Fabrication, Polarization of Electrospun Polyvinylidene Fluoride Electret Fibers and Effect on Capturing Nanoscale Solid Aerosols †
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Description
2.1. Materials
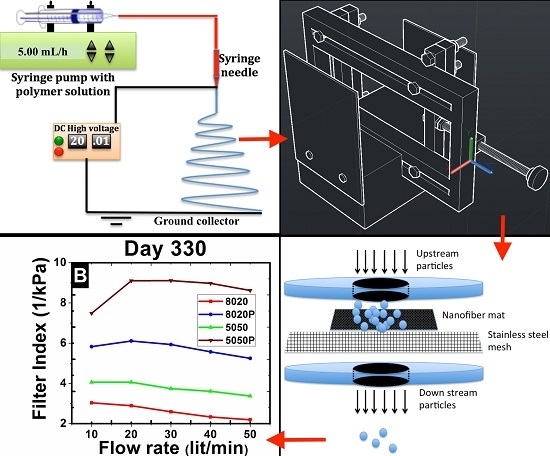
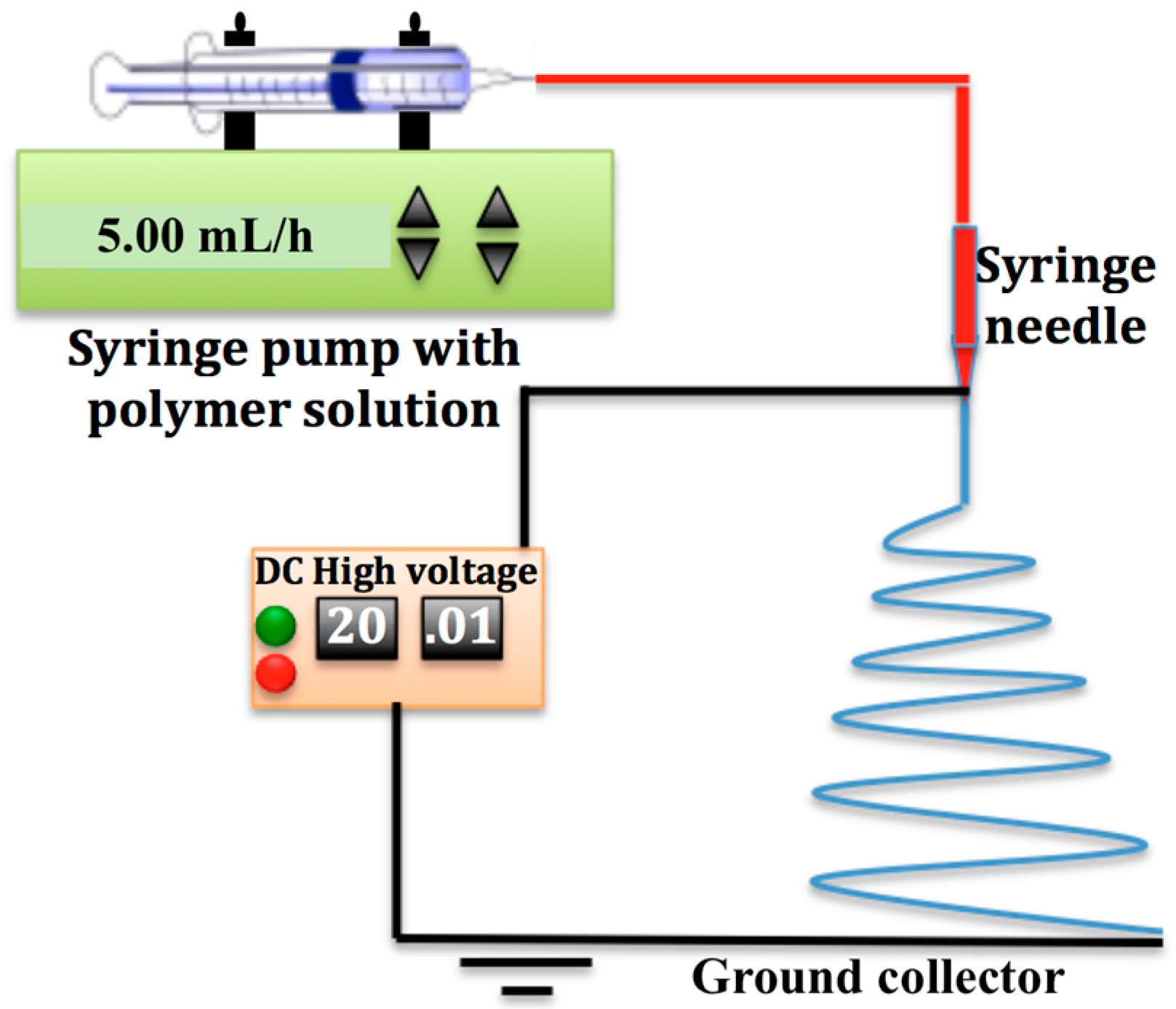
2.2. Electrospinning
2.2.1. Polarization of Electrospun PVDF Fibers
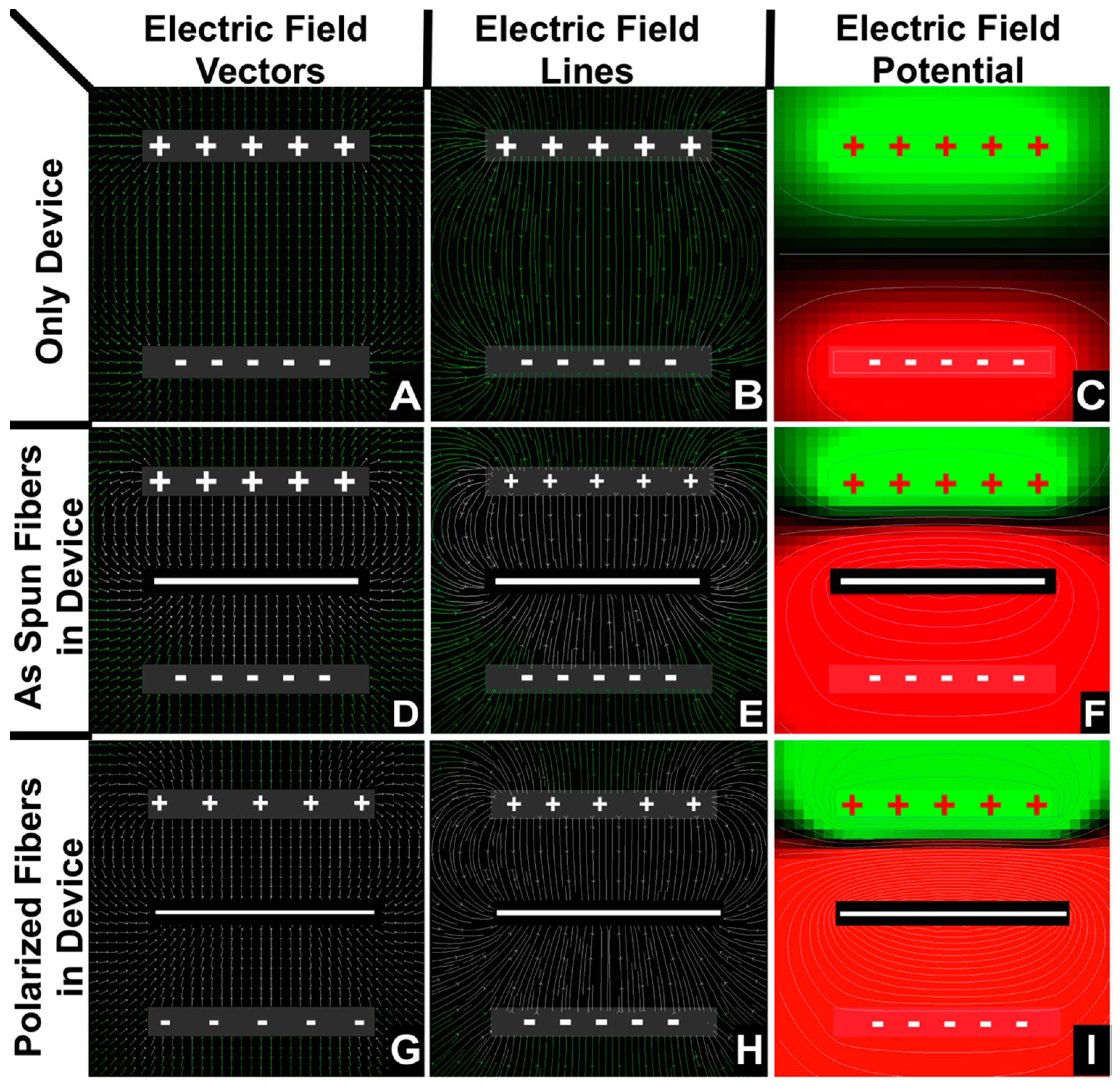
2.2.2. Modelling of the Polarization Device Showed in Section 2.3.1
2.3. Characterization
2.3.1. Morphology Analysis
2.3.2. Thermal Analysis
2.3.3. Electrostatic Analysis
2.3.4. Filtration Performance Analysis
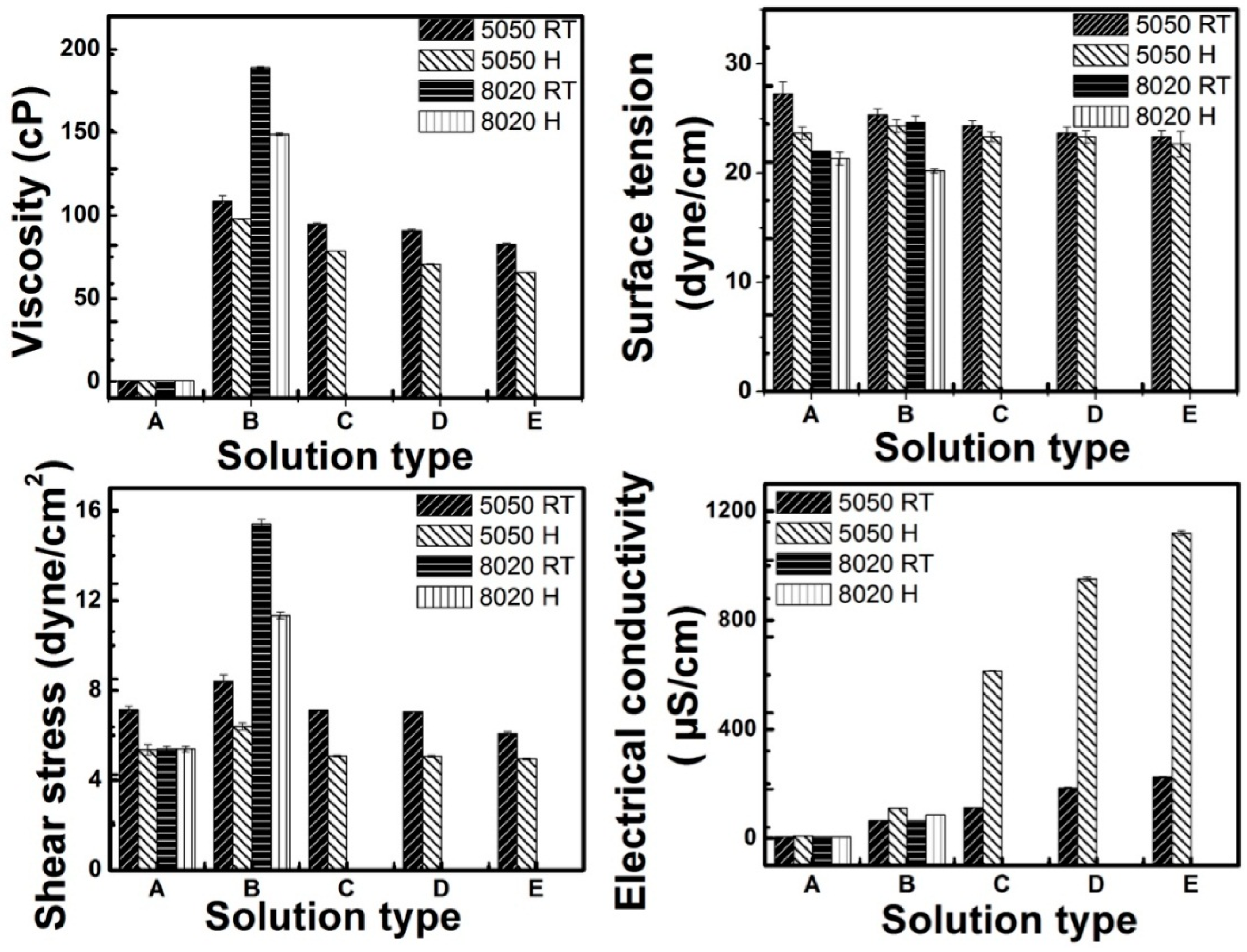
2.4. Solution Properties
3. Discussion of Results
3.1. Electrospun Fiber Characterization
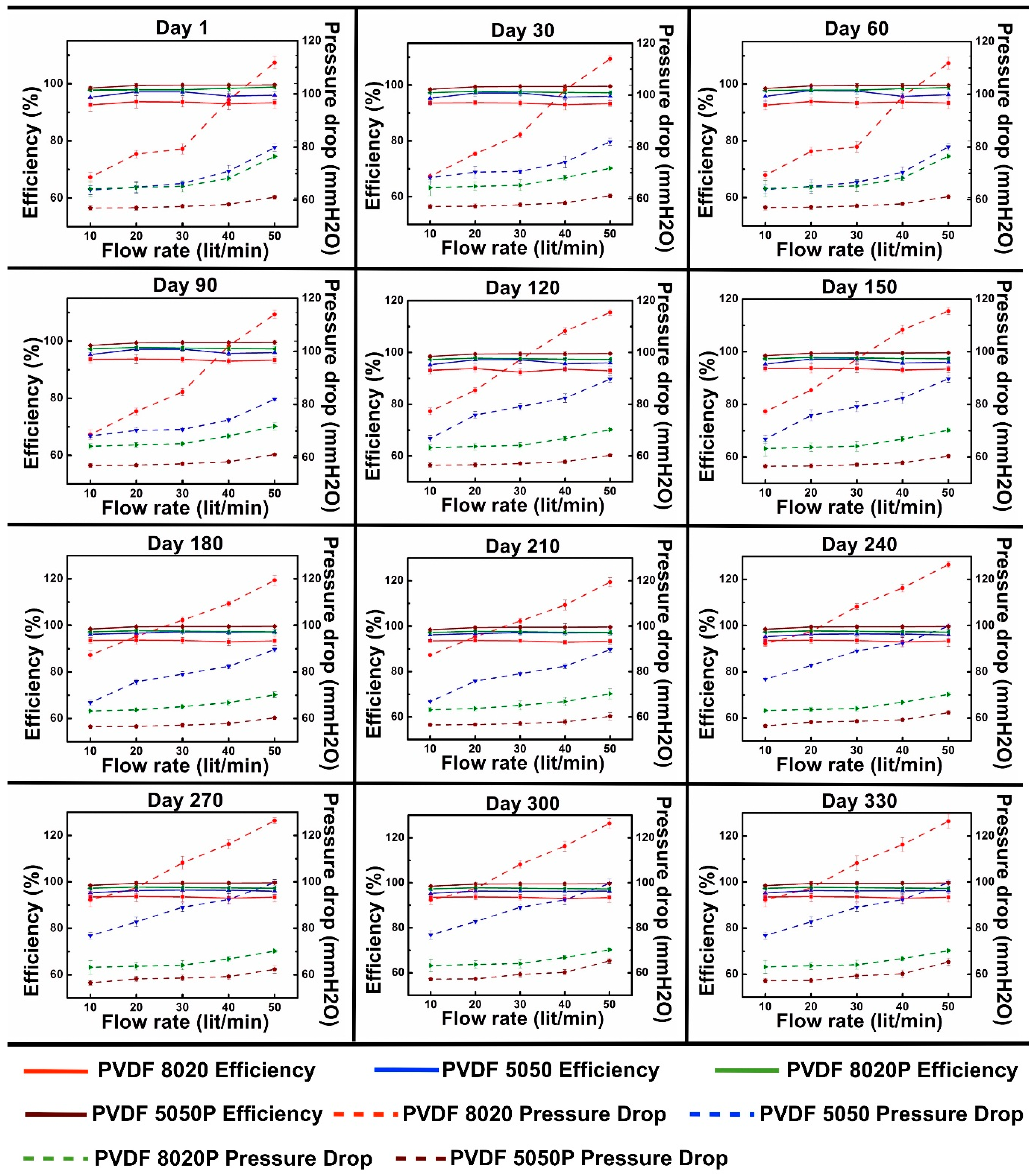
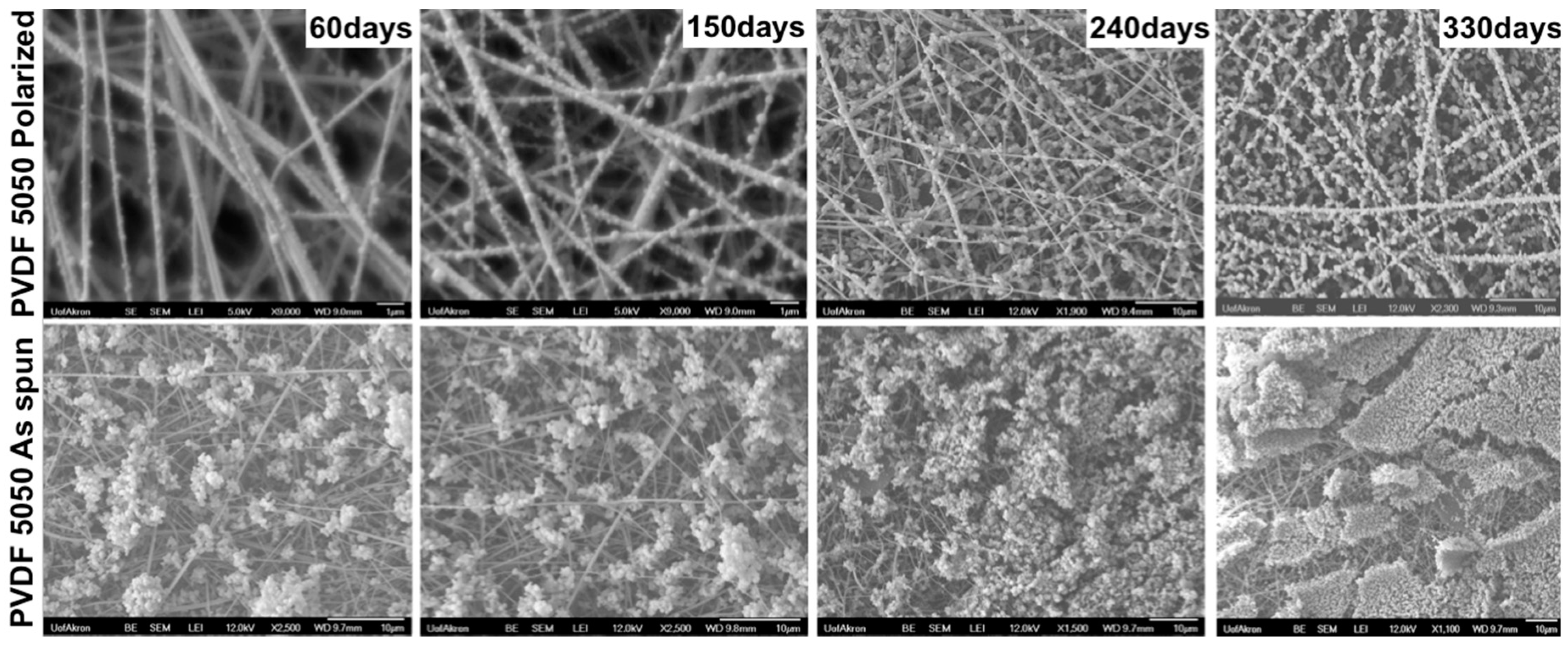
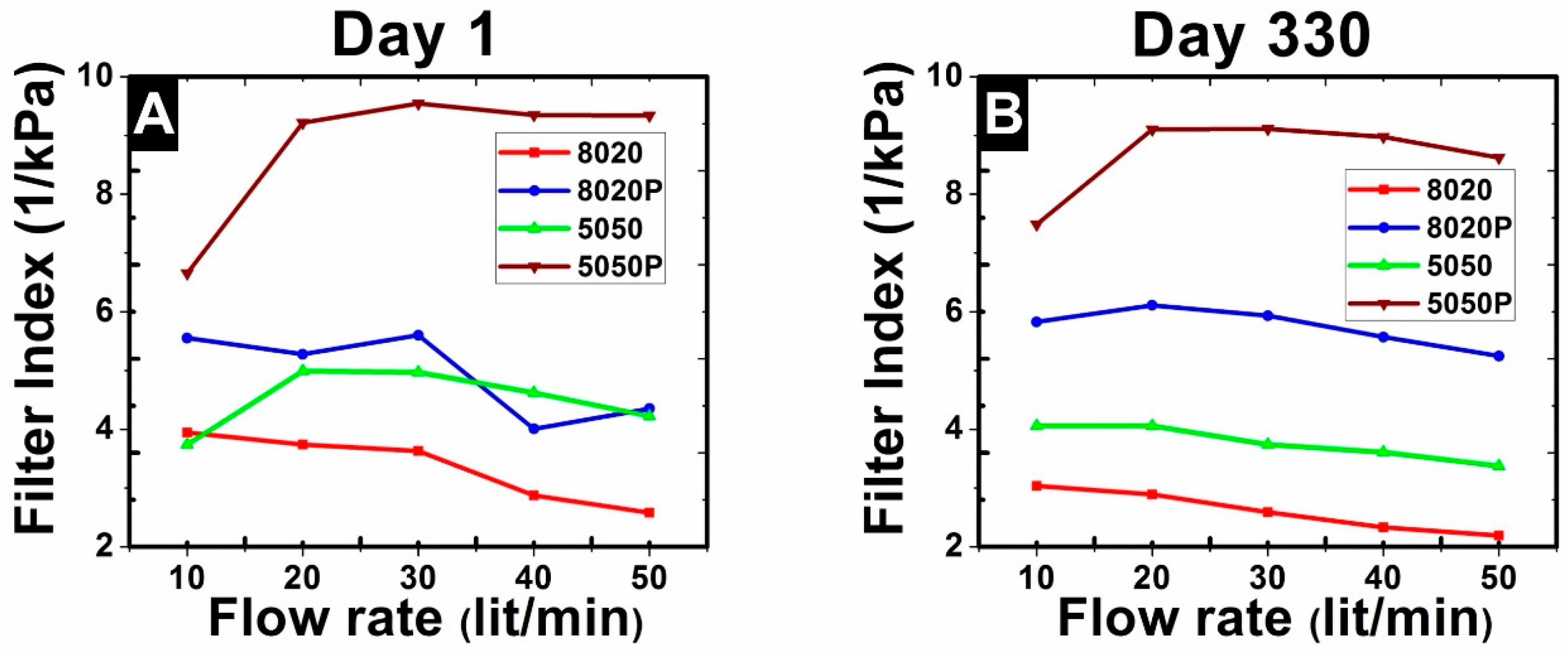
3.2. TSI8130: Filter Media Test Results
4. Summary and Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bernstein, J.A.; Alexis, N.; Barnes, C.; Bernstein, I.L.; Nel, A.; Peden, D.; Diaz-Sanchez, D.; Tarlo, S.M.; Williams, P.B.; Bernstein, J.A. Health effects of air pollution. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2004, 114, 1116–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kampa, M.; Castanas, E. Human health effects of air pollution. Environ. Pollut. 2008, 151, 362–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pope, C.A.; Dockery, D.W. Health effects of fine particulate air pollution: Lines that connect. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2006, 56, 709–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pope, C.A.; Bates, D.V.; Raizenne, M.E. Health effects of particulate air pollution: Time for reassessment? Environ. Health Perspect. 1995, 103, 472–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seaton, A.; MacNee, W.; Donaldson, K.; Godden, D. Particulate air pollution and acute health effects. Lancet 1995, 345, 176–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Wang, H.; Chase, G.G. Performance of Hydrophilic Glass Fiber Media to Separate Dispersed Water Drops from Ultra Low Sulfur Diesel Supplemented by Vibrations. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2015, 156, 665–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, S.U.; Manzo, G.M.; Patel, S.U.; Kulkarni, P.S.; Chase, G.G. Permeability of electrospun superhydrophobic nanofiber mats. J. Nanotechnol. 2012, 2012, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viswanadam, G.; Chase, G.G. Water-diesel secondary dispersion separation using superhydrophobic tubes of nanofibers. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2013, 104, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, S.U.; Chase, G.G. Separation of water droplets from water-in-diesel dispersion using superhydrophobic polypropylene fibrous membranes. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2014, 126, 62–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davoudi, M.; Fang, J.; Chase, G.G. Barrel shaped droplet movement at junctions of perpendicular fibers with different orientations to the air flow direction. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2016, 162, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doshi, J.; Reneker, D.H. Electrospinning process and applications of electrospun fibers. J. Electrost. 1995, 35, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, H.U.; Lolla, D.; Nikolov, Z.; Chase, G.G. Pd-Au Nanoparticles Supported by TiO2 Fibers for Catalytic NO Decomposition by CO. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2015, 33, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajala, J.; Shin, H.; Lolla, D.; Chase, G. Core-Shell Electrospun Hollow Aluminum Oxide Ceramic Fibers. Fibers 2015, 3, 450–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reneker, D.H.; Chun, I. Nanometre diameter fibres of polymer, produced by electrospinning. Nanotechnology 1999, 7, 216–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Clark, D.M.; Yu, X.; Zhong, Z.; Liu, K.; Reneker, D.H. Mechanical properties of polymer nanofibers revealed by interaction with streams of air. Polymer 2012, 53, 782–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, C.J.; Chase, G.G.; Yarin, A.L.; Reneker, D.H. Effects of parameters on nanofiber diameter determined from electrospinning model. Polymer 2007, 48, 6913–6922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, H.U.; Li, Y.; Paynter, A.; Nartetamrongsutt, K.; Chase, G.G. Vertical rod method for electrospinning polymer fibers. Polymer 2015, 65, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, J.; Bhatta, R.S.; Reneker, D.H.; Tsige, M.; Taylor, P.L. Molecular dynamics simulations of relaxation in stretched PVDF nanofibers. Polymer 2014, 56, 482–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wisniewski, C.; Ferreira, G.F.L.; Moura, W.A.; Giacometti, J.A.; Wisniewski, C.; Ferreira, G.F.L. Study of ferroelectric polarization in poly(vinylidene fluoride) using the constant current method. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2000, 33, 2483–2488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Liu, J.; Ni, C.; Martin, D.C.; Chase, D.B.; Rabolt, J.F. Molecular orientation in electrospun poly(vinylidene fluoride) fibers. ACS Macro Lett. 2012, 1, 428–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lolla, D.; Gorse, J.; Kisielowski, C.; Miao, J.; Taylor, P.L.; Chase, G.G.; Reneker, D.H. Polyvinylidene fluoride molecules in nanofibers, imaged at atomic scale by aberration corrected electron microscopy. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 120–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lovinger, A.J. Ferroelectric Polymers. Science 1983, 220, 1115–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baji, A.; Mai, Y.-W.; Li, Q.; Liu, Y. Electrospinning induced ferroelectricity in poly(vinylidene fluoride) fibers. Nanoscale 2011, 3, 3068–3071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bormashenko, Y.; Pogreb, R.; Stanevsky, O.; Bormashenko, E. Vibrational spectrum of PVDF and its interpretation. Polym. Test. 2004, 23, 791–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, B.; Raghuvanshi, S.K.; Sharma, N.P.; Krishna, J.B.M.; Wahab, M.A. 1.25 MeV Gamma Irradiated Induced Physical and Chemical Changes in Poly Vinylidene Fluoride (PVDF) Polymer. Prog. Nanotechnol. Nanometer 2013, 2, 42–46. [Google Scholar]
- Lanceros-Méndez, S.; Mano, J.F.; Costa, A.M.; Schmidt, V.H. Ftir and DSC Studies of Mechanically Deformed Β-Pvdf Films. J. Macromol. Sci. Part B 2001, 40, 517–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ignatova, M.; Yovcheva, T.; Viraneva, A.; Mekishev, G.; Manolova, N.; Rashkov, I. Study of charge storage in the nanofibrous poly(ethylene terephthalate) electrets prepared by electrospinning or by corona discharge method. Eur. Polym. J. 2008, 44, 1962–1967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali Kilic, B.-Y.Y.; Shim, E.; Pourdeyhimi, B. Aerosol Filtration Properties of Nucleating Agent Containing Electret Filters. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walls, H.J.; Ensor, D.S.; Andrady, A.L.; Walker, T.A. Particle Filter System Incorporating Electret Nanofibers. U.S. Patent No. 20110174158 A1, 21 July 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Cho, D.; Naydich, A.; Frey, M.W.; Joo, Y.L. Further improvement of air filtration efficiency of cellulose filters coated with nanofibers via inclusion of electrostatically active nanoparticles. Polymer 2013, 54, 2364–2372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.-S. Electrostatic forces in fibrous filters—A review. Powder Technol. 2001, 118, 166–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dargaville, T.R.T.; Celina, M.C.; Elliot, J.; Chaplya, P.M.; Elliott, J.M.; Jones, G.D.; Mowery, D.M.; Assink, R.A.; Clough, R.L.; Martin, J.W. Characterization, Performance and Optimization of PVDF as a Piezoelectric Film for Advanced Space Mirror Concepts; Sandia National Laboratories: Livermore, CA, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Tsai, P.P.; Schreuder-Gibson, H.; Gibson, P. Different electrostatic methods for making electret filters. J. Electrostat. 2002, 54, 333–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goel, M. Electret sensors, filters and MEMS devices: New challenges in materials research. Curr. Sci. 2003, 85, 443–453. [Google Scholar]
- Iverson, W.P. Separator for separating fluid media from minute particles of impurities. U.S. Patent No. 4492633 A, 8 January 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Emi, H.; Wang, C. Filtration Model Filters. AlChE J. 1982, 28, 397–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilic, A.; Shim, E.; Yeom, B.Y.; Pourdeyhimi, B. Improving electret properties of PP filaments with barium titanate. J. Electrostat. 2013, 71, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutten, I.M. Handbook of Nonwoven Filter Media; Elsivier: Oxford, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Salimi, A.; Yousefi, A.A. Analysis Method. Polym. Test. 2003, 22, 699–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khayet, M.; Khulbe, K.; Matsuura, T. Characterization of membranes for membrane distillation by atomic force microscopy and estimation of their water vapor transfer coefficients in vacuum membrane distillation process. J. Memb. Sci. 2004, 238, 199–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Cooper, R.; Wang, K.; Liang, H. Nano-Scale Characterization of a Piezoelectric Polymer (Polyvinylidene Difluoride, PVDF). Sensors 2008, 8, 7359–7368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barhate, R.S.; Ramakrishna, S. Nanofibrous filtering media: Filtration problems and solutions from tiny materials. J. Memb. Sci. 2007, 296, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzo, G.M.; Wu, Y.; Chase, G.G.; Goux, A. Comparison of nonwoven glass and stainless steel microfiber media in aerosol coalescence filtration. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2016, 162, 14–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nartetamrongsutt, K.; Chase, G.G. The influence of salt and solvent concentrations on electrospun polyvinylpyrrolidone fiber diameters and bead formation. Polymer 2013, 54, 2166–2173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Zhuang, M.; Yu, Z.; Zheng, G.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, H.; Sun, D. The Effect of Surfactants on the Diameter and Morphology of Electrospun Ultrafine Nanofiber. J. Nanomater. 2014, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, X.; Trudick, E.; Chase, G.G. Simulation of electrostatic field in electrospinning of polymer nanofibers. Nanoscale Syst. Math. Model. Theory Appl. 2015, 4, 35–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rengasamy, S.; Eimer, B.C.; Shaffer, R.E. Comparison of Nanoparticle Filtration Performance of NIOSH-approved and CE-Marked Particulate Filtering Facepiece Respirators. Ann. Occup. Hyg. 2009, 53, 117–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaffer, R.E.; Rengasamy, S. Respiratory protection against airborne nanoparticles: A review. J. Nanopart. Res. 2009, 11, 1661–1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westfall, C. How Argonne’s Intense Pulsed Neutron Source Came to Life and Gained Its Niche: The View from an Ecosystem Perspective. Argonne Natl. Lab. 2012, 5, 1–58. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, R.C. Air Filtration: An Integrated Approach to the Theory and Application of Fibrous Filters, 1st ed.; Pergamon Press: New York, NY, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]

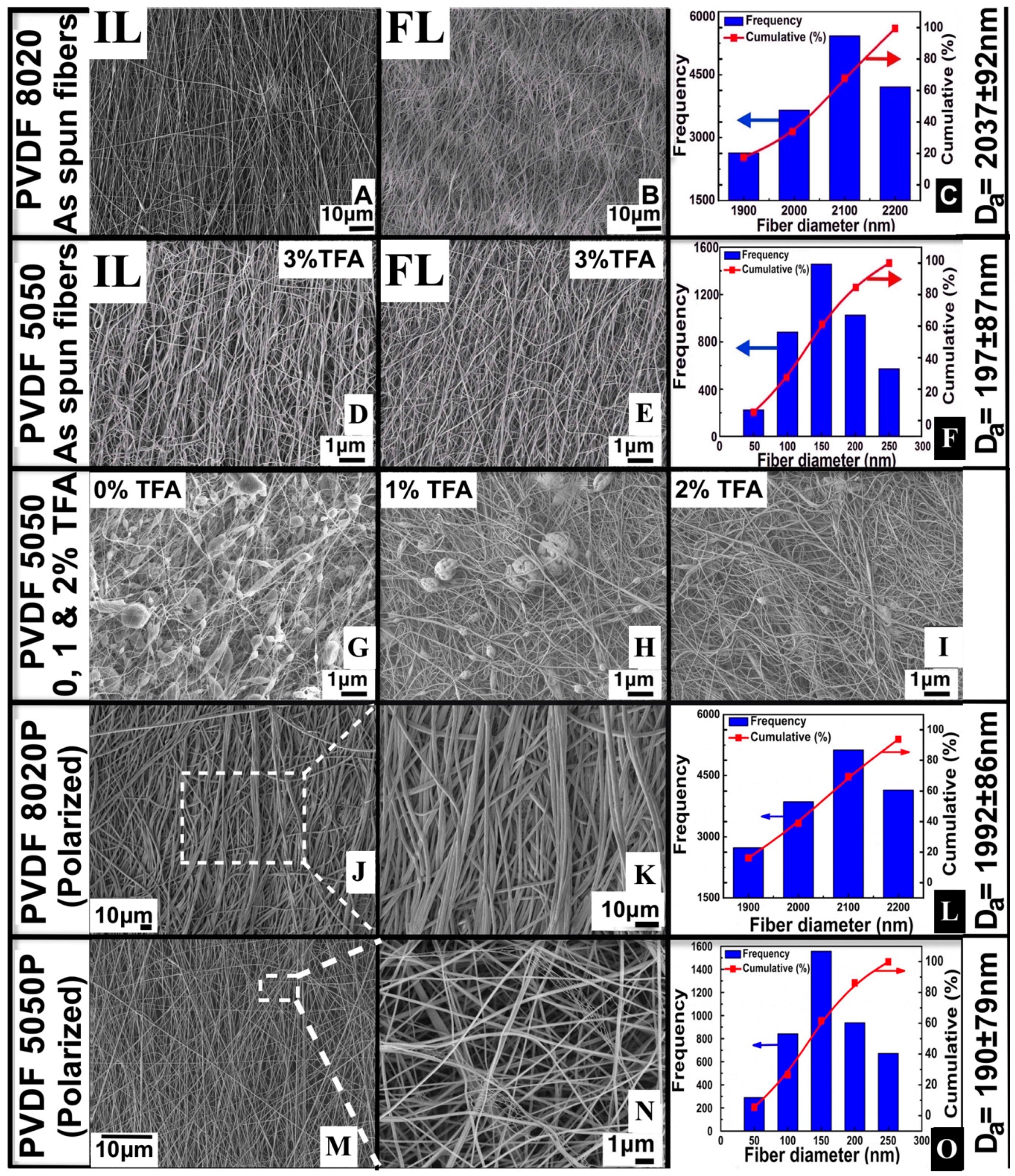

| Polymer Solution Concentration (wt./wt. %) | Solvent Ratio (Acetone:DMF) | TFA Concentration in Solution (wt./wt. %) | Applied Voltage (kV) | Tip to Collector Distance (cm) | Drum Rotation Speed (RPM) | Syringe Flow Rate (mL/h) | Fiber Diameter Range (nm) | Average Fiber Diameter (nm) | Fiber Diameter Standard Deviation (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 20% | 80:20 | 0 | 20 | 12 | 100 | 15 | 1800–2900 | 2037 | 92 |
| 10% | 50:50 | 3% | 17 | 20 | 100 | 5 | 5–293 | 197 | 87 |
| Type of Fiber Sample | Porosity (ε) by Gas Expansion Method | Porosity (ε) by Mass Balance Method | DSC-Crystallinity XC (%) | DSC-Crystallization Temperature TC,P (°C) | TGA-CH2 Degradation Peak (°C) | TGA-CF2 Degradation Peak (°C) | BET Surface Area (M2/g) | Average Surface Pore Size (Nm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PVDF 8020 | 0.89 ± 0.24 | 0.92 ± 0.22 | 49.3 ± 2.32 | 128.9 ± 2.32 | 407.1 ± 2.31 | 426.1 ± 2.47 | 36.48 ± 1.23 | 13.16 ± 1.26 |
| PVDF 5050 | 0.92 ± 0.75 | 0.94 ± 0.23 | 57.7 ± 1.73 | 127.2 ± 1.49 | 412.3 ± 3.12 | 428.2 ± 2.12 | 42.57 ± 2.07 | 6.72 ± 1.33 |
| PVDF 8020P | 0.90 ± 0.66 | 0.98 ± 0.53 | 69.6 ± 1.89 | 123.7 ± 3.36 | 411.6 ± 1.25 | 492.0 ± 2.19 | 35.21 ± 2.16 | 19.47 ± 2.09 |
| PVDF 5050P | 0.94 ± 0.02 | 0.99 ± 0.42 | 79.2 ± 1.79 | 123.4 ± 2.22 | 416.7 ± 3.14 | 503.4 ± 2.37 | 41.26 ± 1.21 | 11.21 ± 1.92 |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lolla, D.; Lolla, M.; Abutaleb, A.; Shin, H.U.; Reneker, D.H.; Chase, G.G. Fabrication, Polarization of Electrospun Polyvinylidene Fluoride Electret Fibers and Effect on Capturing Nanoscale Solid Aerosols. Materials 2016, 9, 671. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma9080671
Lolla D, Lolla M, Abutaleb A, Shin HU, Reneker DH, Chase GG. Fabrication, Polarization of Electrospun Polyvinylidene Fluoride Electret Fibers and Effect on Capturing Nanoscale Solid Aerosols. Materials. 2016; 9(8):671. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma9080671
Chicago/Turabian StyleLolla, Dinesh, Manideep Lolla, Ahmed Abutaleb, Hyeon U. Shin, Darrell H. Reneker, and George G. Chase. 2016. "Fabrication, Polarization of Electrospun Polyvinylidene Fluoride Electret Fibers and Effect on Capturing Nanoscale Solid Aerosols" Materials 9, no. 8: 671. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma9080671
APA StyleLolla, D., Lolla, M., Abutaleb, A., Shin, H. U., Reneker, D. H., & Chase, G. G. (2016). Fabrication, Polarization of Electrospun Polyvinylidene Fluoride Electret Fibers and Effect on Capturing Nanoscale Solid Aerosols. Materials, 9(8), 671. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma9080671