The Effect of Cryogenic Treatment and Tempering Duration on the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Martensitic Stainless Steel 13Cr-2Ni-2Mo
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Heat Treatments
2.2. Microstructure and Mechanical Properties Analysis
3. Results and Discussions
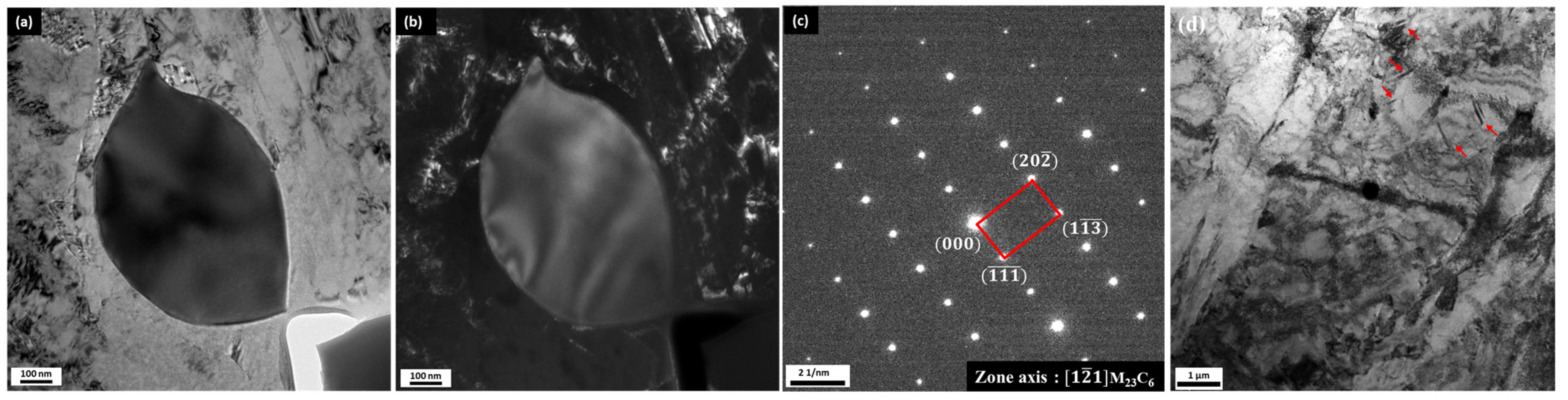
3.1. Microstructure of As-Quenched and Conventionally Quenched-Tempered Samples

3.2. Effects of Cryogenic Treatment
3.2.1. Microstructural Characterization
3.2.2. Mechanical Properties
3.2.3. Microstructural Evolution with Different Tempering Duration
4. Conclusions
- The as-quenched sample (CHT) of 13Cr-2Ni-2Mo contains lath martensite, retained austenite, undissolved carbide, and δ-ferrite. Cryogenic treatment (CT) facilitates the conversion of retained austenite into martensite, resulting in increased hardness compared to conventional QT treatment (CHT/T2).
- The predominant carbide types are nanosized M23C6 and a few instances of M3C (cementite), along with a smaller grain size distribution relative to the CHT process. Following cryogenic treatment durations of 2 h, 12 h, and 20 h, the average prior austenite grain boundary (PAGB) sizes were found to be 41.14 ± 9.22 μm, 27.58 ± 9.06 μm, and 24.84 ± 8.05 μm, respectively.
- Variations in tempering duration can lead to an increase in PAGB size, which is associated with the coarsening of carbides and grain size. After tempering for 2 h, 5 h, and 10 h at 200 °C, the PAGB sizes were 41.14 ± 9.22 μm, 43.24 ± 12.24 μm, and 55.73 ± 14.08 μm, respectively.
- Extended durations of cryogenic treatment can result in decreased hardness compared to the as-quenched sample, primarily due to a reduction in the solid solution strengthening effect. After cryogenic treatment for 2 h, 12 h, and 20 h followed by tempering, the hardness values relative to the as-quenched state were 543 ± 8.67 HV (−5.04%), 541 ± 6.12 HV (−5.32%), and 524 ± 6.53 HV (−8.36%), respectively.
- The hardness of samples subjected to different tempering durations post-cryogenic treatment were 2 h, 5 h, and 10 h at 200 °C, compared to the as-quenched sample, yielded values of 543 ± 8.67 HV (−5.04%), 531 ± 8.73 HV (−7.24%), and 530 HV ± 7.49 (−7.32%), respectively.
- 13Cr-2Ni-2Mo martensitic stainless steel, which is intended for automobile applications requiring high hardness and good toughness, and a combination of cryogenic treatment for 2 h at −150 °C, followed by tempering for 2 h at 200 °C (CT2/T2), was the optimal processing route in this study. Cryogenic treatment contributes to a reduction in retained austenite content effectively, which prevents dimensional changes caused by austenite transformation during service, thereby avoiding failure and effectively improving the service life of the experimental steel.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jiang, W.; Wu, D.; Zhang, Q.; Li, M.; Liu, W. Effect of Tempering Time on the Microstructure and Properties of Martensitic Stainless Steel. Metals 2014, 14, 322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Pablos, J.L.; Sierra-Soraluce, A.; Sabirov, I.; Muratori, M.; Smith, A. Assessing the Feasibility of Cold Forming of Automotive Parts from Quenched and Partitioned Martensitic Stainless Steels. Steel Res. Int. 2024, 95, 2300280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Xiao, M.; Ye, G.; Zhao, K.; Yang, M. Effects of deep cryogenic treatment on microstructural evolution and alloy phases precipitation of a new low carbon martensitic stainless bearing steel during aging. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2018, 732, 167–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, C.; Liu, F.; Jiang, Z.; Suo, H.; Yu, X.; Zhang, H.; Ding, S. Effect of cryogenic treatment on microstructure evolution and mechanical properties of high nitrogen plastic die steel. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2021, 15, 5128–5140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurči, P.; Dlouhý, I. Cryogenic Treatment of Martensitic Steels: Microstructural Fundamentals and Implications for Mechanical Properties and Wear and Corrosion Performance. Materials 2014, 17, 548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Lu, S.P.; Xiao, N.M.; Li, D.Z.; Li, Y.Y. Effect of delta ferrite on impact properties of low carbon 13Cr-4Ni martensitic stainless steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2010, 527, 3210–3216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klug, P.J. Mechanisms and Effect of Deep Cryogenic Treatment on Steel Properties. Ph.D. Thesis, Jožef Stefan International Postgraduate School, Ljubljana, Slovenia, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Li, D.; Li, Z.; Xiao, M.; Li, S.; Zhao, K.; Yang, M. Effect of Deep Cryogenic Treatment on Mechanical Property and Microstructure of a Low Carbon High Alloy Martensitic Bearing Steel during Tempering. Chin. J. Mater. Res. 2019, 33, 561–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jovičević-Klug, P.; Jovičević-Klug, M.; Sever, T.; Feizpour, D.; Podgornik, B. Impact of steel type, composition and heat treatment parameters on effectiveness of deep cryogenic treatment. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2021, 14, 1007–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Huang, P.; Feng, Z.; Wei, Z.; Zu, G. Effect of Deep Cryogenic Time on Martensite Multi-Level Microstructures and Mechanical Properties in AISI M35 High-Speed Steel. Materials 2022, 15, 6618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, G.; Pandey, K.N. Effect of cryogenic treatment on properties of materials: A review. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part E-J. Process Mech. Eng. 2022, 236, 1758–1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jatczak, C.F. Retained Austenite and Its Measurement by X-Ray Diffraction. In Proceedings of the Automotive Engineering Congress and Exposition, Detroit, OH, USA, 25–29 February 1980, ISSN 0148-7191. [Google Scholar]
- He, J.; Wang, Y.; Qiu, X.; Yang, B.; Gu, J.; Chi, H.; Cheng, X. Effect of tempering time on microstructure and mechanical properties of a low carbon stainless bearing steel. Mater. Today Commun. 2025, 42, 111305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM E290-22; Standard Test Methods for Bend Testing of Materials for Ductility. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2022.
- Li, S.; Yuan, X.; Jiang, W.; Sun, H.; Li, J.; Zhao, K.; Yang, M. Effects of heat treatment influencing factors on microstructure and mechanical properties of a low-carbon martensitic stainless bearing steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2014, 605, 229–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Jiang, L.; Yuan, C.; Zhang, J.; Yan, Q. Advancement of strength and toughness in ultra-low carbon martensitic stainless steel by reversed austenite. Nucl. Mater. Energy 2024, 38, 101601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Zeng, T.; Shi, Q.; Wang, N.; Zhang, S.; Yang, K.; Yan, W.; Wei, W. Microstructure evolution and mechanical properties during long-term tempering of a low carbon martensitic stainless bearing steel. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2023, 25, 297–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Li, J.; Gu, J.; Liao, L.; Deng, Y. Effect of nitrogen and tempering temperature on microstructure evolution and mechanical properties of 0Cr15Ni6Mo2 martensitic stainless steel. Ironmak. Steelmak. 2022, 49, 311–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, S.; Hao, H.; Meng, L.; Zhang, X. Effect of deep cryogenic treatment parameters on martensite multi-level microstructures and properties in a lath martensite/ferrite dual-phase steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2021, 810, 141022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abid, A.A.H.; Muhammad, H.B. Effect of Cryogenic Treatment on the Tensile Properties of Carbon Dual Phase Steel. J. Eng. 2013, 19, 574–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.G.; Li, D.Y. Effects of the sub-zero treatment condition on microstructure, mechanical behavior and wear resistance of W9Mo3Cr4V high speed steel. Wear 2013, 302, 854–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savyasachi, N.; Reji, R.; Sajan, J.A.; Rafi, A.M. A Review on the Cryogenic Treatment of Stainless Steels, Tool Steels, and Carburized Steels. Int. J. Innov. Sci. Res. Technol. 2020, 5, 31–38. [Google Scholar]
- Li, D.H.; He, W.C.; Zhang, X.; Xiao, M.G.; Li, S.H.; Zhao, K.Y.; Yang, M.S. Effects of traditional heat treatment and a novel deep cryogenic treatment on microstructure and mechanical properties of low-carbon high-alloy martensitic bearing steel. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 2021, 28, 370–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villa, M.; Somers, M. Cryogenic Treatment of Steel: From Concept to Metallurgical Understanding. In Proceedings of the 24th International Feration for Heat Treatment and Surface Engineering Congress, Nice, France, 26–29 June 2017; pp. 26–29. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Z.; Liu, Z.; Liang, J.; Yang, Z.; Sheng, G. Elucidating the role of secondary cryogenic treatment on mechanical properties of a martensitic ultra-high strength stainless steel. Mater. Charact. 2021, 178, 111277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prieto, G.; Ipiña, J.P.; Tuckart, W.R. Cryogenic treatments on AISI 420 stainless steel: Microstructure and mechanical properties. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2014, 605, 236–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prieto, G.; Tuckart, W.R.; Perez Ipiña, J.E. Influence of a Cryogenic Treatment on the Fracture Toughness of an AISI 420 Martensitic Stainless Steel. Mater. Technol. 2017, 51, 591–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Zhou, B.; Li, Z.; Huo, D.; Xiong, J.; Zhang, S. Effect of tempering process on the cryogenic impact toughness of 13Cr4NiMo martensitic stainless steel. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2023, 23, 5618–5630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antony, A.; Schmerl, N.M.; Sokolova, A.; Mahjoub, R.; Fabijanic, D.; Stanford, N.E. Quantification of the Dislocation Density, Size, and Volume Fraction of Precipitates in Deep Cryogenically Treated Martensitic Steels. Metals 2020, 10, 1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, X.; Hu, X.; Zheng, L.; Li, D. Redistribution of C and N Atoms in High Nitrogen Martensitic Stainless Steel During Cryogenic Treatment. Acta Metall. Sin. Engl. Lett. 2022, 35, 591–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, J.; Nath, S.K. Effects of Cyclic Heat Treatment on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of 13%Cr-4%Ni Martensitic Stainless Steel. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2020, 29, 2478–2490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villa, M.; Pantleon, K.; Somers, M.A. Evolution of compressive strains in retained austenite during sub-zero Celsius martensite formation and tempering. Acta Mater. 2014, 65, 383–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yildiz, E.; Özbek, N. Effect of cryogenic treatment and tempering temperature on mechanical and microstructural properties of AISI 431 steel. Int. J. 3D Print. Technol. Digit. Ind. 2022, 6, 74–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sola, R.; Giovanardi, R.; Parigi, G.; Veronesi, P. A Novel Method for Fracture Toughness Evaluation of Tool Steels with Post-Tempering Cryogenic Treatment. Metals 2017, 7, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idayan, A.; Gnanavelbabu, A.; Rajkumar, K. Influence of Deep Cryogenic Treatment on the Mechanical Properties of AISI 440C Bearing Steel. Procedia Eng. 2014, 97, 1683–1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, D.; Dutta, A.K.; Ray, K.K. Sub-zero treatments of AISI D2 steel: Part I. Microstructure and hardness. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2010, 527, 2182–2193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyshchenko, A.I.; Theisen, W.; Oppenkowski, A.; Siebert, S.; Razumov, O.N.; Skoblik, A.P.; Sirosh, V.A.; Petrov, Y.N.; Gavriljuk, V.G. Low-temperature martensitic transformation and deep cryogenic treatment of a tool steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2010, 527, 7027–7039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Essam, M.A.; Shash, A.Y.; El-Fawakhry, M.K.; El-Kashif, E.; Megahed, H. Effect of Deep Cryogenic Treatment on Wear Behavior of Cold Work Tool Steel. Metals 2023, 13, 382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özbek, N.A.; Özbek, O. Investigation of The Effects of Shallow Cryogenic Treatment on the Mechanical and Microstructural Properties of 1.2436 Tool Steel. J. Mater. Mechatron. A 2022, 3, 151–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, K.; Zhong, Z.; Wang, H.; Xu, H.; Yu, F.; Wang, C.; Wu, G.; Liang, J.; Godfrey, A.; Cao, W. Obtaining Excellent Mechanical Properties in an Ultrahigh-Strength Stainless Bearing Steel via Solution Treatment. Metals 2023, 13, 1824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.Y.; Jin, J.J.; Jiang, Z.H.; Wang, X.Z.; Hu, C.W. Effect of Heat Treatment Temperature on Microstructure and Properties of New Maraging Stainless Steel. J. Mater. Eng. 2019, 47, 152–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, P.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, G. Effect of Normalizing Temperature on High Strength of 13Cr4Ni Martensitic Stainless Steel. Metall. Eng. 2022, 9, 321–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Ye, D.; Li, J.; Su, J.; Zhao, K. Reverse Transformation Mechanism of Martensite to Austenite in 00Cr15Ni7Mo2WCu2 Super Martensitic Stainless Steel. Steel Res. Int. 2014, 85, 1150–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsiao, P.C. The Effect of Heat Treatment on Microstructure, Mechanical Properties, and Corrosion Resistance of 13Cr-2Ni-2Mo Martensitic Stainless Steel. Master’s Thesis, Material Science and Engineering, National Taiwan University, Taipei, Taiwan, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, R.; Li, F.; Wu, Z.; Kang, Y.; Fan, J.; Yu, Z.; Yan, Y.; Du, S.; Eckert, J. Precipitation and Transformation of Carbides during Tempering of 7Cr14 Martensitic Stainless Steel. Steel Res. Int. 2023, 95, 2300248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X.H.; Yang, M.S.; Zhao, K.Y. Effects of Microstructure Transformation on Strengthening and Toughening for Heat-Treated Low Carbon Martensite Stainless Bearing Steel. Mater. Sci. Forum 2015, 817, 667–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burja, J.; Šuler, B.; Češnjaj, M.; Nagode, A. Effect of Intercritical Annealing on the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of 0.1C-13Cr-3Ni Martensitic Stainless Steel. Metals 2021, 11, 392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chenna Krishna, S.; Srinath, J.; Jha, A.K.; Pant, B.; Sharma, S.C.; George, K.M. Effect of Heat Treatment on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of 12Cr–10Ni–0.25Ti–0.7Mo Stainless Steel. Metallogr. Microstruct. Anal. 2013, 2, 234–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Li, H.; Qu, F.; Han, J.; Cheng, L.; Wu, B.; Lu, Y.; Ma, Y. Precipitates and Particles Coarsening of 9Cr-1.7W-0.4Mo-Co Ferritic Heat-Resistant Steel after Isothermal Aging. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 5859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Dong, C.; Yu, Q.; Man, C.; Hu, Y.; Dai, Z.; Li, X. The Correlation Between the Distribution/Size of Carbides and Electrochemical Behavior of 17Cr-1Ni Ferritic-Martensitic Stainless Steel. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2019, 50, 388–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedoseeva, A.; Dolzhenko, A.; Kaibyshev, R. Thermo-Mechanical Processing as Method Decreasing Delta-Ferrite and Improving the Impact Toughness of the Novel 12% Cr Steels with Low N and High B Contents. Materials 2022, 15, 8861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wang, L.; Wang, H.; Zhang, P.; Guo, F.; Zhang, X. Dissolution Behavior of Delta Ferrites in Martensitic Heat-resistant Steel for Ultra Supercritical Units Blades. J. Wuhan Univ. Technol. Mater. Sci. Ed. 2022, 37, 730–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.Y.; Ren, J.K.; Xie, Z.L.; Zhang, W.N.; Chen, J.; Liu, Z.Y. Correlation between reversed austenite and mechanical properties in a low Ni steel treated by ultra-fast cooling, intercritical quenching and tempering. J. Mater. Sci. 2020, 55, 1840–1853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]














| MSS | C | Cr | Ni | Mo | Si | Mn | N | Fe |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 13Cr-2Ni-2Mo | 0.17 ± 0.03 | 12.9 ± 0.05 | 1.8 ± 0.07 | 1.92 ± 0.06 | 0.36 ± 0.02 | 0.08 ± 0.01 | 0.12 ± 0.04 | Bal. |
| Identification | Description |
|---|---|
| As-received | Prior heat treatment |
| CHT | Conventionally heat-treated (as-quenched) |
| CHT/T2 | As-quenched + Tempering at 200 °C for 2 h |
| CT2/T2 | As-quenched + cryogenically at −150 °C for 2 h + Tempering at 200 °C for 2 h |
| CT2/T5 | As-quenched + cryogenically at −150 °C for 2 h + Tempering at 200 °C for 5 h |
| CT2/T10 | As-quenched + cryogenically at −150 °C for 2 h + Tempering at 200 °C for 10 h |
| CT12/T2 | As-quenched + cryogenically at −150 °C for 12 h + Tempering at 200 °C for 2 h |
| CT20/T2 | As-quenched + cryogenically at −150 °C for 20 h + Tempering at 200 °C for 2 h |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fatih, M.R.R.; Chen, H.-J.; Lin, H.-C. The Effect of Cryogenic Treatment and Tempering Duration on the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Martensitic Stainless Steel 13Cr-2Ni-2Mo. Materials 2025, 18, 1784. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18081784
Fatih MRR, Chen H-J, Lin H-C. The Effect of Cryogenic Treatment and Tempering Duration on the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Martensitic Stainless Steel 13Cr-2Ni-2Mo. Materials. 2025; 18(8):1784. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18081784
Chicago/Turabian StyleFatih, Muhammad R. R., Hou-Jen Chen, and Hsin-Chih Lin. 2025. "The Effect of Cryogenic Treatment and Tempering Duration on the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Martensitic Stainless Steel 13Cr-2Ni-2Mo" Materials 18, no. 8: 1784. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18081784
APA StyleFatih, M. R. R., Chen, H.-J., & Lin, H.-C. (2025). The Effect of Cryogenic Treatment and Tempering Duration on the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Martensitic Stainless Steel 13Cr-2Ni-2Mo. Materials, 18(8), 1784. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18081784






