Abstract
The primary aim of this study was to analyse the correlation between topographical features and chemical composition with the changes in wettability and the surface free energy of microstructured titanium (Ti) surfaces. Periodic microscale structures on the surface of Ti substrates were fabricated via direct laser interference patterning (DLIP). Radio-frequency magnetron sputter deposition of ultrathin nanostructured hydroxyapatite (HA) films was used to form an additional nanoscale grain morphology on the microscale-structured Ti surfaces to generate multiscale surface structures. The surface characteristics were evaluated using atomic force microscopy and contact angle and surface free energy measurements. The structure and phase composition of the HA films were investigated using X-ray diffraction. The HA-coated periodic microscale structured Ti substrates exhibited a significantly lower water contact angle and a larger surface free energy compared with the uncoated Ti substrates. Control over the wettability and surface free energy was achieved using Ti substrates structured via the DLIP technique followed by the deposition of a nanostructured HA coating, which resulted in the changes in surface chemistry and the formation of multiscale surface topography on the nano- and microscale.
1. Introduction
Currently, a large number of devices and implants are used in medicine [1]. Biomaterials in the form of implants (e.g., ligaments, vascular grafts, heart valves, intraocular lenses, and dental implants) and medical devices (e.g., pacemakers, biosensors, and artificial hearts) are extensively used to replace and/or restore the function of disturbed or deteriorated tissues or organs, and thus improve the quality of life and longevity of human beings [2,3]. The field of biomaterials has shown rapid growth in keeping up with the demands of an aging population [2,3].
Implants should not only be mechanically resistant, but should also be able to rapidly heal the host organism. When implanted into living tissue, all materials initiate a host response, and this represents the first steps of tissue repair [4,5]. Modern implant design is directed towards making use of this immune response to improve implant integration while preventing the perpetuation of the immune response, which leads to chronic inflammation, foreign body reactions, and thus loss of the intended function [4,5]. In addition to determining some of the deformation and strength characteristics of implants (such as the durability, elasticity, and shape stability), it is necessary to minimize the trauma caused by their use and to view the implantation with respect to healing a wound in order to achieve a fast and full postoperative rehabilitation of patients [5]. As a result, it is necessary to fulfil frequently inconsistent requirements with respect to the physical and mechanical properties of the materials used to manufacture the specified products [5]. The physicochemical properties of implants strongly depend on the method used to form the surface of the implants. Numerous techniques have been used to enhance the surface compatibility of tissue implants. Most of these methods involve multiple preparation procedures that incorporate coating and/or patterning steps. Direct laser interference patterning (DLIP) requires a single processing step and can be applied to a wide range of materials. The principle behind this method is based on the unique intensity pattern generated by interfering laser beams, which show periodicities in the (sub-)micron range [6,7,8].
The compatibility of the medical implant surface with biological tissues is achieved through the use of a biocompatible coating, which can be a layer of calcium phosphate (CaP). Biologically-relevant CaP belongs to the orthophosphate group, and naturally occurs in several biological structures, including teeth and bone [9]. Bone consists of an inorganic component of biological apatite as well as an organic component, which primarily consists of collagen and water. Currently, hydroxyapatite (HA), Ca10(PO4)6(OH)2, is an optimum material for clinical practice, with a similar structure to that of the mineral component of bone tissue [9]. The basic technological methods that are used to prepare biocompatible coatings include plasma spraying, ion-beam deposition, radio-frequency (rf) magnetron sputtering, and electrochemical deposition. Rf magnetron sputtering is a prospective technique for the fabrication of implant coatings, because it can be used to form HA films that have low roughness and exhibit good adhesion to Ti substrate [10,11]. The plasma parameters of the rf magnetron sputtering process affect the physicochemical and mechanical properties of the CaP films [12]. The deposition parameters can be adjusted to produce single-phase HA films generated at a high deposition rate and high thermal stability. Moreover, the chemical composition of the precursor material used to deposit the HA coating is preserved [13]. The biocompatibility of HA has been thoroughly investigated and established, and it has been shown to promote the proliferation and differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells and adhesion of human keratinocyte cell lines. In addition, the improved adhesion, proliferation, and differentiation, the increased alkaline phosphatase activity of primary human osteoblast cells, and the normal cell growth of human embryonic kidney cell lines in the presence of HA have been shown experimentally [14].
The living tissue and the artificial implant interact at the molecular level, and the size of the biological structures ranges from a few nanometres to tens of micrometres. The scientific experience gained to date has demonstrated that the successful interaction between the biotissue and the surface of the implant frequently depends on physico-chemical material properties, such as the chemical composition, microstructure, roughness, wetting angle, and free surface energy (FSE) [15]. Thus, the aim of this study was to achieve the surface structuring of Ti using the DLIP technique followed by HA coating deposition through rf magnetron sputtering with pure HA. Analyses of the correlation between variations in the topographical multiscale Ti surface feature, including Ti coated with HA, and changes in the surface wettability and energy are reported.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Preparation
Technically pure Ti was used as a substrate. A high-powered pulsed Nd:YAG laser (Quanta-Ray PRO210, Spectra Physics, Santa Clara, CA, USA) was used for laser interference patterning. The repetition rate and pulse duration of the laser were 10 Hz and 10 ns, respectively. The fundamental wavelength of the Nd:YAG laser system was 1064 nm, and shorter wavelengths were obtained through second-harmonic generation. Samples with a surface area of 20 × 20 were irradiated at 355 nm with multiple adjacent 1 × 1–2 × 2 mm2 spots at a fluency of 3.05 ± 0.15 J·cm2. Line-like structures with periodicities of approximately 4.5 µm and 8.4 µm were obtained using a two-beam laser setup. For cross-like structure types with the same periodicity, samples were structured once, rotated 90°, and then structured a second time.
2.2. Coating Deposition
A commercially available apparatus with a rf magnetron source (13.56 MHz) was used to deposit the nanostructured HA coating [12,13]. The HA coating was deposited at an operating pressure of 0.4 Pa (the vacuum chamber was evacuated to 10−4 Pa) at a target–substrate distance of 40 mm, with argon as the working gas, and with an rf generator power of 500 W. The HA coating was deposited for 8 h onto a substrate mounted on a grounded substrate holder, which resulted in a coating thickness of 650 ± 50 nm. A target of pure HA—synthesized by the mechanochemical method—was prepared according to the previously described procedures [16,17]. The target for rf magnetron sputtering (220 mm diameter, 10 mm thick) was prepared via ceramic technology—i.e., the powder was pressed at a pressure of 70 MPa and then annealed at 1100 °C for 1 h in air.
2.3. Atomic Force Microscopy (AFM) Measurements
The quantitative analysis of the surface morphology of the uncoated and HA-coated substrates was performed with a Solver P47-PRO (NT-MDT, Moscow, Russia) atomic force microscope (AFM) using triangular golden silicon probes (NT-NDT) with a typical spring constant of 28 N· and a resonance frequency of 420 kHz. All of the images were collected in contact AFM mode in air at a typical frequency of 1.5 Hz with an image resolution of 256 points per line. Squares of different sizes (5 × 5 and 35 × 35 ) were scanned, and the Nova SPM software (NT-MDT, Moscow, Russia) was used to analyse the surface roughness. Three different 3D parameters were used to characterize the surface roughness: (Sa), which is the arithmetic mean of the absolute values of the surface departure from the mean plane in the samples area; the root mean square roughness (Sq), which is an index used to represent the standard deviation of the surface heights; and Sdr, which is the developed interfacial area ratio.
2.4. X-ray Diffraction (XRD)
An X-ray diffractometer (Shimadzu XRD-6000, Tokyo, Japan) was used to identify the crystalline structure of the HA-coated Ti that were previously treated to prepare parallel and crossed grooves with different periodicities. The typical irradiation conditions were 40 kV and 30 mA using Cu-Kα radiation (1.5405 Å); the 2θ scan ranged from 10° to 60° with a step size of 0.02° at a speed of 2 deg/min and a grazing angle of 3°. The average crystallite size was determined using Scherrer’s equation from the broadening of the diffraction peaks; this determination was performed with the Powder Cell 2.4 software (FIMRT, Berlin, Germany), and the instrumental broadening was considered. An instrumental broadening of 0.1° in 2θ was determined by the full width at half maximum (FWHM) of a silicon powder.
2.5. Contact Angle and Surface Free Energy Measurements
Contact angle analyses were performed using an optical contact angle apparatus (OCA15 Plus Data Physics Instruments GmbH, Filderstadt, Germany) along with the SCA20 software (Data Physics Instruments GmbH, Filderstadt, Germany). The contact angle (CA) of water in air was measured using a sessile drop method. A minimum of 10 droplets (2 μL, 5 μL) of water and three droplets of diiodomethane or ethylene glycol were seeded on the surface of each sample. The surface free energy was calculated using the Owens–Wendt–Rabel–Kaelble (ORWK) method. Three different media (water, diiodomethane, and ethylene glycol) were used for the calculations, and all the measurements were performed according to the study [18]. The phenomenon of contact angle hysteresis was also observed in the optical contact angle apparatus using a sessile liquid (water) droplet. After the liquid has advanced over a previously unwetted surface (i.e., when the solid/liquid contact area increases), the maximum contact angle at the three-phase contact line is referred to as the advancing angle (). A minimum contact angle is measured at the contact line when the liquid is retracted over a previously wetted surface (i.e., when the contact area shrinks); this is referred to as a receding angle (). Contact angle hysteresis is defined as the difference between the (maximum) advancing and (minimum) receding angles: [19].
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Surface Roughness and Morphology
To study the changes in the morphology, AFM analysis was carried out on the uncoated and HA-coated patterned Ti substrates. The results presented in Figure 1 reveal that deposition of the HA coating resulted in changes in microscale surface roughness of the initial structured Ti substrate. In general, after HA coating deposition, the roughness parameters Sa and Sq decreased. For the grooves with a periodicity of 8.4 , the average surface roughness after deposition of the HA coating was lower than that of the structured Ti substrate. This phenomenon may be related to the growth mechanism of the HA coating. During the growth, the HA coating tends to fill the grooves, which results in a surface smoothening effect.
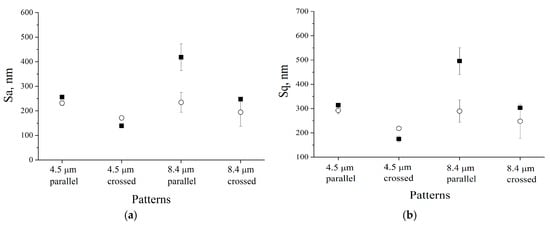
Figure 1.
The roughness parameters of different Ti surface patterns with a 35 × 35 scan area: ■—without hydroxyapatite (HA) film, and ○—with HA film. (a) Sa roughness parameter; (b) Sq roughness parameter.
Figure 2, Figure 3, Figure 4 and Figure 5 show typical AFM images of the HA coating prepared using rf magnetron sputtering on the laser micro-textured Ti surfaces. The microstructure of the surfaces is easily observed using 35 × 35 scan areas. For the 5 × 5 µm2 scan area, clear grains of the HA coating with definite boundaries can be observed (Figure 2d and Figure 3d). The deposited coating was homogenous and revealed a regular grain-like morphology, which is typical for a thin film deposited by rf magnetron sputtering [20,21]. The surface had a grain-like morphology with a grain size from 0.36 to 0.73 µm in the 5 × 5 scan area (Figure 2d and Figure 3d). Therefore, the surface of the treated Ti substrates exhibited a multiscale structure.
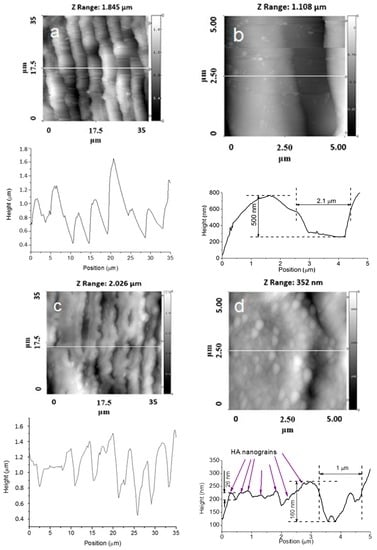
Figure 2.
Atomic force microscopy (AFM) images of the surface topographies of Ti samples with parallel grooves and a periodicity of approximately 4.5 µm. (a) 35 × 35 ; (b) 5 × 5 without a HA film; (c) 35 × 35 ; and (d) 5 × 5 with a HA film.
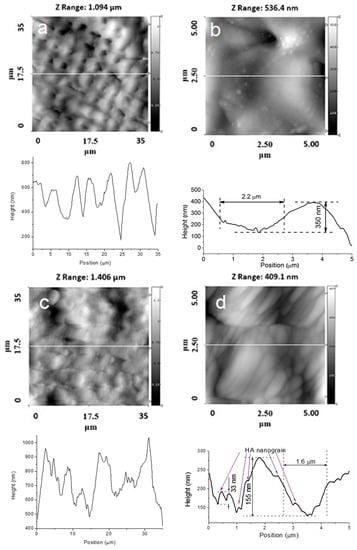
Figure 3.
AFM images of the topographies of Ti samples with a crossed periodicity of approximately 4.5 µm. (a) 35 × 35 ; (b) 5 × 5 without a HA film; (c) 35 × 35 ; and (d) 5 × 5 with a HA film.
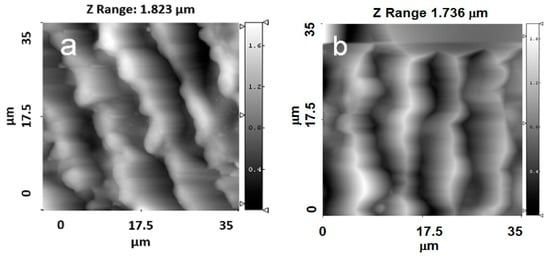
Figure 4.
AFM images of the topographies of Ti samples with parallel grooves with a periodicity of approximately 8.4 µm. (a) 35 × 35 ; (b) 35 × 35 with a HA film.
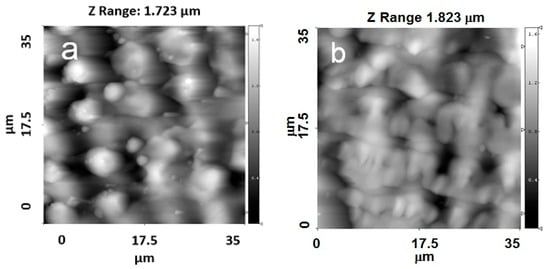
Figure 5.
AFM images of the topographies of Ti samples with crossed grooves with a periodicity of approximately 8.4 µm. (a) 35 × 35 ; (b) 35 × 35 with a HA film.
The surface topography on the microscale, sub-microscale, and nanoscale changed after the HA coating deposition, and this was observed in the AFM profile. Scans obtained for the 35 × 35 µm2 scan area showed that changes in the surface topography occurred after the HA coating deposition. During deposition, the film presumably fills the grooves of the Ti substrate. The AFM profile analysis of the HA-coated Ti shows a surface decorated with nanoscale grains (Figure 2d and Figure 3d). The average grain height was approximately 30 nm, which resulted in an increase in the nanoscale roughness of the surface. The most significant changes of the surface topography occurred in surface structured Ti with parallel grooves. For a 5 × 5 µm2 scan area, the HA coating resulted in significant shrinkage in the as-prepared grooves, and the structure of the grooves was modified (Figure 2b,d). As shown in Figure 2b, separate grooves with parallel periodicity can be characterized with a full width at half-maximum (FWHM) of ~2.2 µm and an average groove depth of ~500 nm. After the HA coating deposition, the FWHM decreased to ~1.8 µm and the average groove depth reduced to ~200 nm (Figure 2d).
Changes in the surface topography can be observed for the crossed patterns on the Ti surface. Moreover, after deposition of the HA coating, the cross-pattern topography could no longer be clearly observed, as the grooves were filled with the coating material. For the Ti samples with parallel grooves with a periodicity of 8.4 µm, a lower amount of the coating material filled the grooves (Figure 4a,b).
For the Ti samples with crossed grooves with a periodicity of approximately 8.4 µm, the changes in the surface topography were more pronounced than in the grooves with a periodicity of approximately 4.5 µm (Figure 5a,b). The crossed patterns on the Ti surface were still observed after the deposition process.
Topographical features on material surfaces are important to cell and tissue response to biomaterials [22,23,24]. Micro-rough surfaces may stimulate greater bone contact with the material by promoting the production of local osteogenic factors and the expression of differentiation markers. However, the role of nanometer roughness has not been clearly defined [22,23,24].
Previously published results showed that the topography of micro-rough Ti surfaces can significantly influence the attachment and growth of cells [22]. Multidirectional groove designs have been shown to contribute to improved MC3T3-E1 cell adhesion in different directions [24]. Larger microgrooves (greater than ~1 μm in depth) have been proposed to increase plaque uptake in dental applications.
Ulerich et al. investigated the effect of multiscale laser texturing of a Ti6Al4V substrate on the adhesion of osteoblasts [25]. The surface chemical composition can influence cell attachment and reaction to a metal by modifying the adsorption of proteins or by activating different cellular pathways of nearby cells [25]. Unique laser-induced structures can modify the morphology and local chemistry of the surface, which makes it more favourable for cells to grow in certain patterns or to grow at a particular density, depending on the features at various size scales [26].
3.2. Phase and Structure Characterization
The typical XRD patterns of HA-coated patterned Ti substrates with crossed grooves and periodicities of 4.5 µm and 8.4 µm are presented in Figure 6. Only the reflexes attributed to the HA coating are observed, which confirms that the HA film is crystalline and phase-pure. The preferential (002) crystallographic orientation is observed, which is typical for an rf magnetron sputter-deposited thin film [27]. Moreover, the crystallographic orientations of the deposited HA coating can be controlled to either (002) or (300) by modulating the deposition parameters, the thickness of the HA film, and the movement of the substrate during the deposition process [12]. The crystallite size and microstrain determined for the HA coating were 34 ± 1 nm and 0.06%, respectively. In the pattern, only the peaks attributed to the hexagonal α-Ti phase were identified. The lattice parameters of the Ti substrate were determined to be b = a = 2.9458 and c = 4.677 Å. The lattice parameters of the HA coating prepared on the Ti surface were determined as b = a = 9.4125 and c = 6.9167 Å. The crystallite size and microstrain evaluated for the Ti substrate were 42 ± 2 nm and 0.05%, respectively. No significant effect of the Ti surface, which was patterned by the DLIP technique, was observed on the phase composition of either the Ti substrates or the HA-coated structured Ti substrates. Thus, according to the XRD results, no surface TiOx (x < 2) layer was formed through surface processing by the DLIP technique. It has also been reported elsewhere that DLIP processing of the Ti surface does not result in the formation of an oxide layer [7,28]. This is the primary difference between surface processing of Ti by DLIP and conventional heat treatment of Ti in dry air, where Ti is oxidized [29].
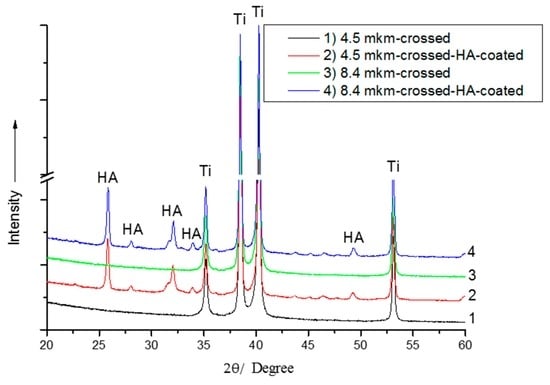
Figure 6.
A typical X-ray diffraction (XRD) pattern of HA-coated structured Ti with crossed grooves and a periodicity of 4.5 µm.
3.3. Wettability and Surface Free Energy
The evolution of the contact angle and water hysteresis for droplets on the laser-treated uncoated (■) and HA-coated (○) Ti surfaces is presented in Figure 7. The contact angle for the crossed grooves with a periodicity of approximately 8.4 µm is larger than that for the parallel grooves with a periodicity of approximately 8.4 µm for both the HA-coated and uncoated substrates.
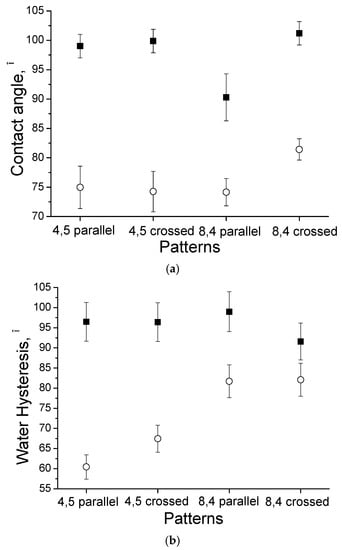
Figure 7.
The contact angle (a) and water hysteresis; (b) measurements for different patterns on the surface of Ti: ■—without HA film, and ○—with HA film.
The uncoated Ti surface with parallel grooves and a periodicity of approximately 4.5 µm resulted in a high static water CA of 99° ± 2°, which is indicative of surface hydrophobicity. The average water CA for the Ti substrate after the deposition of the HA film was measured as 75° ± 4°, which is associated with surface hydrophilicity. In Figure 6, the water CA hysteresis was determined to be 96.4° ± 1.9° and 67.4° ± 3.4° for the uncoated and HA-coated Ti surfaces, respectively.
The surface wettability of artificial materials is one of the most important factors that determines cell adhesion. Tamada et al. claimed that a surface with a water contact angle of 70° represents the most suitable surface for cell adhesion [30]. In our study, the water contact angle was close to 70° after the deposition of HA. Therefore, the coating can provide beneficial effects for cell adhesion compared with uncoated Ti surfaces. Surface nanotextures—which provide increased surface area and finer surface roughness—may result in improved mechanical interlocking between the tissue and implant [31].
The surface free energy σ calculations using the CA data indicated that HA-coated Ti surfaces with parallel grooves and a periodicity of approximately 8.4 µm had a significantly larger surface energy than uncoated Ti surfaces (Table 1). The surface free energy of the uncoated substrates was 28.04 mJ/. Compared with the uncoated Ti surface, HA-coated Ti showed a significantly increased polar component and a larger total surface free energy σ (37.73 mJ/) (Figure 8). The surface free energy is known to have an effect on cell attachment and spreading [32]. The study in [33] demonstrated a strong mutual dependence of cell adhesion and proliferation and platelet activity on the surface free energy of the tested implants, and this was particularly true for polar components. Ti substrates with a low polar component exhibited a very low adhesion shear strength, and the adhesion shear strength of the adhered fibroblasts increased as increased.

Table 1.
The surface wettability parameters of uncoated structured Ti and HА-coated structured Ti.
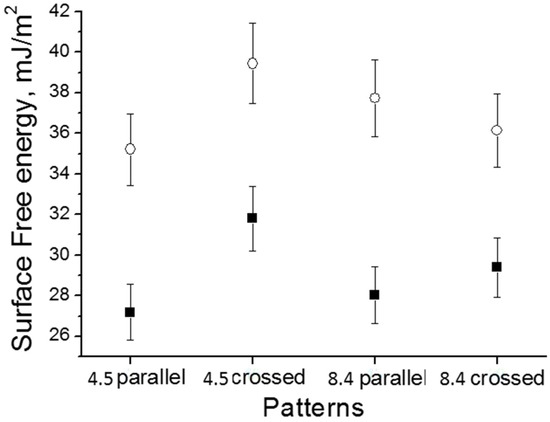
Figure 8.
The surface free energy measurements for different patterned Ti surfaces: ■—without a HA film, and ○—with a HA film.
The water hysteresis of the uncoated Ti surfaces was larger than that of the HA-coated Ti surfaces. After deposition of the HA coating, Ti surfaces with parallel grooves and a periodicity of approximately 4.5 µm had the lowest water hysteresis (60.40° ± 1.21°). The largest water hysteresis of HA-coated Ti surfaces with crossed grooves and a periodicity of approximately 8.4 µm was 82.09° ± 4.10°. Therefore, the water hysteresis for the hydrophilic surface was less than that for the more hydrophobic Ti surface. In other studies [34,35], it was determined that the magnitude of the hysteresis obtained for the films cast from hydrophobic solvents was less than that for hydrophilic solvents. In addition, the contact-angle hysteresis increased as the contact angle decreased; however, the opposite results were obtained here. The contact angle hysteresis was strongly influenced by the surface roughness and the surface heterogeneity.
The basic correlations between the surface roughness and contact angle hysteresis were originally defined by Wenzel, Cassie, and Baxter [36]. The Cassie–Baxter bridging state represents a non-wetting contact mode where water droplets can roll off easily due to the low contact angle hysteresis. The Wenzel state denotes a wetting contact mode where water droplets can be pinned on the surface to form a high contact angle hysteresis [36]. However, during the culturing time under the conditions used, a partial transition from a Cassie–Baxter state to a Wenzel state may occur [37,38]. In the Wenzel state, the liquid medium is in intimate contact with the solid aspirates, which increases the surface contact area for possible cell contact. In this context, it is worth mentioning a previous controversial discussion on the correlation between the wettability and the water repellence on a cell’s behaviour. Koc et al. presented data that identifies the negative influences of interfacial slip between the liquid and implant surface on protein adsorption [39]. This work indicated that protein adsorption onto superhydrophobic surfaces occurs, and depends on the penetration of the protein solution and available surface area for adsorption. For cells, the aspect of protein adsorption is of utmost importance. An additional related report has been presented by Mano [37], who reported that cells mainly adhered to some points of the aspirates at the surfaces, limiting adhesion and further proliferation.
However, contradictory reports exist regarding the influence of contact angle hysteresis on cell behaviour. As demonstrated in a study by Hsu et al. [40], cell migration on a suitable biomaterial surface may be associated with the ease with which the cell “glides” on the surface. A strong relationship between the sliding angle and cell migration rate was observed. As shown by Hsu and co-workers, a larger cell migration rate correlated with a smaller sliding angle of the substrate. Therefore, the assumption that cell migration could be correlated with the contact angle hysteresis appeared to be reasonable, although the low angle hysteresis describes the ease with which a water droplet rolls off or slides along the surface.
It is known that both surface topography and chemistry influence surface wettability [41]. The roughness parameters measured via AFM revealed that the different rf power levels resulted in changes in the surface roughness parameters (Figure 1). Using the following equation, r = 1 + Sdr/100 (Sdr—developed interfacial area ratio), it was possible to obtain the values of the roughness factor (r). The following Wenzel equation cosθm = rcosθy (θm—measured contact angle, θy—Young contact angle) was used to derive the values of the Young contact angles from the measured values of the contact angles. It is important to notice that the Wenzel equation is based on the assumption that the liquid penetrates into the roughness grooves (Table 2) [42,43]. By considering the calculated and measured values of the Young contact angles (which were very similar), it is possible to conclude that the change in the surface chemistry, which was linked to deposition of the HA coating, played a more significant role in the surface wettability change compared to the surface roughness.

Table 2.
Summary of the θm and θy calculated for a 35 × 35 scan area.
3.4. Antibacterial Properties
Additionally, HA coatings have been applied for many decades to enhance the biocompatibility of the surface of an osteointegrated implant [41,44]. Despite mostly successful procedures and the success of HA-coated implants, post-operative infection remains one of the most common and serious complications. Long-term antibacterial properties are desirable in a biomaterial to prevent implant-associated infections. The broad spectrum of antimicrobial effects associated with silver and its compounds against different microbes has been known for centuries [45,46]. This bactericidal activity is best represented by the release of silver ions in a cooperative oxidation process that requires both dissolved oxygen and protons [47,48], with an amount of evidence that silver nanoparticles themselves can damage microbial cell membranes [49,50]. Much less attention is paid on the literature to investigating the surface topography, wettability, or energy effect on biofilm formation or bacterial adhesion [41]. A balance between the effective antimicrobial activity, cytotoxicity, and mechanical stability of the coatings should be achieved.
Bacterial adhesion on surfaces with different surface free energies has been widely studied, and it has been confirmed that the surface free energy can significantly influence bacterial adhesion [18]. A relationship between bacterial adhesion and the surface free energy was reported, and a surface free energy between 23 and 30 mN·m−1 was related to the lowest bacterial adhesion [51]. This is consistent with other reported results. For example, a minimum Escherichia coli adhesion was reported for the surface free energy range between 21 and 29 mN·m−1 [18]. Boyd et al. found that enhanced adhesion of S. aureus occurred on rougher stainless steel compared to smooth surfaces. Surfaces with features on the same scale as the S. aureus cells (1 µm) appeared to promote the strongest attachment, due to maximal cell–substrate contact area [52,53]. Whitehead et al. also observed similar trends for bacterial species of different sizes [54]. On the other hand, bacteria have been found to colonize smooth surfaces, such as electropolished stainless steel [55].
It is reported that superhydrophobic surfaces promote the reduction of bacterial adhesion [18]. The presented results revealed that all of the investigated microtopographies provoked a significant reduction (30%–45%) in bacterial adhesion relative to the smooth control samples, regardless of the surface hydrophobicity/hydrophilicity [56]. Cell (Escherichia coli) cluster formation per unit area on 5 μm wide line patterns was reduced by 14-fold compared to flat poly(dimethylsiloxane) [57]. When the surface chemistry was the same, the nanorough surface had higher surface energy than the smooth surface of Ti and showed lower bacterial colonization [58].
Thus, macroscopic grooves fabricated on the surface of Ti substrates using the DLIP technique can provide a preferential site for the deposition of bacteria within the valleys, while the microscopic and nanoroughness of the valleys coated with nanostructured HA coating will determine the actual interaction between the surface and bacteria, which should prevent undesired bacterial adhesion in the developed patterned substrates.
4. Conclusions
In this study, investigations of the surface microstructure of Ti surfaces produced by the DLIP technique were performed. To generate multiscale structures on microscale Ti surfaces, rf magnetron sputter deposition of ultrathin nanostructured HA films was used to form an additional nanoscale grain morphology. The three-dimensional roughness parameters Sa and Sq tended to decrease after deposition of the HA coating. The grain-like morphology of the surface with an average grain size from 0.36 to 0.73 µm for a 5 × 5 scan area was described. Uncoated Ti surfaces with parallel grooves and a periodicity of 4.5 µm resulted in a static water contact angle of 99° ± 2°, which confirmed the hydrophobic nature of the surface. An average value of the water contact angle for the Ti substrate after the fabrication of the HA film was measured as 75° ± 4°, demonstrating the hydrophilic nature of the surface. In this study, a moderately hydrophilic surface with a contact angle close to 70° was obtained for HA-coated substrates. A significant increase in the polar component and total surface free energy σ (37.73 mJ/) for the HA-coated Ti surface compared to the uncoated Ti surface (28.04 mJ/) was demonstrated. Therefore, the significance of the obtained results is that different topographical surface features and different surface chemical compositions can be obtained, which can significantly affect cell attachment, proliferation, and differentiation by changing the way that proteins adsorb or by activating different cellular pathways of nearby cells.
Acknowledgments
The authors are thankful to Christian Oehr (Fraunhofer IGB, Stuttgart, Germany) and Maxim Syrtanov (Tomsk Polytechnic University, Tomsk, Russia) for their assistance with the sample characterizations. This research was supported by the Federal Target Program #14.587.21.0013 (a unique application number 2015-14-588-0002-5599), the Russian President’s grants MK-7907.2016.8, MK-6459.2016.8 and the State order NAUKA #11.1359.2014/K.
Author Contributions
Roman Surmenev and Maria Surmeneva conceived and designed the experiments; Roman Surmenev and Michael Hans performed the experiments; Polina Nikityuk and Maria Surmeneva analyzed the data; Roman Surmenev and Maria Surmeneva contributed reagents/materials/analysis tools; Roman Surmenev and Maria Surmeneva wrote the paper.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Holzapfel, B.M.; Reichert, J.C.; Schantz, J.T.; Gbureck, U.; Rackwitz, L.; Nöth, U.; Jakob, F.; Rudert, M.; Groll, J.; Hutmacher, D.W. How smart do biomaterials need to be? A translational science and clinical point of view. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2013, 65, 581–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Majeed, A.; He, J.; Jiao, L.; Zhong, X.; Sheng, Z. Surface properties and biocompatibility of nanostructured TiO2 film deposited by RF magnetron sputtering. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2015, 10, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geetha, M.; Singh, A.K.; Asokamani, R.; Gogia, A.K. Ti based biomaterials, the ultimate choice for orthopaedic implants—A review. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2009, 54, 397–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franz, S.; Rammelt, S.; Scharnweber, D.; Simon, J.C. Immune responses to implants—A review of the implications for the design of immunomodulatory biomaterials. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 6692–6709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, D.F. On the mechanisms of biocompatibility. Biomaterials 2008, 29, 2941–2953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hans, M.; Müller, F.; Grandthyll, S.; Hüfner, S.; Mücklich, F. Anisotropic wetting of copper alloys induced by one-step laser micro-patterning. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2012, 263, 416–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hans, M.; Gachot, C.; Müller, F.; Mücklich, F. Direct laser interference structuring as a tool to gradually tune the wetting response of titanium and polyimide surfaces. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2009, 11, 795–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mücklich, F.; Lasagni, A.; Daniel, C. Laser interference metallurgy: Using interference as a tool for micro/nano structuring. Int. J. Mater. Res. 2006, 97, 1337–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorozhkin, S.V.; Epple, M. Biological and medical significance of calcium phosphates. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2002, 41, 3130–3146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surmeneva, M.A.; Surmenev, R.A.; Pichugin, V.F.; Koval, N.N.; Teresov, A.D.; Ivanova, A.A.; Grubova, I.Yu.; Ignatov, V.P.; Prymak, O.; Epple, M. Adhesion properties of a silicon-containing calcium phosphate coating deposited by RF magnetron sputtering on a heated substrate. J. Surf. Investig. X-ray Synchrotron Neutron Tech. 2013, 7, 944–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surmeneva, M.A.; Mukhametkaliyev, T.M.; Tyurin, A.I.; Teresov, A.D.; Koval, N.N.; Pirozhkova, T.S.; Shuvarin, I.A.; Shuklinov, A.V.; Zhigachev, A.O.; Oehr, C.; et al. Effect of silicate doping on the structure and mechanical properties of thin nanostructured RF magnetron sputter-deposited hydroxyapatite films. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2015, 275, 176–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanova, A.A.; Surmeneva, M.A.; Surmenev, R.A.; Depla, D. Influence of deposition conditions on the composition, texture and microstructure of RF-magnetron sputter-deposited hydroxyapatite thin films. Thin Solid Films 2015, 591, 368–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanova, A.A.; Surmeneva, M.A.; Tyurin, A.I.; Pirozhkova, T.S.; Shuvarin, I.A.; Prymak, O.; Epple, M.; Chaikina, M.V.; Surmenev, R.A. Fabrication and physico-mechanical properties of thin magnetron sputter deposited silver-containing hydroxyapatite films. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 360, 929–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shadanbaz, S.; Dias, G.J. Calcium phosphate coatings on magnesium alloys for biomedical applications: A review. Acta Biomater. 2012, 8, 20–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Surmeneva, M.A.; Kluger, P.J.; Schönhaar, V.; Müller, M.; Hein, S.B.; Wittmar, A.; Ulbricht, M.; Prymak, O.; Oehr, C.; Surmenev, R.A. Nano-hydroxyapatite-coated metal-ceramic composite of iron-tricalcium phosphate: Improving the surface wettability, adhesion and proliferation of mesenchymal stem cells in vitro. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2015, 135, 386–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Surmenev, R.A.; Surmeneva, M.A.; Evdokimov, K.E.; Pichugin, V.F.; Peitsch, T.; Epple, M. The influence of the deposition parameters on the properties of an rf-magnetron-deposited nanostructured calcium phosphate coating and a possible growth mechanism. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2011, 205, 3600–3606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surmeneva, M.A.; Chaikina, M.V.; Zaikovskiy, V.I.; Pichugin, V.F.; Buck, V.; Prymak, O.; Epple, M.; Surmenev, R.A. The structure of an RF-magnetron sputter-deposited silicate-containing hydroxyapatite-based coating investigated by high-resolution techniques. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2013, 218, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, L.; Levänen, E. Superhydrophobic surfaces for the reduction of bacterial adhesion. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 12003–12020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Extrand, C.W.; Kumagai, Y. An experimental study of contact angle hysteresis. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1997, 191, 378–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Surmeneva, M.A.; Surmenev, R.A. Microstructure characterization and corrosion behaviour of a nano-hydroxyapatite coating deposited on AZ31 magnesium alloy using radio frequency magnetron sputtering. Vacuum 2015, 117, 60–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grubova, I.Y.; Surmeneva, M.A.; Ivanova, A.A.; Kravchuk, K.; Prymak, O.; Epple, M.; Buck, V.; Surmenev, R.A. The effect of patterned titanium substrates on the properties of silver-doped hydroxyapatite coatings. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2015, 276, 595–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padial-Molina, M.; Galindo-Moreno, P.; Fernández-Barbero, J.E.; O’Valle, F.; Jódar-Reyes, A.B.; Ortega-Vinuesa, J.L.; Ramón-Torregrosa, P.J. Role of wettability and nanoroughness on interactions between osteoblast and modified silicon surfaces. Acta Biomater. 2011, 7, 771–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wennerberg, A.; Albrektsson, T. Effects of titanium surface topography on bone integration: A systematic review. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2009, 20, 172–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Guehennec, L.; Lopez-Heredia, M.A.; Enkel, B.; Weiss, P.; Amouriq, Y.; Layrolle, P. Osteoblastic cell behaviour on different titanium implant surfaces. Acta Biomater. 2008, 4, 535–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ulerich, J.P.; Ionescu, L.C.; Chen, J.; Soboyejo, W.O.; Arnold, C.B. Modifications of Ti-6Al-4V surfaces by direct-write laser machining of linear grooves. Photon Processing in Microelectronics and Photonics VI. Proc. SPIE 2007, 6458, 645819. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, M.S.; Arnold, C.B. Fundamentals of laser-material interaction and application to multiscale surface modification. In Laser Precision Microfabrication; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2010; Volume 135, p. 91. [Google Scholar]
- Surmeneva, M.A.; Surmenev, R.A.; Nikonova, Y.A.; Selezneva, I.I.; Ivanova, A.A.; Putlyaev, V.I.; Prymak, O.; Epple, M. Fabrication, ultra-structure characterization and in vitro studies of RF magnetron sputter deposited nano-hydroxyapatite thin films for biomedical applications. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2014, 317, 172–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenkranz, A.; Hans, M.; Gachot, C.; Thome, A.; Bonk, S.; Mücklich, F. Direct laser interference patterning: Tailoring of contact area for frictional and antibacterial properties. Lubricants 2016, 4, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gemelli, E.; Camargo, N.H.A. Oxidation kinetics of commercially pure titanium. Matér. (Rio Jan.) 2007, 12, 525–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamada, Y.; Ikada, Y. Effect of preadsorbed proteins on cell adhesion to polymer surfaces. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1993, 155, 334–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meirelles, L.; Albrektsson, T.; Kjellin, P.; Arvidsson, A.; Franke-Stenport, V.; Andersson, M.; Currie, F.; Wennerberg, A. Bone reaction to nano hydroxyapatite modified titanium implants placed in a gap-healing model. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2008, 87, 624–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eliaz, N.; Shmueli, S.; Shur, I.; Benayahu, D.; Aronov, D.; Rosenman, G. The effect of surface treatment on the surface texture and contact angle of electrochemically deposited hydroxyapatite coating and on its interaction with bone-forming cells. Acta Biomater. 2009, 5, 3178–3191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pešáková, V.; Kubies, D.; Hulejová, H.; Himmlová, L. The influence of implant surface properties on cell adhesion and proliferation. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2007, 18, 465–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, Y.-H.; Yang, J.-T.; Shieh, D.-B. A microchip fabricated with a vapor-diffusion self-assembled-monolayer method to transport droplets across superhydrophobic to hydrophilic surfaces. Lab Chip 2010, 10, 499–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Z.G.; Black, R.A.; Curran, J.M.; Hunt, J.A.; Rhodes, N.P.; Williams, D.F. Surface properties and biocompatibility of solvent-cast poly [ε-caprolactone] films. Biomaterials 2004, 25, 4741–4748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, L.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Y.; Qiang, X. Superhydrophobic alumina surface with high adhesive force and long-term stability. Colloids Surfaces A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2012, 410, 66–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, S.M.; Song, W.; Alves, N.M.; Mano, J.F. Chemical modification of bioinspired superhydrophobic polystyrene surfaces to control cell attachment/proliferation. Soft Matter 2011, 7, 8932–8941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenzel, R.N. Resistance of solid surfaces to wetting by water. Ind. Eng. Chem. 1936, 28, 988–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koc, Y.; Mello, A.J.; McHale, G.; Newton, M.I.; Roach, P.; Shirtcliffe, N.J. Nano-scale superhydrophobicity: Suppression of protein adsorption and promotion of flow-induced detachment. Lab Chip 2008, 8, 582–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, S.H.; Tang, C.M.; Chiu, J.J.; Liao, T.C.; Lin, C.C.; Iwata, H. Cell migration rate on poly(ε-caprolactone)/poly(ethylene glycol) diblock copolymers and correlation with the material sliding angle. Macromol. Biosci. 2007, 7, 482–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Surmenev, R.A.; Surmeneva, M.A.; Ivanova, A.A. Significance of calcium phosphate coatings for the enhancement of new bone osteogenesis—A review. Acta Biomater. 2014, 10, 557–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marmur, A.; Bittoun, E. When Wenzel and Cassie are right: Reconciling local and global considerations. Langmuir 2009, 25, 1277–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandez, L.; Sanchez, M.; Carmona, F.J.; Palacio, L.; Calvo, J.I.; Hernandez, A.; Pradanos, P. Analysis of the grafting process of PVP on a silicon surface by AFM and contact angle. Langmuir 2011, 27, 11636–11649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Surmenev, R.A. A review of plasma-assisted methods for calcium phosphate-based coatings fabrication. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2012, 206, 2035–2056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimazaki, T.; Miyamoto, H.; Ando, Y.; Noda, I.; Yonekura, Y.; Kawano, S.; Miyazaki, M.; Mawatari, M.; Hotokebuchi, T. In vivo antibacterial and silver-releasing properties of novel thermal sprayed silver-containing hydroxyapatite coating. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2010, 92, 386–389. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ando, Y.; Miyamoto, H.; Noda, I.; Sakurai, N.; Akiyama, T.; Yonekurac, Y.; Shimazakic, T.; Miyazakic, M.; Mawataric, M.; Hotokebuchic, T. Calcium phosphate coating silver shows high antibacterial activity and low cytotoxicity and inhibit bacterial adhesion. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2010, 30, 175–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kittler, S.; Greulich, C.; Diendorf, J.; Koeller, M.; Epple, M. Toxicity of silver nanoparticles increases during storage because of slow dissolution under release of silver ions. Chem. Mater. 2010, 22, 4548–4554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greulich, C.; Diendorf, J.; Simon, T.; Eggeler, G.; Epple, M.; Koeller, M. Uptake and intracellular distribution of silver nanoparticles in human mesenchymal stem cells. Acta Biomater. 2011, 7, 347–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sondi, I.; Salopek-Sondi, B. Silver nanoparticles as antimicrobial agent: A case study on E. coli as a model for Gram-negative bacteria. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2004, 275, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.-R.; Xie, X.-B.; Shi, Q.-S.; Zeng, H.-Y.; OU-Yang, Y.-S.; Chen, Y.-B. Antibacterial activity and mechanism of silver nanoparticles on Escherichia coli. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2010, 85, 1115–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Q.; Wang, S.; Mueller-Steinhagen, H. Tailored surface free energy of membrane diffusers to minimize microbial adhesion. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2004, 230, 371–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyd, R.D.; Verran, J.; Jones, M.V.; Bhakoo, M. Use of the atomic force microscope to determine the effect of substratum surface topography on bacterial adhesion. Langmuir 2002, 18, 2343–2346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, L.C.; Fang, J.; Borca-Tasciuc, D.A.; Worobo, R.W.; Morarua, C.I. Effect of micro- and nanoscale topography on the adhesion of bacterial cells to solid surfaces. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 79, 2703–2712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whitehead, K.A.; Colligon, J.; Verran, J. Retention of microbial cells in substratum surface features of micrometer and sub-micrometer dimensions. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2005, 41, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woodling, S.E.; Moraru, C.I. Influence of surface topography on the effectiveness of pulsed light treatment for the inactivation of Listeria innocua on stainless-steel surfaces. J. Food Sci. 2005, 70, m345–m351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perera-Costa, D.; Morales Bruque, J.; Luisa González-Martín, M.; Cándido Gómez-García, A.; Vadillo-Rodríguez, V. Studying the influence of surface topography on bacterial adhesion using spatially organized microtopographic surface patterns. Langmuir 2014, 30, 4633–4641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, H.; Chen, A.; Song, X.; Brasch, M.E.; Henderson, J.H.; Ren, D. How Escherichia coli lands and forms cell clusters on a surface: A new role of surface topography. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 29516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puckett, S.D.; Taylor, E.; Raimondo, T.; Webster, T.J. The relationship between the nanostructure of titanium surfaces and bacterial attachment. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 706–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).