Structural Interpretation of the Large Slowdown of Water Dynamics at Stacked Phospholipid Membranes for Decreasing Hydration Level: All-Atom Molecular Dynamics
Abstract
:1. Introduction
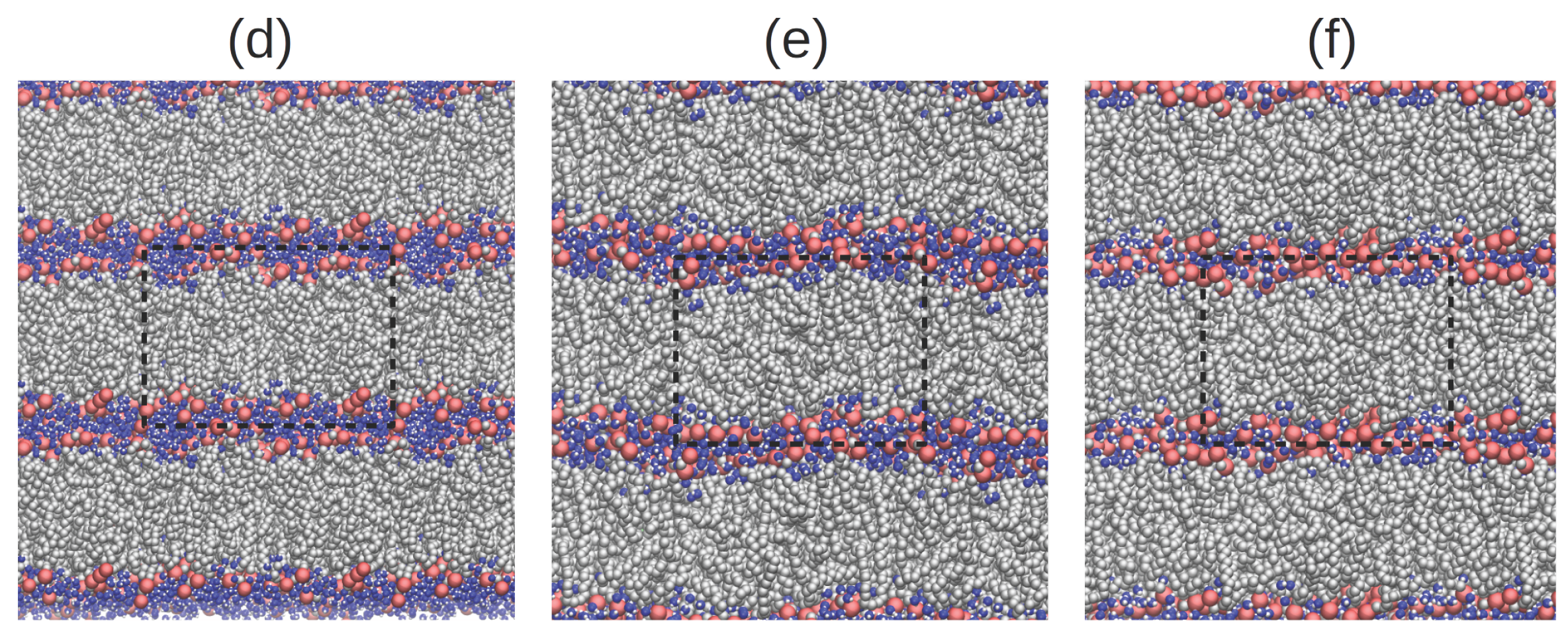
2. Results and Discussion
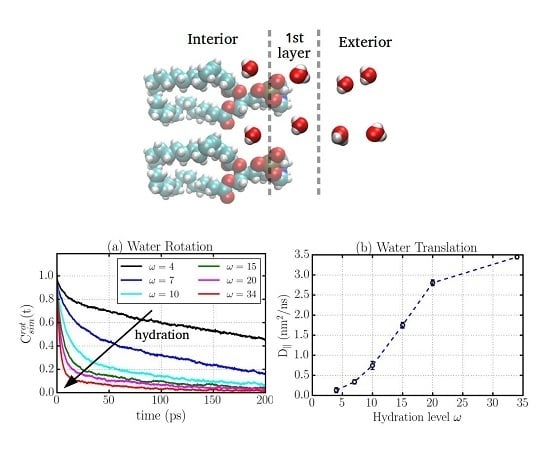
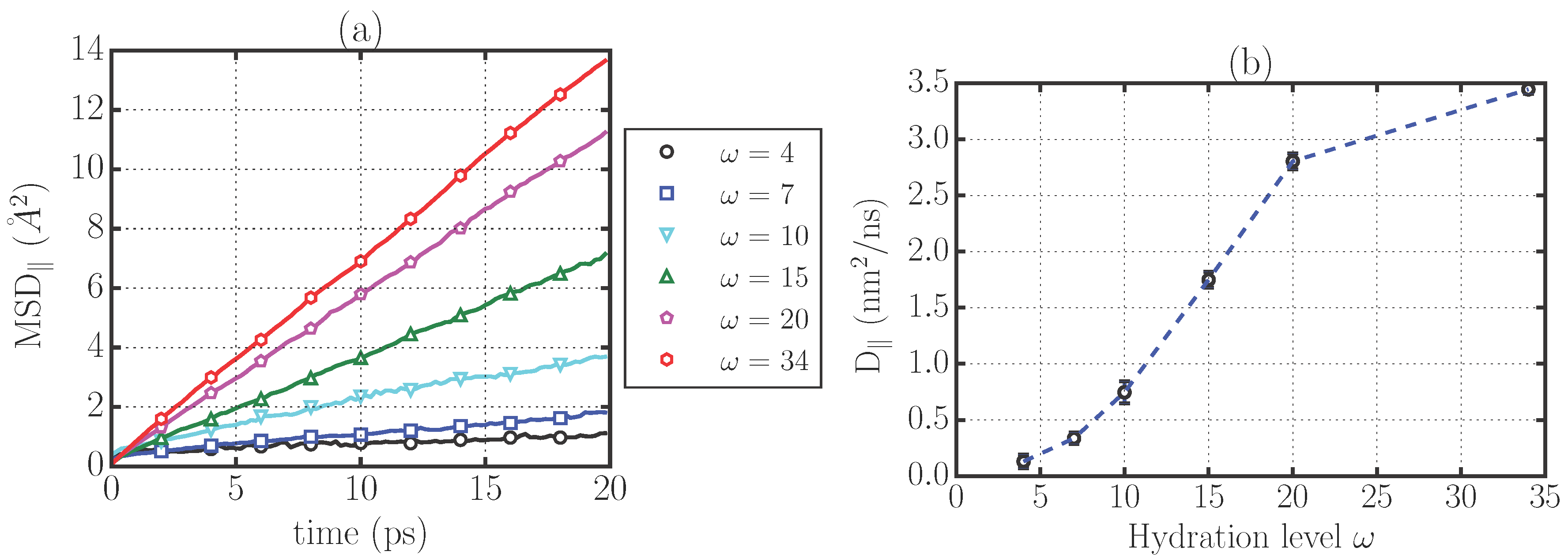
2.1. Translational Dynamics
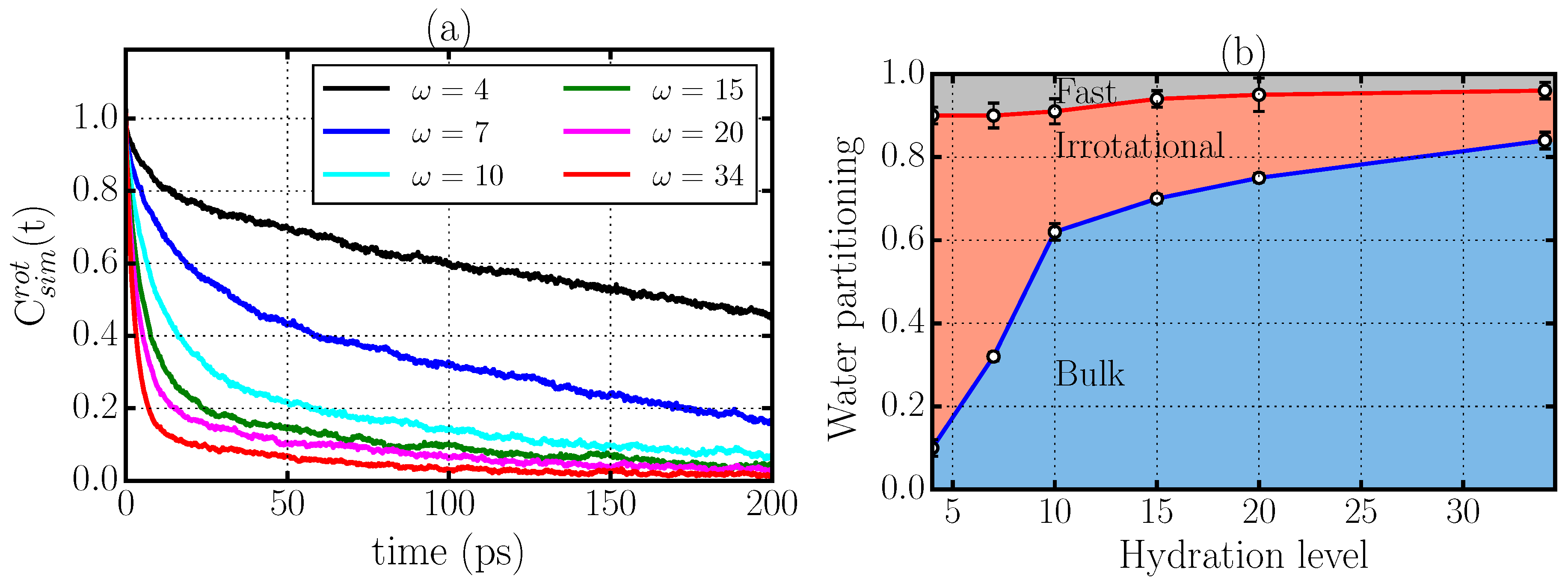
2.2. Rotational Dynamics
2.3. Criticism to the Interpretation of the Rotational Dynamics in Terms of Different Types of Water Molecules
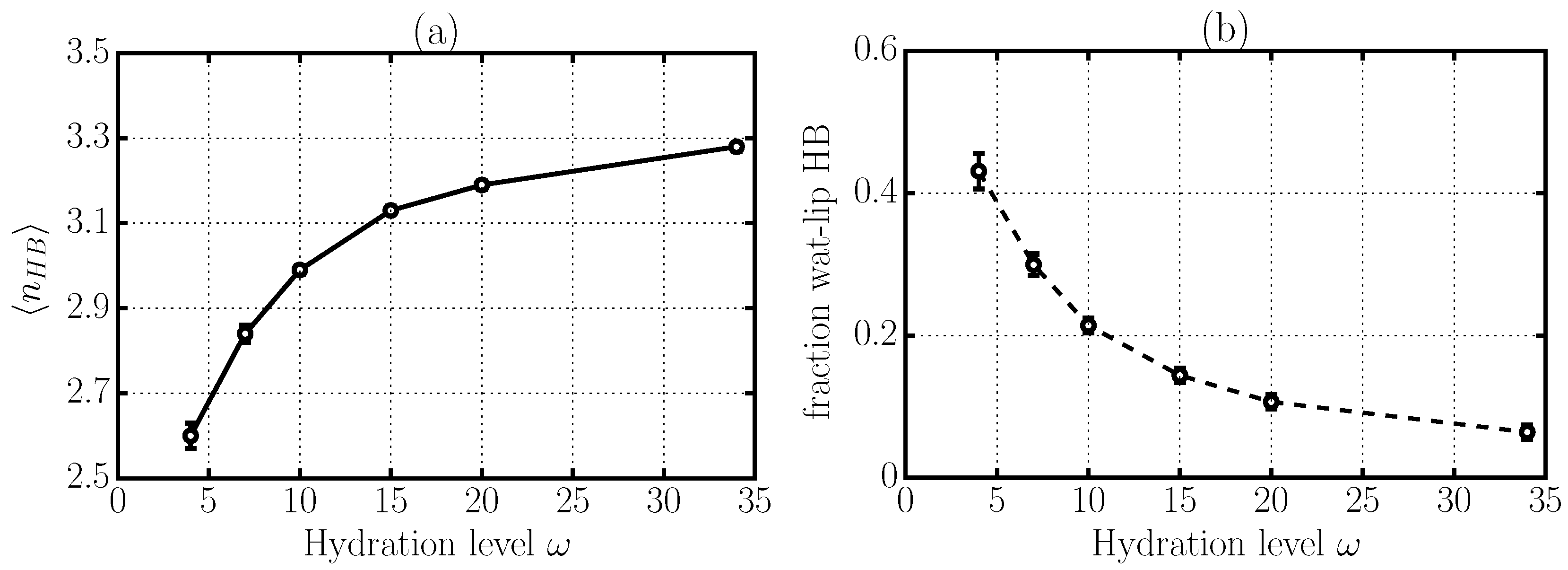
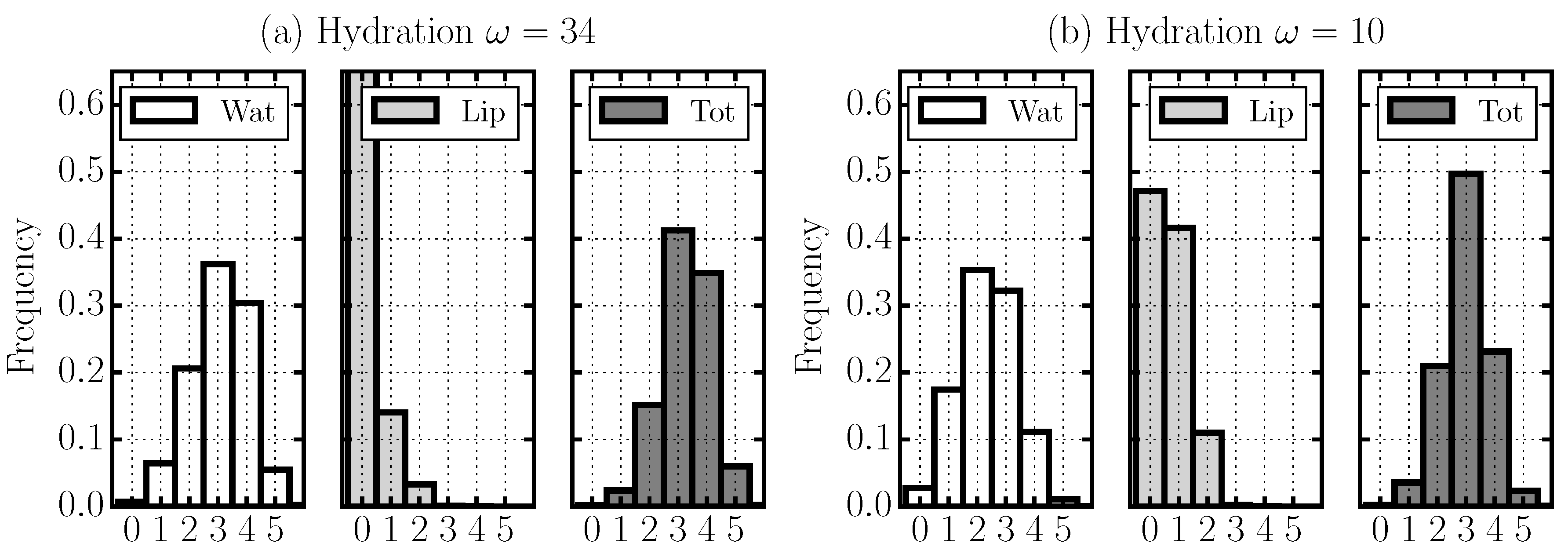
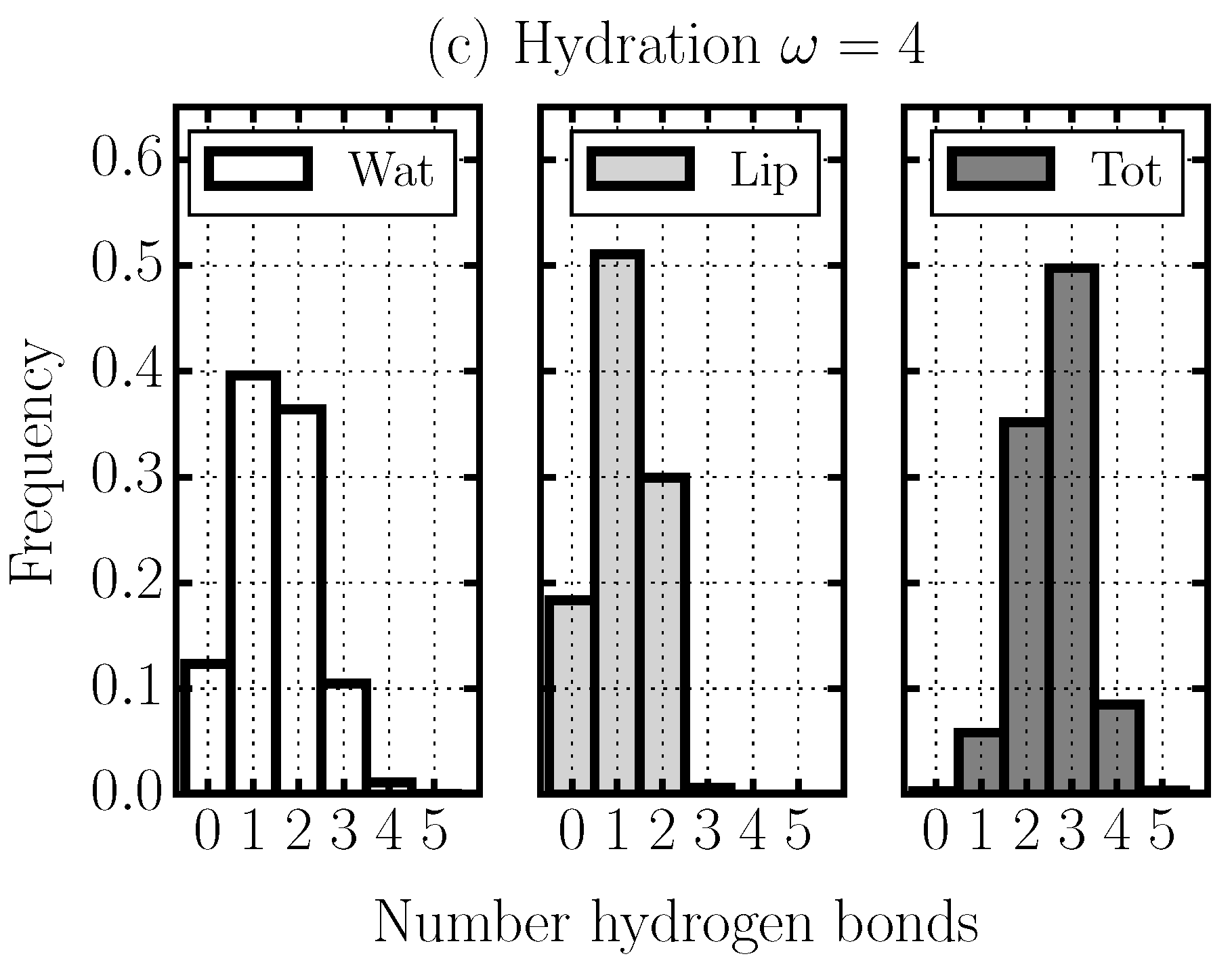
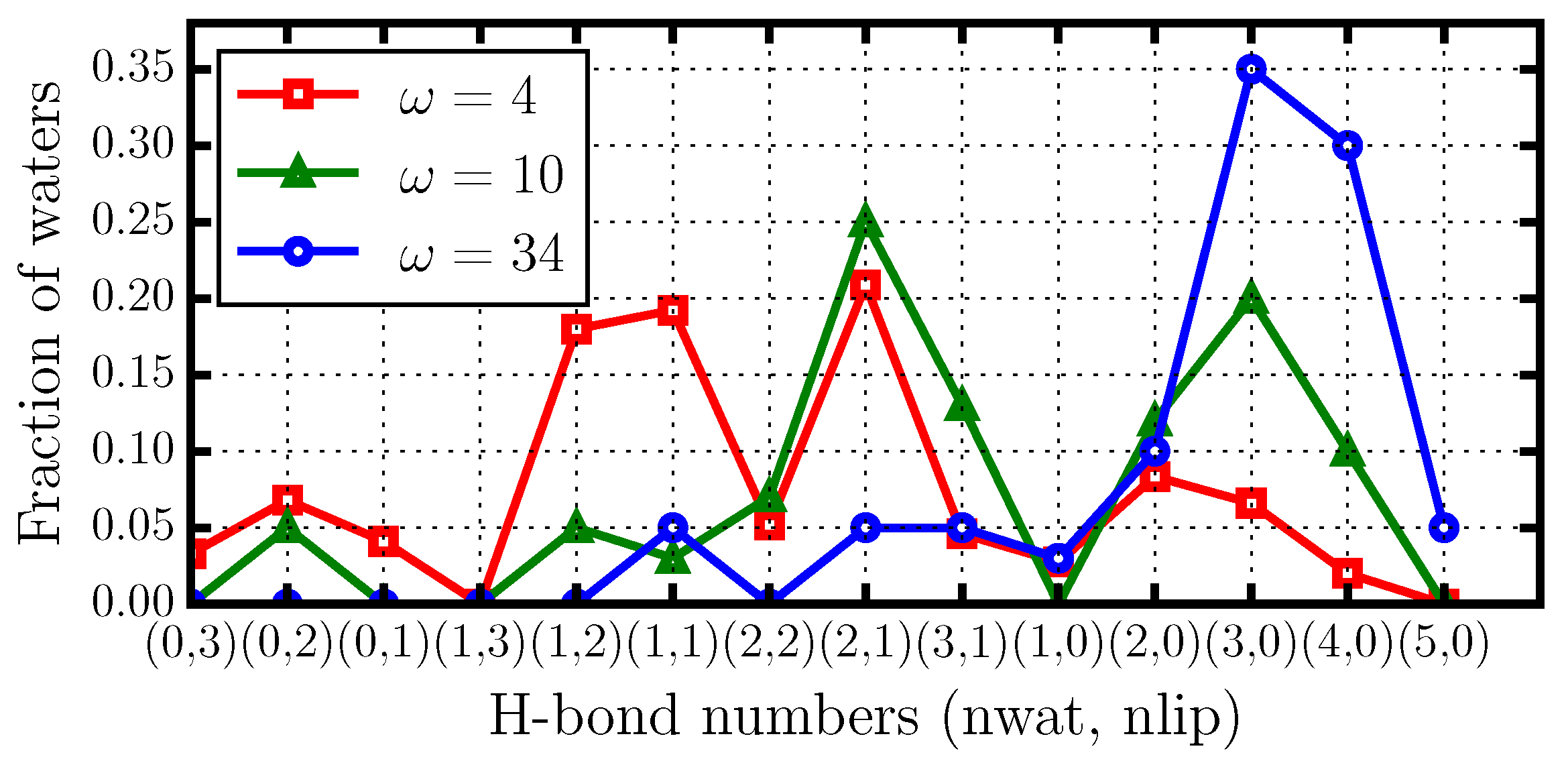
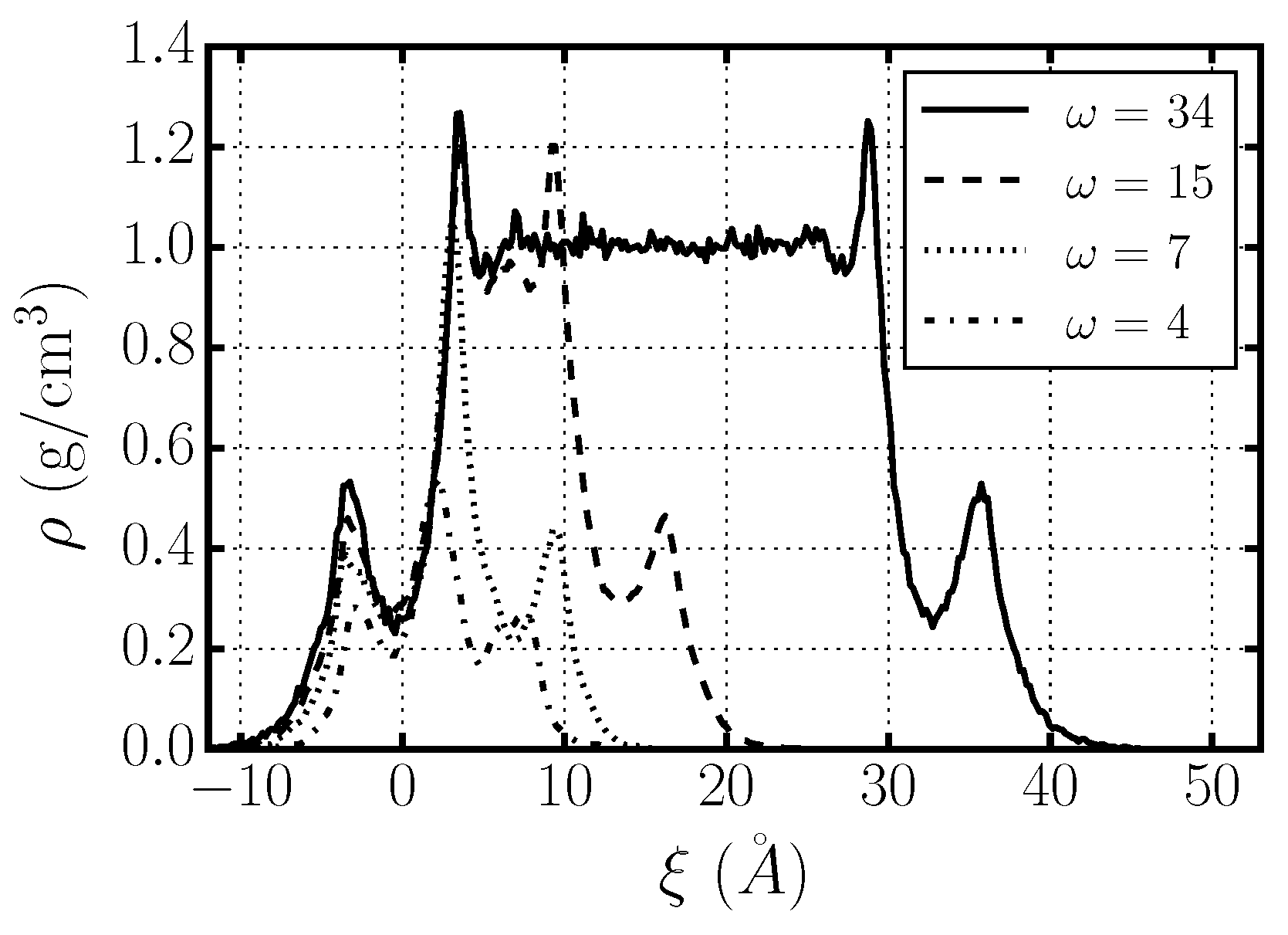
2.4. Hydrogen Bond Structure
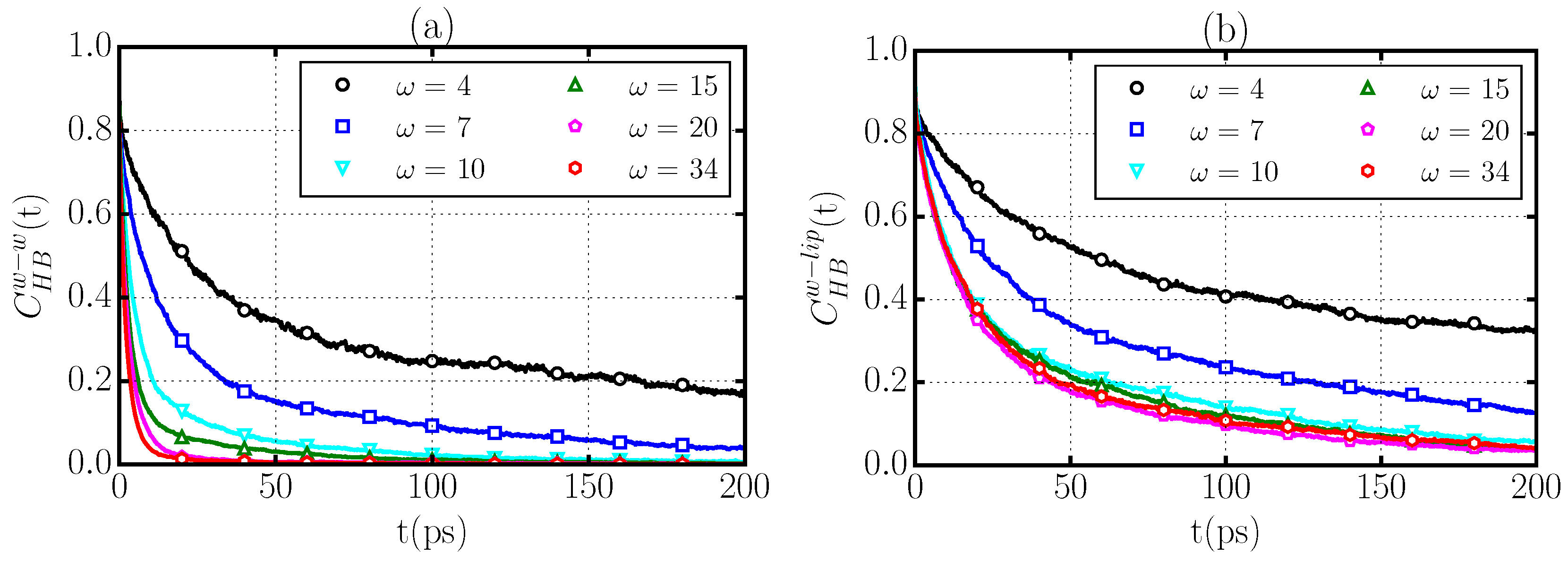
2.5. Hydrogen Bond Dynamics
- the formation of water–water HBs that are in turn bonded through long-lived HBs to the phospholipid (Figure 7b), and
2.6. Water Dynamics Determined by Distance to Membrane
3. Methods
4. Conclusions
- (i)
- the slow dynamics of water–lipid HBs,
- (ii)
- the higher proportion of water–lipid HBs at low hydrations,
- (iii)
- the slowdown of water–water HBs that bridge between persistent water–lipid HBs, and
- (iv)
- the slowdown of HB-switching due to the decrease of water density.
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hamley, I.W. Introduction to Soft Matter; John Wiley and Sons: West Sussex, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Nagle, J.F.; Tristram-Nagle, S. Structure of lipid bilayers. Biophys. Acta 2000, 1469, 159–195. [Google Scholar]
- Berkowitz, M.L.; Bostick, D.L.; Pandit, S. Aqueous solutions next to phospholipid membrane surfaces: Insights from simulations. Chem. Rev. 2006, 106, 1527–1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fitter, J.; Lechner, R.E.; Dencher, N.A. Interactions of hydration water and biological membranes studied by neutron scattering. J. Phys. Chem. B 1999, 103, 8036–8050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trapp, M.; Gutberlet, T.; Juranyi, F.; Unruh, T.; Demé, B.; Tehei, M.; Peters, J. Hydration dependent studies of highly aligned multilayer lipid membranes by neutron scattering. J. Chem. Phys. 2010, 133, 164505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazza, M.G.; Stokely, K.; Pagnotta, S.E.; Bruni, F.; Stanley, H.E.; Franzese, G. More than one dynamic crossover in protein hydration water. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 19873–19878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wassall, S.R. Pulsed field gradient-spin echo NMR studies of water diffusion in a phospholipid model membrane. Biophys. J. 1996, 71, 2724–2732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volkov, V.V.; Palmer, D.J.; Righini, R. Distinct Water species confined at the interface of a phospholipid membrane. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2007, 99, 078302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, W.; Moilanen, D.E.; Fenn, E.E.; Fayer, M.D. Water at the surfaces of aligned phospholipid multibilayer model membranes probed with ultrafast vibrational spectroscopy. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 13927–13937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tielrooij, K.J.; Paparo, D.; Piatkowski, L.; Bakker, H.J.; Bonn, M. Dielectric relaxation dynamics of water in model membranes probed by Terahertz spectroscopy. Biophys. J. 2009, 97, 2848–2492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Róg, T.; Murzyn, K.; Pasenkiewicz-Gierula, M. The dynamics of water at the phospholipid bilayer surface: A molecular dynamics simulation study. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2002, 352, 323–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhide, S.Y.; Berkowitz, M.L. Structure and dynamics of water at the interface with phospholipid bilayers. J. Chem. Phys. 2005, 123, 224702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Von Hansen, Y.; Gekle, S.; Netz, R.R. Anomalous anisotropic diffusion dynamics of hydration water at lipid membranes. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2013, 111, 118103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Berkowitz, M.L. Orientational dynamics of water in phospholipid bilayers with different hydration levels. J. Phys. Chem. B 2009, 113, 7676–7680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gruenbaum, S.; Skinner, J. Vibrational spectroscopy of water in hydrated lipid multi-bilayers. I. Infrared spectra and ultrafast pump-probe observables. J. Chem. Phys. 2011, 135, 075101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagle, J.F.; Zhang, R.; Tristram-Nagle, S.; Petrache, H.I.; Suter, R.M. X-ray structure determination of fully hydrated L alpha phase dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine bilayers. Biophys. J. 1996, 70, 1419–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudakova, M.; Filippov, A.; Skirda, V. Water diffusivity in model biological membranes. Appl. Magn. Reson. 2004, 27, 519–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seki, K.; Bagchi, K.; Bagchi, B. Anomalous dimensionality dependence of diffusion in a rugged energy landscape: How pathological is one dimension? arXiv Preprint 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Franzese, G.; Stanley, H.E. Liquid-liquid critical point in a Hamiltonian model for water: Analytic solution. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2002, 14, 2201–2209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Franzese, G.; Buldyrev, S.V.; Stanley, H.E. Molecular dynamics study of orientational cooperativity in water. Phys. Rev. E 2006, 73, 041505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laage, D.; Hynes, J.T. A molecular jump mechanism of water reorientation. Science 2006, 311, 832–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stokely, K.; Mazza, M.G.; Stanley, H.E.; Franzese, G. Effect of hydrogen bond cooperativity on the behavior of water. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 1301–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De los Santos, F.; Franzese, G. Relations between the diffusion anomaly and cooperative rearranging regions in a hydrophobically nanoconfined water monolayer. Phys. Rev. E 2012, 85, 010602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kučerka, N.; Liu, Y.; Chu, N.; Petrache, H.I.; Tristram-Nagle, S.; Nagle, J.F. Structure of fully hydrated fluid phase DMPC and DLPC lipid bilayers using X-ray scattering from oriented multilamellar arrays and from unilamellar vesicles. Biophys. J. 2005, 88, 2626–2637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandit, S.A.; Bostick, D.; Berkowitz, M.L. An algorithm to describe molecular scale rugged surfaces and its application to the study of a water/lipid bilayer interface. J. Chem. Phys. 2003, 119, 2199–2205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez, C.F.; Nielsen, S.O.; Klein, M.L.; Moore, P.B. Hydrogen bonding structure and dynamics of water at the dimyristoylphosphatidylcholine lipid bilayer surface from a molecular dynamics simulation. J. Phys. Chem. B 2004, 108, 6603–6610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, J.C.; Braun, R.; Wang, W.; Gumbart, J.; Tajkhorshid, E.; Villa, E.; Chipot, C.; Skeel, R.D.; Kalé, L.; Schulten, K. Scalable molecular dynamics with NAMD. J. Comput. Chem. 2005, 26, 1781–1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klauda, J.B.; Venable, R.M.; Freites, J.A.; O’Connor, J.W.; Tobias, D.J.; Mondragon-Ramirez, C.; Vorobyov, I.; MacKerell, A.D.; Pastor, R.W. Update of the CHARMM all-atom additive force field for lipids: Validation on six lipid types. J. Phys. Chem. B 2010, 114, 7830–7843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, J.B.; Rogaski, B.; Klauda, J.B. Update of the cholesterol force field parameters in CHARMM. J. Phys. Chem. B 2012, 116, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jorgensen, W.L.; Chandrasekhar, J.; Madura, J.D.; Impey, R.W.; Klein, M.L. Comparison of simple potential functions for simulating liquid water. J. Chem. Phys. 1983, 79, 926–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacKerell, A.D., Jr.; Bashford, D.; Bellott, M.L.D.R.; Dunbrack, R.L., Jr.; Evanseck, J.D.; Field, M.J.; Fischer, S.; Gao, J.; Guo, H.; Ha, S. All-atom empirical potential for molecular modeling and dynamics studies of proteins. J. Phys. Chem. B 1998, 102, 3586–3616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Essmann, U.; Perera, L.; Berkowitz, M.L.; Darden, T.; Lee, H.; Pedersen, L.G. A smooth particle mesh Ewald method. J. Chem. Phys. 1995, 103, 8577–8593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berendsen, H.J.C.; Postma, J.P.M.; Gunsteren, W.; DiNola, A.; Haak, J.R. Molecular dynamics with coupling to an external bath. J. Phys. Chem. 1984, 81, 3684–3690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feller, S.E.; Zhang, Y.; Pastor, R.W.; Brooks, B.R. Constant pressure molecular dynamics simulation: The Langevin piston method. J. Phys. Chem. 1995, 103, 4613–4621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basconi, J.E.; Shirts, M.R. Effects of temperature control algorithms on transport properties and kinetics in molecular dynamics simulations. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2013, 9, 2887–2899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aksimentiev, A.; Schulten, K. Imaging α-hemolysin with molecular dynamics: Ionic conductance, osmotic permeability, and the electrostatic potential map. Biophys. J. 2005, 88, 3745–3761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahoney, M.W.; Jorgensen, W.L. Diffusion constant of the TIP5P model of liquid water. J. Chem. Phys. 2001, 114, 363–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Hydration (ω) | 4 | 7 | 10 | 15 | 20 | 34 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (ps) | 290 ± 10 | 99 ± 4 | 45.6 ± 0.5 | 29.0 ± 0.5 | 21.7 ± 0.3 | 12.4 ± 0.3 |
| ω | (ps) | (ps) | (ps) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4 | 0.53 | 5.1 | 321 | 0.10 | 0.10 | 0.8 |
| 7 | 0.48 | 9.8 | 168 | 0.11 | 0.31 | 0.58 |
| 10 | 0.5 | 10.3 | 154 | 0.09 | 0.62 | 0.29 |
| 15 | 0.44 | 4.8 | 121 | 0.06 | 0.70 | 0.24 |
| 20 | 0.48 | 5.2 | 130 | 0.05 | 0.75 | 0.2 |
| 34 | 0.47 | 3.2 | 117 | 0.04 | 0.85 | 0.11 |
| Hydration (ω) | (ps) | (ps) | (g/cm) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4 | 110 | 242 | 0.21 | 2.2 |
| 7 | 31 | 80 | 0.30 | 2.6 |
| 10 | 12 | 44 | 0.37 | 3.7 |
| 15 | 7.1 | 38 | 0.45 | 5.3 |
| 20 | 5.1 | 35 | 0.52 | 6.7 |
| 34 | 4.0 | 38 | 0.65 | 9.5 |
| bulk | 1.8 | – | 0.99 | – |
| Layer | D (nm/ns) | (ps) |
|---|---|---|
| Interior | 0.19 ± 0.05 | 270 |
| 1st hydration layer | 0.81 | 37 ± 5 |
| Exterior | 4.10 | 3.3 ± 0.2 |
| Bulk | 5.5 | 2.4 ± 0.1 |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Calero, C.; Stanley, H.E.; Franzese, G. Structural Interpretation of the Large Slowdown of Water Dynamics at Stacked Phospholipid Membranes for Decreasing Hydration Level: All-Atom Molecular Dynamics. Materials 2016, 9, 319. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma9050319
Calero C, Stanley HE, Franzese G. Structural Interpretation of the Large Slowdown of Water Dynamics at Stacked Phospholipid Membranes for Decreasing Hydration Level: All-Atom Molecular Dynamics. Materials. 2016; 9(5):319. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma9050319
Chicago/Turabian StyleCalero, Carles, H. Eugene Stanley, and Giancarlo Franzese. 2016. "Structural Interpretation of the Large Slowdown of Water Dynamics at Stacked Phospholipid Membranes for Decreasing Hydration Level: All-Atom Molecular Dynamics" Materials 9, no. 5: 319. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma9050319
APA StyleCalero, C., Stanley, H. E., & Franzese, G. (2016). Structural Interpretation of the Large Slowdown of Water Dynamics at Stacked Phospholipid Membranes for Decreasing Hydration Level: All-Atom Molecular Dynamics. Materials, 9(5), 319. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma9050319