Tensor Completion Based on Triple Tubal Nuclear Norm
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Notations and Preliminaries
2.1. Notations
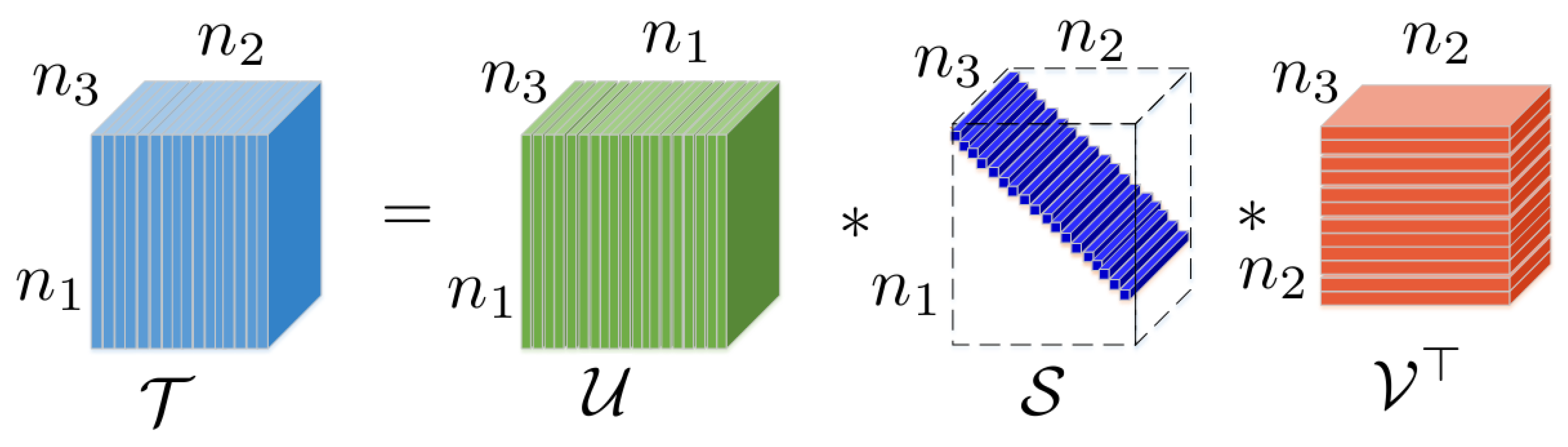
2.2. Tensor Singular Value Decomposition
3. The Triple Tubal Nuclear Norm
3.1. Tubal Nuclear Norm
3.2. Twist Tubal Nuclear Norm
3.3. A Circular Interpretation of TNN and t-TNN
3.4. The Proposed Row Twist Tubal Nuclear Norm and Triple Tubal Nuclear Norm
4. TriTNN-Based Tensor Completion
4.1. Problem Formulation
4.2. An ADMM Solver to Problem (21)
| Algorithm 1 Solving Problem (21) using ADMM. |
| Input: The observed tensor , the parameters . |
| Output:. |
4.3. Convergence of Algorithm 1
4.4. Differences from Prior Work
5. Experiments
- The tensor nuclear norm-based model with ADMM solver: high accuracy low-rank tensor completion (HaLRTC, denoted by SNNin this paper) (code available: http://www.cs.rochester.edu/u/jliu/publications.html) [2], The tensor nuclear norm is defined as the weighted sum of nuclear norms of the unfolding matrices along each mode (thus, we denote this model as SNN):where , are positive parameters and , , is the unfolding matrix of tensor along the i-th mode [2].
- The latent tensor nuclear norm-based model (LatentNN) (code available: https://github.com/ryotat/tensor) [21]. The latent tensor nuclear norm is defined as:where and are the first-mode, second-mode and third-mode unfoldings of latent tensors and , respectively.
- The square nuclear norm-based model (SquareNN) (code available: https://sites.google.com/site/mucun1988/publi) [23]. The square nuclear norm of a tensor is defined as the nuclear norm of the most balanced unfolding of a tensor (see [7,23]).
- The most related tubal nuclear norm-based model (TNN) (code available: https://github.com/jamiezeminzhang/) [30] and the twist tubal nuclear norm-based model (t-TNN) [16].
5.1. Color Image Inpainting
5.2. Video Inpainting
5.3. A Dataset for Autonomous Driving
6. Conclusions
- Computational inefficiency: Compared to TNN and t-TNN, it is more time-consuming since it involves computing TNN, t-TNN and rt-TNN (see Equation (18)).
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kilmer, M.E.; Braman, K.; Hao, N.; Hoover, R.C. Third-order tensors as operators on matrices: A theoretical and computational framework with applications in imaging. SIAM J. Matrix Anal. Appl. 2013, 34, 148–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Musialski, P.; Wonka, P.; Ye, J. Tensor completion for estimating missing values in visual data. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2013, 35, 208–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, A.; Jin, Z. Near-optimal Noisy Low-tubal-rank Tensor Completion via Singular Tube Thresholding. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Data Mining Workshop (ICDMW), New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–21 November 2017; pp. 553–560. [Google Scholar]
- Signoretto, M.; Dinh, Q.T.; Lathauwer, L.D.; Suykens, J.A.K. Learning with tensors: a framework based on convex optimization and spectral regularization. Mach. Learn. 2014, 94, 303–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cichocki, A.; Mandic, D.; De Lathauwer, L.; Zhou, G.; Zhao, Q.; Caiafa, C.; Phan, H.A. Tensor decompositions for signal processing applications: From two-way to multiway component analysis. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 2015, 32, 145–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.; Feng, J.; Chen, Y.; Liu, W.; Lin, Z.; Yan, S. Tensor Robust Principal Component Analysis: Exact Recovery of Corrupted Low-Rank Tensors via Convex Optimization. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 5249–5257. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, D.; Wang, A.; Wang, B.; Feng, X. Tensor Completion Using Spectral (k, p) -Support Norm. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 11559–11572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Shang, F. An Efficient Matrix Factorization Method for Tensor Completion. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2013, 20, 307–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Lu, H. Multilinear Regression for Embedded Feature Selection with Application to fMRI Analysis. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, San Francisco, CA, USA, 4–9 February 2017; pp. 2562–2568. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, H.; Feng, G.; Feng, J.; Wang, W.; Zhang, Y.J.; Li, F. A tensor-based method for missing traffic data completion. Transp. Res. Part C 2013, 28, 15–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Zhang, L.; Cichocki, A. Bayesian CP Factorization of Incomplete Tensors with Automatic Rank Determination. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2015, 37, 1751–1763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cichocki, A.; Lee, N.; Oseledets, I.; Phan, A.H.; Zhao, Q.; Mandic, D.P. Tensor Networks for Dimensionality Reduction and Large-scale Optimization: Part 1 Low-Rank Tensor Decompositions. Found. Trends Mach. Learn. 2016, 9, 249–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harshman, R.A. Foundations of the PARAFAC Procedure: Models and Conditions for an “Explanatory” Multi-Modal Factor Analysis; University of California: Los Angeles, CA, USA, 1970. [Google Scholar]
- Kolda, T.G.; Bader, B.W. Tensor decompositions and applications. SIAM Rev. 2009, 51, 455–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tucker, L.R. Some mathematical notes on three-mode factor analysis. Psychometrika 1966, 31, 279–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, W.; Tao, D.; Zhang, W. The twist tensor nuclear norm for video completion. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2017, 28, 2961–2973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, M.; Zhang, C.H. Incoherent Tensor Norms and Their Applications in Higher Order Tensor Completion. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 2017, 63, 6753–6766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Q.; Ge, H.; Caverlee, J.; Hu, X. Tensor Completion Algorithms in Big Data Analytics. arXiv, 2017; arXiv:1711.10105. [Google Scholar]
- Candès, E.J.; Tao, T. The power of convex relaxation: near-optimal matrix completion. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 2010, 56, 2053–2080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillar, C.J.; Lim, L. Most Tensor Problems Are NP-Hard. J. ACM 2009, 60, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomioka, R.; Suzuki, T. Convex tensor decomposition via structured schatten norm regularization. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Lake Tahoe, NV, USA, 5–10 December 2013; pp. 1331–1339. [Google Scholar]
- Semerci, O.; Hao, N.; Kilmer, M.E.; Miller, E.L. Tensor-Based Formulation and Nuclear Norm Regularization for Multienergy Computed Tomography. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2014, 23, 1678–1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mu, C.; Huang, B.; Wright, J.; Goldfarb, D. Square Deal: Lower Bounds and Improved Relaxations for Tensor Recovery. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, Beijing, China, 21–26 June 2014; pp. 73–81. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Q.; Meng, D.; Kong, X.; Xie, Q.; Cao, W.; Wang, Y.; Xu, Z. A Novel Sparsity Measure for Tensor Recovery. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Santiago, Chile, 7–13 December 2015; pp. 271–279. [Google Scholar]
- Tomioka, R.; Hayashi, K.; Kashima, H. Estimation of low-rank tensors via convex optimization. arXiv, 2010; arXiv:1010.0789. [Google Scholar]
- Chretien, S.; Wei, T. Sensing tensors with Gaussian filters. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 2017, 63, 843–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghadermarzy, N.; Plan, Y.; Yılmaz, Ö. Near-optimal sample complexity for convex tensor completion. arXiv, 2017; arXiv:1711.04965. [Google Scholar]
- Ghadermarzy, N.; Plan, Y.; Yılmaz, Ö. Learning tensors from partial binary measurements. arXiv, 2018; arXiv:1804.00108. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Shang, F.; Fan, W.; Cheng, J.; Cheng, H. Generalized Higher-Order Orthogonal Iteration for Tensor Decomposition and Completion. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Palais des Congrès de Montréal, Montréal, Canada, 8–13 December 2014; pp. 1763–1771. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Ely, G.; Aeron, S.; Hao, N.; Kilmer, M. Novel methods for multilinear data completion and de-noising based on tensor-SVD. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Columbus, OH, USA, 23–28 June 2014; pp. 3842–3849. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Aeron, S. Exact Tensor Completion Using t-SVD. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2017, 65, 1511–1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Chen, Y.; Huang, L.; So, H.C. Tensor Completion via Generalized Tensor Tubal Rank Minimization using General Unfolding. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, P.; Lu, C.; Lin, Z.; Zhang, C. Tensor Factorization for Low-Rank Tensor Completion. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2018, 27, 1152–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ely, G.T.; Aeron, S.; Hao, N.; Kilmer, M.E. 5D seismic data completion and denoising using a novel class of tensor decompositions. Geophysics 2015, 80, V83–V95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Aeron, S.; Aggarwal, V.; Wang, X.; Wu, M. Adaptive Sampling of RF Fingerprints for Fine-grained Indoor Localization. IEEE Trans. Mob. Comput. 2016, 15, 2411–2423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.Q.; Ng, M.K. Exact Tensor Completion from Sparsely Corrupted Observations via Convex Optimization. arXiv, 2017; arXiv:1708.00601. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.Y.; Aeron, S.; Aggarwal, V.; Wang, X. Low-tubal-rank tensor completion using alternating minimization. arXiv, 2016; arXiv:1610.01690. [Google Scholar]
- Boyd, S.; Parikh, N.; Chu, E.; Peleato, B.; Eckstein, J. Distributed optimization and statistical learning via the alternating direction method of multipliers. Found. Trends Mach. Learn. 2011, 3, 1–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, P.; Feng, J. Outlier-Robust Tensor PCA. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, J.F.; Candès, E.J.; Shen, Z. A singular value thresholding algorithm for matrix completion. SIAM J. Opt. 2010, 20, 1956–1982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gleich, D.F.; Greif, C.; Varah, J.M. The power and Arnoldi methods in an algebra of circulants. Numer. Linear Algebra Appl. 2013, 20, 809–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granata, J.; Conner, M.; Tolimieri, R. The tensor product: a mathematical programming language for FFTs and other fast DSP operations. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 1992, 9, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Bovik, A.C.; Sheikh, H.R.; Simoncelli, E.P. Image quality assessment: from error visibility to structural similarity. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2004, 13, 600–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oymak, S.; Jalali, A.; Fazel, M.; Eldar, Y.C.; Hassibi, B. Simultaneously structured models with application to sparse and low-rank matrices. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 2015, 61, 2886–2908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, C.; Zhang, Y.; Wright, J.; Goldfarb, D. Scalable Robust Matrix Recovery: Frank-Wolfe Meets Proximal Methods. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 2016, 38, A3291–A3317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richard, E.; Obozinski, G.R.; Vert, J.P. Tight convex relaxations for sparse matrix factorization. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Montreal, QC, Canada, 8–13 December 2014; pp. 3284–3292. [Google Scholar]
- Yokota, T.; Zhao, Q.; Cichocki, A. Smooth PARAFAC Decomposition for Tensor Completion. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2016, 64, 5423–5436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.L.; Hsu, C.T.; Liao, H.Y.M. Simultaneous Tensor Decomposition and Completion Using Factor Priors. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2014, 36, 577–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xutao Li, Y.Y.; Xu, X. Low-Rank Tensor Completion with Total Variation for Visual Data Inpainting. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, San Francisco, CA, USA, 4–9 February 2017; pp. 2210–2216. [Google Scholar]
- Yokota, T.; Erem, B.; Guler, S.; Warfield, S.K.; Hontani, H. Missing Slice Recovery for Tensors Using a Low-rank Model in Embedded Space. arXiv, 2018; arXiv:1804.01736. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, J.; Cheng, J. Matrix completion by deep matrix factorization. Neural Netw. 2018, 98, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, C.D.; Shafer, R.; Larue, B. An Order-p Tensor Factorization with Applications in Imaging. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 2013, 35, A474–A490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.Y.; Wang, X. Fourth-order tensors with multidimensional discrete transforms. arXiv, 2017; arXiv:1705.01576. [Google Scholar]
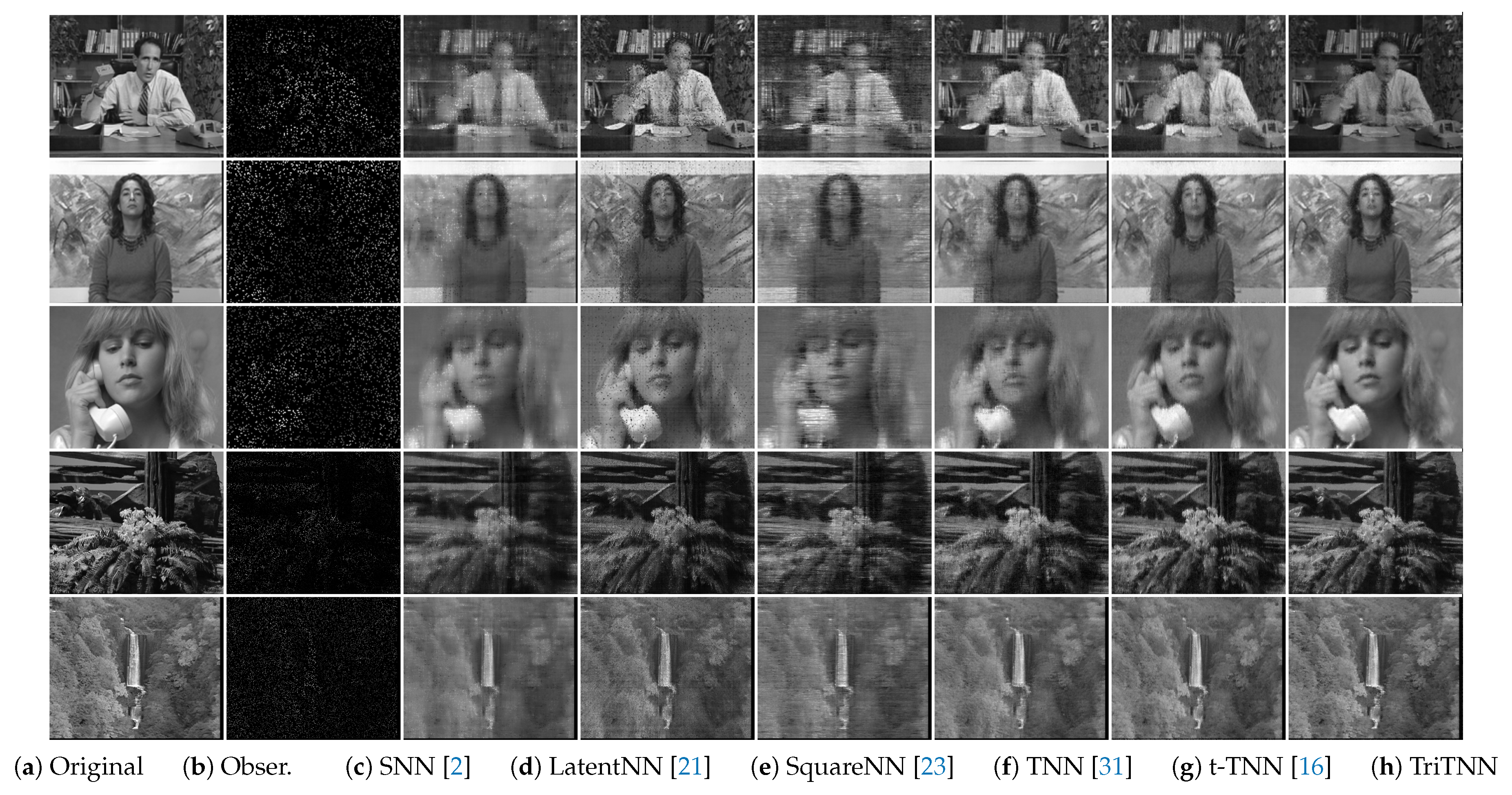







| Video | SNN [2] | LatentNN [21] | SquareNN [23] | TNN [31] | t-TNN [16] | TriTNN |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| salesman_qcif | 21.10 | 24.21 | 20.31 | 25.56 | 25.73 | 26.18 |
| silent_qcif | 24.07 | 23.95 | 22.98 | 27.93 | 28.03 | 28.47 |
| suzie_qcif | 25.79 | 24.63 | 24.48 | 27.92 | 29.47 | 29.70 |
| tempete_cif | 19.10 | 18.45 | 19.23 | 20.65 | 21.21 | 21.46 |
| waterfall_cif | 24.10 | 22.39 | 24.06 | 26.71 | 27.44 | 28.22 |
| Sampling Ratio | SNN [2] | LatentNN [21] | SquareNN [23] | TNN [31] | t-TNN [16] | TriTNN |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 14.58 | 15.50 | 17.27 | 17.23 | 17.29 | 17.45 | |
| 17.79 | 17.27 | 18.16 | 18.32 | 18.59 | 18.74 | |
| 18.74 | 18.36 | 18.80 | 19.04 | 19.12 | 19.53 | |
| 19.29 | 19.02 | 19.21 | 19.50 | 19.44 | 20.02 | |
| 19.61 | 19.43 | 19.49 | 19.82 | 19.64 | 20.28 | |
| 19.80 | 19.70 | 19.69 | 20.06 | 19.76 | 22.01 | |
| 19.90 | 19.83 | 19.84 | 20.23 | 19.85 | 22.41 |
| Sampling Ratio | SNN [2] | LatentNN [21] | SquareNN [23] | TNN [31] | t-TNN [16] | TriTNN |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 17.80 | 16.90 | 17.64 | 19.03 | 18.67 | 18.91 | |
| 19.26 | 18.48 | 18.94 | 20.04 | 19.60 | 20.09 | |
| 20.33 | 19.71 | 19.94 | 20.93 | 20.41 | 21.04 | |
| 21.24 | 20.67 | 20.89 | 21.74 | 21.17 | 21.92 | |
| 22.05 | 21.55 | 21.75 | 22.47 | 21.88 | 22.72 | |
| 22.82 | 22.39 | 22.56 | 23.16 | 22.61 | 23.68 | |
| 23.54 | 23.21 | 23.34 | 23.79 | 23.35 | 24.51 |
| Sampling Ratio | SNN [2] | LatentNN [21] | SquareNN [23] | TNN [31] | t-TNN [16] | TriTNN |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 17.30 | 17.63 | 17.57 | 18.31 | 18.62 | 18.36 | |
| 18.79 | 19.30 | 18.92 | 19.50 | 19.61 | 19.63 | |
| 19.85 | 20.29 | 19.93 | 20.38 | 20.37 | 20.45 | |
| 20.84 | 21.11 | 20.90 | 21.24 | 21.08 | 21.30 | |
| 21.72 | 21.86 | 21.76 | 22.05 | 21.78 | 22.18 | |
| 22.51 | 22.62 | 22.53 | 22.79 | 22.50 | 22.94 | |
| 23.39 | 23.40 | 23.39 | 23.59 | 23.27 | 23.80 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wei, D.; Wang, A.; Feng, X.; Wang, B.; Wang, B. Tensor Completion Based on Triple Tubal Nuclear Norm. Algorithms 2018, 11, 94. https://doi.org/10.3390/a11070094
Wei D, Wang A, Feng X, Wang B, Wang B. Tensor Completion Based on Triple Tubal Nuclear Norm. Algorithms. 2018; 11(7):94. https://doi.org/10.3390/a11070094
Chicago/Turabian StyleWei, Dongxu, Andong Wang, Xiaoqin Feng, Boyu Wang, and Bo Wang. 2018. "Tensor Completion Based on Triple Tubal Nuclear Norm" Algorithms 11, no. 7: 94. https://doi.org/10.3390/a11070094
APA StyleWei, D., Wang, A., Feng, X., Wang, B., & Wang, B. (2018). Tensor Completion Based on Triple Tubal Nuclear Norm. Algorithms, 11(7), 94. https://doi.org/10.3390/a11070094





