Hydrogel–Flexible Electronics Integrated Platforms for Diabetic Wound Management
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Challenges in Diabetic Wound Healing
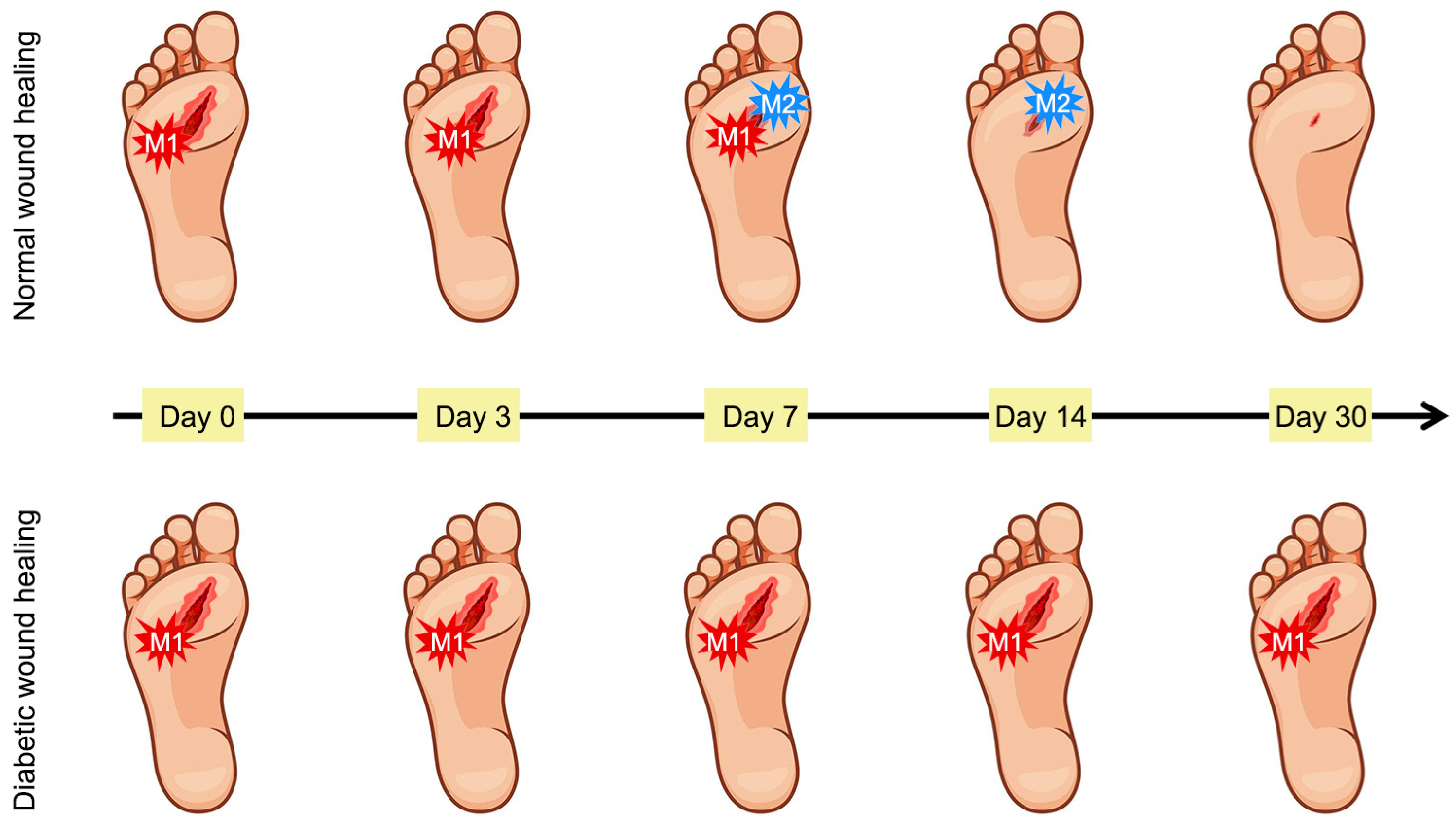
2.1. Normal Wound Healing Process
2.2. Wound Healing Process in Diabetes
2.2.1. Hyperglycemia
2.2.2. Accumulation of Reactive Oxygen Species
2.2.3. Inflammatory Infiltration
2.2.4. Bacterial Infection
3. Hydrogel-Based Diabetic Wound Therapy
3.1. Angiogenesis-Promoting Hydrogel Wound Dressings
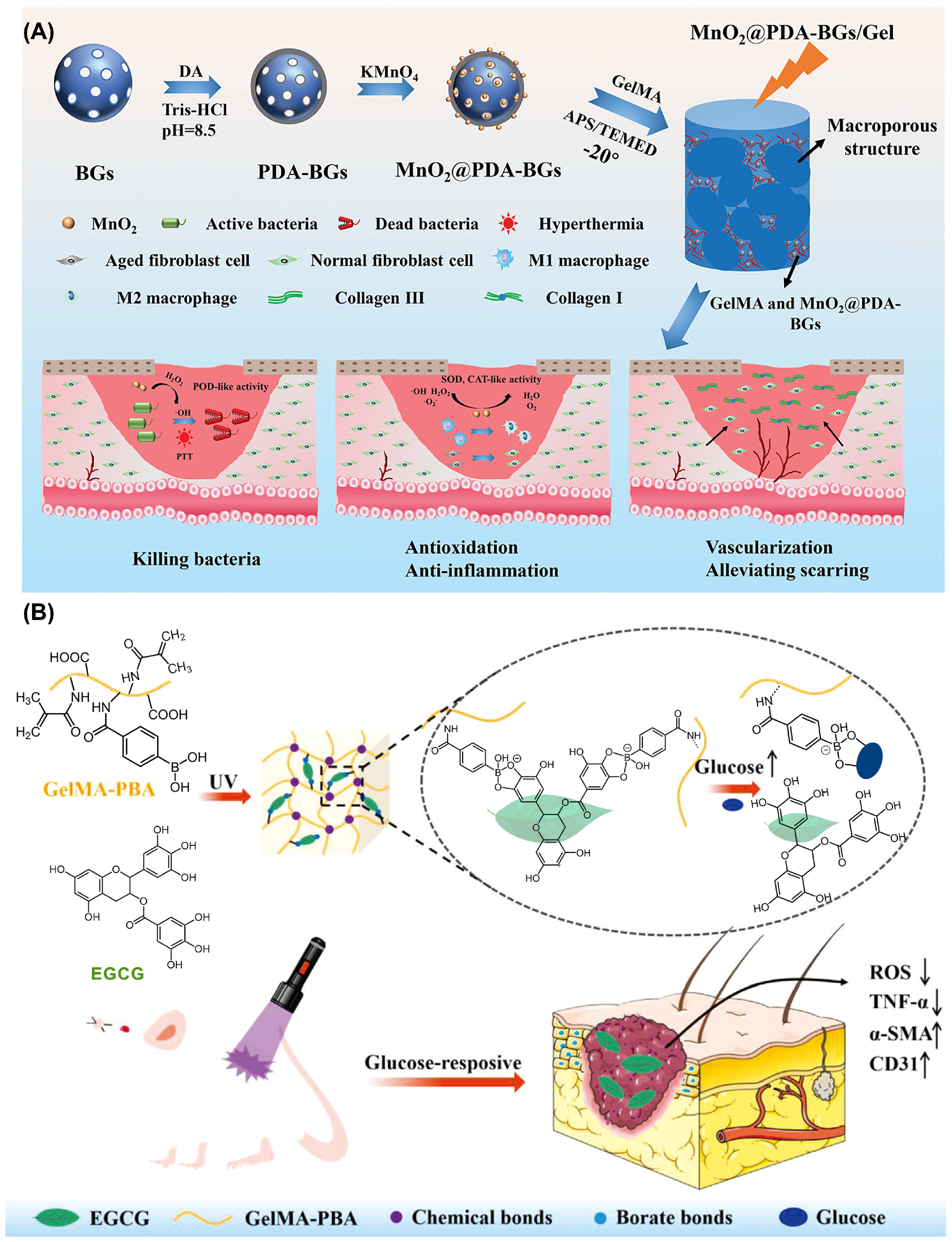
3.2. Antioxidant Hydrogel Wound Dressings
3.3. Anti-Inflammatory Hydrogel Wound Dressings
3.4. Antibacterial Hydrogel Wound Dressings
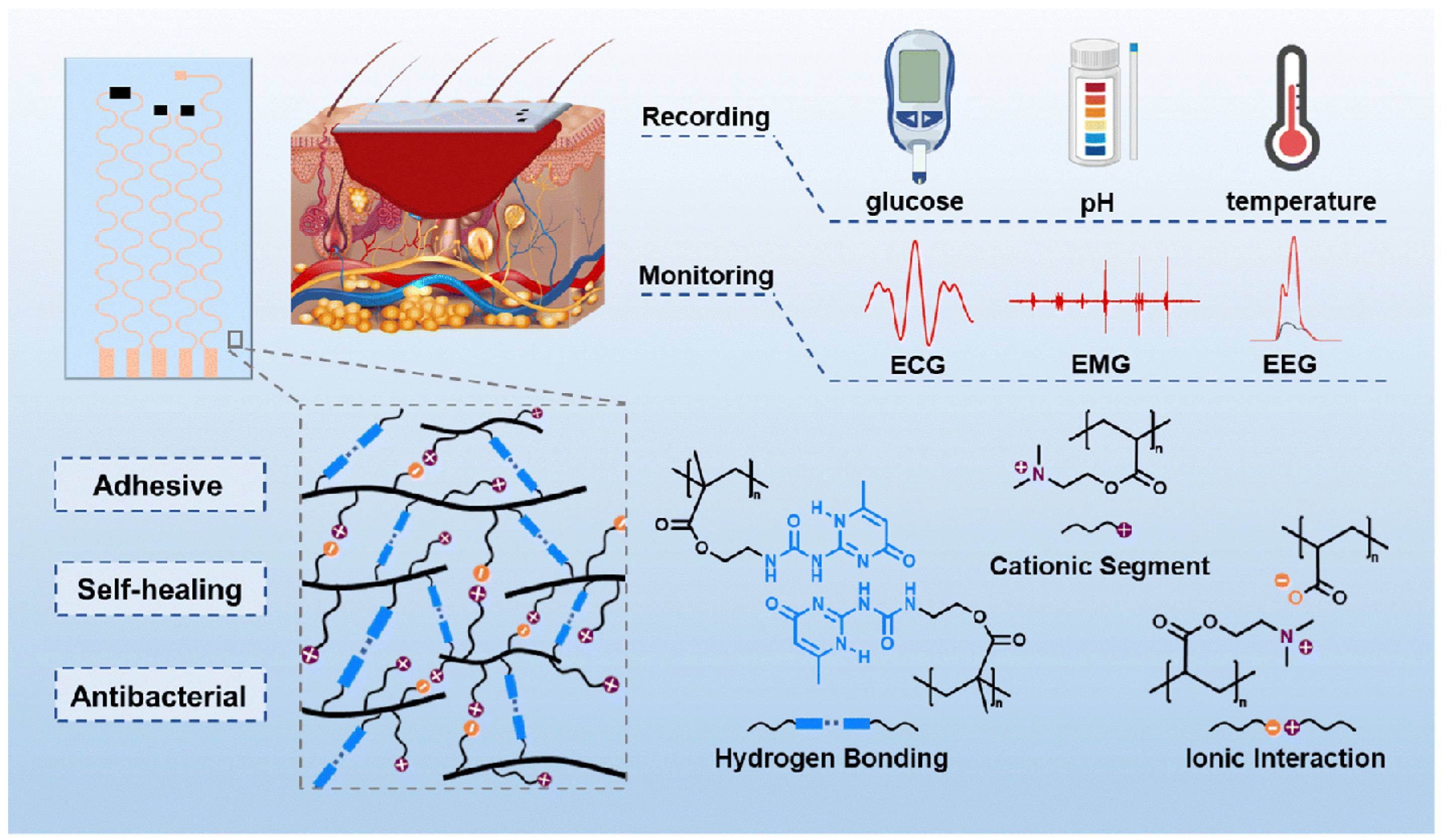
3.5. Conductive Hydrogel Wound Dressings
4. Flexible Electronic Devices
4.1. Overview of Flexible Electronic Devices
4.2. Flexible Electronic Devices for Diabetic Wound Monitoring
4.3. Flexible Electronic Devices for Diabetic Wound Treatment
4.4. Integrated Hydrogel–Electronics Platforms for Theranostics
4.4.1. Conductive and Responsive Hydrogel Architectures
4.4.2. Bioresponsive Closed-Loop Systems
4.4.3. Integrated Intelligent Platforms
5. Challenges and Future Prospects
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AGEs | Advanced glycation end products |
| CPBA | 4-Carboxyphenylboronic acid |
| EGCG | (-)-Epigallocatechin gallate |
| GelMA | Methacryloyl gelatin |
| PBA | Phenylboronic acid |
| PVA | Polyvinyl alcohol |
| PVDF | Polyvinylidene fluoride |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| VEGF | Vascular endothelial growth factor |
References
- Joslin, E.P. The prevention of diabetes mellitus. JAMA 2021, 325, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gromada, J.; Chabosseau, P.; Rutter, G.A. The α-cell in diabetes mellitus. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2018, 14, 694–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilg, H.; Moschen, A.R.; Roden, M. NAFLD and diabetes mellitus. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2016, 14, 32–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conte, C.; Cipponeri, E.; Roden, M. Diabetes mellitus, energy metabolism, and COVID-19. Endocr. Rev. 2024, 45, 281–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomic, D.; Shaw, J.E.; Magliano, D.J. The burden and risks of emerging complications of diabetes mellitus. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2022, 18, 525–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hart, T.; Milner, R.; Cifu, A. Management of a diabetic foot. JAMA 2017, 318, 1387–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
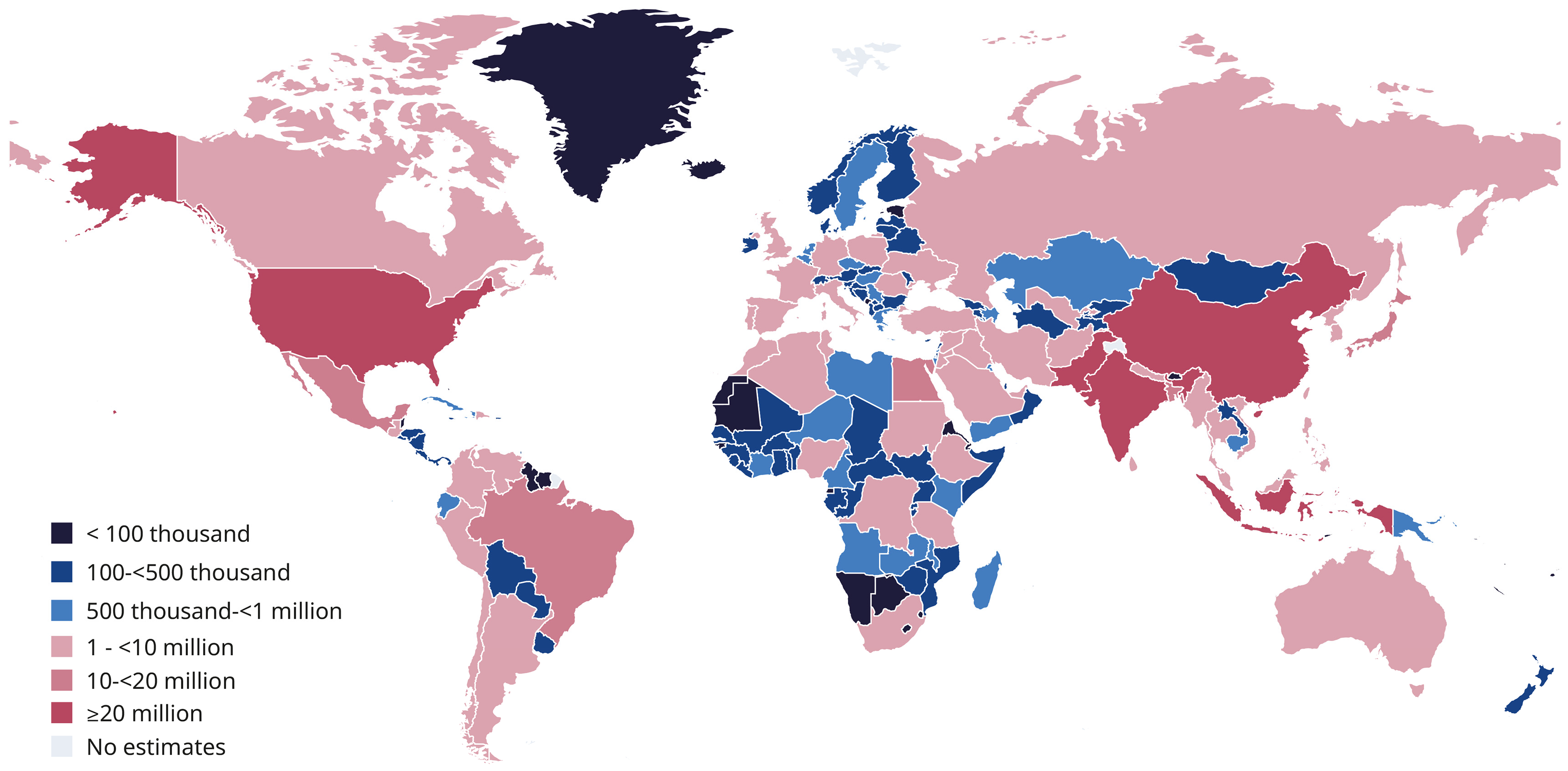
- IDF. IDF Diabetes Atlas, 11th ed.; IDF: Brussels, Belgium, 2025; Available online: https://diabetesatlas.org/resources/idf-diabetes-atlas-2025/ (accessed on 8 December 2025).
- Grennan, D. Diabetic foot ulcers. JAMA 2019, 321, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, S.C.; Chhatbar, K.C.; Kashikar, A. Diabetic foot. BMJ 2017, 359, j5064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobalem, M.; Uçkay, I. Evolution of a diabetic foot infection. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 369, 2252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, K.; Deng, S.; Zhu, Y.; Yang, W.; Chen, W.; Huang, L.; Zhang, C.; Li, M.; Ao, L.; Jiang, Y.; et al. Platelet rich plasma loaded multifunctional hydrogel accelerates diabetic wound healing via regulating the continuously abnormal microenvironments. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2023, 12, 2301370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y.; Chu, X.; Yu, T.; Knoedler, S.; Schroeter, A.; Lu, L.; Zha, K.; Lin, Z.; Jiang, D.; Rinkevich, Y.; et al. Reactive oxygen species-scavenging nanosystems in the treatment of diabetic wounds. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2023, 12, 2300779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bokinni, Y. Barbados is in the grip of a diabetic foot amputation crisis. BMJ 2024, 385, q350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, R.; Guo, B. Smart wound dressings for wound healing. Nano Today 2021, 41, 101290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, X.; Tao, S.; Wang, Q.; Ma, P.-Q.; Li, Z.-B.; Wu, Y.-L.; Li, D.-W. Research advances in smart responsive-hydrogel dressings with potential clinical diabetic wound healing properties. Mil. Med. Res. 2023, 10, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shang, S.; Zhuang, K.; Chen, J.; Zhang, M.; Jiang, S.; Li, W. A bioactive composite hydrogel dressing that promotes healing of both acute and chronic diabetic skin wounds. Bioact. Mater. 2024, 34, 298–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zhong, S.; Meng, F.; Cui, X. Multi-Functional hydrogels to promote diabetic wound Healing: A review. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 497, 154855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte, J.; Mascarenhas-Melo, F.; Pires, P.C.; Veiga, F.; Paiva-Santos, A.C. Multifunctional hydrogels-based therapies for chronic diabetic wound healing. Eur. Polym. J. 2024, 211, 113026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Yan, Y.; Xu, H.; Liu, J.; Fan, J.; Gan, L.; Wan, H.; Zhou, G. Tannic acid-mediated hydrogel crosslinking boosts diabetic wound healing via antibacterial and pro-angiogenesis. Eur. Polym. J. 2025, 236, 114168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Liu, J.; Li, C.; Cheng, P.; Liu, P.; Liu, Y.; Guan, F.; Yao, M. Horseradish peroxidase/hydrogen peroxide-driven photothermally enhanced hydrogel loaded with black rice extract for treating infected skin wound. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 305, 140827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Ma, Y.; Wang, H.; Li, C.; Li, C.; Zhang, R.; Zhong, S.; He, W.; Cui, X. Chitosan-based hydrogel dressings with antibacterial and antioxidant for wound healing. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 280, 135939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Zheng, J.; Li, S.; Deng, Y.; Zhao, S.; Tao, N.; Chen, W.; Li, J.; Liu, Y.-N. Nitric oxide-releasing multifunctional catechol-modified chitosan/oxidized dextran hydrogel with antibacterial, antioxidant, and pro-angiogenic properties for MRSA-infected diabetic wound healing. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 263, 130225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, L.; Wang, S.; Chen, H.; Wang, D.; Li, A.; Huang, Y.; Pu, Y.; Xiong, X.; Lui, X.; et al. The extracellular matrix promotes diabetic oral wound healing by modulating the microenvironment. Biomater. Res. 2025, 29, 0169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, J.; Fang, Y.; Yu, H.; Yi, J.; Ma, Y.; Lei, P.; Yang, Q.; Jin, L.; Wu, W.; Li, H.; et al. Recent advances in living algae seeding wound dressing: Focusing on diabetic chronic wound healing. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2024, 34, 2308387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunt, M.; Torres, M.; Bachar-Wikstrom, E.; Wikstrom, J.D. Cellular and molecular roles of reactive oxygen species in wound healing. Commun. Biol. 2024, 7, 1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, M.; Kosaric, N.; Bonham, C.A.; Gurtner, G.C. Wound healing: A cellular perspective. Physiol. Rev. 2019, 99, 665–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Lin, Z.; Li, Y.; Chen, L.; Reddy, S.K.; Hu, Z.; Garza, L.A. Colonizing microbiota is associated with clinical outcomes in diabetic wound healing. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2023, 194, 114727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, Y.; Liang, B.; Gong, Y.; Wu, L.; Li, P.; Gong, C.; Wang, P.; Yu, Z.; Sheng, L.; Yang, D.-P.; et al. Mxene-based mild hyperthemia microneedle patch for diabetic wound healing. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 481, 148592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhu, M.; Ou, J.; Li, K.; Ju, X.; Tian, Y.; Niu, Z. Multi-responsive sodium hyaluronate/tannic acid hydrogels with ROS scavenging ability promote the healing of diabetic wounds. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 278, 134896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Black, H.S. A synopsis of the associations of oxidative stress, ROS, and antioxidants with diabetes mellitus. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wu, C.; Xu, Y.; Chen, Z.; Li, L.; Chen, J.; Ning, N.; Guo, Y.; Yang, Z.; Hu, X.; et al. Conductive hydrogels with hierarchical biofilm inhibition capability accelerate diabetic ulcer healing. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 463, 142457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buch Pranali, J.; Chai, Y.; Goluch Edgar, D. Treating polymicrobial infections in chronic diabetic wounds. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2019, 32, 10–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Li, H.; Lv, X.; Xu, Y.; Xie, Y.; Yuwen, L.; Song, Y.; Li, S.; Shao, J.; Yang, D. Stimuli-responsive therapeutic systems for the treatment of diabetic infected wounds. Nanoscale 2022, 14, 12967–12983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Xu, Z.; Zhao, M.; Liu, G.; Wu, J. Advances of hydrogel dressings in diabetic wounds. Biomater. Sci. 2021, 9, 1530–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunnill, C.; Patton, T.; Brennan, J.; Barrett, J.; Dryden, M.; Cooke, J.; Leaper, D.; Georgopoulos, N.T. Reactive oxygen species (ROS) and wound healing: The functional role of ROS and emerging ROS-modulating technologies for augmentation of the healing process. Int. Wound J. 2017, 14, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, M.; Ouyang, J.; Wei, C.; Li, H.; Chen, W.; Liu, Y.-N. Artificial enzyme catalyzed cascade reactions: Antitumor immunotherapy reinforced by NIR-II light. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 17425–17432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Wang, Z. ROS-scavenging materials for skin wound healing: Advancements and applications. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2023, 11, 1304835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, M.; Xu, W.; Zhou, X.; Tang, F.; Chen, Q.; Zhang, X.; Bai, X.; Li, Z.; Jiang, X.; Chen, Q. An ROS-scavenging treg-recruiting hydrogel patch for diabetic wound healing. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2024, 34, 2314500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, G.; Li, Z.; Le, H.; Jiang, Z.; Sun, Y.; Liu, H.; Chang, F. Green tea derivative-based hydrogel with ROS-scavenging property for accelerating diabetic wound healing. Mater. Des. 2023, 225, 111452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Liu, K.; Guo, S.; Chang, R.; Zhang, C.; Guan, F.; Yao, M. Multifunctional hydrogel with reactive oxygen species scavenging and photothermal antibacterial activity accelerates infected diabetic wound healing. Acta Biomater. 2023, 155, 199–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, X.; Shu, J.; Wang, Y.; Deng, H.; Zhang, J.; He, J.; Wu, F. ROS-scavenging hydrogel to accelerate wound healing and reduce scar formation. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 474, 145941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Luo, J.; Zhang, Q.; Deng, T. Growth factors, as biological macromolecules in bioactivity enhancing of electrospun wound dressings for diabetic wound healing: A review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 193, 205–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Fan, D.; Shen, S.; Ma, X. An M2 macrophage-polarized anti-inflammatory hydrogel combined with mild heat stimulation for regulating chronic inflammation and impaired angiogenesis of diabetic wounds. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 433, 133859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Chen, K.; Liu, C.; Qu, X. Harnessing strategies for enhancing diabetic wound healing from the perspective of spatial inflammation patterns. Bioact. Mater. 2023, 28, 243–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louiselle, A.E.; Niemiec, S.M.; Zgheib, C.; Liechty, K.W. Macrophage polarization and diabetic wound healing. Transl. Res. 2021, 236, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Gu, Z.; Lu, C.; Zhang, T.; Guo, X.; Xue, G.; Zhang, L. Neutrophil extracellular traps are markers of wound healing impairment in patients with diabetic foot ulcers treated in a multidisciplinary setting. Adv. Wound Care 2020, 9, 16–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phillipson, M.; Kubes, P. The healing power of neutrophils. Trends Immunol. 2019, 40, 635–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chai, C.; Zhang, P.; Ma, L.; Fan, Q.; Liu, Z.; Cheng, X.; Zhao, Y.; Li, W.; Hao, J. Regenerative antibacterial hydrogels from medicinal molecule for diabetic wound repair. Bioact. Mater. 2023, 25, 541–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simões, D.; Miguel, S.P.; Ribeiro, M.P.; Coutinho, P.; Mendonça, A.G.; Correia, I.J. Recent advances on antimicrobial wound dressing: A review. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2018, 127, 130–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siddiqui, A.R.; Bernstein, J.M. Chronic wound infection: Facts and controversies. Clin. Dermatol. 2010, 28, 519–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, G.A.; Swogger, E.; Wolcott, R.; Pulcini, E.d.; Secor, P.; Sestrich, J.; Costerton, J.W.; Stewart, P.S. Biofilms in chronic wounds. Wound Repair Regen. 2007, 16, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, B.; Li, G.; Cao, E.; Luo, J.; Zhao, X.; Huang, H. Recent progress of antibacterial hydrogels in wound dressings. Mater. Today Bio 2023, 19, 100582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Qin, M.; Xu, M.; Miao, F.; Merzougui, C.; Zhang, X.; Wei, Y.; Chen, W.; Huang, D. The fabrication of antibacterial hydrogels for wound healing. Eur. Polym. J. 2021, 146, 110268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuo, S.; Liang, Y.; Wu, Z.; Zhao, X.; Han, Y.; Guo, B. Supramolecular hydrogels for wound repair and hemostasis. Mater. Horiz. 2024, 11, 37–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Q.; Wang, Y.; Ma, K.; Li, Q.; Li, B.; Hu, W.; Fu, X.; Zhang, C. Extracellular vesicles from human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells facilitate diabetic wound healing through mir-17-5P-mediated enhancement of angiogenesis. Stem Cell Rev. Rep. 2021, 18, 1025–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galkowska, H.; Wojewodzka, U.; Olszewski, W.L. Chemokines, cytokines, and growth factors in keratinocytes and dermal endothelial cells in the margin of chronic diabetic foot ulcers. Wound Repair Regen. 2006, 14, 558–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tejedor, S.; Wågberg, M.; Correia, C.; Åvall, K.; Hölttä, M.; Hultin, L.; Lerche, M.; Davies, N.; Bergenhem, N.; Snijder, A.; et al. The combination of vascular endothelial growth factor A (VEGF-A) and fibroblast growth factor 1 (FGF1) modified mRNA improves wound healing in diabetic mice: An ex vivo and in vivo investigation. Cells 2024, 13, 414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zha, W.; Wang, J.; Guo, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Dong, S.; Liu, C.; Xing, H.; Li, X. Efficient delivery of VEGF-A mRNA for promoting diabetic wound healing via ionizable lipid nanoparticles. Int. J. Pharm. 2023, 632, 122565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, H.; Dong, W.; Sun, W.; Zhao, Y. Responsive and self-healing structural color supramolecular hydrogel patch for diabetic wound treatment. Bioact. Mater. 2022, 15, 194–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, L.; Ou, X.; Wang, Z.; Li, X.; Feng, Y.; Yang, X.; Qu, W.; Yang, B.; Lin, Q. Electrical stimulation-based conductive hydrogel for immunoregulation, neuroregeneration and rapid angiogenesis in diabetic wound repair. Sci. China Mater. 2023, 66, 1237–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Yu, Y.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, Z.; Yuan, X.; Cao, J.; Meng, W.; Ye, L.; Lin, W.; Wang, G. A biocompatible self-powered piezoelectric poly(Vinyl alcohol)-based hydrogel for diabetic wound repair. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 46273–46289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Long, L.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Lu, Y.; Yang, Z.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, J.; Hu, X.; Wang, Y. Injectable conductive and angiogenic hydrogels for chronic diabetic wound treatment. J. Control. Release 2022, 344, 249–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, C.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, G.; Zhu, Z.; Zheng, H.; Sun, X.; Heng, Y.; Pan, S.; Xiu, H.; Zhang, J.; et al. Hyaluronic acid-based reactive oxygen species-responsive multifunctional injectable hydrogel platform accelerating diabetic wound healing. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2024, 13, 2302626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Liu, G.; Huang, J.; Wu, J. Novel glucose-responsive antioxidant hybrid hydrogel for enhanced diabetic wound repair. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 7680–7689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhao, M.; Liang, J.; Geng, Z.; Fan, Y.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, X. Hollow copper sulfide photothermal nanodelivery platform boosts angiogenesis of diabetic wound by scavenging reactive oxygen species. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2024, 16, 4395–4407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Li, M.; Wang, Z.; Feng, Q.; Gao, H.; Li, Q.; Chen, X.; Cao, X. Bioactive glasses-based nanozymes composite macroporous cryogel with antioxidative, antibacterial, and pro-healing properties for diabetic infected wound repair. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2023, 12, 2302073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Qin, J.; Wu, P.; Gao, W.; Sun, G. Glucose-responsive antioxidant hydrogel accelerates diabetic wound healing. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2023, 12, 2300074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, T.; Lu, H.; Zhu, J.; Zhou, X.; He, C.; Li, F.; Yang, G. Naturally derived dual dynamic crosslinked multifunctional hydrogel for diabetic wound healing. Compos. Part B 2023, 257, 110687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Liu, T.; Liu, X.; Han, C.; Li, L.; Zhang, Q.; Sui, X. Ganoderma lucidum polysaccharide hydrogel accelerates diabetic wound healing by regulating macrophage polarization. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 260, 129682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Qu, M.; Wang, C.; Xue, Y.; Huang, H.; Chen, Q.; Sun, W.; Zhou, X.; Xu, G.; Jiang, X. A dual-cross-linked hydrogel patch for promoting diabetic wound healing. Small 2022, 18, 2106172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Xiao, K.; Chen, J.; Lin, J.; He, Y.; He, X.; Cheng, F.; Li, Z.; Li, J.; Luo, F.; et al. Immune-microenvironment modulatory polyurethane-hyaluronic acid hybrid hydrogel scaffolds for diabetic wound treatment. Carbohydr. Polym. 2023, 320, 121238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Mao, W.; Shen, C.; Xiong, W.; Yao, Y.; Zhao, X.; Hu, Y.; Zou, Z.; et al. Symbiotic algae–bacteria dressing for producing hydrogen to accelerate diabetic wound healing. Nano Lett. 2022, 22, 229–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, A.; Zhang, N.; Su, S.; Shi, H.; Lu, D.; Li, X.; Zhang, X.; Feng, X.; Wen, Z.; Ma, G.; et al. A highly stretchable, adhesive, and antibacterial hydrogel with chitosan and tobramycin as dynamic cross-linkers for treating the infected diabetic wound. Carbohydr. Polym. 2024, 324, 121543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khunmanee, S.; Choi, A.; Ahn, I.Y.; Kim, W.J.; Bae, T.H.; Kang, S.H.; Park, H. Effective wound healing on diabetic mice by adhesive antibacterial GNPs-lysine composited hydrogel. iScience 2024, 27, 108860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, Y.; Nie, T.; Li, G.; Wang, L.; Du, J.; Wu, J. Multifunctional antibiotic hydrogel doped with antioxidative lycopene-based liposome for accelerative diabetic wound healing. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 480, 147930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Dong, S.; Xu, W.; Tu, S.; Yan, L.; Zhao, C.; Ding, J.; Chen, X. Antibacterial hydrogels. Adv. Sci. 2018, 5, 1700527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, Y.; Lüchow, M.; Zhang, Y.; Lin, J.; Fortuin, L.; Mohanty, S.; Brauner, A.; Malkoch, M. Nanogel encapsulated hydrogels as advanced wound dressings for the controlled delivery of antibiotics. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2006453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.; Wu, F.; Wang, X.; Song, Q.; Ye, Z.; Mohammadniaei, M.; Zhang, M.; Chu, X.; Xi, S.; Zhou, N.; et al. An optimally designed engineering exosome–reductive cof integrated nanoagent for synergistically enhanced diabetic fester wound healing. Small 2022, 18, 2200895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Zhao, B.; Wang, L.; Yang, L.; Chen, H.; Chen, W.; Qiao, H.; Qian, H. A glucose-responsive nitric oxide release hydrogel for infected diabetic wounds treatment. J. Control Release 2023, 359, 147–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Xu, Q.; Wang, X.; Shi, L.; Yang, X.; Sun, J.; Mei, X. Preparation of antibacterial, arginine-modified Ag nanoclusters in the hydrogel used for promoting diabetic, infected wound healing. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 12653–12663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, C.; Fan, Y.; Liu, G.; Li, W.; Ma, J.; Xiao, J. One-step fabrication of an injectable antibacterial collagen hydrogel with in situ synthesized silver nanoparticles for accelerated diabetic wound healing. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 480, 148288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Jing, X.; Yu, Z.; Huang, Y. Diverse antibacterial treatments beyond antibiotics for diabetic foot ulcer therapy. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2023, 12, 2300375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Xu, J.; Dong, Y.; Wang, Y.; Yu, C.; Li, Y.; Zhang, C.; Chen, Q.; Chen, S.; Peng, Q. Drug-free and non-crosslinked chitosan/hyaluronic acid hybrid hydrogel for synergistic healing of infected diabetic wounds. Carbohydr. Polym. 2023, 314, 120962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolcott, L.E.; Wheeler, P.C.; Hardwicke, H.M.; Rowley, B.A. Accelerated healing of skin ulcer by electrotherapy: Preliminary clinical results. South. Med. J. 1969, 62, 795–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amirabdollahian, F.; Ash, R. The effect of supplemental zinc on the zinc intake of British adults. Public Health Nutr. 2008, 11, 650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, F.; Baldessari, F.; Gyenge, C.C.; Sato, T.; Chambers, R.D.; Santiago, J.G.; Butcher, E.C. Lymphocyte electrotaxis in vitro and in vivo. J. Immunol. 2008, 181, 2465–2471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Wang, Z.; Kang, H.; Luo, P.; Su, J.; Wei, W.; Zhou, P.; Yu, A.; Dai, H. A flexibility self-powered band-aid for diabetes wound healing and skin bioelectronics. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 481, 148096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korupalli, C.; Li, H.; Nguyen, N.; Mi, F.-L.; Chang, Y.; Lin, Y.-J.; Sung, H.-W. Conductive materials for healing wounds: Their incorporation in electroactive wound dressings, characterization, and perspectives. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2021, 10, 2001384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Hu, H.; Dai, Y.; Xin, L.; Pang, Q.; Zhang, S.; Ma, L. A conductive multifunctional hydrogel dressing with the synergistic effect of ROS-scavenging and electroactivity for the treatment and sensing of chronic diabetic wounds. Acta Biomater. 2023, 167, 348–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, X.; Shang, Y.; Zou, Y.; Xiao, M.; Huang, H.; Zhu, S.; Liu, N.; Li, J.; Wang, W.; Zhu, P. Injectable hypoxia-induced conductive hydrogel to promote diabetic wound healing. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 56681–56691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, T.; Huang, Z.; Yang, J. A new class of electronic devices based on flexible porous substrates. Adv. Sci. 2022, 9, 2105084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Zheng, H.; Duan, Y.; Xu, T.; Xie, H.; Du, H.; Si, C. Nanocellulose-graphene composites: Preparation and applications in flexible electronics. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 253, 126903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhu, Z.; Zhou, P.; Zou, Y.; Yang, J.; Haick, H.; Wang, Y. Soft bioelectronics for therapeutics. ACS Nano 2023, 17, 17634–17667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, R.; Lei, M.; Ding, S.; Cheng, Q.; Ma, Z.; Wang, L.; Tang, Z.; Zhou, B.; Zhou, Y. Applications of flexible electronics related to cardiocerebral vascular system. Mater. Today Bio 2023, 23, 100787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Liu, N.; Xu, J.; Liu, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Yang, Y.; Li, S.; Huang, Y.; Jiang, S. Flexible electronics for cardiovascular healthcare monitoring. Innovation 2023, 4, 100485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gould, L.; Li, W.W. Defining complete wound closure: Closing the gap in clinical trials and practice. Wound Repair Regen. 2019, 27, 201–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Bai, M.; Zhu, Y.; Liu, X.; Tian, S.; Long, Y.; Ma, Y.; Wen, C.; Li, Q.; Yang, J.; et al. Pro-healing zwitterionic skin sensor enables multi-indicator distinction and continuous real-time monitoring. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2106406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Wang, L.; Xu, T.; Zhang, X. Luminescent MOF-based nanofibers with visual monitoring and antibacterial properties for diabetic wound healing. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2023, 15, 9110–9119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khor, S.M.; Choi, J.; Won, P.; Ko, S.H. Challenges and strategies in developing an enzymatic wearable sweat glucose biosensor as a practical point-of-care monitoring tool for type II diabetes. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garland, N.T.; Song, J.W.; Ma, T.; Kim, Y.J.; Vázquez-Guardado, A.; Hashkavayi, A.B.; Ganeshan, S.K.; Sharma, N.; Ryu, H.; Lee, M.-K.; et al. A miniaturized, battery-free, wireless wound monitor that predicts wound closure rate early. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2023, 12, 2301280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, W.; Zhu, Z.; Pei, X. Recent advances of hydrogels as smart dressings for diabetic wounds. J. Mater. Chem. B 2024, 12, 1126–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Z.; Wang, T.; Wang, L.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Li, P.; Huang, W. Skin-adhesive and self-healing diagnostic wound dressings for diabetic wound healing recording and electrophysiological signal monitoring. Mater. Horiz. 2024, 11, 1997–2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Feng, J.; Zhang, X.; Su, W.; Zhou, Y.; Wei, P.; Low, S.S.; Li, H.N. Battery-free and multifunctional microfluidic janus wound dressing with biofluid management, multi-indicator monitoring, and antibacterial properties. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2024, 16, 50321–50334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Xu, K.; Zhao, P.; Ji, L.; Hua, C.; Jia, X.; Wu, X.; Diao, L.; Zhong, W.; Lyu, G.; et al. Microgels sense wounds’ temperature, pH and glucose. Biomaterials 2025, 314, 122813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, D.-M.; Chen, S.; Zhang, W.-X.; Yu, Y.-L.; Wang, J.-H. Portable photoacoustic analytical system combined with wearable hydrogel patch for PH monitoring in chronic wounds. Anal. Chem. 2024, 96, 11595–11602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Li, Z.; Sun, M.; Zhou, L.; Wu, X.; Lu, Y.; Shao, Y.; Liu, C.; Huang, N.; Hu, B.; et al. Flexible bioelectronic systems with large-scale temperature sensor arrays for monitoring and treatments of localized wound inflammation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2024, 121, e2412423121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.W.; Wang, Y.H.; Yang, F.; Liu, D.X.; Lu, G.H.; Li, S.T.; Wei, Z.X.; Shen, X.; Jiang, Z.D.; Zhao, Y.F.; et al. Flexible organic photovoltaic-powered hydrogel bioelectronic dressing with biomimetic electrical stimulation for healing infected diabetic wounds. Adv. Sci. 2023, 11, 2307746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mostafalu, P.; Tamayol, A.; Rahimi, R.; Ochoa, M.; Khalilpour, A.; Kiaee, G.; Yazdi, I.K.; Bagherifard, S.; Dokmeci, M.R.; Ziaie, B.; et al. Smart bandage for monitoring and treatment of chronic wounds. Small 2018, 14, 1703509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, M.; Wan, P.; Ma, D.; Zhong, M.; Liao, M.; Ye, J.; Shi, R.; Zhang, L. Flexible breathable nanomesh electronic devices for on-demand therapy. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 29, 1902127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostafalu, P.; Kiaee, G.; Giatsidis, G.; Khalilpour, A.; Nabavinia, M.; Dokmeci, M.R.; Sonkusale, S.; Orgill, D.P.; Tamayol, A.; Khademhosseini, A. A textile dressing for temporal and dosage controlled drug delivery. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2017, 27, 1702399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.-F.; Li, M.-L.; Fang, Q.-Q.; Zhao, W.-Y.; Lou, D.; Hu, Y.-Y.; Chen, J.; Wang, X.-Z.; Tan, W.-Q. Flexible electrical stimulation device with Chitosan-Vaseline® dressing accelerates wound healing in diabetes. Bioact. Mater. 2021, 6, 230–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, Q.; Zhang, X.; Yang, Y.; Chen, Q.; Su, J.; Tang, Y.; Fang, L. Wearable magnetoelectric stimulation for chronic wound healing by electrospun CoFe2O4@CTAB/PVDF dressings. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2024, 16, 9839–9853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Trotsyuk, A.A.; Niu, S.; Henn, D.; Chen, K.; Shih, C.-C.; Larson, M.R.; Mermin-Bunnell, A.M.; Mittal, S.; Lai, J.-C.; et al. Wireless, closed-loop, smart bandage with integrated sensors and stimulators for advanced wound care and accelerated healing. Nat. Biotechnol. 2022, 41, 652–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, X.; Yang, J.; Zheng, Y.; Chen, S.; Duan, H.; Gao, J.; Haick, H.; Yi, C.; Jiang, L. Polymer hydrogel-based multifunctional theranostics for managing diabetic wounds. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2024, 34, 2315564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziyazadeh, M.; Vafaiee, M.; Mohammadpour, R.; Ehtesabi, H. Dual-sided and flexible triboelectric nanogenerator-based hydrogel skin patch for promoting wound healing. Nano Energy 2025, 134, 110558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, S.; Yi, S.; Ke, Q.; Liu, K.; Xu, H. A self-powered hydrogel/Nanogenerator system accelerates wound healing by electricity-triggered on-demand phosphatase and tensin homologue (PTEN) Inhibition. ACS Nano 2023, 17, 19652–19666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, N.; Fan, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, H.; Lyu, Y.; Cai, R.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, T.; Guan, Y.; Nan, K. Wireless, Programmable, and Refillable Hydrogel Bioelectronics for Enhanced Diabetic Wound Healing. Adv. Sci. 2024, 11, 2407820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Luo, X.; Li, L.; Chen, L.; Qiao, Z.; Si, C.; Haiyan, J.; Liu, X. Wearable, battery-free, and wireless microneedle-based bioelectronics for robustly-integrated chronic wound management and therapeutic diagnosis. Nano Energy 2025, 138, 110909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Ma, S.; Zhang, H. Multi-functional conductive hydrogels based on heparin–polydopamine complex reduced graphene oxide for epidermal sensing and chronic wound healing. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2023, 21, 343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.; Li, H.; Xu, C.; Wu, G.; Chen, J.; Zhang, J.; Liang, L.; Wu, Q.; Liang, Y.; Li, G.; et al. Ag@polydopamine-functionalized borate ester-linked chitosan hydrogel integrates monitoring with wound healing for epidermal sensor. npj Flex. Electron. 2024, 8, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Wang, S.; Li, Y.; Meng, X.; Wei, Y.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Xiao, Y.; Cheng, Y. An integrated all-natural conductive supramolecular hydrogel wearable biosensor with enhanced biocompatibility and antibacterial properties. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2024, 16, 51618–51629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Cheng, S.; Gong, F.; Yang, X.; Pei, Z.; Cui, X.; Hou, G.; Yang, N.; Han, Z.; Chen, Y.; et al. A closed-loop patch based on bioinspired infection sensor for wound management. Nano Today 2024, 57, 102400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, B.; Ren, X.; Wang, X.; Wen, Y.; Yang, J.; Li, L.; Bai, P.; Lang, F.; Li, L.; Zhang, R. Four-in-one pH/glucose-responsive engineered hydrogel for diabetes wound healing. Nano Today 2025, 62, 102725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, W.; Wang, Q.; Li, M.; Li, N.; Wang, X.; Yu, J.; Li, F.; Wu, D. 3D hybrid scaffold with aligned nanofiber yarns embedded in injectable hydrogels for monitoring and repairing chronic wounds. Compos. Part B 2022, 234, 109688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, D.; Liang, L.; Su, K.; Gu, H.; Wang, X.; Wang, Y.; Shang, X.; Huang, W.; Chen, H.; Wu, X.; et al. Smart hydrogel dressing for machine learning-enabled visual monitoring and promote diabetic wound healing. Nano Today 2025, 60, 102559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, L.; Tan, M.; Wu, C. Thermoelectric Hydrogel Composite Dressing for Promoting Diabetic Ulcer Repair and Loading Targeted Modified Exosome and Preparation Method Thereof. CN119925682, 6 May 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Hui, J.; Liu, W.; Fan, D.; Zheng, X.; Yao, B.; Gao, Q. Preparation Method of Hydrogel Dressing Capable of Treating Diabetic Wounds in Combination with Electrical Stimulation. CN117653775, 8 March 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Tang, L.; Sun, X.; Wang, P.; Li, N. Preparation Method and Application of Conductive Hydrogel Flexible Electrode. CN118718028, 1 October 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, H.; Yang, G.; Wen, J.; Gong, H. 3D printing Hydrogel Electrode for Diagnosis and Treatment of Diabetic Neuropathy. CN118000742, 10 May 2024. [Google Scholar]






| Functions | Technical Subcategory | Mechanisms | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Monitoring and Sensing | Single-parameter sensing | Temperature mapping | [106] |
| pH monitoring | [105] | ||
| Multi-parameter sensing | Microfluidic sensing of temperature, pH and uric acid | [103] | |
| Microgel sensing of temperature, pH and glucose | [104] | ||
| Active Therapy | Electrical stimulation | Self-powered electrical stimulation through biomechanical energy conversion | [87,126] |
| Programmable electrical stimulation with parameter control | [117,127] | ||
| TENG-based electrical stimulation from mechanical motion | [115] | ||
| Controlled Drug delivery | Electrically triggered on-demand drug release using conductive hydrogels | [116] | |
| Minimally invasive transdermal delivery via bioinspired microneedles | [118] | ||
| Integrated Theranostics | Conductive/Responsive Hydrogel Architectures | High-conductivity hydrogel platform combining sensing and stimulation | [119,120,121,128] |
| Bioresponsive Closed-Loop Systems | Closed-loop infection response with automated detection and treatment | [122] | |
| Glucose–pH dual-responsive release of therapeutic agents | [123] | ||
| Integrated intelligent platforms | 3D hybrid scaffold providing structural guidance and real-time monitoring | [124,129] | |
| Machine learning-assisted visual wound monitoring and assessment | [125] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2026 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.
Share and Cite
Liu, Z.; Zhang, H.; Li, Y.; Xu, S.; Fu, N.; Wang, F.; Chen, W. Hydrogel–Flexible Electronics Integrated Platforms for Diabetic Wound Management. Materials 2026, 19, 509. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma19030509
Liu Z, Zhang H, Li Y, Xu S, Fu N, Wang F, Chen W. Hydrogel–Flexible Electronics Integrated Platforms for Diabetic Wound Management. Materials. 2026; 19(3):509. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma19030509
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Zhenjun, Huanping Zhang, Yuqing Li, Shengxi Xu, Ning Fu, Fang Wang, and Wansong Chen. 2026. "Hydrogel–Flexible Electronics Integrated Platforms for Diabetic Wound Management" Materials 19, no. 3: 509. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma19030509
APA StyleLiu, Z., Zhang, H., Li, Y., Xu, S., Fu, N., Wang, F., & Chen, W. (2026). Hydrogel–Flexible Electronics Integrated Platforms for Diabetic Wound Management. Materials, 19(3), 509. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma19030509






