(Bi,Sr) (Fe1−x,Mx)O3−δ (M = Co, Ni and Mn) Cathode Materials with Mixed Electro-Ionic Conductivity
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
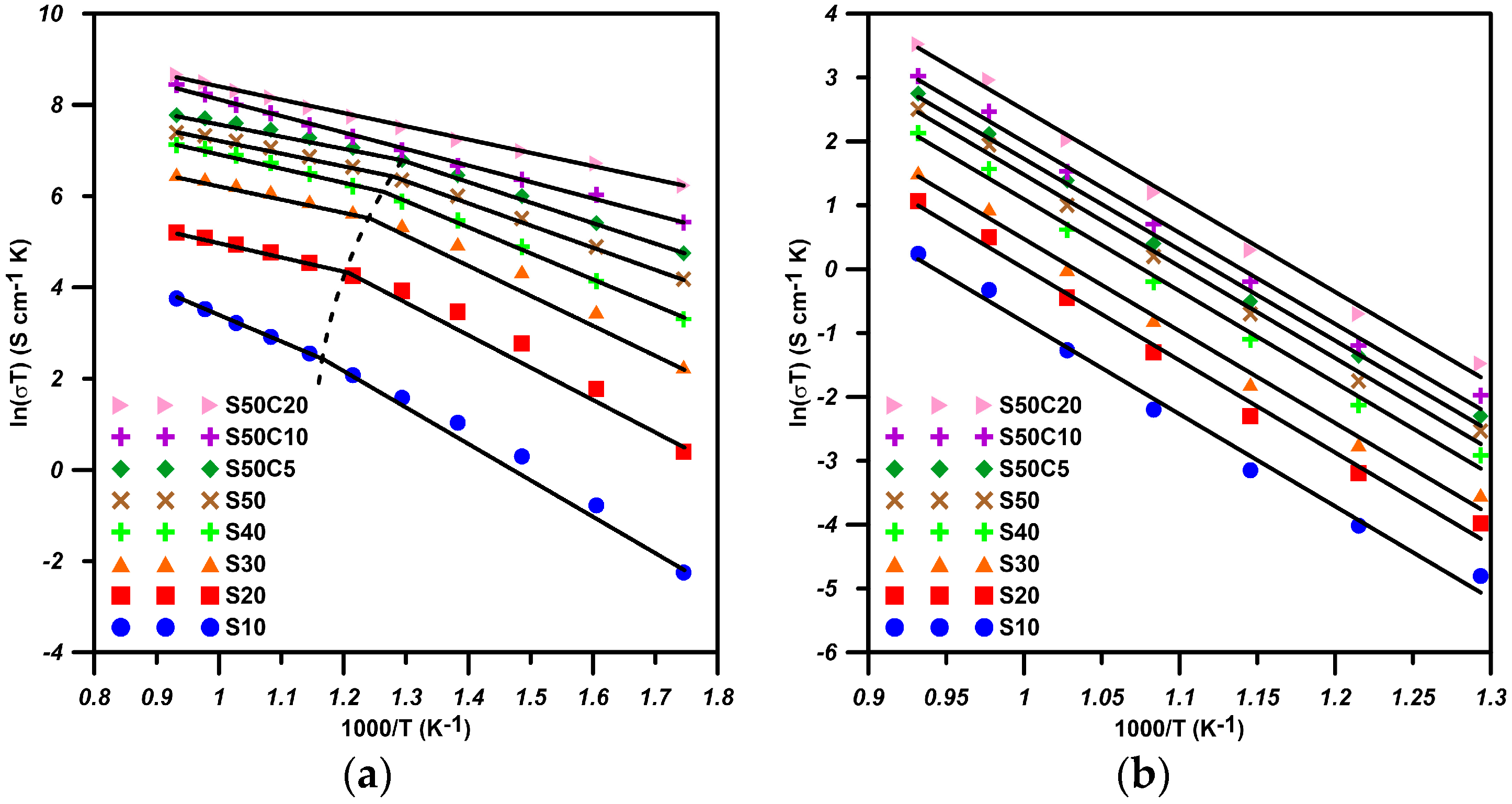
2.1. BSF with Co-Doping
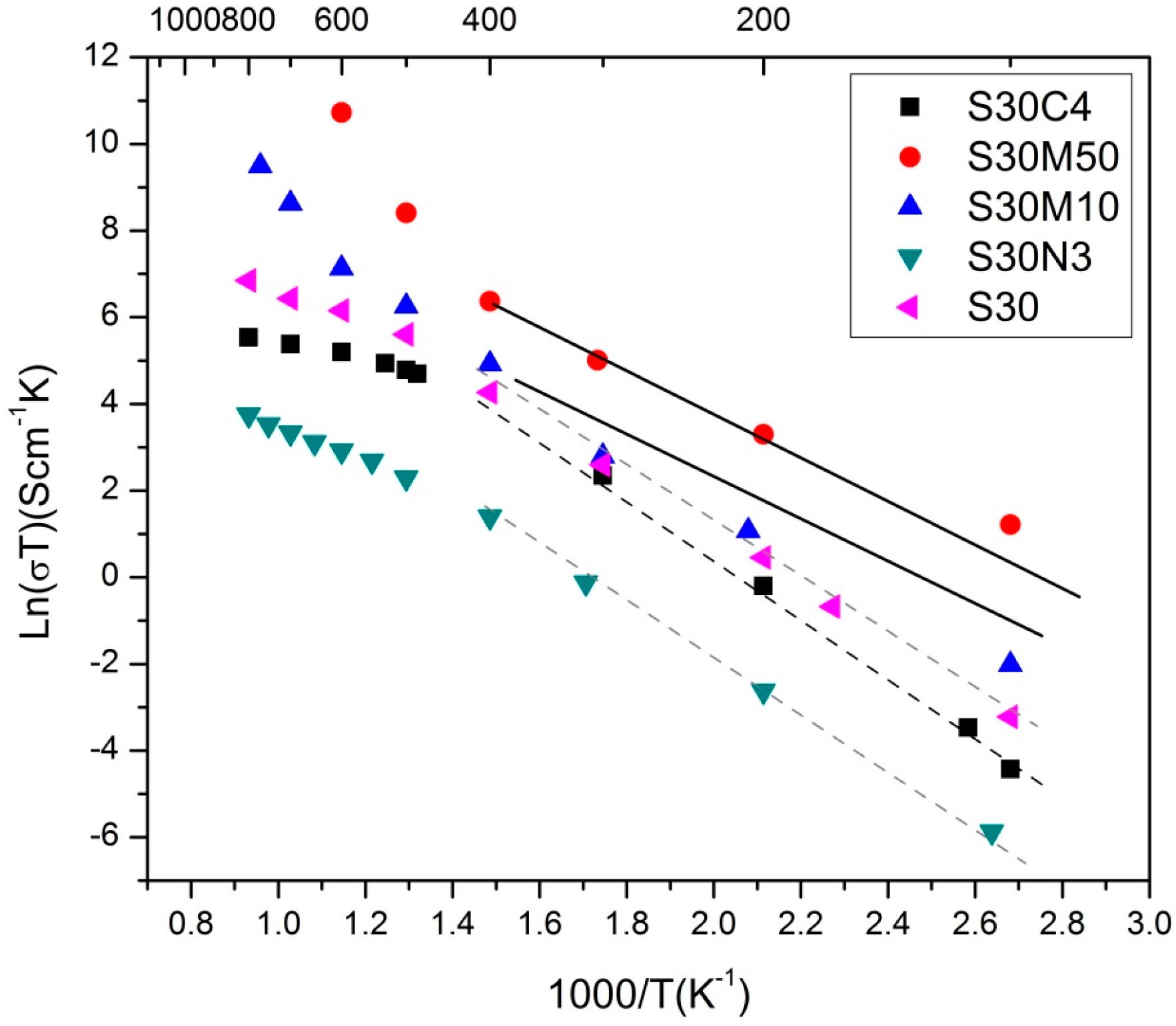
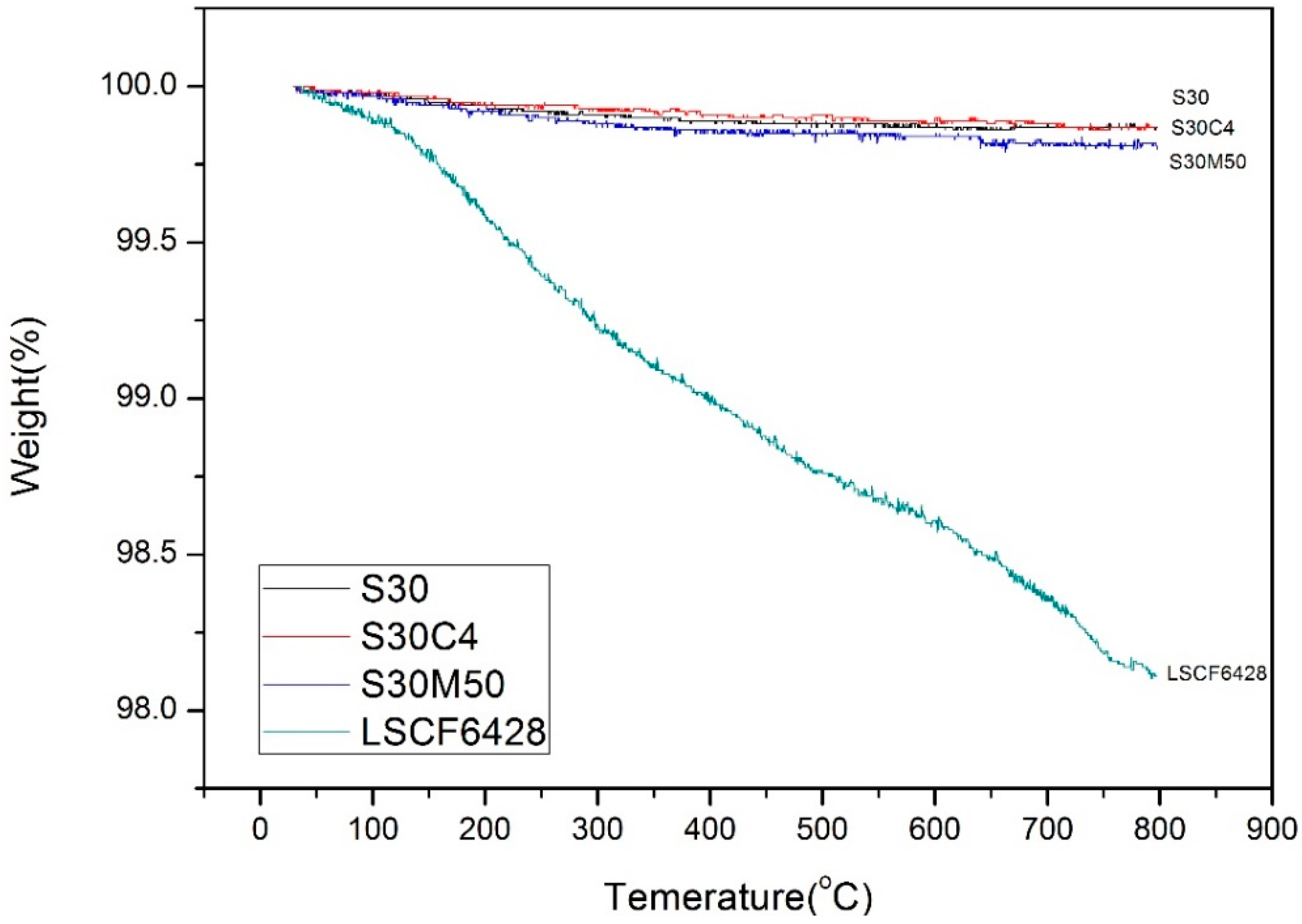
2.2. S30 with Co, Ni or Mn Doping
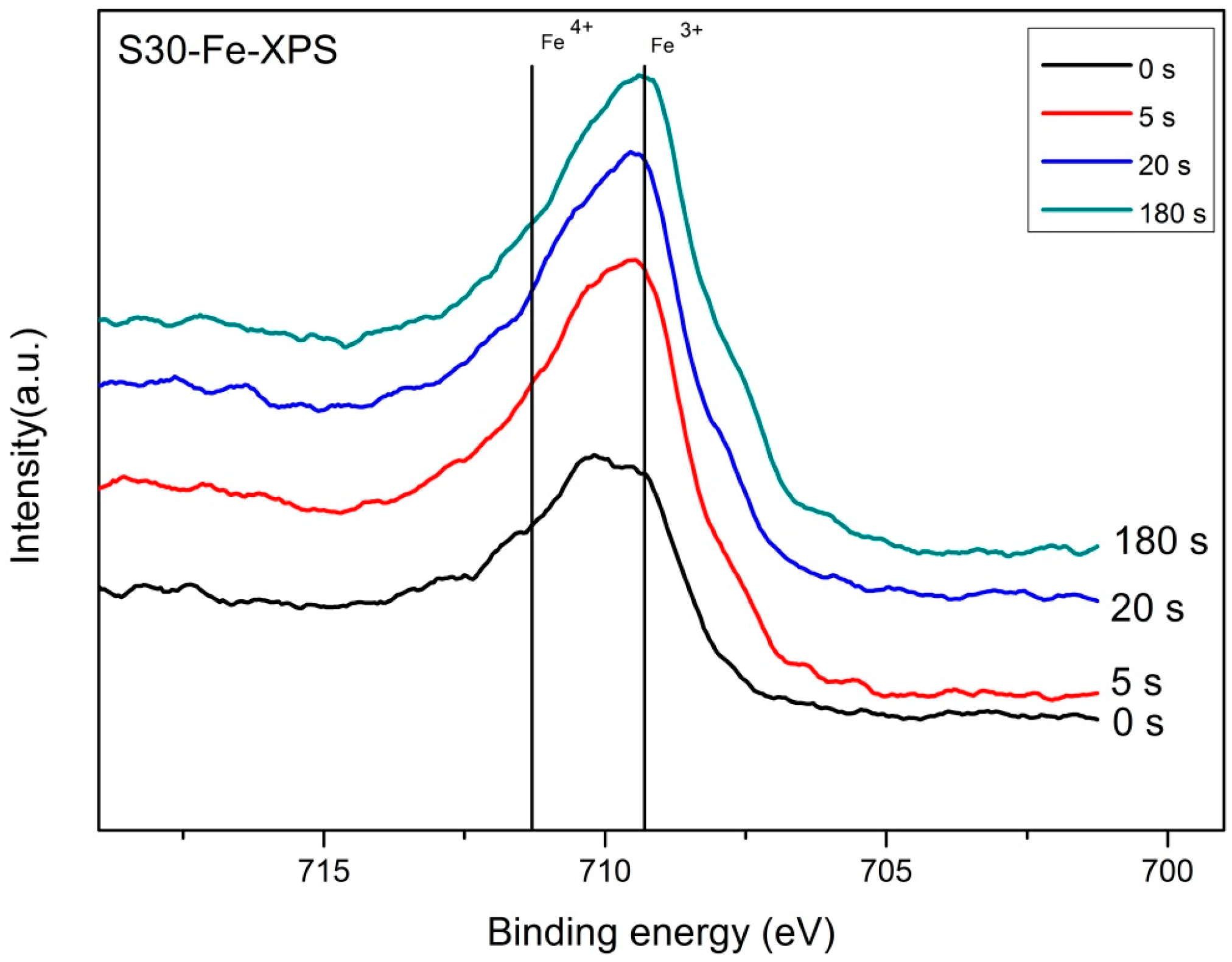
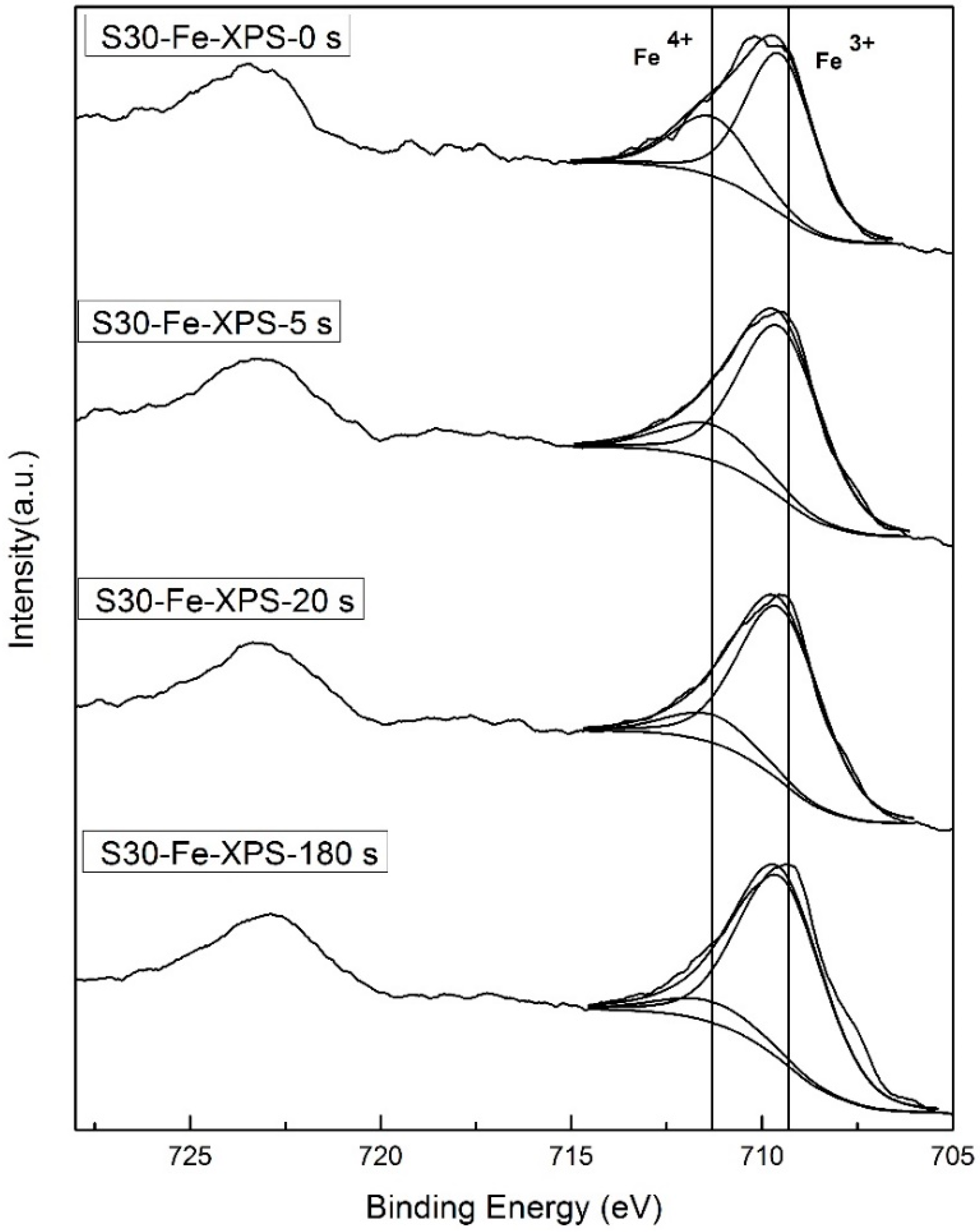
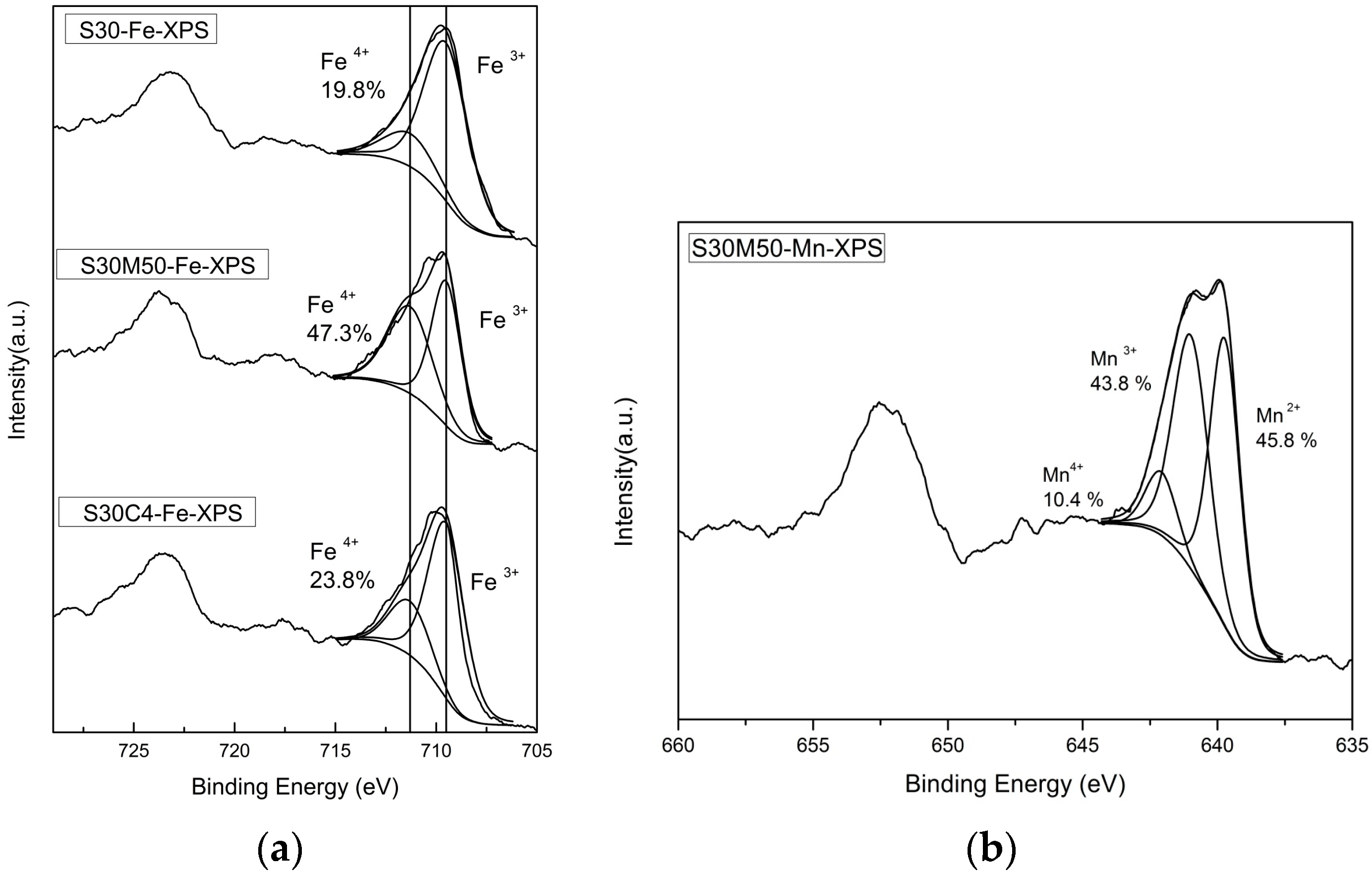
2.3. Valence State Analysis
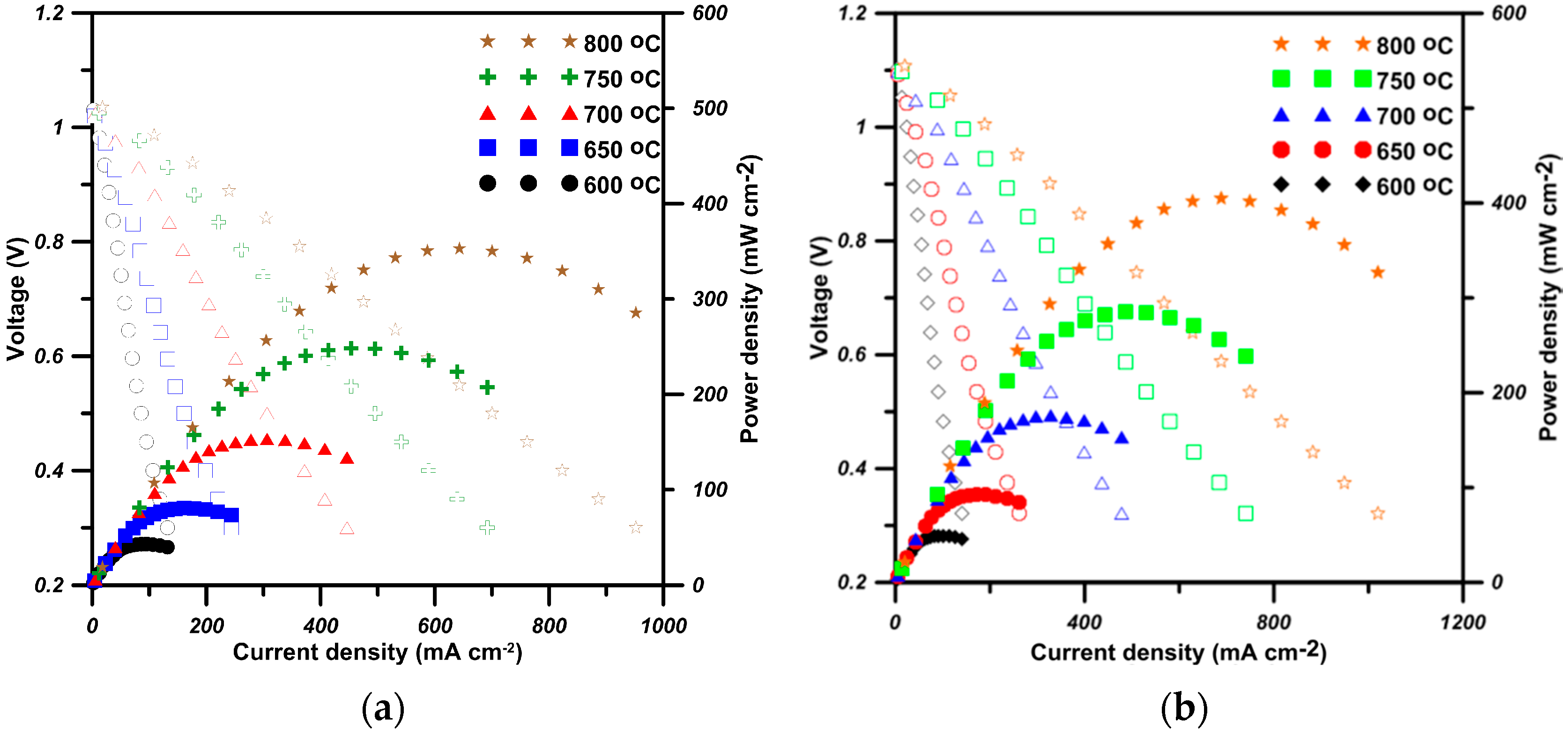
2.4. Performance of Cells
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Experimental Procedures
4.1. Synthesis of Cathode Materials
4.2. Preparation of Fuel Cell
4.3. Characterization
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- Wachsman, E.D.; Lee, K.T. Lower the temperature of solid oxide fuel cells. Science 2011, 334, 935–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ralph, J.M.; Rossignol, C.; Kumar, R. Cathode materials for reduced- temperature SOFCs. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2003, 150, A1518–A1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.Y.; Wei, W.C.J. Processing and characterization of ultra-thin yttria stabilized zirconia (YSZ) electrolytic film for SOFC. Solid State Ion. 2006, 177, 351–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Ran, R.; Shao, Z.P. Progress in understanding and development of Ba0.5Sr0.5Co0.2Fe0.8O3−δ–based cathode for intermediate-temperature solid oxide fuel cells: A review. J. Power Sources 2009, 192, 231–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Z.P.; Haile, S.M. A high-performance cathode for the next generation of solid oxide fuel cells. Nature 2004, 431, 170–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.T.; Manthiram, A. A comparison of Ln0.6Sr0.4CoO3−δ (Ln = La, Pr, Nd, Sm, and Gd) as cathode materials for intermediate temperature solid oxide fuel cells. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2006, 153, A794–A798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Manthiram, A. LnBaCo2O5 oxides as cathodes for intermediate- temperature solid oxide fuel cells. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2008, 155, B358–B390. [Google Scholar]
- Tai, L.W.; Nasrallah, M.M.; Anderson, H.U.; Sparlin, D.M.; Sehlin, S.R. Structure and electrical-properties of La1−xSrxCo1−yFeyO3. Part 2. The system La1−xSrxCo0.2Fe0.8O3. Solid State Ion. 1995, 76, 273–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petric, A.; Huang, P.; Tietz, F. Evaluation of La-Sr-Co-Fe-O perovskites for SOFC and gas separation membranes. Solid State Ion. 2000, 135, 719–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsipis, E.V.; Kharton, V.V. Electrode materials and reaction mechanisms in SOFCS: A brief review. J. Solid State Electron. 2008, 12, 1367–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullmann, H.; Trofimenko, N.; Tietz, F.; Stove, D.; Ahmad-Khanlou, A. Correlation between thermal expansion and oxide ion transport in mixed conducting perovskite-type oxides for SOFC cathodes. Solid State Ion. 2000, 138, 79–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, J.P.; Tao, Y.; Wang, J.X.; Xu, C.; Wang, W.G. Investigation of precursors in the preparation of nanostructured LSCF6428 via a modified combined complexing method. J. Alloys Compd. 2009, 484, 263–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brinkman, K.; Iijima, T.; Takamura, H. The oxygen permeation characteristics of Bi1−xSrxFeO3 mixed ionic and electronic conducting ceramics. Solid State Ion. 2010, 181, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Y.J.; Zhou, W.; Sunarso, J.; Ge, L.; Zhu, Z.H.; Shao, Z.P. High performance cobalt-free perovskite cathode for intermediate temperature SOFCs. J. Mater. Chem. 2010, 20, 9619–9622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Y.J.; Sunarso, J.; Zhou, W.; Liang, F.L.; Ge, L.; Zhu, Z.H.; Shao, Z.P. Evaluation and optimization of Bi1−xSrxFeO3−δ perovskites as cathodes of solid oxide fuel cells. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2011, 36, 3179–3186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Y.J.; Sunarso, J.; Liang, F.L.; Zhou, W.; Zhu, Z.H.; Shao, Z.P. A comparative study of oxygen reduction on Bi- and La-doped SrFeO3−δ perovskite cathodes. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2011, 158, B132–B138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wedig, A.; Merkle, R.; Stuhlhofer, B.; Habermeier, H.-U.; Maier, J.; Heifets, E. Fast oxygen exchange kinetics of pore-free Bi1−xSrxFeO3−δ thin film. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2011, 13, 16530–16533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wedig, A.; Merkle, R.; Stuhlhofer, B.; Habermeier, H.-U.; Heifets, E.; Maier, J. Searching for fast oxygen exchange kinetics: (Bi,Sr)(Fe,Co)O3−δ perovskite. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2012, 45, 213–214. [Google Scholar]
- Maso, N.; West, A.R. Electrical properties of Ca-doped BiFeO3 ceramics: From p-type semiconduction to oxide-ion conduction. Chem. Mater. 2012, 24, 2127–2131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, D.; Kamegawa, A.; Takamura, H. Mixed conductivity and electrode properties of Mn-doped Bi-Fr-Fe-based perovskite-type oxides. Solid State Ion. 2013, 253, 211–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wedig, A.; Merkle, R.; Maier, J. Oxygen exchange kinetics of (Bi,Sr)(Co,Fe)O3−δ thin-film microelectrodes. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2014, 161, F23–F32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizusaki, J.; Yonemura, Y.; Kamata, H.; Ohyama, K.; Mori, N.; Takai, H.; Tagawa, H.; Doyiya, M.; Naraya, K.; Sasamoto, T.; et al. Electronic conductivity, Seebeck coefficient, defect and electronic structure of non-stoichiometric La1−xSrxMnO3. Solid State Ion. 2000, 132, 167–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuller, H.L.; Nowick, A.S. Small polaron electron transport in reduced CeO2 single crystals. J. Phys. Solid 1977, 38, 859–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duran, A.; Verdin, E.; Escamilla, R.; Morales, F.; Escudero, R. Mechanism of small-polaron formation in the biferroic YCrO3 doped with cacium. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2012, 133, 1011–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taguchi, H.; Hirata, K.; Kido, H.; Takeda, Y.; Kato, M.; Hirota, K. Hopping conductivity of distorted K2NiF4-type (Ca1+x)Nd1−x)CrO4. Solid State Ion. 2009, 11, 1222–1225. [Google Scholar]
- Taraoka, Y.; Zhang, H.M.; Okamoto, K.; Yamazoe, N. Mixed ionic-electronic conductivity of La1−xSrxCo1−yFeyO3−δ perovskite-type oxides. Mater. Res. Bull. 1988, 23, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.H. Synthesis, Material and Electrical Conductivity Properties of Bi-Based Cathode for IT-SOFC. Master’s Thesis, National Taiwan University, Taipei, Taiwan, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, F.; Shen, Y.; Wang, R.; He, T. Double-perovskite PrBaCo2/3Fe2/3Cu2/3O5+δ as cathode material for intermediate-temperature solid-oxide fuel cells. J. Power Sources 2013, 234, 244–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaffari, M.; Shannon, M.; Hui, H.; Tan, O.K.; Irannejad, A. Preparation, surface state and band structure studies of SrTi(1−x)Fe(x)O(3−δ) (x = 0–1) perovskite-type nano structure by X-ray and ultraviolet photoelectron spectroscopy. Surf. Sci. 2012, 606, 670–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, C.; Qin, H.; Zhao, M.; Wang, X.; Li, L.; Hu, J. Investigation on electrical transport, CO sensing characteristics and mechanism for nanocrystalline La1−xCaxFeO3 sensors. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 190, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, F.; Xu, H.; Long, W.; Shen, Y.; He, T. Characterization and evaluation of double perovskites LnBaCoFeO5+δ (Ln = Pr and Nd) as intermediate-temperature solid oxide fuel cell cathodes. J. Power Sources 2013, 243, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Pang, S.; Shen, X.; Jiang, X.; Wang, W. Evaluation of Ba-deficient PrBa1−xFe2O5+δ oxides as cathode materials for intermediate-temperature solid oxide fuel cells. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 13829–13836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhou, Q.; He, Q.; He, T. Double-perovskites A2FeMoO6−δ (A = Ca, Sr, Ba) as anodes for solid oxide fuel cells. J. Power Sources 2010, 195, 6356–6366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brundle, C.R.; Chuang, T.J.; Wandelt, K. Core and valence level photoemission studies of iron oxide surfaces and the oxidation of iron. Surf. Sci. 1977, 68, 459–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, C.F.; Lin, J.P.; Wu, J.M. Influence of Mn and Nb dopants on electric properties of chemical-solution-deposited BiFeO3 films. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2006, 88, 242909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richter, J.; Holtappels, P.; Graule, T.; Nakamura, T.; Gauckler, L.J. Materials design for perovskite SOFC cathodes. Monatsh. Chem. 2009, 140, 985–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.-J. Bismuth-Based Perovskite as Cathode Materials for Intermediate-Temperature Solid Oxide Fuel Cells. Master’s Thesis, National Taiwan University, Taipei, Taiwan, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Goldschmidt, V.; Barth, T.; Lunde, G.; Zachariasen, W.H. Geochemical distribution law of the elements. VII Summary of the Chemistry of Crystals. Skr. Nor. Vidensk. Akad. 1926, 1, 1–117. [Google Scholar]
- Shannon, R.D. Revised effective ionic radii and systematic studies of interatomic distances in halides and chalcogenides. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. A 1976, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atou, T.; Chiba, H.; Ohoyama, K.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Syono, Y. Structure determination of ferromagnetic perovskite BiMnO3. J. Solid State Chem. 1999, 145, 639–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukunaga, O.; Fujita, T. The relation between ionic radii and cell volumes in the perovskite compounds. J. Solid State Chem. 1973, 8, 331–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sammells, A.F.; Cook, R.L.; White, J.H.; Osborne, J.J.; Macduff, R.C. Rational selection of advanced solid electrolytes for intermediate temperature fuel-cells. Solid State Ion. 1992, 52, 111–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, H.; Inaba, H.; Matsuyama, M.; Lan, N.G.; Dokiya, M.; Tagawa, H. Structural consideration on the ionic conductivity of perovskite-type oxides. Solid State Ion. 1999, 122, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patra, H.; Rout, S.K.; Pratihar, S.K.; Bhattacharya, S. Effect of process parameters on combined EDTA–citrate synthesis of Ba0.5Sr0.5Co0.8Fe0.2O3−δ perovskite. Powder Technol. 2011, 209, 98–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
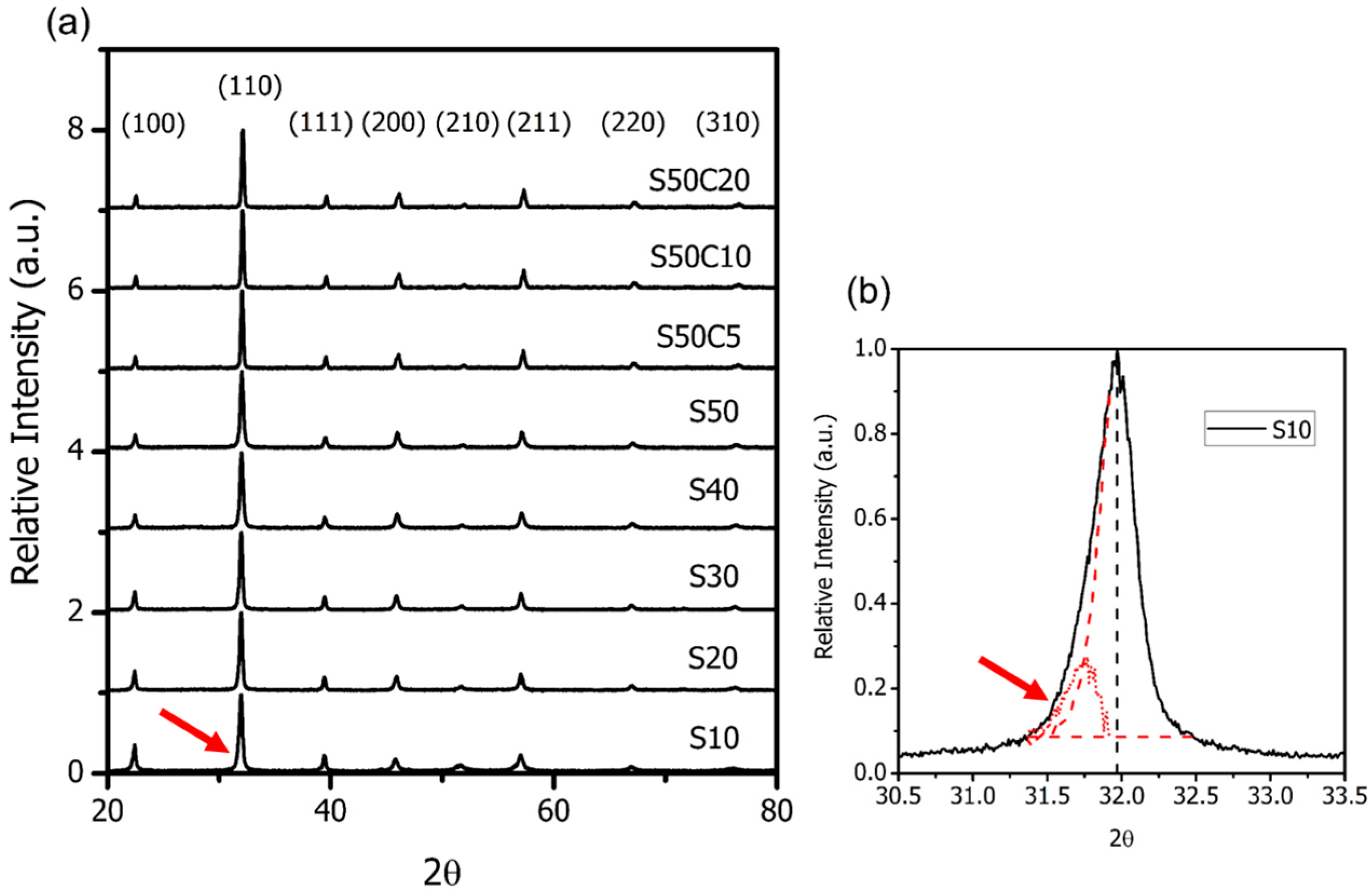
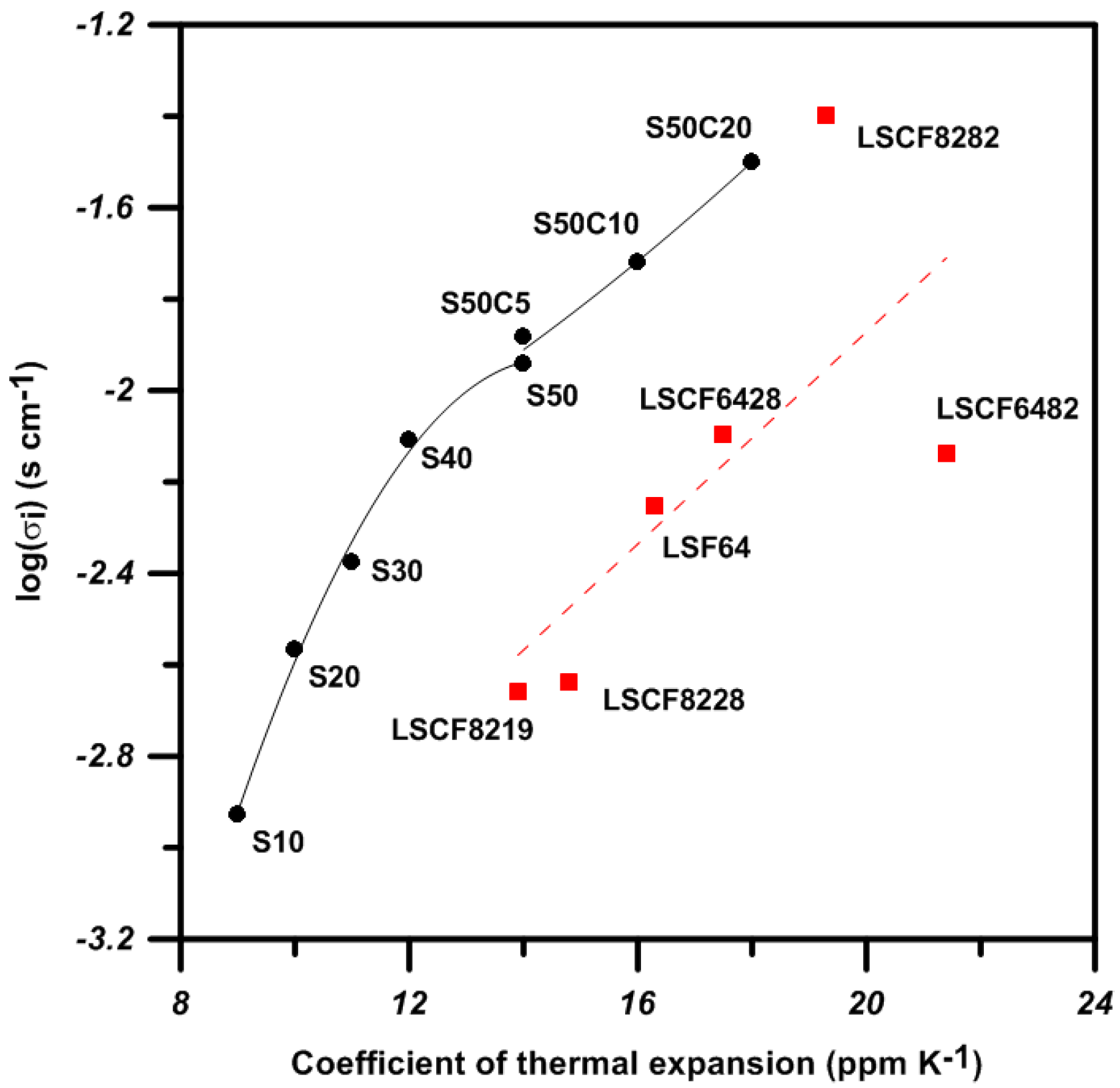
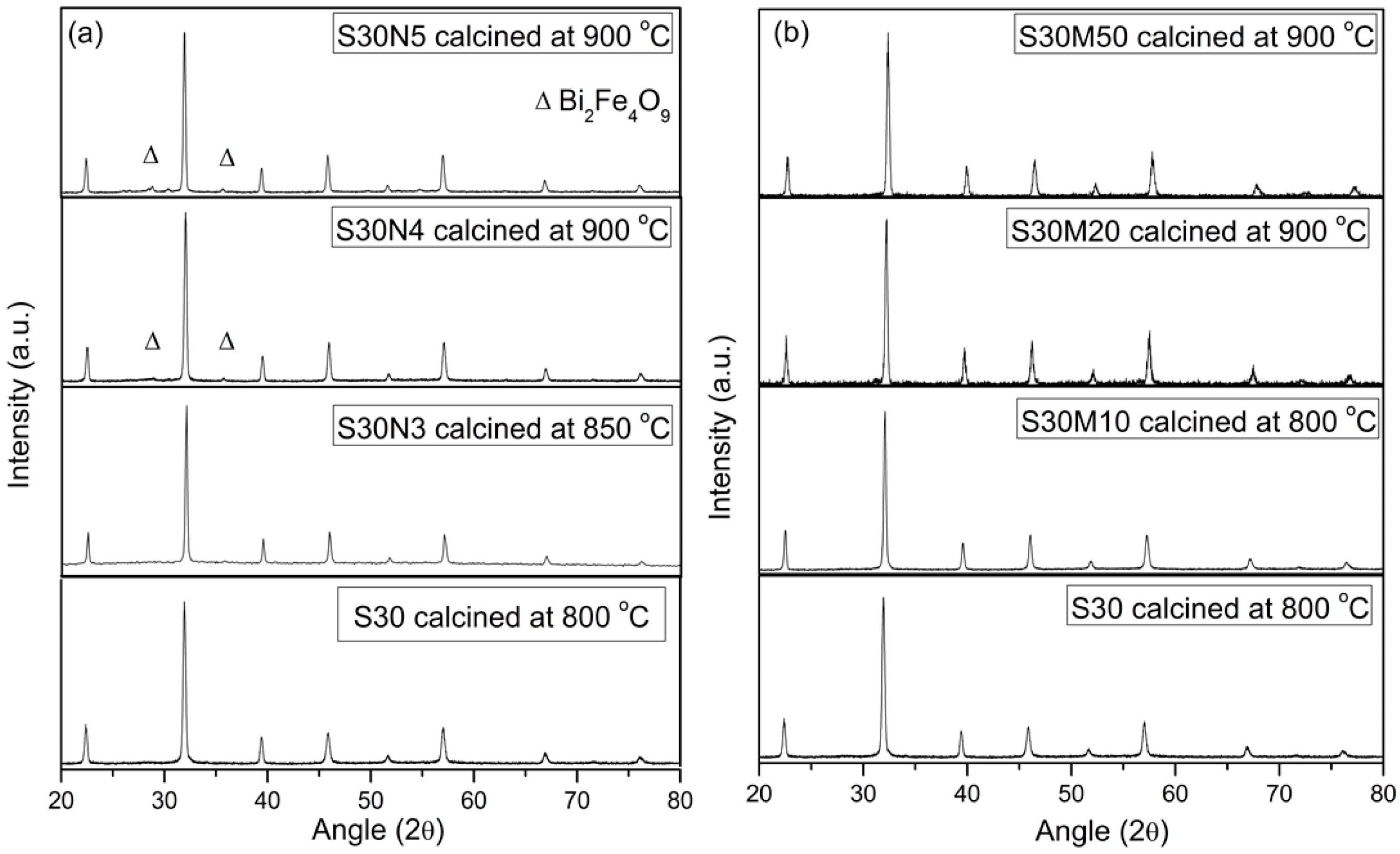
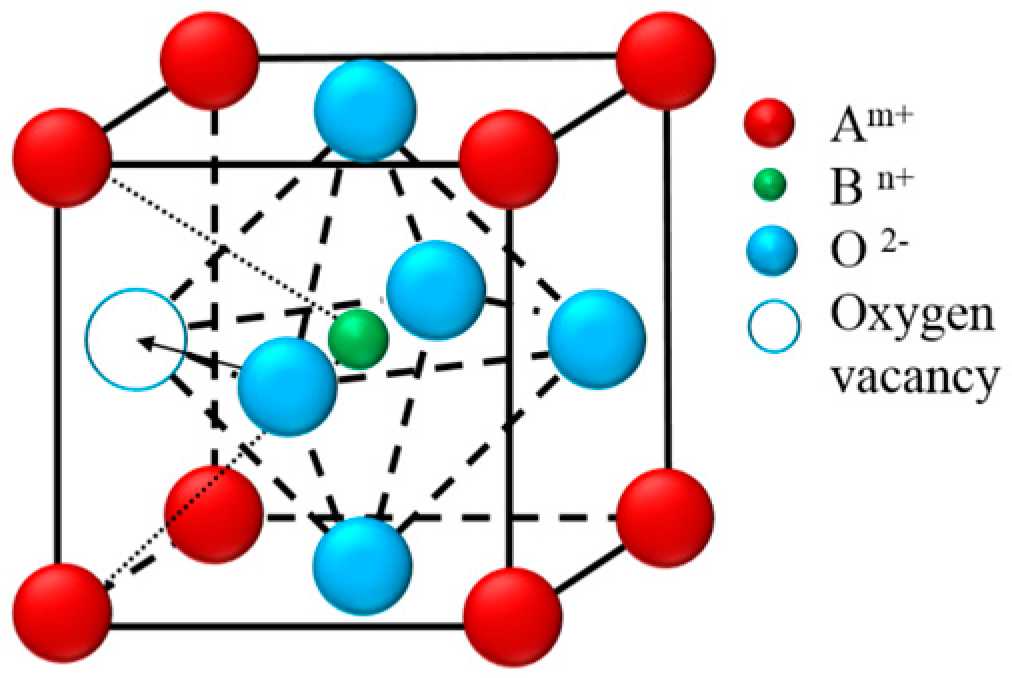
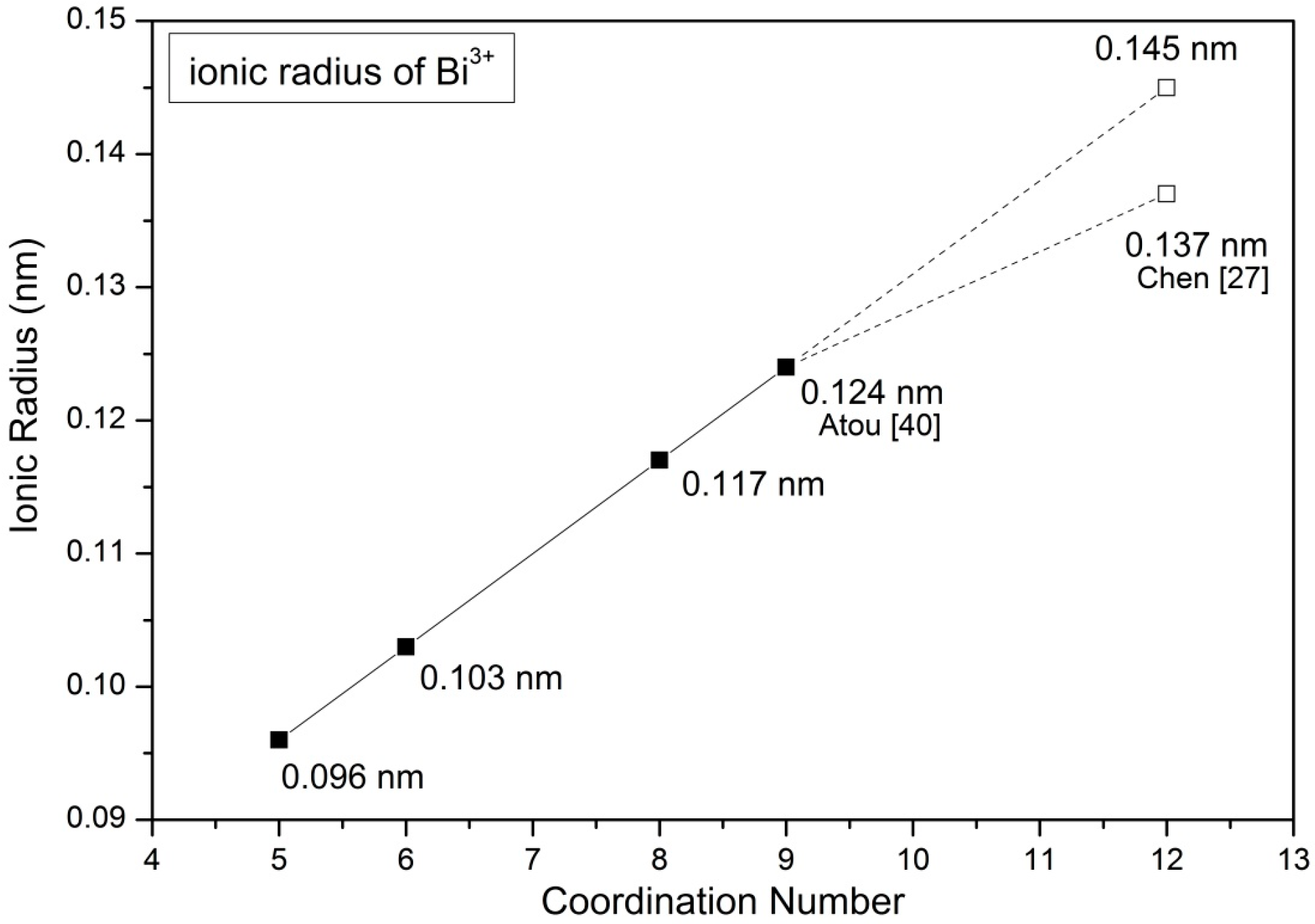
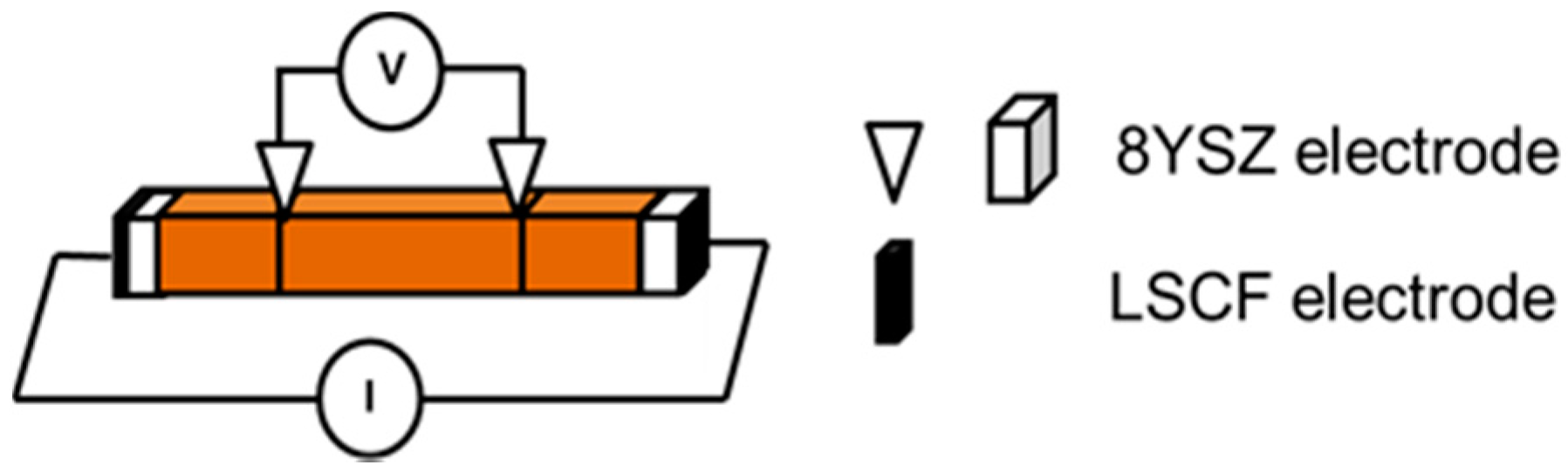
| SrO-Doping (Sx-Series) | Abbreviation | Sintering Temperature (°C) for 5 h | Sintered Density (% T.D.) | CTE |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bi0.9Sr0.1FeO3 | S10 | 950 | 96.4 | 10.0 |
| Bi0.8Sr0.2FeO3 | S20 | 1000 | 95.9 | 11.5 |
| Bi0.7Sr0.3FeO3 | S30 | 1000 | 95.5 | 13.6 |
| Bi0.6Sr0.4FeO3 | S40 | 1050 | 95.3 | 14.3 |
| Bi0.5Sr0.5FeO3 | S50 | 1050 | 95.1 | 15.1 |
| SrO- and CoO-Doping (SxCy-Series) | Abbreviation | Sintering Temperature (°C) for 5 h | Sintered Density (% T.D.) | CTE |
| Bi0.5Sr0.5Fe0.95 Co0.05O3 | S50C5 | 1000 | 95.1 | 15.4 |
| Bi0.5Sr0.5Fe0.9 Co0.1O3 | S50C10 | 950 | 95.3 | 16.9 |
| Bi0.5Sr0.5Fe0.8 Co0.2O3 | S50C20 | 950 | 96.0 | 19.3 |
| Composition | Ea(HT) (eV) | Ea(LT) (eV) | Ttr (°C) |
|---|---|---|---|
| S10 | 0.48 | 0.70 | 527 |
| S20 | 0.27 | 0.65 | 523 |
| S30 | 0.24 | 0.57 | 516 |
| S40 | 0.22 | 0.48 | 506 |
| S50 | 0.21 | 0.40 | 502 |
| S50C5 | 0.20 | 0.38 | 497 |
| S50C10 | 0.31 | - | NA |
| S50C20 | 0.25 | - | NA |
| Composition | Ea(LT) (eV) | Ea(HT) (eV) | Ttr (°C) |
|---|---|---|---|
| S30 | 0.57 | 0.24 | 516 |
| S30N03 | 0.54 | 0.36 | 431 |
| S30C4 [27] | 0.59 | 0.25 | 496 |
| S30M10 | 0.44 | 1.09 | 489 |
| S30M50 | 0.37 | 1.09 | 396 |
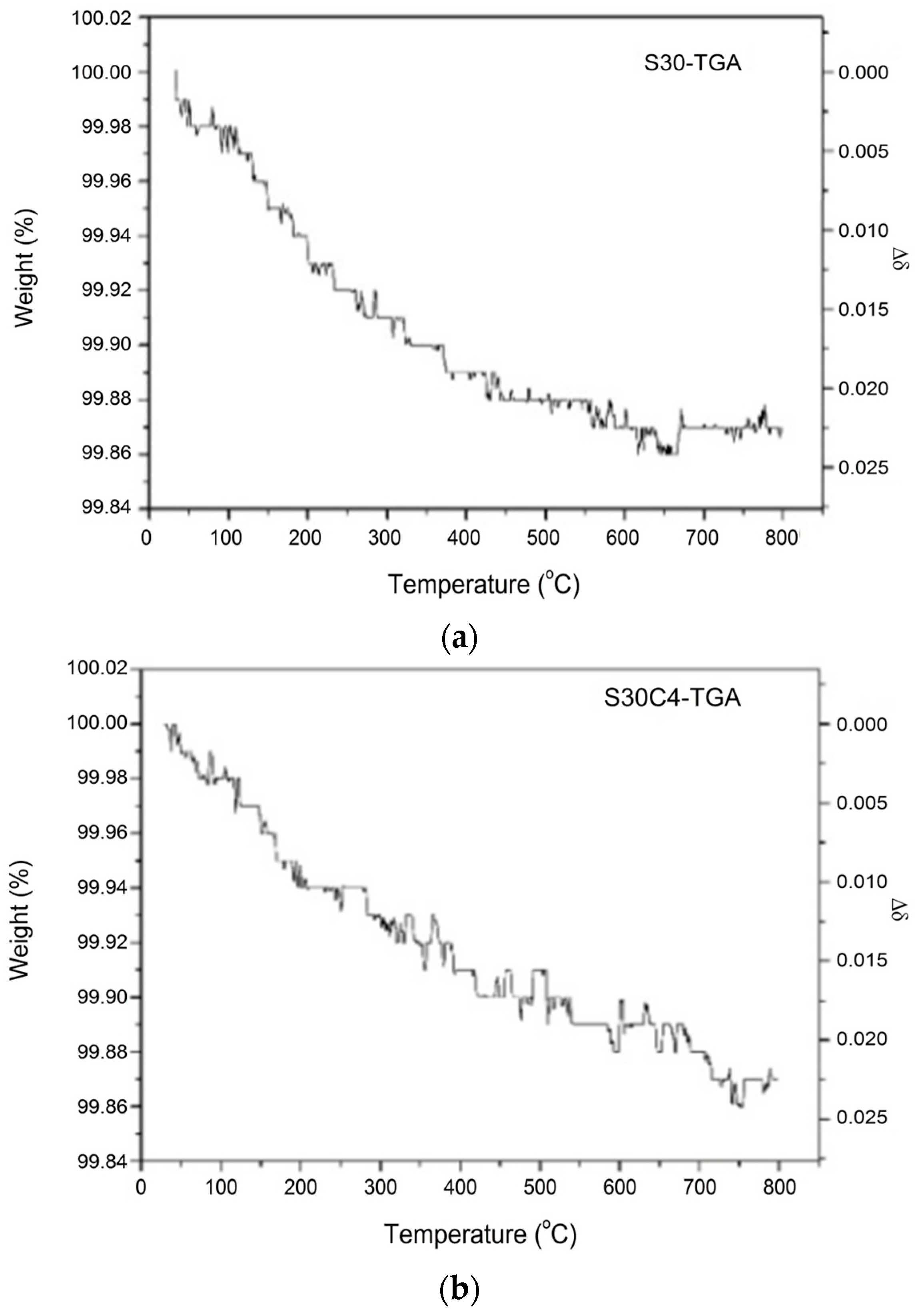
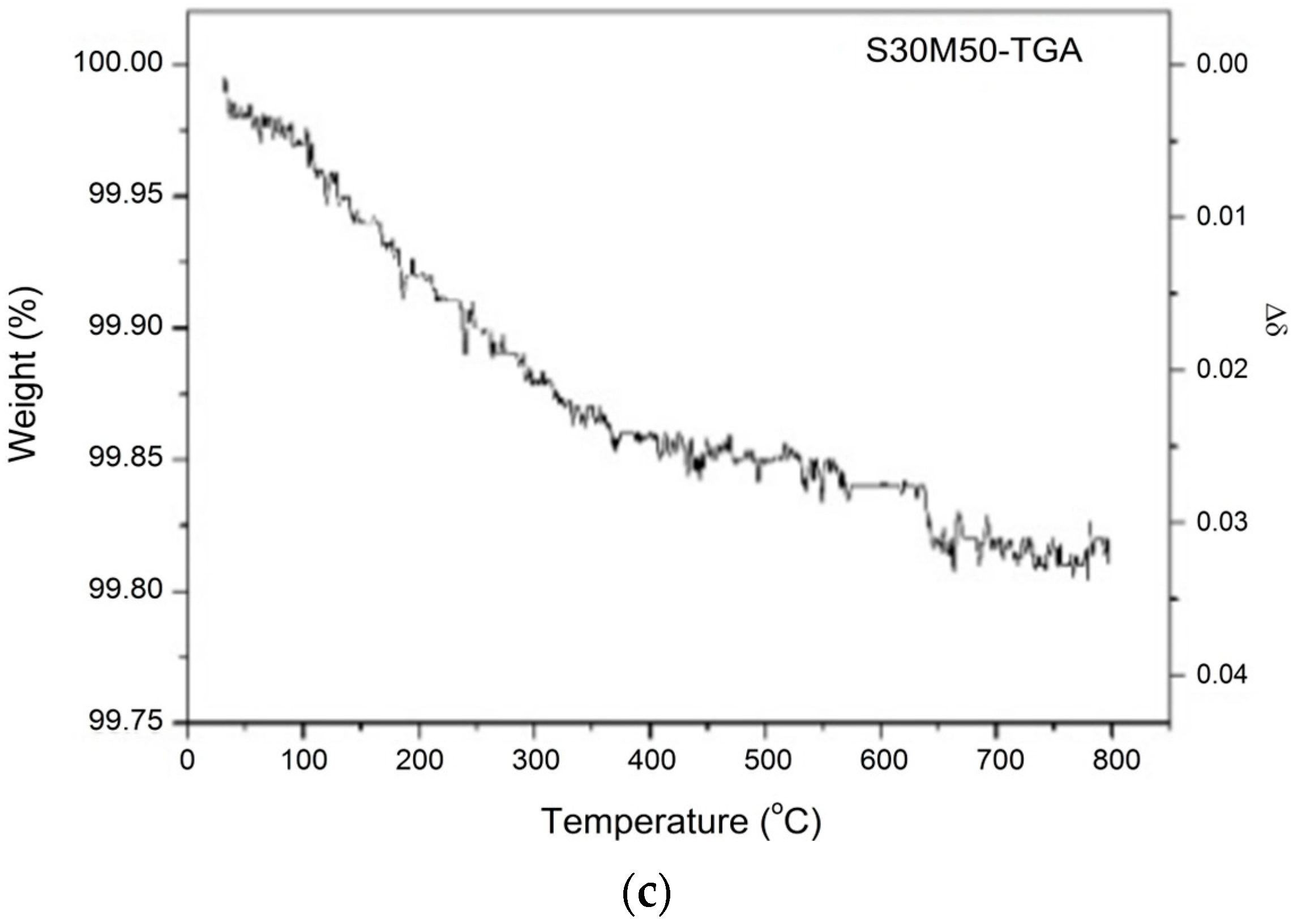
| Formula of the Doped S30 at 25 °C | Msample | Moxygen | Δm/ms | Δδ |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bi0.7Sr0.3FeO2.95 | 275.617 | 16.0 | 0.13% | 0.022 |
| Bi0.7Sr0.3Fe0.96Co0.04O2.97 | 276.060 | 16.0 | 0.13% | 0.022 |
| Bi0.7Sr0.3Fe0.5Mn0.5O2.88 | 274.047 | 16.0 | 0.20% | 0.034 |
| La0.4Sr0.4Co0.2Fe0.8O3−δ | 222.862 | 16.0 | 1.89% | 0.26 |
| Properties | A Site | B Site | O2− | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| La3+ | Sr2+ | Bi3+ | Mn3+ a | Fe3+ a | Co3+ | Ni3+ | ||
| Ionic radius unit: Å | 1.36 | 1.44 | 1.45 b | 0.645 | 0.645 | 0.545 | 0.56 | 1.40 |
| 1.37 c | ||||||||
| CN | 12 | 12 | 12 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 |
| Atomic mass | 138.90 | 87.62 | 209.0 | 54.94 | 55.85 | 58.93 | 58.69 | 16.0 |
| Composition | Tolerance Factor, S | Critical Radius, rcr (Å) | Specific Free Volume, Vsf (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| La0.6Sr0.4Co0.2Fe0.8O3 | 0.975 | 0.910 | 20.1 |
| Bi0.7Sr0.3FeO3 | 0.984 | 0.902 | 22.6 |
| Bi0.7Sr0.3Fe0.97Ni0.03O3 | 0.986 | 0.901 | 22.5 |
| Bi0.7Sr0.3Fe0.5Mn0.5O3 | 0.984 | 0.902 | 22.6 |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wei, W.-C.J.; Huang, D.-R.; Wang, D. (Bi,Sr) (Fe1−x,Mx)O3−δ (M = Co, Ni and Mn) Cathode Materials with Mixed Electro-Ionic Conductivity. Materials 2016, 9, 922. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma9110922
Wei W-CJ, Huang D-R, Wang D. (Bi,Sr) (Fe1−x,Mx)O3−δ (M = Co, Ni and Mn) Cathode Materials with Mixed Electro-Ionic Conductivity. Materials. 2016; 9(11):922. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma9110922
Chicago/Turabian StyleWei, Wen-Cheng J., Der-Rong Huang, and Dan Wang. 2016. "(Bi,Sr) (Fe1−x,Mx)O3−δ (M = Co, Ni and Mn) Cathode Materials with Mixed Electro-Ionic Conductivity" Materials 9, no. 11: 922. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma9110922
APA StyleWei, W.-C. J., Huang, D.-R., & Wang, D. (2016). (Bi,Sr) (Fe1−x,Mx)O3−δ (M = Co, Ni and Mn) Cathode Materials with Mixed Electro-Ionic Conductivity. Materials, 9(11), 922. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma9110922





