Abstract
Positron Emission Tomography/Computed Tomography (PET/CT) using Fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) is an important imaging modality for assessing treatment outcomes in patients with pulmonary malignant neoplasms undergoing radiation therapy. However, distinguishing between benign post-radiation changes and residual or recurrent malignancies on PET/CT images is challenging. Leveraging the potential of artificial intelligence (AI), we aimed to develop a hybrid fusion model integrating radiomics and Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) architectures to improve differentiation between benign post-radiation changes and residual or recurrent malignancies on PET/CT images. We retrospectively collected post-radiation PET/CTs with identified labels for benign changes or residual/recurrent malignant lesions from 95 lung cancer patients who received radiation therapy. Firstly, we developed separate radiomics and CNN models using handcrafted and self-learning features, respectively. Then, to build a more reliable model, we fused the probabilities from the two models through an evidential reasoning approach to derive the final prediction probability. Five-folder cross-validation was performed to evaluate the proposed radiomics, CNN, and fusion models. Overall, the hybrid fusion model outperformed the other two models in terms of sensitivity, specificity, accuracy, and the area under the curve (AUC) with values of 0.67, 0.72, 0.69, and 0.72, respectively. Evaluation results on the three AI models we developed suggest that handcrafted features and learned features may provide complementary information for residual or recurrent malignancy identification in PET/CT.
1. Introduction
Lung cancer remains the leading cause of cancer-related mortality worldwide, with its incidence second only to breast cancer among women since 2020 [1]. One of the primary treatments for lung cancer is radiation therapy, with or without adjuvant or neo-adjuvant chemotherapy, depending on the staging and grading of the malignant disease process [2]. Several radiation therapy modalities exist for lung cancer, but regardless of the method used, radiation-induced changes are inevitable. These changes typically manifest as benign inflammatory responses in the lung parenchyma surrounding the irradiated tumor, which may later develop into chronic fibrosis [3,4].
Post-treatment assessment of lung cancer often relies on Fluorodeoxyglucose F18 (FDG) PET/CT to evaluate the metabolic activity of residual lesions. While CT imaging alone is sometimes used, PET/CT offers additional metabolic information that aids in distinguishing between active disease and post-radiation changes [5]. However, differentiating between benign post-radiation inflammation and residual or recurrent malignancies remains a significant challenge for clinicians, as both conditions exhibit increased FDG uptake due to heightened metabolic activity [6,7]. Figure 1 displays a total of four examples, with two each representing benign inflammation and residual/recurrent malignancy as shown on PET/CT scans.
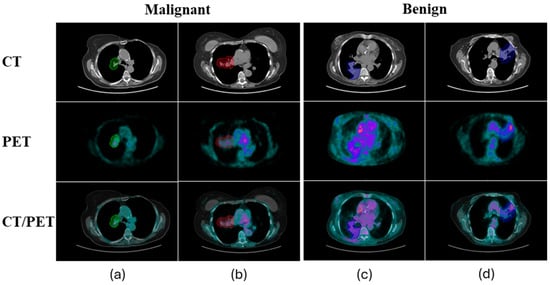
Figure 1.
Four examples, with two each representing benign inflammation (a,b) and residual/recurrent malignancy (c,d), as shown on PET/CT scans. The colorful contours overlaid on the images are the regions of interest drawn by nuclear medicine physicians.
The difficulty in interpreting these PET/CT images, particularly following radiation therapy, introduces considerable variability in human interpretation. Studies have shown that the accuracy of these evaluations largely depends on the experience and expertise of nuclear medicine physicians and radiologists. This variability is reflected in a wide range of interobserver agreement scores, with kappa values ranging from moderate agreement (κ = 0.57–0.69) to low agreement (κ as low as 0.22) in more ambiguous cases [8]. Such variability underscores the inherent limitations of human interpretation, especially in complex or borderline cases where distinguishing inflammation from malignancy is crucial for guiding further treatment.
To address this critical clinical issue, this study aims to develop an artificial intelligence (AI) model specifically designed to analyze post-radiation PET/CT scans in lung cancer patients. The primary goal is to accurately classify these scans as either positive or negative for residual or recurrent malignancy—a distinction essential for optimizing subsequent treatment decisions.
Quantitative image feature analysis, including radiomics, has shown substantial promise in enhancing the differentiation between local recurrence and radiation-induced inflammatory changes. Radiomics-based models [9,10] extract and analyze a wide range of quantitative imaging features, offering an objective approach that has been demonstrated to outperform traditional visual assessments by physicians. For example, radiomics-based approaches have demonstrated superior performance over evaluation by physicians for the early classification of local recurrence on follow-up CT scans after lung RT [11]. For early local recurrence detection within 6 months following definitive lung SBRT, Mattonen et al. reported that five of six physicians (including three thoracic radiation oncologists and three thoracic radiologists) had a 100% false negative rate using a follow-up CT image to assess benign injury or recurrence [11]. The false negative rate was greatly reduced to 23.1% by a radiomics-based model consisting of five imaging features.
Meanwhile, deep learning-based approaches have demonstrated remarkable success in image-based classification problems. Unlike radiomics, which depends on hand-crafted features, deep learning approaches automatically learn underlying representations that differentiate malignant from benign lesions. This ability to autonomously identify and utilize complex patterns in data makes deep learning a powerful tool in medical imaging and diagnostic applications. However, deep learning-based modeling requires a large amount of training data. Unlike applications based on natural images, where training samples are often abundant, many medical applications face limitations in the availability of cases.
To address this challenge, instead of relying solely on radiomics or deep learning, a hybrid approach has been developed. This approach integrates radiomics and deep learning-based modeling, leveraging the advantages of both handcrafted features and learned features. Specifically, our approach uses two distinct models based on radiomics and Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs), with the results of each model being fused through an evidential reasoning (ER) approach [12,13]. By integrating the predictive probabilities from these two models, we capitalize on the handcrafted features identified by radiomics and the deep, abstract representations learned by CNNs. This fusion facilitates a more comprehensive and nuanced analysis, enhancing overall predictive accuracy and reliability. Furthermore, this integrative approach mitigates the individual limitations of each model, resulting in a synergistic effect that enhances the robustness of the predictive outcomes.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Collection and Pre-Processing
We selected PET/CTs from 95 patients (one PET/CT from each patient), retrospectively, who received radiation therapy from 1 October 2006 to 6 August 2019. The following criteria were used to select these PET/CTs:
- Patients should have had an FDG PET/CT scan within two years after receiving radiation therapy to the lungs;
- Only the PET/CTs with abnormally increased radiotracer (FDG) uptake in the lungs were used;
- Abnormal radiotracer uptake should have been identified as benign post-radiation changes or malignant disease, by tissue sampling or follow-up imaging (CT or PET/CT) for at least 2 years;
- On follow-up imaging, stable or regressing lung parenchymal abnormalities at the site of radiation were considered benign. Progressively expanding lesions were considered malignant.
Out of 95 patients, 26 patients had biopsies performed for indeterminant imaging findings after receiving radiation therapy. Out of these patients, 17 patients demonstrated positive findings for malignancy on biopsy, while 9 patients had benign findings (negative for malignancy). Follow-up CT and PET/CT images from the rest of the patients (69 patients) were evaluated for up to two years after the first post-radiation PET/CT. On follow-up imaging, 28 patients demonstrated progressive abnormalities indicating positive lung malignancy at the post-radiation site. Forty-one patients demonstrated regression of imaging abnormalities on two-year follow-up images, indicating non-malignant benign post-radiation changes on first post-radiation PET/CT.
Table 1 summarizes the patient demographics and tumor characteristics, with data categorized into benign and malignant groups. The study cohort consisted of 95 patients, including 43 males and 52 females. The median age was 72 years, ranging from 46 to 94 years. Primary tumors were most frequently located in the upper lobe of the lung (58 cases), followed by the lower lobe (34 cases), and the middle lobe (3 cases). Laterality of disease was fairly balanced, with 52 cases on the right lung and 43 on the left. In terms of clinical staging, 49 patients were classified as early-stage (stages 0–1), 30 as intermediate-stage (stages 2–3), and 6 as advanced-stage (stage 4 or higher), while 10 cases remained unclassified. The breakdown between benign and malignant lesions revealed similar distributions across gender, age, and tumor location, with 50 benign cases and 45 malignant cases. This balance indicates the need for better diagnostic tools in distinguishing benign post-treatment changes from residual or recurrent malignancies.

Table 1.
Patient demographics and tumor characteristics.
In this study, all PET/CT images were acquired using the same Siemens PET/CT scanner, following a standardized imaging protocol. PET images were reconstructed using either the OSEM2D 4i8s or PSF3i21s algorithms, with pixel spacing of 4.0728 mm and slice thickness of 5 mm. The administered radiopharmaceutical dose ranged from 298 MBq to 4030 MBq, with a median dose of 417 MBq. During pre-processing, all CT images were resampled to match the resolution of the PET images. Additionally, PET intensity values were converted to standardized uptake values (SUVs) to ensure consistency for model development and subsequent inference. A nuclear medicine physician manually delineated the region of interest (ROI) on the slice with the largest lesion area. This 2D contour was then extended to 3D using a similarity variation model, as described in a previous study [14]. Based on these 3D tumor representations, we developed radiomics, CNN, and fusion models. Figure 2 outlines the workflow, from data acquisition to the final prediction of whether post-radiation changes are benign or represent residual/recurrent malignancies based on the follow-up PET/CT images.
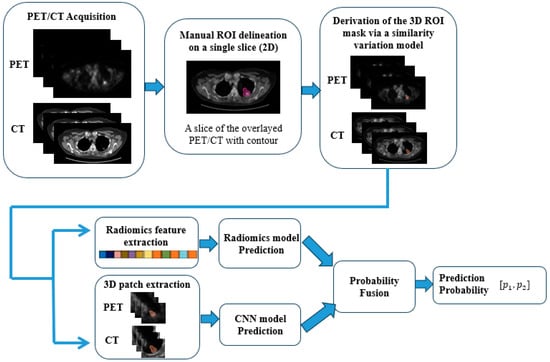
Figure 2.
A flow diagram of the proposed method. The pink contour is the contour provided by the nuclear medicine physician on the slice with the largest area of the region of interest. The orange contours are the 3D contours derived from the similarity variation model.
To facilitate the evaluation of the proposed radiomics, CNN, and fusion models, we divided the dataset into five folders, each containing data from 20, 20, 18, 20, and 17 patients, respectively. This division allowed us to perform a five-folder cross-validation. In each iteration of this process, we used data from three folders for model training, one folder for model validation and selection, and the remaining folder for testing. This ensured that each folder was used for testing at least once. The distributions of benign changes and malignant diseases in each of these folders are detailed in Table 2.

Table 2.
Distributions of benign and malignant samples in five folders.
2.2. Radiomics Model
In the radiomics model, a total of 106 handcrafted features, encompassing intensity, geometry, and texture properties of the regions of interest, were extracted from CT and PET images. Nine intensity features, including minimum, maximum, mean, median, standard deviation, sum, skewness, kurtosis, and variance, were initially calculated for each imaging modality (CT or PET). Subsequently, eight geometry features were derived from the mask of the regions of interest in the paired PET and CT images.
Additionally, forty texture features were calculated for each imaging modality. In contrast to most commonly used radiomics models, which typically extract texture features purely based on the Gray Level Co-occurrence Matrix (GLCM) calculated from imaging data, in our study, we employed a more comprehensive approach to texture extraction by utilizing four gray level-based matrices including the Gray Level Run Length Matrix (GLRLM), Gray Level Size Zone Matrix (GLSZM), Neighboring Gray Tone Difference Matrix (NGTDM), and GLCM. GLCM focuses on spatial relationships and texture patterns [15], while GLRLM assesses the length of homogeneous pixel runs, capturing texture roughness [16]. GLSZM evaluates the size distribution of homogeneous zones, providing insight into texture zone uniformity [17]. NGTDM examines local intensity variations, highlighting subtle texture changes [18]. This multi-faceted methodology provides a more robust and detailed characterization of tissue heterogeneity compared to the exclusive use of GLCM. Each matrix captures distinct aspects of texture information from medical images, thereby enhancing the overall predictive capability of our radiomics model. Detailed features for each category are listed in Table 3.

Table 3.
Handcrafted features of the regions of interest extracted from PET and CT images.
A predictive model was then constructed using the Gaussian kernel-based support vector machine (SVM) algorithm. The Gaussian kernel was selected due to its capability to model the non-linear relationships inherent in the radiomics features. Given that represents the feature vector for each sample , consisting of the 106 radiomics features extracted from the images, and is the class label (malignant: 2 and benign: 1), the optimization problem is formulated as:
where:
- is the feature mapping induced by the Gaussian kernel;
- is the weight vector, which determines the orientation of the hyperplane in the feature space, and b is the bias term, which shifts the hyperplane;
- are the slack variables that allow some flexibility in the classification for non-linearly separable data;
- is the box constraint that controls the trade-off between maximizing the margin and minimizing the classification error.
To solve the above optimization problem, we utilized the method of Lagrange multipliers, transforming the primal problem into its dual form, which is as follows:
where:
- are the Lagrange multipliers, and is the Gaussian kernel function.
Then, Sequential Minimal Optimization (SMO), an iterative algorithm, was used to find the optimal values of , and finally w and b can be calculated. During the training phase, the model’s hyperparameters were tuned and selected based on the highest validation accuracy. Particularly, the box constraint was set to a value of 100 to prevent overfitting by controlling the maximum penalty imposed on margin-violating observations.
For testing, the trained SVM model was evaluated on the samples from a folder, distinct from data from the training and validation folders (four folders in total). This procedure provides an unbiased assessment of the model’s predictive accuracy. Performance metrics such as accuracy, sensitivity, specificity, and the area under the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve were computed to quantify the model’s effectiveness.
2.3. CNN Model
The CNN model, on the other hand, used the 3D patches of regions of interest from PET and CT images, each sized at 48 × 48 × 48, for prediction. These patches, including the 3D-contoured potential residual/recurrent lesions and the surrounding voxels, served as inputs for the CNN model. Unlike the radiomics model, the CNN model was designed to learn features from the input 3D patches and make predictions automatically. The proposed CNN architecture consists of eight 3D convolutional layers, three max-pooling layers, one global-average-pooling layer, and two fully connected layers. Each convolutional layer was equipped with ReLu activation and batch normalization. In addition, a Ɩ1 kernel regularizer with a weighting factor of 0.01 and a dropout rate of 0.01 was also embedded in each convolutional layer to reduce the potential of overfitting. The architecture was designed by alternating convolutional layers (two stacked layers each time) with the max-pooling layer to gradually capture the local to global features. The feature volumes of each two-stacked convolutional layer from the beginning to the end are 3, 6, 12, and 24, respectively. After the global max-pooling layer, two fully connected layers were used to reduce features and finally generate the predicted probabilities for two different categories: benign or malignant.
To compensate for the large scale of the CNN architecture, we implemented data augmentation through 3D image rotation. The rotation angle was randomly selected within the range of [−10,10] degrees along one of the x, y, or z axes. Specifically, for each training sample, 20 augmented samples were generated by rotating the images along a random axis. An example of the augmented sample is shown in Figure 3. For CNN model training, binary cross entropy was utilized as the loss function, and Adam was the optimization algorithm. The models with the best prediction results on the validation dataset were selected for testing.
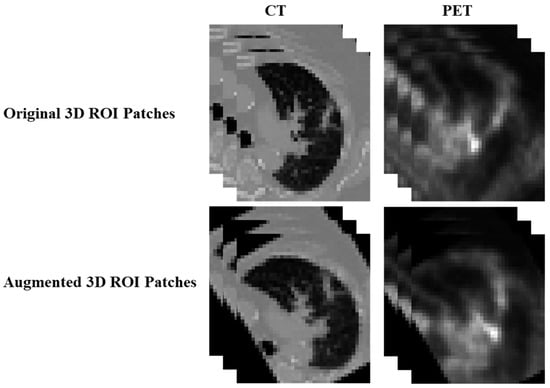
Figure 3.
An example of the augmented sample through 3D image rotation method.
2.4. Fusion Model
Radiomics models excel in extracting quantitative features related to tissue heterogeneity and texture from medical images, offering detailed insights into subtle and often imperceptible patterns. Conversely, CNN models are highly proficient in learning complex spatial hierarchies and patterns directly from raw imaging data through advanced deep learning techniques. Fusing the predictive probabilities from radiomics models and CNN models leverages the complementary strengths of both methodologies to achieve more robust results.
The fusion process was realized by an evidential reasoning approach [13], which integrates evidence from various sources (the radiomics and the CNN models) under uncertainty consideration. Figure 4 illustrates the workflow of the fusion model.
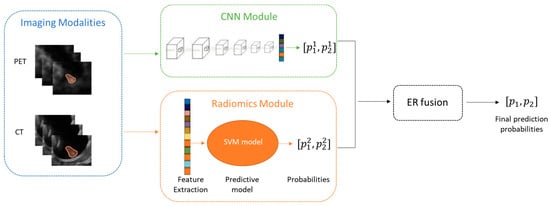
Figure 4.
Workflow of the fusion model combining radiomics and CNN models.
In the ER fusion stage, firstly we converted the probabilities from each model into basic probabilities assignments (BPAs) based on the Dempster–Shafer theory [19]. BPAs reflect the degree of belief in each possible outcome given the evidence from each model. Then based on Dempster’s combination rule accounting for both the agreement and conflict between the two models, a combined BPA that represents a consensus of the evidence via mathematically aggregating the BPAs from each model is derived (see Equations (3)–(6)). For hypothesis :
where
Here, and are the weighting factors to adjust the contribution of each model based on their relative importance or reliability. In this study, the weighting factors were derived to achieve the best validation performance.
The combined BPA is the final prediction probability that we use for decision-making.
3. Results
To evaluate the performance of our proposed methods, we compared the radiomics-SVM model, the CNN model, and the fusion model against several baseline models. The baseline models included in this study were the Logistic Regression (LR) model and the Random Forest (RF) model, both referenced from reference [20]. However, it is important to note that while reference [20] applied these models to predict EGFR mutation status, our study focuses on differentiating between benign post-RT changes and residual/recurrent malignancies, which presents a distinct challenge in PET/CT imaging. Due to the differences in datasets and objectives, the results from reference [20] are not directly comparable to ours. In this study, we implemented LR and RF in our dataset, and these baseline models utilized the same radiomics features as those used in our proposed SVM model. The evaluation criteria used were sensitivity, specificity, accuracy, and area under the ROCs (AUC). The ROC comparison curves for all models are illustrated in Figure 5.
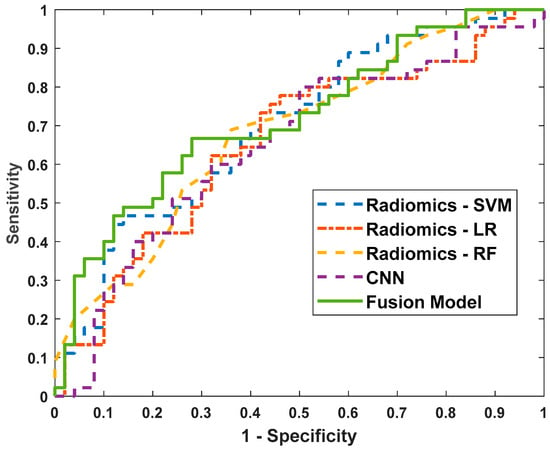
Figure 5.
The receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves of the radiomics-LR model, the radiomics-RF model, the radiomics-SVM model, the CNN model, and the fusion model.
The performance of various models for predicting benign versus malignant cases is summarized in Table 4. The radiomics-LR model demonstrated a sensitivity of 0.60, specificity of 0.68, accuracy of 0.64, and an AUC of 0.66. The radiomics-RF model showed a similar sensitivity of 0.60 but slightly a lower specificity of 0.66 and an accuracy of 0.63, with an AUC of 0.68. The radiomics-SVM model achieved a sensitivity of 0.60, specificity of 0.64, accuracy of 0.62, and an AUC of 0.70, indicating a relatively higher AUC among the radiomics-based models.

Table 4.
Benign vs. malignancy prediction performance of the radiomics-LR model, radiomics-RF model, radiomics—model, the CNN model, and the fusion model.
The CNN model, while having a lower sensitivity of 0.56, maintained a specificity of 0.68, an accuracy of 0.62, and an AUC of 0.65. Notably, the fusion model, which combines predictive probabilities from both radiomics-SVM and CNN models, outperformed the individual models. It achieved the highest sensitivity (0.67), specificity (0.72), accuracy (0.69), and AUC (0.72).
These results indicate that the fusion model, leveraging the strengths of both radiomics-based and deep learning-based approaches, provides a more robust and accurate prediction performance for distinguishing between benign and malignant cases. This integrated approach enhances the model’s ability to capture diverse and complementary aspects of the imaging data, leading to improved diagnostic capabilities.
The ROC comparison curves (Figure 5) further illustrate the performance differences among the models. The fusion model consistently outperforms the individual radiomics and CNN models, as evidenced by its superior ROC curve positioning, which corresponds to higher sensitivity and specificity across various threshold settings. This graphical representation reinforces the quantitative results presented in Table 4, highlighting the efficacy of the fusion model in achieving robust predictive performance.
To further demonstrate the effectiveness of the fusion strategy, we applied ER fusion to combine the predictive probabilities from the LR and RF radiomics models with the CNN model. The fusion results are presented in Table 5, showing that fusion models consistently deliver more robust and accurate prediction performance. This confirms that the proposed probability fusion approach is both versatile and applicable to similar tasks.

Table 5.
Benign vs. malignancy prediction performance of the fusion models derived from LR/RF and CNN models.
4. Discussion
Lung cancer is the leading cause of cancer death in the world, as nearly one-quarter of all cancer deaths worldwide are due to lung cancer. Most of the inoperable early-stage lung cancer cases are treated with radiotherapy alone or radiotherapy with chemotherapy [21]. While the distribution of FDG on a post-radiation PET/CT is affected by the inflammatory changes caused by radiation itself, FDG PET/CT remains the most common modality for identifying the treatment response of lung cancer after radiation therapy [7,22]. Recent advancements in radiomics have led to the development of models capable of extracting complex information from CT scans—information that includes features not readily visible or quantifiable to the human eye. These models [11,23] have shown promise in detecting local cancer recurrence following stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT) for lung cancer, indicating radiomics’ potential to identify early changes linked to local recurrence, which are often overlooked in conventional medical assessments. Similarly, the CNN models, known for their capability in image recognition and classification, have also been developed to address the challenge of detecting recurrence after lung SBRT [24], demonstrating their capability to predict patient outcomes.
In our study, we aimed to enhance the reliability of post-radiation lung cancer treatment response assessment based on post-radiation PET/CT images by integrating the predictions of a radiomics model and a CNN model through the ER approach. This integration seeks to address the limitations of using either model in isolation by leveraging their complementary strengths. Our model was able to achieve a predictability with AUC of 0.72, in order to differentiate PET/CTs with only benign post-radiation changes from PET/CTs with malignant lesions. The 0.02 increase in AUC compared to the individual models indicates that the fusion model has the potential to make more accurate predictions in cases where malignancy detection is challenging. While the model showed a notable improvement in accuracy and AUC, further studies are needed to validate its performance in larger and more diverse datasets. In addition, although this level of accuracy (~70%) may not yet meet the standards for direct clinical application, our comprehensive literature review revealed no prior attempts to leverage AI for this specific purpose. Therefore, we consider the radiomics model, CNN model, and their fusion as promising prototypes for the development of more sophisticated AI models in this domain.
5. Conclusions
In conclusion, this study demonstrates the potential of combining radiomics and CNN models to enhance the detection of residual or recurrent lung malignancies following radiation therapy. Our fusion model outperforms the individual models, offering improved accuracy in distinguishing between benign and malignant post-radiation PET/CT findings. Despite the relatively modest accuracy, this approach highlights the feasibility of AI-driven solutions in complex clinical scenarios where traditional assessments may fall short. Further research with larger and more varied datasets is essential to fully evaluate the clinical applicability of these AI models.
6. Future Work
Our future work will involve integrating pre-radiation FDG PET/CT scans, 3D dose maps, and post-radiation FDG PET/CT scans. This multi-modal approach holds the potential to enhance prediction accuracy and provide a more comprehensive assessment of treatment response in lung cancer patients. The primary limitation of this study is the relatively small dataset, which may limit the generalizability of the results. Additionally, the retrospective nature of the data and the use of a single institution’s PET/CT scans may introduce selection bias. To further validate and refine our models, additional research is necessary, particularly studies that compare AI-driven assessments with traditional clinical evaluations in larger, more diverse patient populations. Such investigations will be crucial for establishing the clinical relevance and applicability of AI in the context of lung cancer treatment and management.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, L.C., A.L. and J.W.; methodology, L.C., A.L. and J.W.; validation, L.C., A.L. and J.W.; formal analysis, L.C., A.L. and J.W.; writing—original draft preparation, L.C., A.L. and J.W.; writing—review and editing, L.C., A.L. and J.W.; supervision, J.W. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
The datasets presented in this article are not readily available due to university and hospital restrictions. Requests to access the datasets should be directed to the authors, and a data use agreement needs to be approved by the university and hospital.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Cao, W.; Chen, H.-D.; Yu, Y.-W.; Li, N.; Chen, W.-Q. Changing profiles of cancer burden worldwide and in China: A secondary analysis of the Global cancer statistics 2020. Chin. Med. J. 2021, 134, 783–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smythe, W.R. Treatment of stage I non-small cell lung carcinoma. Chest 2003, 123, 181S–187S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmichael, J.; Degraff, W.G.; Gamson, J.; Russo, D.; Gazdar, A.F.; Levitt, M.L.; Minna, J.D.; Mitchell, J.B. Radiation sensitivity of human lung cancer cell lines. Eur. J. Cancer Clin. Oncol. 1989, 25, 527–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hicks, R.J.; Mac Manus, M.P.; Matthews, J.P.; Hogg, A.; Binns, D.; Rischin, D.; Ball, D.L.; Peters, L.J. Early FDG-PET imaging after radical radiotherapy for non–small-cell lung cancer: Inflammatory changes in normal tissues correlate with tumor response and do not confound therapeutic response evaluation. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2004, 60, 412–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larici, A.R.; Del Ciello, A.; Maggi, F.; Santoro, S.I.; Meduri, B.; Valentini, V.; Giordano, A.; Bonomo, L. Lung abnormalities at multimodality imaging after radiation therapy for non–small cell lung cancer. Radiographics 2011, 31, 771–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Baardwijk, A.; Bosmans, G.; Dekker, A.; van Kroonenburgh, M.; Boersma, L.; Wanders, S.; Öllers, M.; Houben, R.; Minken, A.; Lambin, P.; et al. Time trends in the maximal uptake of FDG on PET scan during thoracic radiotherapy. A prospective study in locally advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients. Radiother. Oncol. 2007, 82, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheikhbahaei, S.; Mena, E.; Marcus, C.; Wray, R.; Taghipour, M.; Subramaniam, R.M. 18F-FDG PET/CT: Therapy response assessment interpretation (Hopkins criteria) and survival outcomes in lung cancer patients. J. Nucl. Med. 2016, 57, 855–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Brose, A.; Michalski, K.; Ruf, J.; Tosch, M.; Eschmann, S.M.; Schreckenberger, M.; König, J.; Nestle, U.; Miederer, M. PET/CT reading for relapse in non-small cell lung cancer after chemoradiotherapy in the PET-Plan trial cohort. Cancer Imaging 2023, 23, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Zhang, Z.; Yi, H.; Wang, J.; Li, J.; Wang, X.; Bai, H.; Ge, H.; Zheng, X.; Ni, J.; et al. A PET/CT radiomics model for predicting distant metastasis in early-stage non–small cell lung cancer patients treated with stereotactic body radiotherapy: A multicentric study. Radiat. Oncol. 2024, 19, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianconi, F.; Palumbo, I.; Spanu, A.; Nuvoli, S.; Fravolini, M.L.; Palumbo, B. PET/CT radiomics in lung cancer: An overview. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattonen, S.A.; Palma, D.A.; Johnson, C.; Louie, A.V.; Landis, M.; Rodrigues, G.; Chan, I.; Etemad-Rezai, R.; Yeung, T.P.; Senan, S.; et al. Detection of Local Cancer Recurrence after Stereotactic Ablative Radiation Therapy for Lung Cancer: Physician Performance versus Radiomic Assessment. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2016, 94, 1121–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Dohopolski, M.; Zhou, Z.; Wang, K.; Wang, R.; Sher, D.; Wang, J. Attention guided lymph node malignancy prediction in head and neck cancer. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2021, 110, 1171–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Zhou, Z.; Sher, D.; Zhang, Q.; Shah, J.; Pham, N.-L.; Jiang, S.; Wang, J. Combining many-objective radiomics and 3D convolutional neural network through evidential reasoning to predict lymph node metastasis in head and neck cancer. Phys. Med. Biol. 2019, 64, 075011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Shen, C.; Zhou, Z.; Maquilan, G.; Thomas, K.; Folkert, M.R.; Albuquerque, K.; Wang, J. Accurate segmenting of cervical tumors in PET imaging based on similarity between adjacent slices. Comput. Biol. Med. 2018, 97, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haralick, R.M.; Shanmugam, K.; Dinstein, I.H. Textural features for image classification. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. 1973, SMC-3, 610–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xinli, W.; Albregtsen, F.; Foyn, B. Texture Features from Gray Level Gap Length Matrix. In Proceedings of the MVA’94 IAPR Workshop on Machine Vision Applications, Kawasaki, Japan, 13–15 December 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Thibault, G.; Angulo, J.; Meyer, F. Advanced statistical matrices for texture characterization: Application to cell classification. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2013, 61, 630–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amadasun, M.; King, R. Textural features corresponding to textural properties. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. 1989, 19, 1264–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.-M.; Yang, J.-B.; Xu, D.-L. Environmental impact assessment using the evidential reasoning approach. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2006, 174, 1885–1913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Niu, R.; Shi, Y.; Shao, X.; Jiang, Z.; Ge, X.; Wang, Y.; Shao, X. The predictive value of [18F] FDG PET/CT radiomics combined with clinical features for EGFR mutation status in different clinical staging of lung adenocarcinoma. EJNMMI Res. 2023, 13, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timmerman, R.; Paulus, R.; Galvin, J.; Michalski, J.; Straube, W.; Bradley, J.; Fakiris, A.; Bezjak, A.; Videtic, G.; Johnstone, D.; et al. Stereotactic body radiation therapy for inoperable early stage lung cancer. JAMA 2010, 303, 1070–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdi, Y.E.; Macapinlac, H.; Rosenzweig, K.E.; Humm, J.L.; Larson, S.M.; Erdi, A.K.; Yorke, E.D. Use of PET to monitor the response of lung cancer to radiation treatment. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. 2000, 27, 861–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mattonen, S.A.; Palma, D.A.; Haasbeek, C.J.; Senan, S.; Ward, A.D. Early prediction of tumor recurrence based on CT texture changes after stereotactic ablative radiotherapy (SABR) for lung cancer. Med. Phys. 2014, 41, 033502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wankhade, S.; Vigneshwari, S. A novel hybrid deep learning method for early detection of lung cancer using neural networks. Healthc. Anal. 2023, 3, 100195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).