Effect of Stem Snapping on Aspen Timber Assortment Recovery in Hemiboreal Forests
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
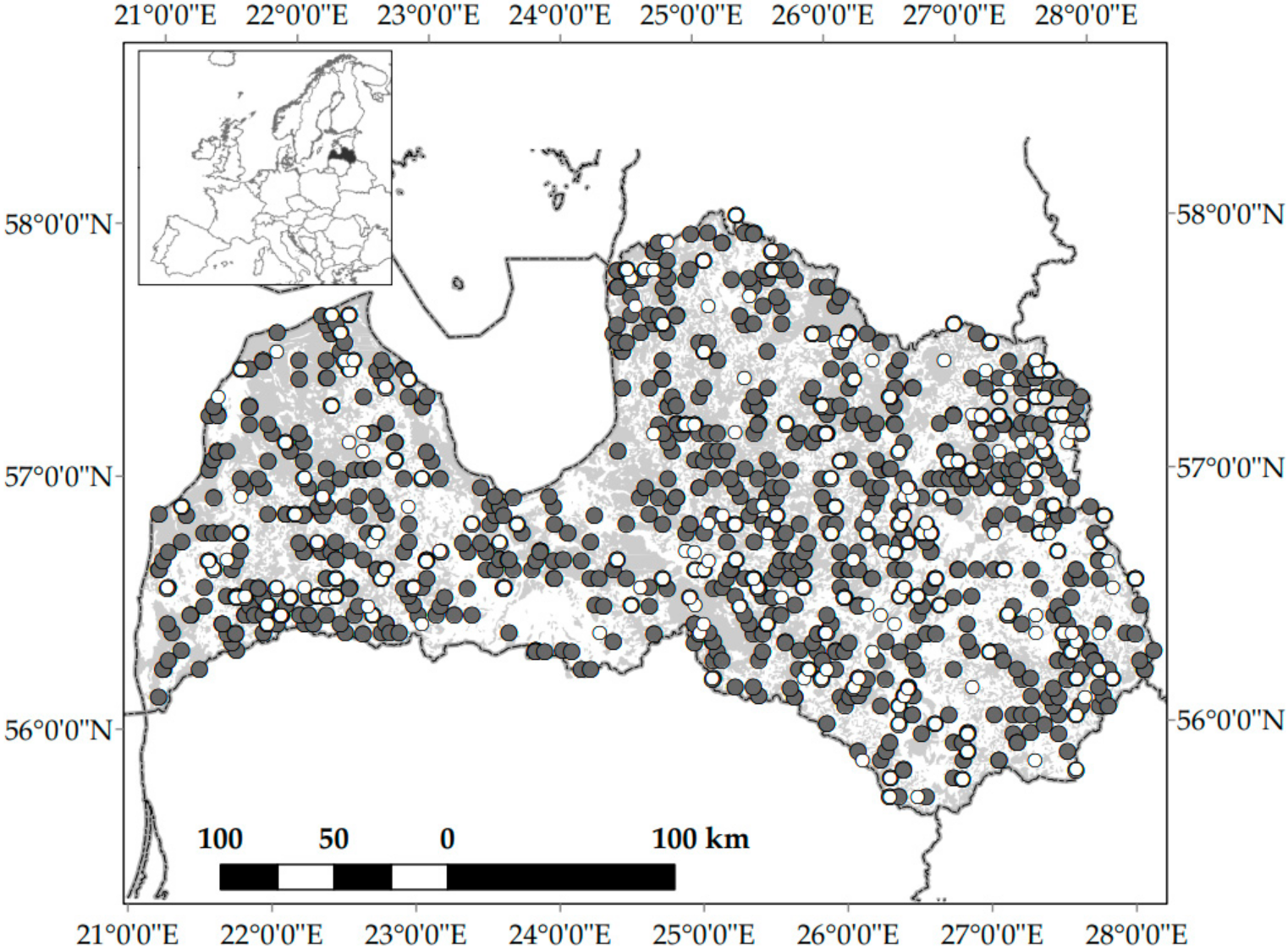
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data
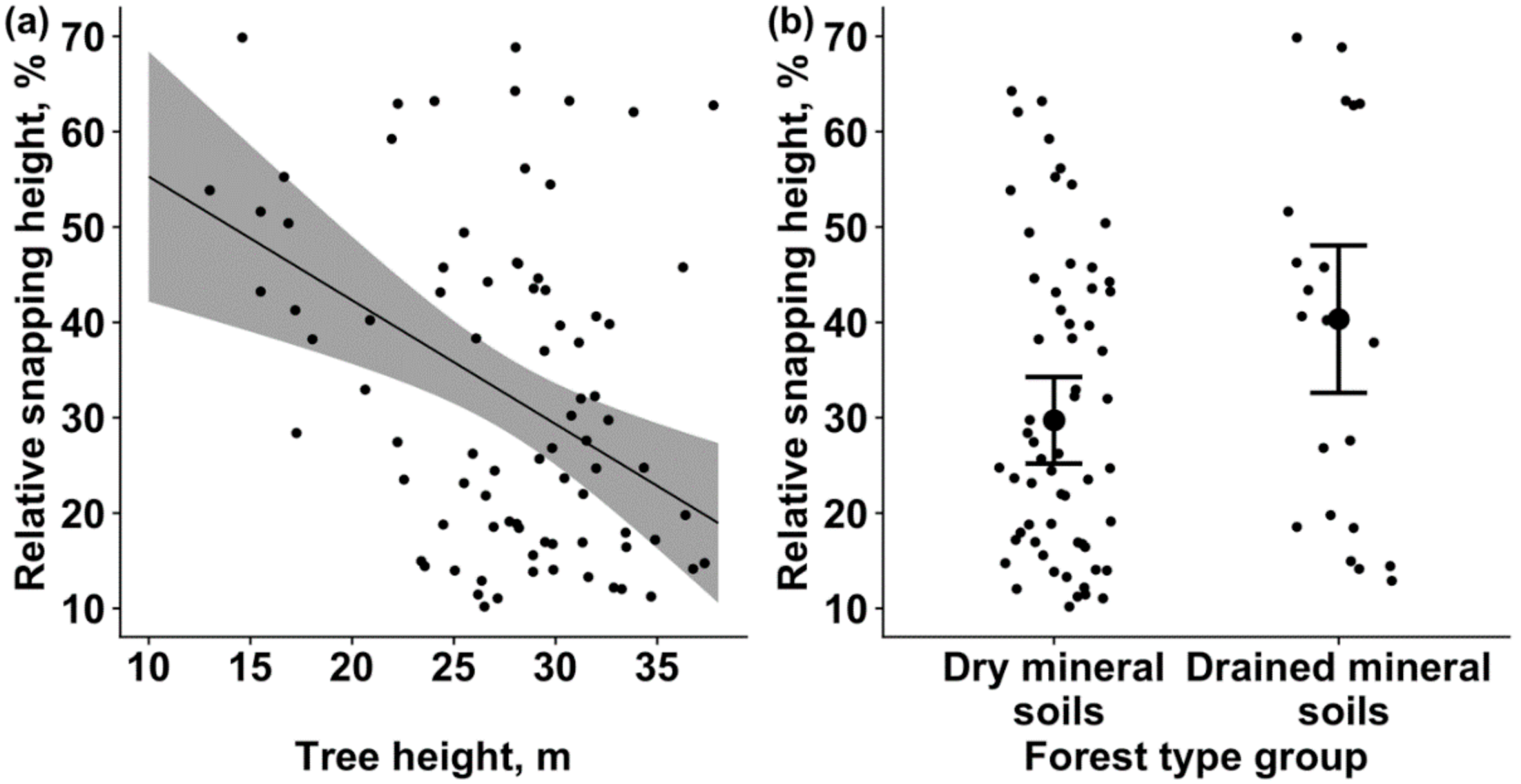
2.3. Modeling of Snapping Height
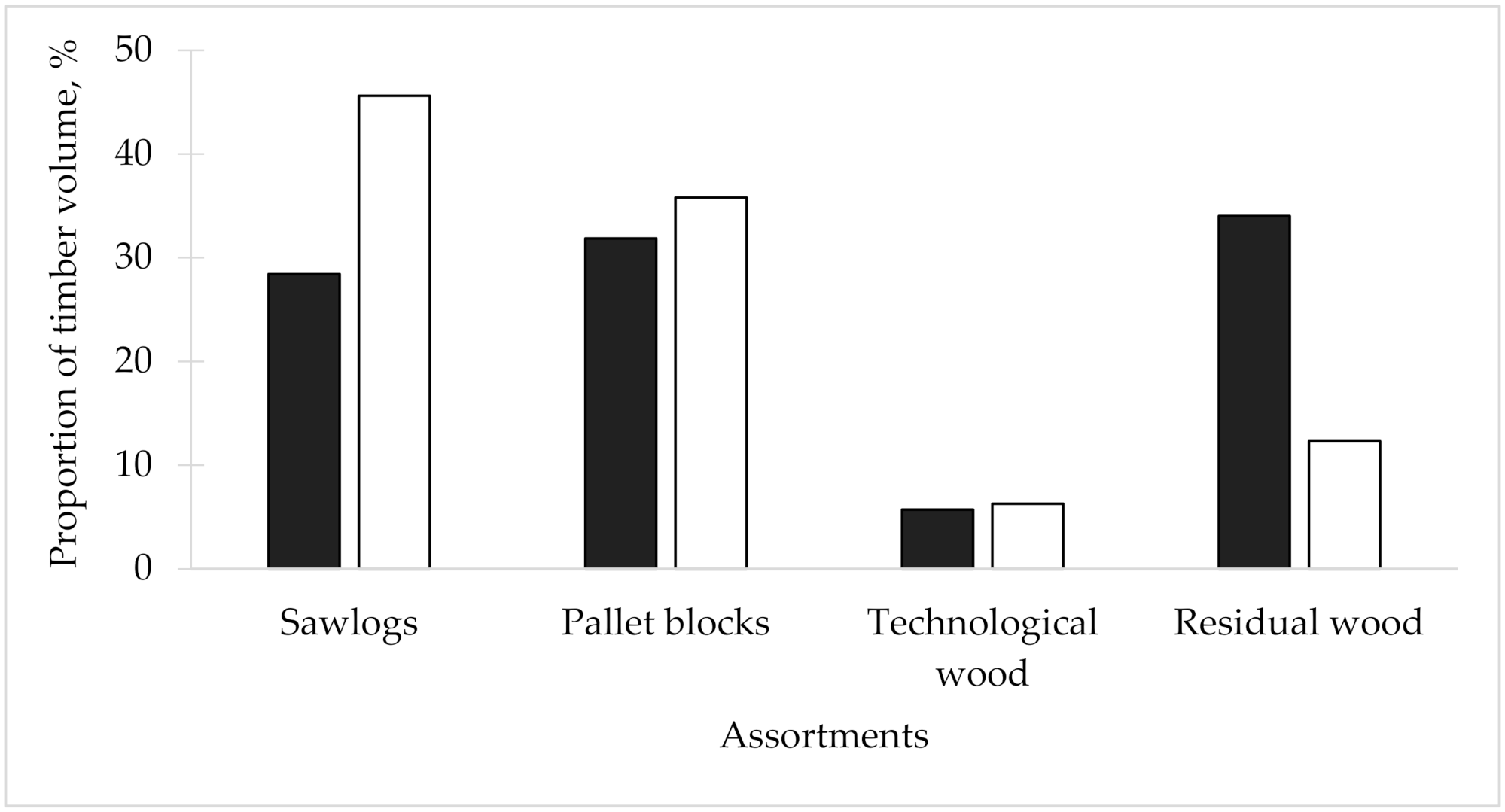
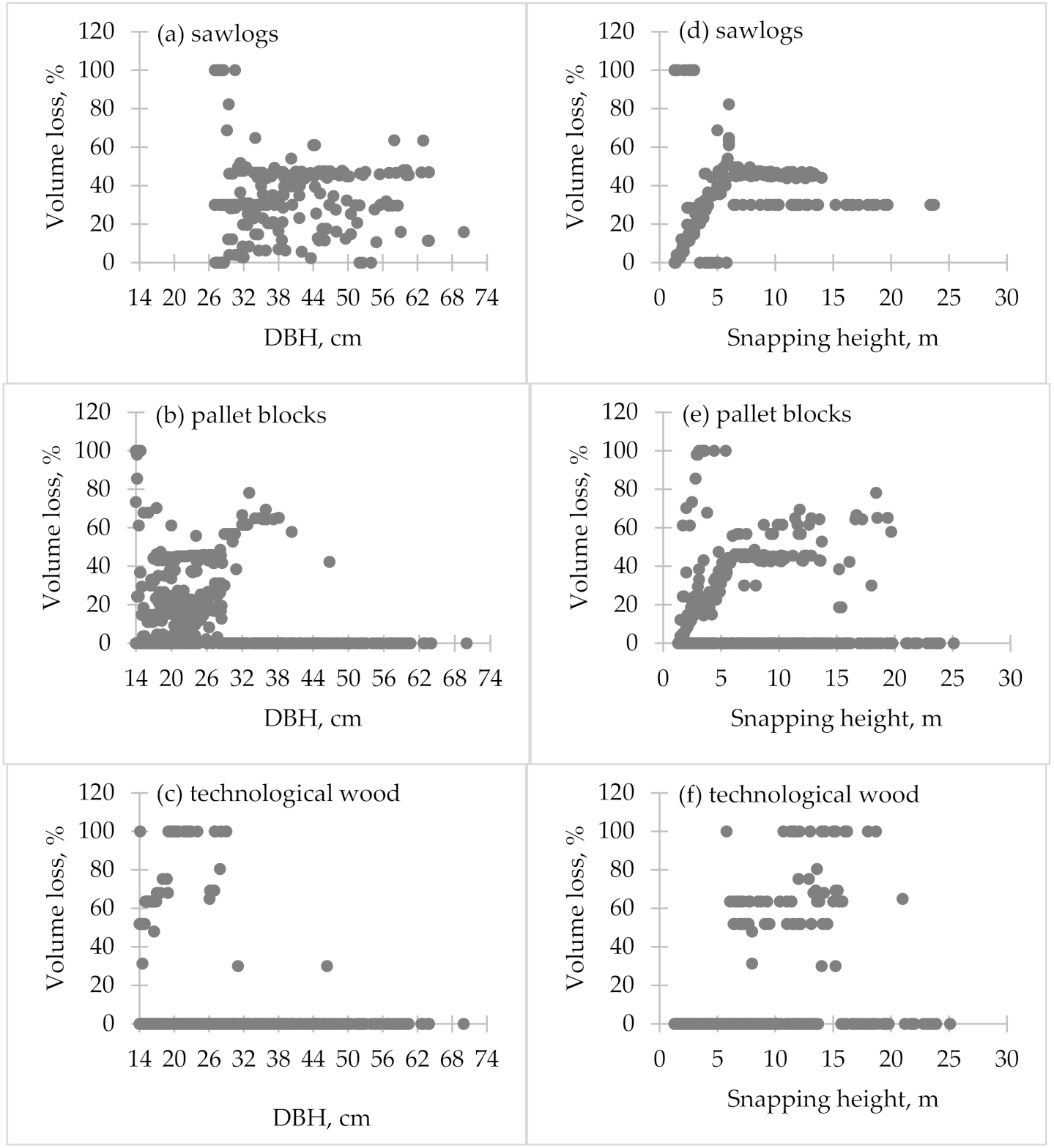
2.4. Calculations of Timber Assortment Recovery
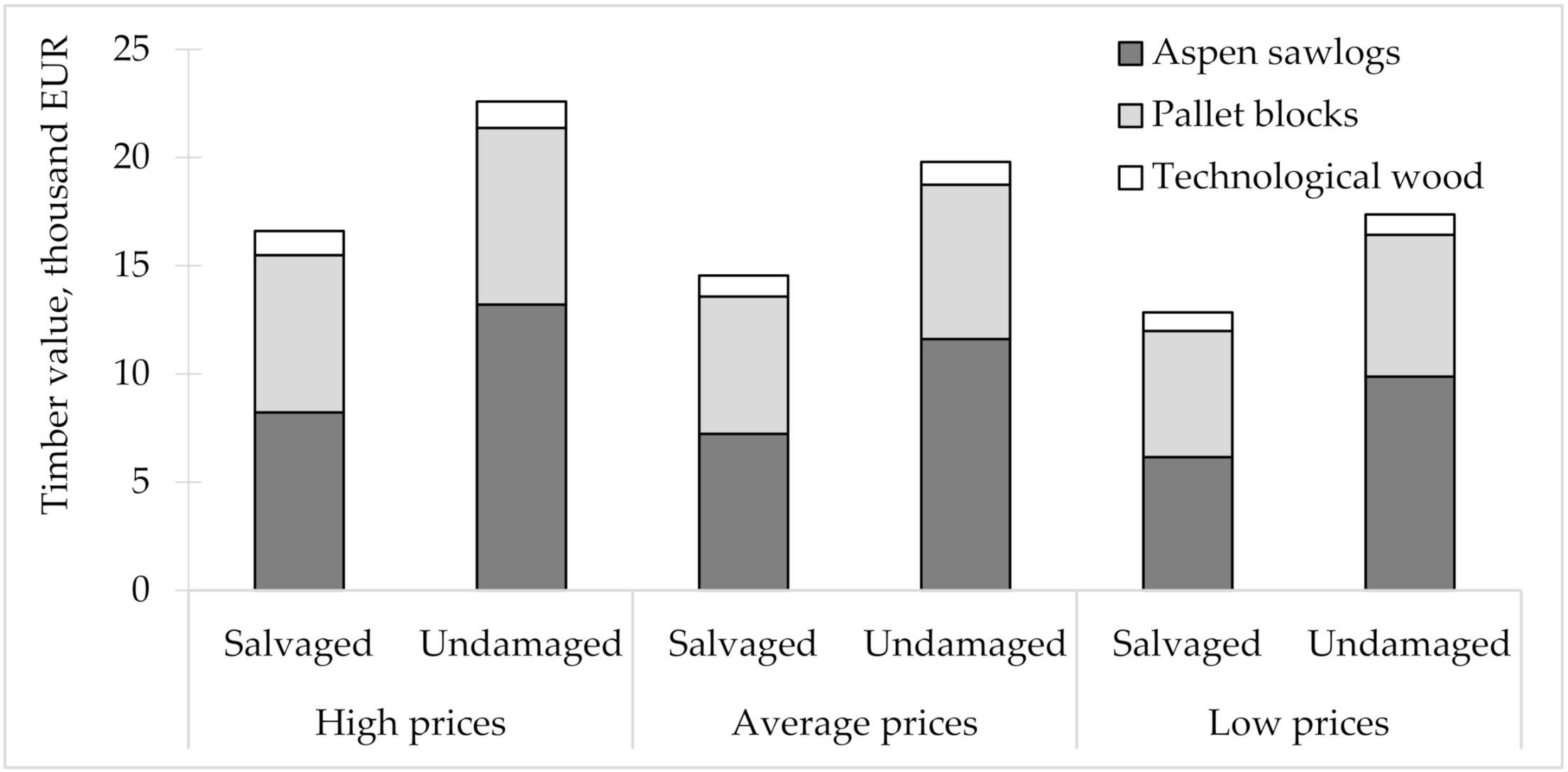
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Schelhaas, M.J.; Nabuurs, G.J.; Schuck, A. Natural disturbances in the European forests in the 19th and 20th centuries. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2003, 9, 1620–1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardiner, B.; Schuck, A.; Schelhaas, M.-J.; Orazio, C.; Blennow, K.; Nicoll, B. Living with Storm Damage to Forests; European Forest Institute: Joensuu, Finland, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Donis, J.; Saleniece, R.; Krisans, O.; Dubrovskis, E.; Kitenberga, M.; Jansons, A. A financial assessment of windstorm risks for scots pine stands in hemiboreal forests. Forests 2020, 11, 566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seidl, R.; Thom, D.; Kautz, M.; Martin-Benito, D.; Peltoniemi, M.; Vacchiano, G.; Wild, J.; Ascoli, D.; Petr, M.; Honkaniemi, J.; et al. Forest disturbances under climate change. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2017, 7, 395–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forzieri, G.; Pecchi, M.; Girardello, M.; Mauri, A.; Klaus, M.; Nikolov, C.; Rüetschi, M.; Gardiner, B.; Tomastik, J.; Small, D.; et al. A spatially explicit database of wind disturbances in European forests over the period 2000-2018. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2020, 12, 257–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leckebusch, G.C.; Koffi, B.; Ulbrich, U.; Pinto, J.G.; Spangehl, T.; Zacharias, S. Analysis of frequency and intensity of European.pdf. Clim. Res. 2006, 31, 59–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seidl, R.; Schelhaas, M.; Rammer, W.; Verkerk, P.J. Increasing forest disturbances in Europe and their impact on carbon storage. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2014, 4, 806–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruosteenoja, K.; Vihma, T.; Venäläinen, A. Projected changes in european and north atlantic seasonal wind climate derived from CMIP5 simulations. J. Clim. 2019, 32, 6467–6490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kellomäki, S.; Maajärvi, M.; Strandman, H.; Kilpeläinen, A.; Peltola, H. Model computations on the climate change effects on snow cover, soil moisture and soil frost in the boreal conditions over Finland. Silva. Fenn. 2010, 44, 213–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laapas, M.; Lehtonen, I.; Venäläinen, A.; Peltola, H. The 10-year return levels of maximum wind speeds under frozen and unfrozen soil forest conditions. Climate 2019, 7, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leverkus, A.B.; Lindenmayer, D.B.; Thorn, S.; Gustafsson, L. Salvage logging in the world’s forests: Interactions between natural disturbance and logging need recognition. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2018, 27, 1140–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prestemon, J.P.; Holmes, T.P. Timber Salvage Economics. In The Economics of Forest Disturbances; Holmes, T.P., Prestemon, J.P., Abt, K.L., Eds.; Springer Science + Business Media: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2008; pp. 167–190. [Google Scholar]
- Stadelmann, G.; Bugmann, H.; Meier, F.; Wermelinger, B.; Bigler, C. Effects of salvage logging and sanitation felling on bark beetle (Ips typographus L.) infestations. For. Ecol. Manag. 2013, 305, 273–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Økland, B.; Nikolov, C.; Krokene, P.; Vakula, J. Transition from windfall-to patch-driven outbreak dynamics of the spruce bark beetle Ips typographus. For. Ecol. Manag. 2016, 363, 63–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardiner, B.; Peltola, H.; Kellomäki, S. Comparison of two models for predicting the critical wind speeds required to damage coniferous trees. Ecol. Modell. 2000, 129, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, K. Dynamic loading of trees. J. Arboric. 2003, 29, 165–171. [Google Scholar]
- Petty, J.A.; Worrell, R. Stability of coniferous tree stems in relation to damage by snow. Forestry 1981, 54, 115–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ancelin, P.; Courbaud, B.; Fourcaud, T. Development of an individual tree-based mechanical model to predict wind damage within forest stands. For. Ecol. Manag. 2004, 203, 101–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunham, R.A.; Cameron, A.D. Crown, stem and wood properties of wind-damaged and undamaged Sitka spruce. For. Ecol. Manag. 2000, 135, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishimura, T.B. Tree characteristics related to stem breakage of Picea glehnii and Abies sachalinensis. For. Ecol. Manag. 2005, 215, 295–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallentin, C.; Nilsson, U. Storm and snow damage in a Norway spruce thinning experiment in southern Sweden. Forestry 2014, 87, 229–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieuwenhuis, M.; Fitzpatrick, P.J. An assessment of stem breakage and the reduction in timber volume and value recovery resulting from a catastrophic storm: An irish case study. Forestry 2002, 75, 513–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snepsts, G.; Kitenberga, M.; Elferts, D.; Donis, J.; Jansons, A. Stem damage modifies the impact of wind on Norway Spruces. Forests 2020, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Environment Agency. European Forest Types. Categories and Types for Sustainable Forest Management Reporting and Policy; Technical Report; European Environment Agency: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Ērglis, D. 1967. un 1969. gadu vētru sekas Latvijas PSR valsts mežos [Windstorm damage in 1967 and 1969 in forests of Latvian SSR]. Mežsaimniecība un Mežrūpniecība 1977, 4, 23–34. [Google Scholar]
- Valsts meža dienests. 2006. Gada Publiskais Pārskats; Annual report 2006; VMD: Riga, Latvia, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Valsts meža Dienests. 2017. gada publiskais pārskats; Annual report 2017; VMD: Riga, Latvia, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Valsts meža dienests. 2019. gada publiskais pārskats; Annual report 2019; VMD: Riga, Latvia, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Jansons, J.; Līcīte, I. Latvia. In National Forest Inventories: Pathways for Common Reporting; Tomppo, E., Gschwantner, T., Lawrence, M., McRoberts, R.E., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2010; pp. 341–350. [Google Scholar]
- Bušs, K. Forest ecosystem classification in Latvia. Proc. Latv. Acad. Sci. Sect. B Nat. Exact Appl. Sci. 1997, 51, 204–218. [Google Scholar]
- Rust, S. Analysis of regional variation of height growth and slenderness in populations of six urban tree species using a quantile regression approach. Urban. For. Urban. Green. 2014, 13, 336–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grabosky, J.; Bassuk, N. Seventeen years’ growth of street trees in structural soil compared with a tree lawn in New York City. Urban. For. Urban. Green. 2016, 16, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozolins, R. Forest stand assortment structure analysis using mathematical modelling. Metsanduslikud Uurim. For. Stud. 2002, 37, 33–42. [Google Scholar]
- Von Gadow, K.; Hui, G. Modelling Forest Development; Forestry Sciences; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1999; Volume 57. [Google Scholar]
- Latvijas Valsts meži. Joint Stock Company ‘Latvia’s State Forests’ Apaļo Kokmateriālu Cenas. Round Assortment Prices. Available online: https://www.lvm.lv/biznesa-partneriem/produkti/koksnes-produkti/fakti-un-dati (accessed on 13 November 2020).
- Peltola, H.; Kellomäki, S.; Väisänen, H.; Ikonen, V.P. A mechanistic model for assessing the risk of wind and snow damage to single trees and stands of Scots pine, Norway spruce, and birch. Can. J. For. Res. 1999, 29, 647–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilisson, T.; Metslaid, M.; Vodde, F.; Jõgiste, K.; Kurm, M. Storm disturbance in forest ecosystems in Estonia. Scand. J. For. Res. 2005, 20, 88–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peltola, H.; Kellomäaki, S. A mechanistic model for calculating windthrow and stem breakage of Scots Pine at stand adge. Silva. Fenn. 1993, 2, 99–111. [Google Scholar]
- Sellier, D.; Fourcaud, T. Crown structure and wood properties:Influence on tree sway and response to high winds. Am. J. Bot. 2009, 96, 885–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardiner, B.; Blennow, K.; Carnus, J.; Fleischer, P.; Ingemarson, F.; Landmann, G.; Lindner, M.; Marzano, M.; Nicoll, B.; Orazio, C.; et al. Destructive Storms in European Forests: Past and Forthcoming Impacts; European Forest Institute: Joensuu, Finland, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- King, D.A. Tree form, height growth, and susceptibility to wind damage in Acer saccharum. Ecology 1986, 67, 980–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cremer, K.; Borough, C.; Mckinnell, F.; Carter, A. Effects of stocking and thinning on wind damage in plantations. N. Z. J. For. Sci. For. Sci. 1982, 12, 244–268. [Google Scholar]
- Lõhmus, A. Aspen-inhabiting aphyllophoroid fungi in a managed forest landscape in Estonia. Scand. J. For. Res. 2011, 26, 212–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeps, M.; Senhofa, S.; Zadina, M.; Neimane, U.; Jansons, A. Stem damages caused by heart rot and large poplar borer on hybrid and European aspen. For. Stud. 2017, 66, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Debell, D.S.; Harrington, C.A.; Clendenen, G.W.; Zasada, J.C. Tree growth and stand development of four Populus clones in large monoclonal plots. New For. 1997, 14, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krisans, O.; Matisons, R.; Rust, S.; Burnevica, N.; Bruna, L.; Elferts, D.; Kalvane, L.; Jansons, A. Presence of root rot reduces stability of Norway spruce (Picea abies): Results of static pulling tests in Latvia. Forests 2020, 11, 416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magagnotti, N.; Picchi, G.; Spinelli, R. A versatile machine system for salvaging small-scale forest windthrow. Biosyst. Eng. 2013, 115, 381–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kärhä, K.; Anttonen, T.; Poikela, A.; Palander, T.; Laurén, A.; Peltola, H.; Nuutinen, Y. Evaluation of salvage logging productivity and costs in windthrown Norway spruce-dominated forests. Forests 2018, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eliasson, L.; Manner, J.; Thor, M. Costs for thinning and final felling operations in Sweden, 2000–2017. Scand. J. For. Res. 2019, 34, 627–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Stand Characteristics | Description | Classes/Range | Number of Observations/Mean ± SD | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| P1 | P2 | |||
| Age, years | Age of the overstory dominant species | 10–171 | 50.9 ± 18.0 | 52.8 ± 19.7 |
| Height, m | Height of the overstory dominant species | 5.9–40.1 | 24.9 ± 5.1 | 25.9 ± 5.5 |
| DBH, cm | Diameter at breast height of the overstory dominant species | 6.9–74.3 | 26.3 ± 9.0 | 27.6 ± 10.0 |
| Volume, m3 ha⁻¹ | The standing volume of the dominant canopy | 5–1058 | 370 ± 155 | 386 ± 168 |
| Density, trees ha⁻¹ | Number of trees of the dominant canopy | 100–9020 | 1306 ± 1004 | 1181 ± 840 |
| Basal area, m2 ha⁻¹ | Basal area of the dominant canopy | 1–76 | 32.9 ± 10.3 | 33.0 ± 10.6 |
| Site type | Site type groups, based on the depth of the peat layer and moisture regime | Dry mineral soil | 2221 | 2048 |
| Wet mineral soil | 350 | 305 | ||
| Peat soil | 36 | 73 | ||
| Drained mineral soil | 1309 | 978 | ||
| Drained peat soil | 196 | 161 | ||
| Dominant species | Overstory species with the highest growing stock | Pine | 140 | 135 |
| Spruce | 299 | 239 | ||
| Birch | 560 | 533 | ||
| Black alder | 82 | 58 | ||
| Aspen | 2884 | 2461 | ||
| Grey alder | 103 | 83 | ||
| Other broadleaved species | 44 | 56 | ||
| Sample size | Number of trees per plot | 1–54 | 4.9 ± 6.8 | 4.6 ± 6.0 |
| Assortments | Dimensions | Price a, EUR m⁻3 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Diameter c, cm | Length, m | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 b | Mean | |
| Aspen sawlogs | ≥24.0 | 2.4 | 38.71 | 39.67 | 47.65 | 51.74 | 49.77 | 45.51 |
| Pallet blocks | 12.0–23.9 | 2.4 | 32.68 | 30.64 | 39.78 | 40.75 | 33.98 | 35.57 |
| Technological wood d | 5.0–11.9 | 3.0 | 26.94 | 27.04 | 33.68 | 34.71 | 29.00 | 30.27 |
| Model | Explanatory Variables | Parameter Estimates | Model Estimates | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Est. | SE | t-Value | p-Value | Adj. R2 | AIC | p-Value | ||
| 1 | Tree height | −1.42 | 0.42 | −3.37 | 0.001 | 0.090 | 939.1 | 0.003 |
| H2D⁻¹ | 0.20 | 0.24 | 0.82 | 0.412 | ||||
| Intercept | 66.11 | 10.34 | 6.39 | <0.001 | ||||
| 2 | Stand age | 0.01 | 0.12 | 0.10 | 0.918 | −0.015 | 950.6 | 0.808 |
| HD⁻¹ | 4.58 | 7.10 | 0.65 | 0.520 | ||||
| Intercept | 27.12 | 10.29 | 2.63 | 0.001 | ||||
| 3 | Tree height | −1.30 | 0.36 | −3.62 | <0.001 | 0.131 | 934.3 | <0.001 |
| Forest type group | −10.61 | 4.52 | −2.35 | 0.021 | ||||
| Intercept | 76.14 | 10.81 | 7.04 | <0.001 | ||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Čakša, L.; Šēnhofa, S.; Šņepsts, G.; Elferts, D.; Liepa, L.; Jansons, Ā. Effect of Stem Snapping on Aspen Timber Assortment Recovery in Hemiboreal Forests. Forests 2021, 12, 28. https://doi.org/10.3390/f12010028
Čakša L, Šēnhofa S, Šņepsts G, Elferts D, Liepa L, Jansons Ā. Effect of Stem Snapping on Aspen Timber Assortment Recovery in Hemiboreal Forests. Forests. 2021; 12(1):28. https://doi.org/10.3390/f12010028
Chicago/Turabian StyleČakša, Linda, Silva Šēnhofa, Guntars Šņepsts, Didzis Elferts, Līga Liepa, and Āris Jansons. 2021. "Effect of Stem Snapping on Aspen Timber Assortment Recovery in Hemiboreal Forests" Forests 12, no. 1: 28. https://doi.org/10.3390/f12010028
APA StyleČakša, L., Šēnhofa, S., Šņepsts, G., Elferts, D., Liepa, L., & Jansons, Ā. (2021). Effect of Stem Snapping on Aspen Timber Assortment Recovery in Hemiboreal Forests. Forests, 12(1), 28. https://doi.org/10.3390/f12010028







