybrid hazelnut to salt stress and their evaluation of salt tolerance. Chin. J. Ecol. 2023, 42, 1–8. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Luo, D.; Wu, Z.B.; Song, F.H.; Shi, Y.J. Ion flux characteristics of root and their response to ion transport inhibitors of Corylus heterophylla × C. avellana seedlings under salt stress. Plant Physiol. J. 2023, 59, 889–898. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Luo, D.; Wu, Z.B.; Shi, Y.J.; Song, F.H. Effects of salt stress on leaf anatomical structure and ion absorption, transportation and distribution of three Ping’ou hybrid hazelnut seedlings. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2022, 42, 1876–1888. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Jia, Z.G.; Ma, Q.H.; Wang, G.X. Effects of saline-alkali stresses on the growth and endogenous hormone contents in leaves of hybrid hazelnut Liaozhen 3. For. Res. 2015, 28, 394–401. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Tang, X.Q.; Yang, X.Y.; Li, H.Y.; Zhang, H.X. Maintenance of K+/Na+ balance in the roots of Nitraria sibirica Pall. in response to NaCl stress. Forests 2018, 9, 601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Chen, S.L.; Dai, S.X.; Wang, R.G.; Li, N.Y.; Shen, X.; Zhou, X.Y.; Lu, C.F.; Zheng, X.J.; Hu, Z.X.; et al. NaCl-induced alternations of cellular and tissue ion fluxes in roots of salt-resistant and salt-sensitive poplar species. Plant Physiol. 2009, 149, 1141–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Zhang, H.X.; Liu, T.; Wu, H.W.; Ni, J.W.; Chen, Q.X. Study on ion metabolism characteristics of Elaeagnus angustifolia seedlings under NaCl stress. For. Res. 2016, 29, 140–146. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Isayenkov, S.V.; Maathuis, F.J.M. Plant salinity stress: Many unanswered questions remain. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.D.; Wang, C.; Ma, Z.H.; Hou, R.F.; Gao, Q.; Chen, Q. Effect of short term salt stress on the absorption of K+ and accumulation of Na+, K+ in seedlings of different wheat varieties. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2011, 31, 2822–2830. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Y.; Cao, H.S.; Yang, L.; Chen, C.; Shabala, L.; Xiong, M.; Niu, M.L.; Liu, J.; Zheng, Z.H.; Zhou, L.J.; et al. Tissue-specific respiratory burst oxidase homologue-dependent H2O2 signaling to the plasma membrane H+-ATPase confers potassium uptake and salinity tolerance in Cucurbitaceae. J. Exp. Bot. 2019, 70, 5879–5893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, D.D.; Liu, A.Q.; Li, H.T.; Yu, Y.Y.; Wei, Z.C.; Wang, J.N.; Zhou, L.L. Applications and advances of non-invasive micro-test technology in plant physiological-ecology research. Chin. J. Appl. Environ. Biol. 2017, 23, 175–182. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Chen, T.X.; Wang, W.L.; Xu, K.; Xu, Y.; Ji, D.H.; Chen, C.S.; Xie, C.T. K+ and Na+ transport contribute to K+/Na+ homeostasis in Pyropia haitanensis under hypersaline stress. Algal Res. 2019, 40, 101526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Hong, Y.C.; Zhu, G.T.; Li, Y.M.; Niu, Q.Y.; Yao, J.J.; Hua, K.; Bai, J.J.; Zhu, Y.F.; Shi, H.Z.; et al. Loss of salt tolerance during tomato domestication conferred by variation in a Na+/K+ transporter. EMBO J. 2020, 39, e103256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.; Zhang, H.X.; Chen, Q.X.; Yang, X.Y. Responses of apical ion fluxes to NaCl stress in Elaeagnus angustifolia seedlings. Chin. J. Plant Ecol. 2017, 41, 489–496. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Sun, J.; Dai, S.X.; Wang, R.G.; Chen, S.L.; Li, N.Y.; Zhou, X.Y.; Lu, C.F.; Shen, X.; Zheng, X.J.; Hu, Z.X. Calcium mediates root K+/Na+ homeostasis in poplar species differing in salt tolerance. Tree Physiol. 2009, 29, 1175–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, H.; Golldack, D.; Zhao, C.S.; Bohnert, H.J. The expression of HAK-type K+ transporters is regulated in response to salinity stress in common ice plant. Plant Physiol. 2002, 129, 1482–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.H.; Pottosin, I.I.; Cuin, T.A.; Fuglsang, A.T.; Tester, M.; Jha, D.; Zepeda-Jazo, I.; Zhou, M.X.; Palmgren, M.G.; Newman, I.A.; et al. Root plasma membrane transporters controlling K+/Na+ homeostasis in salt stressed barley. Plant Physiol. 2007, 145, 1714–1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuin, T.A.; Betts, S.A.; Chalmandrier, R.; Shabala, S. A root’s ability to retain K+ correlates with salt tolerance in wheat. J. Exp. Bot. 2008, 59, 2697–2706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, X.Q.; Luo, Z.; Dong, H.Z.; Eneji, A.E.; Li, W.J. Effects of non-uniform root zone salinity on water use, Na+ recirculation, and Na+ and H+ flux in cotton. J. Exp. Bot. 2012, 63, 2105–2116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Q.; Li, Y.X.; Yuan, H.J.; Hu, J.; Wei, L.; Bao, A.K.; Zhang, J.L.; Wang, S.M. ZxSOS1 is essential for long-distance transport and spatial distribution of Na+ and K+ in the xerophyte Zygophyllum xanthoxylum. Plant Soil 2014, 374, 661–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.X.; He, G.F.; Li, J.F.; Perez-Hormaeche, J.; Becker, T.; Luo, M.Q.; Wallrad, L.; Gao, J.P.; Li, J.; Pardo, J.M. A salt stress-activated GSO1-SOS2-SOS1 module protects the Arabidopsis root stem cell niche by enhancing sodium ion extrusion. EMBO J. 2023, 42, e113004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Luo, D.; Song, F.; Lu, M.; Shi, Y.; Ma, Q. Salt-Stress-Induced Ion Transport Contributes to K+/Na+ Homeostasis in Roots of Ping’ou Hybrid Hazelnut. Forests 2023, 14, 1651. https://doi.org/10.3390/f14081651
Luo D, Song F, Lu M, Shi Y, Ma Q. Salt-Stress-Induced Ion Transport Contributes to K+/Na+ Homeostasis in Roots of Ping’ou Hybrid Hazelnut. Forests. 2023; 14(8):1651. https://doi.org/10.3390/f14081651
Chicago/Turabian StyleLuo, Da, Fenghui Song, Mingyan Lu, Yanjiang Shi, and Qinghua Ma. 2023. "Salt-Stress-Induced Ion Transport Contributes to K+/Na+ Homeostasis in Roots of Ping’ou Hybrid Hazelnut" Forests 14, no. 8: 1651. https://doi.org/10.3390/f14081651
APA StyleLuo, D., Song, F., Lu, M., Shi, Y., & Ma, Q. (2023). Salt-Stress-Induced Ion Transport Contributes to K+/Na+ Homeostasis in Roots of Ping’ou Hybrid Hazelnut. Forests, 14(8), 1651. https://doi.org/10.3390/f14081651




