Abstract
Forest type conversion is an important factor affecting soil carbon (C) and nitrogen (N) pools. Planting precious trees in moso bamboo forest is an important measure taken to establish a mixed forest due to the vulnerable ecological functioning of moso bamboo forest. However, the ways in which soil C and N pools in moso bamboo forest are affected by precious tree introduction are still unclear. A pure moso bamboo forest (BF), a bamboo forest interplanted with Phoebe chekiangensis (BPC), and a bamboo forest interplanted with Taxus wallichiana var. mairei (BTW) were selected. Soil organic C (SOC), total N, microbial biomass C (MBC), microbial biomass N (MBN), water-soluble organic C (WSOC), water-soluble organic N (WSON), and litter C and N concentrations were determined. Our results showed that the concentrations of SOC and N in BF were significantly lower than those in BPC and BTW. The total SOC and N concentrations decreased with increasing soil depth, and they were significantly higher at 0–20 cm than those at 20–40 cm and 40–60 cm. The biomasses of litters and their concentrations of C and N were increased after planting precious trees in moso bamboo forest, and they were significantly lower in BF than in BPC and BTW. In addition, precious tree introduction also improved the concentrations of soil MBC, MBN, WSOC, and WSON. To conclude, planting precious trees in moso bamboo forest significantly increased SOC and N concentrations at soil depths of 0–60 cm.
1. Introduction
Carbon (C) and nitrogen (N) are important elements that constitute components of forest ecosystems and play important roles in global C and N cycles [1,2,3]. Numerous studies have illustrated that accumulations of C and N are affected by vegetation type and forest composition [4,5,6,7]. The conversion of forest type is an important pattern of land use change in the middle subtropical area [8,9], which affects community structure and function by changing the interactions and relationships between tree species [10] and also affects soil C and N pools by changing litters, root exudates, and soil microbial communities [11,12,13,14], affecting the cycles of whole ecosystems [10]. Therefore, it is of great significance to further understand the effect of forest type change on the cycles of C and N by analyzing the effects of changes in plant community compositions on soil C and N pools.
Moso bamboo (Phyllostachys edulis) is an important forest type in Southern China, characterized by its high growth rate during sprouting and rapid biomass accumulation [15,16,17]. Moso bamboo is a clonal plant with strong reproduction, and their culms are connected to each other through their rhizome–root systems, which provide strong supports for their rapid and continuous expansion [18,19,20]. With the encroachment of moso bamboo, soil organic C (SOC) and N concentrations have been found to decrease, and the changes occurred mainly in the topsoil [2]. It was also found that changes in SOC and N were mainly related to soil microbial biomass C (MBC), microbial biomass N (MBN), water-soluble organic C (WSOC), and water-soluble organic N (WSON). However, an opposite situation was observed by Song et al., who found an increasing trend with the expansion of moso bamboo into a broadleaved forest in China [21]. These studies showed that conversion from a pure broadleaved or pure coniferous forest to a mixed forest invaded by moso bamboo altered soil C and N concentrations. In addition, many of these studies have focused on mixed forests formed by the expansion of moso bamboo. However, the ways in which soil C and N concentrations in moso bamboo forests are affected by precious tree introduction are still unclear.
In China, the area of moso bamboo forest is 4.68 million ha, according to the 9th National Forest Resources Inventory, accounting for 72.96% of the total area of bamboo forest [22]. The long-term, highly intensive management has resulted in a single structure of moso bamboo forest, which has significantly reduced the ecosystem stability and ecological function [23]. The establishment of a multi-storied forest is an important measure to solve the problem of weak ecological functioning in a single-storied forest [24,25]. Phoebe chekiangensis and Taxus wallichiana var. mairei are endangered tree species and excellent precious timber species with high wood densities and radial uniformity. They are representatives of broadleaved and coniferous species, respectively, which have been widely planted in moso bamboo forests. Precious tree species introduced into moso bamboo change the forest composition (tree species), which may influence the inputs and outputs of soil C and N [7]. This process also has an impact on soil microbial processes associated with C and N cycling in forest ecosystems due to differences in the quality, quantity, and decomposition rates of litters [26,27,28]. However, the effects of planting precious tree species in moso bamboo forests on soil C and N pools remain unclear. Therefore, the purposes of this study were (1) to determine soil C and N changes due to planting precious tree species in moso bamboo forests and (2) to explore the potential mechanism of soil C and N changes.
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Study Site
This study was conducted on the Xikou forest farm of Longyou County, Zhejiang Province, China (119°12′38″–119°35′47″ E, 28°53′25″–28°92′74″ N). This area has a subtropical monsoon climate, an average annual temperature of 17.1 °C, a mean annual sunshine duration of 1762 h, a mean annual precipitation of 1603 mm, and a mean relative humidity of 79%. The altitude above sea level at the experimental site is 247 m, and the slope is 23°–27°. The soil is Ultisol, and the soil properties (0–60 cm) are shown in Table 1.

Table 1.
Soil properties of the experimental site.
2.2. Experimental Design
Moso bamboo forests regenerate naturally, and management mainly focuses on bamboo shoot harvesting and bamboo timber cutting. Combined with timber cutting, tending and thinning in the moso bamboo forest were conducted in January 2012. The stand density of bamboo forest was 1537 individuals ha−1, with a canopy cover of 60%. A standard plot with an area of 3 ha (300 m × 100 m) was established and divided into three subplots (100 m × 100 m). Phoebe chekiangensis and Taxus wallichiana var. mairei were introduced into the moso bamboo forest in April 2012. Then, three forest types were established, namely, (1) a pure moso bamboo forest (BF), (2) a bamboo forest interplanted with Phoebe chekiangensis (BPC), and a bamboo forest interplanted with Taxus wallichiana var. mairei (BTW). BF was located between BPC and BTW. Two-year-old seedlings were planted, and the spacing in the rows was 5 m × 5 m. The bamboo timber was cut down every two years in the off-year to maintain a reasonable density.
In October 2020, the diameter at breast height (DBH, 1.3 m) of each bamboo culm was measured and recorded. At the same time, the age of each bamboo culm was recorded. Bamboo age was defined as “du” because of the unique phenomenon of the on-year and off-year in moso bamboo forests [17,29]. One (I) “du” represents 1–2 years; similarly, 2 (II) and 3 (III) “du” correspond to 3–4 and 5–6 years, respectively [29,30]. In addition, the ground diameters and seedling heights of the precious tree species were measured and recorded. The values for Phoebe chekiangensis and Taxus wallichiana var. mairei were 25.83 mm and 62.27 mm for ground diameter and 1.76 m and 4.07 m for seedling height, respectively. Brief descriptions of the stand characteristics are presented in Table 2.

Table 2.
Brief descriptions of the three experimental stands.
2.3. Soil and Litter Sampling
In October 2020, we established three standard plots (20 m × 20 m) in the three forest types, respectively. Soil samples were collected using a soil sampler (5 cm in diameter) from the 0–60 cm soil layer at five random points in each standard plot and separated into 20 cm depth increments. Before soil sampling, the surface litters (1 m × 1 m) in the standard plots were collected, and the soil particles and stones were removed artificially. Then, the litters were dried at 70 °C to a constant weight for the determination of biomass. Each soil sample was put into two sample bags. One bag was stored at −20 °C in a refrigerator, and the other bag was stored at room temperature. The frozen samples were used to determine the microbiological indexes, and the air-dried samples were used to analyze the chemical properties after being ground and sieved through 2 mm and 0.15 mm meshes. The dried litters were also ground and sieved through 2 mm and 0.15 mm meshes for the determination of C and N concentrations.
2.4. Measurements
Total SOC concentrations and litter C concentrations were measured by the K2Cr2O7-H2SO4 wet oxidation method [31], and soil total N concentrations and litter N concentrations were determined by the Kjeldahl digestion–distillation method [8]. Soil microbial biomass C (MBC) and soil microbial biomass N (MBN) were determined using the chloroform fumigation extraction method [32]. The concentration of water-soluble organic C (WSOC) was measured using the method described by Jiang et al. [33]. The concentration of organic N (WSON) was measured using the method described by Bai et al. [2].
2.5. Statistical Analysis
One-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) and least significant difference tests were used to determine the significant differences between treatments for each variable over the whole experiment. Statistical significance was evaluated at p < 0.05. All statistical analyses were conducted in the SAS 9.0 software. Figures were prepared using the Origin 8.6 software program.
3. Results
3.1. SOC and N Concentrations
The introduction of precious trees into moso bamboo forest led to a large increase in SOC concentrations (Figure 1). At a depth of 0–20 cm, the SOC concentration in BF was significantly lower than in BPC and BTW (p < 0.05), while no significant difference was found between BPC and BTW (p > 0.05). At depths of 20–40 and 40–60 cm, there were no significant differences in SOC concentrations between the three forest types (p > 0.05). The SOC concentrations showed decreasing trends with soil depth in the three forest types and were significantly higher at depths of 0–20 cm than at 20–40 and 40–60 cm (p < 0.05).
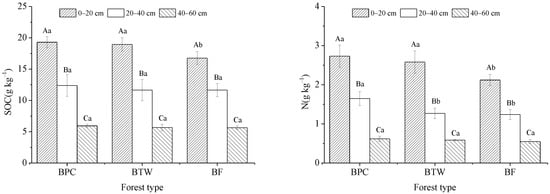
Figure 1.
SOC and N concentrations in BPC, BTW, and BF. Capital letters indicate the differences between different soil depths in the same forest type, and lowercase letters indicate the differences between different forest types at the same soil depth. BF, BPC, and BTW represent pure moso bamboo forest, bamboo forest interplanted with Phoebe chekiangensis, and bamboo forest interplanted with Taxus wallichiana var. maireii, respectively.
The introduction of precious trees into moso bamboo forest also increased soil total N concentrations (Figure 1). At a depth of 0–20 cm, the total N concentrations in BPC and BTW were significantly higher than in BF (p < 0.05), while there was no significant difference between BPC and BTW (p > 0.05). At a depth of 20–40 cm, the total N concentration in BPC was significantly higher than in BTW and BF (p < 0.05), while at depths of 40–60 cm no significant difference was found between the three forest types (p > 0.05). The distribution of total N concentrations showed a decreasing trend with increasing soil depth, which was similar to what was observed for SOC concentrations. The total N concentration at a depth of 0–20 cm was the highest, and it was significantly higher than those at 20–40 and 40–60 cm (p < 0.05).
3.2. Litter C and N Concentrations
The litter biomasses and concentrations of C and N increased after planting precious trees in moso bamboo forest (Table 3). Planting precious trees in moso bamboo forest significantly increased litter biomass (p < 0.05). The litter C and N concentrations in BPC and BTW were significantly higher than in BF (p < 0.05), while no significant difference was found between BPC and BTW (p > 0.05).

Table 3.
Litter biomasses and concentrations of C and N in BPC, BTW, and BF.
3.3. MBC and MBN Concentrations
The MBC and MBN concentrations increased after planting precious trees in the moso bamboo forests (Figure 2). At a depth of 0–20 cm, the MBC and MBN concentrations in BF were significantly lower than in BPC and BTW (p < 0.05), while no significant difference was found between BPC and BTW (p > 0.05). At depths of 20–40 and 40–60 cm, there was no significant difference in MBC and MBN concentrations between the three forest types (p > 0.05). Soil MBC and MBN concentrations also decreased with increasing soil depth for all three forest types, and the differences were significant (p < 0.05).
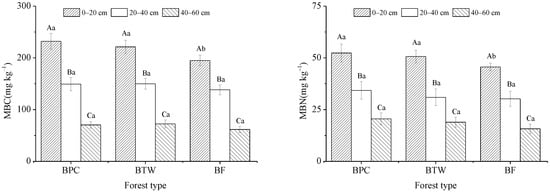
Figure 2.
MBC and MBN concentrations in BPC, BTW, and BF. Capital letters indicate the differences between different soil depths in the same forest type, and lowercase letters indicate the differences between different forest types at the same soil depth. BF, BPC, and BTW represent pure moso bamboo forest, bamboo forest interplanted with Phoebe chekiangensis, and bamboo forest interplanted with Taxus wallichiana var. maireii, respectively.
3.4. WSOC and WSON Concentrations
Details about the WSOC and WSON concentrations for each treatment are shown in Figure 3. At depths of 0–20 and 20–40 cm, the WSOC and WSON concentrations in BPC and BTW were significantly higher than in BF (p < 0.05), while no significant difference was found between BPC and BTW (p > 0.05). At a depth of 40–60 cm, there was no significant difference between the three forest types (p > 0.05). Soil WSOC and WSON concentrations also decreased with increasing soil depth in all three forest types, and the differences were significant (p < 0.05).
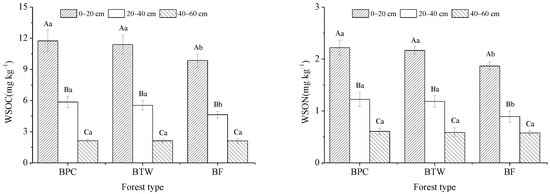
Figure 3.
WSOC and WSON concentrations in BPC, BTW, and BF. Capital letters indicate the differences between different soil depths in the same forest type, and lowercase letters indicate the differences between different forest types at the same soil depth. BF, BPC, and BTW represent pure moso bamboo forest, bamboo forest interplanted with Phoebe chekiangensis, and bamboo forest interplanted with Taxus wallichiana var. maireii, respectively.
4. Discussion
Forest conversion can markedly influence SOC and N concentrations [8,34]. A previous study showed that concentrations of SOC and N decreased with the encroachment of moso bamboo on native evergreen broadleaved forests and that they were significantly higher in the transition zone (mixed forest formed by native evergreen broadleaved forest and expanded moso bamboo) than in pure moso bamboo forest [35,36], which suggested that mixed forest could significantly improve concentrations of SOC and N. In our study, the conversion from moso bamboo forest to mixed forest by planting precious tree species increased SOC and N concentrations. This result was consistent with the findings of Bai et al. [2]. The higher concentrations of SOC and N in BPC and BTW compared to BF indicated that precious tree species introduction into moso bamboo forest to produce a mixed forest could increase SOC and N pools, which is consistent with the results of Wang et al. [35] and Li et al. [36].
In the present study, conversion from pure moso bamboo forest to mixed forest by planting precious tree species increased the concentrations of SOC and N at 0–20 cm depths but not in deeper soil. This result showed no difference from those of Yang et al. [37] and Gelaw et al. [38], who considered that soil disturbances only happened in the topsoil in these ecosystems. This may be related to the longer planting time (8 years after planting). In deep soil, the concentrations of SOC and N returned to the levels before the planting of precious trees, while their concentrations in surface soil were affected by the increase in litter biomass. In addition, a negative correlation between SOC and N concentrations and soil depth was found in BF, BPC, and BTW. The result was similar to that of Guan et al., who found a declining trend in SOC and N concentrations with increasing soil depth [8]. In our research, the high concentrations of SOC and N in topsoil have two possible explanations: first, the decomposition of surface litter increased SOC and N concentrations [35]; second, the high activities of microorganisms on the surface soil accelerated the decomposition of litter [39].
The changes in SOC and N concentrations in moso bamboo forest due to precious tree species introduction are complex, being mainly affected by species compositions, litters, and microbial communities [3]. In our study, the high SOC and N concentrations in BPC and BTW may depend on several factors. First, the increase in SOC and N concentrations may be partly determined by litter quantity and quality. Planting precious tree species in moso bamboo forest altered plant diversity, especially understory diversity. Previous studies have shown that relatively poor plant diversity decreased soil C inputs and accumulation [2]. Moreover, mixed forest was able to produce and accumulate more litter due to precious trees and other vegetation [40], which was beneficial for maintaining and improving soil fertility [41]. In our study, litter C and N concentrations in BPC and BTW were significantly higher than in BF (Table 3). The decomposition of mixed litter may promote the release of nutrient elements [42].
Second, increased microbial activity may be an important factor in the improvement of SOC and N pools. MBC and MBN are soil microbial active resource banks, which can sensitively reflect soil microbial activities [2]. In this study, concentrations of soil MBC and MBN in BPC and BTW were significantly higher than in BF (Figure 2), which was consistent with previous results [12,43]. The increases in MBC and MBN concentrations in BPC and BTW might be attributed to the increases in soil microbial communities and diversity due to the precious tree introduction [2]. After planting precious tree species in moso bamboo forest, the biomasses of litter and root exudates increased (Table 3), which provided favorable conditions for microbial growth and reproduction. The increases in microbial communities further promoted litter decomposition, accelerating the release of effective nutrients, and subsequently improved the concentrations of SOC and N.
Finally, the increased WSOC and WSON may be another important factor affecting SOC and N concentrations. Previous studies have shown that WSOC and WSON are mainly released through litter decomposition, root exudation, and the mineralization of soil organic matter through microbial activities [2,44,45]. In this study, precious tree species introduction changed the compositions and decomposition rates of litters and subsequently increased the concentrations of WSOC and WSON (Figure 3), illustrating that the mixed forests favored the processes of transformation of soil C and N. Additionally, soil WSOC and WSON were organic C and N sources, which can be directly utilized by soil microorganisms [46]. The increase in WSOC and WSON in BPC and BTW indicated that the mixed forests had strong microbial activities, which can improve SOC and N concentrations.
5. Conclusions
This study clearly demonstrated that SOC and N concentrations were significantly influenced by the conversion of a pure moso bamboo forest to a mixed forest. The concentrations of SOC and N in BF were lower than in BPC and BTW, indicating that planting precious trees in the moso bamboo forests increased the SOC and N concentrations. In addition, converting pure moso bamboo forests to mixed forests by planting precious trees not only increased the biomasses of litters and their concentrations of C and N, but also increased the concentrations of soil MBC, MBN, WSOC, and WSON. The results indicated that the conversion of a pure moso bamboo forest to a mixed forest by planting precious trees significantly increased SOC and N concentrations at soil depths of 0–60 cm. Continuous research on the interactions between precious trees and moso bamboo should be explored in further studies.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.Z. and Z.Y.; Formal Analysis, J.Z., B.W. and Z.Y.; Investigation, J.Z., B.W. and Z.Y.; Writing—Original Draft, J.Z.; Writing—Review and Editing, Z.Y. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was financially supported by the Key Research and Development Program of Zhejiang Province (Grant No. 2020C02008).
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Nieder, R.; Benbi, D.K. Carbon and Nitrogen in the Terrestrial Environment; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, S.; Conant, R.T.; Zhou, G.; Wang, Y.; Wang, N.; Li, Y.; Zhang, K. Effects of moso bamboo encroachment into native, broad-leaved forests on soil carbon and nitrogen pools. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 31480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, R.N.; Chu, H.Y.; Li, Y.Q.; Zheng, Y.; Zheng, W.; Yang, L.M.; Zhang, W.Q.; Li, J.W.; Chen, H.Y. Effects of forest conversion on soil carbon and nitrogen storage in different soil layers. J. Subtrop. Res. Environ. 2019, 14, 23–29, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Priess, J.A.; de Koning, G.H.J.; Veldkamp, A. Assessment of interactions between land use change and carbon and nutrient fluxes in Ecuador. Agr. Ecosyst. Environ. 2001, 85, 269–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shedayi, A.A.; Xu, M.; Naseer, I.; Khan, B. Altitudinal gradients of soil and vegetation carbon and nitrogen in a high altitude nature reserve of Karakoram ranges. SpringerPlus 2016, 5, 320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Ai, J.; Sun, Q.; Li, Z.; Hou, L.; Song, L.; Tang, G.; Li, L.; Shao, G. Soil organic carbon and total nitrogen stocks as affected by vegetation types and altitude across the mountainous regions in the Yunnan Province, southwestern China. Catena 2021, 196, 104872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menyailo, O.V.; Hungate, B.A.; Zech, W. The effect of single tree species on soil microbial activities related to C and N cycling in the Siberian artificial afforestation experiment. Plant Soil 2002, 242, 183–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, F.; Tang, X.; Fan, S.; Zhao, J.; Peng, C. Changes in soil carbon and nitrogen stocks followed the conversion from secondary forest to Chinese fir and Moso bamboo plantations. Catena 2015, 133, 455–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, M.; Chen, H.Y.H.; Lin, J.; Liu, X.; Guo, X.; Yuan, Y.; Zhang, J. Long term forest conversion affected soil nanoscale pores in subtropical China. Catena 2020, 185, 104289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.H.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, L.X.; Wang, F.G.; Xu, Z.C.; Wu, S.G.; Yang, J.; Wen, L. Effects of vegetation degradation on carbon and nitrogen distribution of roots-soil system in temperate typical steppe. Acata Ecol. Sin. 2018, 38, 5340–5350, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Deng, Q.; Cheng, X.; Hui, D.; Zhang, Q.; Li, M.; Zhang, Q. Soil microbial community and its interaction with soil carbon and nitrogen dynamics following afforestation in central China. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 541, 230–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, X.; Zhang, J.; Meng, M.; Guo, X.; Wu, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhao, K.; Ding, Z.; Shao, Y.; Fu, W. Forest-type shift and subsequent intensive management affected soil organic carbon and microbial community in southeastern China. Eur. J. For. Res. 2017, 136, 689–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Cao, J.; He, X.; Liu, T.; Shao, Y.; Zhang, C.; Zhou, Q.; Li, F.; Mao, P.; Tao, L.; et al. Plant leaf litter plays a more important role than roots in maintaining earthworm communities in subtropical plantations. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2020, 144, 107777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, F.; Cui, X.; Sang, Y.; Song, J. Changes in soil organic carbon and total nitrogen as affected by primary forest conversion. For. Ecol. Manag. 2020, 463, 118013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.H. Bamboo and Rattan in the World; China Forest Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, J.; Wang, B.; Li, Q.; Yang, H.; Xu, K. Analysis of soil degradation causes in Phyllostachys edulis forests with different mulching years. Forests 2018, 9, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, W.; Fan, S.; Zhao, J.; Cai, C. Effects of various fertilization placements on the fate of urea-15N in moso bamboo forests. For. Ecol. Manag. 2019, 453, 117632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, R.A.F.; Rother, D.C.; Muler, A.E.; Lepsch, I.F.; Rodrigues, R.R. Bamboo overabundance alters forest structure and dynamics in the Atlantic Forest hotspot. Biol. Conserv. 2012, 147, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Ge, Z.; Deng, X.; Shi, Y.; Xu, L.; Zhou, G.; Ye, Y.; Zhang, F.; Zhou, Y.; Li, C.; et al. Abandonment lead to structural degradation and changes in carbon allocation patterns in Moso bamboo forests. For. Ecol. Manag. 2019, 449, 117449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.F.; Liang, C.F.; Chen, J.H.; Li, Y.C.; Qin, H.; Fuhrmann, J.J. Rapid bamboo invasion (expansion) and its effects on biodiversity and soil processes. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2020, 21, e00787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Q.N.; Yang, Q.P.; Liu, J.; Yu, D.K.; Fang, K.; Xu, P.; He, Y.J. Effects of Phyllostachys edulis expansion on soil nitrogen mineralization and its availability in evergreen broadleaf forest. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2013, 24, 338–344, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- National Forestry and Grassland Administration. Report for Chinese Forest Resource–The 9th National Forest Inventory; China Forest Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2019. (In Chinese)
- Zhou, Y.; Dong, J.; Guan, F.; Fan, S. Progress and prospects of the research on mixed bamboo and broadleaf forest. For. Res. Manag. 2016, 38, 145–150, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Gärtner, S.; Reif, A. The impact of forest transformation on stand structure and ground vegetation in the southern Black Forest, Germany. Plant Soil 2004, 264, 35–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaitaniemi, P.; Lintunen, A. Neighbor identity and competition influence tree growth in Scots pine, Siberian larch, and silver birch. Ann. For. Sci. 2010, 67, 604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morisada, K.; Ono, K.; Kanomata, H. Organic carbon stock in forest soils in Japan. Geoderma 2004, 119, 21–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Inubushi, K. Effects of N sources and methane concentrations on methane uptake potential of a typical coniferous forest and its adjacent orchard soil. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2004, 40, 215–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.F.; Jiang, P.K.; Wu, J.S.; Zhou, G.M.; Shen, R.F.; Fuhrmann, J.J. Bamboo invasion of native broadleaf forest modified soil microbial communities and diversity. Biol. Invasions 2015, 17, 433–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Fan, S.; Qi, L.; Guan, F.; Du, M.; Zhang, H. Soil respiration and net ecosystem production in relation to intensive management in Moso bamboo forests. Catena 2016, 137, 219–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Su, W.; Fan, S.; Cai, C.; Su, H.; Zeng, X. Ammonia volatilization and nitrogen runoff losses from moso bamboo forests under different fertilization practices. Can. J. Forest Res. 2019, 49, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Shao, M.; Wei, X.; Horton, R. Soil organic carbon and total nitrogen as affected by vegetation types in Northern Loess Plateau of China. Geoderma 2010, 155, 31–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, X.; Chen, F.; Huang, R.; Deng, X.; Jiang, Y. Seasonal dynamics of soil microbial biomass C and N of Keteleeria fortune var. cyclolepis forests with different ages. J. For. Res. 2020, 31, 2377–2384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, P.; Xu, Q.; Xu, Z.; Cao, Z. Seasonal changes in soil labile organic carbon pools within a Phyllostachys praecox stand under high rate fertilization and winter mulch in subtropical China. For. Ecol. Manag. 2006, 236, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, J.; Chang, S.X.; Jiang, P.; Zhou, G.; Shen, Z.; Wu, J.; Lin, L.; Wang, Z.; Shen, M. Converting native shrub forests to Chinese chestnut plantations and subsequent intensive management affected soil C and N pools. For. Ecol. Manag. 2014, 312, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Tian, G.; Chiu, C. Invasion of moso bamboo into a Japanese cedar plantation affects the chemical composition and humification of soil organic matter. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 32211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Li, Y.; Chang, S.X.; Xu, Q.; Guo, Z.; Gao, Q.; Qin, Z.; Yang, Y.; Chen, J.; Liang, X. Bamboo invasion of broadleaf forests altered soil fungal community closely linked to changes in soil organic C chemical composition and mineral N production. Plant Soil 2017, 418, 507–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.C.; Huang, J.H.; Pan, Q.M.; Tang, J.W.; Han, X.G. Long-term impacts of land-use change on dynamics of tropical soil carbon and nitrogen pools. J. Environ. Sci. 2004, 16, 256–261. [Google Scholar]
- Gelaw, A.M.; Singh, B.R.; Lal, R. Soil organic carbon and total nitrogen stocks under different land uses in a semi-arid watershed in Tigray, Northern Ethiopia. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2014, 188, 256–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Fu, W.; Ping, Q.; He, X.Y.; Chen, W.; Wu, X.; Su, L.L.; Huang, Y.Q. Advance in studies on the effects of climate change on decomposition of tree litters. Chin. J. Ecol. 2017, 36, 3266–3272, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.; Su, J. Study on the soil properties of bamboo and broadleaved mixed forest. J. Nanjing For. Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2007, 31, 81–84, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, L.; Sun, Y.; Saeed, A.; Zhang, B.; Luo, M. The difference of soil properties between pure and mixed Chinese fir (Cunninghamia lanceolata) plantations depends on tree species. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2020, 22, e01009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, L.N.; Liu, S.R.; Cai, C.J.; Wang, Y.; Wu, X.P.; Guo, M.M. Decomposition characteristics of the fine root of Phyllostachys edulis and Dicranopteris pedata in southern Sichuan. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2018, 38, 7638–7646, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Cai, X.; Lin, Z.; Penttinen, P.; Li, Y.; Li, Y.; Luo, Y.; Yue, T.; Jiang, P.; Fu, W. Effects of conversion from a natural evergreen broadleaf forest to a Moso bamboo plantation on the soil nutrient pools, microbial biomass and enzyme activities in a subtropical area. For. Ecol. Manag. 2018, 422, 161–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.R.; Xu, Z.H.; Zhang, S.L.; Keay, P. Soluble organic nitrogen pools in forest soils of subtropical Australia. Plant Soil 2005, 277, 285–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filep, T.; Rékási, M. Factors controlling dissolved organic carbon (DOC), dissolved organic nitrogen (DON) and DOC/DON ratio in arable soils based on a dataset from Hungary. Geoderma 2011, 162, 312–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Zhu, J.; Yan, Q.; Zhang, J. Soil enzyme activities as potential indicators of soluble organic nitrogen pools in forest ecosystems of Northeast China. Ann. Forest Sci. 2012, 69, 795–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).