Microscopic Characterization of Individual Submicron Bubbles during the Layer-by-Layer Deposition: Towards Creating Smart Agents
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Materials
2.2. Experimental Setup
2.3. Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Evaluating Hydrodynamic Diamters of Bare SBs

3.2. pH Effects on Bare SBs and M-SBs
| Salt conditions | pH | Zeta potential (mV) |
|---|---|---|
| HCl (0.1 mM) | 4.1 | +14 |
| Buffer (1 mM) | 7.1 | −38 |
| Salt free | 7.1 | −40 |
| NaOH (0.1 mM) | 10.4 | −50 |

3.3. Comparison of the Charge-Reversal Phenomena Due to the Mono-and Double-Layer Depositions
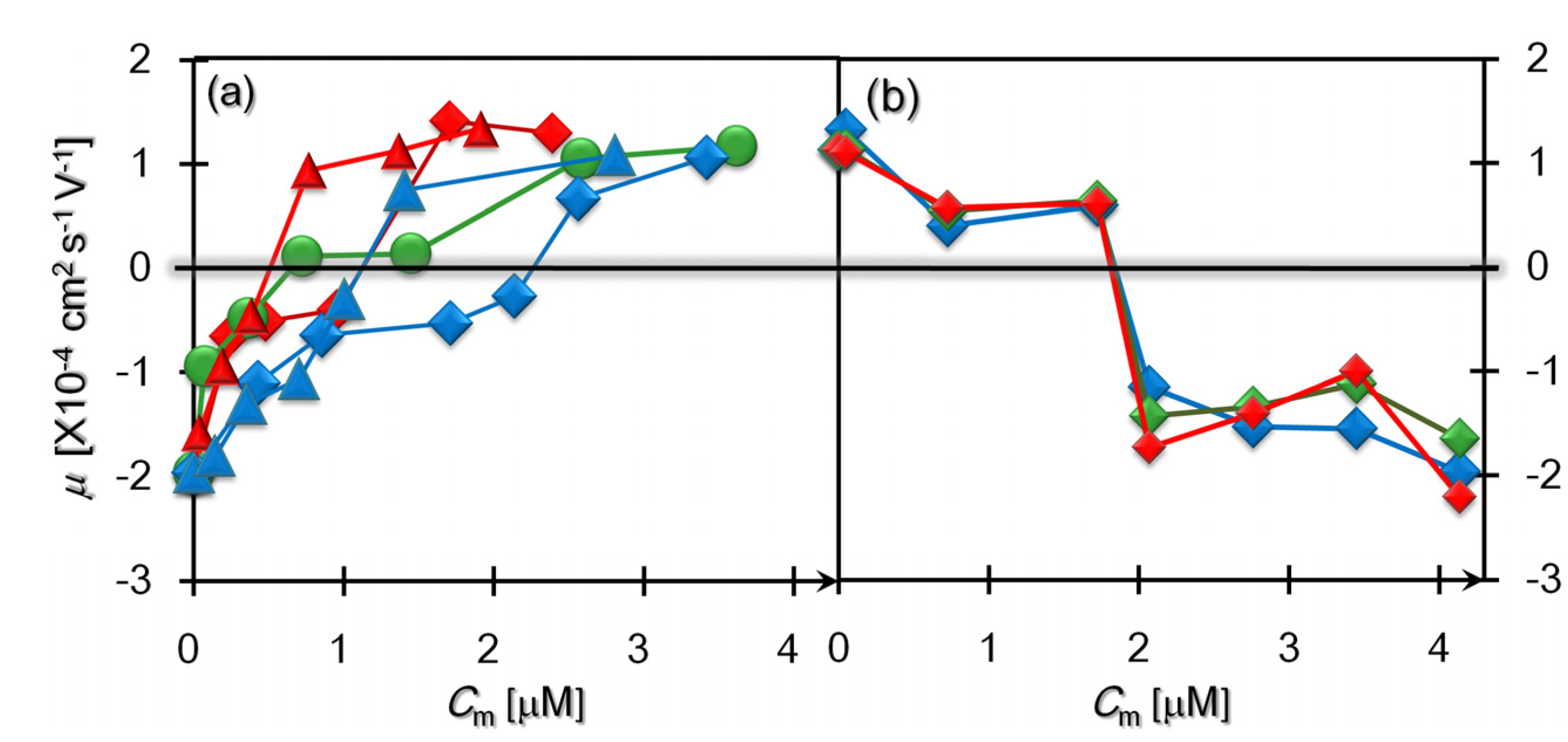
| Polycations | Ccm (μM) | Charge ratio α (×104) |
|---|---|---|
| pDADMAC | 0.4–0.7 | 6–12 |
| L-PLL | 1.0–1.7 | 16–28 |
| S-PLL | 0.4–0.8 | 6–13 |
| L-PAH | 2.1–2.6 | 35–42 |
| S-PAH | 1.0–1.4 | 16–23 |
3.4. Particle Size Distributions with Polyelectrolytes Added
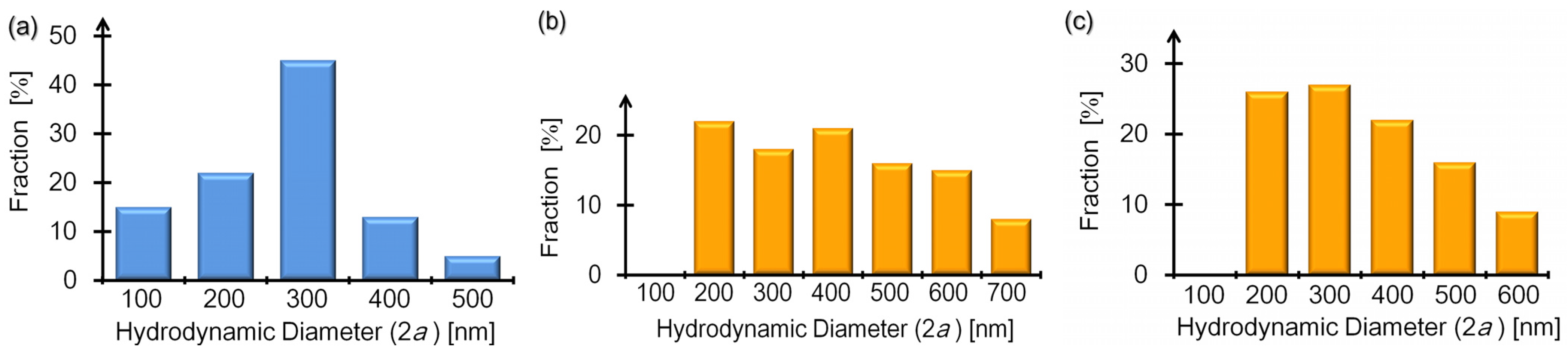
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tsuge, H. Micro-and Nanobubbles: Fundamentals and Applications; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Stride, E.; Edirisinghe, M. Novel microbubble preparation technologies. Soft Matter 2008, 4, 2350–2359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirsi, S.R.; Borden, M.A. Microbubble compositions, properties and biomedical applications. Bubble Sci. Eng. Technol. 2009, 1, 3–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borden, M. Nanostructural features on stable microbubbles. Soft Matter 2009, 5, 716–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dressaire, E.; Bee, R.; Bell, D.C.; Lips, A.; Stone, H.A. Interfacial polygonal nanopatterning of stable microbubbles. Science 2008, 320, 1198–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lentacker, I.; De Smedt, S.C.; Sanders, N.N. Drug loaded microbubble design for ultrasound triggered delivery. Soft Matter 2009, 5, 2161–2170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duncan, P.B.; Needham, D. Test of the Epstein-Plesset model for gas microparticle dissolution in aqueous media: Effect of surface tension and gas undersaturation in solution. Langmuir 2004, 20, 2567–2578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, H.; Morita, A. A molecular dynamics study on inner pressure of microbubbles in liquid argon and water. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2013, 573, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shchukin, D.G.; Köhler, K.; Möhwald, H.; Sukhorukov, G.B. Gas-filled polyelectrolyte capsules. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2005, 44, 3310–3314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winterhalter, M.; Sonnen, A.F.P. Stable air bubbles—catch them if you can! Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2006, 45, 2500–2502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lentacker, I.; De Geest, B.G.; Vandenbroucke, R.E.; Peeters, L.; Demeester, J.; De Smedt, S.C.; Sanders, N.N. Ultrasound-responsive polymer-coated microbubbles that bind and protect DNA. Langmuir 2006, 22, 7273–7278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Borden, M.A.; Caskey, C.F.; Little, E.; Gillies, R.J.; Ferrara, K.W. DNA and polylysine adsorption and multilayer construction onto cationic lipid-coated microbubbles. Langmuir 2007, 23, 9401–9408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossi, S.; Waton, G.; Krafft, M.P. Small phospholipid-coated gas bubbles can last longer than larger ones. Chem. Phys. Chem. 2007, 9, 1982–1985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lentacker, I.; De Smedt, S.C.; Demeester, J.; Van Marck, V.; Bracke, M.; Sanders, N.N. Lipoplex-loaded microbubbles for gene delivery: A Trojan horse controlled by ultrasound. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2008, 17, 1910–1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Park, J.I.; Tumarkin, E.; Kumacheva, E. Small, stable, and monodispersed bubbles encapsulated with biopolymers. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2010, 31, 222–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.I.; Jagadeesan, D.; Williams, R.; Oakden, W.; Chung, S.; Stanisz, G.J.; Kumacheva, E. Microbubbles loaded with nanoparticles: A route to multiple imaging modalities. ACS Nano 2010, 4, 6579–6586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daiguji, H.; Matsuoka, E.; Muto, S. Fabrication of hollow poly-allylamine hydrochloride/poly-sodium styrene sulfonate microcapsules from microbubble templates. Soft Matter 2010, 6, 1892–1897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornejo, J.J.M.; Matsuoka, E.; Daiguji, H. Size control of hollow poly-allylamine hydrochloride/poly-sodium styrene sulfonate microcapsules using the bubble template method. Soft Matter 2011, 7, 1897–1902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Nakajima, M.; Liu, Z; Shiina, T. Biosurfactants for microbubble preparation and application. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2011, 12, 462–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakatsuka, M.A.; Mattrey, R.F.; Esener, S.C.; Cha, J.N.; Goodwin, A.P. Aptamer-crosslinked microbubbles: Smart contrast agents for thrombin-activated ultrasound imaging. Adv. Mater. 2012, 24, 6010–6016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yap, R.K.; Whittaker, M.; Diao, M.; Stuetz, R.M.; Jefferson, B.; Bulmuş, V.; Peirson, W.L.; Nguyen, A.V.; Henderson, R.K. Hydrophobically-associating cationic polymers as micro-bubble surface modifiers in dissolved air flotation for cyanobacteria cell separation. Water Res. 2014, 61, 253–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kovalenko, A.; Polavarapu, P.; Pourroy, G.; Waton, G.; Krafft, M.P. pH-controlled microbubble shell formation and stabilisation. Langmuir 2014, 30, 6339–6347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahalingam, S.; Raimi-Abraham, B.T.; Craig, D.Q.; Edirisinghe, M. Formation of protein and protein–gold nanoparticle stabilized microbubbles by pressurized gyration. Langmuir 2014, 31, 659–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohgaki, K.; Khanh, N.Q.; Joden, Y.; Tsuji, A.; Nakagawa, T. Physicochemical approach to nanobubble solutions. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2010, 65, 1296–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ushikubo, F.Y.; Furukawa, T.; Nakagawa, R.; Enari, M.; Makino, Y.; Kawagoe, Y.; Shiina, T.; Oshita, S. Evidence of the existence and the stability of nano-bubbles in water. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2010, 361, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frusawa, H.; Inoue, M. When microbubble-polyelectrolyte complexes overcharge: A comparative study using electrophoresis. Chem. Lett. 2011, 40, 372–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frusawa, H.; Yoshida, R. A non-stoichiometric universality in microbubble-polyelectrolyte complexation. J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 2012, 81, SA008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Kawagoe, Y.; Makino, Y.; Oshita, S. Effects of nanobubbles on the physicochemical properties of water: The basis for peculiar properties of water containing nanobubbles. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2013, 93, 250–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Nesset, K.; Masliyah, J.; Xu, Z. Generation and characterization of submicron size bubbles. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2012, 179, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weijs, J.H.; Seddon, J.R.T.; Lohse, D. Diffusive shielding stabilizes bulk nanobubble clusters. ChemPhysChem 2012, 13, 2197–2204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uchida, T.; Oshita, S.; Ohmori, M.; Tsuno, T.; Soejima, K.; Shinozaki, S.; Take, Y.; Mitsuda, K. Transmission electron microscopic observations of nanobubbles and their capture of impurities in wastewater. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2011, 6, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agarwal, A.; Ng, W.J.; Liu, Y. Principle and applications of microbubble and nanobubble technology for water treatment. Chemosphere 2011, 84, 1175–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, Y.; Powell, R.L.; Longo, M.L. Interfacial and stability study of microbubbles coated with a monostearin/monopalmitin-rich food emulsifier and PEG40 stearate. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2008, 321, 186–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikeura, H.; Hamasaki, S.; Tamaki, M. Effects of ozone microbubble treatment on removal of residual pesticides and quality of persimmon leaves. Food Chem. 2013, 138, 366–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newman, C.M.H.; Bettinger, T. Gene therapy progress and prospects: Ultrasound for gene transfer. Gene Ther. 2007, 14, 465–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernot, S.; Klibanov, A.L. Microbubbles in ultrasound-triggered drug and gene delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2008, 60, 1153–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavalieri, F.; Finelli, I.; Tortora, M.; Mozetic, P.; Chiessi, E.; Polizio, F.; Brismar, T.B.; Paradossi, G. Polymer microbubbles as diagnostic and therapeutic gas delivery device. Chem. Mater. 2008, 20, 3254–3258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tinkov, S.; Bekeredjian, R.; Winter, G.; Coester, C. Microbubbles as ultrasound triggered drug carriers. J. Pharm. Sci. 2009, 98, 1935–1961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, T.; Wang, P.; Li, J.; Zheng, R.; Zheng, B.; Cheng, D.; Li, R.; Lai, J.; Shuai, X. Ultrasound-sensitive siRNA-loaded nanobubbles formed by hetero-assembly of polymeric micelles and liposomes and their therapeutic effect in gliomas. Biomaterials 2013, 34, 4532–4543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, T.; Wang, P.; Zheng, R.; Zheng, B.; Cheng, D.; Zhang, X.; Shuai, X. Nanobubbles for enhanced ultrasound imaging of tumors. Int. J. Nanomed. 2012, 7, 895. [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki, R.; Takizawa, T.; Negishi, Y.; Utoguchi, N.; Maruyama, K. Effective gene delivery with novel liposomal bubbles and ultrasonic destruction technology. Int. J. Pharm. 2008, 354, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brotchie, A.; Zhang, X.H. Response of interfacial nanobubbles to ultrasound irradiation. Soft Matter 2011, 7, 265–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavalli, R.; Bisazza, A.; Lembo, D. Micro-and nanobubbles: A versatile non-viral platform for gene delivery. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 456, 437–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kleimann, J.; Gehin-Delval, C.; Auweter, H.; Borkovec, M. Super-stoichiometric charge neutralization in particle-polyelectrolyte systems. Langmuir 2005, 21, 3688–3698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, M. ζ potential of microbubbles in aqueous solutions: Electrical properties of the gas-water interface. J. Phys. Chem. B 2005, 109, 21858–21864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira, C.; Rubio, J. Zeta potential of single and polymer-coated microbubbles using an adapted microelectrophoresis technique. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2011, 98, 118–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, J.; Priel, Z.; Rabin, Y. Viscosity of dilute polyelectrolyte solutions. J. Chem. Phys. 1988, 88, 7111–7116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palberg, T.; Versmold, H. Electrophoretic-electroosmotic light scattering. J. Phys. Chem. 1989, 93, 5296–5301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohshima, H.; Furusawa, K. Electrical Phenomena at Interfaces: Fundamentals: Measurements, and Applications; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1998; Volume 76. [Google Scholar]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kato, R.; Frusawa, H. Microscopic Characterization of Individual Submicron Bubbles during the Layer-by-Layer Deposition: Towards Creating Smart Agents. Materials 2015, 8, 4176-4190. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma8074176
Kato R, Frusawa H. Microscopic Characterization of Individual Submicron Bubbles during the Layer-by-Layer Deposition: Towards Creating Smart Agents. Materials. 2015; 8(7):4176-4190. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma8074176
Chicago/Turabian StyleKato, Riku, and Hiroshi Frusawa. 2015. "Microscopic Characterization of Individual Submicron Bubbles during the Layer-by-Layer Deposition: Towards Creating Smart Agents" Materials 8, no. 7: 4176-4190. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma8074176





