Effect of Mo and B on Microstructure and Impact Toughness of Coarse Grain Heat-Affected Zone in Low-Carbon V-Ti-N Micro-Alloyed Steel
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
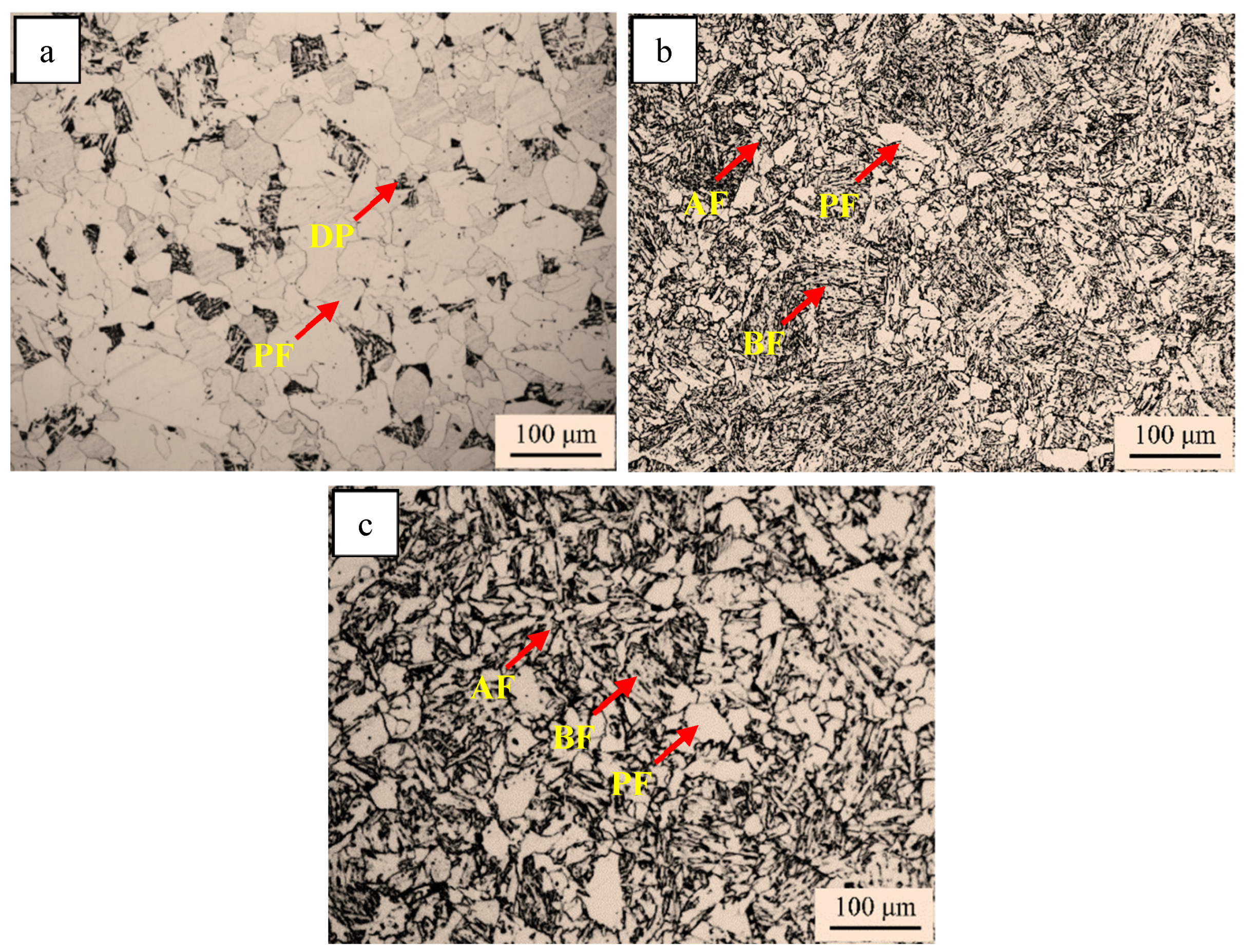
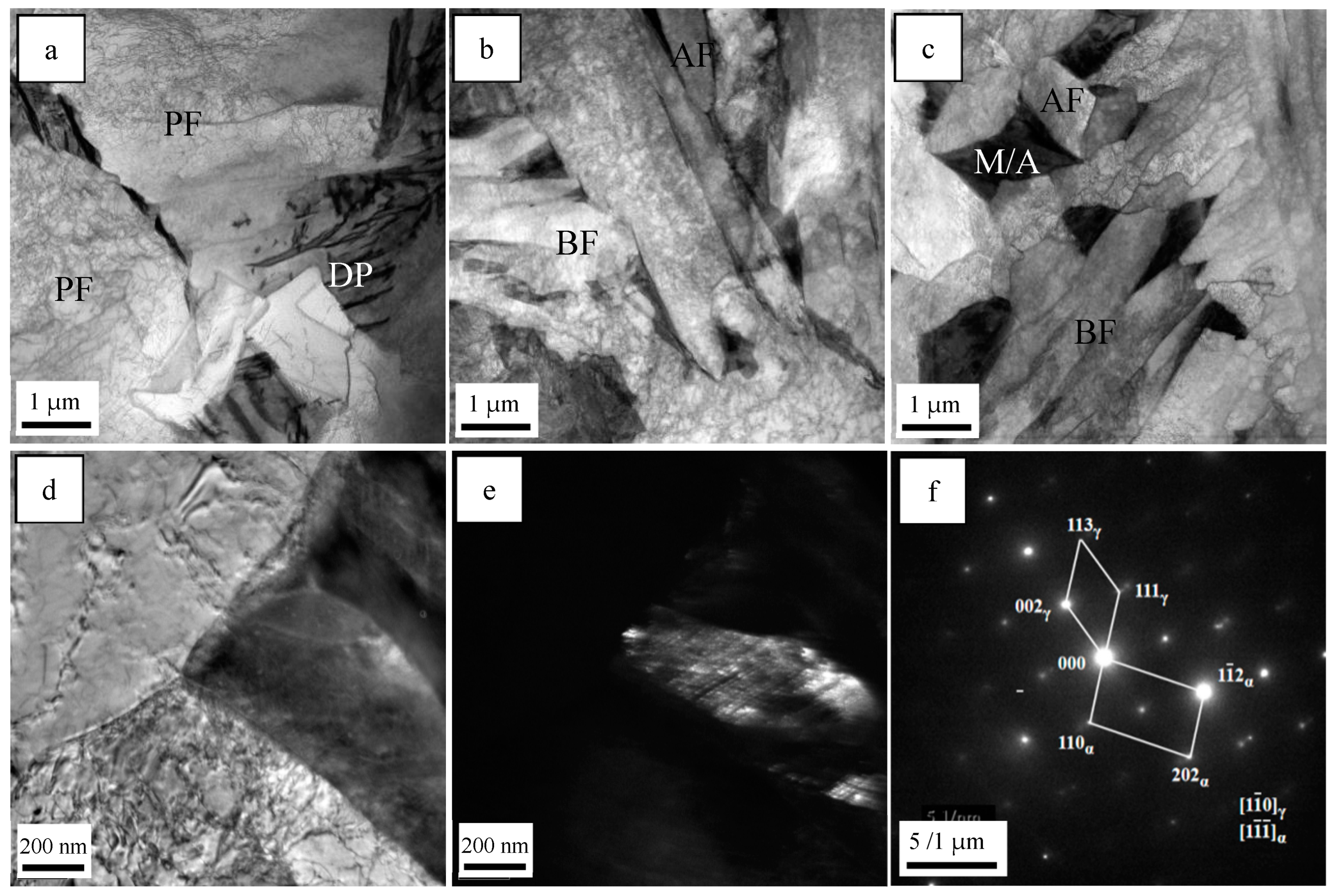
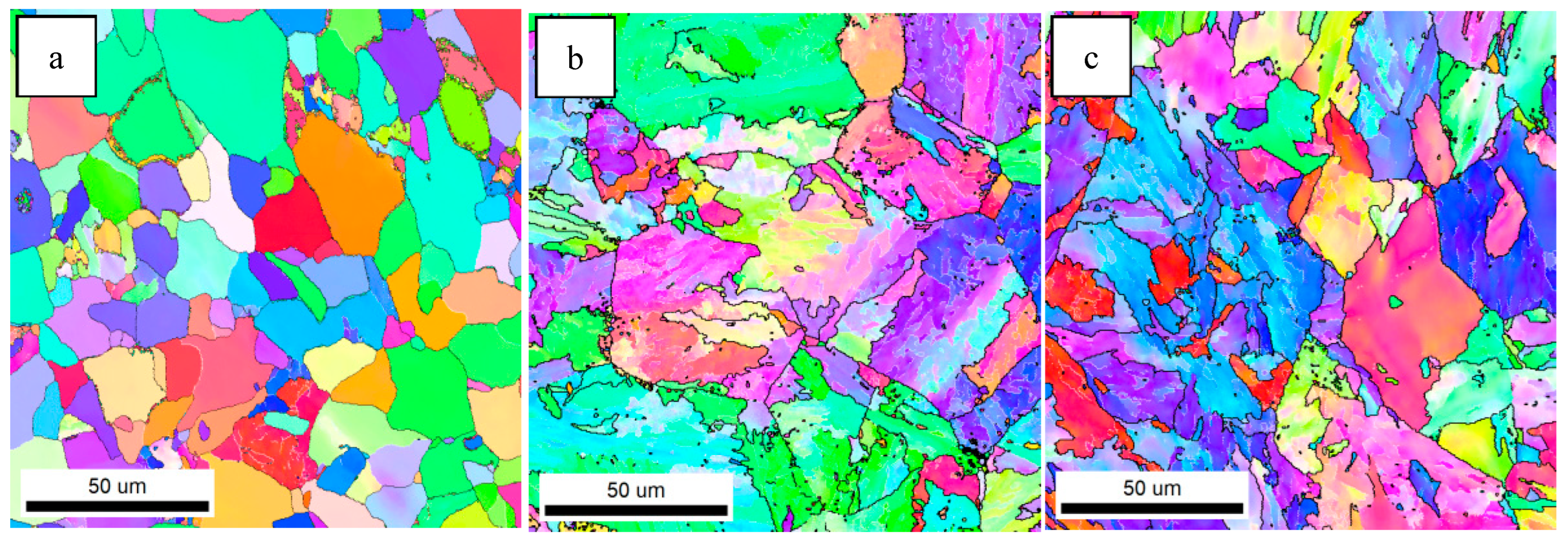
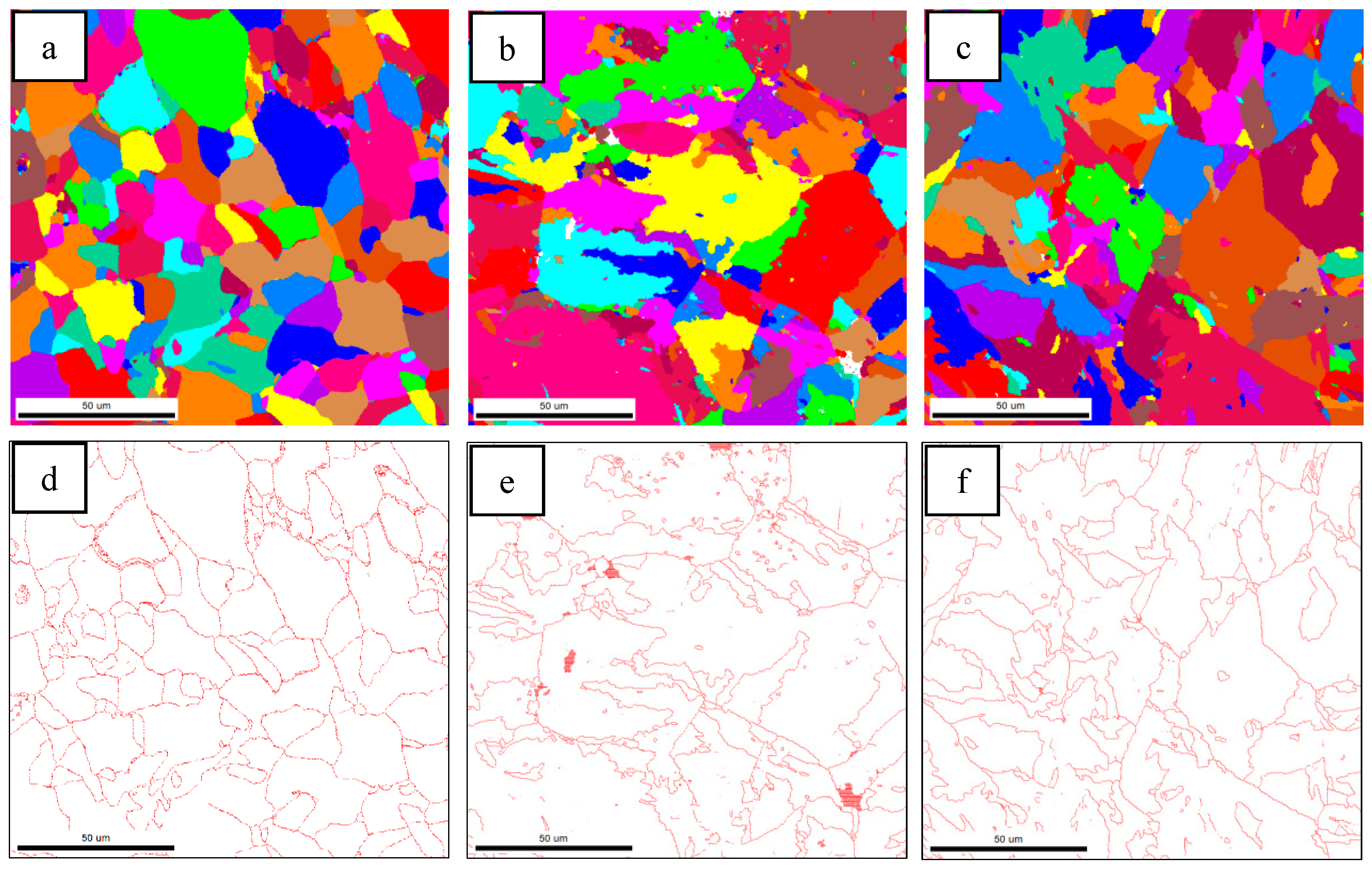
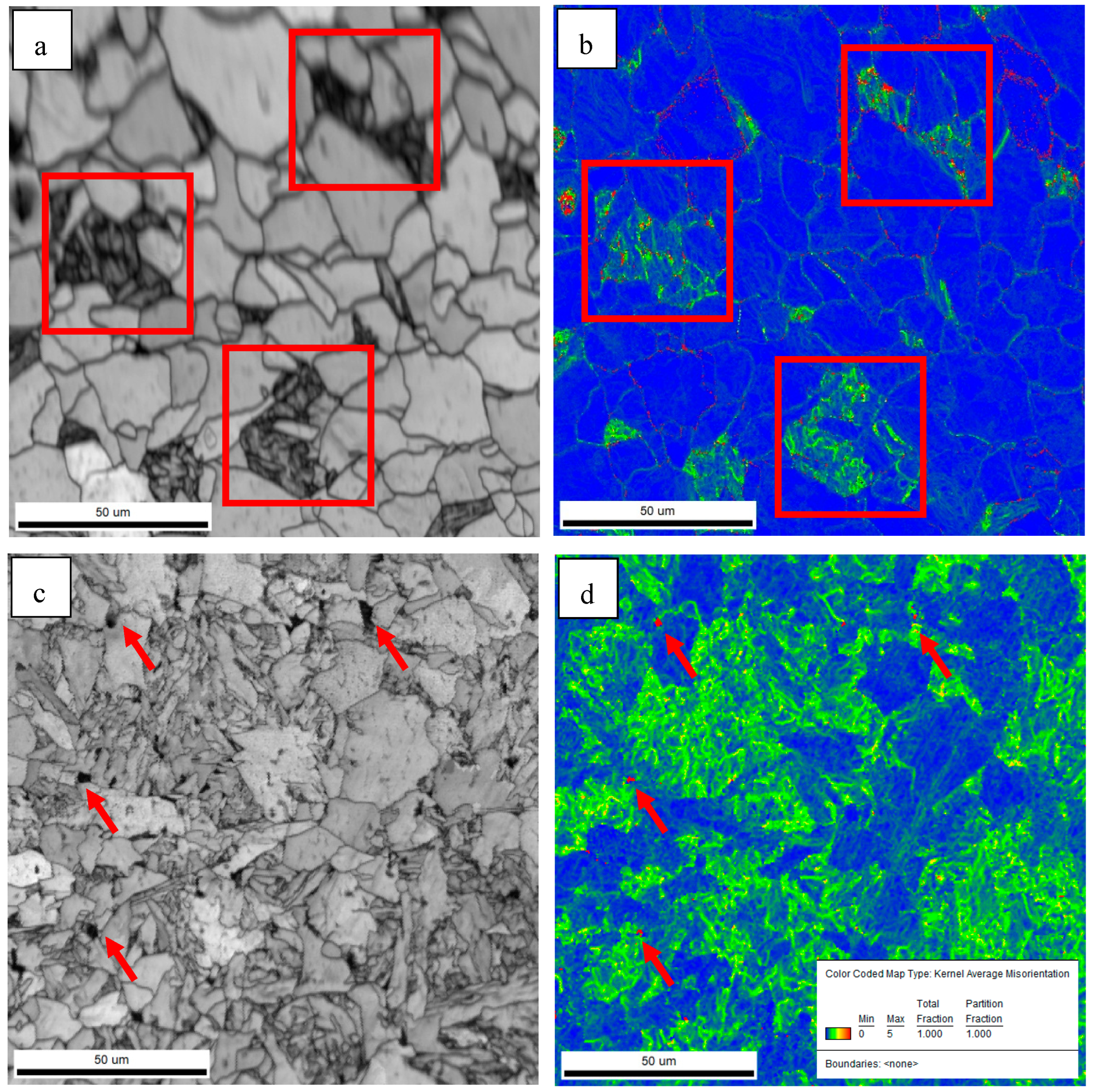
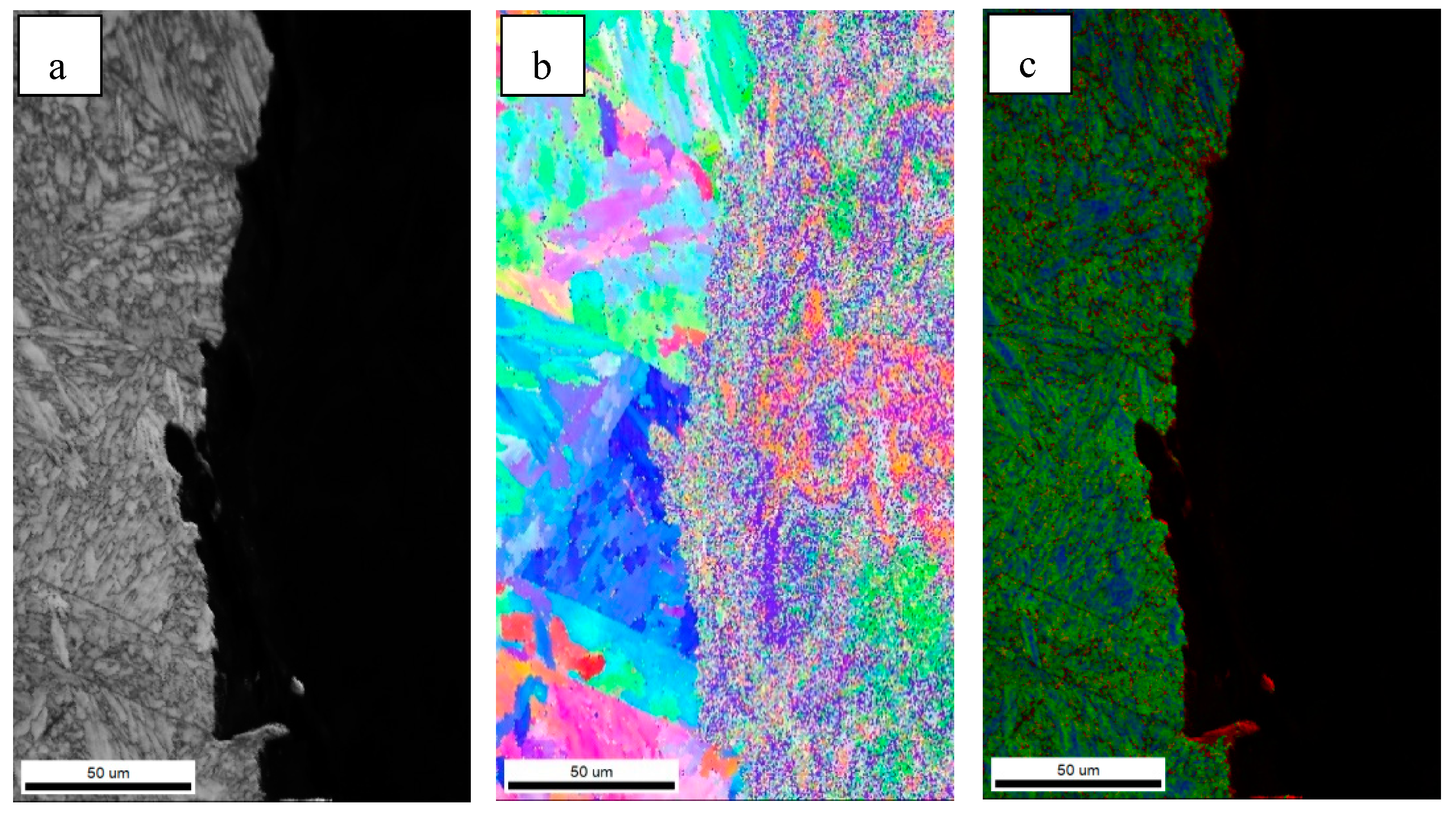
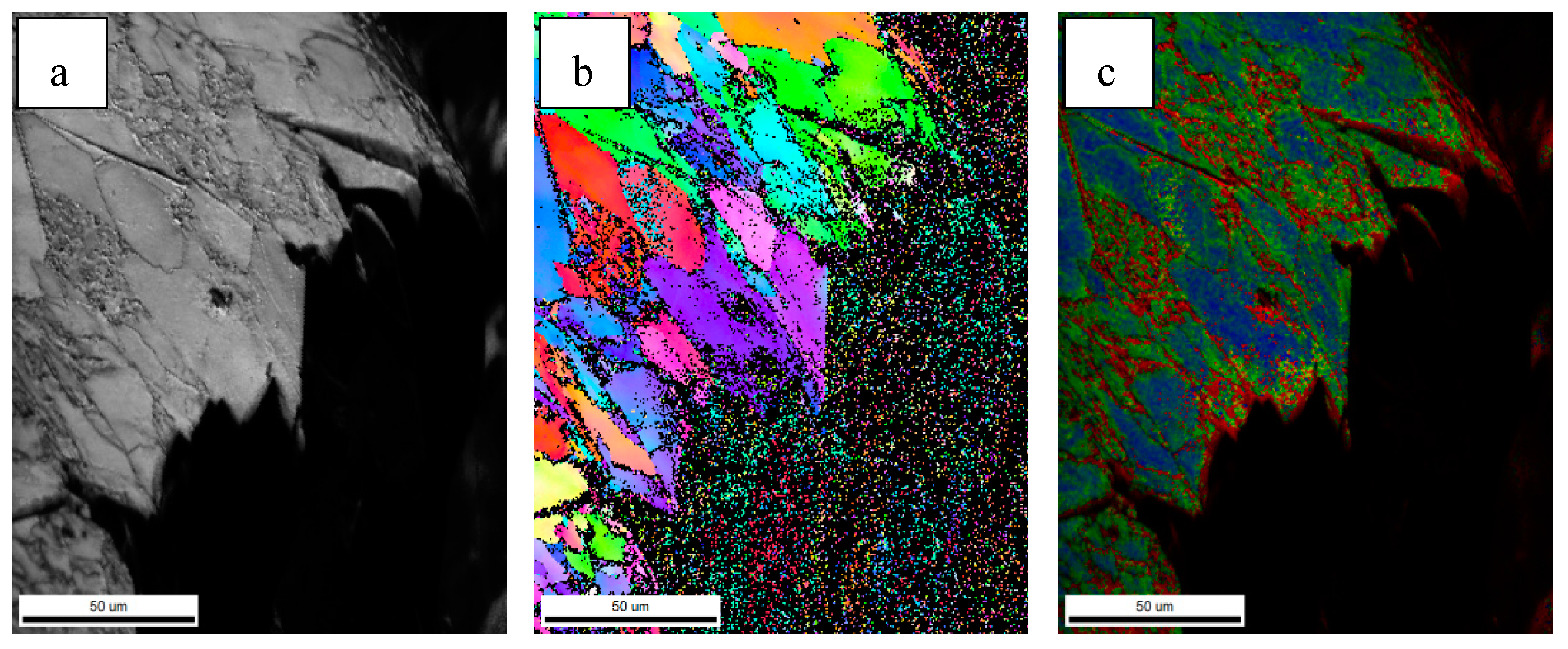
3.1. Microstructure of the Simulated Samples
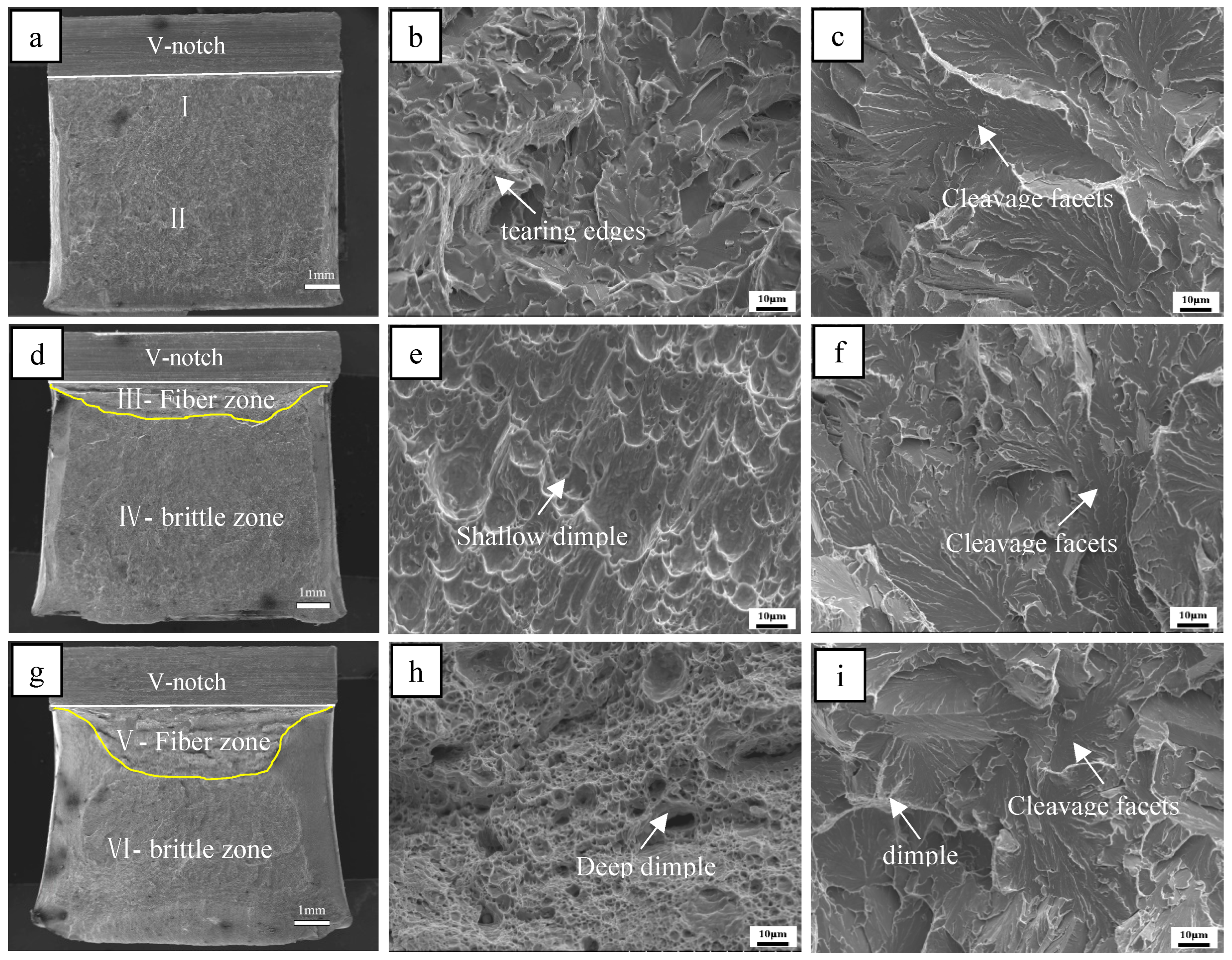
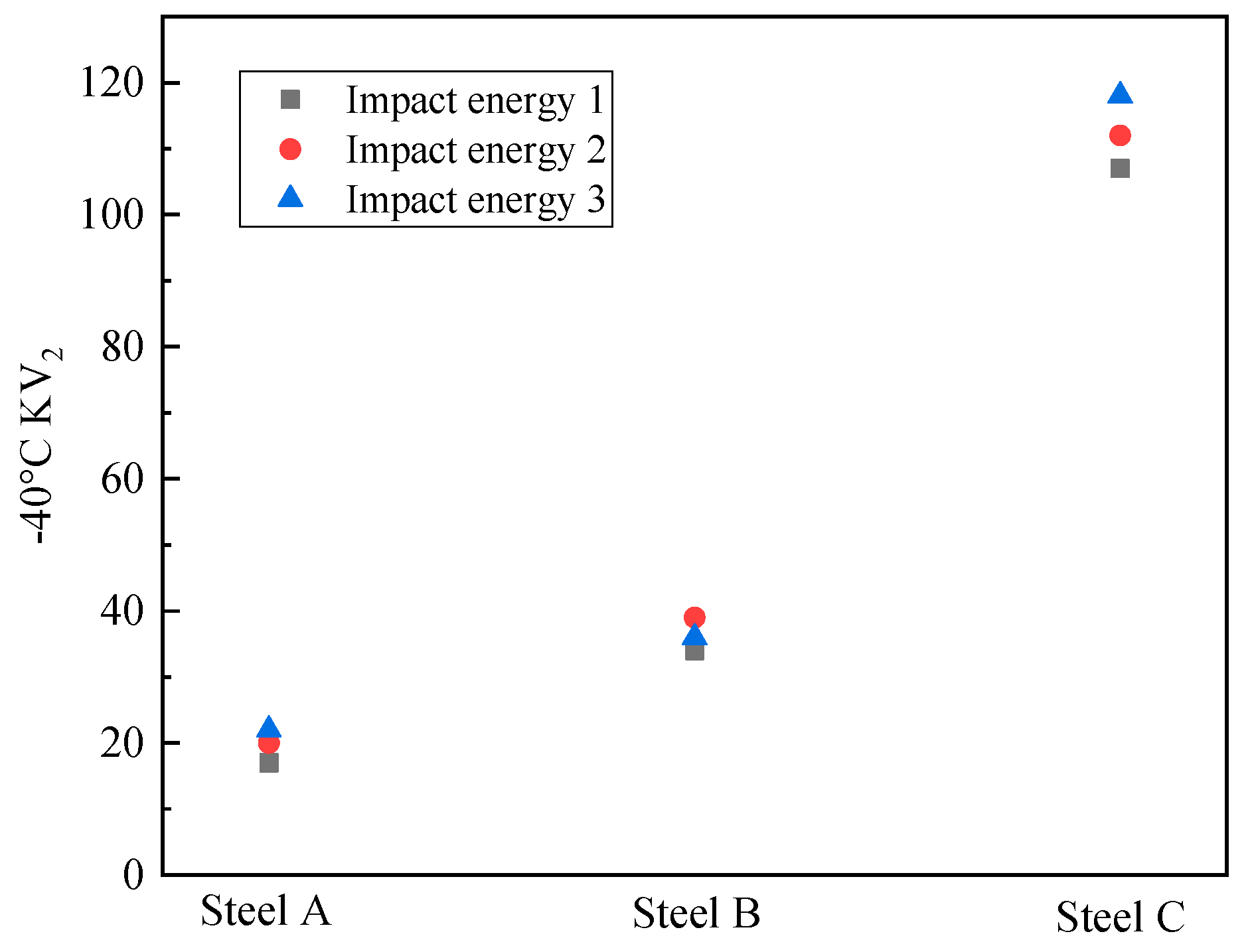
3.2. Impact Toughness of the Simulated Specimens
4. Discussion
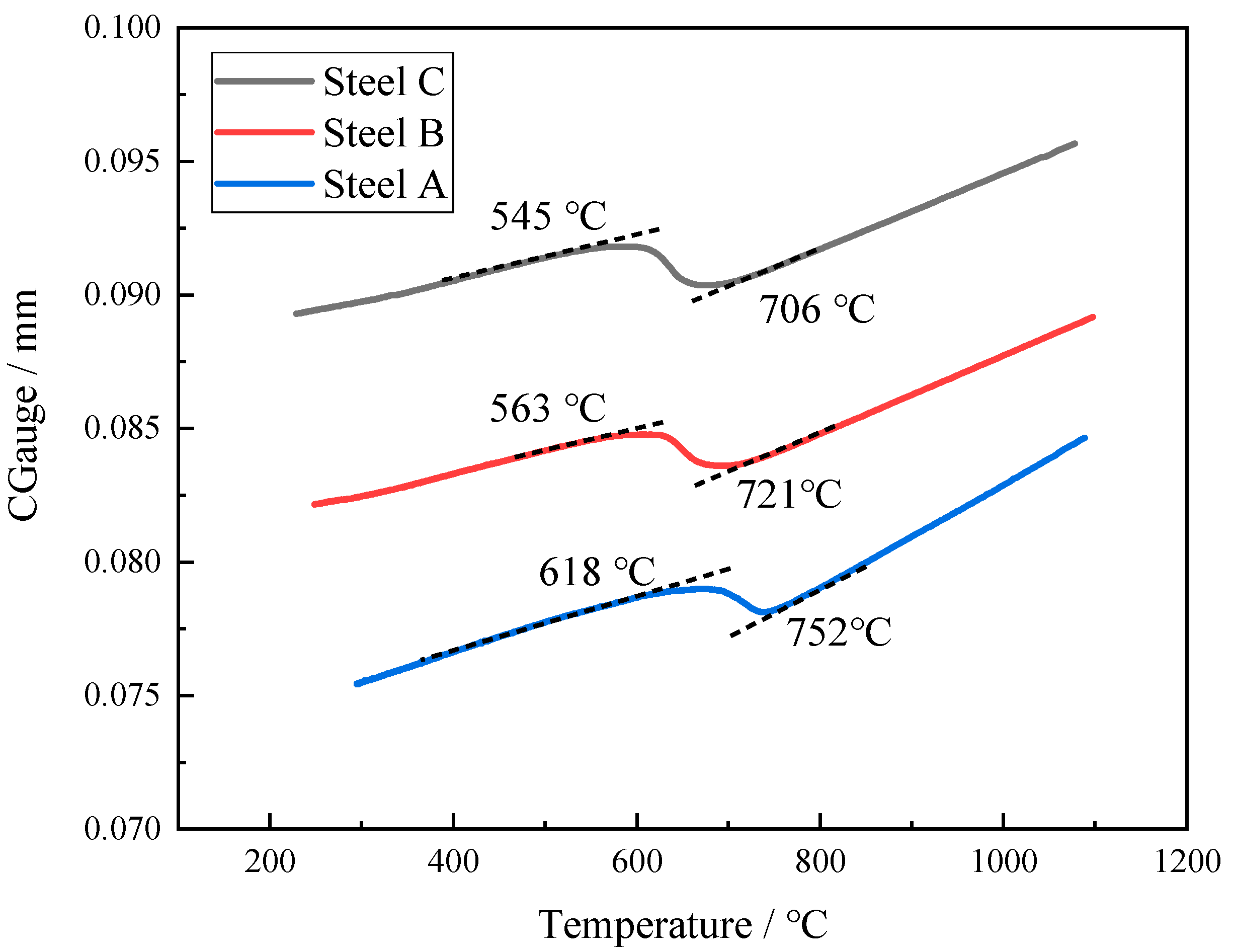
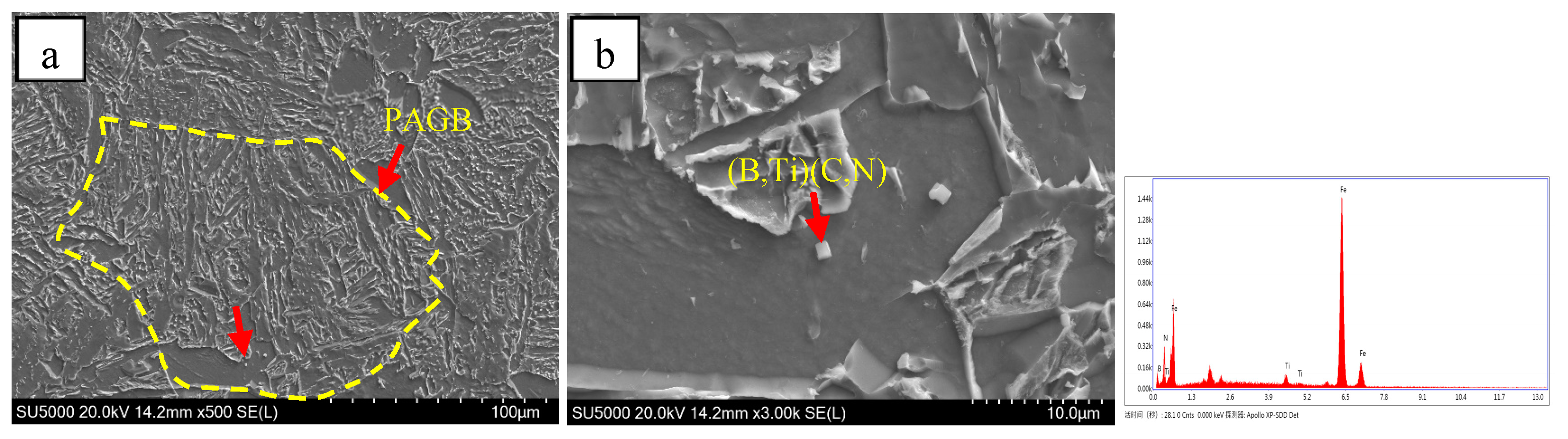
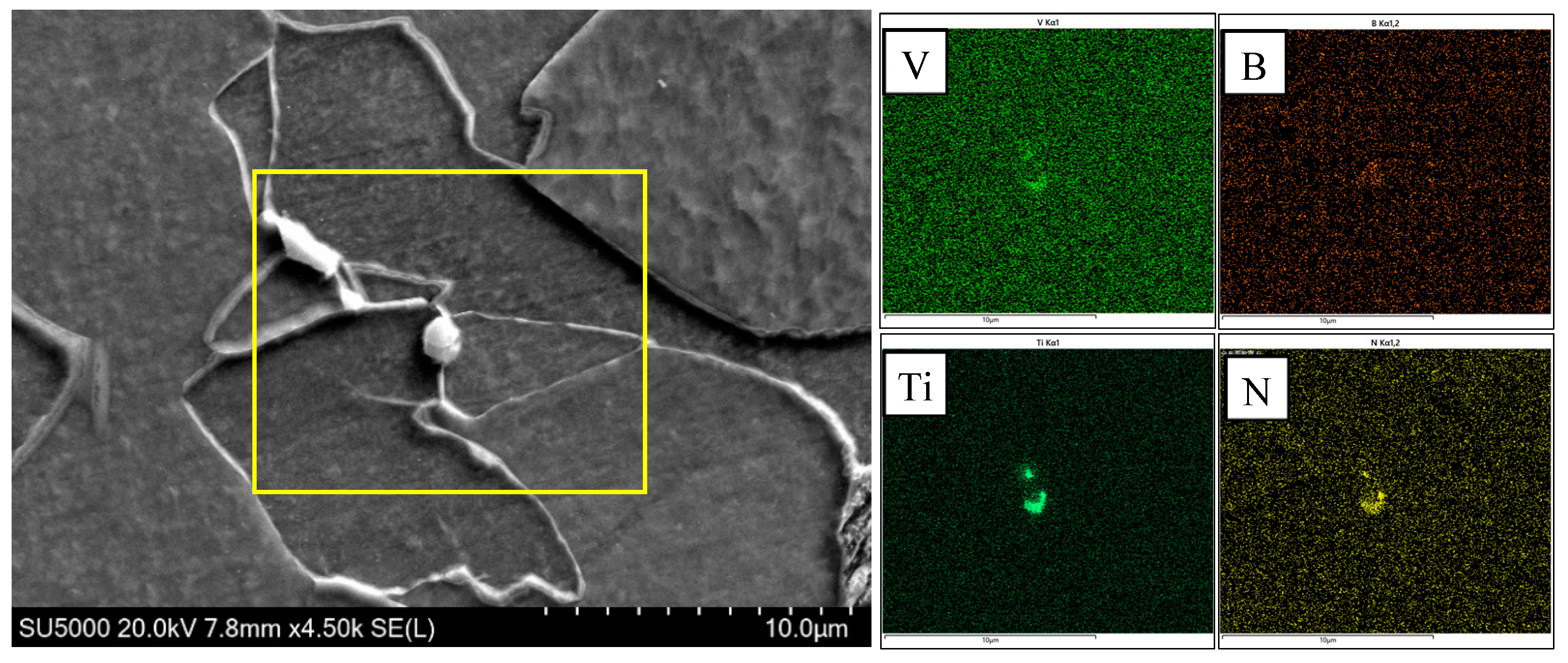
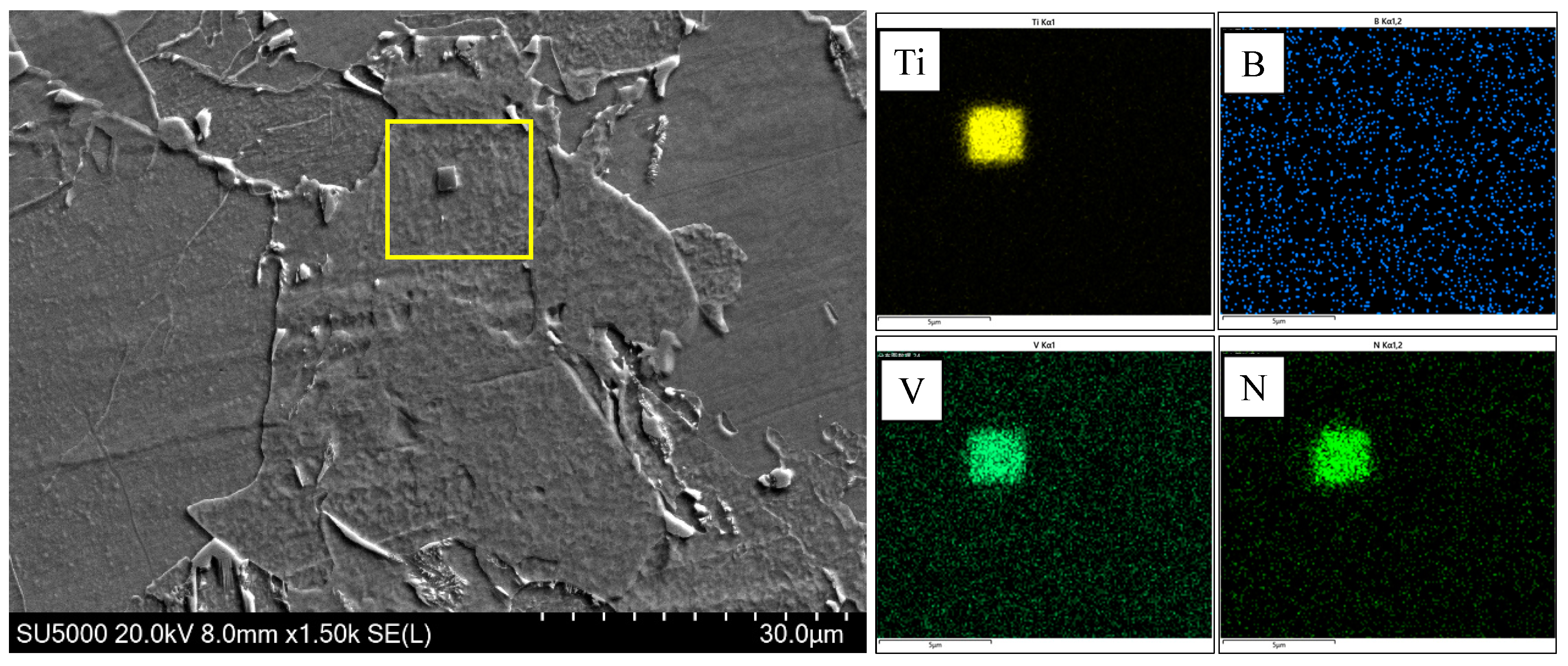
4.1. The Effect of Mo and B on Microstructure
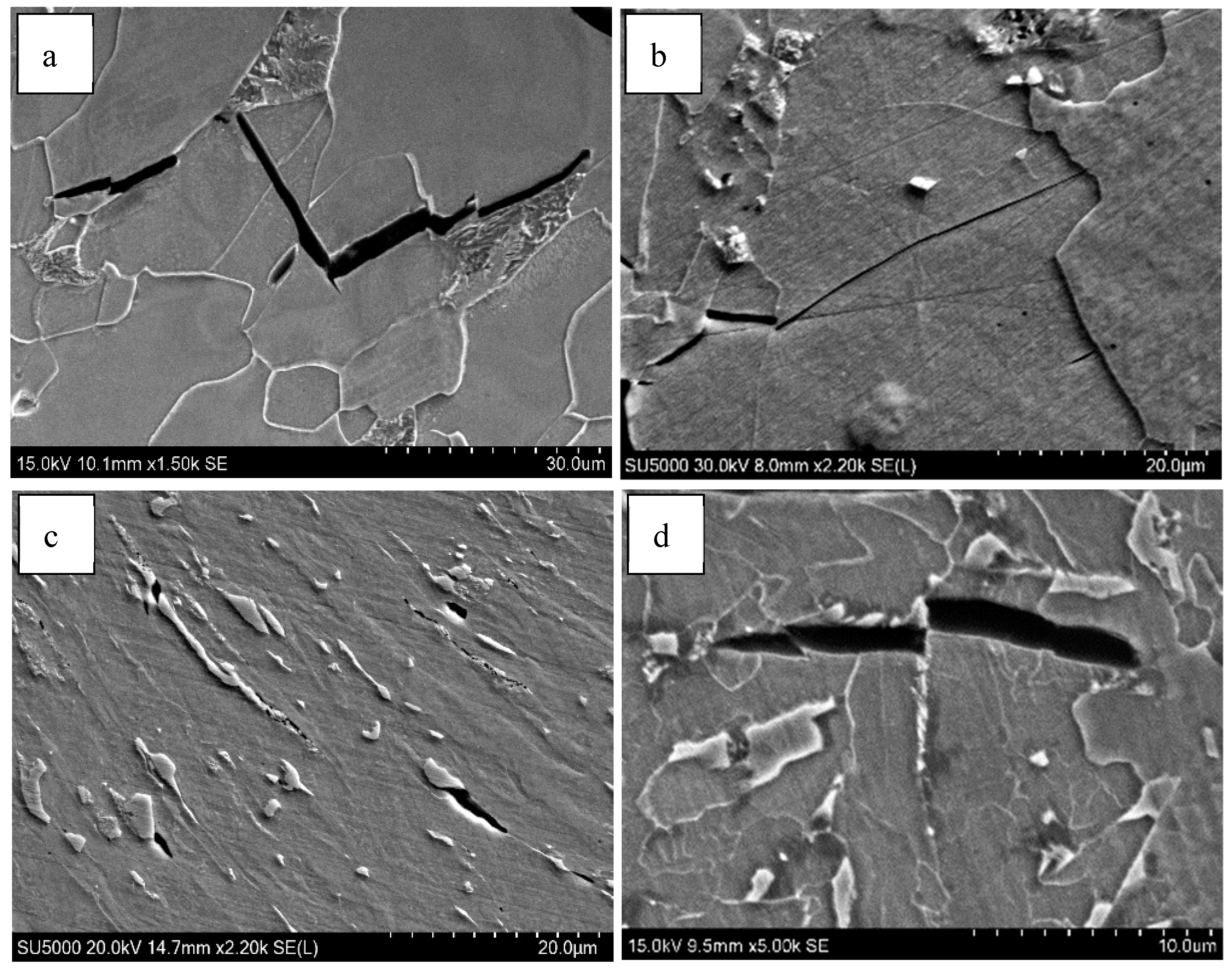
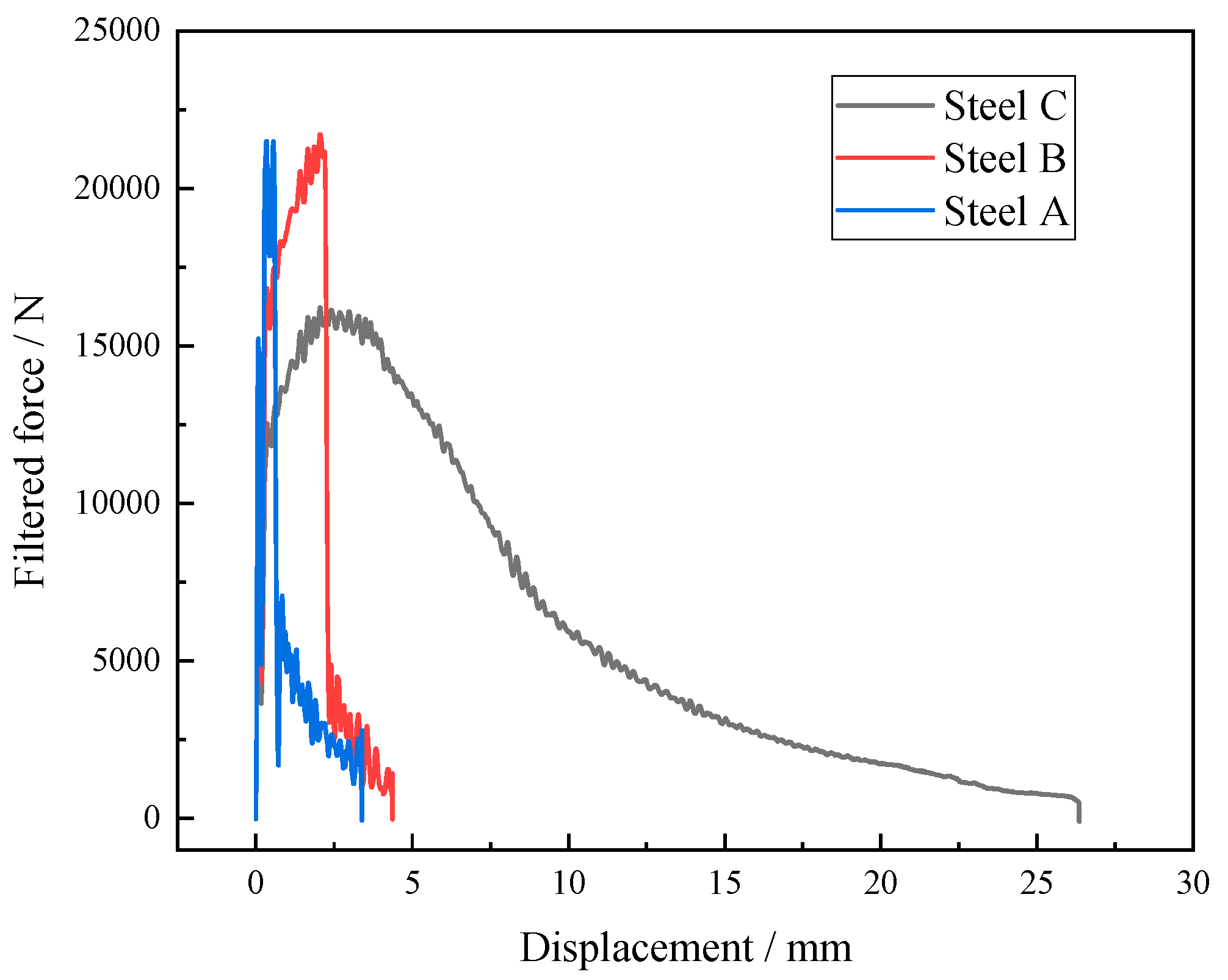
4.2. Effect of Ferrite Morphology on Impact Toughness
5. Conclusions
- Adding 0.28% Mo element to the V-Ti micro-alloy steel significantly reduces the Ar3 from 752 °C to 721 °C and delays the transformation of austenite, and the microstructure of the CGHAZ changes from PF + DP to GB + a small amount of AF.
- When Mo and B elements are added together, B segregated at the grain boundary and combined with N in the steel and precipitates on the Ti(C,N) particles to form composite (B,Ti)(C,N) particles. The (B,Ti)(C,N) particles at the grain boundary act as nucleation sites of ferrite, and the ferritic transformation occurs preferentially at the austenite grain boundary. The formation of ferrite occupies the nucleation position of bainite and inhibits the transformation of GB, thus creating the conditions for the nucleation and growth of ferrite on the precipitated particles in the austenite grain. The microstructure of the CGHAZ changes from GB + a little AF to a small amount of PF + a large amount of AF, which makes the microstructure of the CGHAZ refined, and the mean grain size decreases from 10.1 μm to 4.2 μm.
- The impact toughness of the CGHAZ of the test steel was significantly improved from 20 J to 111 J by adding Mo and B. Meanwhile, the fracture behavior changed from brittle fracture to ductile fracture, which could be attributed to a decrease in the size of the hard constituents and the microstructure refinement and the good deformation ability of acicular ferrite.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yang, Y.L.; Jia, X.; Ma, Y.X.; Wang, P.; Zhu, F.X.; Yang, H.F.; Wang, C.; Wang, S.G. Effect of Nb on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties between Base Metal and High Heat Input Coarse-Grain HAZ in a Ti-Deoxidized Low Carbon High Strength Steel. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2022, 18, 2399–2412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.T.; Yang, J.; Zhang, Y.H.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Chen, Y.L.; Xu, L.Y.; Li, R.B. Inclusions and Microstructures in Coarse-Grained Heat-Affected Zone of Al–Ti–Ca Deoxidized Shipbuilding Steels with Different Al Contents after High-Heat Input Welding. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2024, 30, 174–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Leng, J.; Wang, C. On the Heterogeneous Microstructure Development in the Welded Joint of 12MnNiVR Pressure Vessel Steel Subjected to High Heat Input Electrogas Welding. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2019, 35, 1747–1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Du, L.X.; Wang, J.J.; Gao, C.R. Effect of Welding Heat Input on Microstructures and Toughness in Simulated CGHAZ of V–N High Strength Steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2013, 577, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Xin, W.B.; Ge, Z.W.; Luo, G.P.; Peng, J. Effect of High Heat Input Welding on the Microstructures, Precipitates and Mechanical Properties in the Simulated Coarse Grained Heat Affected Zone of a Low Carbon Nb-V-Ti-N Microalloyed Steel. Mater. Charact. 2023, 199, 112849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, M.; Fan, H.; Shi, G.H.; Wang, L.P.; Wang, Q.M.; Wang, Q.F.; Liu, R.P. Effect of Welding Heat Input on Microstructure and Impact Toughness in the Simulated CGHAZ of Low Carbon Mo-V-Ti-N-B Steel. Metals 2021, 11, 1997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.; Wang, R.; Su, H.; Chai, F.; Wang, Q.; Yang, C. Effect of Nitrogen Content on the Second Phase Particles in V–Ti Microalloyed Shipbuilding Steel during Weld Thermal Cycling. Mater. Des. 2016, 96, 241–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, H.B.; Shi, G.H.; Peng, T.; Wang, Q.M.; Wang, L.P.; Wang, Q.F.; Zhang, F.C. N-Induced Microstructure Refinement and Toughness Improvement in the Coarse Grain Heat-Affected Zone of a Low Carbon Mo–V–Ti–B Steel Subjected to a High Heat Input Welding Thermal Cycle. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2021, 824, 141799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Mateo, C.; Capdevila, C.; Caballero, F.G.; de Andrés, C.G. Influence of V Precipitates on Acicular Ferrite Transformation Part 1: The Role of Nitrogen. ISIJ Int. 2008, 48, 1270–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, B.; Shi, G.H.; Wang, Q.M.; Zhao, L.Y.; Fan, H.B.; Tang, Y.C.; Wang, W.; Wang, Q.F.; Liu, R.P. Elucidating the Heat Input on CGHAZ Microstructure and Its Irregular Effect on Impact Toughness for a Novel V–N Microalloying Weathering Steel. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2023, 25, 5888–5906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.R.; Yang, C.F.; Wang, R.Z.; Su, H.; Chai, F.; Chu, J.F.; Wang, Q.F. Effect of Nitrogen on the Microstructures and Mechanical Properties in Simulated CGHAZ of Vanadium Microalloyed Steel Varied with Different Heat Inputs. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2016, 649, 270–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, L.; Wu, K.M. New Insights into Intragranular Ferrite in a Low-Carbon Low-Alloy Steel. Acta Mater. 2009, 57, 3754–3762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, J.; Lin, Z.; Bin, G.; Pinghe, L.; Aihua, W.; Changsheng, X. Influence of Mo Content on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of High Strength Pipeline Steel. Mater. Des. 2004, 25, 723–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, K.; Matsuda, S.; Haze, T.; Chijiiwa, R.; Mimura, H. A Newly Developed Ti-Oxide Bearing Steel Having High HAZ Toughness. In Residual and Unspecified Elements in Steel; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Zafra, A.; Álvarez, G.; Belzunce, J.; Alegre, J.M.; Rodríguez, C. Fracture Toughness of Coarse-Grain Heat Affected Zone of Quenched and Tempered CrMo Steels with Internal Hydrogen: Fracture Micromechanisms. Eng. Fract. Mech. 2021, 241, 107433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tweed, J.H.; Knott, J.F. Micromechanisms of Failure in C-Mn Weld Metals. Acta Metall. 1987, 35, 1401–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujishiro, Y.; Hashimoto, T.; Ohtani, H. Influence of Boron and Nitrogen Contents on Strength and Toughness of Controlled-Rolled Low Carbon-Boron Steel. Scr. Metall. 1988, 22, 431–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Kang, Y.; Lee, C. Variation in Microstructures and Mechanical Properties in the Coarse-Grained Heat-Affected Zone of Low-Alloy Steel with Boron Content. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2013, 559, 178–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Y.; Xiao, F.; Zhang, J.; Shan, Y.; Wei, W.; Yang, K. In Situ TEM Study of the Effect of M/A Films at Grain Boundaries on Crack Propagation in an Ultra-Fine Acicular Ferrite Pipeline Steel. Acta Mater. 2006, 54, 435–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, C.; Mahapatra, M.M.; Kumar, P.; Thakre, J.; Saini, N. Role of Evolving Microstructure on the Mechanical Behaviour of P92 Steel Welds Joint in As-Welded and Post Weld Heat Treated State. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2018, 263, 241–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Dong, J.; Liu, Y.; Liu, C.; Yu, L.; Huang, Y.; Li, H. Austenite to Polygonal-Ferrite Transformation and Carbide Precipitation in High Strength Low Alloy Steel. Int. J. Mater. Res. 2017, 108, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, K.-T.; Hwang, S.W.; Ji, J.H.; Lee, C.H. Inclusions Nucleating Intragranular Polygonal Ferrite and Acicular Ferrite in Low Alloyed Carbon Manganese Steel Welds. Met. Mater. Int. 2011, 17, 349–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Li, Z.; Yang, G.; Liu, X.; Du, X.; Shi, W.; Yang, S. Effect of Mo addition on microstructure and mechanical properties of Cu-12.5Ni-5Sn alloy. J. Mater. Today Commun. 2024, 41, 110407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, Y.-C.; Kim, S.-J.; Ohmori, Y. Morphology and Growth Process of Bainitic Ferrite in Steels. Met. Mater. Int. 1998, 4, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takayama, N.; Miyamoto, G.; Furuhara, T. Effects of Transformation Temperature on Variant Pairing of Bainitic Ferrite in Low Carbon Steel. Acta Mater. 2012, 60, 2387–2396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Ponge, D.; Choi, P.; Raabe, D. Atomic Scale Investigation of Non-Equilibrium Segregation of Boron in a Quenched Mo-Free Martensitic Steel. Ultramicroscopy 2015, 159, 240–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, J.; Ishikawa, K.; Kawakami, K.; Fujioka, M.; Kubota, N. Atomic-Scale Study on Segregation Behavior at Austenite Grain Boundaries in Boron- and Molybdenum-Added Steels. Acta Mater. 2017, 133, 41–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.; Wang, J.; Chai, X.; Wang, S.; Chen, G.; Wang, R. Effect of Boron on Intragranular Ferrite Nucleation Mechanism in Coarse Grain Heat-Affected Zone of High-Nitrogen Steel. Mater. Lett. 2020, 258, 126819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilman, M.N.; Cochrane, R.C.; Evans, G.M. Effect of Nitrogen and Boron on the Development of Acicular Ferrite iN Reheated C-Mn-Ti Steel Weld Metals. Weld. World 2013, 56, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z. A Brief Introduction to Bainitic Transformation. Heat Treat. 2006, 2, 1–20. [Google Scholar]
- Tong, M.; Di, X.; Li, C.; Wang, D. Toughening mechanism of inter-critical heat-affected zone in a 690 MPa grade rack plate steel. Mater. Charact. 2018, 144, 631–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Wang, Q.; Shi, G.; Yang, X.; Qiao, M.; Wu, J.; Zhang, F. In-depth understanding of the relationship between dislocation substructure and tensile properties in a low-carbon microalloyed steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2022, 854, 143681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, D.; Karjalainen, L.; Qian, B.; Chen, X. Cleavage Fracture Model for Granular Bainite in Simulated Coarse-Grained Heat-Affected Zones of High-Strength Low-Alloyed Steels. JSME Int. J. Ser. A Solid Mech. Mater. Eng. 1997, 40, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Wang, X.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, N.; Wang, C.; Yuan, G. An Improved Toughness Process for High-Temperature Hot-Rolled HSLA Steel via Inclusion-Induced Acicular Ferrite Nucleation. Mater. Lett. 2024, 360, 135969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, S.; Wu, H.-H.; Wang, K.; Wang, S.; Wu, G.; Gao, J.; Yang, X.-S.; Zhu, J.; Mao, X. The Microstructure Evolution and Influence Factors of Acicular Ferrite in Low Alloy Steels. Comput. Mater. Sci. 2023, 218, 111989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Steel | C | Si | Mn | S | P | Mo | V | Ti | N | B |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 0.077 | 0.20 | 1.50 | 0.006 | 0.007 | - | 0.060 | 0.015 | 0.0091 | - |
| B | 0.065 | 0.293 | 1.55 | 0.002 | 0.004 | 0.28 | 0.067 | 0.017 | 0.0097 | - |
| C | 0.063 | 0.274 | 1.55 | 0.001 | 0.004 | 0.28 | 0.066 | 0.016 | 0.0110 | 0.0011 |
| Experimental Steels | Phase Composition Fraction | Et/J | Ei/J | Ej/J |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Steel A | 78% PF + 22% DP | 20 | 9 | 11 |
| Steel B | 23% PF + 13% AF + 64% GB | 35 | 29 | 6 |
| Steel C | 71% AF + 18% GB + 11% PF | 111 | 23 | 88 |
| Simple | Matrix/GPa | Hard Phase/GPa | Difference/GPa |
|---|---|---|---|
| Steel A | 3.6 | 8.7 | 4.1 |
| Steel C | 3.4 | 6.9 | 3.5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qiao, M.; Fan, H.; Wang, S.; Huang, Y.; Wang, Q.; Liu, R. Effect of Mo and B on Microstructure and Impact Toughness of Coarse Grain Heat-Affected Zone in Low-Carbon V-Ti-N Micro-Alloyed Steel. Materials 2025, 18, 1667. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18071667
Qiao M, Fan H, Wang S, Huang Y, Wang Q, Liu R. Effect of Mo and B on Microstructure and Impact Toughness of Coarse Grain Heat-Affected Zone in Low-Carbon V-Ti-N Micro-Alloyed Steel. Materials. 2025; 18(7):1667. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18071667
Chicago/Turabian StyleQiao, Mingliang, Huibing Fan, Shibiao Wang, Yixin Huang, Qingfeng Wang, and Riping Liu. 2025. "Effect of Mo and B on Microstructure and Impact Toughness of Coarse Grain Heat-Affected Zone in Low-Carbon V-Ti-N Micro-Alloyed Steel" Materials 18, no. 7: 1667. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18071667
APA StyleQiao, M., Fan, H., Wang, S., Huang, Y., Wang, Q., & Liu, R. (2025). Effect of Mo and B on Microstructure and Impact Toughness of Coarse Grain Heat-Affected Zone in Low-Carbon V-Ti-N Micro-Alloyed Steel. Materials, 18(7), 1667. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18071667





