Examining the Neurophysiology of Attentional Habituation to Repeated Presentations of Food and Non-Food Visual Stimuli
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
2.1. Participants
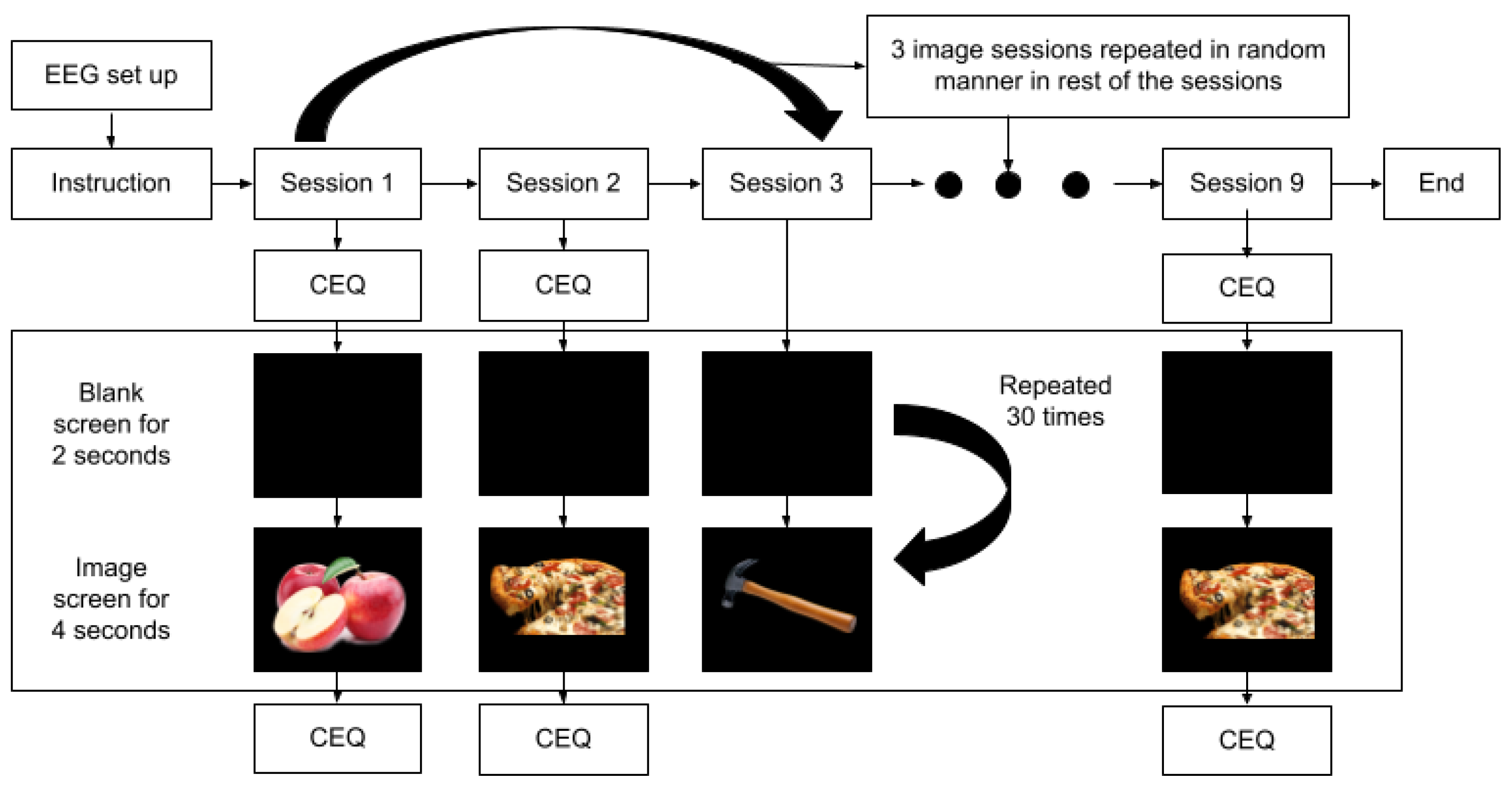
2.2. Experimental Design and Procedure
2.3. EEG Data Acquisition and Pre-Processing
2.4. Statistical Assessment
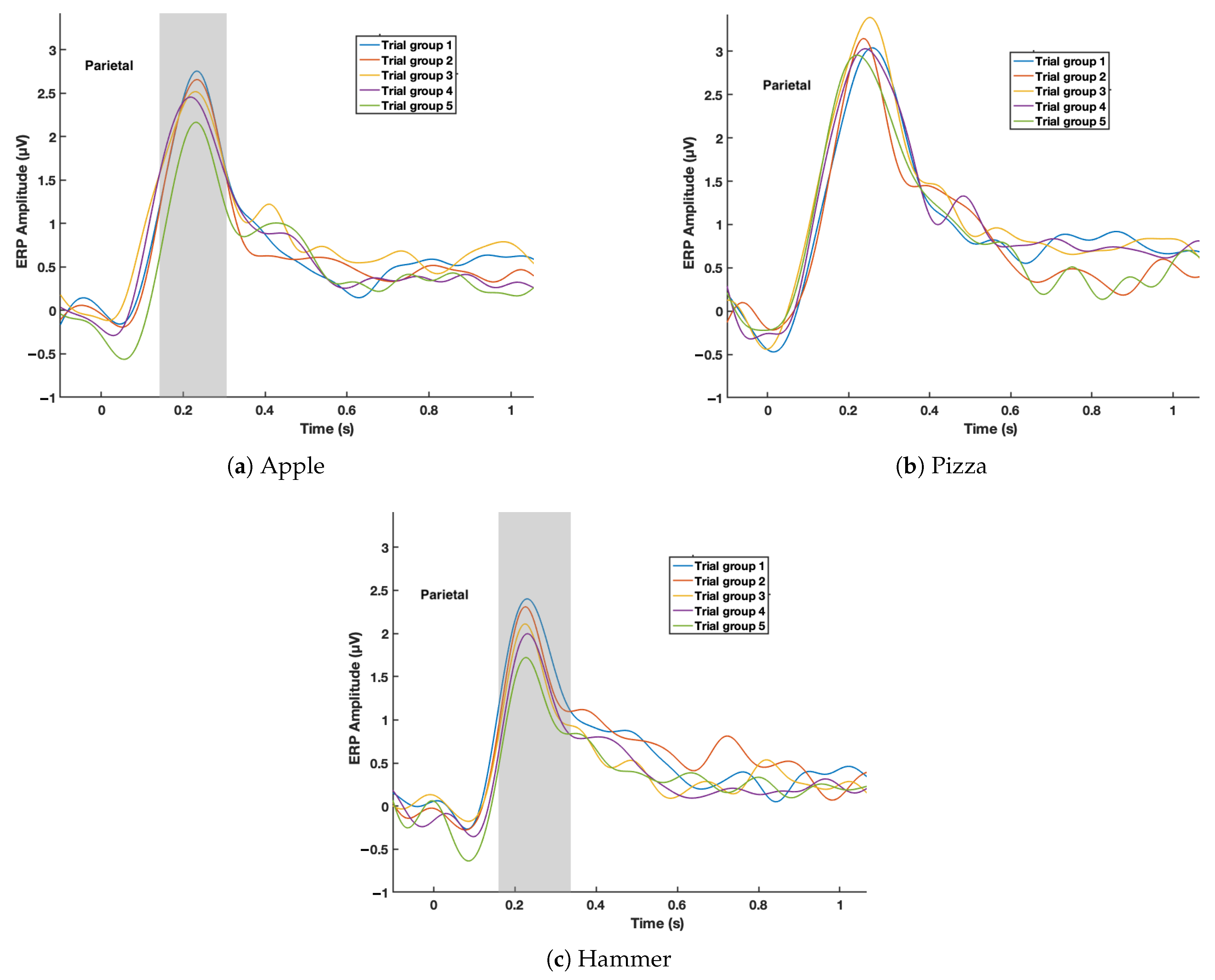
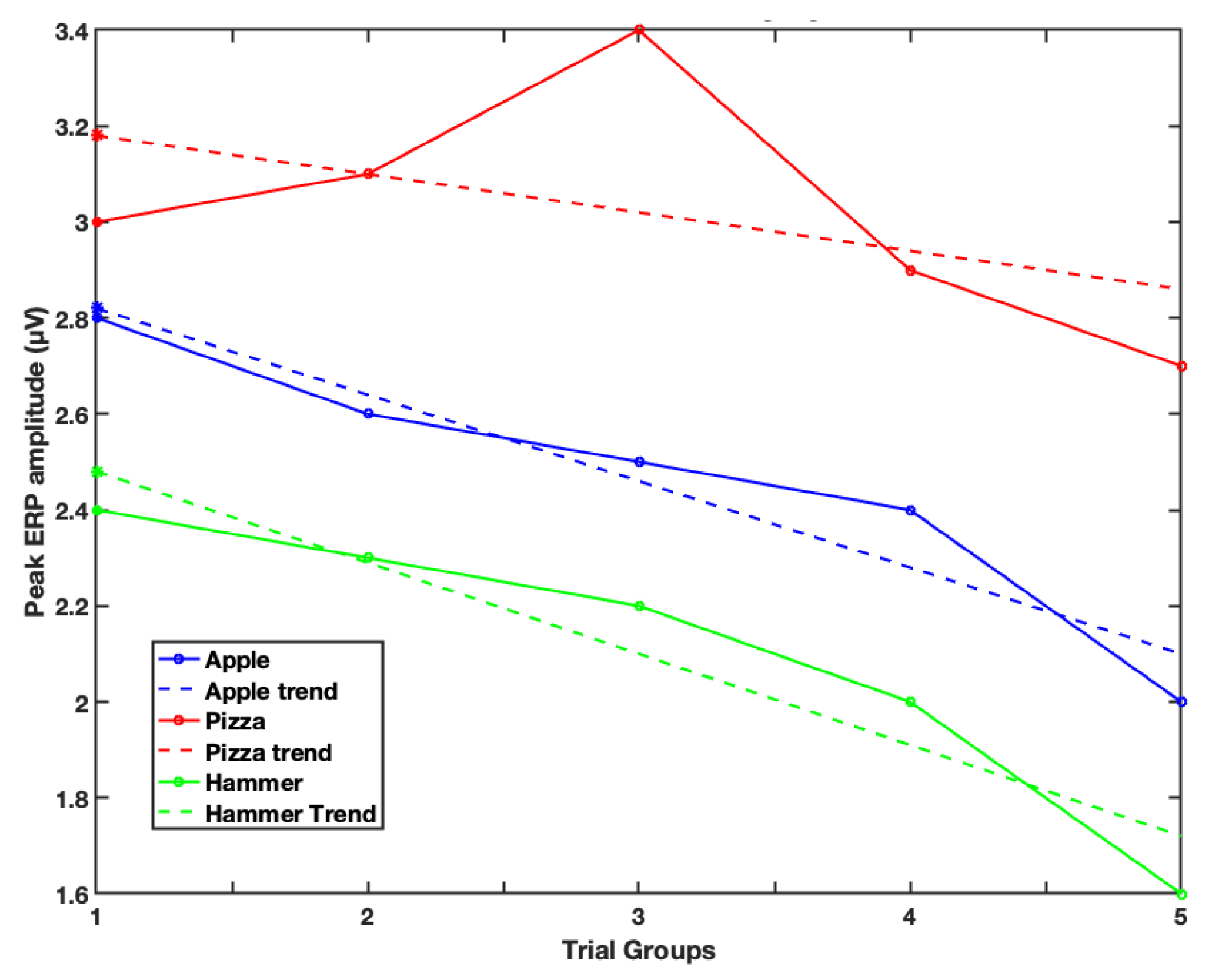
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| EEG | Electroencephalogram |
| ERP | Event-Related Potential |
| CEQ | Craving Experience Questionnaire |
| ISI | Inter-Stimulus Interval |
References
- Epstein, L.H.; Temple, J.L.; Roemmich, J.N.; Bouton, M.E. Habituation as a determinant of human food intake. Psychol. Rev. 2009, 116, 384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Epstein, L.H.; Paluch, R.A. Habituation of facial muscle responses to repeated food stimuli. Appetite 1997, 29, 213–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Temple, J.L.; Kent, K.M.; Giacomelli, A.M.; Paluch, R.A.; Roemmich, J.N.; Epstein, L.H. Habituation and recovery of salivation and motivated responding for food in children. Appetite 2006, 46, 280–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Temple, J.L.; Giacomelli, A.M.; Roemmich, J.N.; Epstein, L.H. Habituation and within-session changes in motivated responding for food in children. Appetite 2008, 50, 390–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Epstein, L.H.; Rodefer, J.S.; Wisniewski, L.; Caggiula, A.R. Habituation and dishabituation of human salivary response. Physiol. Behav. 1992, 51, 945–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Epstein, L.H.; Robinson, J.L.; Temple, J.L.; Roemmich, J.N.; Marusewski, A.; Nadbrzuch, R. Sensitization and habituation of motivated behavior in overweight and non-overweight children. Learn. Motiv. 2008, 39, 243–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Temple, J.L.; Giacomelli, A.M.; Roemmich, J.N.; Epstein, L.H. Overweight children habituate slower than non-overweight children to food. Physiol. Behav. 2007, 91, 250–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Epstein, L.H.; Robinson, J.L.; Temple, J.L.; Roemmich, J.N.; Marusewski, A.L.; Nadbrzuch, R.L. Variety influences habituation of motivated behavior for food and energy intake in children. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2009, 89, 746–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCrory, M.A.; Fuss, P.J.; McCallum, J.E.; Yao, M.; Vinken, A.G.; Hays, N.P.; Roberts, S.B. Dietary variety within food groups: Association with energy intake and body fatness in men and women. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1999, 69, 440–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asmaro, D.; Jaspers-Fayer, F.; Sramko, V.; Taake, I.; Carolan, P.; Liotti, M. Spatiotemporal dynamics of the hedonic processing of chocolate images in individuals with and without trait chocolate craving. Appetite 2012, 58, 790–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nijs, I.M.; Muris, P.; Euser, A.S.; Franken, I.H. Differences in attention to food and food intake between overweight/obese and normal-weight females under conditions of hunger and satiety. Appetite 2010, 54, 243–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolz, I.; Sauvaget, A.; Granero, R.; Mestre-Bach, G.; Baño, M.; Martín-Romera, V.; Veciana De Las Heras, M.; Jiménez-Murcia, S.; Jansen, A.; Roefs, A.; et al. Subjective craving and event-related brain response to olfactory and visual chocolate cues in binge-eating and healthy individuals. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 41736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwab, D.; Zorjan, S.; Schienle, A. Face the food: Food plating with facial patterns influences appetite and event-related brain potentials. Motiv. Emot. 2021, 45, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, P.; Wang, J.; Ding, X.; Li, C.; Guo, F.; Ding, X. How do extrinsic cues influence consumers’ online hotel booking decisions? An event-related potential experiment. Front. Psychol. 2022, 13, 990640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolan, R.J.; Fink, G.; Rolls, E.; Booth, M.; Holmes, A.; Frackowiak, R.; Friston, K. How the brain learns to see objects and faces in an impoverished context. Nature 1997, 389, 596–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grill-Spector, K.; Henson, R.; Martin, A. Repetition and the brain: Neural models of stimulus-specific effects. Trends Cogn. Sci. 2006, 10, 14–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillaume, C.; Guillery-Girard, B.; Chaby, L.; Lebreton, K.; Hugueville, L.; Eustache, F.; Fiori, N. The time course of repetition effects for familiar faces and objects: An ERP study. Brain Res. 2009, 1248, 149–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tacikowski, P.; Jednoróg, K.; Marchewka, A.; Nowicka, A. How multiple repetitions influence the processing of self-, famous and unknown names and faces: An ERP study. Int. J. Psychophysiol. 2011, 79, 219–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duraisingam, A.; Palaniappan, R.; Soria, D. Attentional bias towards high and low caloric food on repeated visual food stimuli: An ERP study. In Proceedings of the 2021 43rd Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine & Biology Society (EMBC), Virtual, 1–5 November 2021; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2021; pp. 740–743. [Google Scholar]
- Leung, S.O. A comparison of psychometric properties and normality in 4-, 5-, 6-, and 11-point Likert scales. J. Soc. Serv. Res. 2011, 37, 412–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, Y.M. Italian Cuisine Is World’s Most Popular. 2019. Available online: https://yougov.co.uk/topics/consumer/articles-reports/2019/03/12/italian-cuisine-worlds-most-popular (accessed on 4 November 2022).
- Blechert, J.; Meule, A.; Busch, N.A.; Ohla, K. Food-pics: An image database for experimental research on eating and appetite. Front. Psychol. 2014, 5, 617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- May, J.; Andrade, J.; Kavanagh, D.J.; Feeney, G.F.; Gullo, M.J.; Statham, D.J.; Skorka-Brown, J.; Connolly, J.M.; Cassimatis, M.; Young, R.M.; et al. The Craving Experience Questionnaire: A brief, theory-based measure of consummatory desire and craving. Addiction 2014, 109, 728–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geisler, M.W.; Polich, J. P300, Food Consumption, and Memory Performance. Psychophysiology 1992, 29, 76–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wardle, J. Eating style: A validation study of the Dutch Eating Behaviour Questionnaire in normal subjects and women with eating disorders. J. Psychosom. Res. 1987, 31, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toepel, U.; Knebel, J.F.; Hudry, J.; le Coutre, J.; Murray, M.M. The Brain Tracks the Energetic Value in Food Images. NeuroImage 2009, 44, 967–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zorjan, S.; Gremsl, A.; Schienle, A. Changing the Visualization of Food to Reduce Food Cue Reactivity: An Event-Related Potential Study. Biol. Psychol. 2021, 164, 108173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maris, E.; Oostenveld, R. Nonparametric statistical testing of EEG- and MEG-data. J. Neurosci. Methods 2007, 164, 177–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, G.Y.; Luck, S.J. Dissociable decoding of spatial attention and working memory from EEG oscillations and sustained potentials. J. Neurosci. 2018, 38, 409–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oostenveld, R.; Fries, P.; Maris, E.; Schoffelen, J.M. FieldTrip: Open source software for advanced analysis of MEG, EEG, and invasive electrophysiological data. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2011, 2011, 156869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Larios, J.; Faber, P.; Achermann, P.; Tei, S.; Alaerts, K. From thoughtless awareness to effortful cognition: Alpha-theta cross-frequency dynamics in experienced meditators during meditation, rest and arithmetic. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 5419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quiroga-Martinez, D.R.; Hansen, N.C.; Højlund, A.; Pearce, M.; Brattico, E.; Vuust, P. Decomposing neural responses to melodic surprise in musicians and non-musicians: Evidence for a hierarchy of predictions in the auditory system. NeuroImage 2020, 215, 116816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lietti, C.V.; Murray, M.M.; Hudry, J.; le Coutre, J.; Toepel, U. The role of energetic value in dynamic brain response adaptation during repeated food image viewing. Appetite 2012, 58, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duraisingam, A.; Soria, D.; Palaniappan, R. The Habituation-Dishabituation ERP Responses to Repeated Visual Food Cues. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE-EMBS Conference on Biomedical Engineering and Sciences (IECBES), Penang, Malaysia, 11–13 December 2024; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2024; pp. 413–418. [Google Scholar]
- Duraisingam, A.; Soria, D.; Palaniappan, R. Unraveling Neurophysiological Attentional Habituation Dynamics of Food and Non-Food Paradigms: ERP Correlates with BMI in Response to Repetitive Visual Stimuli. In Proceedings of the 2024 5th International Conference on Data Intelligence and Cognitive Informatics (ICDICI), Tirunelveli, India, 18–20 November 2024; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2024; pp. 318–325. [Google Scholar]
- Berthoud, H.R. Metabolic and hedonic drives in the neural control of appetite: Who is the boss? Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2011, 21, 888–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lowe, M.R.; Butryn, M.L. Hedonic hunger: A new dimension of appetite? Physiol. Behav. 2007, 91, 432–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carnell, S.; Wardle, J. Appetite and adiposity in children: Evidence for a behavioral susceptibility theory of obesity1. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2008, 88, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

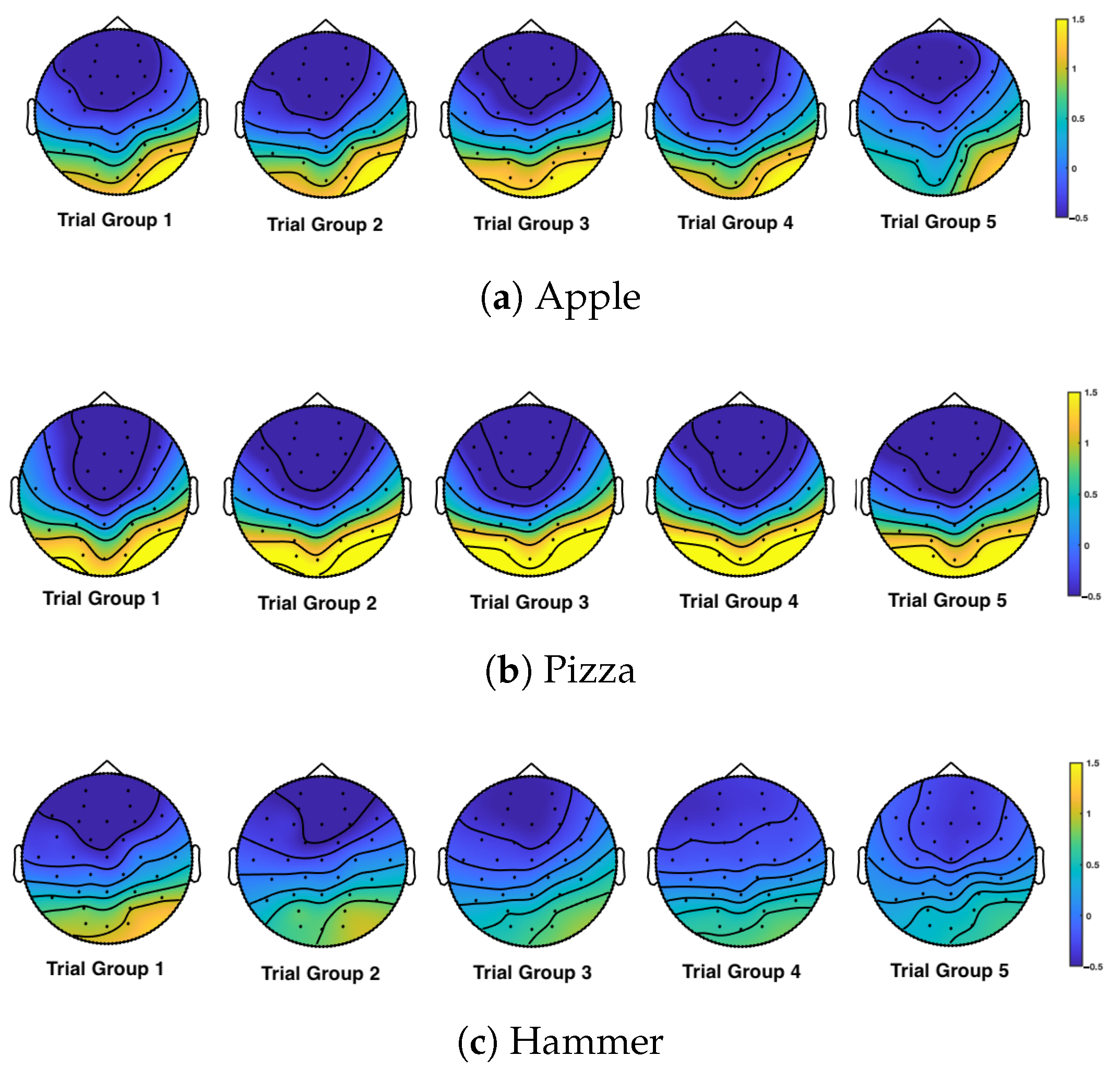
| ROI | Apple | Pizza | Hammer |
|---|---|---|---|
| Frontal | 0.241 | 0.382 | 0.196 |
| Central | 0.198 | 0.457 | 0.273 |
| Temporal | 0.324 | 0.511 | 0.209 |
| Occipital | 0.275 | 0.398 | 0.287 |
| Parietal | 0.016 | 0.213 | 0.011 |
| Image | Slope | Intercept |
|---|---|---|
| Apple | −0.18 | 3.01 |
| Pizza | −0.06 | 3.22 |
| Hammer | −0.19 | 2.67 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Duraisingam, A.; Soria, D.; Palaniappan, R. Examining the Neurophysiology of Attentional Habituation to Repeated Presentations of Food and Non-Food Visual Stimuli. Algorithms 2025, 18, 525. https://doi.org/10.3390/a18080525
Duraisingam A, Soria D, Palaniappan R. Examining the Neurophysiology of Attentional Habituation to Repeated Presentations of Food and Non-Food Visual Stimuli. Algorithms. 2025; 18(8):525. https://doi.org/10.3390/a18080525
Chicago/Turabian StyleDuraisingam, Aruna, Daniele Soria, and Ramaswamy Palaniappan. 2025. "Examining the Neurophysiology of Attentional Habituation to Repeated Presentations of Food and Non-Food Visual Stimuli" Algorithms 18, no. 8: 525. https://doi.org/10.3390/a18080525
APA StyleDuraisingam, A., Soria, D., & Palaniappan, R. (2025). Examining the Neurophysiology of Attentional Habituation to Repeated Presentations of Food and Non-Food Visual Stimuli. Algorithms, 18(8), 525. https://doi.org/10.3390/a18080525







