Secondary Electron Emission Materials for Transmission Dynodes in Novel Photomultipliers: A Review
Abstract
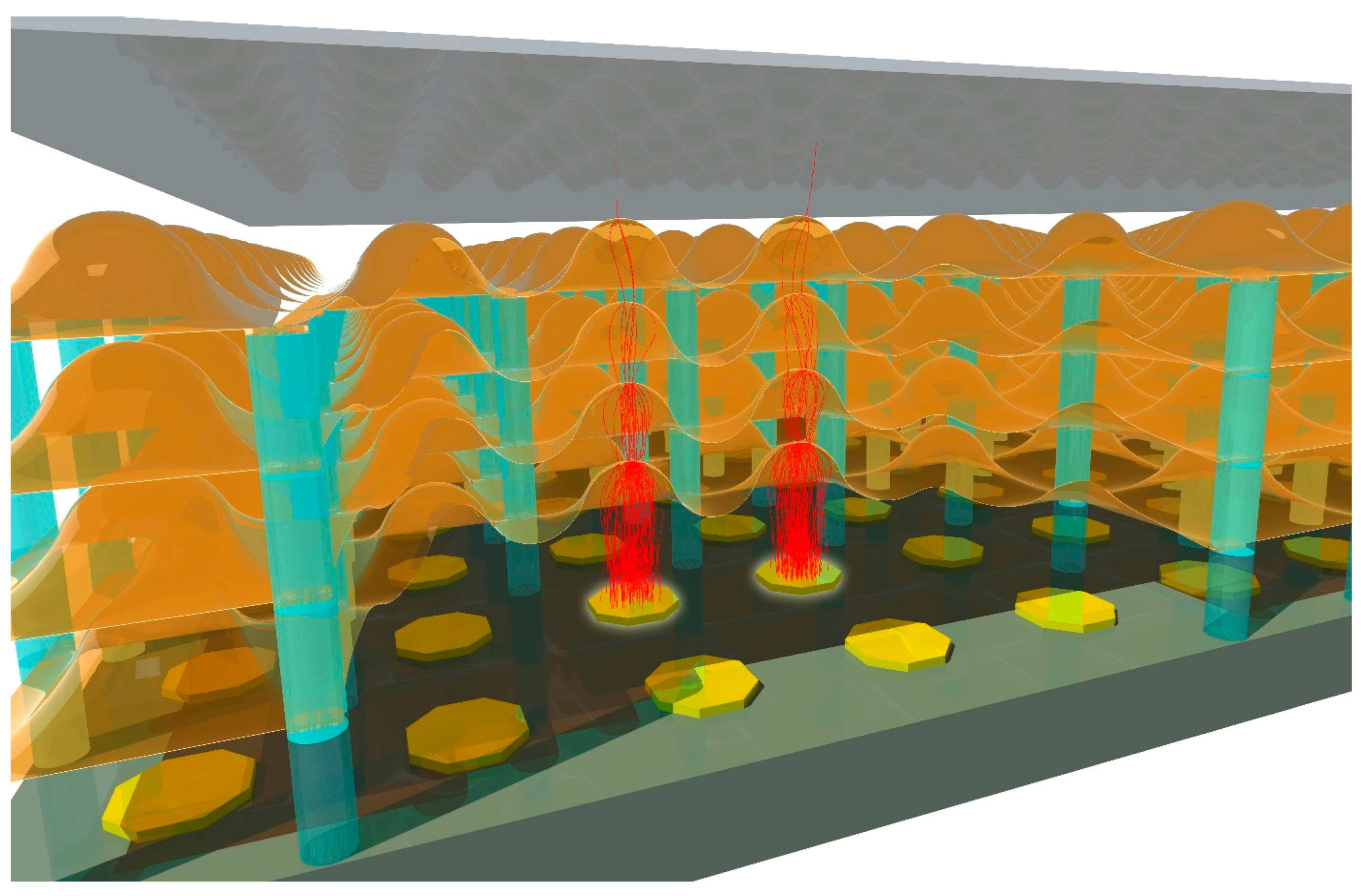
:1. Introduction
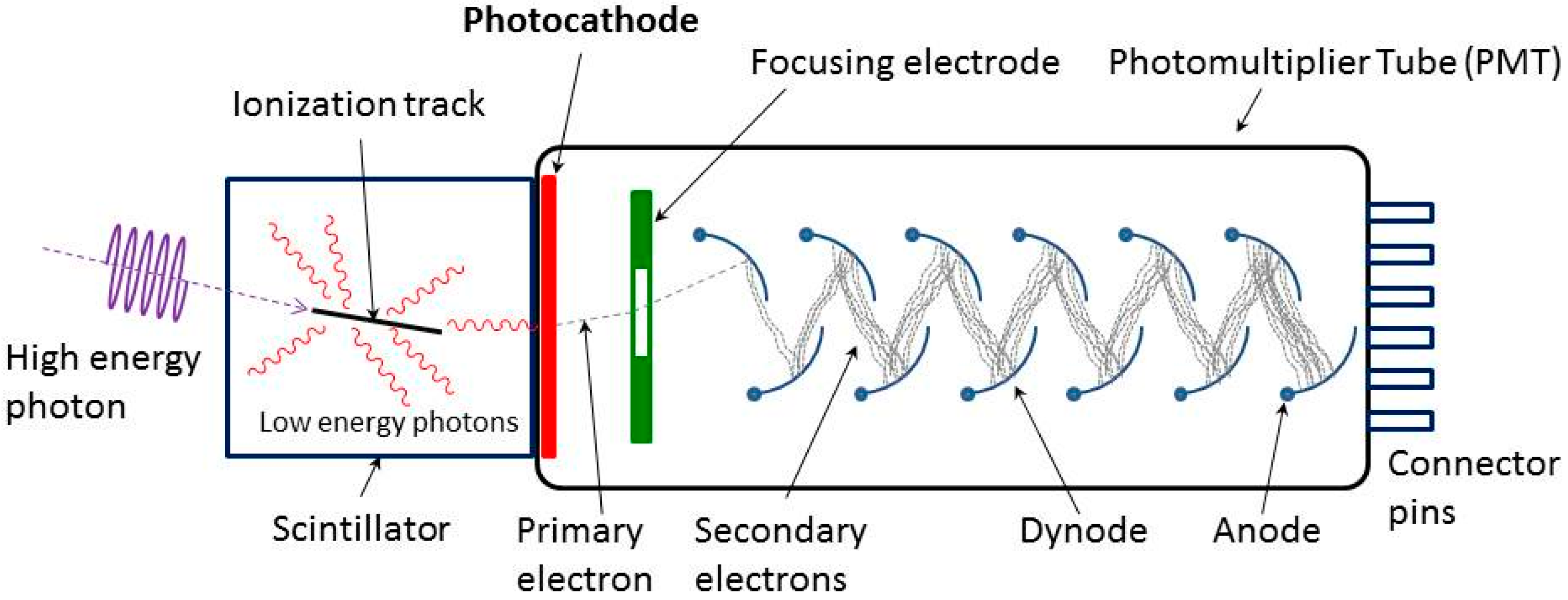
2. The Basics of the PMTs
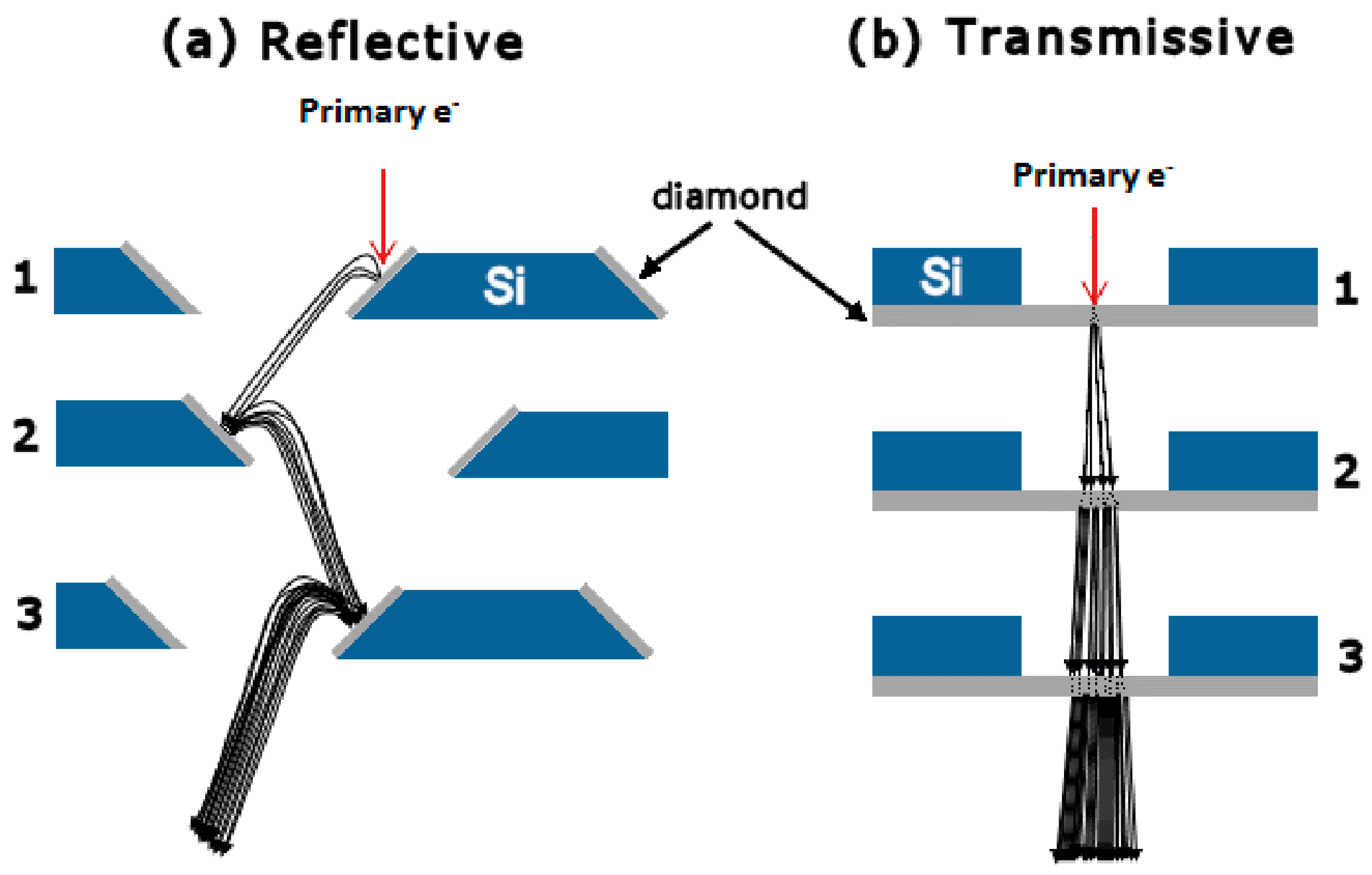
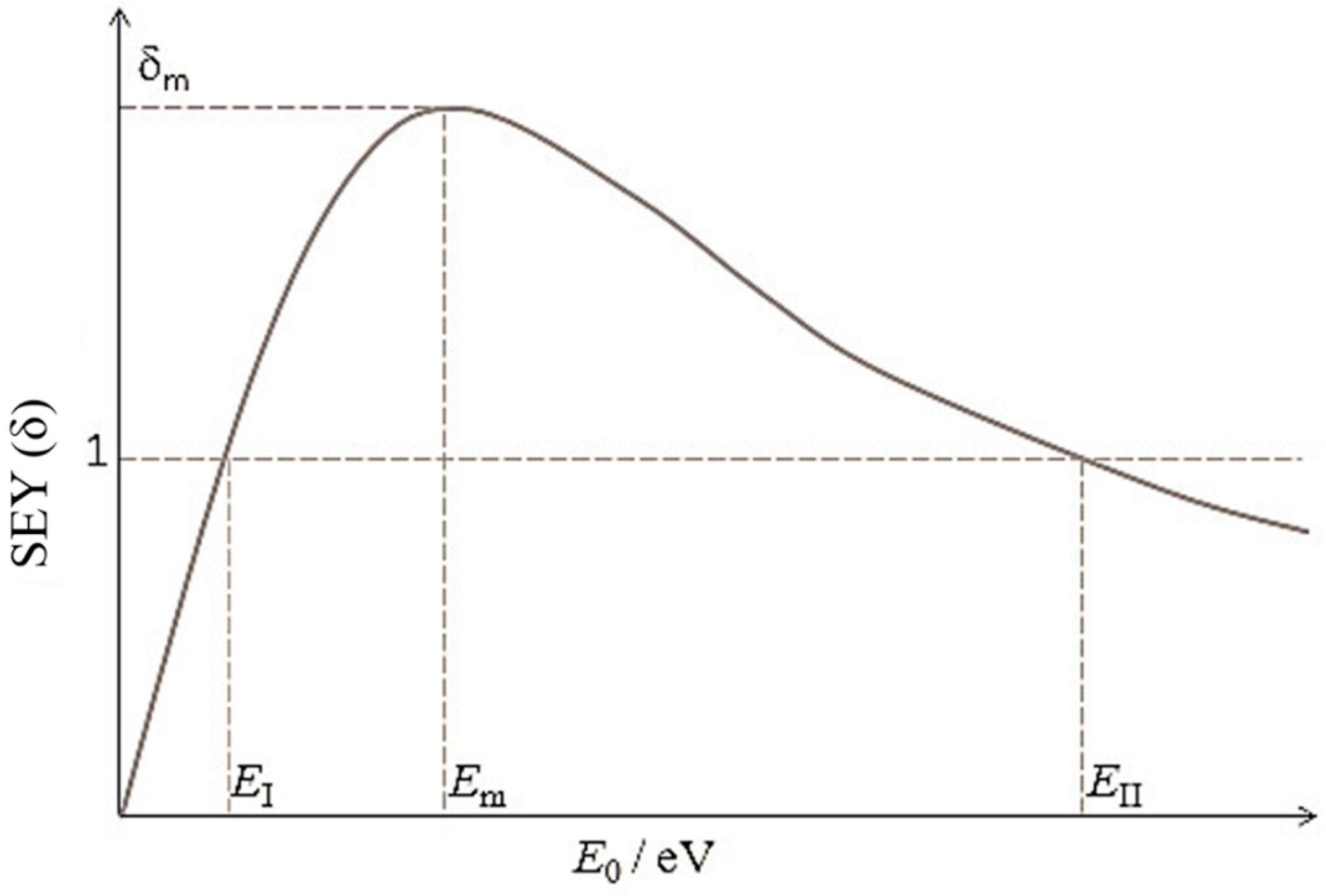
3. SEY and SEE Mechanism
4. Reflection Secondary Electron Yield
4.1. Compound Insulators
4.2. Diamond
4.3. ALD-Synthesized MgO and Al2O3
4.3.1. LAPPD
4.3.2. MEMBrane Project
5. Transmission Secondary Electron Yield
5.1. Bulk KCl (50s and 60s)
5.2. Low Density KCl (1962)
5.3. Bulk CsI Activated with Cs (1972)
5.4. Semiconductors with NEA: GaAs and Si (1970–1976)
5.5. Diamond (90s to Now)
5.6. Ultrathin ALD Synthesized Transmission Dynodes (after 2010s)
6. Outlook for High TSEY Materials
6.1. ALD
6.1.1. ALD MgO
6.1.2. Tunable Properties in ALD Processes
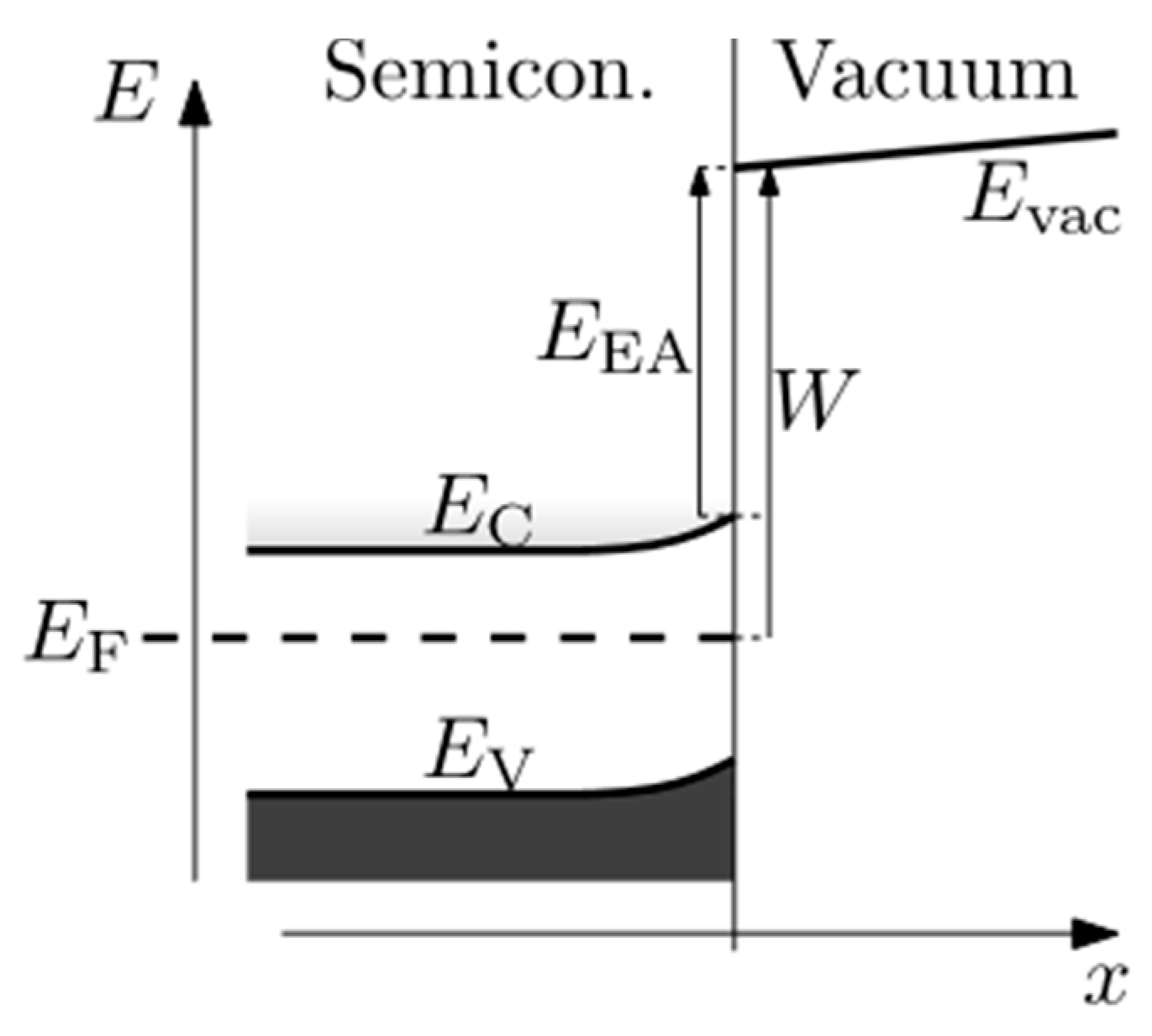
6.2. NEA
6.3. Field-Assisted Emission
6.4. Design of the Conductive Layer for Transmission Dynodes
7. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Joy, D.C. EM Facility, University of Tennessee, and Oak Ridge National Laboratory a Data Base of Electron-Solid Interactions. Available online: http://web.utk.edu/~srcutk/htm/interact.htm (accessed on 12 December 2016).
- Seiler, H. Secondary electron emission in the scanning electron microscope. J. Appl. Phys. 1983, 54, R1–R18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Photocathode Technology. Available online: http://www.hamamatsu.com/jp/en/technology/innovation/photocathode/index.html (accessed on 12 December 2016).
- Photomultiplier Tubes. Available online: http://psec.uchicago.edu/links/pmt_handbook_complete.pdf (accessed on 12 December 2016).
- Photomultiplier Tubes-Principles & Applications. Available online: http://www2.pv.infn.it/~debari/doc/Flyckt_Marmonier.pdf (accessed on 12 December 2016).
- Vaz, R.; May, P.W.; Fox, N.A.; Harwood, C.J.; Chatterjee, V.; Smith, J.A.; Horsfield, C.J.; Lapington, J.S.; Osbourne, S. Measurement of the secondary electron emission from CVD diamond films using phosphor screen detectors. J. Instrum. 2015, 10, P03004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Photomultiplier. Available online: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Photomultiplier (accessed on 12 December 2016).
- Sternglass, E.J. High-Speed Electron Multiplication by. Transmission Secondary Electron. Rev. Sci. Instr. 1955, 26, 1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stemglass, E.J.; Wachtel, M.M. Transmission Secondary Electron Multiplication for High-Speed Pulse Counting. IRE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 1956, 3, 29–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wachtel, M.M.; Doughty, D.D.; Goetze, G.; Anderson, A.E.; Sternglass, E.J. Image Intensification by Transmission Secondary Electron Emission. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 1960, 31, 576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sternglass, E.J.; Goetze, G.W. Filed-enhanced transmission secondary electron emission for high-speed counting. IRE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 1962, 9, 97–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shih, A.; Yater, J.; Hor, C.; Abrams, R. Secondary electron emission studies. Appl. Surf. Sci. 1997, 111, 251–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Electron Affinity. Available online: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Electron_affinity (accessed on 12 December 2016).
- Vaz, R. Studies of the Secondary Electron Emission from Diamond Films. Ph.D. Thesis, School of Chemistry, University of Bristol, Bristol, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Jenkins, R.O.; Trodden, W.G. Electron and Ion Emission from Solids; Jacobs, L., Ed.; Routledge and Kegan Paul: London, UK, 1965; pp. 54–67. [Google Scholar]
- Bruining, H.; de Boer, J.H. Secondary Electron Emission. Part IV. Compounds with a high capacity for secondary electron emission. Physica 1939, 6, 823–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vudynski, M.M. Secondry electron emission from thin dielectric layers. J. Tech. Phys. 1939, 9, 271. [Google Scholar]
- Whetten, N.R. Cleavage in High Vacuums of Alkali Halide Single Crystals—Secondary Electron Emission. J. Appl. Phys. 1964, 35, 3279–3282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whetten, N.R. Methods in Experimental Physics, and 1962 IV; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1962. [Google Scholar]
- Whetten, N.R.; Laponsky, A.B. Secondary electron emission of single crystals of MgO. J. Appl. Phys. 1957, 28, 515–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruining, H.; de Boer, J.H. Secondary Electron Emission. Part I. secondary electron emission of metals. Physica 1939, 5, 17–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ushio, Y.; Banno, T.; Matuda, N.; Baba, S.; Kinbara, A. Secondary electron emission studies on MgO films. Thin Solid Film 1988, 167, 299–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawson, P.H. Secondary emission yields of some ceramics. J. Appl. Phys. 1966, 37, 3644–3645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arifov, U.A. (Ed.) Secondary Emission and Structural Properties of Solids; Consultants Bureau: New York, NY, USA, 1971; p. 30.
- McKay, K.G. Bell Telephone Laboratories, Murry Hill, N.Y. Secondary Electron Emission, Advances in Electronics, Volume I; Acedemic Press Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1948. [Google Scholar]
- Van der Graaf, H.; Akhtar, H.; Budko, N.; Chan, H.W.; Hagen, C.W.; Hansson, C.C.T.; Nützel, G.; Pinto, S.D.; Prodanović, V.; Raftari, B.; et al. The Tynode: A new vacuum electron multiplier. Inst. Methods Phys. Res. A 2016. accepted for publication. [Google Scholar]
- Jokela, S.J.; Veryovkina, I.V.; Zinoviev, A.V.; Elamb, J.W.; Maneb, A.U.; Pneg, Q.; Insepovc, Z. The Large Area Picosecond Photodetector Collaboration, Secondary electron yield of emissive materials for large-area micro-channel plate detectors: Surface composition and film thickness dependencies. Phys. Procedia 2012, 37, 740–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jokela, S.J.; Veryovkina, I.V.; Zinoviev, A.V.; Elamb, J.W.; Pneg, Q.; Mane, A.U. The Characterization of Secondary Electron Emitters for Use in Large Area Photo-Detectors. In Proceedings of the Application of Accelerators in Research and Industry: Twenty-First International Conference, Fort Worth, TX, USA, 8–13 August 2011; pp. 208–212.
- Himpsel, F.J.; Knapp, J.A.; Van Vechten, J.A.; Eastman, D.E. Quantum photo yield of diamond (111)—A stable negative-affinity emitter. Phys. Rev. B 1979, 20, 624627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yater, J.E.; Shih, A. Secondary electron emission characteristics of single-crystal and polycrystalline diamond. J. Appl. Phys. 2000, 87, 8103–8112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Large-Area Picsecond Photo-Deteactors Project. Available online: http://psec.uchicago.edu/ (accessed on 12 December 2016).
- Bilevych, Y.S.; Brunner, E.; Chan, H.W.; Charbon, E.; van der Graaf, H.; Hagen, C.W.; Nützel, G.; Pinto, S.D.; Prodanović, V.; Rotman, D.; et al. Potential applications of electron emission membranes in medicine. Nucl. Instr. Meth. Phys. Res. 2016, 171, 809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Graaf, H.; Visschers, J.L. Photon Detector with High Time Resolution and High Spatial Resolution. Patent No. P2012NL007.
- Rajopadhye, N.R.; Joglekar, V.A.; Bhoraskar, V.N.; Bhoraskar, S.V. Ion secondary electron emission from Al2O3 and MgO films. Solid State Commun. 1986, 60, 675–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagino, M.; Yoshizaki, S.; Kinoshita, M.; Nishida, R. Caesium Activated CsI Transmission-type Secondary Emission Dynode. Adv. Electron. Electron Phys. 1972, 33, 469–482. [Google Scholar]
- Gutierrez, W.A.; Pommerrenig, H.D.; Holt, S.L. Secondary electron emission from GaAs. J. Appl. Phys. 1972, 21, 249–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinelli, R.U.; Schultz, M.L.; Gossenbergert, H.F. Reflection and transmission secondary emission from GaAs. Appl. Phys. 1972, 43, 4803–4804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinelli, R.U. Reflection and transmission secondary emission from Si. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1970, 17, 313–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howorth, J.R.; Folkes, J.R.; Palmer, I.C. Transmission silicon photo emitters and electron multipliers. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 1976, 9, 785–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yater, J.E.; Shih, A.; Butler, J.E.; Pehrsson, P.E. Electron transmission studies of diamond films. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2002, 191, 52–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yater, J.E.; Shih, A.; Butler, J.E.; Pehrsson, P.E. Transmission of low-energy electrons in boron-doped nanocrystalline diamond films. J. Appl. Phys. 2003, 93, 3082–3090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dvorkin, V.V.; Dzbanovsky, N.N.; Suetina, N.V.; Poltoratsky, E.A.; Rychkov, G.S.; Il’ichev, E.A.; Gavrilov, S.A. Secondary electron emission from CVD diamond films. Diamond Relat. Mater. 2003, 12, 2208–2218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yater, J.E.; Shaw, J.L.; Jensen, K.L.; Feygelson, T.; Myers, R.E.; Pate, B.B.; Butler, J.E. Secondary electron amplification using single crystal CVD diamond film. Diamond Relat. Mater. 2011, 20, 798–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilcock, W.L.; Emberson, D.L.; Weekley, B. An Image Intensifier with Transmitted Secondary Electron Multiplication. Nature 1960, 185, 370–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miikkulainen, V.; Leskel, M.; Ritala, M.; Puurunen, R.L. Crystallinity of inorganic films grown by atomic layer deposition: Overview and general trends. J. Appl. Phys. 2013, 113, 021301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putkonen, M.; Nieminen, M.; Niinistö, L. Magnesium aluminate thin films by atomic layer deposition from organometallic precursors and water. Thin Solid Films 2004, 466, 103–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarnet, T.; Hatanpää, T.; Laitinen, M.; Sajavaara, T.; Mizohata, K.; Ritala, M.; Leskelä, M. Alkylsilyl compounds as enablers of atomic layer deposition: Analysis of (Et3Si)3 As through the GaAs process. J. Mater. Chem. C 2016, 4, 449–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Donnell, K.M.; Martin, T.L.; Fox, N.A.; Cherns, D. Ab initio investigation of lithium on the diamond C (100) surface. Phys. Rev. B 2010, 82, 115303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Donnell, K.M.; Edmonds, M.T.; Ristein, J.; Tadich, A.; Thomsen, L.; Wu, Q.-H.; Pakes, C.I.; Ley, L. Diamond Surfaces with Air-Stable Negative Electron Affinity and Giant Electron Yield Enhancement. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2013, 23, 5608–5614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Donnell, K.M.; Edmonds, M.T.; Tadich, A.; Thomsen, L.; Stacey, A.; Schenk, A.; Pakes, C.I.; Ley, L. Extremely high negative electron affinity of diamond via magnesium adsorption. Phys. Rev. B 2015, 92, 035303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, X.Y.; Wu, Q.; Ben-Zvi, I.; Burrill, A.; Kewisch, J.; Rao, T.; Smedley, J.; Wang, E.; Muller, E.M.; Busby, R.; et al. Electron Beam Emission from a Diamond Amplifier Cathode. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2010, 105, 164801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, S.X.; Theulings, A.; Smedley, J.; van der Graaf, H. DFT study of electron affinity of hydrogen terminated β-Si3N4. Diamond Relat. Mater. 2015, 53, 52–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, S.X.; Theulings, A.; Smedley, J.; van der Graaf, H. DFT study of electron affinity of alkali metal termination on clean and oxygenated β-Si3N4. Diamond Relat. Mater. 2015, 58, 214–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modinos, A. Field, Thermionic, and Secondary Electron Emission Spectroscopy; Plenum: New York, NY, USA, 1984; p. 327. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, H.; Tan, R.; Park, J.; Kim, H.S.; Blick, R.H. Direct observation of sub-threshold field emission from silicon nanomembranes. J. Appl. Phys. 2011, 109, 124504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, H.; Kim, H.S.; Blick, R.H.; Westphall, M.S.; Smith, L.M. Subthreshold field emission from thin silicon membranes. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2007, 91, 183506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobs, H.; Freely, J.; Brand, F.A. The Mechanism of Field Dependent Secondary Emission. Phys. Rev. 1952, 88, 492–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heo, J.N.; Lee, J.H.; Jeong, T.W.; Lee, C.S.; Kim, W.S.; Jin, Y.W.; Yoo, J.B. Electron emission from carbon nanotube-dispersed MgO layer. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2005, 87, 3–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stadler, A. Transparent Conducting Oxides—An Up-To-Date Overview. Materials 2012, 5, 661–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kieft, E.; Bosch, E. Refinement of Monte Carlo simulations of electron–specimen interaction in low-voltage SEM. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2008, 41, 215310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raftari, B.; Budko, N.V.; Vuik, C. Self-consistent drift-diffusion-reaction model for the electron beam interaction with dielectric samples. J. Appl. Phys. 2015, 118, 204101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Materials | δm | Em (eV) | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| LiF | 5.6 | [16] | |
| NaF | 5.7 | [16] | |
| NaCl | 6.0 | 600 | [17] |
| NaCl | 6.8 | [16] | |
| KCl | 7.5 | [16] | |
| KCl | 13.4 | 1800 | [18] |
| RbCl | 5.8 | [16] | |
| CsCl | 6.5 | [16] | |
| NaBr | 22.5 | 1500 | [18] |
| NaBr | 24.0 | 1800 | [19] |
| NaBr | 6.2 | [16] | |
| KBr | 13.4 | 1800 | [18] |
| KI | 10.8 | 1500 | [18] |
| KI | 10.0 | 1600 | [20] |
| KI | 5.5 | [16] | |
| CaF2 | 3.2 | [16] | |
| BaF2 | 4.5 | [16] | |
| MgO | 4.0 | 400 | [21] |
| MgO | 24.3 | 1300 | [20] |
| MgO | 3.3 | 750 | [22] |
| MgO | 3.6 | 1250 | [22] |
| BaO | 4.8 | 400 | [21] |
| Al2O3 (polished sapphire) | 7.8 | 650 | [23] |
| Al2O3 (sapphire) | 6.4 | 750 | [23] |
| Al2O3 (lucalox) | 19.0 | 1300 | [23] |
| Al2O3 (polished lucalox) | 6.4 | 250 | [23] |
| Al2O3 Mg2SiO4 | 4.9 | 650 | [23] |
| Al2O3 Mg2SiO4 (<1% Ba) | 4.2 | 800 | [23] |
| MgAl2O4 | 4.7 | 600 | [23] |
| MgAl2O4 (0.2%–1% Ca) | 4.1 | 500 | [23] |
| AlBe | 4.5 | 600 | [24] |
| NiCr | 3.7 | 500 | [24] |
| BeO | 3.4 | 2000 | [25] |
| BaO SrO | 8.0 | 1500 | [25] |
| BaO SrO | 5.0–12.0 | 1400 | [25] |
| Al2O3 | 4.8 | 1300 | [25] |
| ALD Al2O3 (12.5 nm) | 3.6 | 400 | [26] |
| ALD MgO (50 nm) | 4.4 | 600 | [26] |
| ALD Al2O3 (20 nm) | 3.7 | 380 | [27] |
| ALD Al2O3 (11 nm) | 3.3 | 350 | [28] |
| ALD MgO (20 nm) | 5.2 | 800 | [27] |
| ALD MgO (29 nm) | 9.6 | 550 | [28] |
| Transmission Dynodes | Thickness | δ | E0 (k·eV) | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SiO | 10 nm | 1.4 | 2 | 11 |
| SiO/Au/KCl | 115 nm (Au 5 nm) | 4.2 | 5 | 11 |
| 60 nm (Au 2 nm) | 8.4 | 3.2 | ||
| SiO/KCl | 115 nm | 1.7 | 2.5 | 11 |
| 260 nm | 1.8 | 4.5 | ||
| 520 nm | 1.7 | 7.0 | ||
| Porous Al/KCl a | 19 µm | 2 | 0.3 (4) | 12 |
| 9 | 0.3 (9) | |||
| 24 | 0.3 (24) | |||
| 37 | 0.3 (37) | |||
| Al2O3/Al/CsI | 60 nm/20 nm/70 nm | 15 | 9 | 35 |
| Al2O3/Al/CsI (Cs) | 60 nm/20 nm/70 nm | 27 | 9 | 35 |
| GaAs | 5 µm | 30 | 10 | 36 |
| GaAs | 3.5 µm | 112 | 20 | 37 |
| Si | 4–5 µm | 725 | 25 | 3838 |
| 10 µm | ~600 | 25 | ||
| Si | 3 µm | ~550 | 22 | 39 |
| 5 µm | ~560 | 21 | 39 | |
| 10 µm | ~600 | 25 | 39 | |
| PCD b diamond | 2 µm | 4 | 5 | 40 |
| 5 µm | 2.5 | 20 | ||
| f-NCD c diamond | 0.15 µm | 1 | 4 | 41 |
| 5 | 7 | |||
| 2.5 µm | 1 | 15 | ||
| 3 | 18 | |||
| PCD diamond | 2.5 µm | 4 | 25 | 42 |
| SCD d (100) diamond | 8.3 µm | 3–4 | 20 | 43 |
| PCD diamond | 2.5 µm | 3–4 | 20 | 43 |
| HF-CVD e | 0.4 µm | 1.2 | 1.3 | 14 |
| TiN/Al2O3 | 5 nm/10 nm | 2.5 | 1.25 | 26 |
| 5 nm/25 nm | 2.1 | 2.3 | ||
| 5 nm/50 nm | 1.8 | 3.4 |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tao, S.X.; Chan, H.W.; Van der Graaf, H. Secondary Electron Emission Materials for Transmission Dynodes in Novel Photomultipliers: A Review. Materials 2016, 9, 1017. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma9121017
Tao SX, Chan HW, Van der Graaf H. Secondary Electron Emission Materials for Transmission Dynodes in Novel Photomultipliers: A Review. Materials. 2016; 9(12):1017. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma9121017
Chicago/Turabian StyleTao, Shu Xia, Hong Wah Chan, and Harry Van der Graaf. 2016. "Secondary Electron Emission Materials for Transmission Dynodes in Novel Photomultipliers: A Review" Materials 9, no. 12: 1017. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma9121017
APA StyleTao, S. X., Chan, H. W., & Van der Graaf, H. (2016). Secondary Electron Emission Materials for Transmission Dynodes in Novel Photomultipliers: A Review. Materials, 9(12), 1017. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma9121017






