1. Introduction
Global demand for goods and services is directly related to the demand for natural resources [
1]. The role that forests play in the environment is fundamental, since they contribute to the oxygen balance and help protect hydrographic basins (areas where water for human consumption comes from [
2]).
Some of these highly-demanded resources are non-renewable resources from forests. According to the World Economic Forum (WEF) [
3], in 2019, 3.8 million hectares of forest cover were lost from primary forests, humid tropical forests, areas of mature tropical forest, which constitute essential elements for biodiversity and air purification. This loss of primary forest is related to the emission of 1.8 megatons of CO
2 emissions. Compared to previous years, 2019 registered an increase of 2.8% compared to 2018. However, this value is lower than in 2016 and 2017.
In addition, the WEF [
3] mentions that deforestation is affected differently depending on the income level of countries. In developed countries, such as Spain, Greece, or Italy, the forest area has registered increases of 9%, 6% and 6%, respectively, since 1990, which is due to government subsidies. In contrast, in countries like Brazil, the Congo or Bolivia, deforestation is advancing at alarming rates, due to commercial logging of trees and the use of land for agriculture. In response to this problem, world organisations generated projects to mitigate environmental degradation. According to the Food and Agriculture Organisation of the United Nations (FAO) [
4], in 2008, the project called “United Nations Programme UNO-REDD, UNJP/ECU/083/ UNJ” was launched, which emerges as a need to reduce deforestation and forest degradation (REDD) in developing countries. In addition, it has the support and experience of the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) and the United Nations Development Programme (UNDP). On the other hand, the increase in the consumption of renewable energy is constituted as one of the main elements to achieve environmental sustainability and conservation of ecosystems [
5,
6,
7,
8,
9].
In this regard, from the 1970s on, the study of the determinants of deforestation takes on great relevance. Thus, Molion [
10] and Lettau et al. [
11] establish that economic activity expansion is one of the main factors associated with deforestation. Since then, an endless number of studies have examined the determinants of deforestation worldwide. For example, Ahmed et al. [
12] examine the effect of economic growth, energy consumption, trade openness and population density on deforestation in Pakistan. As for Tanner and Johnston [
13], they examine the effect of renewable energy on deforestation in 158 countries. However, according to the detailed review of the literature on the subject, there are few studies that consider the role of renewable energy consumption, and even fewer, the non-renewable energy price on the forest area, in countries with different income levels, by using an Autoregressive Distributed Lag (ARDL) model approach, so this constitutes one of the main novelties of the study.
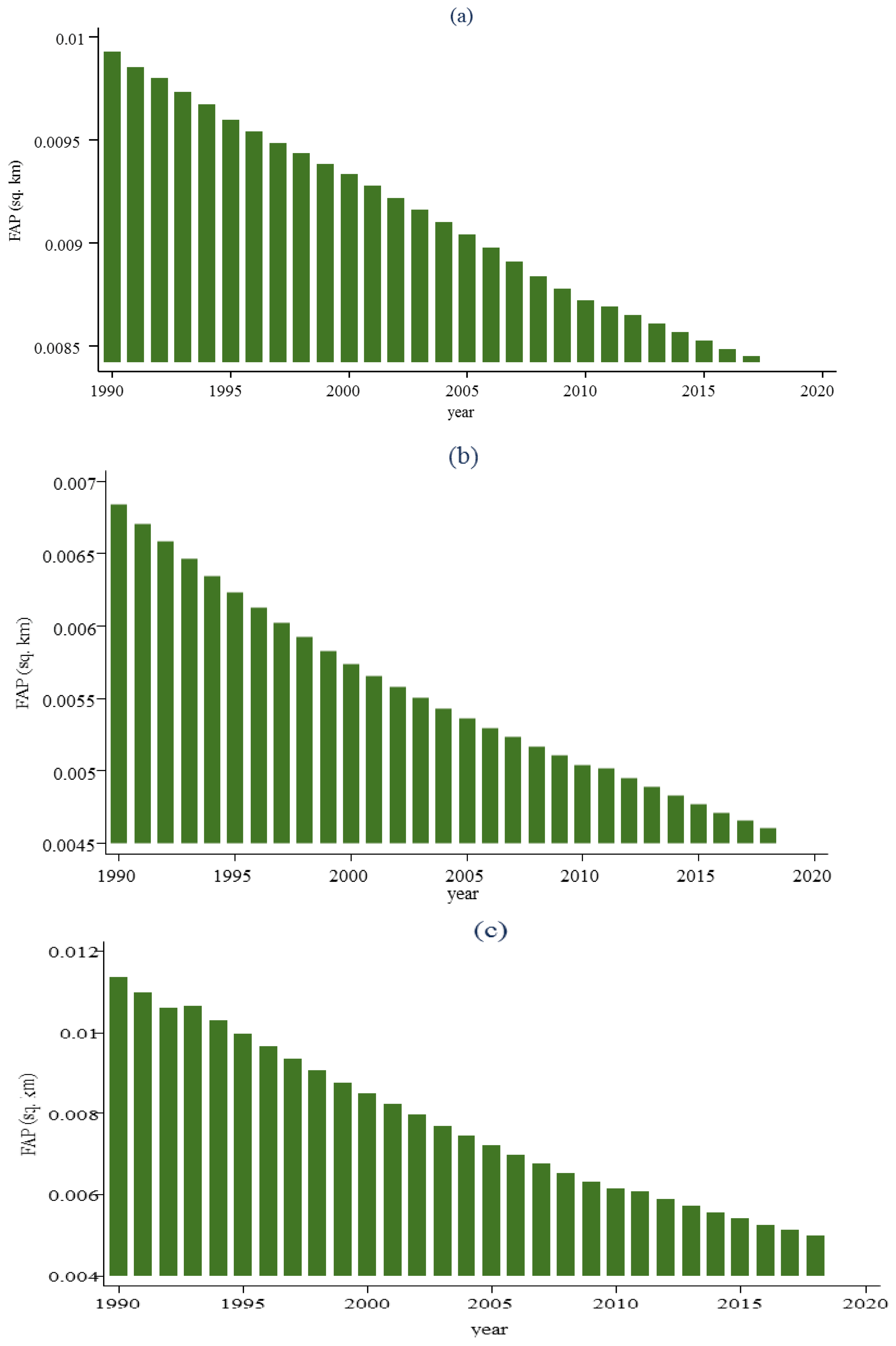
In this context, this research aims to determine the relationship between renewable energy consumption, the gross domestic product (GDP), GDP
2, non-renewable energy price, population growth and the forest area in three groups of countries during the period 1990–2018. Annual aggregated data are used at the level of three large groups of countries: High-income countries (HIC), middle-income countries (MIC) and low-income countries (LIC), to make a comparison of the factors that determine the forest area. Thus, the dependent variable is represented by per capita forest area measured in square kilometres. As explanatory variables, the following are used: renewable energy consumption and it is measured as the percentage of total energy consumption, GDP at constant 2010 prices, the square of the Gross Domestic Product (GDP
2), the non-renewable energy price, measured as the price of a barrel of oil at constant 2018 prices and annual population growth (%). The study supports the hypotheses raised in
Section 2.
The structure of this work is as follows.
Section 2 describes the literature review, and
Section 3 describes the data and the econometric strategy used. In
Section 4, the results and discussion of the research are presented. Finally, the conclusions of the research are discussed in
Section 5. See
Appendix A Table A1.
2. Literature Review
Preserving forest area or reducing deforestation is a global concern, due to the constant demand for forest services [
14] and the increasing rates of environmental degradation. In some countries, governments established incentives to avoid deforestation, given that there is competition for the use of forest area [
15]. However, in others, the measures taken were incipient. In this regard, deforestation was widely studied to learn more about its determinants and to be able to design measures to mitigate its spread. Over the last few years, various studies have been carried out on the subject, evidencing a long-term relationship between deforestation and energy consumption [
12]. Molion [
10] is one of the pioneers in relating deforestation with energy consumption, mentioning that renewable energy can reduce CO
2 emissions from greenhouse gases, caused by energy from the consumption of fossil fuels. Another of the highly cited authors who examine the same relationship, deforestation and energy consumption, is Lettau et al. [
11], who use the hydrological cycle and atmospheric recycling to study deforestation. These authors indicate that the construction of dams, urbanisation, an increase in the capacity of the irrigation system, increasing energy demands and unsustainable economic growth are determinants of a decrease in the forest area. In this regard, several studies have examined the factors that cause deforestation, and this study focuses on the consumption of renewable energy, economic growth and the non-renewable energy price as determinants of forest area. Thus, there is evidence that argues that deforestation shows a long-term equilibrium relationship with its determinants [
12], for which the following hypothesis is established:
Hypothesis 1. (H1) There is a long-term equilibrium relationship between forest area, GDP, renewable energy consumption and the price of non-renewable energy.
Therefore, the empirical evidence is divided into three groups. The first group includes those studies that examine the effect of renewable energy consumption on deforestation, their contributions being very significant. Thus, Tanner and Johnston [
13] found that the government can reduce deforestation rates by applying an ecological policy that expands access to renewable energy to the rural population, so that the consumption of biomass is left for their daily needs. Nazir et al. [
16] study the development of the wind energy atlas as a proposal for a partial solution to the problem, which made it possible to confirm a strong relationship between the use of clean energy and deforestation. On the contrary, in Northern Europe, Enevoldsen [
17] highlights that the development of wind projects in forest areas has a negative effect on deforestation, which is carried out by installing wind turbines to achieve performance enhancement of renewable energy and reduce the cost of energy, which allows access at a low cost and to give up the consumption of polluting energy.
Brazil, launched the Clean Development Mechanism (CDM), taking into account that 60% of its energy comes from sustainable energy sources. Following this line, Moutinho et al. [
18] conduct research, where they show that deforestation rates are related to the energy crisis caused by drought. Stigka et al. [
19] confirm the need to replace fossil fuels with clean or renewable energies when producing electricity.
In the same vein, in China, Bhattacharyya and Ohiare [
20] found a very close long-term relationship between access to electricity and deforestation. This fact leads them to conclude that ensuring access to electricity to the rural population by the State will help reduce deforestation rates significantly. In the north of Angola, Temudo, Cabral, Talhinhas [
21], by using interviews with the heads of households with the observation of the change in vegetation cover, found that deforestation in rural Zaire is comparatively small. Taking into account that the use of biomass for the population’s basic needs has been reduced, the government has intervened by boosting the production of renewable energy.
On the Asian continent, Ahmed et al. [
12] conducted a study in Pakistan, the fifth most populated country in the world. By using time series data from 1980–2013, these authors find the existence of cointegration, both in the short and long term, between deforestation and renewable energy consumption. Undoubtedly, this is one of the studies that enables to reinforce the hypothesis raised in this research on the strong links that exist between deforestation, economic growth and energy consumption. For this reason, Houghton and Nassikas [
22] recommend that good forest management could stabilise CO2 emissions and would serve to make a successful transition from the use of fossil fuels to the use of energy from renewable resources.
In Colombia, when using General Circulation Models (CGM), Poveda and Mesa [
23] mention that a decrease in renewable energy consumption caused by a decrease in river flows leads to an increase in the consumption of forest resources. This in turn, increases deforestation, and consequently, leads to an increase in surface temperature, an increase in atmospheric pressure and mainly a decrease in rainfall in the medium and long term, which generated a decrease in river flows, which in turn, is reflected in severe failures in hydroelectric power systems. The aforementioned circular phenomenon is corroborated by Rojas [
24], who confirms that in Colombia, deforestation causes 2.5% of losses in hydroelectric plants. In this sense, the evidence shows that the consumption of renewable energy is positively related to the forest area [
13,
16], and when there is greater access to clean energy, there is less demand for forest products to use as fuel. Therefore, the following hypothesis of this relationship is proposed:
Hypothesis 2. (H2) The increase in the consumption of renewable energy is related to the increase in forest cover.
The second group comprises of studies that examine the relationship between the non-renewable energy price and deforestation. For example, in Eisner et al. [
25], a positive relationship was found between the rate of global forest loss and the resulting biodiversity loss related to inelastic supplies from oil after 2005. These authors state that while it is true that changes in oil supply and price cause changes in forest cover, this relationship is very challenging, since there are more factors that also influence the change in forest cover, and this is more evident in Southeast Asia and Central America. The authors recommend examining other clean energy options with more elastic prices that do not cause a decrease in forest cover. These recommendations are similar to those made by Scheidel and Sorman [
26]. In the same way, studies, such as the one by Abbaspour and Ghazi [
27], carry out a pilot model in two rural communities in Iran, Yakhkesh and Pechet, in which the authors find that one of the main reasons for deforestation is an increase in the consumption of fossil fuels as the main source of energy. For this reason, they recommend that this scenario should be considered within the Kyoto protocol, which encourages reducing environmental pollution and deforestation. Furthermore, Czúcz et al. [
28] mention that worldwide oil reserves will be depleted, and their price will increase, resulting in consequences for forest conservation, since some non-renewable resources from nature will be used as oil substitutes. Based on the aforementioned, the price of non-renewable energy is a determinant of the forest area [
25,
27]; consequently, the following hypothesis is proposed:
Hypothesis 3. (H3) The increase in the price of non-renewable energy is positively related to the decrease in forest cover.
The third group includes all the studies that relate economic growth with deforestation. Research on climate change also generated strong links between economic growth and trade, positioning them as the main drivers of deforestation. This fact has played a great role in the scientific world since the last years of the previous century. In the 1990s, the environmental Kuznets curve was proposed, which establishes the relationship between environmental degradation and economic growth. Since then, some economists, such as Grossman and Krueger [
29], Panayotou [
30], Selden and Song [
31] and Vincent [
32], used this hypothesis to verify the existence of an inverted U relationship between economic activity and various forms of environmental degradation. The study by Cropper and Griffiths [
33] is one of the pioneers in examining the Kuznets hypothesis, taking into account the relationship between deforestation and economic growth. However, despite the various investigations carried out between deforestation and economic boom, there is no definite consensus on the form that this relationship has [
34].
The antecedents presented by the FAO in 1954 and a growing concern about environmental degradation led the academic community to consider deforestation as one of the key indicators of environmental degradation. Some authors, such as Andrée et al. [
1], have studied this relationship—finding inverted U-shaped relationships specifically between per capita income and environmental degradation indicators, and concluding that the development and economic growth of a country encourages the consumption of non-renewable resources, which is directly related to deforestation.
It is important to highlight that deforestation is advancing extremely quickly, mainly in South America. However, there is no awareness of the environmental problem generated by economic activity. This is the case of Brazil, which represents most of the worldwide flora and fauna biodiversity, but despite this knowledge, humans and the economy are replacing this biodiversity with commercial land use. By using a linear fixed effects model with a balanced panel of 3168 observations, Santiago and Couto [
35] found a long-term relationship between deforestation and the socioeconomic situation between the years 2000 and 2010 in Brazil. The results of this research suggest that investment in agricultural research should be improved to achieve sustainable economic growth and thus, reduce deforestation rates, especially in the Amazon region of Brazil.
In the same country, the authors Arima et al. [
14] mention that economic growth continues to advance as investments continue to be made in hydroelectric energy and road paving, which are associated with a high deforestation rate. By 2020, Brazil will have achieved an 80% reduction in deforestation, especially in the Amazon. The authors Carvalho et al. [
36] investigated the compensation between environmental conservation and economic growth, using an equilibrium model for 30 Amazonian regions and found that the most affected population would be family farms, but to compensate for this loss, it is estimated that to obtain profits each year, they would have to produce 1.4% of the land. In the same country, Tritsch and Arvor [
37] conducted a sub-municipal analysis between socioeconomic development and deforestation in the Brazilian Amazon in their research. Their results confirm a positive relationship between deforestation and economic development, following an environmental Kuznets curve.
In Chile, Apablaza [
38] shows the relationship between economic growth and pollution by using linear regressions. In addition, a dummy variable is also used, which identifies the effectiveness of the environmental policies that follow the conceptual behaviour of the Kuznets [
39] environmental curve. These results coincide with those by Turner [
40]. In Ecuador, Sierra [
41] performs a spatial model, where he manages to determine that an increase in economic activity accelerates deforestation growth, reaching very high rates, and in the same way, when growth decreases, deforestation rates also decrease.
Caravaggio [
42] studied 114 countries, and found that in high-income and middle-income countries, the boom in economic activity is reflected in the conservation of forest cover. Cuaresma and Heger [
43] found that sub-Saharan Africa and low-income group countries have a higher development and deforestation elasticity. Similar results are found in a study carried out by Bhattarai and Hammig [
44], whereby using a panel of 66 countries from Asia, Africa and Latin America, quasi-experimental and difference in differences approaches were applied to assess the changes in deforestation produced by economic activity. On the other hand, Tritsch et al. [
45] propose that it is mandatory to have a Forest Management Plan (FMP) with logging concessions. The results suggest that applying an FMP will help counteract deforestation significantly, enabling logging companies to carry out extraction cycles to avoid overexploitation. Afawubo and Noglo [
46], mention that to reduce deforestation rates, economic development should not be the only focus, but also the institutional quality of countries. This is confirmed by Miyamoto [
47], who reveals that poverty has a strong relationship with the change in the forest area. For this reason, it is considered that economic growth generates a greater demand for land [
27,
36] for other economic and human activities, with which the forest area decreases. Thus, the following hypothesis is established:
Hypothesis 4. (H4) The increase in economic activity is negatively related to the forest area.
4. Discussion of Results
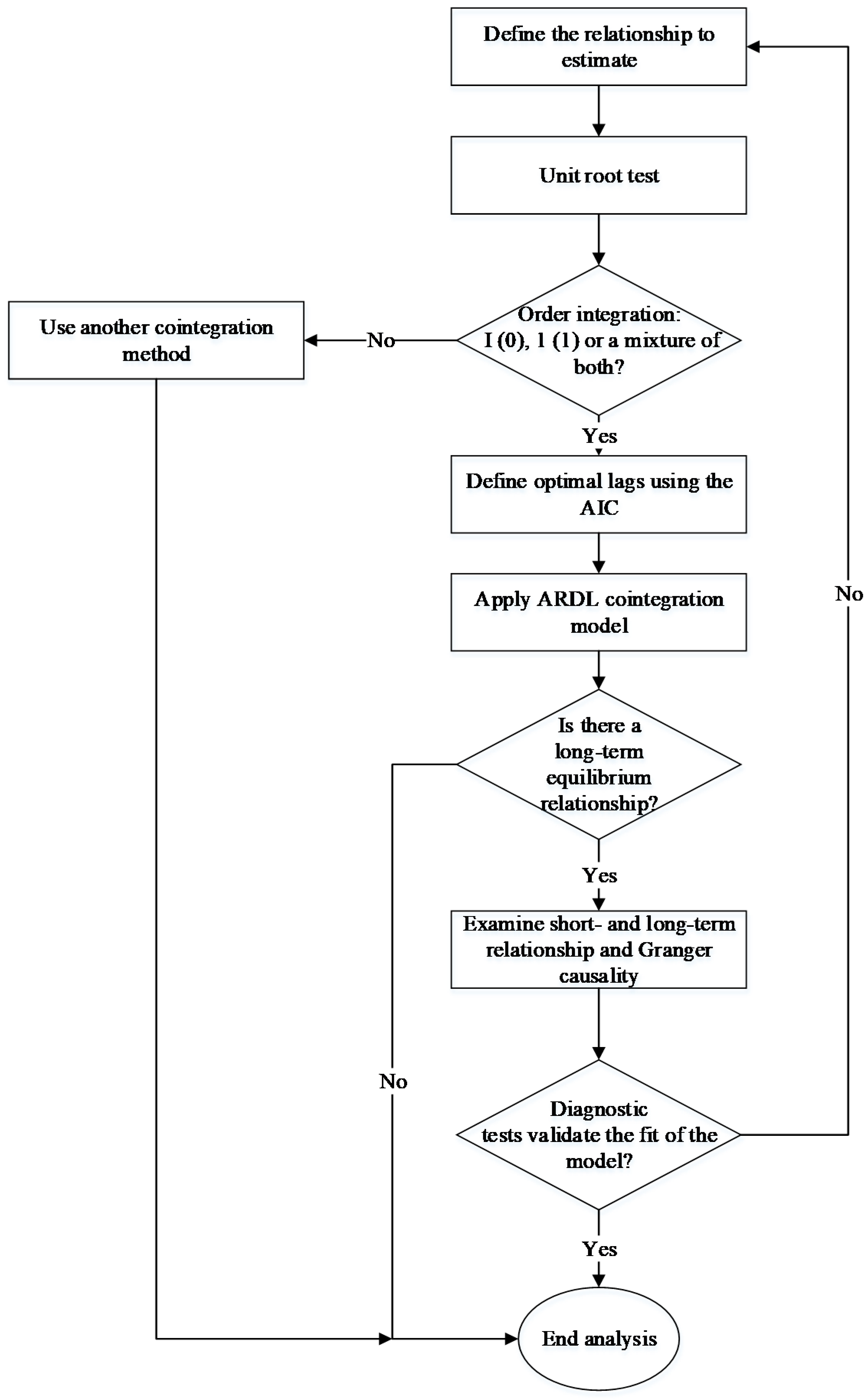
Prior to the long-term analysis, the stationarity of the variables was examined by using the Augmented Dickey-Fuller unit root test (ADF) [
50]. The results of
Table 3 rejects the null hypothesis that assumes the existence of a unit root—that is, the series are stationary. One of the main advantages is that the ARDL approach can use variables with integration order I (0), I (1) or a mixture of both [
65]. Complementarily, it is carried out on Kwiatkowski, Phillips, Schmidt and Shin (KPSS) [
54]. Thus, the forest area and population growth variable for all groups is stationary at levels I (0) and the rest of the independent variables at I (1).
After checking the stationarity of the series,
Table 4 presents the results of the ARDL cointegration test. To properly determine the optimal lag length of each variable, the Akaike information criteria (AIC) is used. In MIC and LIC, the calculated F–statistics are higher than the value of the upper limit proposed by Pesaran, Shin and Smith [
55]. Consequently, at the 1% significance level, the alternative hypothesis that establishes a long-term cointegration relationship between the study variables is accepted, which means that the variables move jointly over time. On the contrary, for HIC, the results show no equilibrium relationship in the model studied.
The findings of the cointegration test evaluate the long-term relationship between the forest area, GDP, GDP
2, renewable energy consumption, non-renewable energy price and population growth. Thus, the ARDL approach is used to estimate the long-term coefficients between the variables.
Table 5 shows the results obtained,
represents the error correction term (ECT), in MIC and LIC is negative and statistically significant as expected. However, in the HIC, its value is positive and not significant, which shows the long-term non-cointegration mentioned above. The values of
range from 0 (no adjustment) to −1 (immediate adjustment) as expected. Its values are small, which is reasonable, since increasing forest cover is a time-consuming process inherent in its nature. That is, when the forest cover area is far from its equilibrium level, it is adjusted by 0.44% and 8.7%, respectively, within the first year. The speed of reaching the equilibrium level is slow and significant. In MIC and LIC, an increase of 1% in renewable energy consumption represents an increase of 0.041512 km2 and 0.027512 km2 of forest area, respectively. That is, energy consumption from renewable sources contributes to reducing deforestation. The increase in the consumption of renewable energy represents an alternative for access to clean energy, instead of wood from forests, which is used as energy sources. These results are consistent with those reported by Tanner and Johnston [
13], Nazir et al. [
16] and Bhattacharyya and Ohiare [
20], who affirm that the State can generate policies so that the rural population can have access to electricity and give up the consumption of products from forests.
Regarding an increase in economic activity in MIC and LIC, measured by GDP, it decreases the forest area. The increase in economic activity brings with it some externalities, such as increased urbanisation, expansion of crops to provide food, among others, which generally is related to a greater demand for land and to achieve this, spaces that are destined for forests are occupied. These findings are also based on the fact that the increase in economic activity demands resources that are found in the forests, which leads to a process of deforestation [
43,
66].
On the other hand, population growth is negatively related to forest area coverage in both groups of countries (
Table 5). That is, as the population increases, a change in land use is generated in which the forest area is used for another type of human activity, such as growing food, spaces for housing, resources (wood) for the construction of houses, among others. These results coincide with those found by Ahmed, Shahbaz, Qasim and Long [
12], who mention that the increase in the population density demands more forest resources for the construction of housing in the rural sector. Moreover, Tritsch and Le Tourneau [
67] find that one third of deforestation in the Amazon region of Brazil is associated with 1.5% of the population. The findings described in this section provide sufficient information to verify the fulfilment of hypotheses H1, H2 and H4 raised in
Section 2. Additionally, it is observed that the price of non-renewable energy is not significant, thus ruling out hypothesis H3. Similarly, GDP
2 is not significant—that is, non-compliance with the environmental Kuznets curve is corroborated [
39].
Following the long-term analysis, the short-term test between the model variables is evaluated.
Table 6 shows that the variation in renewable energy consumption, GDP, GDP
2, the non-renewable energy price, population growth are not related to the immediate changes in the forest area in the short term in all three models.
Subsequently, the error-correction term (ECT) of the Granger causality test is used to detect the direction of long-term causality between the study variables.
Table 7 shows that in the long term, renewable energy consumption, GDP, GDP
2, the non-renewable energy price and population growth causes the forest area in MIC and LIC.
Additionally,
Table 8 shows the diagnostic tests to validate the model fit [
12,
52,
53,
56] for all groups of countries. The
p-value greater than 0.05 of the Ramsey test confirms that the models are correctly specified. The
p-value greater than 0.05 rules out the presence of serial correlation in the estimated models. The
p-value of the heteroscedasticity test, which is greater than 0.05, confirms that the models are homoscedastic. Moreover, the Jarque-Bera normality test with a probability of 0.8204, 0.5734 and 0.7683, confirms that the residuals are normally distributed. Finally, the coefficient of determination of 77.45, 83.87 and 84.89, respectively, indicate the good fit of the model.
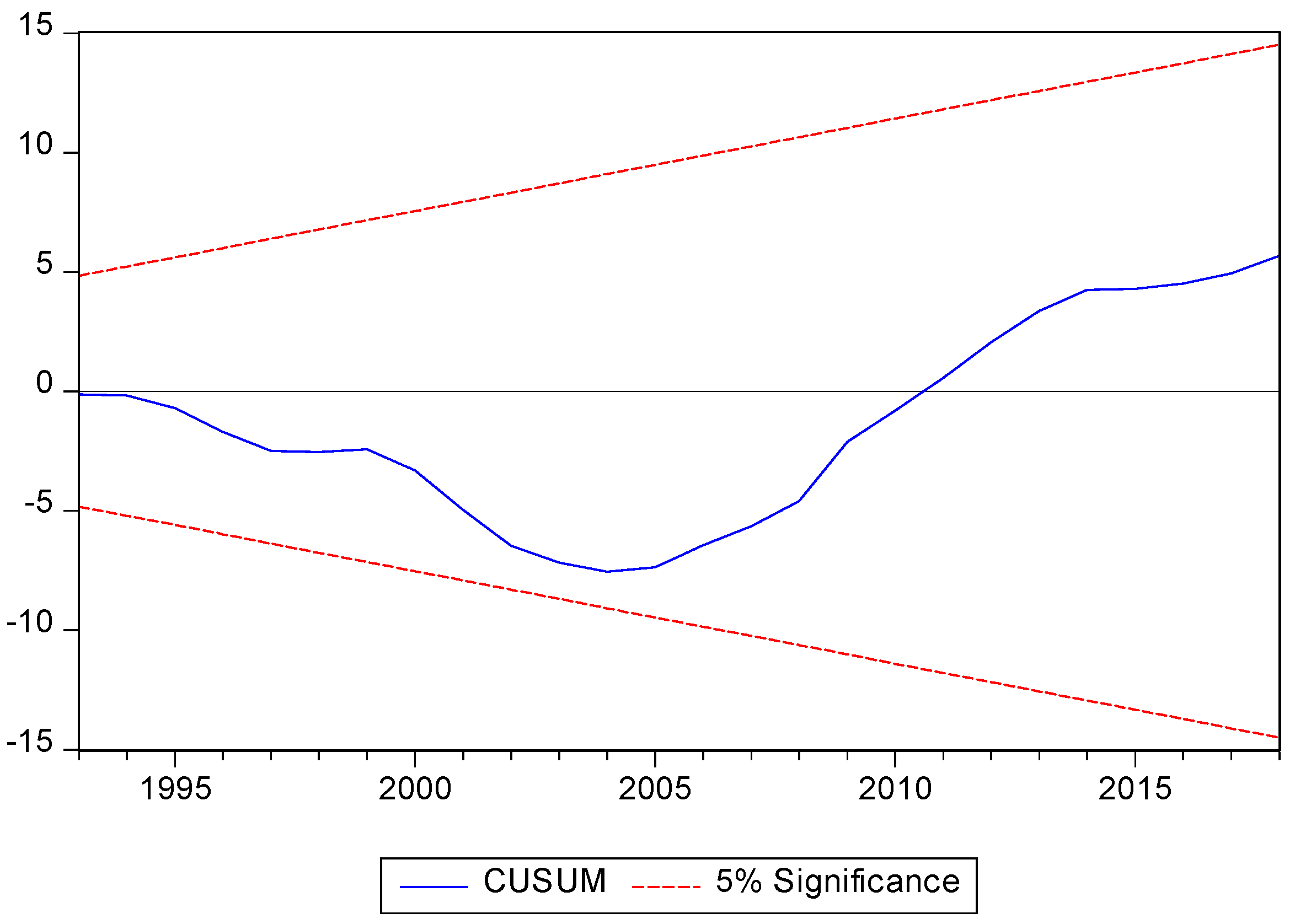
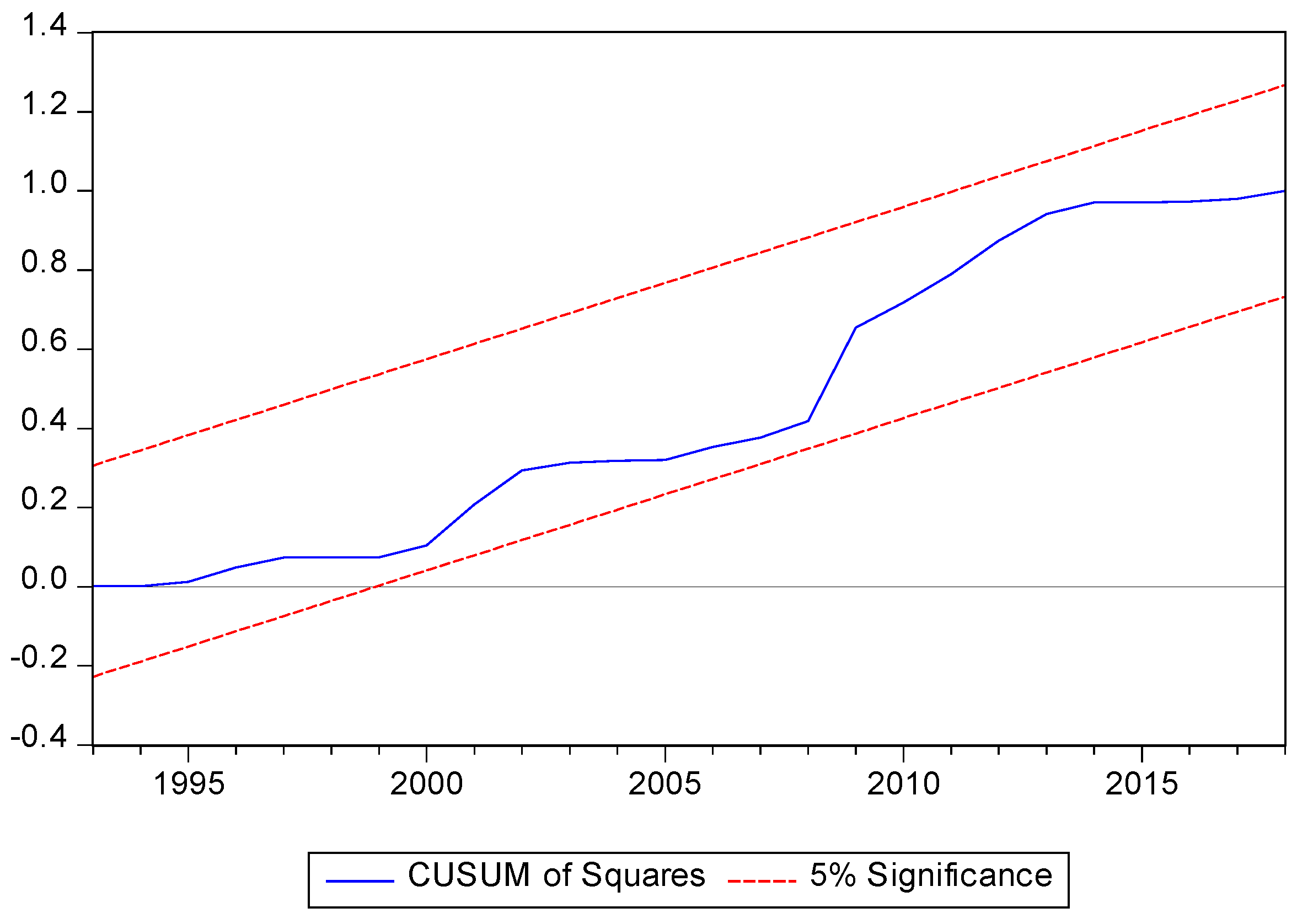
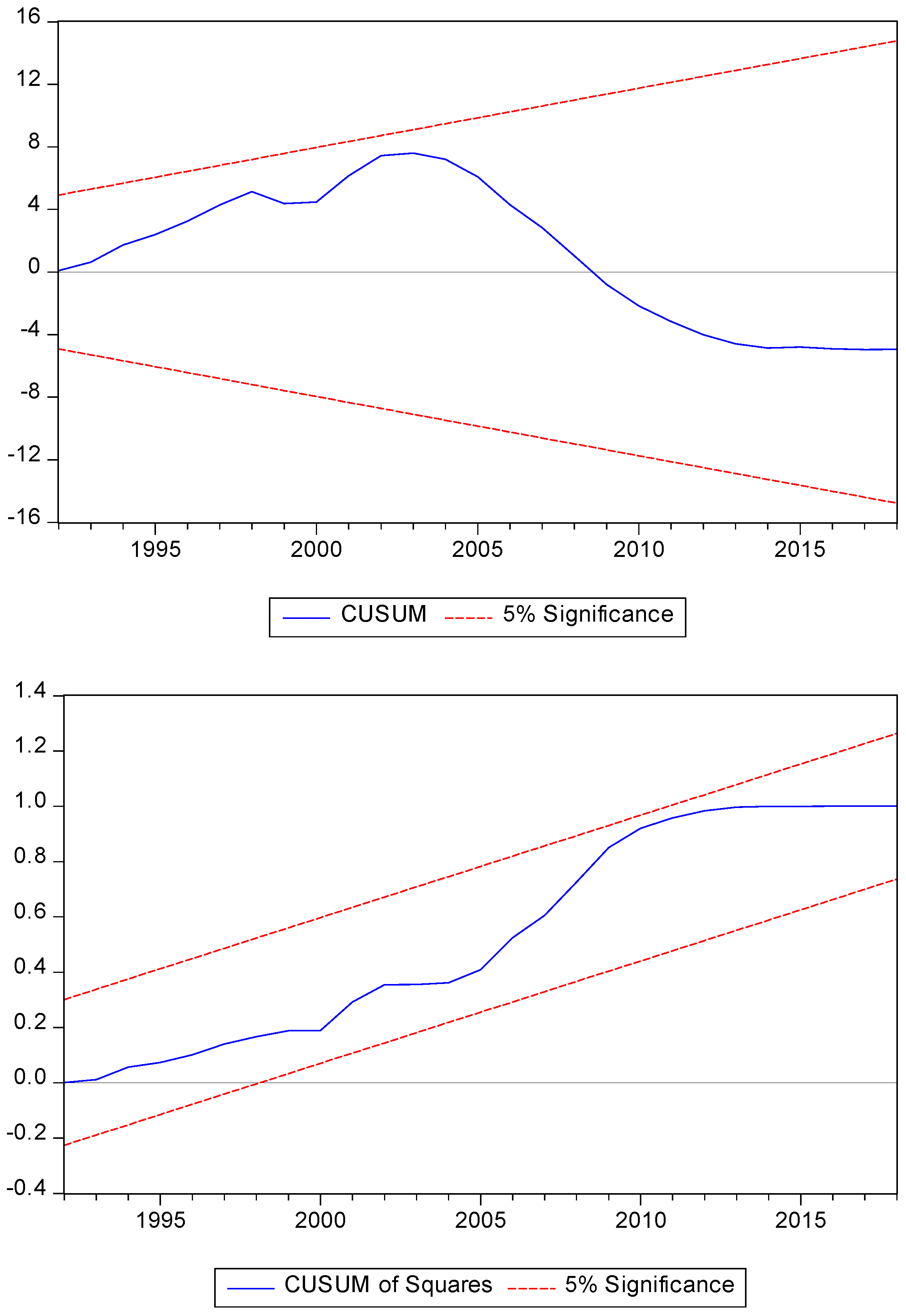
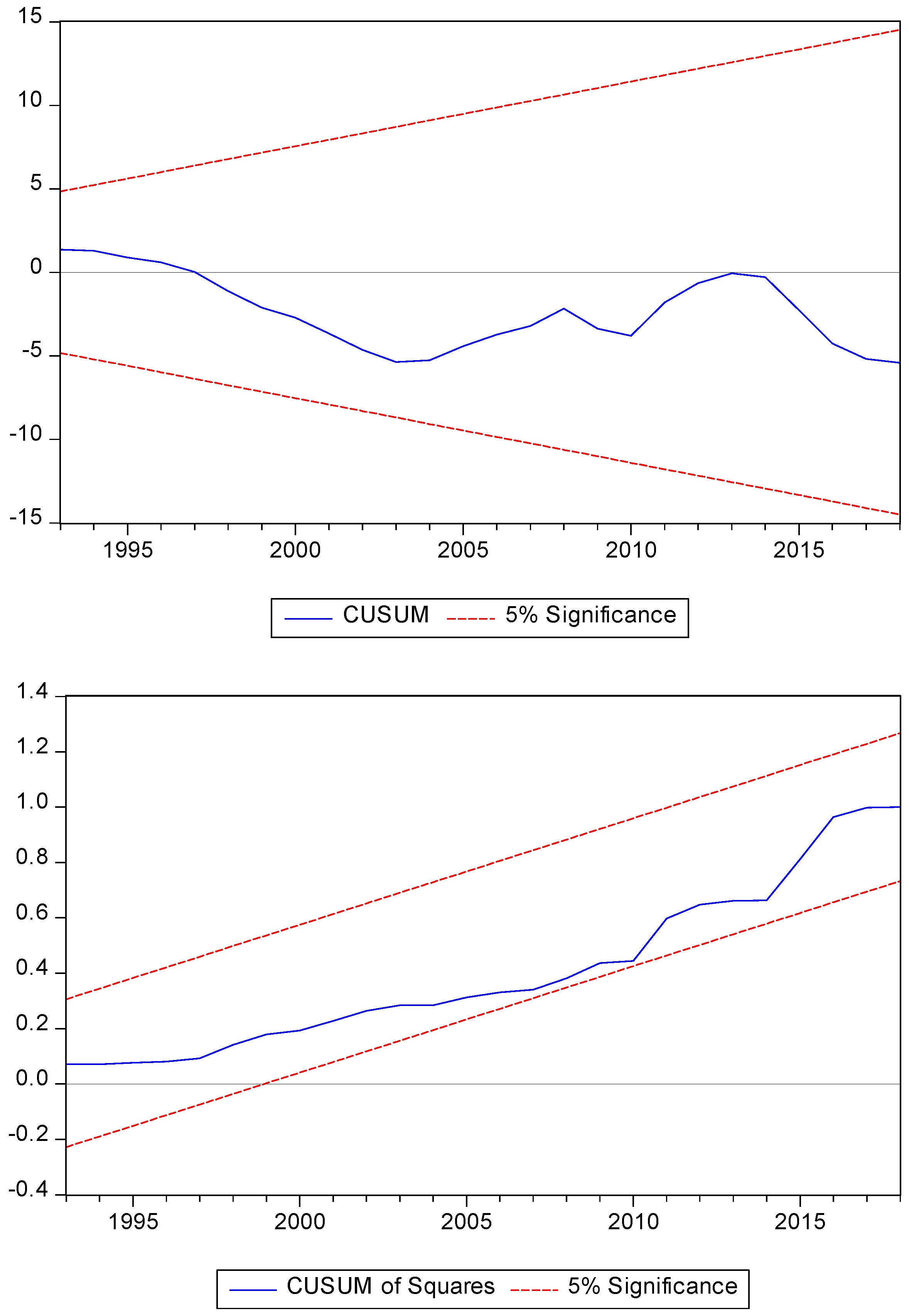
To conclude the study, following Brown et al. [
64], the stability of the parameters is evaluated. The cumulative sum (CUSUM) and cumulative sum of squares (CUSUMQ) are observed in
Figure 3,
Figure 4 and
Figure 5 for all groups of countries. In all three models, the graph shows that the lines are at the critical limit of 95%, which indicates the stability of the coefficients. Diagnostic tests confirm that the ARDL model is reliable for defining policies at the linking point of forest area, renewable energy consumption, GDP, GDP
2, non-renewable energy price and population growth.
5. Conclusions and Policy Implications
Deforestation is a global economic and environmental problem, so trying to understand its determinants is essential to mitigate its accelerated pace. This research examined the long-term equilibrium relationship between renewable energy consumption, GDP, GDP2, renewable energy price, population growth and forest area in high-, middle- and low-income countries, using the ARDL econometric approach.
The results confirm a long-term equilibrium relationship between the mentioned variables for MIC and LIC. The ECT indicates that the speed of forest cover adjustment is slow when it is not at its equilibrium point, approximately it adjusts by 0.44% and 8.7%, respectively, within the first year. Furthermore, the consumption of renewable energy is positively related to the forest area. In contrast, population growth maintains a negative relationship with the forest area. The results obtained provide valuable information to confirm the fulfilment of the hypotheses of this investigation, H1, H2 and H4. On the contrary, the H4 is not fulfilled.
Those responsible for establishing public and environmental policy measures must consider that encouraging the consumption of renewable energy allows for an alternative to the use of forest products and services. In MIC and LIC, the boom in economic activity must take place in scenarios in which environmental sustainability and the care of forests are on the horizon. Population growth must be associated with sustainable measures on land use, thereby ensuring that deforestation does not increase.
One of the main limitations of this research is the lack of information on the price elasticity of demand for agricultural products throughout the period analysed, to include them as an explanatory variable and evaluate how it is correlated with deforestation. Likewise, the period of time examined is a function of the availability of the information.