Abstract
This work aims to constitute a framework dataflow based on the prediction, optimization, and characterization of optimal solutions. To this purpose, a metaheuristic optimization method is used to obtain the optimal design solutions for discrete plane frame structures considering as objective function the minimization of their maximum resultant displacement, subjected to side and behavioral constraints. The design variables that lead to the optimal solutions are constituted into datasets which are subsequently submitted to a clustering analysis. The results obtained provide pertinent insights about the optimal solutions clusters’ ranges, giving effective support to a specific solution selection.
1. Introduction
Optimization methodologies have revolutionized engineering design by replacing manual iterative processes with more efficient algorithmic procedures, which enable accelerating the conceptual improvement process through the automated search for optimal design solutions. To achieve this, requirements and restrictions should first be translated into mathematical terms, in a methodological approach, as precisely as possible, so that the optimization method converges on the best solution [1].
The application of metaheuristics can offer significant advantages in structural optimization and has been extensively considered by a number of researchers using different techniques [2]. For example, in the optimization of steel structures, the main objectives have involved the reduction in weight and costs of large steel frame or building structures [3,4], optimizing the size, shape, and type of steel structures, under Eurocode 3 [5], and on reducing the steel consumption in household structures [6] in which cross-section and length characteristics of H-section steel beams and square tubular columns were optimized. In composite materials, their optimization importance was clearly highlighted in [7], in which the influence of the parameters that characterize the material distribution on their static behavior and natural frequency was demonstrated. This brief overview underscores the value of optimization techniques in project development. While optimization processes require an appropriate procedure dataflow, the benefits that arise with superior solutions usually compensate the required development and/or implementation effort.
Metaheuristic algorithms, such as the Red Fox Optimization (RFO), have been recognized for their ability to address complex, nonlinear problems in structural optimization. Introduced in 2021 [8], the RFO algorithm has been successfully applied across various fields, including computer science, materials science, and engineering. In this latter case, it has been found in application fields such as chemical systems, fuel cells, and functionally graded structures. In the computer science area, a method for detecting malware on Android smartphones based on an algorithm adapted from the RFO was presented by [9], while in [10], RFO was used to optimize hyperparameters in deep learning models. In structural engineering, as far as results from the literature survey, this method was used to optimize the parameters of structures made of functionally graded material [11]. Other engineering areas were covered in [12] where the technique was used to optimize the equilibrium phase and stability of chemical systems, and in [13] to obtain the optimum parameters for solid oxide fuel cells.
In addition, various models have been proposed that combine the RFO algorithm, especially due to its global optimization capabilities, with other metaheuristics that can complement it, depending on the authors’ objectives. For example, Vaiyapuri et al. [14] proposed a model that combines the RFO algorithm with deep-learning-enabled microarray gene expression classification model, which allowed to identify various classes for high-dimensional and small-scale microarray data. In Dixit and Qureshi [15], the Red Fox Optimization and Cluster-based Routing algorithm were combined to facilitate secure and energy-efficient data transmission among sensor nodes. The authors concluded that the proposed protocol performed better than the current routing techniques concerning security robustness, energy efficiency, and network lifetime. In another context, an intelligent waste management system through which waste can be sorted was proposed in [16] through an automated model that combines RFO with a dense network model.
Metaheuristics have also been increasingly used in the broad structural engineering area, with applications that involve, for instance, reducing the weight and cost of steel structures and/or optimizing cross-sectional dimensions and material properties. In a recent overview [17] that illustrates this trend, a Genetic Algorithm-based optimization process was proposed to enhance the design of steel exoskeletons for seismic retrofitting. To achieve this, the study focused on optimizing the spatial arrangement and components’ sizing to minimize the global weight and cost while ensuring structural integrity. The authors achieved significant improvements in retrofit efficiency across various case studies. Goodarzimehr et al. [18] introduced the Improved Marine Predators Algorithm for optimizing the size and shape of truss structures under natural frequency constraints, aiming to minimize weight while preventing resonance and reducing vibrations. The algorithm demonstrated good performance in comparison to a set of other metaheuristics across various truss structures. Cucuzza et al. [19] used a real-coded Genetic Algorithm integrated with the Bin Packing Problem to reduce waste by up to 40% across various 2D and 3D steel structures. A paradigm shift, from minimum weight targeting towards minimizing material waste and promoting standardization in steel structures, was proposed. Zhou et al. [20] introduced the so-called Improved Sine Cosine Algorithm for optimizing the size, shape, and topology of truss structures by incorporating a nonlinear conversion parameter, Lévy flight for global search, an elite guidance strategy for local search, and a greedy selection mechanism. The authors concluded that the technique performed well for truss structure optimization. In a work joining metaheuristics and deep neural networks, [21] considered the African Vulture Optimization Algorithm with Deep Neural Networks to enhance damage detection in large-scale bridges, leveraging the first algorithm’s ability to autonomously adjust parameters and optimize the neural network weights and biases. The approach, validated using Finite Element Model data and real-world measurements, showed improved accuracy and computational efficiency in identifying structural damage. Other researchers considered the use of Differential Evolution (DE) to obtain improved steel frames, as for example, Babaei and Mollayi [22] and Vu et al. [23]. Babaei and Mollayi [22] proposed a constrained differential evolution (iCDE) algorithm for the optimization of steel frames with discrete design variables, whereas Vu et al. [23] proposed a framework for sizing optimization of steel structures using a combination of an improved Differential Evolution approach (2EpDE), Multi-Comparison Technique (MCT), and Promising Individual Method (PIM). Although not for frame structures, Moosavian et al. [24] conducted a comparison study among some metaheuristic algorithms, for example, the DE and the covariance matrix adaptation evolution strategy (CMA-ES) for size optimization of truss structures under natural frequency constraints. These authors concluded that the latter presented the best performance and the best optimal solutions for the design of the truss structures studied.
Optimization studies considering more than one objective function have also been considered. For example, the minimization of mass and nodal displacement of truss structures was addressed by [25] through the Two Archive-boosted Multi-Objective Hippopotamus Optimization Algorithm. The solutions were compared with results obtained via other multi-objective algorithms showing good performance. Near-optimal solutions alongside Pareto-optimal solutions in the standardization process of a multi-objective structural design were obtained by [26] highlighting how standard section selection may influence objective function values. The authors combined a modified Particle Swarm Optimization method and a computationally efficient standardization algorithm, showing that considering near-optimal solutions can reveal superior final designs. Other multiobjective optimization published works in this context are due to Barraza et al. [27], who presented a comparative study focused on structural steel buildings using the Non-dominated Sorting Genetic Algorithm (NSGA-II) and Particle Swarm Optimization (PSO). The authors concluded that although both approaches allowed obtaining an improved structural performance for the buildings, the PSO provided better solutions in general. Notably, the review on multi-objective optimization based on surrogate models for sustainable building design was recently presented by Cruz et al. [28], who besides achieving the state of the art in this domain, pointed out possible development pathways.
From the literature survey performed, it was possible to conclude that the number of published works considering clustering analysis in the structural analysis and optimization domains is scarce. This is evidenced by the survey presented by [29]. Only a very few works were found, for example, the one due to [30] which proposed a cluster-based analysis method for the prediction of nonlinear properties of heterogeneous material. In another context, [31] have used the K-means method to solve general nonlinear multiscale problems without using surrogate models. In both works, the dimensionality reduction of the problem was a major objective.
The present work proposes an integrated framework that enables us to characterize sets of optimal solutions of steel-plane frame structures, using for that purpose the finite element method, the Red Fox Optimization technique, and the K-means method. This specific optimization technique is justified by the good performance it showed as demonstrated by Polap and Wozniak [8] who proposed and tested it with different benchmark and engineering applications, but also because this technique showed a good performance in frame-type structures made of functionally graded materials [11].
Bringing together these techniques with complementary objectives constitutes the major innovative character of the present work, and it is overall important to highlight that besides the achievement of optimized design configurations, their grouping by criteria affinity will enable a more refined and informed selection of a specific optimal configuration.
Following this introductory section, the remainder part of this work is organized as follows: Section 2 describes the methodology considered in the present study, which includes a brief reference to the finite element method, the optimization and the clustering techniques’ descriptions; Section 3 presents and discusses the verification studies and the optimization case studies. In these latter cases, the optimal design variables’ configurations are subsequently the object of an exploratory analysis to determine how many clusters can be identified in the optimal solutions dataset and how those solutions per cluster share specific characteristics. This selection and assignment are performed through the K-means method. Finally, in the last section, some final conclusions are drawn based on the results achieved.
2. Materials and Methods
This study is structured into three main phases. The first part is related to the finite element method (FEM), which will predict the mechanical responses of structures [7,32]. In an intermediate phase, the Red Fox Optimization method (RFO) and the integration of the FEM into it are coded, and the optimal solutions are obtained, and finally, a third stage is devoted to the characterization of the optimal solutions, through the K-means clustering method.
2.1. Finite Element Analyses
The first-order shear deformation theory is used to describe the displacement field, which if assuming a beam deformation in the xz plane, is written as
The parameters correspond, respectively, to the longitudinal (direction ) and transverse (direction ) displacements of the beam’s centerline in the plane, and to the rotation of the beam’s center plane in the direction perpendicular to the plane. Considering the kinematical relations from the Elasticity Theory for small deformations, the constitutive relations and Hamilton’s principle [33,34], the equilibrium equations at the element level are obtained:
By simplifying this equation for linear static or free vibration analysis, it yields
where , and are respectively the element stiffness and mass matrices and the element generalized forces; and stand for the k-th natural frequency and the element generalized degrees of freedom vector.
As the fundamental aim of the present work is the implementation of a dataflow framework integrating the prediction–optimization–optimal solutions analysis for a structure mechanical response, one has selected for that illustrative purpose discrete plane structures submitted to in-plane loads. Under these conditions, the equilibrium equations were implemented using quadratic beam elements (Figure 1) with three degrees of freedom per node—the axial () and transverse () displacements and the rotation —all related to the midplane surface of the beam-bar element.
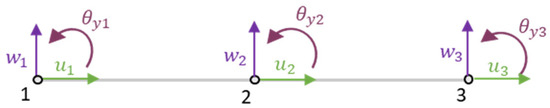
Figure 1.
Quadratic beam element and its degrees of freedom.
The numbering used in Figure 1 is related to the nodes numbering (1 to 3). This numbering when considered in subscript, identify the degrees of freedom associated to each node. For the studies performed, quadratic element allows in general improved accuracy with fewer elements and better convergence rates, when compared to lower order high density meshes. According to the FEM procedure [35], following the calculation of the element matrices and vectors, they are assembled to model the whole discretized domain, being the specified analysis performed after the boundary conditions imposition.
2.2. Red Fox Optimization
The Red Fox Optimization (RFO) algorithm is used to optimize a selected objective function, combining global and local search phases to explore the solution design space. To briefly illustrate how this algorithm works, a schematic dataflow of the key aspects in a single optimization process is presented in Algorithm 1.
| Algorithm 1. Red fox algorithm. Schematic representation |
| Input: Number individuals, Max iterations Output: best solution, associated design variables Initialize, randomly the population For each iteration do For each individual do Compute objective function via FEM maximum value of objective function # Global search phase # Local search phase Initialize, random parameters: If , then End If # Dynamic control of population Initialize random parameter: If , then Initialize new individuals Else End If End For End For |
The schematic dataflow comprises the population initialization, where each individual (red fox) is randomly generated within the design space. Loops are then initiated until convergence criteria are met. Within these loops, the fitness assessment of each individual is carried out considering the selected objective function. Then, the global search (exploration) starts, performing wider searches. The local, detailed, search (exploitation) is then carried out in promising regions, using smaller movements. The population control is implemented in a probabilistic basis, considering a random parameter that will define if the worst individuals will be removed. The global and local searches allow us to adapt the technique approach to the population evolution, avoiding the process to get stuck in a local optimum, and refining near-optimal solutions. Additionally, a continuous improvement of the solutions is achieved by retaining high-quality solutions while ensuring population diversity. Further details about this algorithm can be found in [8]. Unless otherwise stated, in this work, a population of 30 individuals progressing during 100 iterations was used for each optimization process, in this way balancing computational cost and solution accuracy, while observing Central Limit Theorem ([36,37]).
2.3. Optimal Configurations Analysis Using Clustering
The achieved optimal design variables’ configurations are subsequently analyzed to identify if it is possible to establish groups of optimal configurations with similar types of characteristics and mechanical responses and how they will be constituted. To this purpose, an unsupervised machine learning method, the K-means method, is used [38,39]. K-means partitions a dataset into a number of non-overlapping clusters, assigning each data point to a certain cluster. In the present study, we have used the Silhouette method which checks the consistency of clusters’ fit. The procedure dataflow of this method is schematically represented in Algorithm 2, where is the Euclidean distance between two points and and stand for a feature mean value and variance.
| Algorithm 2. Silhouette method. Schematic representation |
| Input: Optimal solutions dataset Output: Silhouette scores Center and Scale Design Variables to and For each number of clusters For each point in cluster # Compute Intra-cluster distance # Compute Inter-cluster distance # Compute point Silhouette score Compute average Silhouette score within cluster () Compute global average Silhouette score End For End For |
The Silhouette score, which varies between −1 and +1, allows us to verify the points’ cohesion within their cluster and how distinctly separated the clusters are from each other. The robustness of the clustering structure increases as the score approximates +1. The K-means method is schematically represented in Algorithm 3.
| Algorithm 3. K-means method. Schematic representation |
| Input: Optimal solutions dataset Output Clusters, Centroids Center and Scale Design Variables to and Select Clusters and Initialize their Centroids While do For each point do Compute Euclidean Distance from Point to Clusters’ Centroids Assign Point i to Cluster with Nearest Centroid End do For each cluster do # Update Centroids # Compute the Euclidean Norm of the Centroids Shifts End For # Check Convergence Based on Centroids Shifts End While |
The initial calculation of the centroids was performed using K-means++ initialization to have better initial centroids and subsequent convergence. In the present work, the datasets for each case study are matrices constituted by a number of lines equal to the number of runs (10) and with a number of features (columns) corresponding to the number of design variables (b1, b2, b3). Each line contains the values each design variable assumes for the best solution found in each optimization run.
3. Results
3.1. Verification Studies
The model implemented was firstly verified through static and dynamic analyses of isotropic beams. The results showed an excellent agreement with reference solutions, confirming the accuracy of the model.
3.1.1. Static Analysis of an Isotropic Beam
The first verification case consists of studying a cantilever beam [40], made of an isotropic material with a modulus of elasticity of 200 GPa, with a length of 3 m, and a cross-section with a second moment of area . In the present study, the cross-section of the beam was considered to be square, with the second moment of the area referenced by [40]. The beam is subjected to a point load of 60 kN at the free end and a uniformly distributed load of 24 kN/m over its entire length. The beam and the actuation direction of these loads are schematically shown in Figure 2.
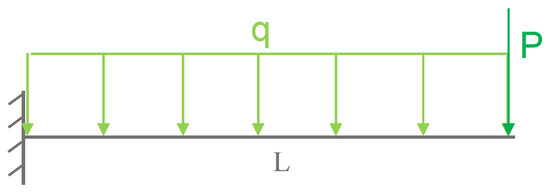
Figure 2.
Cantilever beam with transverse uniformly distributed and tip loads.
Reddy [40] presents the exact value and the one obtained by the finite element method using two elements, for the relation M/EI, where M stands for the bending moment and EI the bending stiffness. This corresponds for the moment, respectively, the values of 288,260 N.m and 283,620 N.m. Table 1 presents for a set of discretizations, the moments, and the relative deviations, in comparison to the values presented by [40].

Table 1.
Bending moment at the beam clamped support.
The discretizations considered were aimed to approximate the bending moment exact value, although for the lower discretization, only two elements, the relative deviation was already very small. These deviations were calculated according to the expression
considering as reference the exact solution [38].
Table 2 shows the transverse displacement and rotation results for the beam along its length, obtained using the finite element method and the reference solution, derived from the expressions defined by the direct integration method. In this case, as it is a beam with a high length-to-thickness ratio, the results from the present model are very close to both the reference solutions [40], based on the Euler–Bernoulli theory, using the exact solution obtained from direct integration of the equilibrium differential equation that rules the problem and the finite element implementation.

Table 2.
Transverse displacement () and rotation ( in the clamped beam.
3.1.2. Free Vibration Analysis of an Isotropic Beam
The second verification case consists of analyzing the free vibration of a cantilever beam made of isotropic material, with a unit length, rectangular cross-section of height h and width b, modulus of elasticity E, density ρ, 2nd moment of area I, Poisson’s ratio ν = 0.25, with EI = 1, ρI = 1, and h taking values such that L/h = 10 and L/h = 100. The results to be compared will be transformed into dimensionless frequency values using the expression
Thus, studies were carried out for two, four, and eight quadratic elements, in order to compare the present predictions with the reference obtained by the Timoshenko (TBT) and Euller–Bernoulli (EBT and EBT*) beam theories, where EBT corresponds to the Euler–Bernoulli beam theory considering rotational inertia, and EBT* corresponds to the Euler–Bernoulli theory considering rotational inertia to be negligible (the results are independent of L/h), for the structure under study, and using the finite element method. Looking at the results presented by Reddy [40] for the exact solutions according to both the Euler–Bernoulli and Timoshenko beam theories (Table 3 and Table 4), it should be noted that when the rotational inertia is neglected (EBT*), the resonance frequencies are slightly higher than the other solutions. Table 3, Table 4, Table 5 and Table 6 show the first four resonance frequencies of the cantilever beam, for L/h = 10 and L/h = 100, respectively, predicted by Reddy’s model, and the resonance frequencies obtained using the implemented model.

Table 3.
First four resonance frequencies of the beam, obtained according to the Timoshenko theory and the Euler–Bernoulli theory, L/h = 10.

Table 4.
First four resonance frequencies of the beam, obtained according to the Timoshenko theory and the Euler–Bernoulli theory, L/h = 100.

Table 5.
Comparison of the first four resonance frequencies calculated using 2, 4, and 8 quadratic elements, with the finite element model of [40], L/h = 10.

Table 6.
Comparison of the first four resonance frequencies calculated using 2, 4, and 8 quadratic elements, with the finite element model of [40], L/h = 100.
It is important to note that, as can be seen in Table 6, the model implemented allows us to obtain not only the resonance frequencies associated with transverse displacement, but also for axial displacement, which is why the positions of the resonance frequencies obtained do not correspond directly to those of Reddy [40]. For example, in the case of modeling the beam with eight quadratic elements, the third fundamental frequency presented in Reddy corresponds to the fourth frequency obtained with this model. For verification purposes, the graphical representation of the first four vibration modes associated with the transverse displacement of the beam considering eight quadratic elements is also shown in Figure 3, in order to compare with [40], in which the same vibration modes were represented considering 16 linear elements, noting that, in the case of the calculated mode 4, it is out of step with the reference mode; however, the model, in terms of representation of vibration modes, is verified, since in this case the comparison is between linear elements (in the referenced author) and quadratic elements (in the present model).
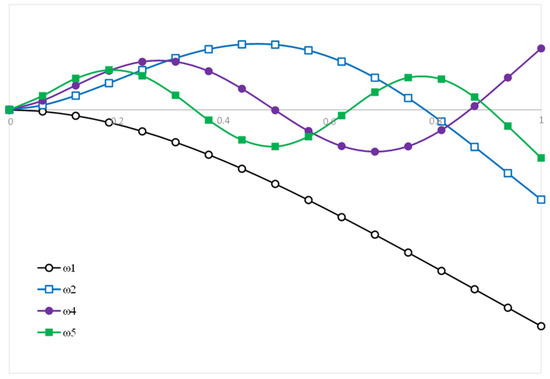
Figure 3.
Graphical representation of the first 4 vibration modes associated with the transverse displacement of the cantilever beam with L/h=10, shown in [40].
3.1.3. Benchmark Function
To verify the Red Fox algorithm, we studied the Jones function [1], which consists of a multimodal function of dimension 2, useful for testing global search algorithms and gradient-based algorithms with different starting points. It is a function that has local maxima and minimum, and a global minimum as presented in Table 7, and is defined by the expression

Table 7.
Global and local minima of Jones benchmark function.
In order to verify and test the behavior of the algorithm, the function was tested for different population values and iterations. Sets of 10 runs were carried out for N 10, 20, 30, 40, and 50 foxes (individuals), for 50, 100, 150, 200, and 1000 iterations, in order to define parameters that would make it possible to reconcile good accuracy and results without compromising computational resources.
Based on the results (means and standard deviations) achieved and presented in Table 8, in the next studies, the evolution of a population of 30 individuals will be analyzed along 100 iterations. As mentioned in Section 2, this population dimension observes the guidelines of the Central Limit Theorem ([36,37]), for each optimization process. In addition to this, a set of 10 runs (10 complete optimization processes) is conducted for each optimization case.

Table 8.
Effect of the optimization parameters tmax and N on the results obtained for the benchmark Jones function.
3.2. Study of a Frame-Type Structure
The optimization studies carried out focus on frame-type structures with square cross-sections, having as a goal the minimization of the maximum resultant displacement while considering mass constraints. Although in the present work only square cross-sections were considered, other geometrical configurations could be considered, either standard or customized ones, as the implementation considered allows us to deal with continuous or discrete design variables. In addition, other constraints could also be accommodated, for example, related to Eurocode design rules, manufacturability constraints, or cost sensitivity factors. However, considering the aim of this work, related to the evaluation of the mentioned dataflow, only stiffness and mass constraints were considered in the next case studies.
The frame-type structures studied have the configuration and loading illustrated in Figure 4. The design variables are related to the members’ cross-section dimensions.
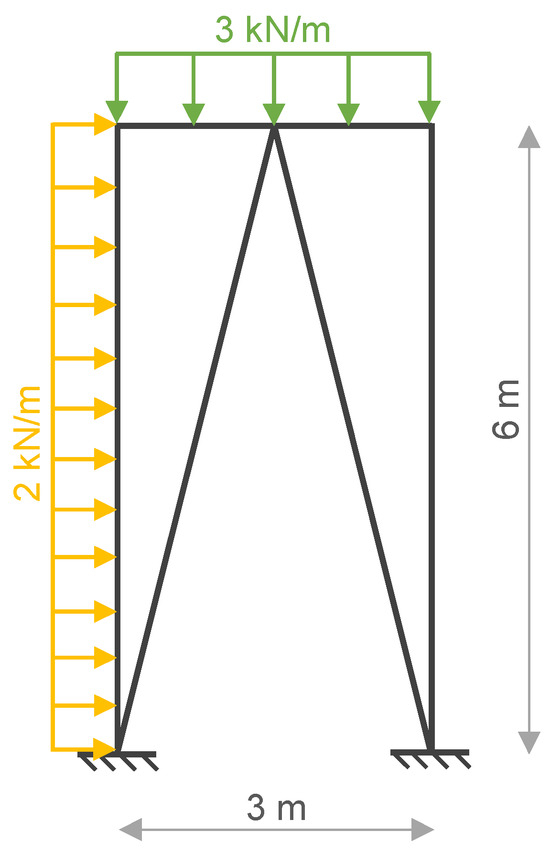
Figure 4.
Schematic representation of geometrical characteristics for the illustrative frame structure studied. Loads and boundary conditions.
In the present study, a selective discretization approach was adopted, considering 10 quadratic beam elements in the member subject to distributed loading, and 5 elements in the remaining ones. This discretized model was selected after convergence tests.
3.2.1. Case Study 1—Optimization of a Frame-Type Structure with Constant Square Cross-Section
The first case study is about the structure presented in Figure 4 considering an equal square cross-section in all elements. Two behavioral constraints were initially considered; the maximum allowable displacement was set to correspond to the length of the member suffering the greatest displacement divided by 200. It was also considered a minimum displacement, to avoid unnecessary over-dimensioning of the structure, defined as the length of the member suffering the greatest displacement divided by 400. It is also assumed that no buckling occurs under the circumstances in which the structures are analyzed.
The results achieved in the 10 runs performed, considering in each run 100 iterations and populations of 30 individuals, are presented in Table 9. The number of runs was limited to 10 as a balance solution between computational resources and solutions’ representativity.

Table 9.
Optimization of the structure with equal constant square cross-section in all members.
The results obtained show a concentration of results at the lower limit defined for the maximum resulting displacement of the structure, corresponding to a cross-section with an edge of approximately 74.75 mm.
3.2.2. Case Study 2—Frame-Type Structure with Constant Square Cross-Section and Mass Restriction
In addition to the structure’s previous constraints, the second case study considers a mass restriction of 1000 kg. The results obtained are presented in Table 10.

Table 10.
Optimization of the structure with equal constant square cross-section in all members with mass restriction.
The application of the mass restriction implies a reduction square cross-section edge value of the members of the structure of near 8.8%, converging to approximately 68.2 mm, with a consequent increase in the value of the maximum resulting displacement of the structure, located close to the average value of the range defined for the displacement to be evaluated. This increase in the maximum displacement is near 44.2%. As an additional consequence of this stiffness reduction, the fundamental frequency shows a decreasing trend of about 8.8%.
3.2.3. Case Study 3—Frame-Type Structure with Different Square Cross-Sections
In the third case study, it is considered that the structure is built with members with different cross-section dimensions, although maintaining the square configuration. This approach took into account the structure characteristics, so, edge b1 was considered for vertical elements, b2 for horizontal elements, and b3 for the inclined ones. The results of this study are shown in Table 11.

Table 11.
Optimization of the structure considering different square cross-section values, using 30 individuals and 100 iterations in each run.
In opposition to previous case studies, in this case as the number of design variables increased, the optimal solutions obtained during the ten runs show a greater dispersion, which is an expected trend. Although the minimum maximum displacement is fairly close among the different runs, the corresponding structures’ masses and fundamental frequencies present, in some cases, significant differences. This is an aspect for which analysis is relevant to better characterize the different optimal design variables’ configurations. To this purpose, the K-means algorithm was used [41] for clustering, while the Silhouette score was considered to determine the number of clusters that should be used in each case. The global average Silhouette scores for the other number of clusters is given in Table 12.

Table 12.
Silhouette score for 2 to 8 clusters in the optimization process using 30 individuals and 100 iterations in each run.
According to the scores in Table 12, we selected three clusters as this number of clusters corresponds to the highest Silhouette score (0.516). The three clusters can be observed in the scatter plot presented in Figure 5, using different colors for the three regions.
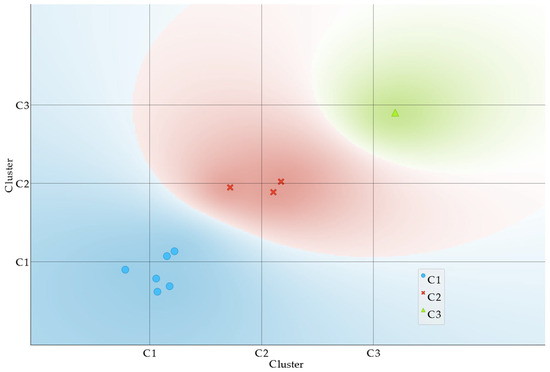
Figure 5.
Clusters for the optimal solutions dataset in the optimization process using 30 individuals and 100 iterations in each run.
In Cluster 1, we have high values for b3 and moderate values for b1 and b2 variables yielding heavier structures with higher fundamental frequencies. In Cluster 2, varied values for b1, very high values of b2, and very low values of b3 are found. This inverse correlation between b2 and b3 leads to very low frequency and mass values. Finally, for Cluster 3, we find a low value for b2 and moderate values for b1 and b3. The centroids and intervals of each cluster considering the original scale of each variable are presented in Table 13.

Table 13.
Cluster centroids for the optimization process using 30 individuals and 100 iterations.
Note that all the instances are effective optimal solutions, so the unique point in the third cluster does not constitute an outlier, but a valid instance as well as the others.
Summarizing the key aspects for this optimization process, we can say that high values of b3 consistently correlate with high frequencies as shown in the first and third cluster. Low values of b3 lead to low frequencies. The structure mass follows a similar trend. These conclusions are supported by the role that the inclined elements play in the analyzed structure. Regarding b2, when these values are very high, Cluster 2 forces b3 values to be lower. However, for moderate b2 values, high values of b3 are found, yielding to high masses and frequencies. Overall, it is seen that b3 has a greater influence on clustering followed by b2 as they possess greater standard deviations, namely 58.25 and 50.81 against 8.19 for b1.
Within the same case study, it was intended to allow the optimization algorithm to progress in a higher number of iterations, although maintaining the same number of function evaluations, so we have further considered the following optimization parameters: 10 runs, where in each run a population of 20 individuals is allowed to progress along 150 iterations. The results obtained in this optimization process are presented in Table 14.

Table 14.
Optimization of the structure considering different square cross-section values, using 20 individuals and 150 iterations in each run.
As expected, and similar to the results obtained previously, Table 13 shows that the results obtained for the objective function are very close, although the design variables’ configurations achieved in each run show clear differences. Thus, as shown previously, we have proceeded to a clustering analysis of those configurations, for a more systematic characterization. In this set of optimal solutions, five clusters were found to be the best clustering arrangement, according to the Silhouette score (0.628). The global average Silhouette scores for other numbers of clusters are given in Table 15.

Table 15.
Silhouette score for 2 to 8 clusters in the optimization process using 20 individuals and 150 iterations in each run.
The clusters’ centroids, considering the original scale of each variable, are presented in Table 16. This table also presents the corresponding optimization runs where those configurations were obtained.

Table 16.
Cluster centroids for the optimization process using 20 individuals and 150 iterations in each run.
From Table 14, we can see that Cluster 1 is particularly characterized by very low values of b3, while b1 and b2 present moderate values. Cluster 2 is characterized by high b3 values and moderate b1 and b2 values. Cluster 3 contains a low value of b3 and b2, and a very high b1 value. Regarding Cluster 4, it includes moderate values of b3 and b1 and very high values of b2. Finally, Cluster 5 includes instances with very high values of b3, high values of b2, and moderate b1 values. Figure 6 presents a scatter plot where these clusters are represented.
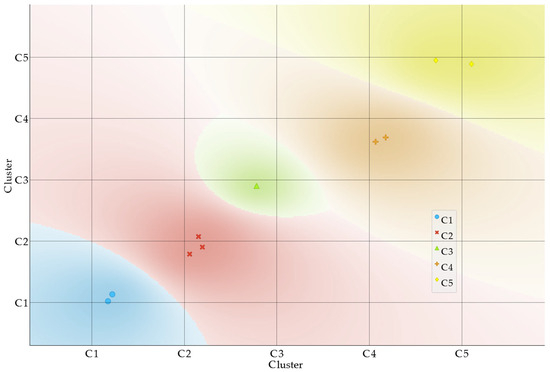
Figure 6.
Clusters for the optimal solutions dataset in the optimization process using 20 individuals and 150 iterations in each run.
According to the achieved clustering, it is possible to summarize that the configurations in Cluster 1 provide the lightest structures with lower fundamental frequencies while the ones in Cluster 5 provide heavier structures with higher frequencies followed by Cluster 3. The remaining configurations demonstrate intermediate values, with opposite range values regarding the b2 and b3 variables.
The design variables of the achieved optimal configurations show less discrepant standard deviations. Now, we have 30.91, 45.73, and 63.89 for the features b1, b2, and b3, respectively. Although b3 continues to be the most influential on clustering, b2 lost some importance while the opposite happened in the case of b1. Again, the influence of b3 from the mechanical perspective supports the results arising from the optimal solutions analysis.
As a final scenario in this case study, we have considered a mass constraint of 1000 kg. The optimal solutions obtained in ten runs, maintaining the latter number of individuals and iterations, are presented in Table 17.

Table 17.
Optimization of the structure considering mass constraint, using 20 individuals and 150 iterations in each run.
Regarding these optimal configurations, the Silhouette score pointed to a two-clusters structure, for which the scatterplot is presented in Figure 7.
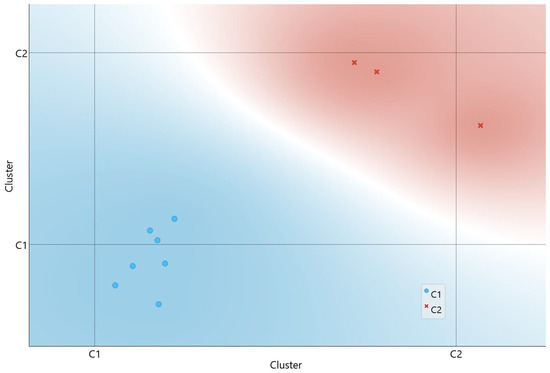
Figure 7.
Clusters for the optimal solutions dataset in the optimization process with mass constraint, using 20 individuals and 150 iterations in each run.
The centroids of the two clusters are characterized in Table 18, being presented also with the corresponding design variables’ intervals and the runs in which solutions were assigned to the clusters.

Table 18.
Cluster centroids for the optimization process with mass constraint, using 30 individuals and 100 iterations in each run.
The imposition of a mass constraint produced a clear effect in narrowing the domain of the previously most influential design variable, b3, significantly reducing its standard deviation. Cluster 2 is characterized by lower b3 values while Cluster 1 possesses slightly higher b3 values. The major difference between the two clusters is related to the variables b1 and b2. Under this constraint the design variable b2 has assumed a more influential role although not as much as the b3 variable played in the previous situations. The masses of the structures are now not significantly different in the two clusters; however, the fundamental frequencies in Cluster 2 are lower than the ones in Cluster 1’s structures.
4. Conclusions
The main goal of the present work is the constitution of a framework that enables the optimization and characterization of optimal solutions regarding the configurations that minimize the maximum resultant displacement of steel-plane frame structures. Although being considered as a single objective problem, multiple solutions will be achieved due to the metaheuristic nature of the process; different runs and a subsequent exploratory data analysis were performed.
Following a schematic dataflow to represent the Red Fox Optimization method interacting with the finite element analysis, followed by the Silhouette method and the K-means method, we present a set of studies aiming in a first stage to verify the implemented analysis and optimization codes and in a second stage to illustrate the global procedure. From the verification cases, the good performance of the implemented codes is concluded.
The optimal solutions dataset exploratory analysis performed through K-means allowed us to identify groups of optimal solutions with specific characteristics that although concurring to the minimum displacement solution present distinct responses regarding the mass of the structures and their fundamental frequency. This demonstrates the need to characterize the different solutions, as this information will provide valuable insights for a better configuration selection. The study carried out also identified the most influential design variables in different situations, information that is supported by the known contribution that the different members in the structure will play whether behavioral constraints are imposed or not.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.A.R.L. and J.I.B.; Data curation, J.S.D.G.; Formal analysis, J.S.D.G., M.A.R.L. and J.I.B.; Methodology, M.A.R.L.; Software, J.S.D.G. and M.A.R.L.; Supervision, M.A.R.L. and J.I.B.; Visualization, J.S.D.G.; Writing—original draft, J.S.D.G.; Writing—review and editing, M.A.R.L. and J.I.B. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
The codes, through their schematic representation, dataflow information and data generated or analyzed are all presented in the manuscript itself, except for the finite element code which is well disseminated in literature.
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge Fundação para a Ciência e a Tecnologia (FCT) for its financial support via the project LAETA Base Funding (DOI: 10.54499/UIDB/50022/2020).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Martins, J.R.R.A.; Ning, A. Engineering Optimization Design; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Szeptyński, P.; Mikulski, L. Preliminary optimization technique in the design of steel girders according to Eurocode 3. Arch. Civ. Eng. 2023, 69, 71–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cicconi, P.; Germani, M.; Bondi, S.; Zuliani, A.; Cagnacci, E. A Design Methodology to Support the Optimization of Steel Structures. Procedia CIRP 2016, 50, 58–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dillen, W.; Lombaert, G.; Mertens, R.; Van Beurden, H.; Jaspaert, D.; Schevenels, M. Optimization in a realistic structural engineering context: Redesign of the Market Hall in Ghent. Eng. Struct. 2021, 228, 111473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dillen, W.; Lombaert, G.; Schevenels, M. A hybrid gradient-based/metaheuristic method for Eurocode-compliant size, shape and topology optimization of steel structures. Eng. Struct. 2021, 239, 112137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Z.; Tielin, L.; Hong, L.; Zheng, W. Optimization Design for Beam and Column of Steel Structure Residence. In Proceedings of the 8th International Conference on Intelligent Computation Technology and Automation, ICICTA 2015, Nanchang, China, 14–15 June 2015; Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2016; pp. 609–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaspar, J.S.D.; Loja, M.A.R.; Barbosa, J.I. Static and Free Vibration Analyses of Functionally Graded Plane Structures. J. Compos. Sci. 2023, 7, 377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Połap, D.; Woźniak, M. Red fox optimization algorithm. Expert. Syst. Appl. 2021, 166, 114107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dulal, A.; Singh, M.; Sharma, G. Static and Dynamic Data Analysis for Android Malware Detection using Red Fox Optimization. Int. J. Res. Publ. 2024, 146, 251–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopi, P.S.S.; Karthikeyan, M. Red fox optimization with ensemble recurrent neural network for crop recommendation and yield prediction model. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2023, 83, 13159–13179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaspar, J.S.D.; Loja, M.A.R.; Barbosa, J.I. Metaheuristic Optimization of Functionally Graded 2D and 3D Discrete Structures Using the Red Fox Algorithm. J. Compos. Sci. 2024, 8, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bamikole, J.O.; Narasigadu, C. Application of Pathfinder, Honey Badger, Red Fox and Horse Herd algorithms to phase equilibria and stability problems. Fluid. Phase Equilib. 2023, 566, 113682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Xu, Z.; Lu, X.; Liu, Y.; Xiao, Q.; Taheri, B. An optimal model identification for solid oxide fuel cell based on extreme learning machines optimized by improved Red Fox Optimization algorithm. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2021, 46, 28270–28281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaiyapuri, T.; Liyakathunisa; Alaskar, H.; Aljohani, E.; Shridevi, S.; Hussain, A. Red fox optimizer with data-science-enabled microarray gene expression classification model. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 4172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixit, S.; Qureshi, S. Security-aware, red fox optimization-based cluster-based routing in wireless sensor network. Peer-to-Peer Netw. Appl. 2025, 18, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devamalar, P.M.B.; Kalaiselvi, K.; Sathikbasha, M.J.; Gopi, A. An optimal solid waste management using red fox optimization and hybrid DenseNet-BiLSTM model. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2023, 195, 1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivo, J.; Cucuzza, R.; Bertagnoli, G.; Domaneschi, M. Optimal design of steel exoskeleton for the retrofitting of RC buildings via genetic algorithm. Comput. Struct. 2024, 299, 107396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodarzimehr, V.; Talatahari, S.; Shojaee, S.; Gandomi, A.H. Computer-aided dynamic structural optimization using an advanced swarm algorithm. Eng. Struct. 2024, 300, 117174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cucuzza, R.; Rad, M.M.; Domaneschi, M.; Marano, G.C. Sustainable and cost-effective optimal design of steel structures by minimizing cutting trim losses. Autom. Constr. 2024, 167, 105724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Yang, X.; Tao, R.; Chen, H. Improved Sine-cosine Algorithm for the Optimization Design of Truss Structures. KSCE J. Civ. Eng. 2024, 28, 687–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, Q.H.; Le, T.X.; Nguyen, D.L.M.; Bui, T.T.; Nguyen, N.C.; Tran, H.N. A Prospective Technique for Damage Detection in Truss Structures Using the Fusion of DNN with AVOA. KSCE J. Civ. Eng. 2024, 28, 2920–2933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babaei, M.; Mollayi, M. An improved constrained differential evolution for optimal design of steel frames with discrete variables. Mech. Based Des. Struct. Mach. 2020, 48, 697–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vu, Q.-A.; Cao, T.-S.; Nguyen, T.-T.-T.; Nguyen, H.-H.; Truong, V.-H.; Ha, M.-H. An efficient differential evolution-based method for optimization of steel frame structures using direct analysis. Structures 2023, 51, 67–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moosavian, H.; Mesbahi, P.; Moosavian, N.; Daliri, H. Optimal design of truss structures with frequency constraints: A comparative study of DE, IDE, LSHADE, and CMAES algorithms. Eng. Comput. 2023, 39, 1499–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tejani, G.G.; Sharma, S.K.; Mashru, N.; Patel, P.; Jangir, P. Optimization of truss structures with two archive-boosted MOHO algorithm. Alex. Eng. J. 2025, 120, 296–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okasha, N.M.; Alzo’ubi, A.K.; Mughieda, O.; Kewalramani, M.; Almasri, A.H. A near-optimum multi-objective optimization approach for structural design. Ain Shams Eng. J. 2024, 15, 102388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barraza, M.; Bojórquez, E.; Fernández-González, E.; Reyes-Salazar, A. Multi-objective optimization of structural steel buildings under earthquake loads using NSGA-II and PSO. KSCE J. Civ. Eng. 2017, 21, 488–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz, A.S.; Caldas, L.R.; Mendes, V.M.; Mendes, J.C.; Bastos, L.E.G. Multi-objective optimization based on surrogate models for sustainable building design: A systematic literature review. Build. Environ. 2024, 266, 112147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omran, M.G.H.; Engelbrecht, A.P.; Salman, A. An overview of clustering methods. Intell. Data Anal. 2007, 11, 583–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, G.; Li, X.; Nie, Y.; Li, H. FEM-Cluster based reduction method for efficient numerical prediction of effective properties of heterogeneous material in nonlinear range. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2019, 348, 157–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benaimeche, M.A.; Yvonnet, J.; Bary, B.; He, Q. A k-means clustering machine learning-based multiscale method for anelastic heterogeneous structures with internal variables. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 2022, 123, 2012–2041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, A.; Silva, T.; Loja, M.A.R.; Damásio, F.R. Assessing the Influence of Material and Geometrical Uncertainty on the Mechanical Behavior of Functionally Graded Materials Plates. Mech. Adv. Mat. Struct. 2017, 24, 417–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loja, M.A.R.; Soares, C.M.M.; Soares, C.A.M. Modelling and design of adaptive structures using B-spline strip models. Compos. Struct. 2002, 57, 245–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, C.M.M.; Soares, C.A.M.; Correia, V.M.F.; Loja, M.A.R. Higher-order B-spline strip models for laminated composite structures with integrated sensors and actuators. Compos. Struct. 2001, 54, 267–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zienkiewicz, O.C.; Taylor, O.C.; Fox, D. The Finite Element Method for Solid and Structural Mechanics; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramachandran, K.M.; Tsokos, C.P. Mathematical Statistics with Applications; Elsevier Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Montgomery, D.C. Design and Analysis of Experiments; John Wiley& Sons, Inc.: NewYork, NY, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Gan, G.; Ma, C.; Wu, J. Data Clustering: Theory, Algorithms, and Applications; ASA-SIAM Series on Statistics and Applied Probability; SIAM, ASA, Alexandria, VA: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Flach, P. Machine Learning: The Art and Science of Algorithms That Make Sense of Data; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Reddy, J.N. An Introduction to the Finite Element Method, 2nd ed.; A.A. Balkema Publishers: Lisse, The Netherlands, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Demšar, J.; Curk, T.; Erjavec, A.; Gorup, Č.; Hočevar, T.; Milutinovič, M.; Možina, M.; Polajnar, M.; Toplak, M.; Starič, A.; et al. Orange: Data Mining Toolbox in Python. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2013, 14, 2349–2353. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).