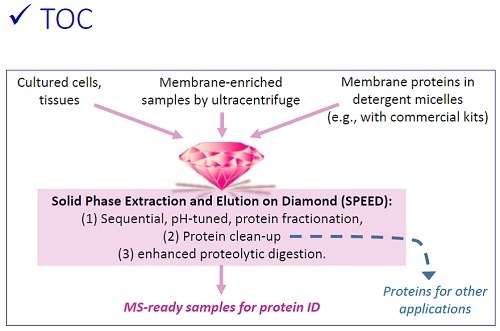
Streamlined Membrane Proteome Preparation for Shotgun Proteomics Analysis with Triton X-100 Cloud Point Extraction and Nanodiamond Solid Phase Extraction
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
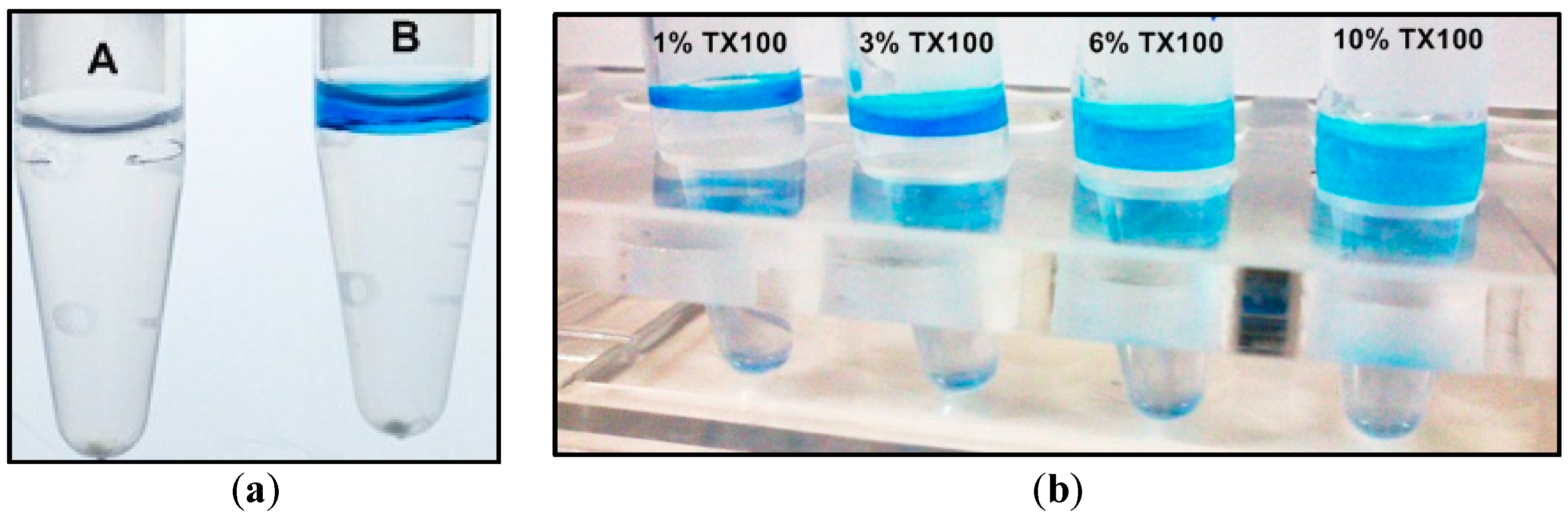
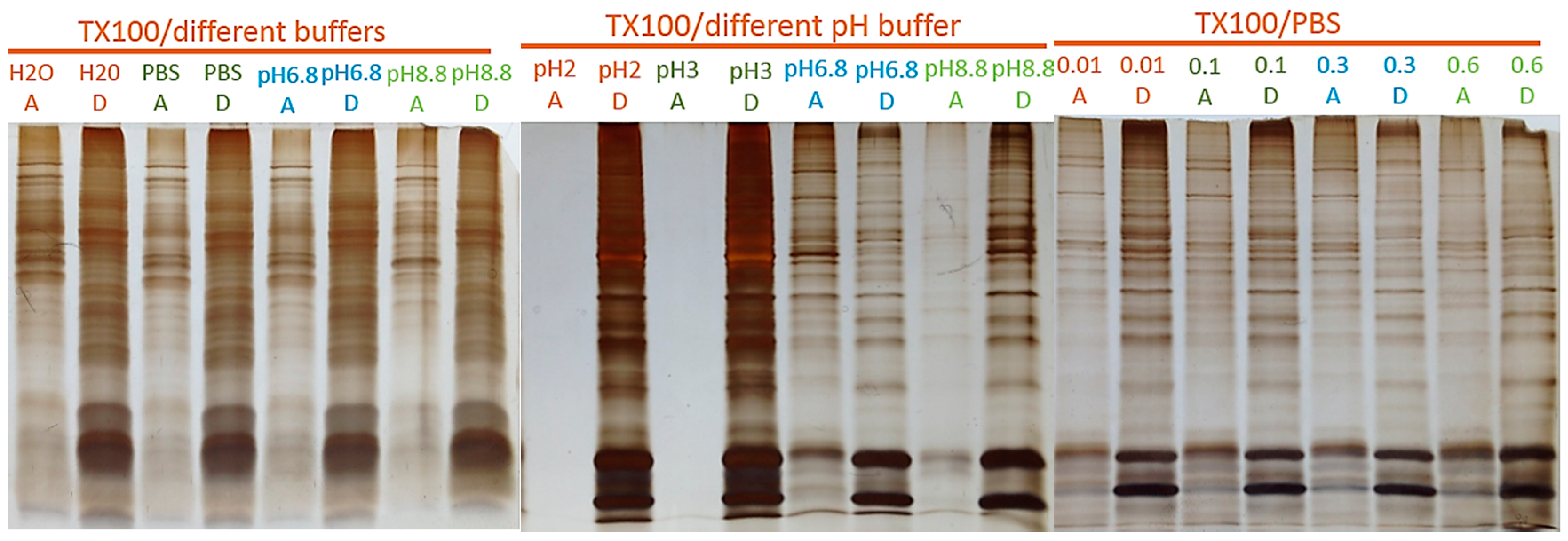
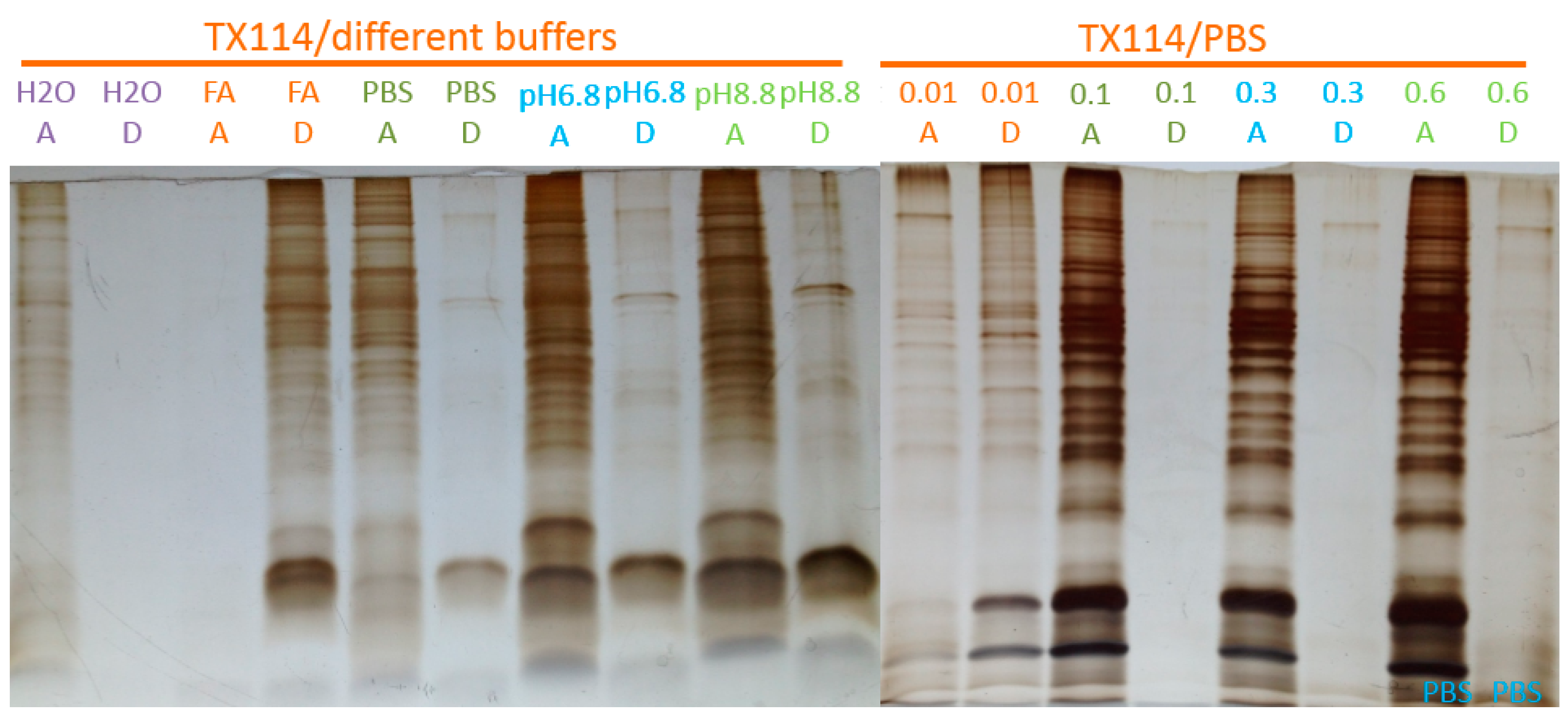
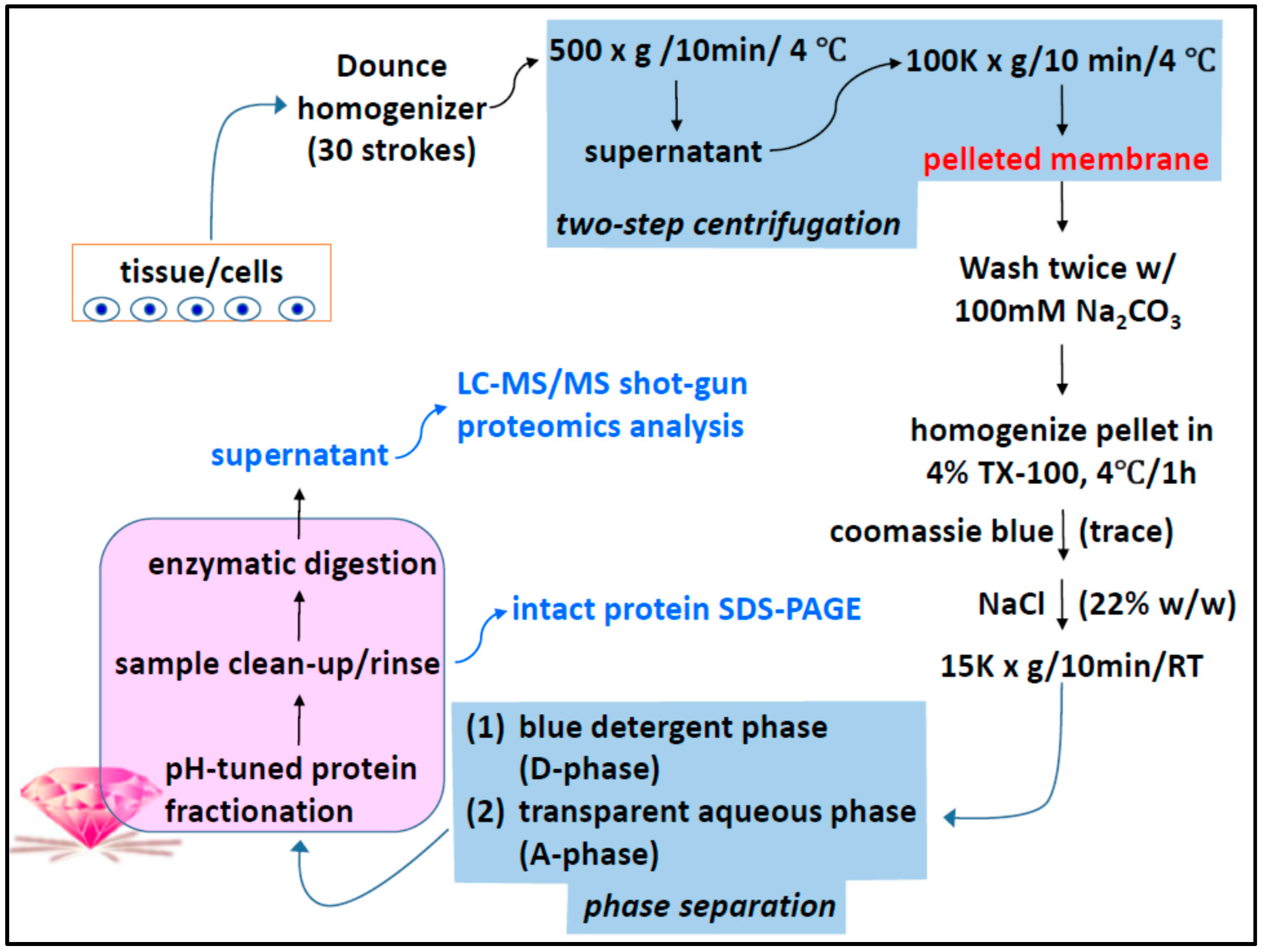
2.1. Two-Phase Membrane Proteome Extraction
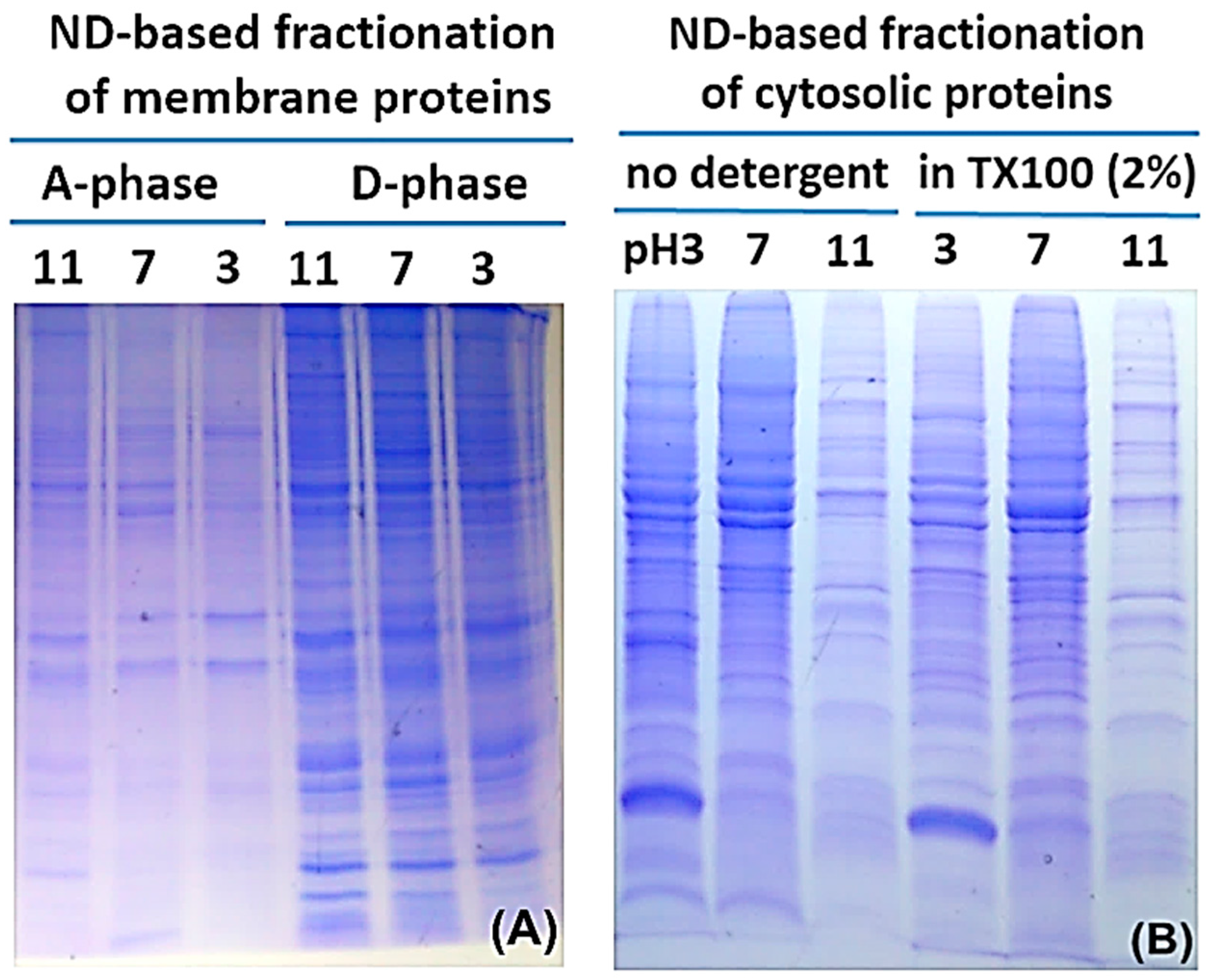
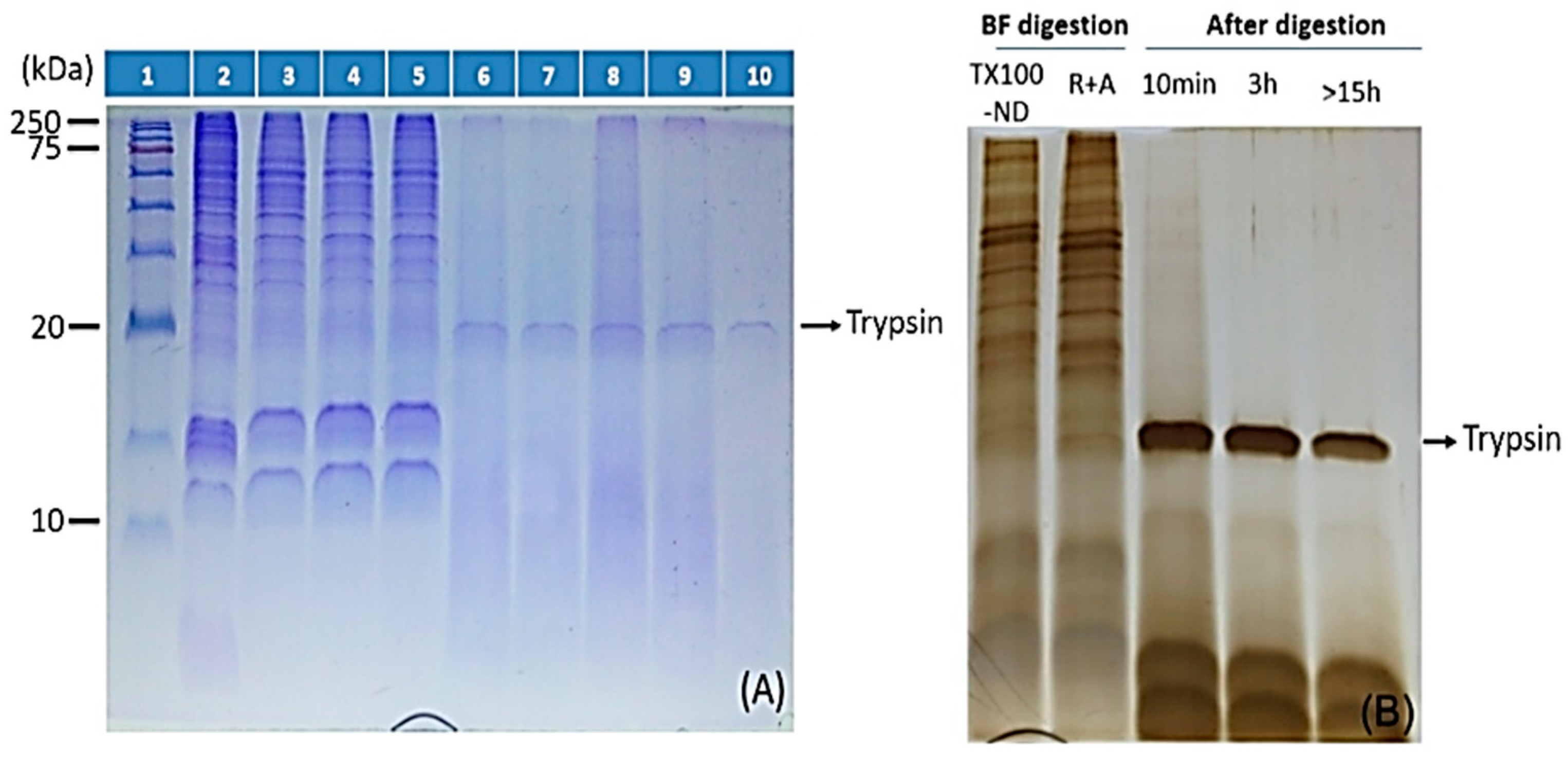
2.2. Protein Adsorption by Surface-Oxidized Nanodiamond Particles
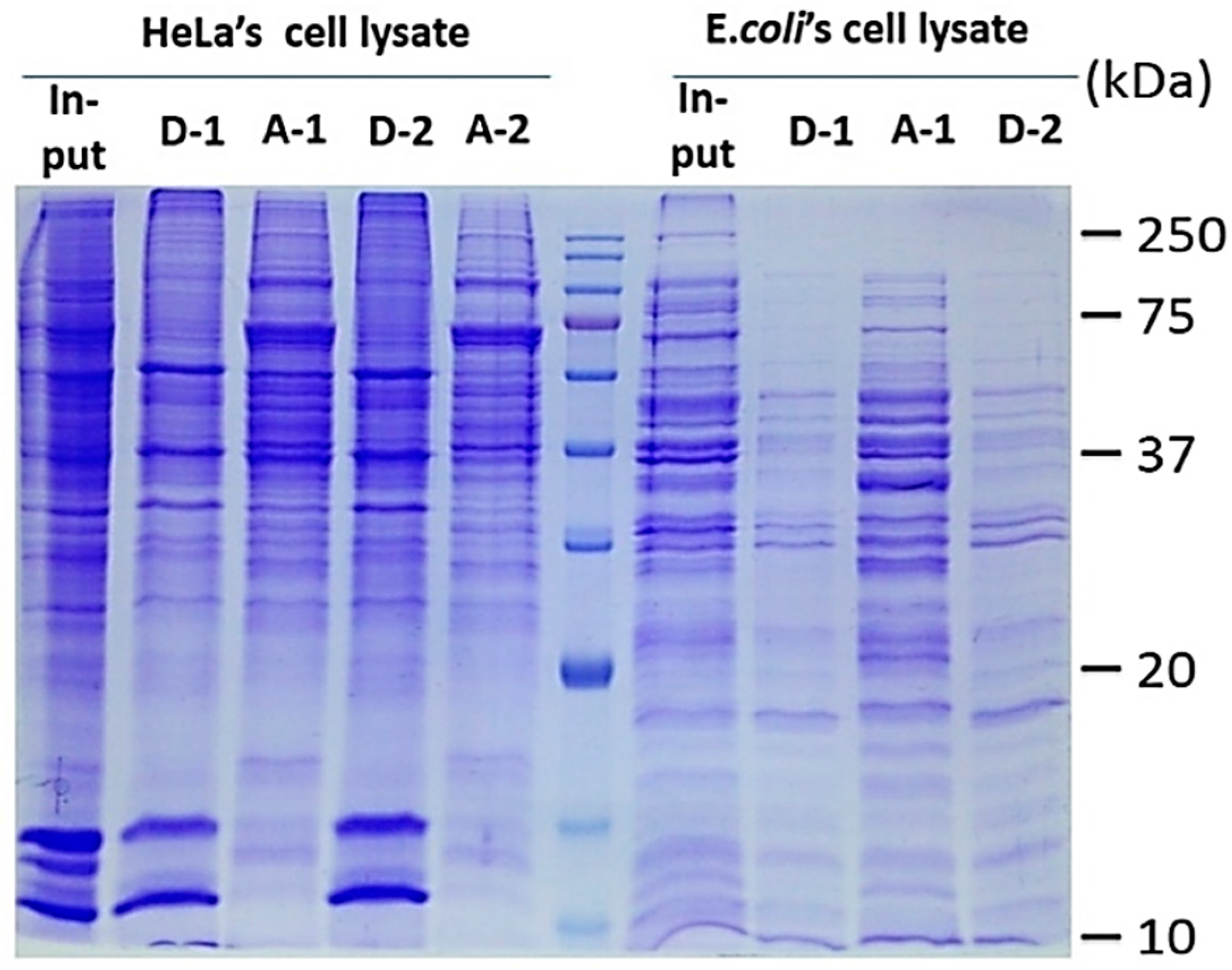
2.3. ND Surface-Enhanced Proteolysis
3. Discussion
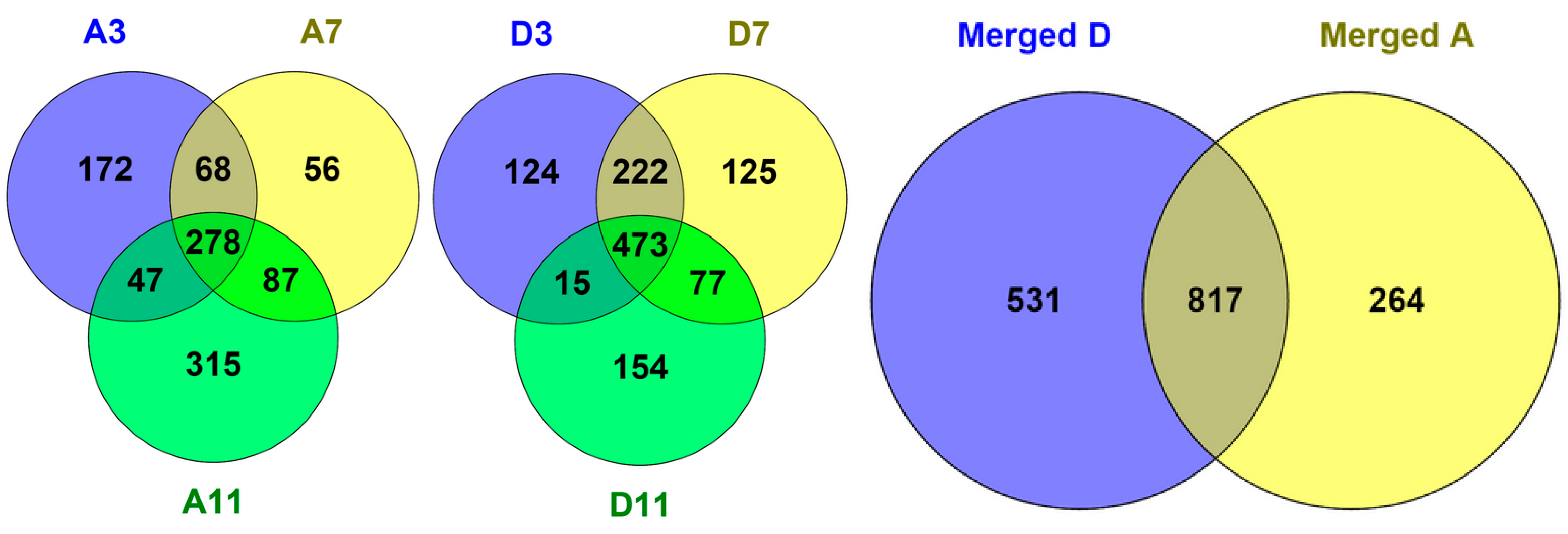
3.1. Sequential, pH-Tuned, ND Extraction and Fractionation For “Shot-Gun” Membrane Proteomics
3.2. Considerations in Using this SPEED Protocol for Membrane Protein Samples
3.3. Room for Improvement
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Two-Phase Separation and Enrichment of MP
4.2. MP Fractionation by ND Physisorption from the Detergent-Rich Phase At Stepwisely Decreased pH
4.3. Surface-Enhanced Proteolytic Digestion of MP on ND
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix: Supplementary Experimental Information
A.1. Cell Culture
A.2. Detergent Stock Solution
A.3. Two-Phase Separation and Enrichment of Membrane Proteins From Intact Mammalian Cells with TX-114
A.4. Two-Step Centrifugation for Membrane-Enrichment
A.5. Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis (12% SDS-PAGE)
A.6. Process Validation
A.7. Nano-LC-MS/MS and Bioinformatics Analysis
References
- Fagerberg, L.; Jonasson, K.; von Heijne, G.; Uhlen, M.; Berglund, L. Prediction of the human membrane proteome. Proteomics 2010, 10, 1141–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiefenauer, L.; Demarche, S. Challenges in the Development of Functional Assays of Membrane Proteins. Materials 2012, 5, 2205–2242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, X. Reproducible method to enrich membrane proteins with high purity and high yield for an LC-MS/MS approach in quantitative membrane proteomics. Electrophoresis 2013, 34, 809–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnold, T.; Linke, D. Phase separation in the isolation and purification of membrane proteins. Biotechniques 2007, 43, 427–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fricke, B. Phase separation of nonionic detergents by salt addition and its application to membrane proteins. Anal. Biochem. 1993, 212, 154–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parish, C.R.; Classon, B.J.; Tsagaratos, J.; Walker, I.D.; Kirszbaum, L.; Mckenzie, I.F.C. Fractionation of Detergent Lysates of Cells by Ammonium Sulfate-Induced Phase-Separation. Anal. Biochem. 1986, 156, 495–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunger, S.; Roblick, U.J.; Habermann, J.K. Comparison of five commercial extraction kits for subsequent membrane protein profiling. Cytotechnology 2009, 61, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.C.; Han, C.C.; Chang, H.C. Applications of Surface-Functionalized Diamond Nanoparticles for Mass-Spectrometry-Based Proteomics. J. Chin. Chem. Soc. 2010, 57, 583–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzeng, Y.K.; Chang, C.C.; Huang, C.N.; Wu, C.C.; Han, C.C.; Chang, H.C. Facile MALDI-MS analysis of neutral glycans in NaOH-doped matrixes: Microwave-assisted deglycosylation and one-step purification with diamond nanoparticles. Anal. Chem. 2008, 80, 6809–6814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabu, S.; Yang, F.C.; Wang, Y.S.; Chen, W.H.; Chou, M.I.; Chang, H.C.; Han, C.C. Peptide analysis: Solid phase extraction-elution on diamond combined with atmospheric pressure matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization-Fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometry. Anal. Biochem. 2007, 367, 190–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.H.; Lee, S.C.; Sabu, S.; Fang, H.C.; Chung, S.C.; Han, C.C.; Chang, H.C. Solid-phase extraction and elution on diamond (SPEED): A fast and general platform for proteome analysis with mass spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 2006, 78, 4228–4234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pham, M.D.; Yu, S.S.F.; Han, C.C.; Chan, S.I. Improved Mass Spectrometric Analysis of Membrane Proteins Based on Rapid and Versatile Sample Preparation on Nanodiamond Particles. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 6748–6755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, X.L.; Huang, L.C.L.; Hsu, C.M.; Chen, W.H.; Han, C.C.; Chang, H.C. High-affinity capture of proteins by diamond nanoparticles for mass spectrometric analysis. Anal. Chem. 2005, 77, 259–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, L.C.L.; Chang, H.C. Adsorption and immobilization of cytochrome c on nanodiamonds. Langmuir 2004, 20, 5879–5884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, O.A.; Hees, J.; Dieker, C.; Jager, W.; Kirste, L.; Nebel, C.E. Size-Dependent Reactivity of Diamond Nanoparticles. Acs Nano 2010, 4, 4824–4830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wisniewski, J.R.; Nagaraj, N.; Zougman, A.; Gnad, F.; Mann, M. Brain Phosphoproteome Obtained by a FASP-Based Method Reveals Plasma Membrane Protein Topology. J. Proteome Res. 2010, 9, 3280–3289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, C.L.; Chien, C.W.; Chen, W.C.; Chen, Y.R.; Wu, C.P.; Li, H.; Chen, Y.J. A multiplexed quantitative strategy for membrane proteomics opportunities for mining therapeutic targets for autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2008, 7, 1983–1997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.J.; Tseng, M.C.; Lin, H.J.; Lin, T.W.; Chen, Y.R. Visual indicator for surfactant abundance in MS-based membrane and general proteomics applications. Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 8283–8290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Helbig, A.O.; Heck, A.J.; Slijper, M. Exploring the membrane proteome—Challenges and analytical strategies. J. Proteom. 2010, 73, 868–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, D.F.; Wang, N.; Li, L. Integrated SDS Removal and Peptide Separation by Strong-Cation Exchange Liquid Chromatography for SDS-Assisted Shotgun Proteome Analysis. J. Proteom. Res. 2012, 11, 818–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran, J.C.; Zamdborg, L.; Ahlf, D.R.; Lee, J.E.; Catherman, A.D.; Durbin, K.R.; Tipton, J.D.; Vellaichamy, A.; Kellie, J.F.; Li, M.X.; et al. Mapping intact protein isoforms in discovery mode using top-down proteomics. Nature 2011, 480, 254–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catherman, A.D.; Durbin, K.R.; Ahlf, D.R.; Early, B.P.; Fellers, R.T.; Tran, J.C.; Thomas, P.M.; Kelleher, N.L. Large-scale Top-down Proteomics of the Human Proteome: Membrane Proteins, Mitochondria, and Senescence. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2013, 12, 3465–3473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeannot, M.A.; Zheng, J.; Li, L. Observation of gel-induced protein modifications in sodium dodecylsulfate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and its implications for accurate molecular weight determination of gel-separated proteins by matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectr. 1999, 10, 784–784. [Google Scholar]
- Solis, N.; Cordwell, S.J. Current methodologies for proteomics of bacterial surface-exposed and cell envelope proteins. Proteomics 2011, 11, 3169–3189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilkins, M.R.; Appel, R.D.; van Eyk, J.E.; Chung, M.C.; Gorg, A.; Hecker, M.; Huber, L.A.; Langen, H.; Link, A.J.; Paik, Y.K.; et al. Guidelines for the next 10 years of proteomics. Proteomics 2006, 6, 4–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Z.G.; Gunaratne, J.; Cheong, L.L.; Liu, S.C.; Koh, T.L.; Huang, G.F.; Blackstock, W.P.; Chng, W.J. Plasma Membrane Proteomics Identifies Biomarkers Associated with MMSET Overexpression in T(4;14) Multiple Myeloma. Oncotarget 2013, 4, 1008–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.C.; Block, G.; Chen, H.; Folch-Puy, E.; Foronjy, R.; Jalili, R.; Jendresen, C.B.; Kimura, M.; Kraft, E.; Lindemose, S.; et al. One-step isolation of plasma membrane proteins using magnetic beads with immobilized concanavalin A. Protein Expres. Purif. 2008, 62, 223–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Everberg, H.; Gustavasson, N.; Tjerned, F. Enrichment of membrane proteins by partitioning in detergent/polymer aqueous two-phase systems. Methods Mol. Biol. 2008, 424, 403–412. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Everberg, H.; Leiding, T.; Schioth, A.; Tjerneld, F.; Gustavsson, N. Efficient and non-denaturing membrane solubilization combined with enrichment of membrane protein complexes by detergent/polymer aqueous two-phase partitioning for proteome analysis. J. Chromatogr. A 2006, 1122, 35–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
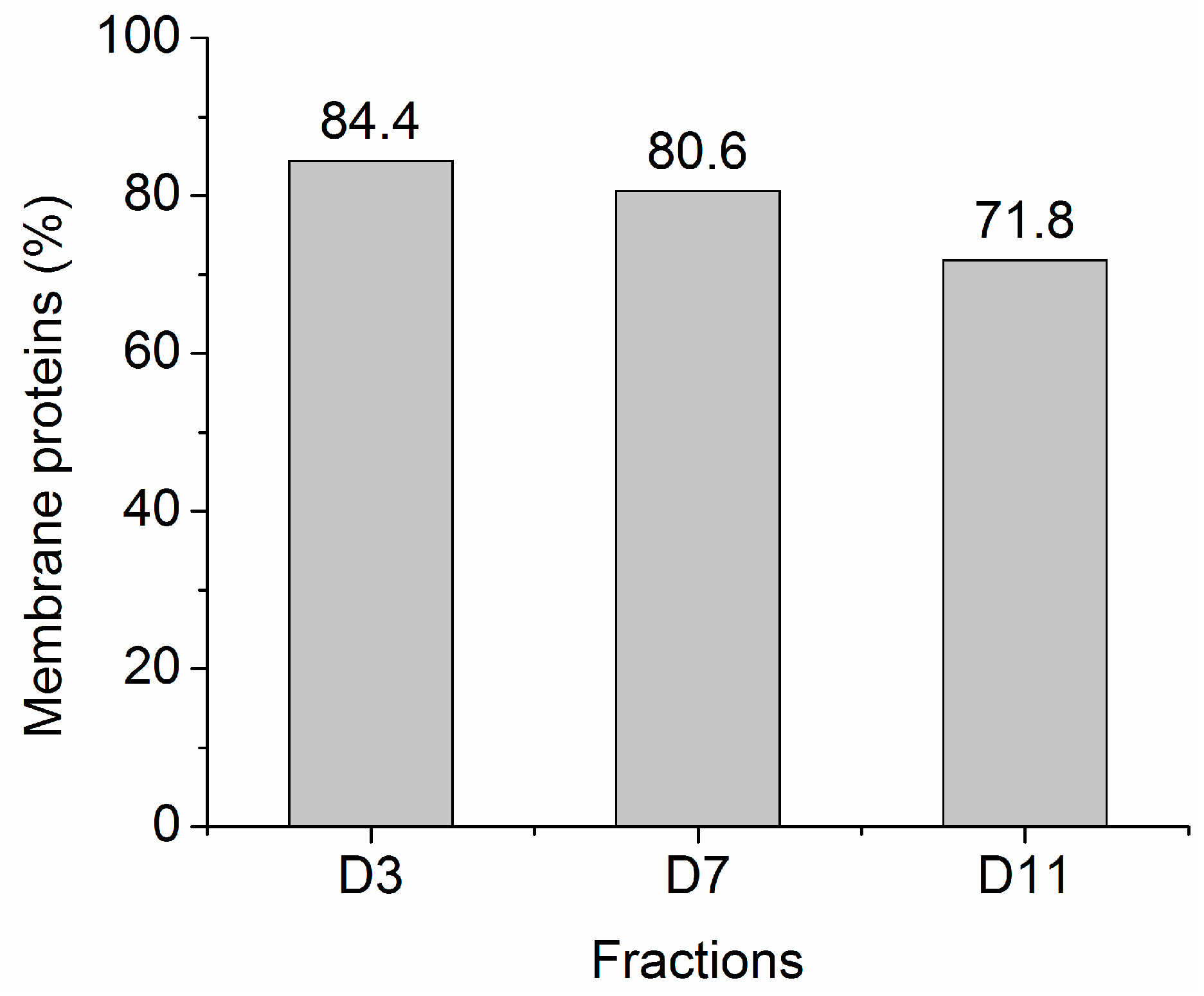
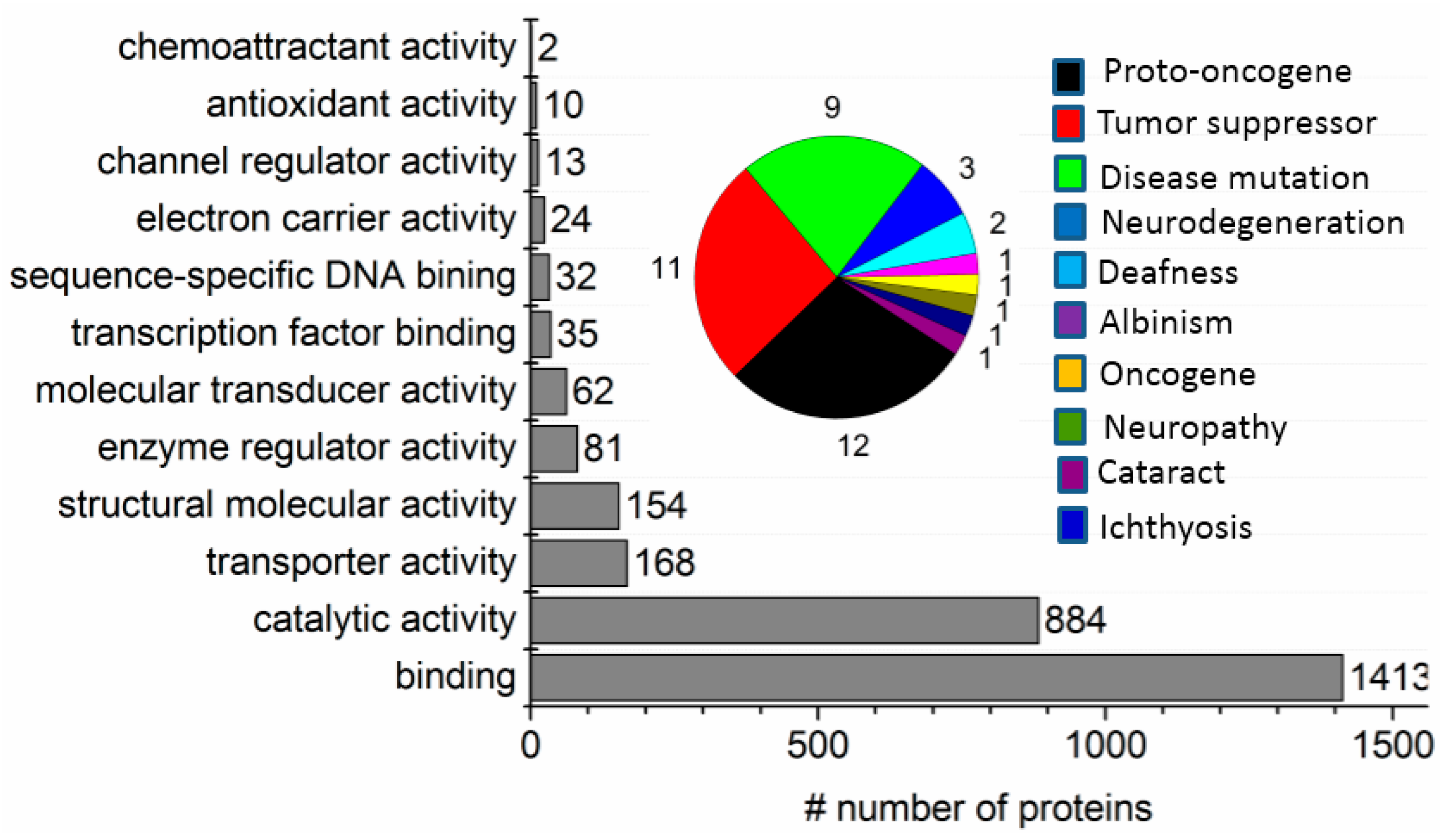
| Origin of MP | TM =1 | TM ≥ 2 | GRAVY > 0 |
|---|---|---|---|
| A-phase | 16% | 12% | 13% |
| D-pH11 | 15% | 13% | 16% |
| D-pH7 | 22% | 21% | 19.2% |
| D-pH3 | 23% | 26% | 24.2% |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pham, M.D.; Wen, T.-C.; Li, H.-C.; Hsieh, P.-H.; Chen, Y.-R.; Chang, H.-C.; Han, C.-C. Streamlined Membrane Proteome Preparation for Shotgun Proteomics Analysis with Triton X-100 Cloud Point Extraction and Nanodiamond Solid Phase Extraction. Materials 2016, 9, 385. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma9050385
Pham MD, Wen T-C, Li H-C, Hsieh P-H, Chen Y-R, Chang H-C, Han C-C. Streamlined Membrane Proteome Preparation for Shotgun Proteomics Analysis with Triton X-100 Cloud Point Extraction and Nanodiamond Solid Phase Extraction. Materials. 2016; 9(5):385. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma9050385
Chicago/Turabian StylePham, Minh D., Ting-Chun Wen, Hung-Cheng Li, Pei-Hsuan Hsieh, Yet-Ran Chen, Huan-Cheng Chang, and Chau-Chung Han. 2016. "Streamlined Membrane Proteome Preparation for Shotgun Proteomics Analysis with Triton X-100 Cloud Point Extraction and Nanodiamond Solid Phase Extraction" Materials 9, no. 5: 385. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma9050385
APA StylePham, M. D., Wen, T.-C., Li, H.-C., Hsieh, P.-H., Chen, Y.-R., Chang, H.-C., & Han, C.-C. (2016). Streamlined Membrane Proteome Preparation for Shotgun Proteomics Analysis with Triton X-100 Cloud Point Extraction and Nanodiamond Solid Phase Extraction. Materials, 9(5), 385. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma9050385