High-Surface-Area, Emulsion-Templated Carbon Foams by Activation of polyHIPEs Derived from Pickering Emulsions
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of HIPEs and Subsequent poly(DVB)HIPEs
2.3. Preparation of carboHIPEs and Activated carboHIPEs
2.4. Characterization
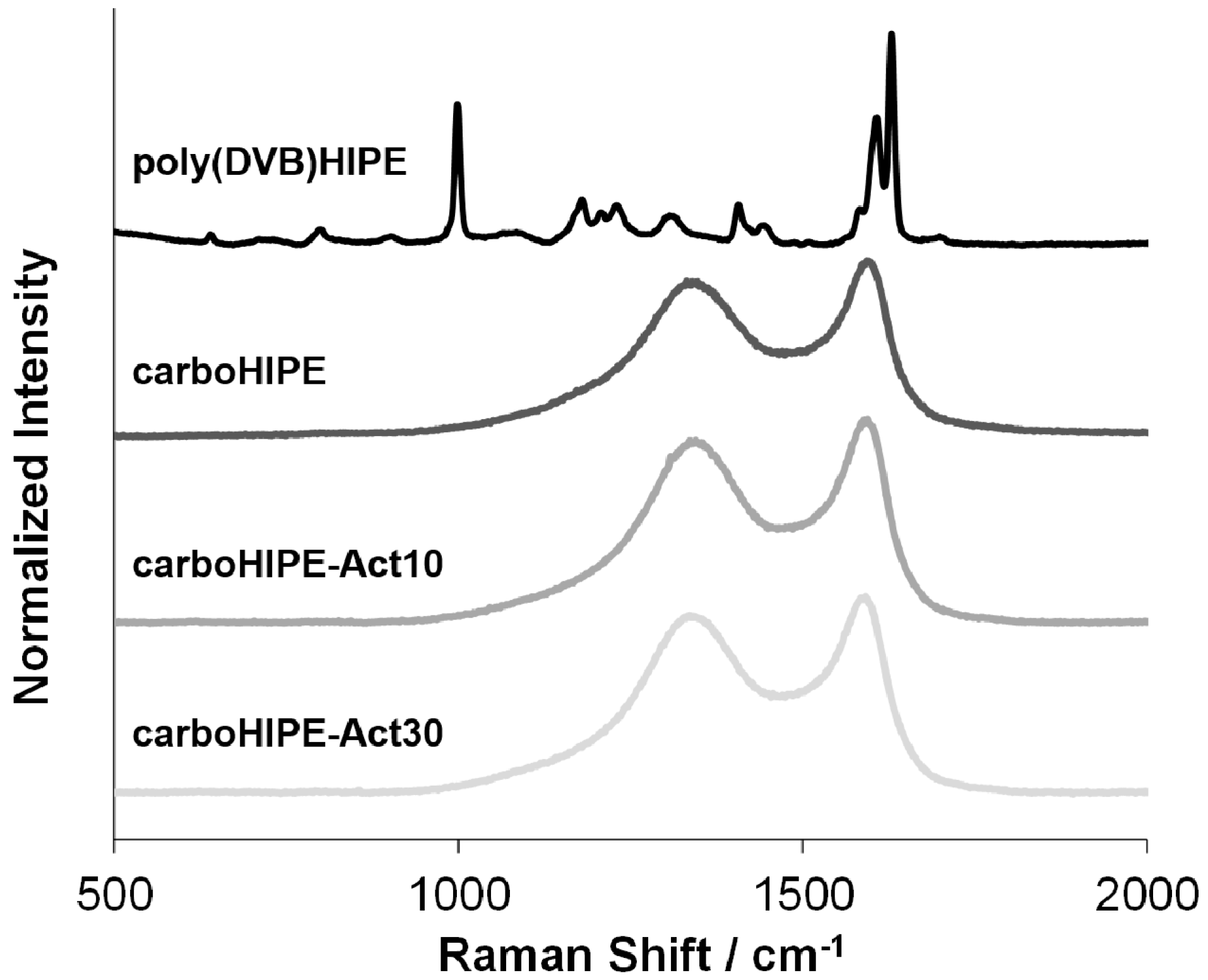
2.5. Research and Discussion
3. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mohan, D.; Sarswat, A.; Ok, Y.S.; Pittman, C.U.J. Organic and inorganic contaminants removal from water with biochar, a renewable, low cost and sustainable adsorbent—A critical review. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 160, 191–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wildgoose, G.G.; Banks, C.E.; Compton, R.G. Metal nanopartictes and related materials supported on carbon nanotubes: Methods and applications. Small 2006, 2, 182–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kemp, K.C.; Seema, H.; Saleh, M.; Le, N.H.; Mahesh, K.; Chandra, V.; Kim, K.S. Environmental applications using graphene composites: Water remediation and gas adsorption. Nanoscale 2013, 5, 3149–3171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, A.D.; Li, X.; Zhang, H.F. Porous carbon spheres and monoliths: Morphology control, pore size tuning and their applications as Li-ion battery anode materials. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2014, 43, 4341–4356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sevilla, M.; Mokaya, R. Energy storage applications of activated carbons: Supercapacitors and hydrogen storage. Energy Environ. Sci. 2014, 7, 1250–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gogotsi, Y.; Nikitin, A.; Ye, H.H.; Zhou, W.; Fischer, J.E.; Yi, B.; Foley, H.C.; Barsoum, M.W. Nanoporous carbide-derived carbon with tunable pore size. Nat. Mater. 2003, 2, 591–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yushin, G.; Dash, R.; Jagiello, J.; Fischer, J.E.; Gogotsi, Y. Carbide-derived carbons: Effect of pore size on hydrogen uptake and heat of adsorption. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2006, 16, 2288–2293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Y.; Gu, D.; Zhang, F.Q.; Shi, Y.F.; Cheng, L.; Feng, D.; Wu, Z.; Chen, Z.; Wan, Y.; Stein, A.; et al. A family of highly ordered mesoporous polymer resin and carbon structures from organic-organic self-assembly. Chem. Mater. 2006, 18, 4447–4464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bear, J.C.; McGettrick, J.D.; Parkin, I.P.; Dunnill, C.W.; Hasell, T. Porous carbons from inverse vulcanized polymers. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2016, 232, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, S.B.; Kim, J.Y.; Yu, J.S. Synthesis of highly ordered nanoporous carbon molecular sieves from silylated MCM-48 using divinylbenzene as precursor. Chem. Commun. 2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, A.H.; Schuth, F. Nanocasting: A versatile strategy for creating nanostructured porous materials. Adv. Mater. 2006, 18, 1793–1805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cameron, N.R.; Sherrington, D.C. High internal phase emulsions (HIPEs)—Structure, properties and use in polymer preparation. In Biopolymers Liquid Crystalline Polymers Phase Emulsion; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1996; pp. 163–214. [Google Scholar]
- Pickering, S.U. CXCVI.—Emulsions. J. Chem. Soc. Trans. 1907, 91, 2001–2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binks, B.P.; Lumsdon, S.O. Influence of particle wettability on the type and stability of surfactant-free emulsions. Langmuir 2000, 16, 8622–8631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menner, A.; Verdejo, R.; Shaffer, M.; Bismarck, A. Particle-stabilized surfactant-free medium internal phase emulsions as templates for porous nanocomposite materials: Poly-pickering-foams. Langmuir 2007, 23, 2398–2403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikem, V.O.; Menner, A.; Bismarck, A. High Internal Phase Emulsions Stabilized Solely by Functionalized Silica Particles. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2008, 47, 8277–8279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, L.L.C.; Ikem, V.O.; Menner, A.; Bismarck, A. Macroporous Polymers with Hierarchical Pore Structure from Emulsion Templates Stabilised by Both Particles and Surfactants. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2011, 32, 1563–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Smith, N.L.; Budd, P.M. Polymerization and carbonization of high internal phase emulsions. Polym. Int. 2005, 54, 297–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asfaw, H.D.; Younesi, R.; Valvo, M.; Maibach, J.; Ångström, J.; Tai, C.-W.; Bacsik, Z.; Sahlberg, M.; Nyholm, L.; Edström, K. Boosting the thermal stability of emulsion–templated polymers via sulfonation: An efficient synthetic route to hierarchically porous carbon foams. Chem. Sel. 2016, 1, 784–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foulet, A.; Birot, M.; Backov, R.; Sonnemann, G.; Deleuze, H. Preparation of hierarchical porous carbonaceous foams from Kraft black liquor. Mater. Today Commun. 2016, 7, 108–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ungureanu, S.; Sigaud, G.; Vignoles, G.L.; Lorrette, C.; Birot, M.; Deleuze, H.; Backov, R. First Biosourced Monolithic Macroporous SiC/C Composite Foams (Bio-SiC/C(HIPE)) Bearing Unprecedented Heat Transport Properties. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2013, 15, 893–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szczurek, A.; Fierro, V.; Pizzi, A.; Celzard, A. Emulsion-templated porous carbon monoliths derived from tannins. Carbon 2014, 74, 352–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, N.; Silverstein, M.S. Synthesis of emulsion-templated porous polyacrylonitrile and its pyrolysis to porous carbon monoliths. Polymer 2011, 52, 282–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodward, R.T.; Fam, D.W.H.; Anthony, D.B.; Hong, J.; McDonald, T.O.; Petit, C.; Shaffer, M.S.P.; Bismarck, A. Hierarchically porous carbon foams from pickering high internal phase emulsions. Carbon 2016, 101, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ungureanu, S.; Birot, M.; Deleuze, H.; Schmitt, V.; Mano, N.; Backov, R. Triple hierarchical micro-meso-macroporous carbonaceous foams bearing highly monodisperse macroporosity. Carbon 2015, 91, 311–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.C.; Kaskel, S. KOH activation of carbon-based materials for energy storage. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 23710–23725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romanos, J.; Beckner, M.; Rash, T.; Firlej, L.; Kuchta, B.; Yu, P.; Suppes, G.; Wexler, C.; Pfeifer, P. Nanospace engineering of KOH activated carbon. Nanotechnology 2012, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.L.; Gao, Q.M.; Hu, J. High Hydrogen Storage Capacity of Porous Carbons Prepared by Using Activated Carbon. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 7016–7022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lozano-Castello, D.; Calo, J.M.; Cazorla-Amoros, D.; Linares-Solano, A. Carbon activation with KOH as explored by temperature programmed techniques, and the effects of hydrogen. Carbon 2007, 45, 2529–2536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, J.; Tanaka, S.; Egashira, Y.; Nishiyama, N. KOH activation of ordered mesoporous carbons prepared by a soft-templating method and their enhanced electrochemical properties. Carbon 2010, 48, 1985–1989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, W.; Huang, C.C.; Zhuo, S.P.; Yuan, X.; Wang, G.Q.; Hulicova-Jurcakova, D.; Yan, Z.F.; Lu, G.Q. Hierarchical porous carbons with high performance for supercapacitor electrodes. Carbon 2009, 47, 1715–1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, C.A.; Rasband, W.S.; Eliceiri, K.W. NIH Image to ImageJ: 25 years of image analysis. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 671–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menner, A.; Ikem, V.; Salgueiro, M.; Shaffer, M.S.P.; Bismarck, A. High internal phase emulsion templates solely stabilised by functionalised titania nanoparticles. Chem. Commun. 2007, 43, 4274–4276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hainey, P.; Huxham, I.M.; Rowatt, B.; Sherrington, D.C.; Tetley, L. Synthesis and ultrastructural studies of styrene divinylbenzene polyhipe polymers. Macromolecules 1991, 24, 117–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sing, K.S.W.; Everett, D.H.; Haul, R.A.W.; Moscou, L.; Pierotti, R.A.; Rouquerol, J.; Siemieniewska, T. Reporting physisorption data for gas solid systems with special reference to the determination of surface-area and porosity (recommendations 1984). Pure Appl. Chem. 1985, 57, 603–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stokr, J.; Schneider, B.; Frydrychova, A.; Coupek, J. Composition analysis of crosslinked styrene-ethylene dimethacrylate and styrene-divinylbenzene copolymers by raman-spectroscopy. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1979, 23, 3553–3561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, A.C.; Robertson, J. Interpretation of Raman spectra of disordered and amorphous carbon. Phys. Rev. B 2000, 61, 14095–14107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Su, S.; Zhou, L.; Abbot, A.M.; Ye, H. Dielectric transition of polyacrylonitrile derived carbon nanofibers. Mater. Res. Express 2014, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
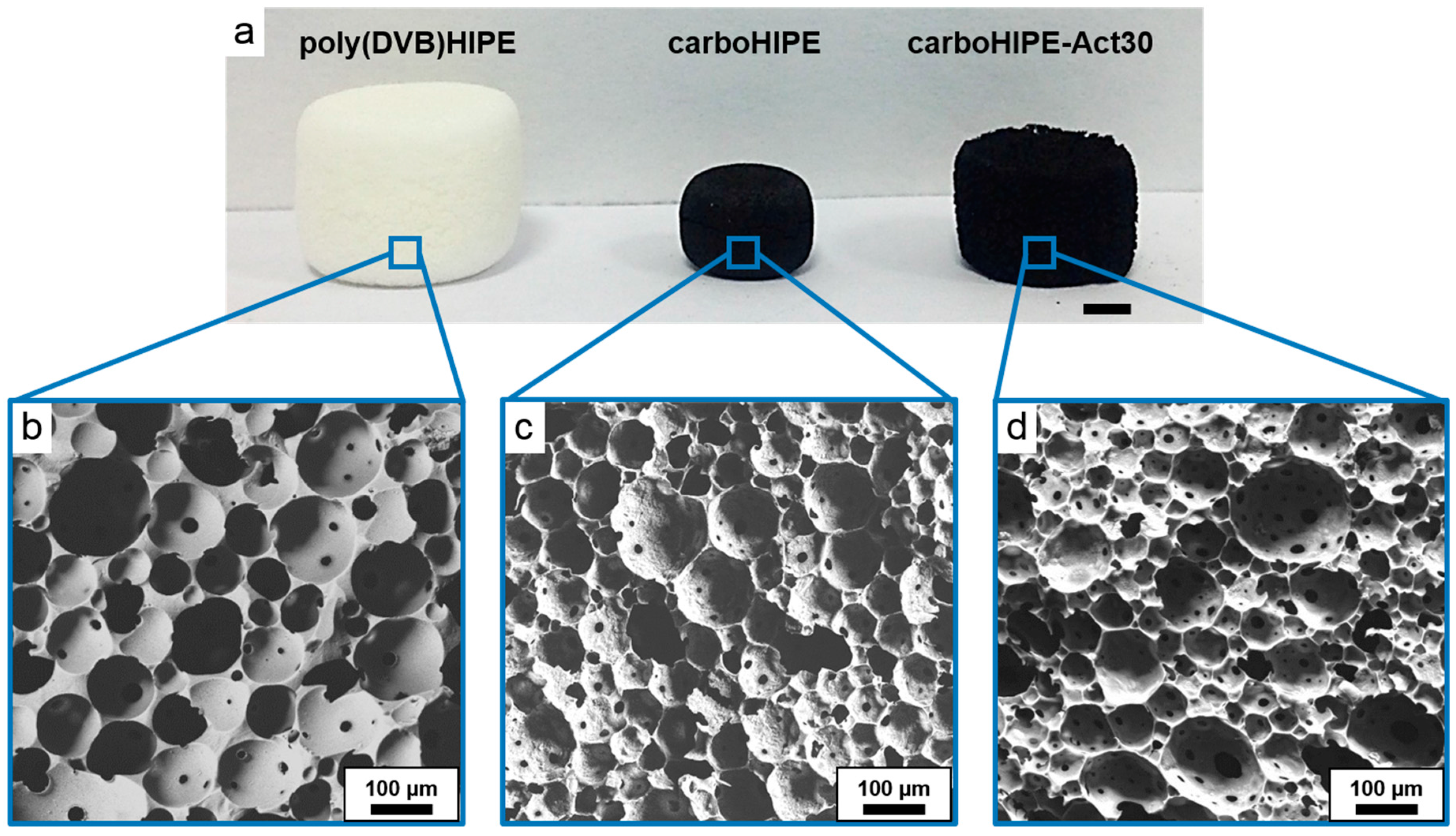
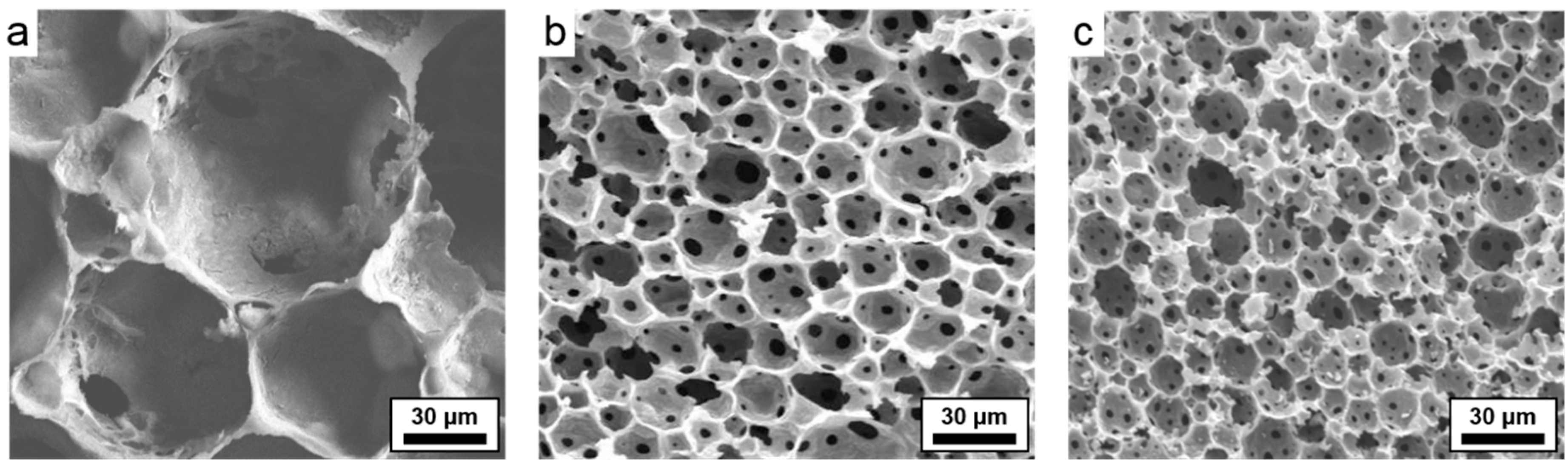
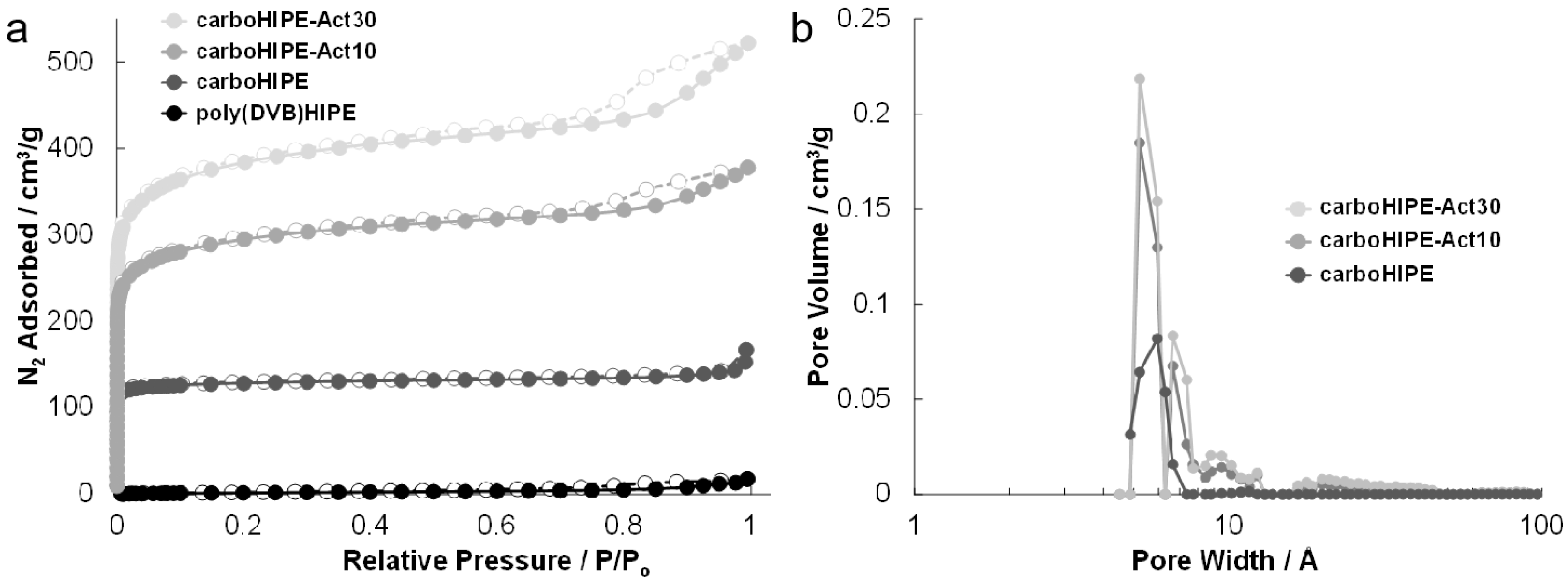
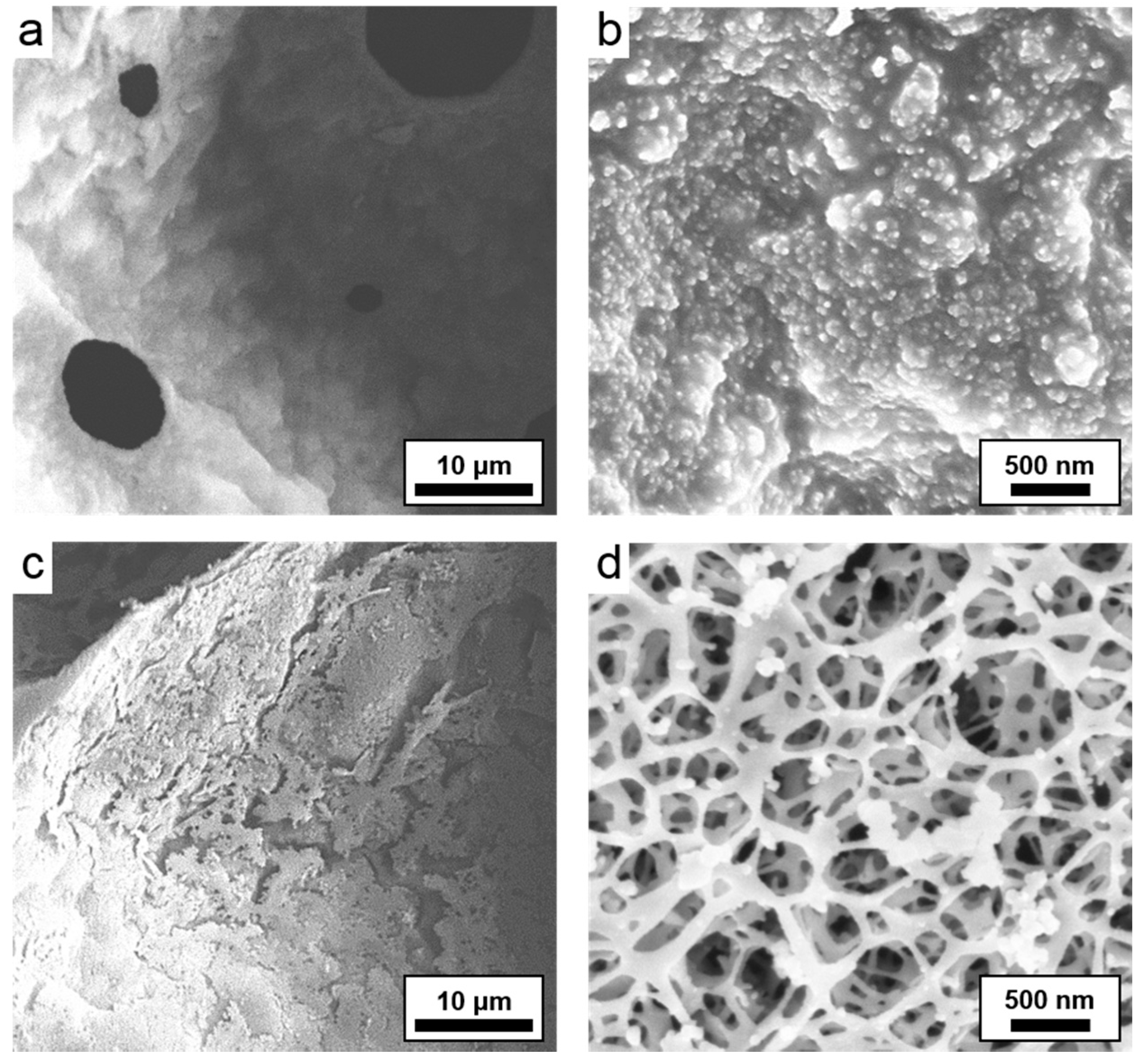
| Sample | Average Macropore Diameter (μm) a | Surface Area (m2/g) b | Micropore vol. (cm3/g) b | Total Pore vol. (g/cm3) b | Porosity (%) c | Char Yield (%) d |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| poly(DVB)HIPE | 82 ± 42 | 8 | 0 | 0.021 | 86 | N/A |
| carboHIPE | 62 ± 28 | 521 | 0.268 | 0.223 | 95 | 22 |
| carboHIPE-Act10 | 72 ± 26 | 1123 | 0.432 | 0.572 | 97 | 13 |
| carboHIPE-Act30 | 74 ± 30 | 1456 | 0.554 | 0.791 | 97 | 12 |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Woodward, R.T.; De Luca, F.; Roberts, A.D.; Bismarck, A. High-Surface-Area, Emulsion-Templated Carbon Foams by Activation of polyHIPEs Derived from Pickering Emulsions. Materials 2016, 9, 776. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma9090776
Woodward RT, De Luca F, Roberts AD, Bismarck A. High-Surface-Area, Emulsion-Templated Carbon Foams by Activation of polyHIPEs Derived from Pickering Emulsions. Materials. 2016; 9(9):776. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma9090776
Chicago/Turabian StyleWoodward, Robert T., François De Luca, Aled D. Roberts, and Alexander Bismarck. 2016. "High-Surface-Area, Emulsion-Templated Carbon Foams by Activation of polyHIPEs Derived from Pickering Emulsions" Materials 9, no. 9: 776. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma9090776
APA StyleWoodward, R. T., De Luca, F., Roberts, A. D., & Bismarck, A. (2016). High-Surface-Area, Emulsion-Templated Carbon Foams by Activation of polyHIPEs Derived from Pickering Emulsions. Materials, 9(9), 776. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma9090776





