Effects of Adding Native Annual Seeds to South Korea Native Perennial Seed Mixture on Early Stage Vegetation Recovery, Soil Enzymes, and Nutrient Dynamics in Post-Fire Soils
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Design
2.2. Plant Analysis
2.3. Soil Analysis
2.4. Nutrient Leaching
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Plant Analysis
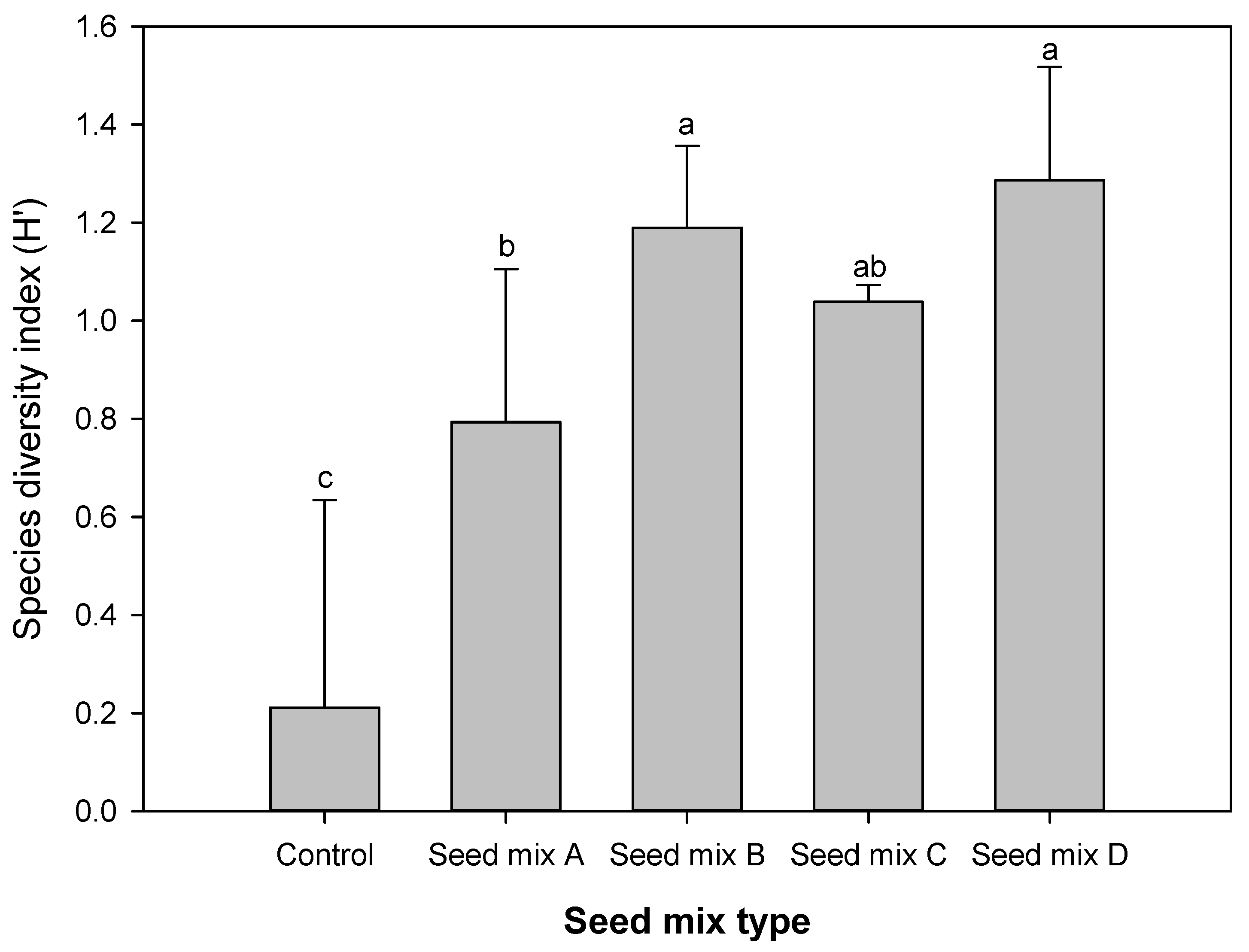
3.1.1. Plant Species
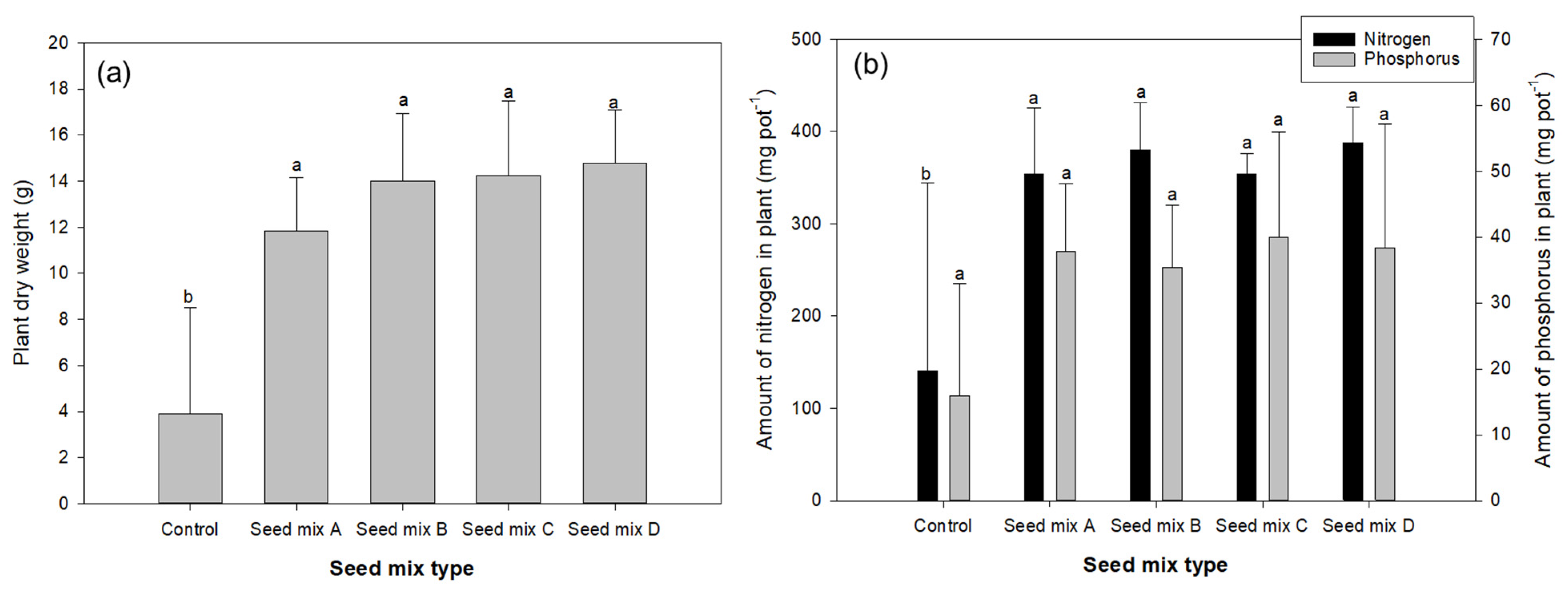
3.1.2. Biomass and N, P Accumulation of Plants
3.2. Soil Analysis
3.2.1. Soil Physico-Chemical Properties including Nutrients
3.2.2. Soil Enzyme Activity
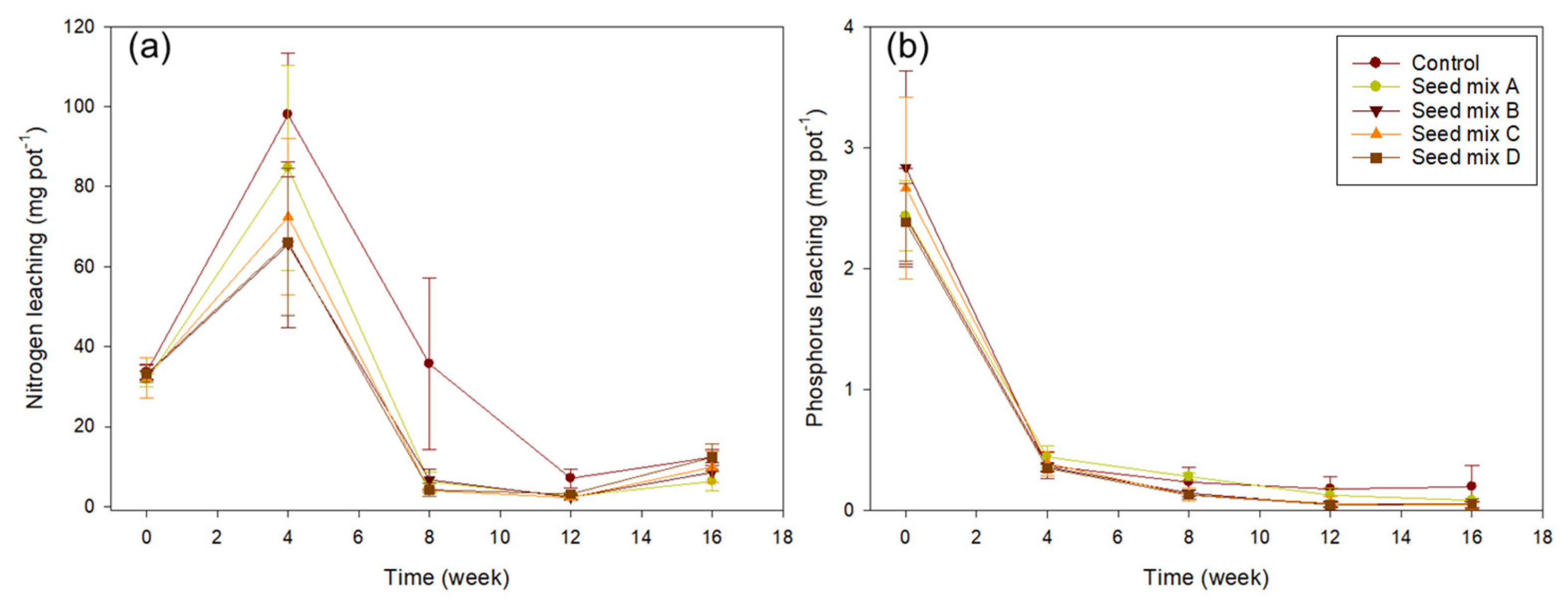
3.3. N, P Leaching
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, K.; Song, C.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Q. Natural Disasters and Economic Development Drive Forest Dynamics and Transition in China. For. Policy Econ. 2017, 76, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbero, M.; Bonin, G.; Loisel, R.; Quézel, P. Changes and Disturbances of Forest Ecosystems Caused by Human Activities in the Western Part of the Mediterranean Basin. Vegetatio 1990, 87, 151–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rengers, F.K.; McGuire, L.A.; Oakley, N.S.; Kean, J.W.; Staley, D.M.; Tang, H. Landslides after Wildfire: Initiation, Magnitude, and Mobility. Landslides 2020, 17, 2631–2641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ríos-Pena, L.; Kneib, T.; Cadarso-Suárez, C.; Marey-Pérez, M. Predicting the Occurrence of Wildfires with Binary Structured Additive Regression Models. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 187, 154–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, J.D.; Johnson, D.W.; Miller, W.W.; Walker, R.F.; Carroll, E.F.; Blank, R.R. Wildfire Effects on Soil Nutrients and Leaching in a Tahoe Basin Watershed. J. Environ. Qual. 2006, 35, 479–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inbar, A.; Lado, M.; Sternberg, M.; Tenau, H.; Ben-Hur, M. Forest Fire Effects on Soil Chemical and Physicochemical Properties, Infiltration, Runoff, and Erosion in a Semiarid Mediterranean Region. Geoderma 2014, 221–222, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Certini, G. Effects of Fire on Properties of Forest Soils: A Review. Oecologia 2005, 143, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutiel, P.; Shaviv, A. Effects of Soil Type, Plant Composition and Leaching on Soil Nutrients Following a Simulated Forest Fire. For. Ecol. Manag. 1992, 53, 329–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Xu, X.; McCarter, C.P.R.; Zhang, N.; Ganzoury, M.A.; Waddington, J.M.; de Lannoy, C.F. Assessing Leached TOC, Nutrients and Phenols from Peatland Soils after Lab-Simulated Wildfires: Implications to Source Water Protection. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 822, 153579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandra, K.; Bhardwaj, A.K.; Chandra, K.K.; Kumar Bhardwaj, A. Incidence of Forest Fire in India and Its Effect on Terrestrial Ecosystem Dynamics, Nutrient and Microbial Status of Soil. Int. J. Agric. 2015, 5, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atutova, Z.V. Post-fire restoration of pine forests in the Badary area, Tunkinskiy National Park, Russia. Nat. Conserv. Res. 2023, 8, 22–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiberio, F.C.S.; Xavier, R.O.; Dodonov, P.; Silva Matos, D.M. Fire has short-term negative effects on a super-dominant native fern, Pteridium arachnoideum (Dennstaedtiaceae), in a Brazilian savanna. Nat. Conserv. Res. 2022, 7, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keeley, J.E.; Brennan, T.J. Fire-Driven Alien Invasion in a Fire-Adapted Ecosystem. Oecologia 2012, 169, 1043–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Xu, M. Runoff and Soil Loss from Revegetated Grasslands in the Hilly Loess Plateau Region, China: Influence of Biocrust Patches and Plant Canopies. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2013, 18, 387–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam-choon, K. Ecological Restoration and Revegetation Works in Korea. Landsc. Ecol. Eng. 2005, 1, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paschke, M.W.; DeLeo, C.; Redente, E.F. Revegetation of Roadcut Slopes in Mesa Verde National Park, U.S.A. Restor. Ecol. 2000, 8, 276–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyser, R.W.; Asebrook, J.M.; Potter, R.W.; Kurth, L.L. Roadside Revegetation in Glacier National Park, U.S.A.: Effects of Herbicide and Seeding Treatments. Restor. Ecol. 1998, 6, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lepŝ, J.; Doleẑal, J.; Bezemer, T.M.; Brown, V.K.; Hedlund, K.; Igual Arroyo, M.; Jörgensen, H.B.; Lawson, C.S.; Mortimer, S.R.; Peix Geldart, A.; et al. Long-term Effectiveness of Sowing High and Low Diversity Seed Mixtures to Enhance Plant Community Development on Ex-arable Fields. Appl. Veg. Sci. 2007, 10, 97–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirmer, A.; Baasch, A.; Tischew, S. Sowing of Low and High Diversity Seed Mixtures in Ecological Restoration of Surface Mined-Land. Appl. Veg. Sci. 2012, 15, 198–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, A.; Kirmer, A.; Kiehl, K.; Tischew, S. Seed Mixture Strongly Affects Species-Richness and Quality of Perennial Flower Strips on Fertile Soil. Basic Appl. Ecol. 2020, 42, 62–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valkó, O.; Deák, B.; Török, P.; Kirmer, A.; Tischew, S.; Kelemen, A.; Tóth, K.; Miglécz, T.; Radócz, S.; Sonkoly, J. High-Diversity Sowing in Establishment Gaps: A Promising New Tool for Enhancing Grassland Biodiversity. Tuexenia 2016, 36, 359–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barr, S.; Jonas, J.L.; Paschke, M.W. Optimizing Seed Mixture Diversity and Seeding Rates for Grassland Restoration. Restor. Ecol. 2017, 25, 396–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keeley, J.E. Ecological Impacts of Wheat Seeding after a Sierra Nevada Wildfire. Int. J. Wildland Fire 2004, 13, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barclay, A.D.; Betancourt, J.L.; Allen, C.D. Effects of Seeding Ryegrass (Lolium multiflorum) on Vegetation Recovery Following Fire in a Ponderosa Pine (Pinus ponderosa) Forest. Int. J. Wildland Fire 2004, 13, 183–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herron, C.M.; Jonas, J.L.; Meiman, P.J.; Paschke, M.W. Using Native Annual Plants to Restore Post-Fire Habitats in Western North America. Int. J. Wildland Fire 2013, 22, 815–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stroot, L.; Brinkert, A.; Hölzel, N.; Rüsing, A.; Bucharova, A. Establishment of Wildflower Strips in a Wide Range of Environments: A Lesson from a Landscape-scale Project. Restor. Ecol. 2022, 30, e13542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheley, R.L.; Half, M.L. Enhancing Native Forb Establishment and Persistence Using a Rich Seed Mixture. Restor. Ecol. 2006, 14, 627–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyvönen, T.; Huusela-Veistola, E. Impact of Seed Mixture and Mowing on Food Abundance for Farmland Birds in Set-Asides. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2011, 143, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arocena, J.M.; Van Mourik, J.M.; Schilder, M.L.M.; Faz Cano, A. Initial Soil Development under Pioneer Plant Species in Metal Mine Waste Deposits. Restor. Ecol. 2010, 18, 244–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beyers, J.L. Postfire Seeding for Erosion Control: Effectiveness and Impacts on Native Plant Communities. Conserv. Biol. 2004, 18, 947–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beyers, J.L.; Wakeman, C.D.; Wohlgemuth, P.M.; Conard, S.G. Effects of Postfire Grass Seeding on Native Vegetation in Southern California Chaparral. In Proceedings of the 19th Annual Forest Vegetation Management Conference: Wildfire Rehabilitation, Forest Vegetation Management Conference, Redding, CA, USA, 20–22 January 1998; pp. 52–64. [Google Scholar]
- Shim, S.-R.; Kim, J.-H. Vegetation Characteristics of Main Herbaceous Flowers for Ecological Restoration. J. Korean Environ. Res. Reveg. Technol. 2006, 9, 64–71. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, C.-G.; Choung, Y.-S.; Joo, K.-Y.; Lee, K.-S. Effects of Hillslope Treatments for Vegetation Development and Soil Conservation in Burned Forests. J. Ecol. Environ. 2006, 29, 295–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, D.W.; Sommers, L.E. Determination of Total Nitrogen in Plant Material 1. Agron. J. 1973, 65, 109–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esslemont, G.; Maher, W.; Ford, P.; Krikowa, F. The Determination of Phosphorus and Other Elements in Plant Leaves by ICP-MS after Low-Volume Microwave Digestion with Nitric Acid. At. Spectrosc. 2000, 21, 42–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marion, B.; Bonis, A.; Bouzillé, J.B. How Much Does Grazing-Induced Heterogeneity Impact Plant Diversity in Wet Grasslands? Ecoscience 2010, 17, 229–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NIAST. Method of SOIL and Plant Analysis; National Institute of Agricultural Sciences and Technology Publishing, Rural Development Administration: Suwon, Republic of Korea, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Nelson, D.W.; Sommers, L.E. Total Carbon, Organic Carbon, and Organic Matter. Methods Soil. Anal. Part. 2 Chem. Microbiol. Prop. 1983, 9, 539–579. [Google Scholar]
- Bremner, J.M.; Mulvaney, C.S. Nitrogen—Total. Methods Soil Anal. Part 2 Chem. Microbiol. Prop. 1983, 9, 595–624. [Google Scholar]
- Keeney, D.R.; Nelson, D.W. Nitrogen—Inorganic Forms. Methods Soil Anal. Part 2 Chem. Microbiol. Prop. 1983, 9, 643–698. [Google Scholar]
- Górecka, H.; Chojnacka, K.; Górecki, H. The Application of ICP-MS and ICP-OES in Determination of Micronutrients in Wood Ashes Used as Soil Conditioners. Talanta 2006, 70, 950–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehlich, A. Mehlich 3 Soil Test Extractant: A Modification of Mehlich 2 Extractant. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 1984, 15, 1409–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandeler, E.; Gerber, H. Short-Term Assay of Soil Urease Activity Using Colorimetric Determination of Ammonium. Biol. Fertil. Soils 1988, 6, 68–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabatabai, M.A.; Bremner, J.M. Use of P-Nitrophenyl Phosphate for Assay of Soil Phosphatase Activity. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1969, 1, 301–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Zhang, C.; Rong, Q.; Li, C.; Mao, J.; Liu, Y.; Chen, J.; Liu, X. Effect of Two Organic Amendments on Atrazine Degradation and Microorganisms in Soil. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2020, 152, 103564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, D.W.; Sommers, L.E. Determination of Total Nitrogen in Natural Waters; Wiley Online Library: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1975. [Google Scholar]
- Maia, P.; Pausas, J.G.; Arcenegui, V.; Guerrero, C.; Pérez-Bejarano, A.; Mataix-Solera, J.; Varela, M.E.T.; Fernandes, I.; Pedrosa, E.T.; Keizer, J.J. Wildfire Effects on the Soil Seed Bank of a Maritime Pine Stand—The Importance of Fire Severity. Geoderma 2012, 191, 80–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keeler-Wolf, T. Post-Fire Emergency Seeding and Conservation in Southern California Shrublands. In Brushfires in California Wildlands: Ecology and Resource Management; International Association of Wildland Fire: Fairfield, Australia, 1995; pp. 127–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, G.; Saqib, M.; Akhtar, J.; Murtaza, G.; Shahid, M.; Hussain, A. Relationship between Rhizosphere Acidification and Phytoremediation in Two Acacia Species. J. Soils Sediments 2016, 16, 1392–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, D.K.; Kumar, S. Nitrate Reductase, Arginine Deaminase, Urease and Dehydrogenase Activities in Natural Soil (Ridges with Forest) and in Cotton Soil after Acetamiprid Treatments. Chemosphere 2008, 71, 412–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.B.; Wang, J.; Liu, W.L.; Zhu, S.X.; Liu, D.; Chang, S.X.; Chang, J.; Ge, Y. Effects of Plant Diversity on Nutrient Retention and Enzyme Activities in a Full-Scale Constructed Wetland. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 1686–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siczek, A.; Frąc, M.; Kalembasa, S.; Kalembasa, D. Soil Microbial Activity of Faba Bean (Vicia faba L.) and Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) Rhizosphere during Growing Season. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2018, 130, 34–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Zhang, Y.; Xia, Y.; Cui, Z.; Cao, C. Soil Microbial Community Succession Based on Phod and Gcd Genes along a Chronosequence of Sand-Fixation Forest. Forests 2021, 12, 1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, R.K.; Kumar, J.; Srivastava, P.K.; Bashri, G.; Prasad, S.M. PSII Photochemistry, Oxidative Damage and Anti-Oxidative Enzymes in Arsenate-Stressed Oryza sativa L. Seedlings. Chem. Ecol. 2017, 33, 34–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavres, J.; Franco, G.C.; de Sousa Câmara, G.M. Soybean Seed Treatment with Nickel Improves Biological Nitrogen Fixation and Urease Activity. Front. Environ. Sci. 2016, 4, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velmourougane, K.; Venugopalan, M.V.; Bhattacharyya, T.; Sarkar, D.; Pal, D.K.; Sahu, A.; Chandran, P.; Ray, S.K.; Mandal, C.; Nair, K.M.; et al. Urease Activity in Various Agro-Ecological Sub-Regions of Black Soil Regions of India. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA India Sect. B Biol. Sci. 2013, 83, 513–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Liu, Y.; Chen, L.; Yang, H.; Wang, G.; Wang, C.; Dong, X. Effects of Excessive Nitrogen on Nitrogen Uptake and Transformation in the Wetland Soils of Liaohe Estuary, Northeast China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 791, 148228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanté, M.; Riah-Anglet, W.; Cliquet, J.B.; Trinsoutrot-Gattin, I. Soil Enzyme Activity and Stoichiometry: Linking Soil Microorganism Resource Requirement and Legume Carbon Rhizodeposition. Agronomy 2021, 11, 2131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, M.; Dick, R.P. Thermal Stability and Activities of Soil Enzymes as Influenced by Crop Rotations. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1995, 27, 1161–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Power, J.F. Growth Characteristics of Legume Cover Crops in a Semiarid Environment. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1991, 55, 1659–1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udawatta, R.P.; Kremer, R.J.; Garrett, H.E.; Anderson, S.H. Soil Enzyme Activities and Physical Properties in a Watershed Managed under Agroforestry and Row-Crop Systems. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2009, 131, 98–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.L.; Chen, L.J.; Chen, X.H.; Tan, M.L.; Duan, Z.H.; Wu, Z.J.; Li, X.J.; Fan, X.H. Response of Soil Enzyme Activity to Long-Term Restoration of Desertified Land. Catena 2015, 133, 64–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, J.; Holden, N.M. The Relationship between Soil Microbial Activity and Microbial Biomass, Soil Structure and Grassland Management. Soil. Tillage Res. 2015, 146, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, J.C.; McCann, K.; Setälä, H.; De Ruiter, P.C. Top-down Is Bottom-up: Does Predation in the Rhizosphere Regulate Aboveground Dynamics? Ecology 2003, 84, 846–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, W.M.; George, T.S.; Stutter, M.I.; Louro, A.; Ali, M.; Haygarth, P.M. Phosphorus Leaching from Riparian Soils with Differing Management Histories under Three Grass Species. J. Environ. Qual. 2020, 49, 74–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Shatnawi, M.K.J.; Makhadmeh, I.M. Ecophysiology of the Plant-Rhizosphere System. J. Agron. Crop Sci. 2001, 187, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pugesgaard, S.; Schelde, K.; Larsen, S.U.; Lærke, P.E.; Jørgensen, U. Comparing Annual and Perennial Crops for Bioenergy Production—Influence on Nitrate Leaching and Energy Balance. GCB Bioenergy 2015, 7, 1136–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, C.T.K.; Watts-Williams, S.J.; Smernik, R.J.; Cavagnaro, T.R. Effects of Plant Roots and Arbuscular Mycorrhizas on Soil Phosphorus Leaching. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 722, 137847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wendel, A.S.; Bauke, S.L.; Amelung, W.; Knief, C. Root-Rhizosphere-Soil Interactions in Biopores. Plant Soil 2022, 475, 253–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brye, K.R.; Andraski, T.W.; Jarrell, W.M.; Bundy, L.G.; Norman, J.M. Phosphorus Leaching under a Restored Tallgrass Prairie and Corn Agroecosystems. J. Environ. Qual. 2002, 31, 769–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, L.; Li, Q.; Chen, H. Effects of a Wildfire on Selected Physical, Chemical and Biochemical Soil Properties in a Pinus Massoniana Forest in South China. Forests 2014, 5, 2947–2966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pappa, A.; Tzamtzis, N.; Koufopoulou, S. Effect of Fire Retardant Application on Phosphorus Leaching from Mediterranean Forest Soil: Short-Term Laboratory-Scale Study. Int. J. Wildland Fire 2006, 15, 287–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, J.; Tang, C.; Robertson, A.; Franks, A.E.; Armstrong, R.; Sale, P. Increased Microbial Activity Contributes to Phosphorus Immobilization in the Rhizosphere of Wheat under Elevated CO2. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2014, 75, 292–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perucci, P. Effect of the Addition of Municipal Solid-Waste Compost on Microbial Biomass and Enzyme Activities in Soil. Biol. Fertil. Soils 1990, 10, 221–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, K.; Sun, T.; Tian, J.; Chen, Z.; Chen, L. Soil Microbial Biomass, Phosphatase and Their Relationships with Phosphorus Turnover under Mixed Inorganic and Organic Nitrogen Addition in a Larix gmelinii Plantation. For. Ecol. Manag. 2018, 422, 313–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Name of Treatment | Number of Seeds per Each Pot | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Isodon inflexus | Lespedeza cuneata | Aster yomena | Dendranthema boreale | Chrysanthemum zawadskii | Cirsium japonicum | Callistephus chinensis | Chamaecrista nomame | |
| Control | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Seed mix A | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 0 | 0 |
| Seed mix B | 17 | 17 | 17 | 17 | 17 | 17 | 17 | 0 |
| Seed mix C | 17 | 17 | 17 | 17 | 17 | 17 | 0 | 17 |
| Seed mix D | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 |
| Seed Mixture Type | Average Number of Plant Species | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Isodon inflexus | Lespedeza cuneata | Aster yomena | Dendranthema boreale | Chrysanthemum zawadskii | Cirsium japonicum | Callistephus chinensis | Chamaecrista nomame | Cyperus microiria | Portulaca oleracea | Phytolacca acinosa | Total | |
| Control | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.5 | 0.7 | 0 | 1.2 |
| Seed mix A | 0 | 2.8 | 7.8 | 0.3 | 0.5 | 0.3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 11.7 |
| Seed mix B | 0 | 1 | 4 | 1 | 0 | 1.3 | 5.8 | 0 | 0.3 | 0 | 0 | 13.4 |
| Seed mix C | 0 | 1 | 6 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 10 | 0.3 | 0 | 0.3 | 18.6 |
| Seed mix D | 0 | 1 | 2.8 | 0.8 | 0 | 0.5 | 5.8 | 8 | 0.3 | 0.3 | 0 | 19.5 |
| Seed Mixture Type | pH 1 | OM 2 (%) | Clay (%) | TN 3 (mg kg−1) | NH4+-N (mg kg−1) | NO3−-N (mg kg−1) | TP 4 (mg kg−1) | M3-P 5 (mg kg−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 6.48 aa | 11.2 a | 5.8 ba | 3969 a | 182.70 a | 26.78 a | 466.48 aa | 098.76 a |
| Seed mix A | 6.37 ba | 12.6 a | 6.3 ab | 3766 a | 168.53 a | 15.93 a | 485.93 ab | 100.59 a |
| Seed mix B | 6.39 ab | 12.1 a | 5.7 ba | 3801 a | 162.23 a | 21.70 a | 492.51 ab | 100.15 a |
| Seed mix C | 6.27 ca | 11.6 a | 6.6 aa | 4025 a | 148.58 a | 24.15 a | 575.09 ba | 104.76 a |
| Seed mix D | 6.30 bc | 11.1 a | 5.9 ba | 3962 a | 159.08 a | 20.83 a | 573.63 ba | 105.06 a |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Min, H.-G.; Wee, J.; Koo, N.; Kim, J.-G. Effects of Adding Native Annual Seeds to South Korea Native Perennial Seed Mixture on Early Stage Vegetation Recovery, Soil Enzymes, and Nutrient Dynamics in Post-Fire Soils. Forests 2023, 14, 2281. https://doi.org/10.3390/f14122281
Min H-G, Wee J, Koo N, Kim J-G. Effects of Adding Native Annual Seeds to South Korea Native Perennial Seed Mixture on Early Stage Vegetation Recovery, Soil Enzymes, and Nutrient Dynamics in Post-Fire Soils. Forests. 2023; 14(12):2281. https://doi.org/10.3390/f14122281
Chicago/Turabian StyleMin, Hyun-Gi, June Wee, Namin Koo, and Jeong-Gyu Kim. 2023. "Effects of Adding Native Annual Seeds to South Korea Native Perennial Seed Mixture on Early Stage Vegetation Recovery, Soil Enzymes, and Nutrient Dynamics in Post-Fire Soils" Forests 14, no. 12: 2281. https://doi.org/10.3390/f14122281
APA StyleMin, H.-G., Wee, J., Koo, N., & Kim, J.-G. (2023). Effects of Adding Native Annual Seeds to South Korea Native Perennial Seed Mixture on Early Stage Vegetation Recovery, Soil Enzymes, and Nutrient Dynamics in Post-Fire Soils. Forests, 14(12), 2281. https://doi.org/10.3390/f14122281





