Optimizing Automated Brain Extraction for Moderate to Severe Traumatic Brain Injury Patients: The Role of Intensity Normalization and Bias-Field Correction
Abstract
1. Introduction
Challenges to Preprocessing of Multi-Site TBI MRI Data
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. MRI Acquisition
2.3. Gold-Standard Brain Extraction Protocol
2.4. Brain Extraction Pipelines
Extraction Configurations
2.5. Intensity Processing Procedures
2.5.1. N3 Inhomogeneity Correction
2.5.2. Z-Score Intensity Normalization
2.5.3. KDE Intensity Normalization
2.5.4. WhiteStripe Intensity Normalization
2.6. Quality Assessment
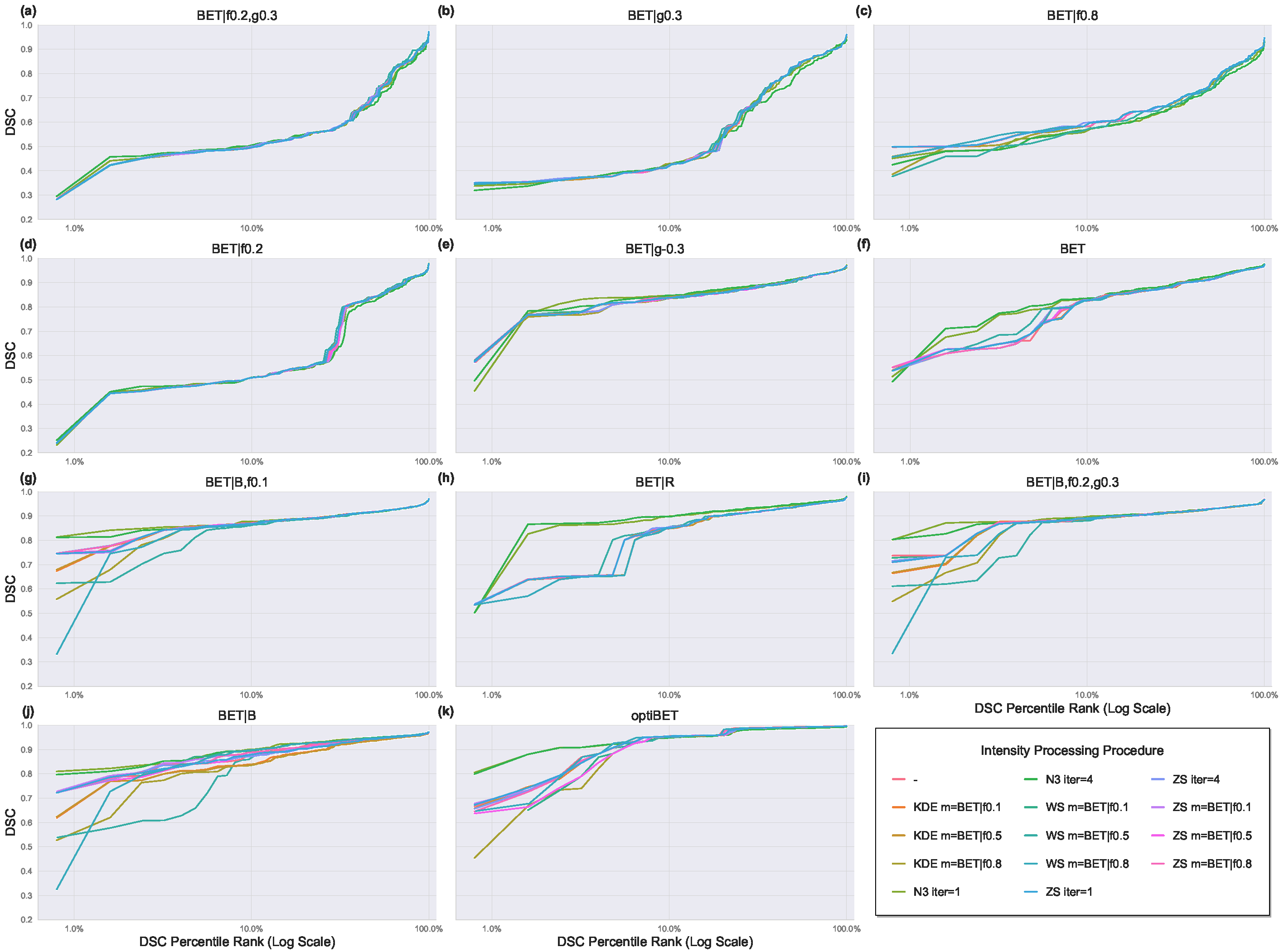
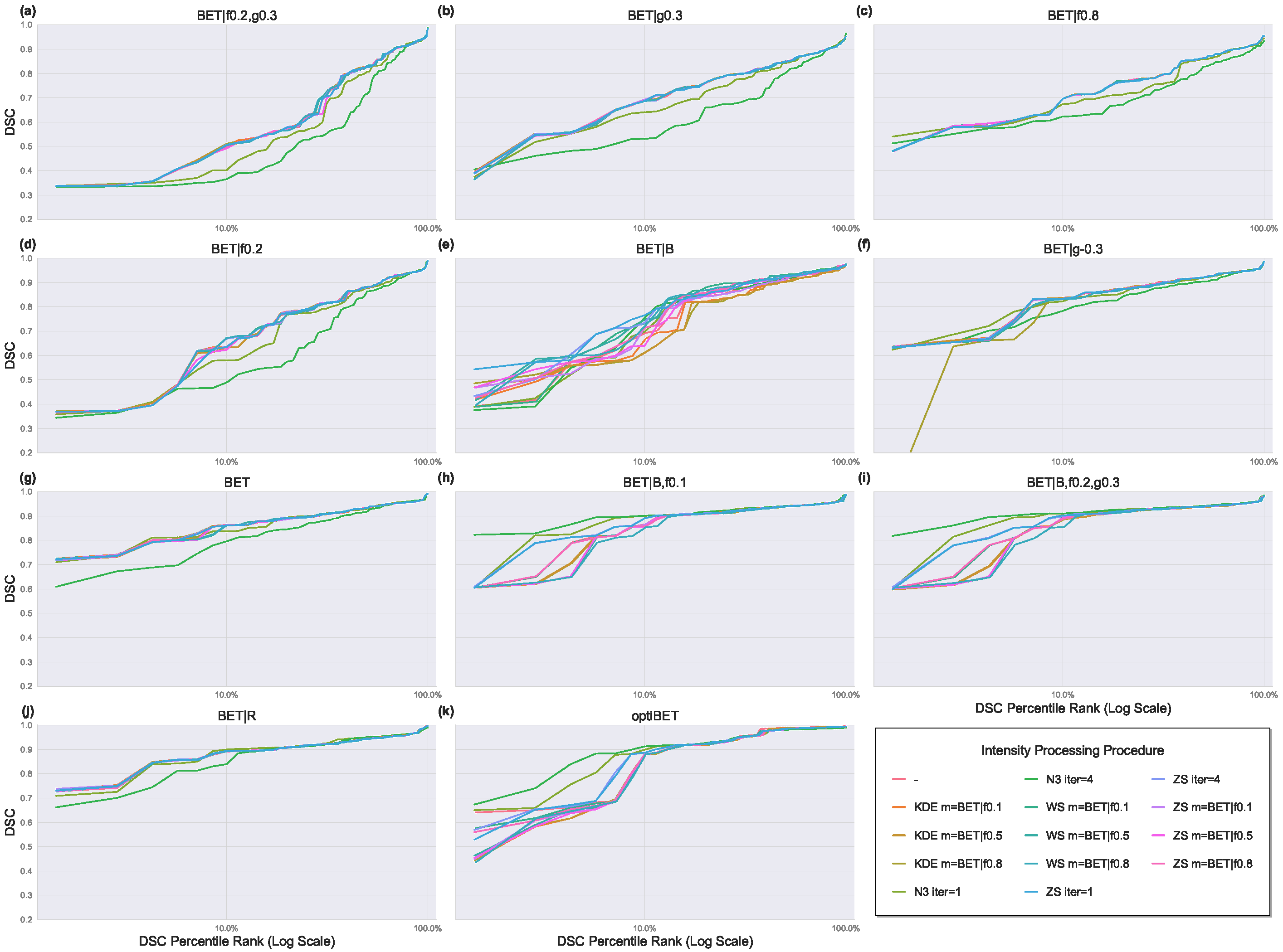
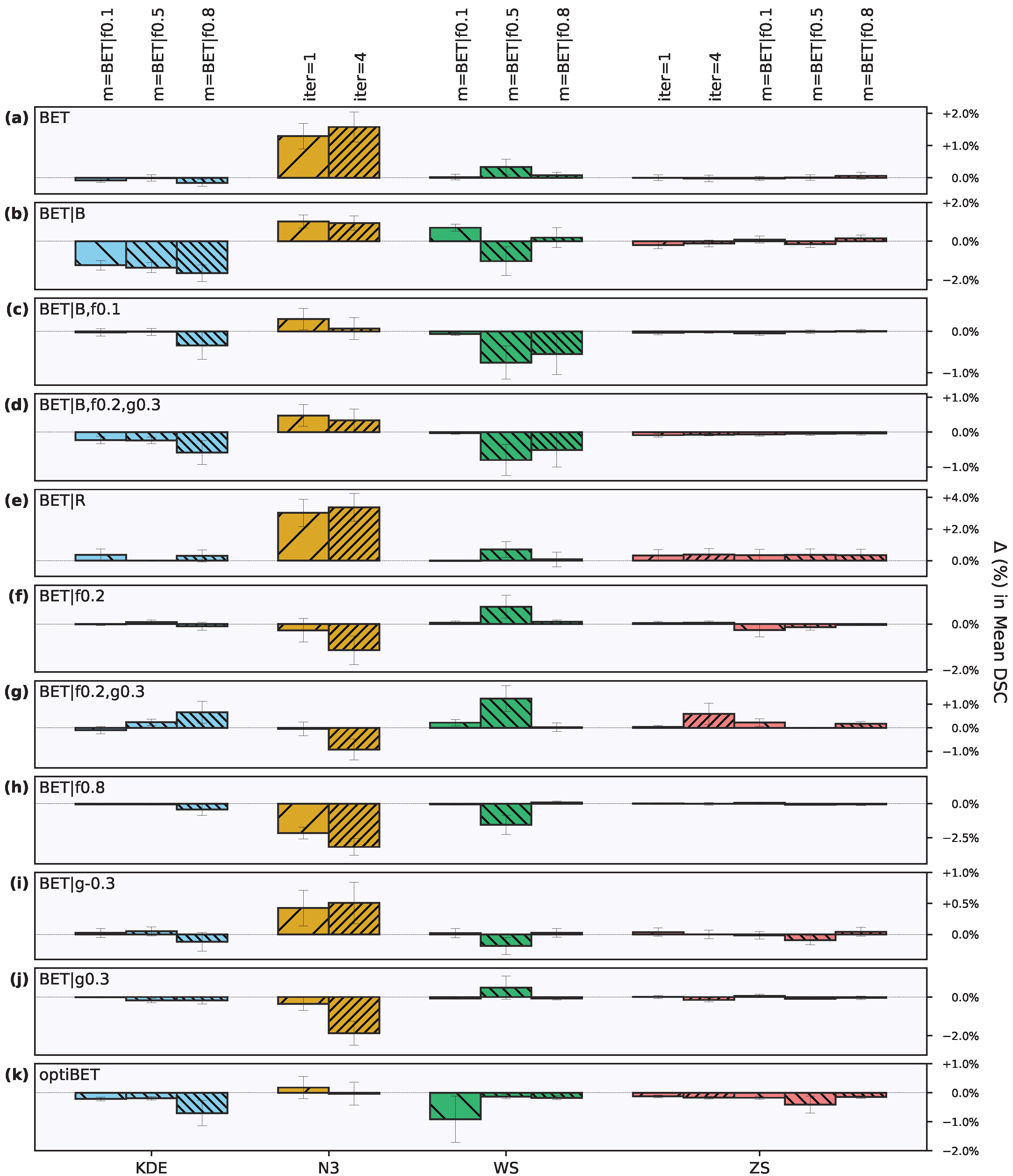
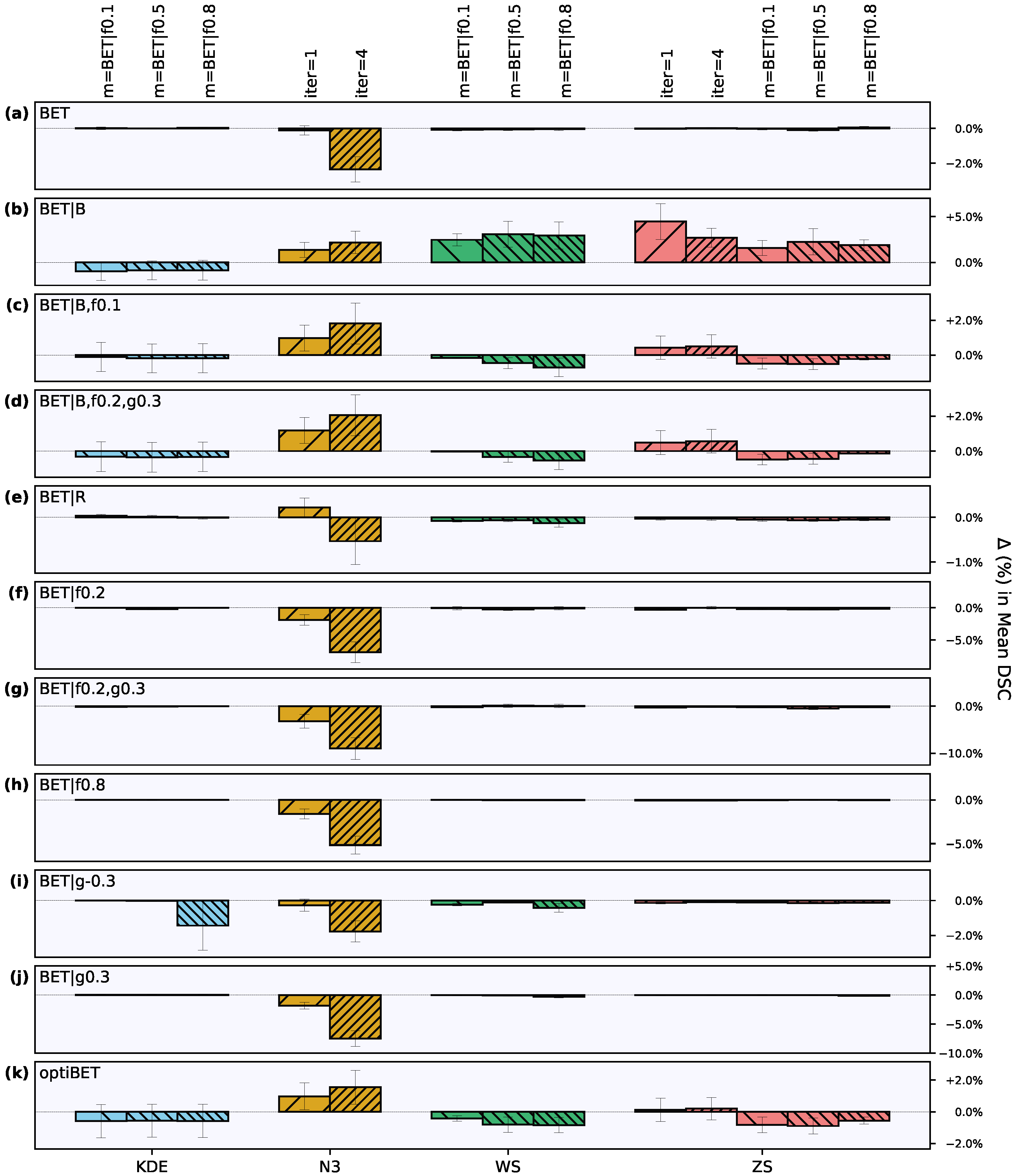
3. Results
3.1. Effect of BET Parameter Configurations
3.2. Effect of Intensity Processing Procedures
3.2.1. Intensity Inhomogeneity Correction
3.2.2. Intensity Normalization
4. Discussion
4.1. Limitations
4.2. Future Work
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ADNI | Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative |
| AIDS | Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome |
| ANTS | Advanced Normalization Tools |
| BET | Brain Extraction Tool |
| CNS | Central Nervous System |
| CT | Computed Tomography |
| COVID-19 | Coronavirus Disease 2019 |
| DSC | Dice similarity coefficient |
| DOAJ | Directory of Open Access Journals |
| EEG | Electroencephalography |
| Ex. Config. | Extraction configuration |
| FLIRT | FMRIB’s Linear Image Registration Tool |
| FNIRT | FMRIB’s Non-linear Image Registration Tool |
| FSL | FMRIB Software Library |
| GCS | Glasgow Coma Scale |
| HIV | Human Immunodeficiency Virus |
| IP | Intensity processing |
| Iter. | Iteration(s) |
| KDE | Kernel density estimation |
| MINC | Medical Imaging NetCDF |
| MNI | Montreal Neurological Institute |
| MRI | Magnetic Resonance Imaging |
| MDPI | Multidisciplinary Digital Publishing Institute |
| N3 | Nonparametric Nonuniform Intensity Normalization |
| OptiBET | Optimized Brain Extraction Tool |
| PTE | Post-traumatic epilepsy |
| T1-MPRAGE | T1-weighted Magnetization-Prepared Rapid Gradient Echo |
| T2-FLAIR | T2-weighted Fluid-Attenuated Inversion Recovery |
| TBI | Traumatic brain injury |
| WS | WhiteStripe |
| ZS | Z-score |
References
- Georges, A.; Das, J.M. Traumatic Brain Injury; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Asikainen, I.; Kaste, M.; Sarna, S. Early and late posttraumatic seizures in traumatic brain injury rehabilitation patients: Brain injury factors causing late seizures and influence of seizures on long-term outcome. Epilepsia 1999, 40, 584–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Englander, J.; Bushnik, T.; Wright, J.M.; Jamison, L.; Duong, T.T. Mortality in late post-traumatic seizures. J. Neurotrauma 2009, 26, 1471–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lowenstein, D.H. Epilepsy after head injury: An overview. Epilepsia 2009, 50 (Suppl. S2), 4–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, J.; Pedersen, M.G.; Pedersen, C.B.; Sidenius, P.; Olsen, J.; Vestergaard, M. Long-term risk of epilepsy after traumatic brain injury in children and young adults: A population-based cohort study. Lancet 2009, 373, 1105–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolkvadze, T.; Pitkänen, A. Development of post-traumatic epilepsy after controlled cortical impact and lateral fluid-percussion-induced brain injury in the mouse. J. Neurotrauma 2012, 29, 789–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garner, R.; La Rocca, M.; Vespa, P.; Jones, N.; Monti, M.M.; Toga, A.W.; Duncan, D. Imaging biomarkers of posttraumatic epileptogenesis. Epilepsia 2019, 60, 2151–2162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vespa, P.M.; Shrestha, V.; Abend, N.; Agoston, D.; Au, A.; Bell, M.J.; Bleck, T.P.; Blanco, M.B.; Claassen, J.; Diaz-Arrastia, R.; et al. The epilepsy bioinformatics study for anti-epileptogenic therapy (EpiBioS4Rx) clinical biomarker: Study design and protocol. Neurobiol. Dis. 2019, 123, 110–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Covington, N.V.; Duff, M.C. Heterogeneity is a hallmark of traumatic brain injury, not a limitation: A new perspective on study design in rehabilitation research. Am. J. Speech. Lang. Pathol. 2021, 30, 974–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maas, A.I.R.; Menon, D.K.; Manley, G.T.; Abrams, M.; Åkerlund, C.; Andelic, N.; Aries, M.; Bashford, T.; Bell, M.J.; Bodien, Y.G.; et al. Traumatic brain injury: Progress and challenges in prevention, clinical care, and research. Lancet Neurol. 2022, 21, 1004–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bigler, E.D. The lesion(s) in traumatic brain injury: Implications for clinical neuropsychology. Arch. Clin. Neuropsychol. 2001, 16, 95–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huisman, T.A.G.M.; Schwamm, L.H.; Schaefer, P.W.; Koroshetz, W.J.; Shetty-Alva, N.; Ozsunar, Y.; Wu, O.; Sorensen, A.G. Diffusion tensor imaging as potential biomarker of white matter injury in diffuse axonal injury. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2004, 25, 370–376. [Google Scholar]
- Nasrallah, F.; Bellapart, J.; Walsham, J.; Jacobson, E.; To, X.V.; Manzanero, S.; Brown, N.; Meyer, J.; Stuart, J.; Evans, T.; et al. PREdiction and Diagnosis using Imaging and Clinical biomarkers Trial in Traumatic Brain Injury (PREDICT-TBI) study protocol: An observational, prospective, multicentre cohort study for the prediction of outcome in moderate-to-severe TBI. BMJ Open 2023, 13, e067740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warner, M.A.; Marquez de la Plata, C.; Spence, J.; Wang, J.Y.; Harper, C.; Moore, C.; Devous, M.; Diaz-Arrastia, R. Assessing spatial relationships between axonal integrity, regional brain volumes, and neuropsychological outcomes after traumatic axonal injury. J. Neurotrauma 2010, 27, 2121–2130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, K.; Johnson, B.; Pennell, D.; Ray, W.; Sebastianelli, W.; Slobounov, S. Are functional deficits in concussed individuals consistent with white matter structural alterations: Combined FMRI & DTI study. Exp. Brain Res. 2010, 204, 57–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bennett, A.; Garner, R.; Morris, M.D.; La Rocca, M.; Barisano, G.; Cua, R.; Loon, J.; Alba, C.; Carbone, P.; Gao, S.; et al. Manual lesion segmentations for traumatic brain injury characterization. Front. Neuroimaging 2023, 2, 1068591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, S.M. Fast robust automated brain extraction. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2002, 17, 143–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, S.M.; Jenkinson, M.; Woolrich, M.W.; Beckmann, C.F.; Behrens, T.E.J.; Johansen-Berg, H.; Bannister, P.R.; De Luca, M.; Drobnjak, I.; Flitney, D.E.; et al. Advances in functional and structural MR image analysis and implementation as FSL. Neuroimage 2004, 23 (Suppl. S1), S208–S219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scopus. 8342 Documents Have Cited: Fast Robust Automated Brain Extraction Smith S.M. (2002) Human Brain Mapping, 17 (3), pp. 143–155. Available online: https://www.scopus.com/results/citedbyresults.uri?sort=plf-f&cite=2-s2.0-0036828879&src=s&imp=t&sid=8fa0fec092d5bcc0661e21ce7b2e1e9e&sot=cite&sdt=a&sl=0&origin=resultslist&editSaveSearch=&txGid=b816cbfcb73daa270492f0a967f89de4 (accessed on 16 March 2024).
- Lutkenhoff, E.S.; Rosenberg, M.; Chiang, J.; Zhang, K.; Pickard, J.D.; Owen, A.M.; Monti, M.M. Optimized brain extraction for pathological brains (optiBET). PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e115551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iglesias, J.E.; Liu, C.Y.; Thompson, P.M.; Tu, Z. Robust brain extraction across datasets and comparison with publicly available methods. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2011, 30, 1617–1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carass, A.; Cuzzocreo, J.; Wheeler, M.B.; Bazin, P.L.; Resnick, S.M.; Prince, J.L. Simple paradigm for extra-cerebral tissue removal: Algorithm and analysis. Neuroimage 2011, 56, 1982–1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Eskildsen, S.F.; Coupé, P.; Fonov, V.; Manjón, J.V.; Leung, K.K.; Guizard, N.; Wassef, S.N.; Østergaard, L.R.; Collins, D.L.; Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative. BEaST: Brain extraction based on nonlocal segmentation technique. Neuroimage 2012, 59, 2362–2373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, S.; Butman, J.A.; Pham, D.L.; Alzheimers Disease Neuroimaging Initiative. Robust skull stripping using multiple MR image contrasts insensitive to pathology. Neuroimage 2017, 146, 132–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hajnal, J.V.; Bryant, D.J.; Kasuboski, L.; Pattany, P.M.; De Coene, B.; Lewis, P.D.; Pennock, J.M.; Oatridge, A.; Young, I.R.; Bydder, G.M. Use of fluid attenuated inversion recovery (FLAIR) pulse sequences in MRI of the brain. J. Comput. Assist. Tomogr. 1992, 16, 841–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganzetti, M.; Wenderoth, N.; Mantini, D. Intensity inhomogeneity correction of structural MR images: A data-driven approach to define input algorithm parameters. Front. Neuroinform. 2016, 10, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chua, Z.Y.; Zheng, W.; Chee, M.W.L.; Zagorodnov, V. Evaluation of performance metrics for bias field correction in MR brain images. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2009, 29, 1271–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nyúl, L.G.; Udupa, J.K.; Zhang, X. New variants of a method of MRI scale standardization. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2000, 19, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhuge, Y.; Udupa, J.K.; Liu, J.; Saha, P.K. Image background inhomogeneity correction in MRI via intensity standardization. Comput. Med. Imaging Graph. 2009, 33, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sled, J.G.; Zijdenbos, A.P.; Evans, A.C. A nonparametric method for automatic correction of intensity nonuniformity in MRI data. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 1998, 17, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reinhold, J.C.; Dewey, B.E.; Carass, A.; Prince, J.L. Evaluating the impact of intensity normalization on MR image synthesis. Proc. SPIE Int. Soc. Opt. Eng. 2019, 10949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkinson, M.; Beckmann, C.F.; Behrens, T.E.J.; Woolrich, M.W.; Smith, S.M. FSL. Neuroimage 2012, 62, 782–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rorden, C.; Brett, M. Stereotaxic display of brain lesions. Behav. Neurol. 2000, 12, 191–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yushkevich, P.A.; Piven, J.; Hazlett, H.C.; Smith, R.G.; Ho, S.; Gee, J.C.; Gerig, G. User-guided 3D active contour segmentation of anatomical structures: Significantly improved efficiency and reliability. Neuroimage 2006, 31, 1116–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCarthy, P. FSLeyes. Available online: https://zenodo.org/records/10122614 (accessed on 18 March 2024).
- Popescu, V.; Battaglini, M.; Hoogstrate, W.S.; Verfaillie, S.C.J.; Sluimer, I.C.; van Schijndel, R.A.; van Dijk, B.W.; Cover, K.S.; Knol, D.L.; Jenkinson, M.; et al. Optimizing parameter choice for FSL-Brain Extraction Tool (BET) on 3D T1 images in multiple sclerosis. Neuroimage 2012, 61, 1484–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischl, B. FreeSurfer. Neuroimage 2012, 62, 774–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jack, R.C., Jr.; Bernstein, M.A.; Fox, N.C.; Thompson, P.; Alexander, G.; Harvey, D.; Borowski, B.; Britson, P.J.; Whitwell, J.L.; Ward, C.; et al. The Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative (ADNI): MRI methods. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2008, 27, 685–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinohara, R.T.; Sweeney, E.M.; Goldsmith, J.; Shiee, N.; Mateen, F.J.; Calabresi, P.A.; Jarso, S.; Pham, D.L.; Reich, D.S.; Crainiceanu, C.M.; et al. Statistical normalization techniques for magnetic resonance imaging. Neuroimage Clin. 2014, 6, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyes, R.G.; Gunter, J.L.; Frost, C.; Janke, A.L.; Yeatman, T.; Hill, D.L.G.; Bernstein, M.A.; Thompson, P.M.; Weiner, M.W.; Schuff, N.; et al. Intensity non-uniformity correction using N3 on 3-T scanners with multichannel phased array coils. Neuroimage 2008, 39, 1752–1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belaroussi, B.; Milles, J.; Carme, S.; Zhu, Y.M.; Benoit-Cattin, H. Intensity non-uniformity correction in MRI: Existing methods and their validation. Med. Image Anal. 2006, 10, 234–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monereo-Sánchez, J.; de Jong, J.J.A.; Drenthen, G.S.; Beran, M.; Backes, W.H.; Stehouwer, C.D.A.; Schram, M.T.; Linden, D.E.J.; Jansen, J.F.A. Quality control strategies for brain MRI segmentation and parcellation: Practical approaches and recommendations-insights from the Maastricht study. Neuroimage 2021, 237, 118174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Primary Option | Option “f” and “g” Values | Label | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BET | - | - | BET | Default BET configuration (f = 0.5 and g = 0). |
| f 0.2 | - | BET|f0.2 | Generates larger brain outline estimates. | |
| f 0.8 | - | BET|f0.8 | Generates smaller brain outline estimates. | |
| - | g -0.3 | BET|g-0.3 | Generates smaller brain outline estimates at the bottom of the image and a larger outline at the top. | |
| - | g 0.3 | BET|g0.3 | Generates a larger outline at the bottom of the image and a smaller outline at the top. | |
| f 0.2 | g 0.3 | BET|f0.2,g0.3 | Generates a larger brain outline estimate, with the bottom of the image having a larger estimate relative to the top. | |
| BET|B | - | - | BET|B | Performs FAST bias-field correction and standard-space masking for image bias-field reduction and neck voxel cleanup. |
| f 0.1 | - | BET|B,f0.1 | Performs bias-field correction and generates a larger brain outline estimate. | |
| f 0.2 | g 0.3 | BET|B,f0.2,g0.3 | Performs bias-field correction and generates a larger brain outline estimate, with the bottom of the image having a larger estimate relative to the top. | |
| BET|R | - | - | BET|R | Runs BET iteratively for robust brain center estimation. |
| optiBET | f 0.1 | - | optiBET | Performs BET|B,f0.1 for the initial extraction and then FLIRT and FNIRT to generate the final extraction by masking the input image with a back-projected standard brain mask. |
| IP | Iter. | Mask | Label | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N3 | 1 | - | N3 iter = 1 | 1 iteration of N3 inhomogeneity correction without a mask. |
| 4 | - | N3 iter = 4 | 4 iterations of N3 without a mask (FreeSurfer default). | |
| ZS | 1 | - | ZS iter = 1 | 1 iteration of Z-score intensity normalization without a mask. |
| 4 | - | ZS iter = 4 | 4 iterations of Z-score int. norm. without a mask. | |
| 1 | BETf0.1 | ZS m = BETf0.1 | 1 iteration of Z-score with a BETf0.1-extracted mask. | |
| 1 | BETf0.5 | ZS m = BETf0.5 | 1 iteration of Z-score with a BETf0.5-extracted mask. | |
| 1 | BETf0.8 | ZS m = BETf0.8 | 1 iteration of Z-score with a BETf0.8-extracted mask. | |
| KDE | 1 | BETf0.1 | KDE m = BETf0.1 | 1 iteration of KDE-based intensity normalization with a BETf0.1-extracted mask. |
| 1 | BETf0.5 | KDE m = BETf0.5 | 1 iteration of KDE with a BETf0.5-extracted mask. | |
| 1 | BETf0.8 | KDE m = BETf0.8 | 1 iteration of KDE with a BETf0.8-extracted mask. | |
| WS | 1 | BETf0.1 | WS m = BETf0.1 | 1 iteration of WhiteStripe intensity normalization with a BETf0.1-extracted mask. |
| 1 | BETf0.5 | WS m = BETf0.5 | 1 iteration of WhiteStripe with a BETf0.5-extracted mask. | |
| 1 | BETf0.8 | WS m = BETf0.8 | 1 iteration of WhiteStripe with a BETf0.8-extracted mask. | |
| - | - | - | - | No intensity processing procedure (control). |
| T1-MPRAGE | T2-FLAIR | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Brain Extraction Pipeline | DSC | Brain Extraction Pipeline | DSC | ||||
| Ex. Config. | IP Procedure | Mean | SD | Ex. Config. | IP Procedure | Mean | SD |
| optiBET | N3 iter = 1 | 0.9780 | 0.0259 | optiBET | N3 iter = 4 | 0.9557 | 0.0544 |
| optiBET | - | 0.9779 | 0.0455 | optiBET | N3 iter = 1 | 0.9525 | 0.0676 |
| optiBET | WS m = BET|f0.8 | 0.9769 | 0.0488 | optiBET | ZS iter = 4 | 0.9475 | 0.0845 |
| optiBET | ZS iter = 1 | 0.9766 | 0.0447 | optiBET | - | 0.9471 | 0.0882 |
| optiBET | ZS m = BET|f0.8 | 0.9766 | 0.0471 | optiBET | ZS iter = 1 | 0.9470 | 0.0874 |
| optiBET | WS m = BET|f0.5 | 0.9766 | 0.0454 | optiBET | WS m = BET|f0.1 | 0.9438 | 0.0926 |
| optiBET | ZS iter = 4 | 0.9763 | 0.0462 | optiBET | ZS m = BET|f0.8 | 0.9427 | 0.0944 |
| optiBET | ZS m = BET|f0.1 | 0.9762 | 0.0450 | optiBET | WS m = BET|f0.5 | 0.9410 | 0.1025 |
| optiBET | KDE m = BET|f0.5 | 0.9761 | 0.0459 | optiBET | KDE m = BET|f0.5 | 0.9409 | 0.1049 |
| optiBET | N3 iter = 4 | 0.9759 | 0.0265 | optiBET | WS m = BET|f0.8 | 0.9409 | 0.1030 |
| optiBET | KDE m = BET|f0.1 | 0.9759 | 0.0460 | optiBET | KDE m = BET|f0.8 | 0.9408 | 0.1052 |
| optiBET | ZS m = BET|f0.5 | 0.9739 | 0.0545 | optiBET | ZS m = BET|f0.1 | 0.9408 | 0.1025 |
| optiBET | KDE m = BET|f0.8 | 0.9711 | 0.0668 | optiBET | KDE m = BET|f0.1 | 0.9407 | 0.1057 |
| optiBET | WS m = BET|f0.1 | 0.9690 | 0.0988 | optiBET | ZS m = BET|f0.5 | 0.9404 | 0.1040 |
| BET|B | N3 iter = 1 | 0.9391 | 0.0299 | BET|B,f0.2,g0.3 | N3 iter = 4 | 0.9384 | 0.0249 |
| BET|R | N3 iter = 4 | 0.9383 | 0.0466 | BET|R | N3 iter = 1 | 0.9343 | 0.0493 |
| BET|B | N3 iter = 4 | 0.9382 | 0.0314 | BET|B,f0.1 | N3 iter = 4 | 0.9342 | 0.0293 |
| BET|B | WS m = BET|f0.1 | 0.9368 | 0.0363 | BET|B,f0.2,g0.3 | N3 iter = 1 | 0.9333 | 0.0474 |
| BET|R | N3 iter = 1 | 0.9352 | 0.0480 | BET|R | KDE m = BET|f0.1 | 0.9324 | 0.0458 |
| BET|B | WS m = BET|f0.8 | 0.9325 | 0.0652 | BET|R | KDE m = BET|f0.5 | 0.9322 | 0.0460 |
| BET|B | ZS m = BET|f0.8 | 0.9317 | 0.0389 | BET|R | KDE m = BET|f0.8 | 0.9320 | 0.0464 |
| BET|B | ZS m = BET|f0.1 | 0.9311 | 0.0381 | BET|R | ZS iter = 1 | 0.9318 | 0.0463 |
| BET|B | - | 0.9306 | 0.0403 | BET|R | ZS iter = 4 | 0.9318 | 0.0458 |
| BET|B | ZS iter = 4 | 0.9294 | 0.0409 | BET|R | ZS m = BET|f0.8 | 0.9317 | 0.0466 |
| BET|B | ZS m = BET|f0.5 | 0.9292 | 0.0419 | BET|R | ZS m = BET|f0.1 | 0.9316 | 0.0458 |
| BET|B | ZS iter = 1 | 0.9286 | 0.0405 | BET|R | ZS m = BET|f0.5 | 0.9315 | 0.0466 |
| BET|B,f0.2,g0.3 | N3 iter = 1 | 0.9262 | 0.0234 | BET|R | WS m = BET|f0.5 | 0.9315 | 0.0464 |
| BET|B,f0.2,g0.3 | N3 iter = 4 | 0.9249 | 0.0256 | BET|R | WS m = BET|f0.1 | 0.9314 | 0.0467 |
| BET|B,f0.2,g0.3 | - | 0.9226 | 0.0330 | BET|R | - | 0.9312 | 0.0467 |
| BET|B,f0.2,g0.3 | ZS m = BET|f0.8 | 0.9223 | 0.0343 | BET|R | WS m = BET|f0.8 | 0.9309 | 0.0461 |
| BET|B,f0.2,g0.3 | WS m = BET|f0.1 | 0.9223 | 0.0335 | BET|B,f0.1 | N3 iter = 1 | 0.9294 | 0.0491 |
| BET|B,f0.2,g0.3 | ZS m = BET|f0.5 | 0.9222 | 0.0341 | BET|B,f0.2,g0.3 | ZS iter = 4 | 0.9280 | 0.0510 |
| BET|B,f0.2,g0.3 | ZS m = BET|f0.1 | 0.9221 | 0.0342 | BET|B,f0.2,g0.3 | ZS iter = 1 | 0.9274 | 0.0518 |
| BET|B,f0.2,g0.3 | ZS iter = 4 | 0.9220 | 0.0340 | BET|R | N3 iter = 4 | 0.9273 | 0.0616 |
| BET|B,f0.2,g0.3 | ZS iter = 1 | 0.9218 | 0.0343 | BET|B,f0.1 | ZS iter = 4 | 0.9255 | 0.0523 |
| BET|B,f0.2,g0.3 | KDE m = BET|f0.1 | 0.9207 | 0.0382 | BET|B,f0.1 | ZS iter = 1 | 0.9249 | 0.0527 |
| BET|B,f0.2,g0.3 | KDE m = BET|f0.5 | 0.9206 | 0.0378 | BET|B,f0.2,g0.3 | - | 0.9247 | 0.0615 |
| BET|B | WS m = BET|f0.5 | 0.9205 | 0.0810 | BET|B,f0.2,g0.3 | WS m = BET|f0.1 | 0.9244 | 0.0615 |
| BET|B | KDE m = BET|f0.1 | 0.9193 | 0.0513 | BET|B,f0.2,g0.3 | ZS m = BET|f0.8 | 0.9235 | 0.0614 |
| BET|B | KDE m = BET|f0.5 | 0.9182 | 0.0519 | BET|B,f0.1 | - | 0.9227 | 0.0621 |
| BET|B,f0.2,g0.3 | WS m = BET|f0.8 | 0.9181 | 0.0622 | BET|B,f0.2,g0.3 | WS m = BET|f0.5 | 0.9220 | 0.0693 |
| BET|R | WS m = BET|f0.5 | 0.9179 | 0.0694 | BET|B,f0.1 | WS m = BET|f0.1 | 0.9213 | 0.0620 |
| BET|B,f0.2,g0.3 | KDE m = BET|f0.8 | 0.9174 | 0.0502 | BET|B,f0.2,g0.3 | ZS m = BET|f0.5 | 0.9211 | 0.0694 |
| BET|R | ZS iter = 4 | 0.9158 | 0.0729 | BET|B,f0.2,g0.3 | ZS m = BET|f0.1 | 0.9207 | 0.0694 |
| BET|R | KDE m = BET|f0.1 | 0.9157 | 0.0731 | BET|B,f0.1 | ZS m = BET|f0.8 | 0.9206 | 0.0621 |
| BET|R | ZS m = BET|f0.5 | 0.9156 | 0.0731 | BET|B,f0.2,g0.3 | KDE m = BET|f0.1 | 0.9203 | 0.0676 |
| BET|R | ZS m = BET|f0.8 | 0.9155 | 0.0732 | BET|B,f0.2,g0.3 | KDE m = BET|f0.8 | 0.9202 | 0.0673 |
| BET|R | ZS m = BET|f0.1 | 0.9155 | 0.0731 | BET|B,f0.1 | KDE m = BET|f0.1 | 0.9202 | 0.0676 |
| BET|B | KDE m = BET|f0.8 | 0.9154 | 0.0625 | BET|B,f0.2,g0.3 | KDE m = BET|f0.5 | 0.9199 | 0.0672 |
| BET|R | ZS iter = 1 | 0.9154 | 0.0732 | BET | ZS m = BET|f0.8 | 0.9197 | 0.0518 |
| BET|B,f0.2,g0.3 | WS m = BET|f0.5 | 0.9152 | 0.0570 | BET | KDE m = BET|f0.8 | 0.9196 | 0.0523 |
| BET|R | KDE m = BET|f0.8 | 0.9150 | 0.0734 | BET|B,f0.2,g0.3 | WS m = BET|f0.8 | 0.9195 | 0.0709 |
| BET|B,f0.1 | N3 iter = 1 | 0.9142 | 0.0280 | BET|B,f0.1 | KDE m = BET|f0.8 | 0.9195 | 0.0673 |
| BET|R | - | 0.9133 | 0.0768 | BET|B,f0.1 | KDE m = BET|f0.5 | 0.9195 | 0.0673 |
| BET|R | KDE m = BET|f0.5 | 0.9133 | 0.0769 | BET | ZS iter = 4 | 0.9193 | 0.0525 |
| BET|R | WS m = BET|f0.8 | 0.9132 | 0.0793 | BET | KDE m = BET|f0.1 | 0.9193 | 0.0527 |
| BET|R | WS m = BET|f0.1 | 0.9131 | 0.0771 | BET | - | 0.9193 | 0.0531 |
| BET|B,f0.1 | N3 iter = 4 | 0.9122 | 0.0301 | BET | KDE m = BET|f0.5 | 0.9193 | 0.0534 |
| BET|B,f0.1 | ZS m = BET|f0.8 | 0.9121 | 0.0339 | BET | ZS iter = 1 | 0.9191 | 0.0524 |
| BET|B,f0.1 | - | 0.9121 | 0.0339 | BET | WS m = BET|f0.8 | 0.9190 | 0.0538 |
| BET|B,f0.1 | KDE m = BET|f0.5 | 0.9121 | 0.0369 | BET | ZS m = BET|f0.1 | 0.9190 | 0.0522 |
| BET|B,f0.1 | ZS m = BET|f0.5 | 0.9120 | 0.0344 | BET|B,f0.1 | WS m = BET|f0.5 | 0.9188 | 0.0696 |
| BET|B,f0.1 | KDE m = BET|f0.1 | 0.9120 | 0.0372 | BET | WS m = BET|f0.5 | 0.9188 | 0.0536 |
| BET|B,f0.1 | ZS iter = 4 | 0.9119 | 0.0339 | BET | WS m = BET|f0.1 | 0.9187 | 0.0535 |
| BET|B,f0.1 | ZS iter = 1 | 0.9118 | 0.0348 | BET|B,f0.1 | ZS m = BET|f0.1 | 0.9186 | 0.0700 |
| BET|B,f0.1 | ZS m = BET|f0.1 | 0.9117 | 0.0350 | BET|B,f0.1 | ZS m = BET|f0.5 | 0.9184 | 0.0700 |
| BET|B,f0.1 | WS m = BET|f0.1 | 0.9113 | 0.0348 | BET | ZS m = BET|f0.5 | 0.9184 | 0.0537 |
| BET | N3 iter = 4 | 0.9097 | 0.0639 | BET | N3 iter = 1 | 0.9181 | 0.0549 |
| BET|B,f0.1 | KDE m = BET|f0.8 | 0.9090 | 0.0485 | BET|B,f0.1 | WS m = BET|f0.8 | 0.9159 | 0.0710 |
| BET | N3 iter = 1 | 0.9075 | 0.0653 | BET|g-0.3 | KDE m = BET|f0.1 | 0.9051 | 0.0672 |
| BET|B,f0.1 | WS m = BET|f0.8 | 0.9073 | 0.0620 | BET|g-0.3 | - | 0.9050 | 0.0672 |
| BET|B,f0.1 | WS m = BET|f0.5 | 0.9052 | 0.0533 | BET|g-0.3 | KDE m = BET|f0.5 | 0.9048 | 0.0678 |
| BET|g-0.3 | N3 iter = 4 | 0.9029 | 0.0537 | BET|g-0.3 | ZS iter = 4 | 0.9042 | 0.0680 |
| BET|g-0.3 | N3 iter = 1 | 0.9025 | 0.0560 | BET|g-0.3 | ZS m = BET|f0.1 | 0.9042 | 0.0683 |
| BET | WS m = BET|f0.5 | 0.9000 | 0.0711 | BET|g-0.3 | WS m = BET|f0.5 | 0.9040 | 0.0682 |
| BET|g-0.3 | KDE m = BET|f0.5 | 0.8991 | 0.0527 | BET|g-0.3 | ZS m = BET|f0.8 | 0.9040 | 0.0685 |
| BET|g-0.3 | ZS m = BET|f0.8 | 0.8990 | 0.0527 | BET|g-0.3 | ZS iter = 1 | 0.9039 | 0.0683 |
| BET|g-0.3 | ZS iter = 1 | 0.8990 | 0.0530 | BET|g-0.3 | ZS m = BET|f0.5 | 0.9038 | 0.0678 |
| BET|g-0.3 | WS m = BET|f0.8 | 0.8989 | 0.0530 | BET|g-0.3 | WS m = BET|f0.1 | 0.9031 | 0.0698 |
| BET|g-0.3 | WS m = BET|f0.1 | 0.8989 | 0.0528 | BET|g-0.3 | N3 iter = 1 | 0.9020 | 0.0654 |
| BET|g-0.3 | - | 0.8988 | 0.0538 | BET|g-0.3 | WS m = BET|f0.8 | 0.9011 | 0.0691 |
| BET|g-0.3 | ZS iter = 4 | 0.8987 | 0.0536 | BET | N3 iter = 4 | 0.8980 | 0.0793 |
| BET|g-0.3 | ZS m = BET|f0.1 | 0.8986 | 0.0534 | BET|B | ZS iter = 1 | 0.8963 | 0.0823 |
| BET | WS m = BET|f0.8 | 0.8984 | 0.0759 | BET|g-0.3 | KDE m = BET|f0.8 | 0.8917 | 0.1263 |
| BET|g-0.3 | KDE m = BET|f0.1 | 0.8984 | 0.0531 | BET|B | WS m = BET|f0.1 | 0.8917 | 0.1156 |
| BET | ZS m = BET|f0.8 | 0.8983 | 0.0766 | BET|B | WS m = BET|f0.5 | 0.8916 | 0.1048 |
| BET | WS m = BET|f0.1 | 0.8979 | 0.0763 | BET|B | WS m = BET|f0.8 | 0.8904 | 0.1098 |
| BET|g-0.3 | ZS m = BET|f0.5 | 0.8979 | 0.0536 | BET|B | ZS iter = 4 | 0.8895 | 0.1030 |
| BET | ZS iter = 1 | 0.8978 | 0.0769 | BET|g-0.3 | N3 iter = 4 | 0.8883 | 0.0736 |
| BET | - | 0.8978 | 0.0762 | BET|B | N3 iter = 4 | 0.8870 | 0.1142 |
| BET | ZS m = BET|f0.5 | 0.8977 | 0.0758 | BET|B | ZS m = BET|f0.8 | 0.8857 | 0.1128 |
| BET | KDE m = BET|f0.5 | 0.8977 | 0.0769 | BET|B | ZS m = BET|f0.5 | 0.8844 | 0.1073 |
| BET|g-0.3 | KDE m = BET|f0.8 | 0.8976 | 0.0544 | BET|B | N3 iter = 1 | 0.8815 | 0.1148 |
| BET | ZS iter = 4 | 0.8976 | 0.0767 | BET|B | ZS m = BET|f0.1 | 0.8811 | 0.1076 |
| BET | ZS m = BET|f0.1 | 0.8975 | 0.0755 | BET|B | - | 0.8724 | 0.1211 |
| BET | KDE m = BET|f0.1 | 0.8971 | 0.0766 | BET|B | KDE m = BET|f0.5 | 0.8609 | 0.1182 |
| BET|g-0.3 | WS m = BET|f0.5 | 0.8970 | 0.0533 | BET|B | KDE m = BET|f0.1 | 0.8609 | 0.1207 |
| BET | KDE m = BET|f0.8 | 0.8964 | 0.0769 | BET|B | KDE m = BET|f0.8 | 0.8604 | 0.1174 |
| BET|f0.2 | WS m = BET|f0.5 | 0.7776 | 0.1711 | BET|f0.2 | ZS iter = 4 | 0.8361 | 0.1394 |
| BET|f0.2 | WS m = BET|f0.8 | 0.7732 | 0.1702 | BET|f0.2 | KDE m = BET|f0.1 | 0.8361 | 0.1397 |
| BET|f0.2 | KDE m = BET|f0.5 | 0.7732 | 0.1704 | BET|f0.2 | - | 0.8361 | 0.1398 |
| BET|f0.2 | WS m = BET|f0.1 | 0.7730 | 0.1704 | BET|f0.2 | KDE m = BET|f0.8 | 0.8359 | 0.1398 |
| BET|f0.2 | ZS iter = 4 | 0.7730 | 0.1703 | BET|f0.2 | WS m = BET|f0.1 | 0.8353 | 0.1400 |
| BET|f0.2 | ZS iter = 1 | 0.7729 | 0.1705 | BET|f0.2 | WS m = BET|f0.8 | 0.8352 | 0.1398 |
| BET|f0.2 | - | 0.7727 | 0.1709 | BET|f0.2 | ZS m = BET|f0.8 | 0.8348 | 0.1406 |
| BET|f0.2 | KDE m = BET|f0.1 | 0.7726 | 0.1707 | BET|f0.2 | KDE m = BET|f0.5 | 0.8346 | 0.1412 |
| BET|f0.2 | ZS m = BET|f0.8 | 0.7724 | 0.1709 | BET|f0.2 | ZS m = BET|f0.1 | 0.8345 | 0.1410 |
| BET|f0.2 | ZS m = BET|f0.5 | 0.7717 | 0.1715 | BET|f0.2 | ZS m = BET|f0.5 | 0.8344 | 0.1420 |
| BET|f0.2 | KDE m = BET|f0.8 | 0.7715 | 0.1696 | BET|f0.2 | ZS iter = 1 | 0.8341 | 0.1421 |
| BET|f0.2 | ZS m = BET|f0.1 | 0.7704 | 0.1719 | BET|f0.2 | WS m = BET|f0.5 | 0.8341 | 0.1411 |
| BET|f0.2 | N3 iter = 1 | 0.7699 | 0.1724 | BET|f0.8 | KDE m = BET|f0.8 | 0.8333 | 0.0999 |
| BET|f0.2 | N3 iter = 4 | 0.7618 | 0.1700 | BET|f0.8 | WS m = BET|f0.1 | 0.8333 | 0.0995 |
| BET|f0.8 | WS m = BET|f0.8 | 0.7536 | 0.1135 | BET|f0.8 | KDE m = BET|f0.1 | 0.8332 | 0.1001 |
| BET|f0.8 | ZS m = BET|f0.1 | 0.7536 | 0.1136 | BET|f0.8 | - | 0.8332 | 0.1001 |
| BET|f0.8 | ZS iter = 1 | 0.7532 | 0.1138 | BET|f0.8 | ZS m = BET|f0.5 | 0.8331 | 0.0997 |
| BET|f0.8 | - | 0.7531 | 0.1138 | BET|f0.8 | KDE m = BET|f0.5 | 0.8331 | 0.1000 |
| BET|f0.8 | ZS iter = 4 | 0.7531 | 0.1142 | BET|f0.8 | ZS m = BET|f0.8 | 0.8330 | 0.1002 |
| BET|f0.8 | KDE m = BET|f0.5 | 0.7529 | 0.1146 | BET|f0.8 | WS m = BET|f0.8 | 0.8330 | 0.1002 |
| BET|f0.8 | KDE m = BET|f0.1 | 0.7529 | 0.1146 | BET|f0.8 | ZS m = BET|f0.1 | 0.8329 | 0.1002 |
| BET|f0.8 | WS m = BET|f0.1 | 0.7529 | 0.1145 | BET|f0.8 | WS m = BET|f0.5 | 0.8329 | 0.1003 |
| BET|f0.8 | ZS m = BET|f0.8 | 0.7528 | 0.1144 | BET|f0.8 | ZS iter = 1 | 0.8327 | 0.1003 |
| BET|f0.8 | ZS m = BET|f0.5 | 0.7528 | 0.1146 | BET|f0.8 | ZS iter = 4 | 0.8327 | 0.1002 |
| BET|f0.8 | KDE m = BET|f0.8 | 0.7495 | 0.1181 | BET|g0.3 | KDE m = BET|f0.8 | 0.8237 | 0.1029 |
| BET|g0.3 | WS m = BET|f0.5 | 0.7446 | 0.1794 | BET|g0.3 | KDE m = BET|f0.5 | 0.8236 | 0.1028 |
| BET|g0.3 | ZS m = BET|f0.1 | 0.7432 | 0.1819 | BET|g0.3 | KDE m = BET|f0.1 | 0.8235 | 0.1032 |
| BET|g0.3 | - | 0.7430 | 0.1822 | BET|g0.3 | ZS m = BET|f0.1 | 0.8234 | 0.1032 |
| BET|g0.3 | ZS iter = 1 | 0.7429 | 0.1821 | BET|g0.3 | - | 0.8233 | 0.1032 |
| BET|g0.3 | KDE m = BET|f0.1 | 0.7429 | 0.1823 | BET|g0.3 | ZS iter = 4 | 0.8232 | 0.1033 |
| BET|g0.3 | ZS m = BET|f0.8 | 0.7427 | 0.1824 | BET|g0.3 | WS m = BET|f0.1 | 0.8231 | 0.1032 |
| BET|g0.3 | WS m = BET|f0.1 | 0.7425 | 0.1822 | BET|g0.3 | ZS iter = 1 | 0.8231 | 0.1032 |
| BET|g0.3 | WS m = BET|f0.8 | 0.7425 | 0.1824 | BET|g0.3 | ZS m = BET|f0.5 | 0.8230 | 0.1034 |
| BET|g0.3 | ZS m = BET|f0.5 | 0.7425 | 0.1826 | BET|g0.3 | WS m = BET|f0.5 | 0.8230 | 0.1048 |
| BET|g0.3 | ZS iter = 4 | 0.7421 | 0.1829 | BET|g0.3 | ZS m = BET|f0.8 | 0.8227 | 0.1048 |
| BET|g0.3 | KDE m = BET|f0.5 | 0.7419 | 0.1831 | BET|g0.3 | WS m = BET|f0.8 | 0.8213 | 0.1046 |
| BET|g0.3 | KDE m = BET|f0.8 | 0.7414 | 0.1818 | BET|f0.2 | N3 iter = 1 | 0.8208 | 0.1508 |
| BET|f0.8 | WS m = BET|f0.5 | 0.7401 | 0.1229 | BET|f0.8 | N3 iter = 1 | 0.8194 | 0.1049 |
| BET|g0.3 | N3 iter = 1 | 0.7395 | 0.1810 | BET|g0.3 | N3 iter = 1 | 0.8094 | 0.1158 |
| BET|f0.8 | N3 iter = 1 | 0.7375 | 0.1203 | BET|f0.8 | N3 iter = 4 | 0.7888 | 0.1093 |
| BET|f0.8 | N3 iter = 4 | 0.7283 | 0.1145 | BET|f0.2 | N3 iter = 4 | 0.7794 | 0.1773 |
| BET|g0.3 | N3 iter = 4 | 0.7265 | 0.1782 | BET|f0.2,g0.3 | WS m = BET|f0.8 | 0.7672 | 0.1780 |
| BET|f0.2,g0.3 | WS m = BET|f0.5 | 0.7128 | 0.1612 | BET|f0.2,g0.3 | WS m = BET|f0.5 | 0.7670 | 0.1761 |
| BET|f0.2,g0.3 | KDE m = BET|f0.8 | 0.7077 | 0.1545 | BET|f0.2,g0.3 | - | 0.7669 | 0.1770 |
| BET|f0.2,g0.3 | ZS iter = 4 | 0.7074 | 0.1552 | BET|f0.2,g0.3 | KDE m = BET|f0.8 | 0.7663 | 0.1765 |
| BET|f0.2,g0.3 | KDE m = BET|f0.5 | 0.7059 | 0.1565 | BET|f0.2,g0.3 | KDE m = BET|f0.5 | 0.7660 | 0.1773 |
| BET|f0.2,g0.3 | ZS m = BET|f0.1 | 0.7057 | 0.1562 | BET|f0.2,g0.3 | ZS iter = 4 | 0.7658 | 0.1773 |
| BET|f0.2,g0.3 | WS m = BET|f0.1 | 0.7057 | 0.1560 | BET|f0.2,g0.3 | KDE m = BET|f0.1 | 0.7657 | 0.1768 |
| BET|f0.2,g0.3 | ZS m = BET|f0.8 | 0.7054 | 0.1562 | BET|f0.2,g0.3 | ZS m = BET|f0.1 | 0.7654 | 0.1772 |
| BET|f0.2,g0.3 | ZS iter = 1 | 0.7045 | 0.1560 | BET|f0.2,g0.3 | WS m = BET|f0.1 | 0.7653 | 0.1777 |
| BET|f0.2,g0.3 | WS m = BET|f0.8 | 0.7043 | 0.1567 | BET|f0.2,g0.3 | ZS m = BET|f0.8 | 0.7651 | 0.1775 |
| BET|f0.2,g0.3 | - | 0.7042 | 0.1560 | BET|f0.2,g0.3 | ZS iter = 1 | 0.7645 | 0.1774 |
| BET|f0.2,g0.3 | ZS m = BET|f0.5 | 0.7042 | 0.1561 | BET|f0.2,g0.3 | ZS m = BET|f0.5 | 0.7632 | 0.1784 |
| BET|f0.2,g0.3 | KDE m = BET|f0.1 | 0.7034 | 0.1562 | BET|g0.3 | N3 iter = 4 | 0.7631 | 0.1424 |
| BET|f0.2,g0.3 | N3 iter = 1 | 0.7027 | 0.1523 | BET|f0.2,g0.3 | N3 iter = 1 | 0.7421 | 0.1943 |
| BET|f0.2,g0.3 | N3 iter = 4 | 0.6948 | 0.1470 | BET|f0.2,g0.3 | N3 iter = 4 | 0.6920 | 0.2104 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Carbone, P.; Alba, C.; Bennett, A.; Kriukova, K.; Duncan, D. Optimizing Automated Brain Extraction for Moderate to Severe Traumatic Brain Injury Patients: The Role of Intensity Normalization and Bias-Field Correction. Algorithms 2024, 17, 281. https://doi.org/10.3390/a17070281
Carbone P, Alba C, Bennett A, Kriukova K, Duncan D. Optimizing Automated Brain Extraction for Moderate to Severe Traumatic Brain Injury Patients: The Role of Intensity Normalization and Bias-Field Correction. Algorithms. 2024; 17(7):281. https://doi.org/10.3390/a17070281
Chicago/Turabian StyleCarbone, Patrick, Celina Alba, Alexis Bennett, Kseniia Kriukova, and Dominique Duncan. 2024. "Optimizing Automated Brain Extraction for Moderate to Severe Traumatic Brain Injury Patients: The Role of Intensity Normalization and Bias-Field Correction" Algorithms 17, no. 7: 281. https://doi.org/10.3390/a17070281
APA StyleCarbone, P., Alba, C., Bennett, A., Kriukova, K., & Duncan, D. (2024). Optimizing Automated Brain Extraction for Moderate to Severe Traumatic Brain Injury Patients: The Role of Intensity Normalization and Bias-Field Correction. Algorithms, 17(7), 281. https://doi.org/10.3390/a17070281





