Abstract
Biological invasion is one of the most important factors affecting global biodiversity change, which can adversely affect ecosystem function. However, little is known about the effects of belowground biological invasions on soil ecosystems. In this study, we conducted a field-based mesocosm experiment to observe the effects of exotic and native earthworms (Pontoscolex corethrurus and Amynthas corticis, respectively) on soil nutrients and micro-decomposers (i.e., soil microorganisms and nematodes) in a subtropical forest in southern China. We found that exotic and native earthworms had different effects on nutrient availability and nematode communities in the soil. Specifically, exotic earthworms significantly decreased the content of nitrates in the soil and tended to decrease the total nematode abundance compared with native earthworms. Furthermore, nematode species richness and Shannon–Wiener index were lowest in the treatment with exotic earthworms and were the highest in the treatment with native earthworms. However, neither native nor exotic earthworms significantly affected soil microbial community composition. The results of redundancy analysis indicated that available phosphorus was positively correlated with nematode community. Our results demonstrated that exotic earthworms had adverse effects on the available nutrient content in the soil, and had a potential negative effect on the abundance of soil microfauna. These findings will be helpful in understanding the influence of exotic earthworms on soil micro-decomposers and the ecological consequences of earthworm invasion.
1. Introduction
Biological invasion has a significant impact on biodiversity in ecosystems [1,2]. Previous invasive ecology studies have focused primarily on invasions by plants and vertebrates, but invasions by soil fauna, such as earthworms, can also be problematic [3]. Earthworms are found on all continents except Antarctica, and some taxa are found globally due to human action [4,5]. Biological invasions by soil invertebrates have been poorly studied compared to biological invasions occurring on the ground, even though they can also dramatically alter the functioning of ecosystems [3,6,7]. In addition, studies have shown that models of aboveground and belowground biodiversity are different. Areas with a mismatch between surface and soil biodiversity account for 27% of the Earth’s land area. For instance, the soil biodiversity is higher than the surface biodiversity in the belt and tundra [8]. Considering the important role of soil biodiversity in maintaining ecosystem functions, we need a better understanding of the consequences of belowground biological invasions on other soil biota.
Earthworms, considered engineers of soil ecosystems, are divided into three categories: epigeic, endogeic, and anecic species. Epigeic species live mainly on the surface of the soil organic layer. Endogeic species live in the soil mineral layer and feed on soil organic matter. Anecic species form vertical burrows that move litter from the surface of the soil into deeper soil horizons [6]. Since earthworms can adapt to a wide range of niches, from traditionally favorable microhabitats to inhospitable areas (e.g., desert oases) [9], it is common for earthworms to be considered invasive species. For example, Pontoscolex corethrurus (Muller, 1856) originates from the Guyana plateau in South America [10]. This endogeic earthworm feeds on organic matter in the soil [11,12] and is found in more than 56 countries, widely distributed throughout subtropical and tropical regions and transition zones [13,14]. It is ubiquitous in our study site, where it accounts for 95% of the earthworm biomass [15]. As ecosystem engineers, earthworms directly and indirectly impact ecosystem functions [16,17]. For instance, their burrowing and casting behavior can directly increase soil nutrient release, change soil structure, and affect both physical and chemical properties of soil [18], which ultimately indirectly affects soil function and resource availability of the soil food web [19,20,21,22]. However, the ecological roles of native and exotic earthworms may differ. Meta-analyses have shown that earthworm invasions can affect soil physical and chemical conditions and biota [23,24,25]. In addition, invasion by exotic earthworms can affect the local soil food web, changing habitat and food resources of microorganisms and other soil animals [26]. The overall impact of earthworm invasion on the soil environment and its litter-feeding soil invertebrates community is negative, while in agricultural environments, their presence may be beneficial [9,27,28,29]. So, the positive or negative impact of earthworm invasion depends on the type of ecosystem. There are few studies evaluating the effects of earthworm invasion on subtropical forest soils, especially on the soil biological community structure and function.
Nematodes are the most abundant animals on Earth [7]. According to van den Hoogen et al. (2019), the number of nematodes contained in the Earth’s surface soil is approximately 4.4 ± 0.64 × 1020 [30]. Nematodes occupy many trophic positions in the soil food web because they feed on a wide variety of different substances [31]. This phylum is classified into groups based on their diet: bacterivores, fungivores, omnivore predators, and herbivores [31]. The diversity and abundance of nematodes make it a good biological indicator of soil quality [32], as does their relationship with soil microbes. Being one or two trophic levels lower than nematodes in the food chain, soil microorganisms play an important role in soil nutrient cycling, and together with soil nematodes, constitute soil micro-decomposers [33]. For instance, micro-decomposers contain 70–80% of carbon and nitrogen easily decomposed in soil, so predation of microorganisms by nematodes can affect the turnover rate of carbon and nitrogen in soil [34].
Previous studies have revealed that nematodes are affected by earthworms [35]. Burrowing and casting by earthworms alter the physical and chemical properties of the soil, and therefore impact the nematode habitat [36]. Additionally, the secretions of the skin surface or digestive tract of earthworms can increase nematode movement and diffusion through the surroundings [37], and earthworm mucus can adversely affect bacterivorous nematodes [38]. Furthermore, predation of earthworms on nematodes affects the nematode community. For example, due to the unpalatability of herbivorous nematodes, earthworms reduced the density of non-parasitic nematodes, such as bacterivores, fungivores, and predators [39], and earthworm activity decreased species richness of nematode communities [40]. Senapati et al. (1992) reported that earthworms increased the activity of microbial feeding nematodes but decreased the activity of plant parasitic nematodes [41]. Earthworm casts also change microbial structure and affect soil nutrient cycling [19]. Earthworm invasion changes microbial community structure by changing the ratio of bacteria to fungi by reducing fungal biomass [42], and exotic earthworms decreased microbial biomass significantly [29]. A large number of studies have reported on the effects of invasive earthworms in North American forest soils, but there are few studies examining the effects of invasive earthworms in tropical China, especially at the level of micro-decomposers [6,9,25,28,29,42,43,44,45].
Earthworm invasion has physical, geochemical, and biological effects [28] on soil ecosystems. Epigeic earthworms cause physical damage to the humus layer of the forest floor. After the surface organic layer is destroyed, endogenic earthworms invade [46]. Furthermore, earthworm invasion decreases soil fungal abundance and vertically shifts the microbial biomass from the forest floor to the soil mineral layer [47]. Previous studies have revealed the key role of earthworms in soil formation, soil structure, and nutrient cycling, but few studies have investigated the effects of earthworm invasion on forest soil micro-decomposers [28,48], especially nematodes. Here, we conducted a field mesocosm experiment to investigate how exotic and native earthworms affect soil properties and soil communities of nematodes and microbes. We hypothesize that exotic earthworms will reduce the abundance and diversity of micro-decomposers and nutrient availability as compared with native earthworms. We aim to expand our understanding of the consequences of earthworm invasion on soil micro-decomposers and related soil nutrient status in subtropical forests.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Site
The experiment was performed at Heshan Hilly Land Interdisciplinary Experimental Station (112°500′ E, 22°340′ N), Chinese Academy of Sciences, Guangdong Province, China. The reserve has a subtropical monsoon climate with a mean annual temperature of 22.4 °C and a mean annual rainfall depth of 1995 mm [49]. Influenced by subtropical monsoons, the region has a distinct wet season from April to September, and a dry season from October to March. There is a 30-year-old subtropical broadleaf plantation dominated by Schima wallichii Choisy at this station, and the soil is classified as Orthic Acrisol [50].
2.2. Experimental Design
The experiment was set in a forest dominated by Schima wallichii. A completely random block design was used to collect samples. There were three treatments with five repetitions randomly arranged on the forest floor, totaling 15 plastic boxes. The length, width, and height of the boxes were 46 cm, 31.5 cm, and 25 cm, respectively. Each box contained 5 cm of quartz sand and 15 cm of soil from the bottom up. The sand was high-temperature sterilized, and soil was collected to a depth of 20 cm from the surface in an area dominated by Schima wallichii and mixed evenly. Earthworms and cocoons in the soil were removed by hand picking. Litter and adult earthworms for the experiment were collected one week prior to the study. Based on the amount of natural litter in the environment, 100 g dry weight of Schma wallichii leaf litter was placed on the soil surface of each box. The wild earthworm density was determined by randomly digging nine 30 cm × 30 cm soil quadrats (to 30 cm depth) on the forest floor, and then the earthworms in each quadrat were picked up and counted according to their species. Based on the number of earthworms in the wild, 30 exotic earthworms (P. corethrurus) and 20 native earthworms (Amynthas corticis) were added into different treatments (double of the density in the wild) [51]. The experiment consisted of three treatments:
- (1)
- Exotic earthworm: 30 exotic earthworms (P. corethrurus) were added;
- (2)
- Native earthworm: 20 native earthworms (Amynthas corticis) were added;
- (3)
- Control: no earthworms.
The experiment lasted 105 days, starting on 17 September 2018 and ending on 30 December 2018. The mean temperature and rainfall in September, October, November, and December were 27.5 °C, 23.9 °C, 21.0 °C, and 16.4 °C, and 259.1 mm, 52.1 mm, 32.1 mm, and 11 mm, respectively. The boxes were left on the forest floor for the entirety of the experiment.
2.3. Soil Sampling and Laboratory Analysis
The soil was sampled on the last day of the experiment. Litter on the surface of the soil was removed before soil samples were taken. Four soil cores (3 cm in diameter and 10 cm deep) were collected from each box and combined into one composite sample. After the soil was evenly mixed, we used this composite sample to analyze soil properties, microbes, and nematode communities.
To measure soil pH, soil was resuspended in deionized water suspension (1:2.5; w:v) and measured using a pH meter (Mettler Toledo, Shanghai, China). Soil moisture (SM, ratio of water to dry soil) was measured by weighing before and after drying for 48 h in an oven at 105 °C. Soil total carbon (TC) was measured using dichromate oxidation, and total nitrogen (TN) was measured using an ultraviolet spectrophotometer after Kjeldahl digestion [52]. Soil total phosphorus (STP) was measured using the molybdenum antimony blue colorimetry method [53]. Available phosphorus (AP) was measured using the molybdenum blue method using Bray’s extraction solution. Soil nitrogen from ammonium (NH4+) and nitrate (NO3−) were measured using a Flow-Injection Autoanalyzer (FIA, Lachat Instruments, Burlington, Vermont, USA) after extraction using 2 M KCl.
We used the phospholipid fatty acid (PLFA) method outlined by Bossio and Scow [54] to measure microbial community structure [55].
For each composite sample, nematodes were extracted from 50 g fresh soil using a Baermann funnel method [56] and counted with an inverted microscope (Nikon TS100, Tokyo, Japan). The first 100 individuals encountered were identified to genus level using a differential interference contrast microscope (Nikon 80i, Tokyo, Japan); for samples with fewer than 100 nematodes, every nematode was identified. Each nematode was assigned to functional guilds according to their colonizer–persister (c-p) value, and into the following trophic groups: bacterivores (Ba), fungivores (Fu), omnivores (Om), predators (Pr), and herbivores (He) [31].
2.4. Data Analysis
2.4.1. Nematode Abundance, Community Indices, and Diversity Indices
The abundance of each nematode trophic group was estimated by calculating all individuals per 100 g dry soil.
Nematode community indices were calculated to assess the impact of exotic and native earthworms, including the enrichment index (EI), structure index (SI), channel index (CI), maturity index (MI), and nematode channel ratio (NCR). These indices were calculated as follows [57].
where b represents the basal component guilds (Ba2, Fu2), e represents the enrichment component guilds (Ba1, Fu2), and s represents the structure component guilds (Ba3–5, Fu3–5, Om3–5, Pr2–5). Bax, Fux, Omx, Prx, and Hex represent functional guilds that reflect nematode trophic groups of bacterivores, fungivores, omnivores, predators, and herbivores, respectively. x is the c-p value.
where v(i) represents the c-p value of genus i and f(i) represents the frequency of that genus in the sample [58].
where Ba represents the abundance of bacterivores, and Fu represents the abundance of fungivores in the sample [32].
Enrichment Index = 100 × (e/(e + b))
Structure Index = 100 × (s/(s + b))
Channel Index = 100 × (0.8Fu2/(0.8Fu2 + 3.2Ba1))
To estimate the nematode diversity, we calculate the Shannon–Wiener index:
where Pi is the proportion of each genus (i) in the nematode community, and S is the number of genera in the community [59].
2.4.2. Analysis of Treatment Effects
One-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) was used to compare soil properties, soil microbial community, and soil nematode community characteristics among treatments. Multiple comparisons of means were determined by the least significant difference (LSD) test. Differences were considered significant when p < 0.05. All statistical analyses were performed with SPSS 19.0.
3. Results
3.1. Soil Chemical Properties
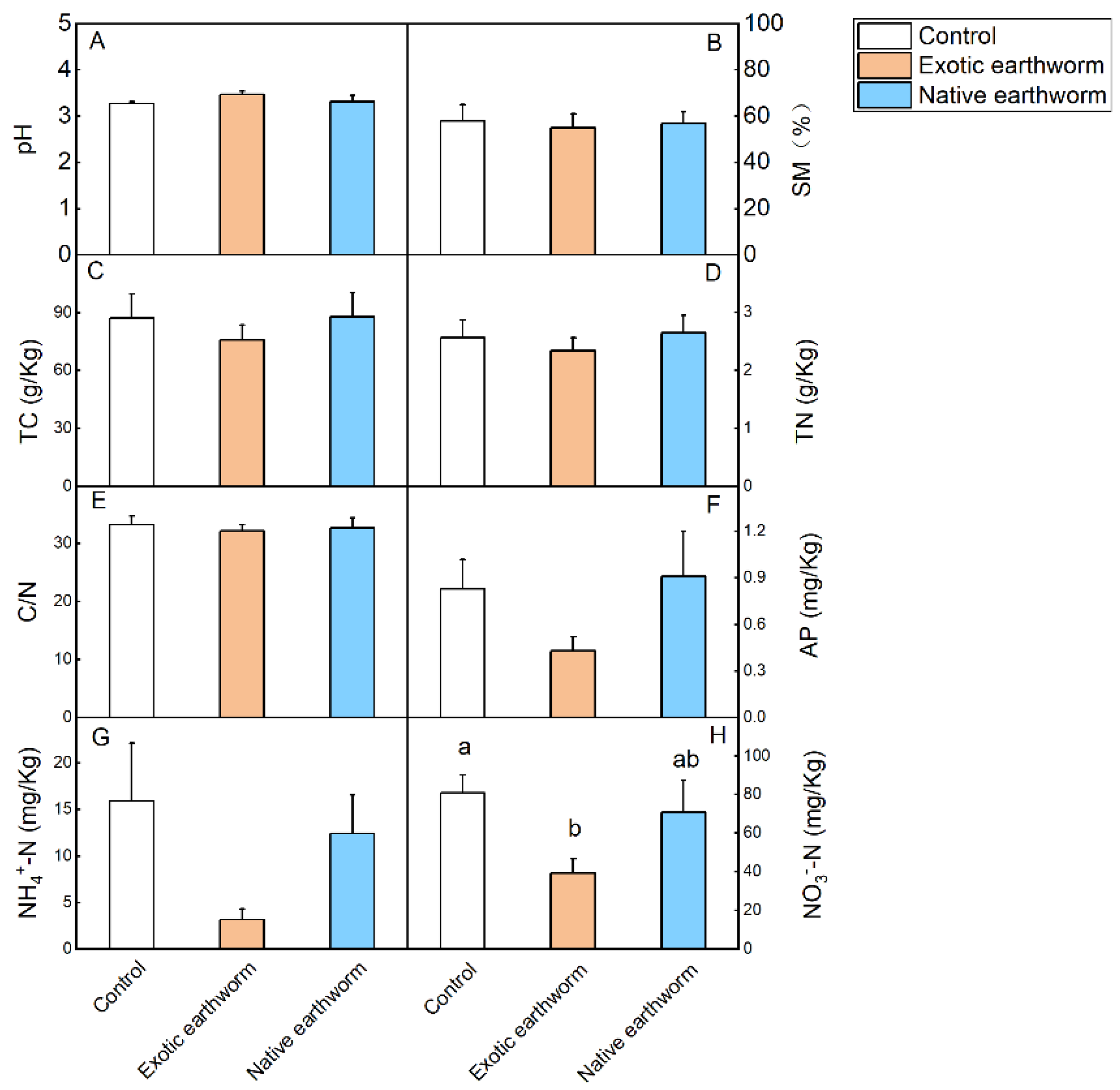
The statistical properties of the data are presented in Table S1. From one-way ANOVA, the results showed that the presence of exotic earthworms significantly reduced the content of NO3−-N compared with the no-earthworm control (p = 0.029, Table S2; Figure 1H), and tended to decrease the content of NO3−-N compared with native earthworms (p = 0.084, Table S2; Figure 1H). The treatment of exotic earthworms tended to decrease the content of NH4+-N compared with the control (p = 0.061, Table S2; Figure 1G).
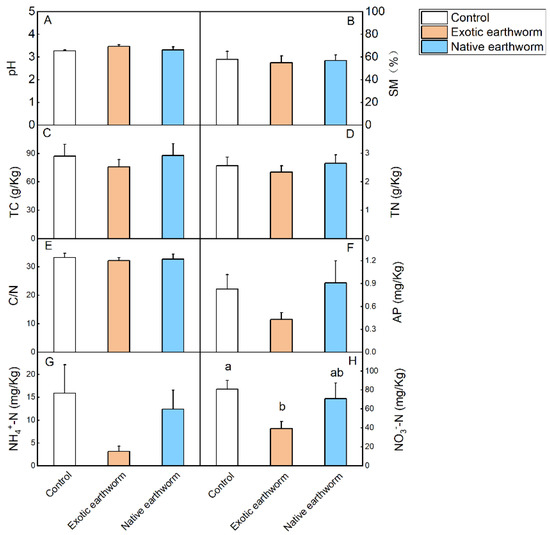
Figure 1.
Soil chemical properties as affected by the presence of exotic and native earthworms. Soil pH (A); SM: soil moisture (B); TC: soil total carbon (g kg−1 dry soil) (C); TN: soil total nitrogen (g kg−1 dry soil) (D); C/N ratio (E); AP: available phosphorus (mg kg−1 dry soil) (F); NH4+-N: nitrogen from ammonium (mg kg−1 dry soil) (G); NO3−-N: nitrogen from nitrate (mg kg−1 dry soil) (H). Data represent means + standard error (n = 5). Significant (p < 0.05) effects based on one-way ANOVA (Table S2) are presented by different lowercase letters above each column. No letters means there was no significant difference.
3.2. Soil Microbial Community Characteristics
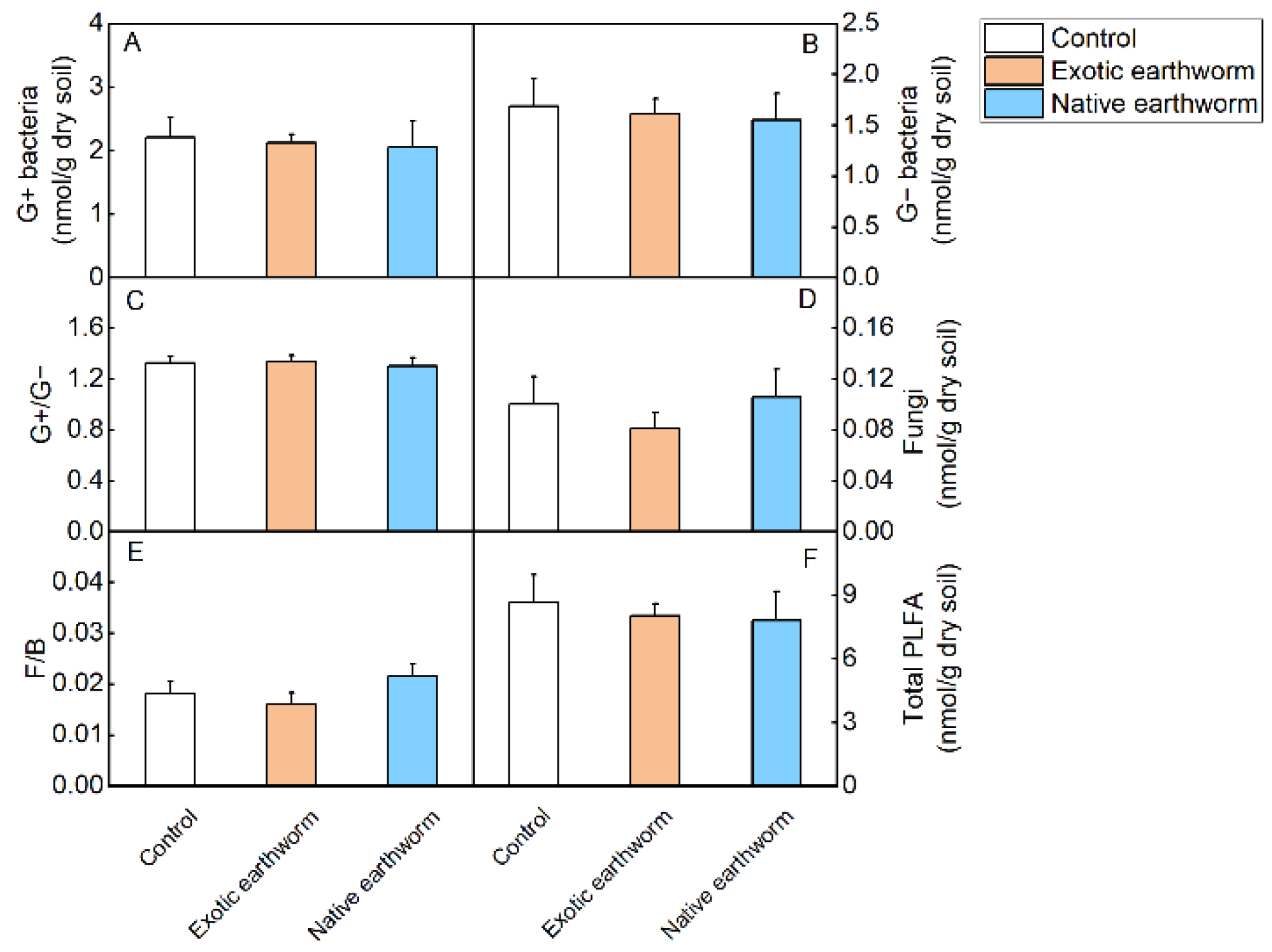
Both native and exotic earthworm treatments had no significant effect on soil microbial community characteristics (Table S3, Figure 2).
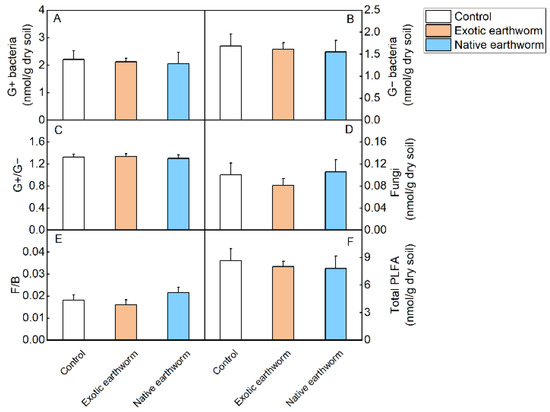
Figure 2.
Soil microbial community characteristics as affected by the presence of exotic and native earthworms. G+: G+ bacteria (A); G−: G− bacteria (B); G+/G− (C); fungi (D); F/B: fungi/(G+ + G−) (E); total PLFA (F). Data represent means + standard error (n = 5). No significant (p < 0.05) effects (Table S3) were found.
3.3. Soil Nematode Community Characteristics
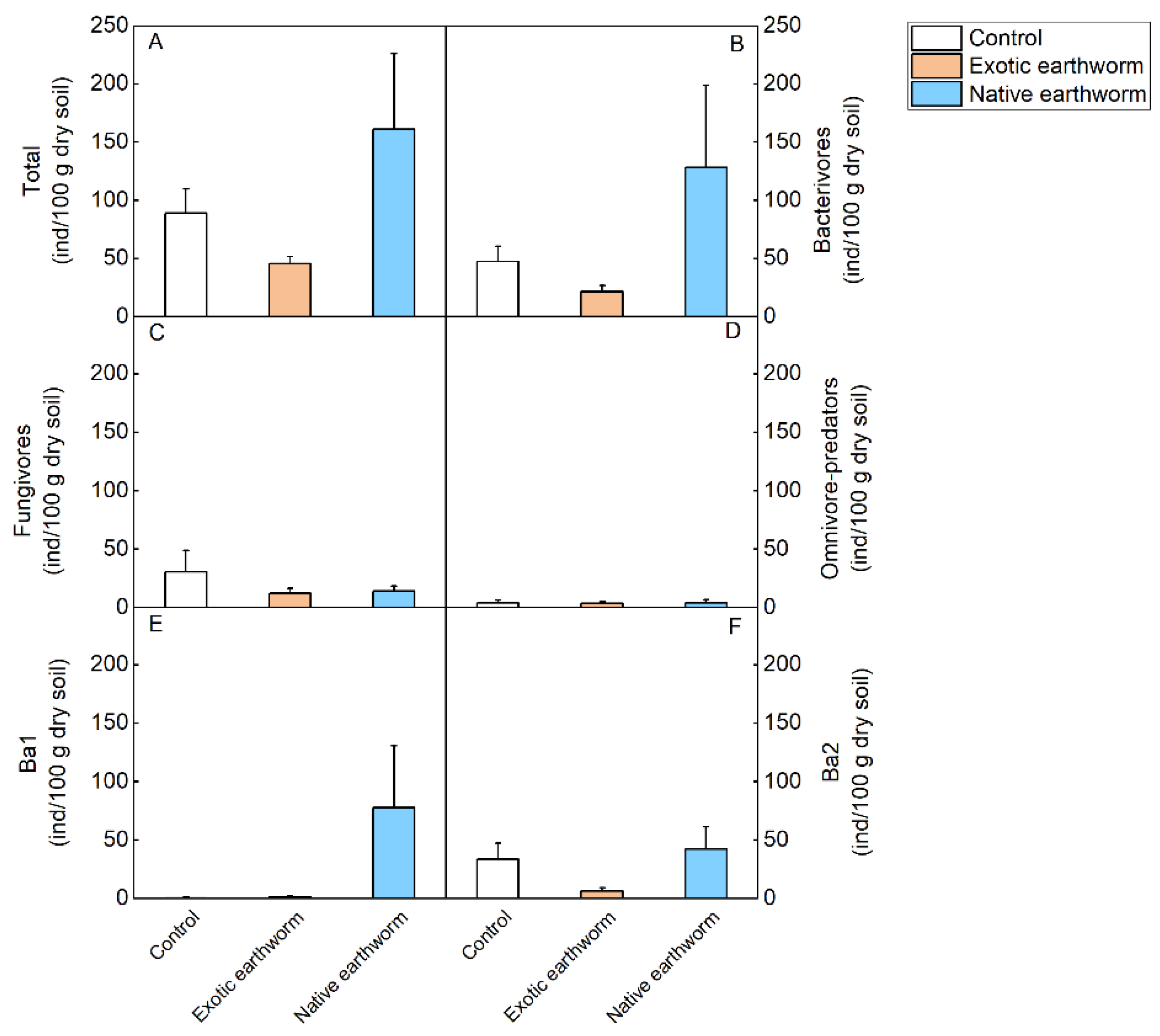
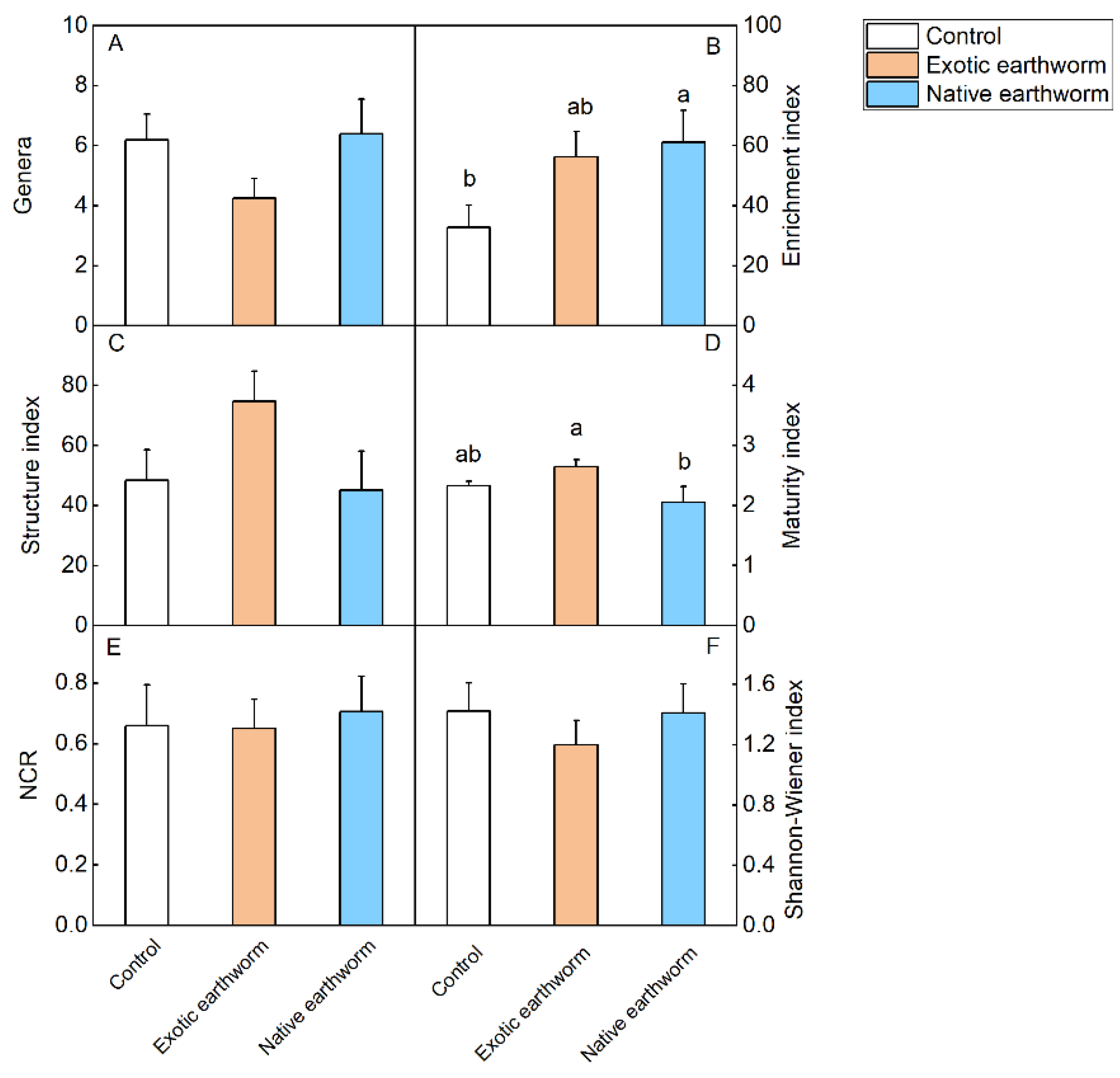
Abundances of all nematode taxa found in the present study are provided in Table S4. Soil nematode abundances did not differ significantly among treatments (Table S5, Figure 3). However, decreasing trends of the total number of nematodes, the number of bacterivorous nematodes, and Ba2 were observed when treated with exotic earthworms compared with native earthworms (p = 0.062, Table S5, Figure 3A; p = 0.094, Table S5, Figure 3B; p = 0.091, Table S5, Figure 3F). The addition of native earthworms resulted in a 1.86-fold increase in EI value compared with the control, while the addition of exotic earthworms did not change the enrichment index compared to the control (Table S6, Figure 4). Compared with exotic earthworms, native earthworms significantly reduced the maturity index (Table S6, Figure 4). Although there was no significant difference in the one-way ANOVA, the nematode genus and Shannon–Wiener index were lowest in the exotic earthworm treatment (Table S6, Figure 4).
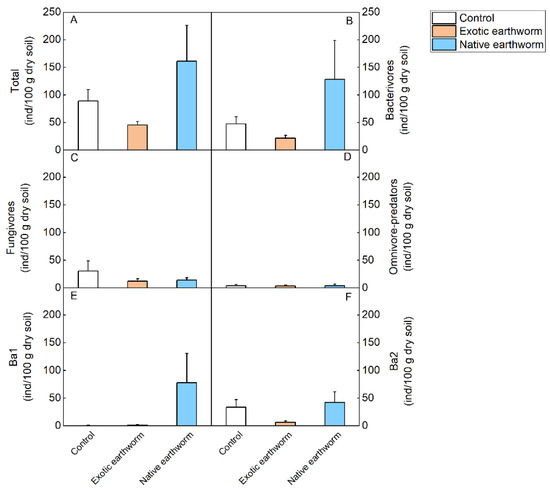
Figure 3.
Comparisons of mean abundances of the nematode trophic groups and functional guilds as affected by the presence of exotic and native earthworms. Total (A); bacterivores (B); fungivores (C); O-P, the sum of omnivores and predators (D); Bax represents the functional guilds that reflect the nematode trophic group of bacterivores; x is the c-p value (E,F). Data represent means + standard error (n = 5). No significant (p < 0.05) effects based on one-way ANOVA (Table S5) were found.
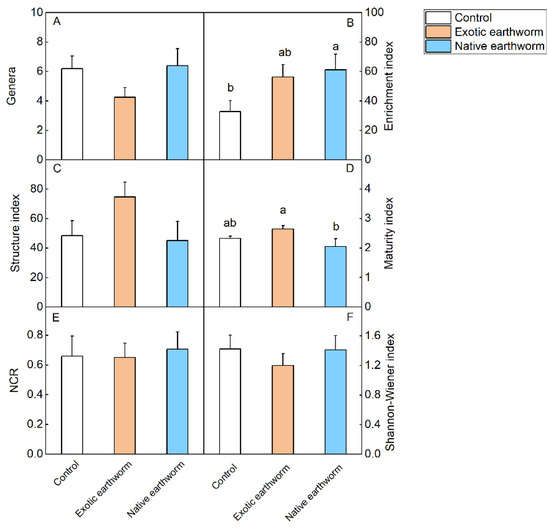
Figure 4.
Nematode community indices as affected by the presence of exotic and native earthworms. Genera: number of genera per sample (A); enrichment index (B); structure index (C); maturity index (D); NCR: nematode channel ratio (E); Shannon–Wiener index (F). Data represent means + standard error (n = 5). Significant (p < 0.05) effects based on one-way ANOVA (Table S6) are presented by different letters above each column. No letters means there was no difference.
3.4. Associations between Soil Properties and Nematode Abundance and Diversity
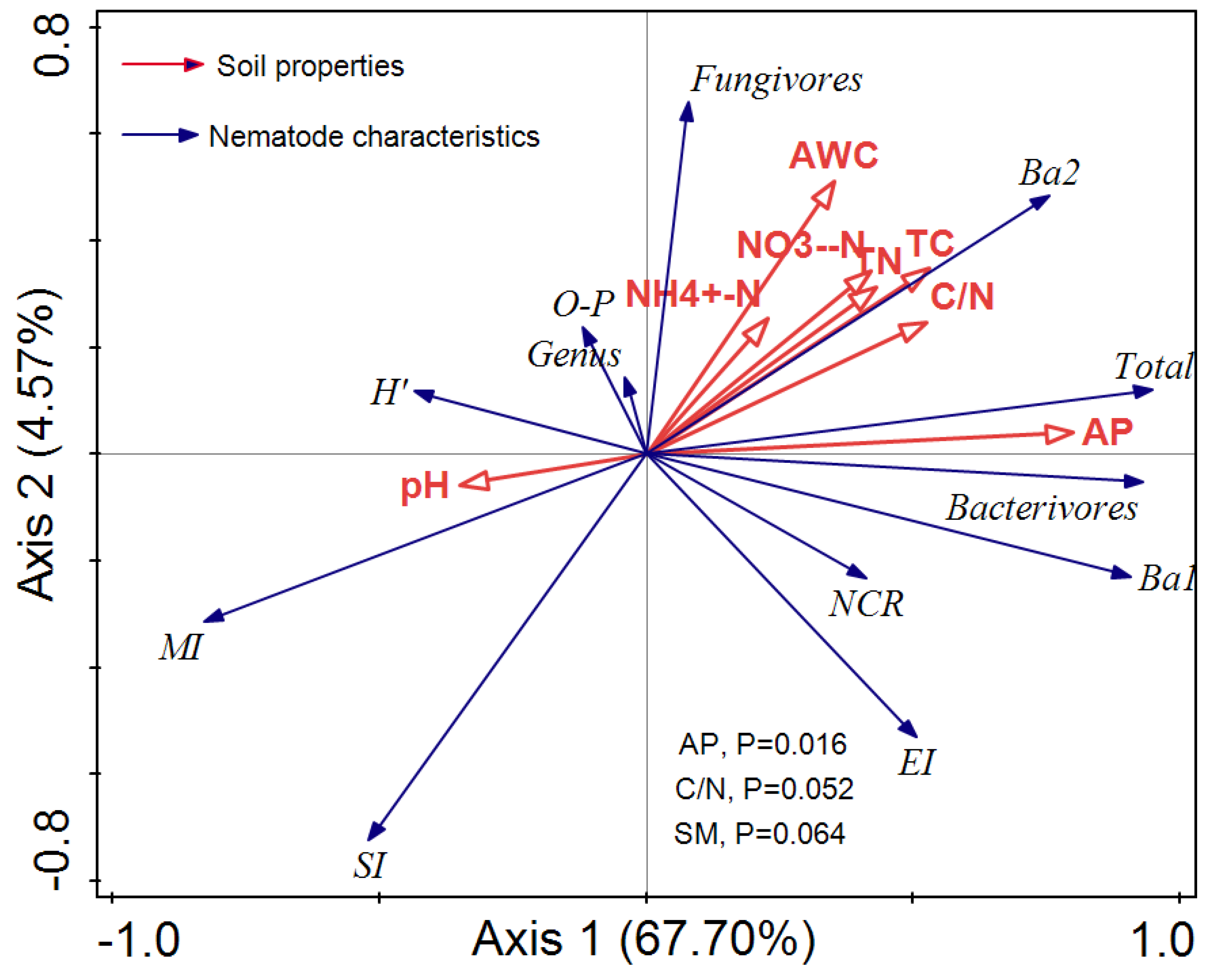
Axis 1 and Axis 2 explained 67.7% and 4.57% of the variation in soil nematode community composition, respectively (Figure 5). AP was significantly and positively correlated with the variation in nematode community structure (p < 0.05), which explained 43.2% of the variation (Figure 5). In addition, the carbon-to-nitrogen ratio (C/N) and SM also had great influence and explained the variation of 7.26% and 7.76%, respectively (Figure 5).
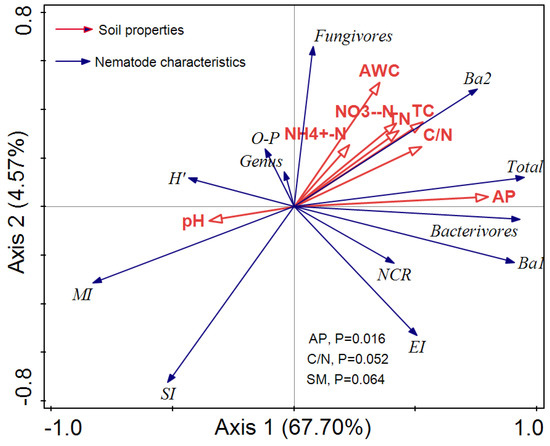
Figure 5.
Redundancy analysis of the relationships between soil properties and the abundances of nematodes at the trophic group level and functional guild level. Blue line vectors represent nematode abundances and community characteristics; red line vectors represent soil chemical properties. The length of the line vectors represents the degree of correlation between an environmental factor and soil nematodes. The longer the connection, the greater the correlation, and vice versa. The smaller the angle, the higher the correlation; otherwise, the lower the correlation. O-P, the sum of omnivores and predators; Bax represents the functional guilds that reflect the nematode trophic group of bacterivores; x is the c-p value. SM, soil moisture; SOC, soil organic carbon; TN, soil total nitrogen; NH4+-N, nitrogen from ammonium; NO3−-N, nitrogen from nitrate; AP, available phosphorus; n = 5.
4. Discussion
We observed that the exotic earthworms had a greater effect on nematodes than on microorganisms. Exotic earthworm invasion had adverse effects on available soil nutrients and the nematode community, which could negatively impact the local ecosystem. This is partially consistent with our hypothesis.
4.1. Effects of Exotic and Native Earthworms on Soil Microbial Community
We found no significant effect of either native or exotic earthworms on soil microbial community composition in the present study. Other studies have reported inconsistent responses of soil microorganisms to the presence of earthworms. For instance, Huang et al. (2015) reported that the exotic earthworm P. corethrurus increased total rhizosphere microbial biomass and shifted rhizosphere microbial community composition [60]. In contrast, our study added only litter, and lacked plant roots to feed the microbes. Therefore, the interaction between earthworms and plants may be responsible for stimulating the growth of microbial biomass and may explain the absence of observed changes in microbial community composition. Furthermore, another study showed that the native earthworm Metaphire guillelmi (Michaelsen) also reduced soil microbial biomass [61]. However, a meta-analysis showed that earthworm invasion had no significant effect on total bacterial and fungal biomass until the researchers stratified the soil and found that the invasion of earthworms reduced soil microbial biomass in the organic layer but increased soil microbial biomass in the mineral layer, so mixing the organic and inorganic layers masked the different responses [24]. The scientists suggested that vertical transport of organic matter and bio-disturbance caused by anecic earthworms and epigeic earthworms reduced microbial populations in the microbe-rich organic layer and increased microbial populations in the mineral layer, which contained fewer microbial resources [24]. In our study, we did not stratify the soil, which may be one reason that no significant change in microbial community composition was observed. Another explanation may be that the overall activity of microorganisms decreased at the initial stage of invasion but recovered gradually over the experimental period [62]. Thus, the microbial community gradually adapted to the physical and chemical changes in soil properties caused by biological invasion. Therefore, the duration of earthworm invasion treatment (105 days) in the present study gives the microbial community enough time to adapt.
4.2. Effects of Exotic and Native Earthworms on Soil Nematode Communities
The results indicated that nematodes were sensitive to earthworm disturbance and may be suitable indicators of the consequences of earthworm invasion. We found that the addition of exotic earthworms only had a trend to inhibit the abundance of bacterivorous nematodes compared to the addition of native earthworms. Previous studies have shown that earthworms and nematodes compete for bacterial food resources [63]. In our experiment, the addition of exotic earthworms did not significantly change bacterial content. Therefore, competition for food was not the main reason for the observed decreasing trend in nematode abundance. Another reason could be predation. Some researchers have reported that earthworms prey on nematodes, especially bacterivores, leading to a decline in nematode populations [39]. Similar studies have shown that the presence of native earthworms also reduces the number of soil nematodes by direct feeding on bacterivorous nematodes [35,39,64]. In our study, there was no significant effect of the native earthworm treatment on soil nematode abundance. However, the total number of nematodes was highest in the native earthworm treatment and lowest in the exotic earthworm treatment. This suggests that the addition of native and exotic earthworms has opposite effects on nematode numbers, which may be due to the earthworms’ lifestyle differences. The native earthworm Amynthas corticis is an epigeic earthworm, which lives close to the surface and excretes on the soil surface. In contrast, the exotic earthworm, P. corethrurus, is endogeic; it lives and excretes in a 0–20 cm soil layer. Therefore, the nematodes may be more disturbed by P. corethrurus because they share more space of the soil together than Amynthas corticis.
In our study, the MI of the nematode community with native earthworms decreased compared with exotic earthworms. MI was correlated with the relative number of omnivore predator nematodes with high c-p values, which indicates succession and restoration of the soil ecosystem [58]. It is worth noting that the higher value of MI in the exotic earthworm treatment was due to a higher proportion but not a higher abundance of high c-p nematodes. Furthermore, higher MI was due to the relatively low abundance of the total nematodes in the exotic earthworm treatment. In addition, the number of genera and the Shannon–Wiener index of nematodes were lowest in the exotic earthworm treatment, while there was no significant difference between native earthworms and the control. We also looked at EI, which represents the input status of external nutrients; the larger the value, the more external nutrients are available [57,65]. Here, we found that the native earthworm treatment significantly increased EI, suggesting that the presence of native earthworms positively enriched soil nutrients. In our study, we only included two species of earthworms, namely exotic P. corethrurus and native Amynthas corticis; therefore, it is not clear if the difference in the impact on soil community is connected with the origin of species (exotic or native) or just with the lifestyle differences. Meta-analyses have shown that anecic and epigeic earthworms can reduce nematode density, but other types of earthworms do not significantly affect nematode biomass [66]. On the one hand, their digestive systems are different. Epigeic earthworms feed and digest nematodes more intensely because they contain more digestive enzymes [67]. An anecic earthworm reuses its own casts so it can feed on nematodes again [66]. On the other hand, there are differences in feeding habits. Disturbance of surface litter feeding by anecic and epigeic earthworms leads to a reduction in organic matter in the soil, which could negatively affect the number of microorganisms [24,40]. The biomass of nematodes decreased with the decrease in microbial biomass. Thus, we believe that the ecological type of earthworms may influence its effect on the nematode community. Although there was no increase in microbial biomass in our results, it is possible that the turnover rate of microorganisms increased and thus enhanced the soil nutritional content. Previous studies have shown that soil nutrient characteristics drive nematode community distribution at the local scale [68]. In conclusion, successful invasion of exotic earthworms may depend on their ability to survive and modify soil nutrients, but an invasion will have adverse consequences on soil biodiversity. In the long run, life history tactics of exotic earthworms are not conducive to maintaining local soil ecosystem functions. However, the relatively short term of this study may limit treatment effects. Furthermore, the activity of earthworms differs in different seasons, which may influence their effects on soil micro-decomposers. Our results demonstrate that exotic earthworms have adverse effects on available nutrient content in soil and on the abundance and diversity of soil nematodes. Longer observation periods and further studies on the interaction between invasive earthworms and nematodes are needed in future experiments.
5. Conclusions
Our experiment partly confirmed our hypothesis that exotic earthworms have a negative impact on available nutrients in the soil compared with native earthworms. Earthworms did not significantly affect nematode abundance and diversity, although the lowest of these values were found in the exotic earthworm treatment. Loss of soil biodiversity has been mostly neglected in the past, especially in the context of belowground biological invasion. It is urgent for us to know how earthworm invasion affects local soil biodiversity and relevant ecosystem functions. Overall, our study showcases the adverse effects of exotic earthworms on soil nitrates and the potential negative effects of exotic earthworms on abundances of native soil nematodes in subtropical forest soil.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/f13111924/s1, Table S1: Descriptive statistics of soil chemical properties, soil microbial community characteristics and nematode community characteristics; Table S2: Results (ANOVA) on soil chemical properties; Table S3: Results (ANOVA) on soil microbial community characteristics; Table S4: Soil nematode taxon list; Table S5: Results (ANOVA) on nematode abundances; Table S6: Results (ANOVA) on nematode community characteristics.
Author Contributions
Data curation, X.W.; Formal analysis, Z.Z.; Funding acquisition, T.L. and X.L.; Writing—original draft preparation, Z.Z.; Writing—review and editing, Z.Z., W.Z. and T.L.; Supervision, T.L. and X.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2021M703257), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (41922056), the Youth Innovation Promotion Association, CAS (201965), and the GDAS Project of Science and Technology Development (2019GDASYL-0103060).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Wardle, D.A.; Bardgett, R.D.; Callaway, R.M.; Van der Putten, W.H. Terrestrial Ecosystem Responses to Species Gains and Losses. Science 2011, 332, 1273–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- FAO. World Soil Day—Keep soil alive, Protect soil biodiversity. In World Soil Day 2020 Campaign Report; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Ehrenfeld, J.G.; Scott, N. Invasive species and the soil: Effects on organisms and ecosystem processes. Ecol. Appl. 2001, 11, 1259–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamieson, B.G.M. On the phylogeny and higher classification of the oligochaeta. Cladistics 1988, 4, 367–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, J.W. Earthworms of the world. Glob. Biodivers. 1994, 4, 11–16. [Google Scholar]
- Eisenhauer, N.; Ferlian, O.; Craven, D.; Hines, J.; Jochum, M. Ecosystem responses to exotic earthworm invasion in northern North American forests. Res. Ideas Outcomes 2019, 5, e34564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bardgett, R.D.; van der Putten, W.H. Belowground biodiversity and ecosystem functioning. Nature 2014, 515, 505–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cameron, E.K.; Martins, I.S.; Lavelle, P.; Mathieu, J.; Tedersoo, L.; Bahram, M.; Gottschall, F.; Guerra, C.A.; Hines, J.; Patoine, G.; et al. Global mismatches in aboveground and belowground biodiversity. Conserv. Biol. 2019, 33, 1187–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendrix, P.F.; Bohlen, P.J. Exotic earthworm invasions in North America: Ecological and policy implications. Bioscience 2002, 52, 801–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Righi, G. Pontoscolex (oligochaeta, glossoscolecidae), a new evaluation. Stud. Neotrop. Fauna Environ. 1984, 19, 159–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, J.A.; Fragoso, C. Influence of different food substrates on growth and reproduction of two tropical earthworm species (Pontoscolex corethrurus and Amynthas corticis). Pedobiologia 2003, 47, 754–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavelle, P.; Pashanasi, B. Soil macrofauna and land management in peruvian amazonia (yurimaguas, loreto). Pedobiologia 1989, 33, 283–291. [Google Scholar]
- Fragoso, C.; Lavelle, P.; Blanchart, E.; Senapati, B.K.; Jimenez, J.J.; Martinez, M.D.; Decaens, T.; Tondoh, J. Earthworm communities of tropical agroecosystems: Origin, structure and influence of management practices. Earthworm Manag. Trop. Agroecosystems 1999, 27–55. [Google Scholar]
- Taheri, S.; Pelosi, C.; Dupont, L. Harmful or useful? A case study of the exotic peregrine earthworm morphospecies Pontoscolex corethrurus. Soil. Biol. Biochem. 2018, 116, 277–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Chen, Y.; Liu, S.; Gunina, A.; Wang, X.; Chen, W.; Shao, Y.; Shi, L.; Yao, Q.; Li, J.; et al. Cooperation of earthworm and arbuscular mycorrhizae enhanced plant N uptake by balancing absorption and supply of ammonia. Soil. Biol. Biochem. 2018, 116, 351–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavelle, P.; Bignell, D.; Lepage, M.; Wolters, V.; Roger, P.; Ineson, P.; Heal, O.W.; Dhillion, S. Soil function in a changing world: The role of invertebrate ecosystem engineers. Eur. J. Soil. Biol. 1997, 33, 159–193. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, T.; Chen, X.; Gong, X.; Lubbers, I.M.; Jiang, Y.; Feng, W.; Li, X.; Whalen, J.K.; Bonkowski, M.; Griffiths, B.S.; et al. Earthworms Coordinate Soil Biota to Improve Multiple Ecosystem Functions. Curr. Biol. 2019, 29, 3420–3429.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puga-Freitas, R.; Barot, S.; Taconnat, L.; Renou, J.-P.; Blouin, M. Signal Molecules Mediate the Impact of the Earthworm Aporrectodea caliginosa on Growth, Development and Defence of the Plant Arabidopsis thaliana. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e49504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blouin, M.; Hodson, M.E.; Delgado, E.A.; Baker, G.; Brussaard, L.; Butt, K.R.; Dai, J.; Dendooven, L.; Peres, G.; Tondoh, J.E.; et al. A review of earthworm impact on soil function and ecosystem services. Eur. J. Soil. Sci. 2013, 64, 161–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lubbers, I.M.; van Groenigen, K.J.; Fonte, S.J.; Six, J.; Brussaard, L.; van Groenigen, J.W. Greenhouse-gas emissions from soils increased by earthworms. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2013, 3, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaborski, E.R.; Soeken Gittenger, L.A.; Roberts, S.J. A possible Phasmarhabditis sp. (Nematoda: Rhabditidae) isolated from Lumbricus terrestris (Oligochaeta: Lumbricidae). J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2001, 77, 284–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheu, S. Effects of earthworms on plant growth: Patterns and perspectives. Pedobiologia 2003, 47, 846–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferlian, O.; Thakur, M.P.; Gonzalez, A.C.; San Emeterio, L.M.; Marr, S.; Rocha, B.D.; Eisenhauer, N. Soil chemistry turned upside down: A meta-analysis of invasive earthworm effects on soil chemical properties. Ecology 2020, 101, e02936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferlian, O.; Eisenhauer, N.; Aguirrebengoa, M.; Camara, M.; Ramirez-Rojas, I.; Santos, F.; Tanalgo, K.; Thakur, M.P. Invasive earthworms erode soil biodiversity: A meta-analysis. J. Anim. Ecol. 2018, 87, 162–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Craven, D.; Thakur, M.P.; Cameron, E.K.; Frelich, L.E.; Beausejour, R.; Blair, R.B.; Blossey, B.; Burtis, J.; Choi, A.; Davalos, A.; et al. The unseen invaders: Introduced earthworms as drivers of change in plant communities in North American forests (a meta-analysis). Glob. Chang. Biol. 2017, 23, 1065–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohlen, P.J.; Scheu, S.; Hale, C.M.; McLean, M.A.; Migge, S.; Groffman, P.M.; Parkinson, D. Non-native invasive earthworms as agents of change in northern temperate forests. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2004, 2, 427–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalby, P.R.; Baker, G.H.; Smith, S.E. Potential impact of an introduced lumbricid on a native woodland in South Australia. Appl. Soil Ecol. 1998, 9, 351–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alban, D.H.; Berry, E.C. Effects of earthworm invasion on morphology, carbon, and nitrogen of a forest soil. Appl. Soil Ecol. 1994, 1, 243–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisenhauer, N.; Partsch, S.; Parkinson, D.; Scheu, S. Invasion of a deciduous forest by earthworms: Changes in soil chemistry, microflora, microarthropods and vegetation. Soil. Biol. Biochem. 2007, 39, 1099–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van den Hoogen, J.; Geisen, S.; Routh, D.; Ferris, H.; Traunspurger, W.; Wardle, D.A.; de Goede, R.G.M.; Adams, B.J.; Ahmad, W.; Andriuzzi, W.S.; et al. Soil nematode abundance and functional group composition at a global scale. Nature 2019, 572, 194–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeates, G.W.; Bongers, T.; Degoede, R.G.M.; Freckman, D.W.; Georgieva, S.S. Feeding-habits in soil nematode families and genera—An outline for soil ecologists. J. Nematol. 1993, 25, 315–331. [Google Scholar]
- Yeates, G.W. Nematodes as soil indicators: Functional and biodiversity aspects. Biol. Fert. Soils 2003, 37, 199–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Wang, X.; Shao, Y.; Xu, G.; Fu, S. Effects of vegetation removal on soil properties and decomposer organisms. Soil. Biol. Biochem. 2011, 43, 954–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Y.H.; Zhang, W.X.; Liu, S.J.; Wang, X.L.; Fu, S.L. Diversity and function of soil fauna. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2015, 35, 6614–6625. [Google Scholar]
- Ilieva-Makulec, K.; Makulec, G. Effect of the earthworm Lumbricus rubellus on the nematode community in a peat meadow soil. Eur. J. Soil. Biol. 2002, 38, 59–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, J.; Chen, X.; Liu, M.; Hu, F.; Griffiths, B.; Li, H. Earthworms change the abundance and community structure of nematodes and protozoa in a maize residue amended rice-wheat rotation agro-ecosystem. Soil. Biol. Biochem. 2009, 41, 898–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shapiro, D.I.; Berry, E.C.; Lewis, L.C. Interactions between nematodes and earthworms-enhanced dispersal of steinernema-carpocapsae. J. Nematol. 1993, 25, 189–192. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, F.; Li, C.; Liu, T.; Li, T.; Hu, F.; Li, H.; Jiao, J. Earthworm mucus interfere in the behavior and physiology of bacterial-feeding nematodes. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2019, 143, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dash, M.C.; Senapati, B.K.; Mishra, C.C. Nematode feeding by tropical earthworms. Oikos 1980, 34, 322–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Räty, M.; Huhta, V. Earthworms and pH affect communities of nematodes and enchytraeids in forest soil. Biol. Fert. Soils 2003, 38, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senapati, B.K. Biotic interactions between soil nematodes and earthworms. Soil. Biol. Biochem. 1992, 24, 1441–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dempsey, M.A.; Fisk, M.C.; Fahey, T.J. Earthworms increase the ratio of bacteria to fungi in northern hardwood forest soils, primarily by eliminating the organic horizon. Soil. Biol. Biochem. 2011, 43, 2135–2141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lejoly, J.; Quideau, S.; Laganiere, J. Invasive earthworms affect soil morphological features and carbon stocks in boreal forests. Geoderma 2021, 404, 115262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.H.; Bartz, M.L.C.; Brown, G.; Callaham, M.A.; Cameron, E.K.; Davalos, A.; Dobson, A.; Gorres, J.H.; Herrick, B.M.; Ikeda, H.; et al. The second wave of earthworm invasions in North America: Biology, environmental impacts, management and control of invasive jumping worms. Biol. Invasions 2021, 23, 3291–3322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jochum, M.; Ferlian, O.; Thakur, M.P.; Ciobanu, M.; Klarner, B.; Salamon, J.A.; Frelich, L.E.; Johnson, E.A.; Eisenhauer, N. Earthworm invasion causes declines across soil fauna size classes and biodiversity facets in northern North American forests. Oikos 2021, 130, 766–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Addison, J.A. Distribution and impacts of invasive earthworms in Canadian forest ecosystems. Biol. Invasions 2009, 11, 59–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendrix, P.F. Biological invasions belowground—Earthworms as invasive species. Biol. Invasions 2006, 8, 1201–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.E.; Foster, R.C. Soil fauna and soil structure. Aust. J. Soil Res. 1991, 29, 745–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Fu, S.; Wang, X.; Li, Z.; Li, J.; Zhang, W. One-Year Monitoring of Daily Earthworm Cast Production: Surface Cast Contribution to Soil Fertility in a Subtropical Forest. Forests 2021, 12, 865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.X.; Li, J.X.; Guo, M.F.; Liao, C.H. Seasonal variation of earthworm community structure as correlated with environmental factors in three plantation of Heshan, Guangdong, China. Acta Ecol. Sinica 2005, 25, 1362–1370. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, T.; Wang, X.; Zhang, W.; Eisenhauer, N.; Shao, Y.; Zhao, J.; Li, J.; He, X.; Tao, L.; Fu, S.; et al. Earthworms regulate the nematode community by directly enhancing the bacterial-based energy channel rather than through the effect of casts. Pedobiologia 2022, 95, 150843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G. Analysis of Soil Physical and Chemical Properties and Description of Soil Profiles; China Standard: Beijing, China, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, Y.T.; Gundersen, P.; Mo, J.M.; Zhu, W.X. Input and output of dissolved organic and inorganic nitrogen in subtropical forests of South China under high air pollution. Biogeosciences 2008, 5, 339–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bossio, D.A.; Scow, K.M. Impacts of carbon and flooding on soil microbial communities: Phospholipid fatty acid profiles and substrate utilization patterns. Microb. Ecol. 1998, 35, 265–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Zhang, H.; Liu, T.; Mao, P.; Zhang, W.; Shao, Y.; Fu, S. An increase in precipitation exacerbates negative effects of nitrogen deposition on soil cations and soil microbial communities in a temperate forest. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 235, 293–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barker, K.R. Nematode extraction and bioassays. In An Advanced Treatise on Meloidogyne; Barker, K.R., Carter, C.C., Sasser, J.N., Eds.; North Carolina State University: Raleigh, NC, USA, 1985; Volume 2, pp. 19–35. [Google Scholar]
- Ferris, H.; Bongers, T.; de Goede, R.G.M. A framework for soil food web diagnostics: Extension of the nematode faunal analysis concept. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2001, 18, 13–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bongers, T. The maturity index—An ecological measure of environmental disturbance based on nematode species composition. Oecologia 1990, 83, 14–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neher, D.A.; Darby, B.J. General community indices that can be used for analysis of nematode assemblages. In Nematodes as Environmental Indicators; Wilson, M.J., Kakouli-Duarte, T., Eds.; CABI: Wallingford, UK, 2009; pp. 107–123. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, J.; Zhang, W.; Liu, M.; Briones, M.J.I.; Eisenhauer, N.; Shao, Y.; Cai, X.a.; Fu, S.; Xia, H. Different impacts of native and exotic earthworms on rhizodeposit carbon sequestration in a subtropical soil. Soil. Biol. Biochem. 2015, 90, 152–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Li, G.; Shen, T.; Wang, J.; Sun, z. Changes in microbial biomass C, N, and P and enzyme activities in soil incubated with the earthworms Metaphire guillelmi or Eisenia fetida. Soil. Biol. Biochem. 2000, 32, 2055–2062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLean, M.A.; Migge-Kleian, S.; Parkinson, D. Earthworm invasions of ecosystems devoid of earthworms: Effects on soil microbes. Biol. Invasions 2006, 8, 1257–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliott, E.T.; Anderson, R.V.; Coleman, D.C.; Cole, C.V. Habitable pore space and microbial trophic interactions. Oikos 1980, 35, 327–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, X.; Zhai, P.; Zhang, W.; Gu, Y. Effects of Earthworms and Agricultural Plant Species on the Soil Nematode Community in a Microcosm Experiment. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 11660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berkelmans, R.; Ferris, H.; Tenuta, M.; van Bruggen, A.H.C. Effects of long-term crop management on nematode trophic levels other than plant feeders disappear after 1 year of disruptive soil management. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2003, 23, 223–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demetrio, W.C.; Dionisio, J.A.; Maceda, A. Negative effects of earthworms on soil nematodes are dependent on earthworm density, ecological category and experimental conditions. Pedobiologia 2019, 76, 150568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curry, J.P.; Schmidt, O. The feeding ecology of earthworms—A review. Pedobiologia 2007, 50, 463–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, H.; Wang, W.; Xia, S.; Li, Z.; Gan, J.; Yang, X. Distributional patterns of soil nematodes in relation to environmental variables in forest ecosystems. Soil Ecol. Lett. 2021, 3, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).