Renewable energy generation is a critical component of energy strategies, supporting economic growth while promoting clean and low-carbon power sources [
1]. Against this backdrop, the integration capacity of distributed generator (DG) continues to increase [
2,
3]. High-penetration DG integration reduces power losses and provides voltage support during faults [
4]. However, as DG capacity grows, traditional current protection faces challenges such as misoperation, failure to operate, loss of selectivity, and reduced sensitivity, failing to meet setting principles. Adaptive three-stage current protection, widely used in 10 kV distribution networks due to its simplicity, low cost, and reliability, requires further improvement under DG integration. Scholars worldwide have conducted extensive research: Reference [
5] conducted an evaluation of fault characteristic differences in differential protection for distribution networks containing distributed generators. It revealed that traditional current differential protection may lead to reduced transition resistance when applied to active distribution networks. In response to this conclusion, an adaptive current differential protection method was proposed by adjusting the phase angle constraints based on the proportional relationship of power frequency full current components at both ends of the line. Reference [
6] addressed the fault current differences caused by boundary condition variations induced by Inverter-Interfaced Distributed Generator (IIDG) integration. By jointly calculating fault currents in distribution networks without IIDG and bus currents connected to IIDG, this study optimized setting value calculation time and improved computational accuracy. Reference [
7] presented a composite sequence network current protection scheme for photovoltaic-integrated distribution networks, effectively expanding local protection coverage. However, its exclusive consideration of single DG integration makes it unsuitable for current multi-DG integration trends. Reference [
8] proposed a DG access capacity calculation method considering distribution network current protection constraints, but imposed limitations on maximum DG integration capacity. Reference [
9] introduced comprehensive protection improvement methods for multi-DG distribution networks, resolving the low DG permeability issue in traditional current protection. Nevertheless, this setting method fails to adapt to DG capacity variations. Reference [
10] incorporated DG transient stability duration as temporal constraints in protection coordination, proposing a novel optimized coordination scheme for inverse-time overcurrent protection characteristics considering DG transient stability. Reference [
11] implemented power flow calculation and fault analysis using system-wide synchronous state signals collected by the main station, then transmitted calculated current protection settings to individual protection devices via communication systems. This formed the basis for an adaptive current protection coordination scheme utilizing main station communication. Reference [
12] addressed coordination challenges between upper/lower-level inverse-time overcurrent protections after DG integration by segmentally linearizing traditional inverse-time operating characteristics, thereby reducing protection operating time while enhancing selectivity. Reference [
13] established multiple setting groups based on short-circuit types and DG capacity, optimizing operating time according to grid-connection status through real-time switching to improve protection sensitivity. Reference [
14] improved overcurrent protection setting methods using the Grey Wolf Algorithm, optimizing premature convergence and low precision issues. Through constraints on protection operating time and setting values, inverse-time overcurrent protection was re-coordinated to meet protection requirements. Some teams investigated potential maloperations of distance relays in wind farm grid-connected substations under different operational conditions, proposing an adaptive protection scheme that calculates quadrilateral distance relay settings based on wind power penetration rates [
15]. Reference [
16] improves the traditional Multi-Objective Artificial Hummingbird Algorithm (MOAHA) by addressing its limitations in initial population diversity, convergence stability, and local optimization capabilities. This enhanced algorithm is applicable to multi-objective optimization in complex engineering fields; however, its effectiveness in scenarios involving new energy grid integration requires further investigation. Reference [
17] proposes an improved algorithm, SACLMOGOA, to tackle issues such as poor initial population diversity and ergodicity, slow convergence speed, and susceptibility to local optima in the traditional Multi-Objective Grasshopper Optimization Algorithm (MOGOA). The algorithm demonstrated certain efficacy in the application of the hybrid energy storage system (HESS) for Changsha Metro Line 1. Nevertheless, the case study is limited to the specific HESS configuration of Changsha Metro Line 1, without considering topological variations in different urban rail transit networks, collaborative optimization of multiple energy storage types, or complex power grid scenarios with renewable energy integration. Reference [
18] proposes to transform the multi-objective optimization problem into a single-objective one for optimization. By using the weighted sum method to balance the priorities of communication and sensing, it is found that when the target angle is close to the angle of the communication user, the sensing and communication channels share information, and the pilot design can optimize the performance of both simultaneously. This method solves multi-objective problems with a single-objective mindset, which effectively reduces the signal conduction error in communication. However, the sensing model of this method assumes that the angles of the target and clutter are known, and does not involve dynamic angle estimation of multiple targets, thus limiting its applicability in mobile target scenarios. Therefore, its universality warrants further validation. After the integration of new energy sources, power fluctuations will change the direction and magnitude of fault currents, which may cause the originally coordinated upper and lower-level protection devices to lose coordination (e.g., the upper-level protection operates before the lower-level one), thus undermining selectivity and expanding the fault impact range. Relay protection must meet such constraints as sensitivity, selectivity, and false operation rate. Power fluctuations of new energy sources may cause these indicators to deviate from the standard range. By dynamically adjusting the protection settings, it can be ensured that the regulatory requirements are still met under different fluctuation scenarios, avoiding the degradation of protection performance caused by parameter mismatch.
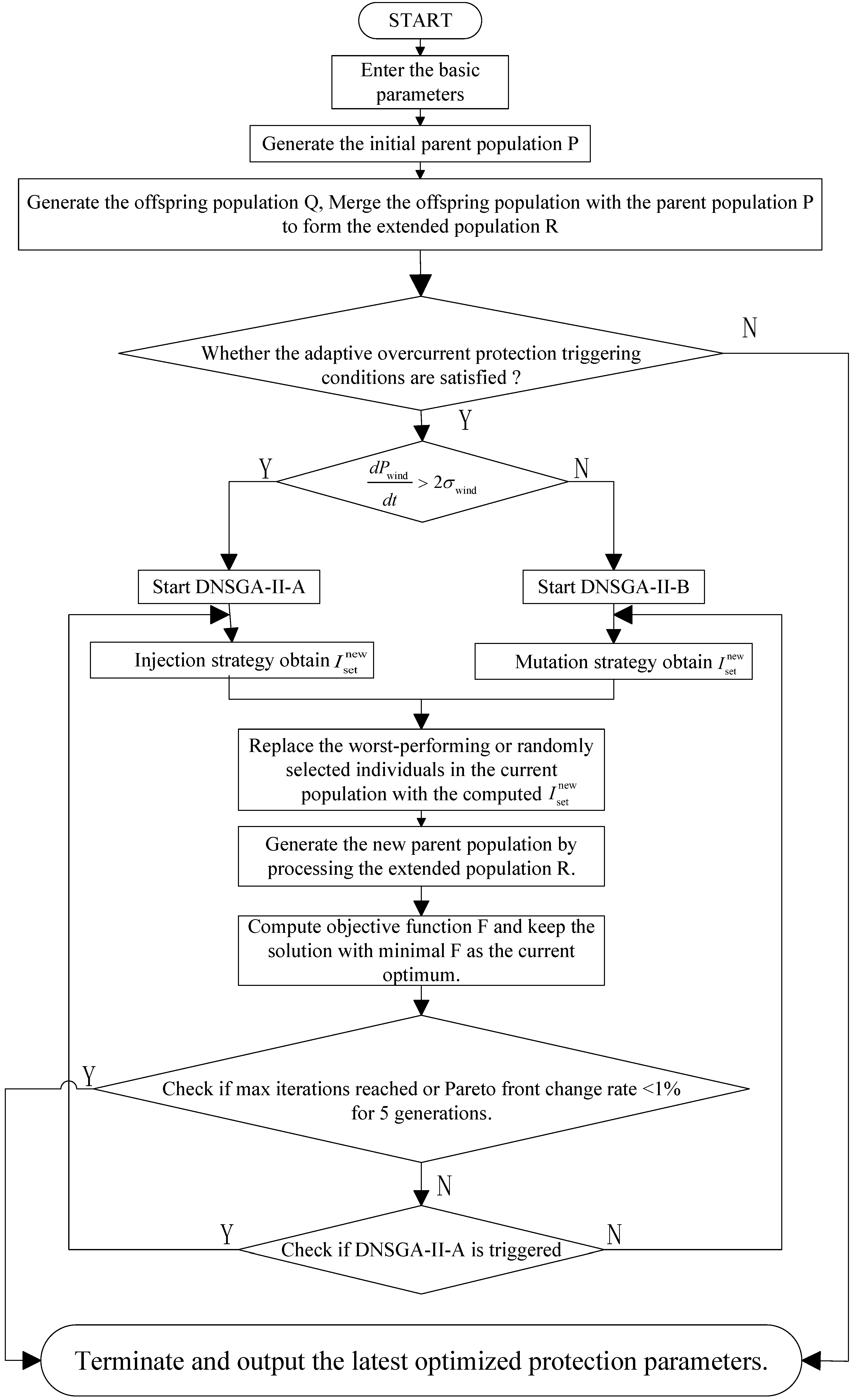
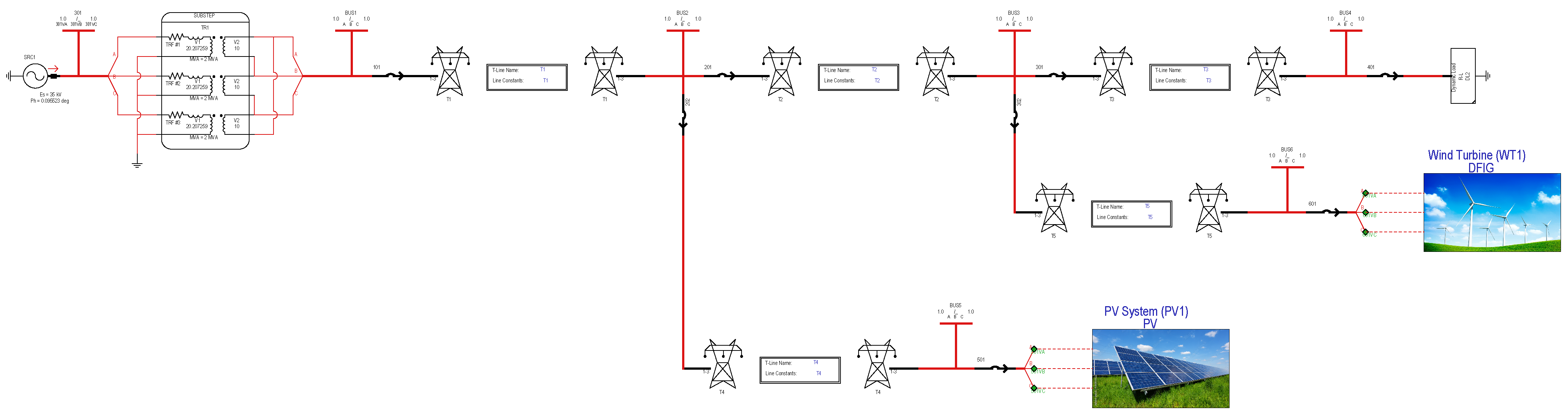
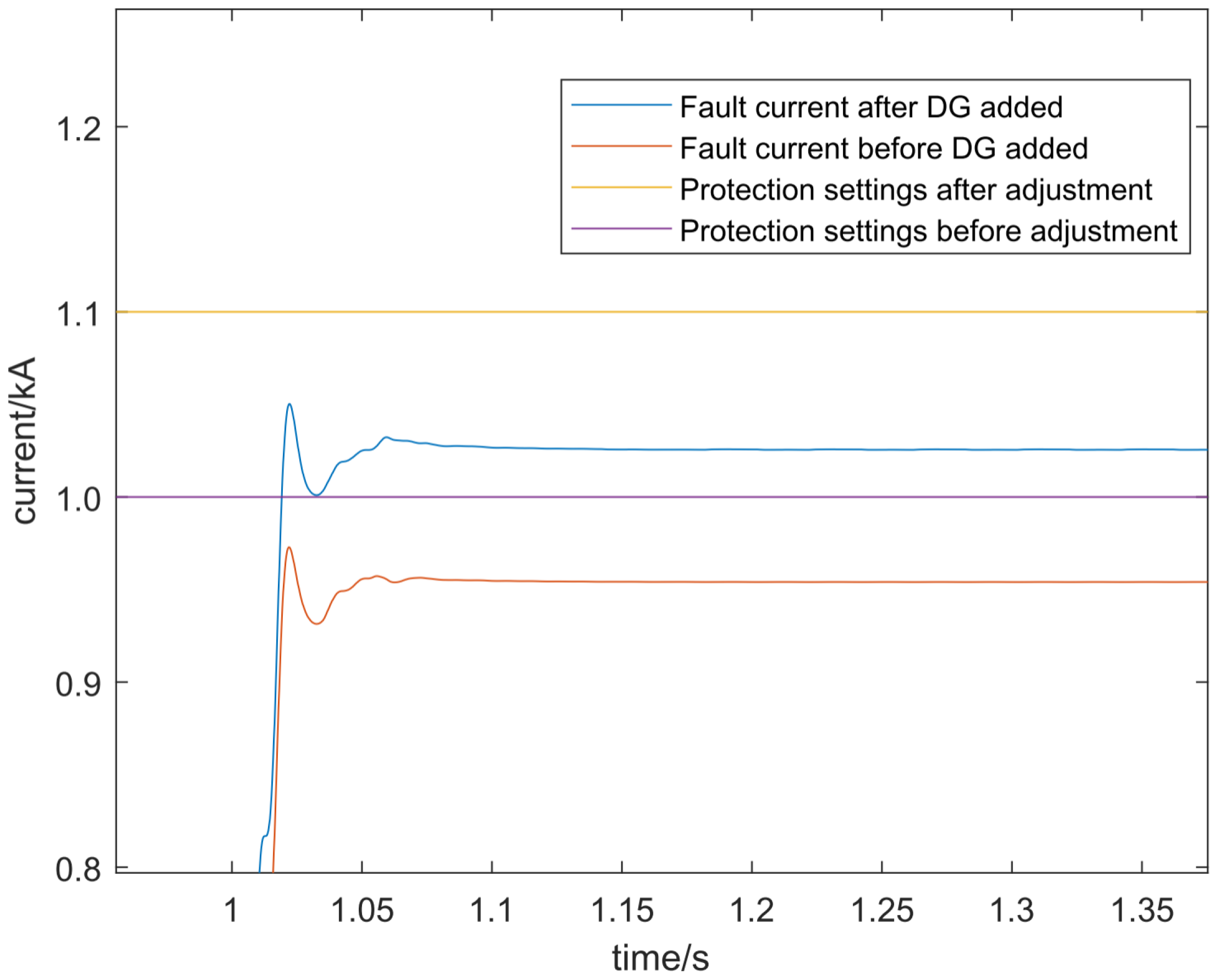
To address the aforementioned issues, this paper proposes a dynamic multi-objective optimization and adaptive overcurrent protection method for distributed networks with renewable energy integration based on an improved NSGA-II (Non-dominated Sorting Genetic Algorithm II) algorithm. This method dynamically detects renewable energy power fluctuations and generates adaptive solutions. Through deep integration of a dynamic triggering mechanism and multi-objective optimization algorithms, it achieves adaptive real-time adjustment of protection settings and online optimization of protection parameters, thereby significantly enhancing the reliability and disturbance resistance capability of the distribution network.