1. Introduction
Due to the possibility of managing thousands of users, covering wide areas and providing a bandwidth which is orders of magnitude faster than traditional networks, all-optical networks are widely exploited nowadays, and are considered to be used also in the future of communication networks. In fact, wavelength division multiplexing (WDM) [
1] allows one to exploit the high bandwidth provided by all-optical networks by partitioning it a large number of parallel high speed channels along the same optical fiber (see [
2,
3] for a survey of the main related results). Motivated by this fact, in this paper, we investigate the existence and performance of Nash equilibria in all-optical networks populated by non-cooperative selfish agents corresponding to point-to-point communication requests. Every agent is interested only in the minimization of its own cost, and, given a graph modelling the optical network, has to choose among a set of possible paths (also called routing strategy) connecting its endpoints. In particular, in our model, a service provider has to design suitable payment functions, charging each agent a cost for her chosen routing strategy. We consider three different kinds of local knowledge that agents may exploit to compute their payments, leading to three corresponding information levels that will be detailed in the following. It is worth noticing that any request is willing to be rerouted each time it may be served by a cheaper path: the evolution of the network can be modelled by the dynamics of a multi-agent system or multi-player game. A routing solution, that is an assignment of paths and colors (a color represents a wavelength) to the requests, in which no request can lower its cost by choosing a different strategy, is said to be a pure Nash equilibrium.
1.1. Related Work
Several routing games have been shown to possess pure Nash equilibria or to converge to a pure Nash equilibrium independently from their starting state (see [
4,
5,
6,
7,
8,
9,
10,
11,
12,
13,
14] for some pioneering work and [
15] for an introduction to algorithmic game theory). The price of anarchy has been introduced in [
12] for the first time in the literature; it measures the loss of the global performance of the system at equilibrium due to the lack of cooperation among the agents, and is defined as the worst-case ratio between the total cost of a Nash equilibrium and that of an optimal solution. One of the most studied and interesting research areas lying on the boundary between computer science and game theory consists of bounding the price of anarchy of selfish routing under different models; see, for example [
13,
14].
Game theory has been applied to optical networks in various contexts (e.g., see [
16,
17,
18]). For instance, it is worth noting that the optimization of the network cost due to expensive hardware components (e.g., add-drop multiplexer) has been widely investigated in the literature (see [
19,
20,
21,
22]), also considering the effect of collusion among agents (see [
23]). Moreover, in [
16], the authors deal with a setting very similar to the one addressed in this paper; they consider several natural cost functions, and for each of them, they examine the problem of the existence of pure Nash equilibria, and of the complexity of recognizing and computing such equilibria.
1.2. Our Contribution
As a first contribution, we determine three notable information levels for the computation of the payment functions that have to be designed by the network provider. In particular, each agent has knowledge of all the other agents and their routing strategies under the complete information level of the wavelengths used along any given edge under the intermediate level, and finally, only of the wavelengths used along any given path connecting its source and destination under the minimal level. Notice that even the minimal level contains the information needed in order to select an available wavelength, without interfering with other requests.
We first show that, under complete level, the network provider can design a payment function inducing the agents to reach a Nash equilibrium mirroring any desired routing. This allows the use of a centralized algorithm for determining an (almost) efficient routing assignment which can be then efficiently enforced to the agents. We then turn our attention to the remaining two levels of information: unfortunately, it holds that the most reasonable functions either do not admit equilibria or induce games with a very high (actually the worst possible) price of anarchy; that is, the resulting Nash equilibrium could assign a different color to each agent. Given this negative result, we focus on more specific network topologies. In particular, we show that a price of anarchy of 8 and 16 can be obtained for chains and rings, respectively, under the minimal level of information. These bounds can be further reduced to and under the intermediate level, with converging to 0 as the load increases. Finally, a price of anarchy logarithmic in the number of agents is shown to hold for tree networks under the minimal level of information.
1.3. Paper Organization
The paper is organized as follows.
Section 2 provides the basic definitions and notation. In
Section 3 we give some preliminary results for our model: in particular, we present the results related to the complete information level and we also define some suitable classes of payment functions able to characterize convergent games in the context of more restrictive information levels.
Section 4 and
Section 5 are devoted to the study of payment functions for the minimal and intermediate levels of information: in particular, in
Section 4, results relative to general networks are presented, while in
Section 5, results for specific network topologies, that is chains, rings and trees, are provided. Finally,
Section 6 gives some conclusive remarks and discusses some open questions.
2. The Model
An all-optical network is modelled by an undirected graph , where nodes in V represent sites and undirected edges in E bidirectional optical fiber links between the sites. Given any two nodes , a communication request between x and y is denoted as . A communication instance in G is a multiset of requests I (i.e., I can contain multiple requests between the same pair of nodes). A path system P for an instance I in G is a set of paths containing a distinguished simple connecting path in G for each request in I. A solution for an instance I in G, for short, is a pair in which is a path system for I and (with being the set of wavelengths) is a function associating a wavelength or color to each request in I. Let denote the path connecting in and be its length in terms of number of edges. A solution is feasible or is a routing for I in G if for any two requests and whose connecting paths and share an edge in G, i.e., the associated colors are different.
Let be the number of colors used by the routing for I in G and be the minimum number of colors used by any routing for I. Analogously, let be the maximum load of an edge in G induced by the routing and be the minimum maximum load of the routings for I in G, also called load of I in G. Clearly, since all the requests sharing an edge must have different colors, for every and thus . Given that the optical spectrum is a scarce resource, in this paper, we aim at determining routings using a number of wavelengths close to the minimum one, i.e., .
In order to model our non-cooperative environment, we assume that each communication request is issued and handled by an agent ; for the sake of simplicity, we consider it as coincident with the request, that is . Our goal is to assign payments (or costs) to the agents so that they are induced to choose in a non-cooperative way a good solution, i.e., a routing with a small number of colors. A payment function associates each possible routing and agent to a cost; in particular, is the cost that agent has to pay to the network provider in order to obtain the asked service if the routing is adopted. In order to give our payment functions a higher generality, we assume the existence of a non-decreasing function associating a cost to every color. Notice that f is non-decreasing because, in such a way, it is possible to implicitly model the increasing cost incurred by the network provider when it has implemented a routing using up to a given wavelength.
A game among the agents belonging to I on the network G induced by the payment function is defined as the set of agents’ strategies , where is the set of connecting paths for and the utility function . A routing is a (pure) Nash equilibrium if, and only if, for any agent and routing differing from only for the path and/or the color associated to , it holds that . Denoted as , the set of the routings at Nash equilibrium, the price of anarchy of the game is defined as the worst case ratio among all the possible games .
The evolution of the game is a sequence of moves starting from an arbitrary routing, where is an agent and and are the old and the new strategies of , respectively. The Nash dynamics of the game are the directed graph , where is the set of possible routings for G and I and there exists an arc if there exists a selfish move from to , i.e., there exists an agent such that . If the Nash dynamics are acyclic for every G and I, the game is said to be convergent. Analogously, any payment function inducing only convergent games is said to be convergent. We say that game converges to routing whenever is convergent and admits the unique pure Nash equilibrium . It is worth noting that, even if the Nash dynamics are cyclic, the game might admit a Nash equilibrium.
Table 1 summarizes all the notations defined above. For ease of notation, when clear from the context, in the following, we will drop the index
from the notation, thus, for instance, writing
,
,
,
and
in place of
,
,
,
and
. Before concluding the section, we finally observe that the payment function
, in a strongly distributed non-cooperative environment, has to be computed by each single agent requiring the communication service. However, the level of global information they have can be limited by technological constraints, as well as privacy policies carried out by the service provider or simply enforced by the law. Therefore, in general,
is not computed, starting from the instance
I and the routing
, but on a more restricted set of information induced by them. To this aim, we introduce the concepts of states and levels of information. The edge state (resp. path state) of the network
G induced by a routing
for
I is a function
(resp.
, where
is the set of all the simple paths in
G) associating to every edge
(resp. path
) the set of the wavelengths used along
e (resp.
p). It is then possible to distinguish among three basic levels of information:
- •
Minimal. Each agent knows the available wavelengths along any given path connecting x to y, that is, the function can be computed, even knowing only the restriction of the path state on the set of the paths from x to y.
- •
Intermediate. Each agent information knows the wavelengths available along any given edge, that is, the function can be computed, even knowing only the edge state .
- •
Complete. Each agent knows the instance I and the routing , that is, the function is not restricted.
Clearly, even if not explicitly mentioned, in any level of information, for each agent , can depend also on the wavelength and the path assigned to in . Recall that the players move sequentially and can choose, as their current strategy, only valid strategies with respect to the current routing. Notice also that even with minimal information, any agent is always able to compute a valid wavelength for the chosen path, so as to not interfere with any other agent, and thus not compromising the feasibility of the solution.
3. Preliminaries
In the first part of this section, we prove that, under complete information, any centralized algorithm for the all-optical routing problem can be suitably used in a non-cooperative environment for achieving a price of anarchy either equal to 1 or k, according to whether is optimal or k-approximating, respectively.
Theorem 1. Given any routing for a game , there exists a payment function letting converge to in at most steps.
Proof. Given any routing
, the payment function is defined as follows.
- •
Convergence. Since the payment function is such that any move of an agent does not affect the cost of any other agent and has a codomain of cardinality 3, any agent can perform at most 3 moves during the game, thus the game converges in at most moves.
- •
Uniqueness. We now show that the only Nash equilibrium for is . Suppose, by contradiction, that in the routing at Nash equilibrium, there exists an agent such that . Agent can clearly perform a move by switching to a color , so as to pay a cost equal to 1, and this contradicts the hypothesis that is a Nash equilibrium. Analogously, suppose that in the routing at Nash equilibrium there exists at least one agent such that . In , is thus assigned the color . Having already proven that cannot pay a cost equal to 2, we have that no agent in the routing is assigned a color unless , that is, unless he is using the same path and the same color of . Thus, agent can perform a move by choosing the same path and color of , so as to pay 0, and this contradicts the hypothesis that is a Nash equilibrium. We have shown that in a routing at Nash equilibrium ; by the definition of , each agent uses the same path and color of the routing , thus .
□
Corollary 1. Let be any k-approximation algorithm for the all-optical routing problem ( if is optimal). Then, there exists a payment function yielding a game , converging in at most steps and having a price of anarchy equal to k. Moreover, the time complexity of the computation of the function is at most the same as .
Proof. The claim is an immediate consequence of Theorem 1: by letting be the routing returned by algorithm , the price of anarchy of is simply the approximation ratio of , and finally, each agent, in order to compute the payment function, has to find the same path and color computed by the algorithm . □
In the sequel, we will focus on the minimal and intermediate information levels. Before proceeding with the presentation of our results, let us first introduce two families of payment functions that provide a useful characterization of a class of convergent games with the worst possible price of anarchy. Given a generic move
performed by an agent
from
to
, let
A be the set of agents sharing at least one edge with
in
and no edges with
in
and
B be the set of agents sharing at least one edge with
in
. We denote with
the set of payment functions, satisfying the following conditions:
Roughly speaking, condition (
1) means that all the players sharing at least an edge with
before her move and no edge after such a move does not increase their costs. Condition (
2) means that given a generic player
sharing at least an edge with
after
and increasing their cost after such a move, the cost of
after
is at most the cost of
after
. Such conditions will be useful for proving the convergence to equilibrium.
Theorem 2. All the payment functions belonging to Π are convergent.
Proof. Let be the sequence of costs ordered in a non-decreasing way and let be the sequence of costs ordered in the same way, that is, the new sequence of costs yielded by the execution of a move performed by the agent . By the definition of the class , can increase the cost of any other agent to reach, at most, the value . Since it holds , we obtain that the sequence is lexicographically smaller than . Notice that such a lexicographic order induces a total order among the nodes of the Nash dynamics. The sequence is the bottom of the lexicographic ordering, hence the thesis. □
As can be easily seen, the number of steps needed to converge to an equilibrium may not be polynomial in the dimensions of the instance.
We now define a subclass of of payment functions inducing games , having a price of anarchy , which is clearly the worst possible, since any feasible solution for the problem uses at most colors, while is the optimal solution.
We denote as the class of payment functions satisfying at least one of the following conditions:
- •
Subclass : depends only on the color and for any and ; that is, the cost for each agent depends only on its own color in the routing and any other agent never gets a benefit in performing a move where .
- •
Subclass : , where is such that for any sets of colors A and B, with , and . In other words, the image according to g of a set containing all the elements of another set A except for at most one element (d), which has to be replaced in the first set by a strictly greater element , cannot be smaller than the image of the second set.
Theorem 3. , that is any function is convergent. Moreover, for each payment function , there exists a game having a price of anarchy .
Proof. We prove that for each payment function
,
and
. Let
be a generic move performed by the agent
from the routing
to the routing
. If
, then both the conditions (
1) and (
2) are satisfied since
. If
, then condition (
1) is satisfied since, setting
,
,
and
, it holds that
, thus, the costs of the agents sharing no edges with
in
cannot increase. Condition (
2) is satisfied by the payment function
, since we are assured that whenever the cost of the agents now sharing an edge with
in
increase, it can never exceed the cost
.
In order to prove the result for the price of anarchy, let G be a ring of nodes (), and be the communication instance. The routing , where , and , is such that , thus = 1. If we consider the routing where , and we have that is, a Nash equilibrium by the definition of . First we note that in , , , that is, all the edges of the ring are occupied by all the colors except for the color i. The proof then proceeds for cases. Depending on the particular subclass of , we have:
- •
Subclass . No agent gets a benefit in performing a move, because he cannot use a color smaller than i;
- •
Subclass . No agent gets a benefit in performing a move, because if he moved to the edge which is the only remaining one in the path of edges thus changing his color, his new path (in the routing ) would contain at least an edge occupied by the set of colors , which would result in .
Since , we obtain that the price of anarchy . The claim for comes observing that in any feasible routing , it holds that . The claim for can be obtained by replicating each request times. By so doing, we can construct, similarly as above, a routing in Nash equilibrium using colors. □
4. Minimal and Intermediate Payment Functions
Even though the results obtained in the case of complete information are fully satisfactory, they have been obtained under the assumption that each agent has full knowledge of the instance and the routing: this assumption is very strong and in real world networks might not be true either due to technological or privacy policies reasons. For this reason, in the sequel, we will focus on payment functions based on a more restricted level of information. Let us first define a set of payment functions that can be computed under a minimal or intermediate information level. Given a routing , we first propose suitable cost functions defined on the edges that will be used as building blocks for the definition of the mentioned payment functions:
- •
: the amount charged to on the edge e is the cost, according to f, of the color he uses.
- •
: the amount charged to on the edge e is the cost of the highest color used along e (considering also the other agents).
- •
: the amount charged to on the edge e is the sum of the costs of all the colors used along e.
- •
: the amount charged to on the edge e is the cost of the highest color used along e, averaged or shared among all the agents traversing e.
- •
: the amount charged to on the edge e is the sum of the costs of all the colors used along e, averaged on all the agents traversing e.
Starting from any edge cost function , it is possible to define the following payment functions:
- •
: the price asked to is the maximum cost, according to , of an edge used by .
- •
: the price asked to is the sum of the costs of the edges used by .
The combination of the introduced edge cost functions with the above two strategies, that is, maximization or summation, gives rise to ten possible payment functions. In all cases, since the function f is non-decreasing, agents have an incentive to choose small colors so as to possibly minimize the overall number of used colors. Notice that all the ten introduced payment functions are computable under an intermediate information level. Moreover, , and require only the minimal level, as , and . The following lemma shows how the families of functions defined in the previous section nicely characterize the class of games induced by them.
Lemma 1. The payment functions and belong to the class .
Proof. It can be easily verified that, by definition, the payment function belongs to , while the payment function belongs to . □
Moreover, a similar result holds for .
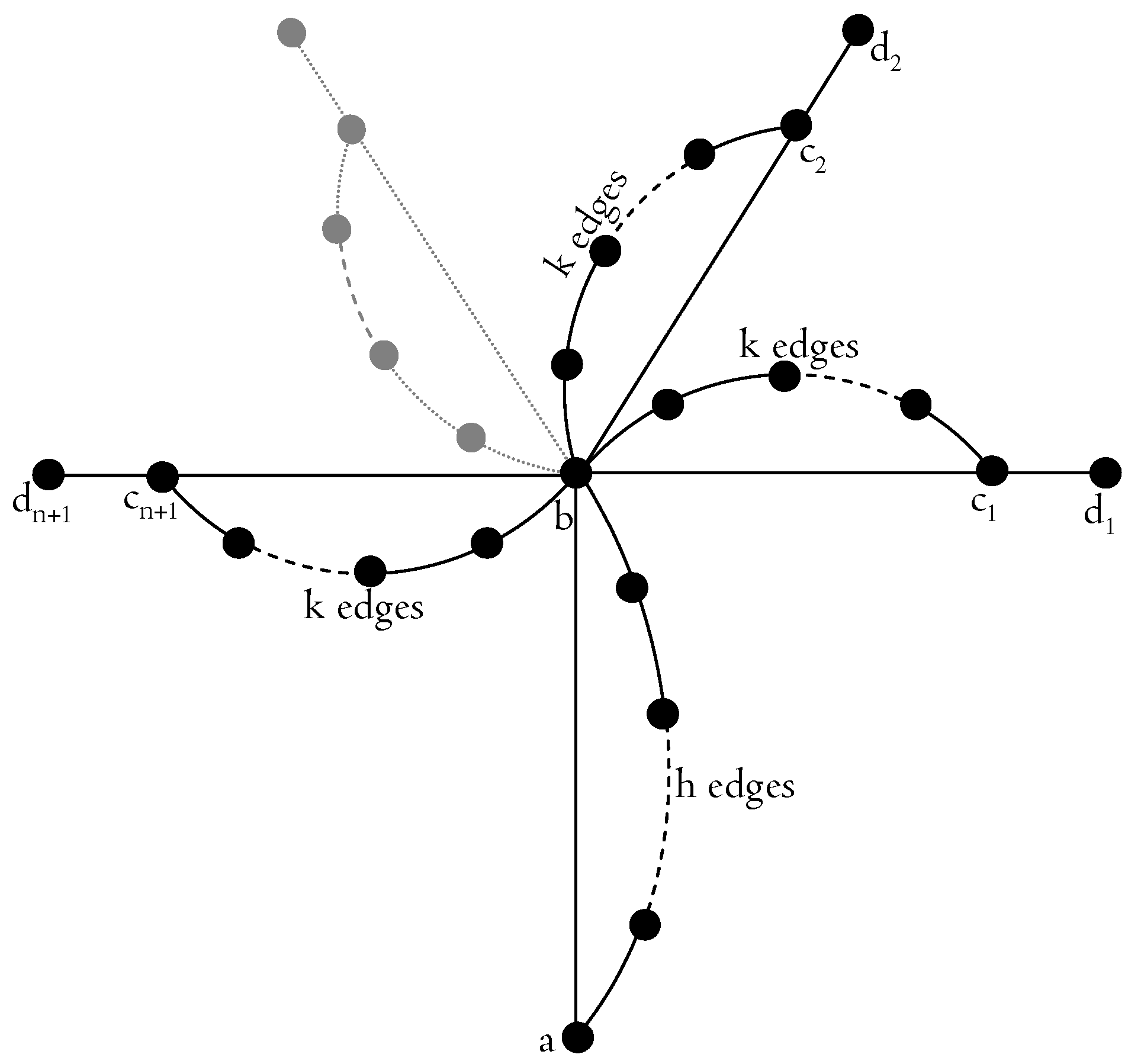
Theorem 4. The payment function belongs to Π, that is, it is convergent, but there exists a game having a price of anarchy .
Proof. The payment function
belongs to
, since it clearly satisfies conditions (
1) and (
2). We now show that the game induced by the function
on the instance
in the graph depicted in
Figure 1 does not admit a Nash equilibrium. Let
k be
. The routing
, where
,
, i.e., each request is routed on a different chain of
k edges, and
is such that
, thus
=1. If we consider the routing
where
,
, then there exists a request using at least color
n. Since
is an equilibrium, the thesis follows. □
Therefore, even if convergent, all the three minimal level functions yield the worst possible price of anarchy. Unfortunately, the following results show that, also, the remaining seven payment functions for the intermediate information level either are not convergent or yield the worst possible price of anarchy.
Theorem 5. The payment function belongs to the class .
Proof. We show that belongs to the subclass of . To this aim, it suffices to show that satisfies, for any sets of colors A and B, the property with , and . Since and f is positive and non decreasing, we have . □
Theorem 6. Nash equilibria are not guaranteed to exist for the games induced by the payment functions.
- (1)
when the pricing function f is unbounded;
- (2)
and when f is such that ;
- (3)
and when the f is such that , that is, f is non-constant.
The proof of Theorem 6 is deferred to the
Appendix A. Finally, we have the following theorem concerning
.
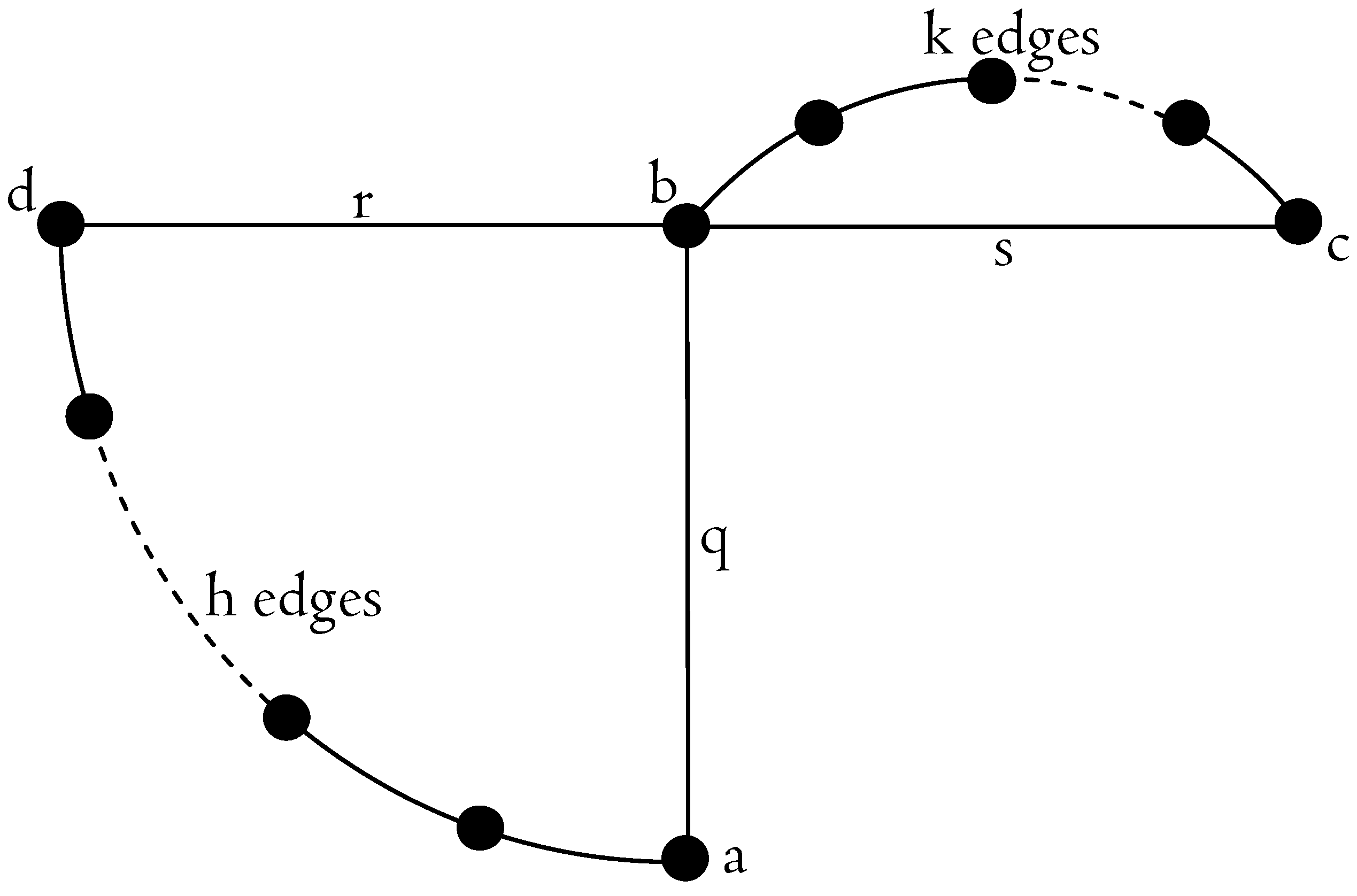
Theorem 7. The payment function is not convergent when the pricing function f is such that .
Proof. We show that, for the problem defined by the graph depicted in
Figure 2 and by the instance
the Nash dynamics are cyclic for any pricing function
f, such that
.
The parameters n, h and k depend on the pricing function f and must be suitably tuned as shown in the sequel of the proof. Let q be the edge , be the path obtained from the union of the path of h edges and the edge , s be the edge , be the path of k edges and r be the edge .
The following conditions suffices to prove that the Nash dynamics are cyclic:
Consider the initial routing
, displayed in
Table 2.
At this first step,
plays the move
because of condition (
3), thus leading to the routing
, displayed in
Table 3.
Now,
plays the move
because of condition (
5), thus leading to the routing
, displayed in
Table 4.
plays the move
because of condition (
4), thus leading to the routing
, displayed in
Table 5.
Finally,
plays the move
because of condition (
6), thus leading the game back to the initial routing
(displayed in
Table 2).
In order to complete the proof, we have to show how to satisfy the conditions (
3)–(
6) and how to tune the parameters
n,
k and
h. The four conditions are satisfied by choosing
k and
h, such that
and
Choosing assures that h and k always exist and are integers. □
5. Results for Specific Topologies
In
Section 4, we have shown that the price of anarchy for general topologies under the intermediate and minimal levels of information can be very high. For this reason, always considering the intermediate and minimal levels of information, in this section, we consider networks having specific topologies, like chains (i.e., sites are connected along a line), and rings (i.e., cycles of sites) and trees. Let us first consider the minimal information level. Any strictly increasing payment function computable under this level, like
, induces games in which a routing
at Nash equilibrium can be seen as a solution of the classical first-fit algorithm for the all-optical routing problem that assigns to each request the smallest available color. In particular, this solution is the one returned by first-fit when requests are considered in non-decreasing order of color in
. Therefore, the induced price of anarchy is bounded by the approximation ratio of first-fit. Concerning the above-mentioned topologies, for any instance
I, first-fit uses a number of colors that are at most
in chains [
24] and at most
in trees [
25]. Recalling that
, the following theorem holds.
Theorem 8. The payment function induces games with a price of anarchy 8 in chains and in trees, both converging in steps from any initial routing.
For rings, it is possible to use the result of [
24] by routing requests on the chain obtained deleting an edge
of the ring. In fact, denoted as
P, the path system containing all such connecting paths, for any routing
with
, it results in
. In other words, this at most doubles the induced load. The following payment function forces Nash equilibria using the set of paths
P:
Since the payment function belongs to and, when restricted to the routings with , is strictly increasing, it follows that each agent has an incentive in choosing the smallest available color. By recalling that, in this case, the load at most doubles with respect to the chain topology, the following theorem holds.
Theorem 9. In ring networks, the above payment function induces games with price of anarchy 16 and converging in steps from any initial routing .
In the remaining part of the section, we show how, raising the level of information to the intermediate one, it is possible to further reduce the price of anarchy for chains and rings. We first focus on ring topologies, as the corresponding results can be directly extended to chains. Our purpose is to force the agents to simulate the behavior of the online algorithm proposed by Slusarek [
26]. In such an algorithm, the path system
P is fixed and the optical spectrum is divided in shelves, numbered consecutively starting from 1. The color assigned to an arriving agent
is the lowest available one in the minimal shelf
i, such that the load induced on the edges of
by all the agents up to shelf
i is at most
i. More precisely, denoted as
, the shelf of a given wavelength
w, the load
of an agent
according to a routing
is
Clearly, any routing
such that
has the same load
and in the routing
returned by the algorithm, at most
shelves are used to allocate all the agents. Moreover, as shown in [
26], during all the executions of the algorithm, the first shelf contains only one color and the other ones no more than three colors, thus yielding
colors, that is, at most 3 times above the optimum.
In devising a payment function that mimics Slusarek’s algorithm, it is necessary to cope with several problems. First of all, it is necessary to fix a path system with a low induced load. This is obtained by giving agents an incentive to use shortest paths, as in any routing
satisfying such a property
, that is, the induced load is at most doubled. Moreover, the convergence of the game is an issue, since the move of an agent might compromise the minimality of the payments of the agents in his shelf and in the above ones. Finally, in order for an agent to always find a proper shelf during the evolution of the game, we have to allow an unlimited number of colors to be contained in each shelf. Since, however, Nash equilibria will use only one wavelength of the first shelf and at most three in the other ones, we have to choose the function
associating colors to shelves trying to minimize, for each
i, the maximum third color of all the shelves up to
i. To this aim, we partition the set of wavelengths
W in two subsets
and
, in which
is the set of the slack wavelengths. Each shelf has an infinite number of wavelengths and the first one of shelf 1 and the first three ones of all the other shelves correspond consecutively to small colors in
, while the other ones to slack colors in
, assigned to the different shelves according to a dove-tail technique in such a way that, for every
and
, there exists a finite wavelength
that corresponds to the
j-th color of shelf
i. As can be easily checked, while the first color of shelf 1 is 3, the third color of each shelf
is at most
. Assuming that the function
realizes the above mapping of colors and that
n is the number of nodes in the ring, the payment function
charges to agent
Intuitively, a routing is at Nash equilibrium if, and only if, each request uses a shortest path and the color that Slusarek’s algorithm assigns to him when agents arrive in non-decreasing order of color in , clearly not using colors in .
Theorem 10. In ring networks, the game induced by the above payment function converges and has a price of anarchy .
Proof. Let us consider any evolution of the game starting from any given configuration and let us show that it converges to a Nash equilibrium in a finite number of agent moves. At any intermediate configuration, let us partition I into two sets A and B, such that A contains all the agents that, in the sequel of the game, will never perform a move to a higher shelf. We show that, after a finite number of moves, a new agent will enter in A, so that in a finite number of steps, it will finally result . This proves the convergence of the game, since starting from such final configuration, the agents cannot perform an infinite number of moves without raising their shelf.
First of all, we note that, since by construction, the number of wavelengths in each shelf is infinite, each agent can always perform a move leading him in a feasible shelf i, that is, such that . Moreover, the moves leading on a shortest path and in a feasible shelf are the only ones which can make ’s cost strictly smaller than . Finally, an agent routing a shortest path and lying in a feasible shelf, maintaining his connection path, decreases his cost if he moves to a lower feasible shelf or to a smaller color of its shelf.
Consider a move of agent to a shelf . The proof proceeds by cases: after the move
- (1)
will never perform a move increasing his shelf. In this case, is entered in A.
- (2)
At a certain point of the game, performs a move increasing his shelf. This is due to another agent who has performed a move to a shelf . However, it cannot be , as increases ’s load to and would have the same load in shelf (i.e., is not feasible for ), thus not decreasing his cost. We can then continue applying the same analysis to . Since the number of shelves in which agents can move is bounded by , we must finally arrive to an agent with for which the first case holds.
As already observed, any routing at Nash equilibrium corresponds to the output of Slusarek’s algorithm without using colors in when the agents arrive in non decreasing order of color in . Thus, the maximum used color in is at most the third one of shelf if , while it is equal to the first one of shelf 1 otherwise. This shows that the maximum used color is at most . Since uses shortest paths, and the resulting price of anarchy is . □
Clearly, a similar function
can be used also in chains, for which connection paths are unique and thus no doubling of the load occurs.
Theorem 11. In chain networks, the game induced by the above payment functions converges and has a price of anarchy .
6. Conclusions
We have considered the problem of determining suitable payment functions for the non-cooperative agents of an all-optical network, in order to induce Nash equilibria using a low number of wavelengths. In particular, we have identified three levels of information, specifying the local knowledge that the agent can exploit when computing their payments. While the complete information level has been fully understood, under the lower levels, the main left open question is the determination of functions that on every topology yield Nash equilibria with a performance better than the worst possible one assigning a different color to each agent. Moreover, still under incomplete information, it would be also nice to improve and extend our results on specific topologies. Furthermore, given that a lot of literature, as discussed in the introduction, focuses on the minimization of the cost due to hardware equipment in optical networks, it would be nice to study the characteristics and performance of games combining our measure (the number of used wavelengths) with other kinds of hardware costs. Moreover, since our findings outline nice connections between payment functions and online algorithms, that allow one to cope with the arbitrary order of the moves of the agents, it would be nice to understand the conditions and eventual systematic methods allowing one to get converging payment functions preserving online algorithms performances under incomplete information. Finally, we would like to remark that this paper constitutes a theoretical contribution to the study of optical networks from a decentralized multi-agent point of view, and it would be interesting to validate the obtained results and proposed approach by some simulation studies to be performed in a future work. To this respect, we believe that many worse lower bounds to the price of anarchy are achieved by exploiting specific and pathological instances, and therefore, the price of anarchy may turn out to be much lower, in practice, in the cases for which the existence of instances with a very large price of anarchy has been theoretically proven.