Experimental Study on Cement-Based Materials Modified by Nano-Zinc Oxide and Nano-Zirconia Based on Response Surface Optimization Design
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Nanomaterials, Cement, and Sand
2.2. The Establishment of a Response Surface Model and the Production of the Specimens
2.2.1. Establishment of Response Surface Model
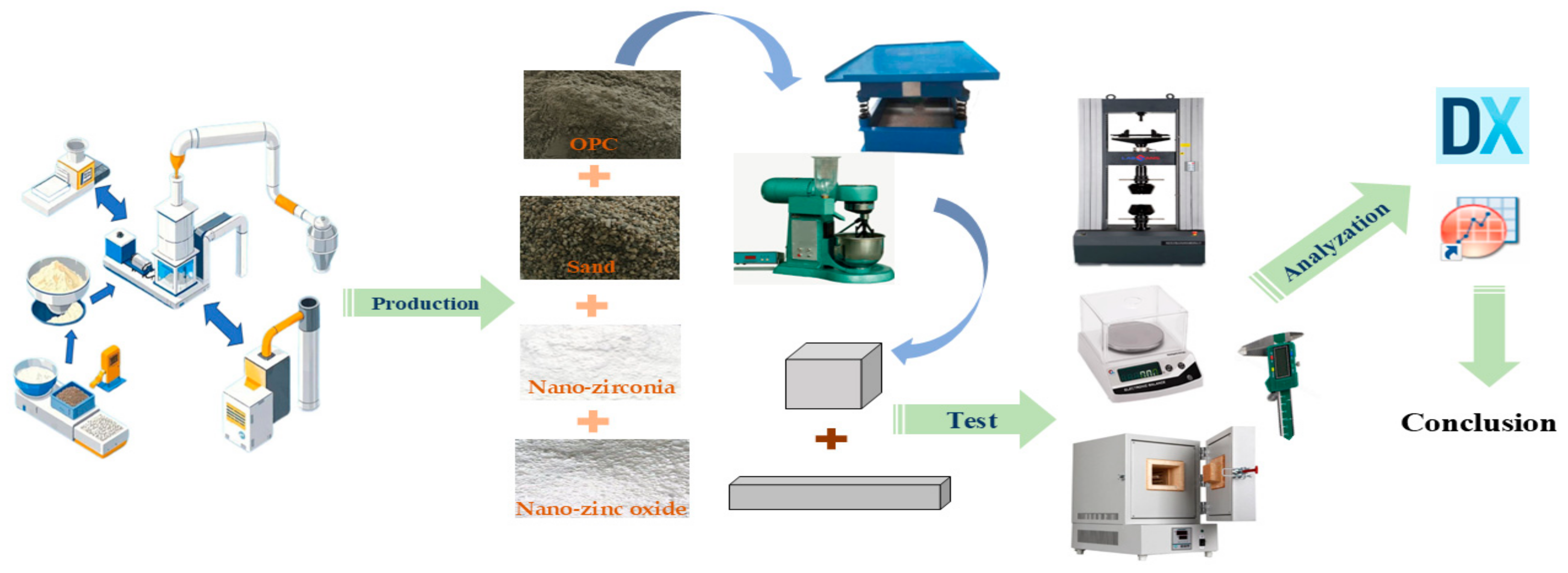
2.2.2. Manufacturing of Specimens
2.3. Experimental Method
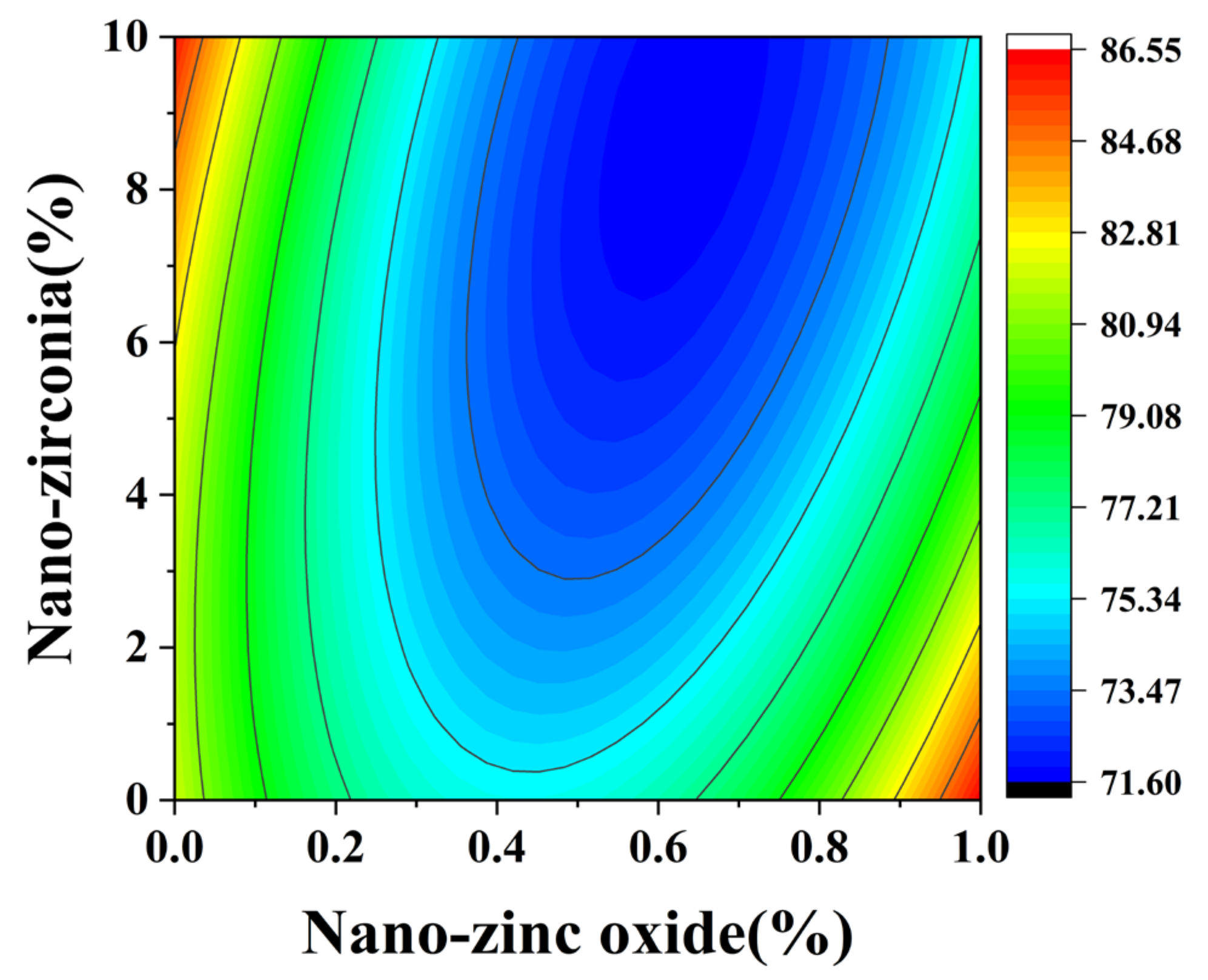
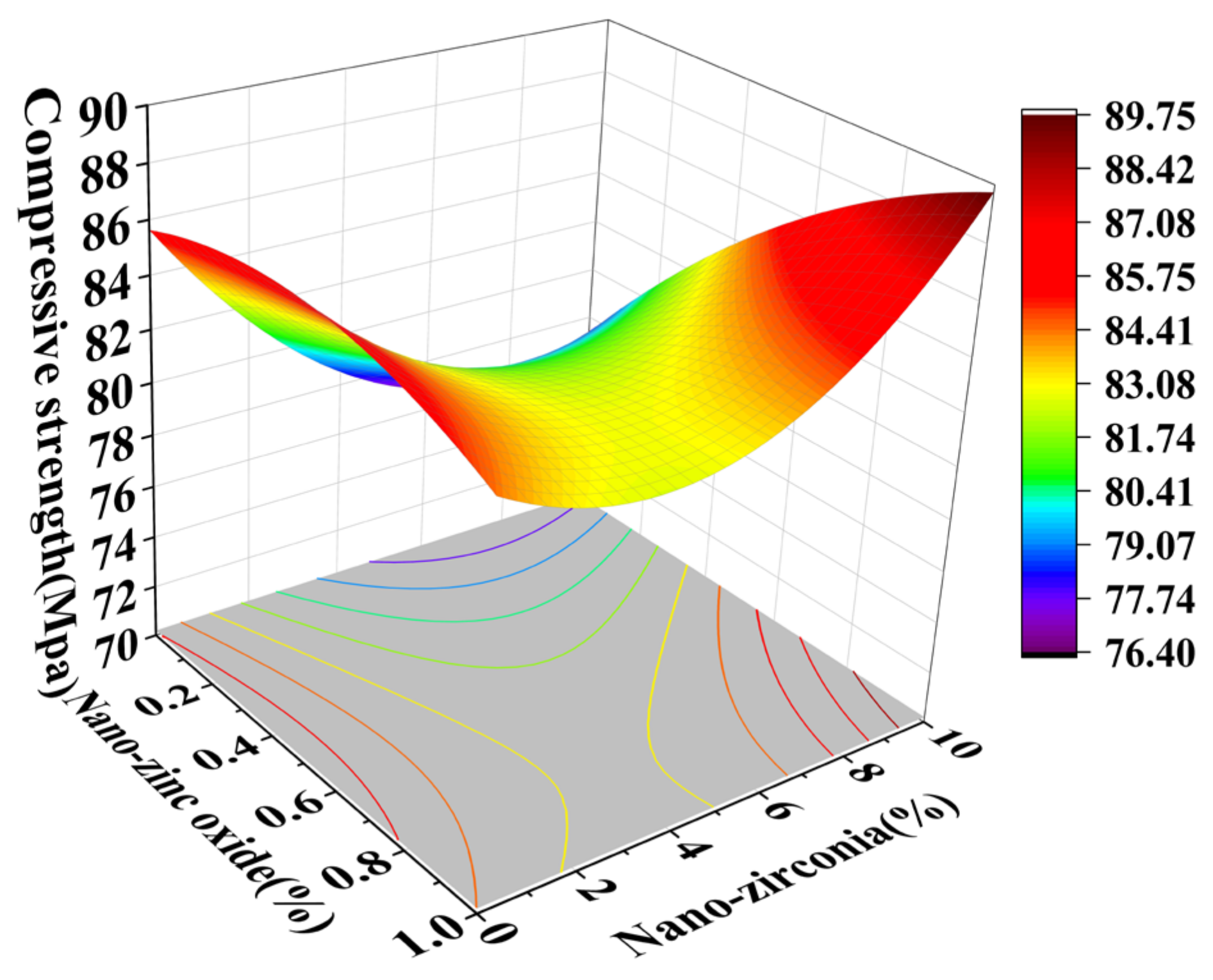
2.3.1. Compressive Strength
2.3.2. Shrinkage Performance
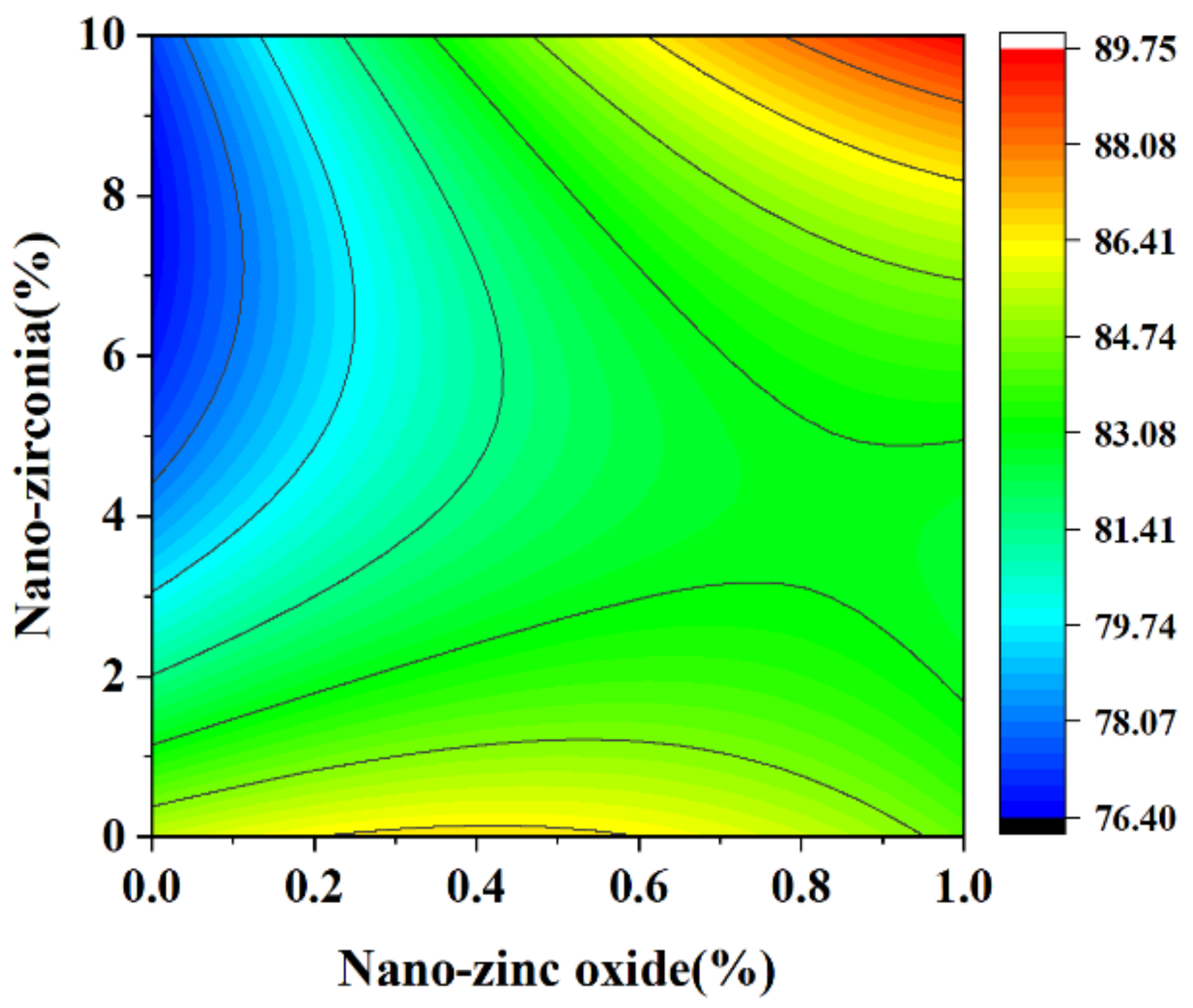
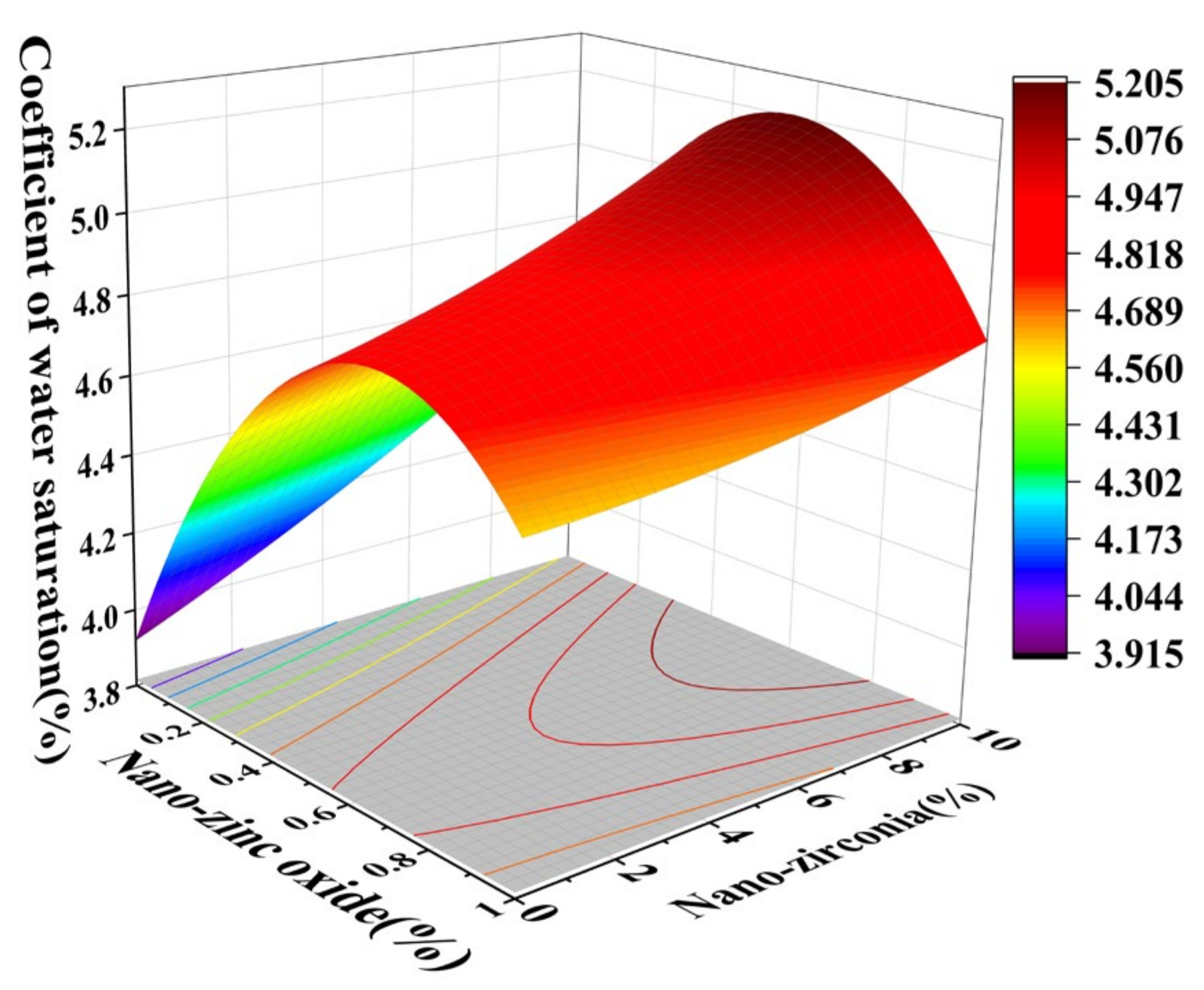
2.3.3. Coefficient of Water Saturation
2.3.4. Contents of Calcium Hydroxide (CH) and Calcium Silicate Hydrate (CSH)
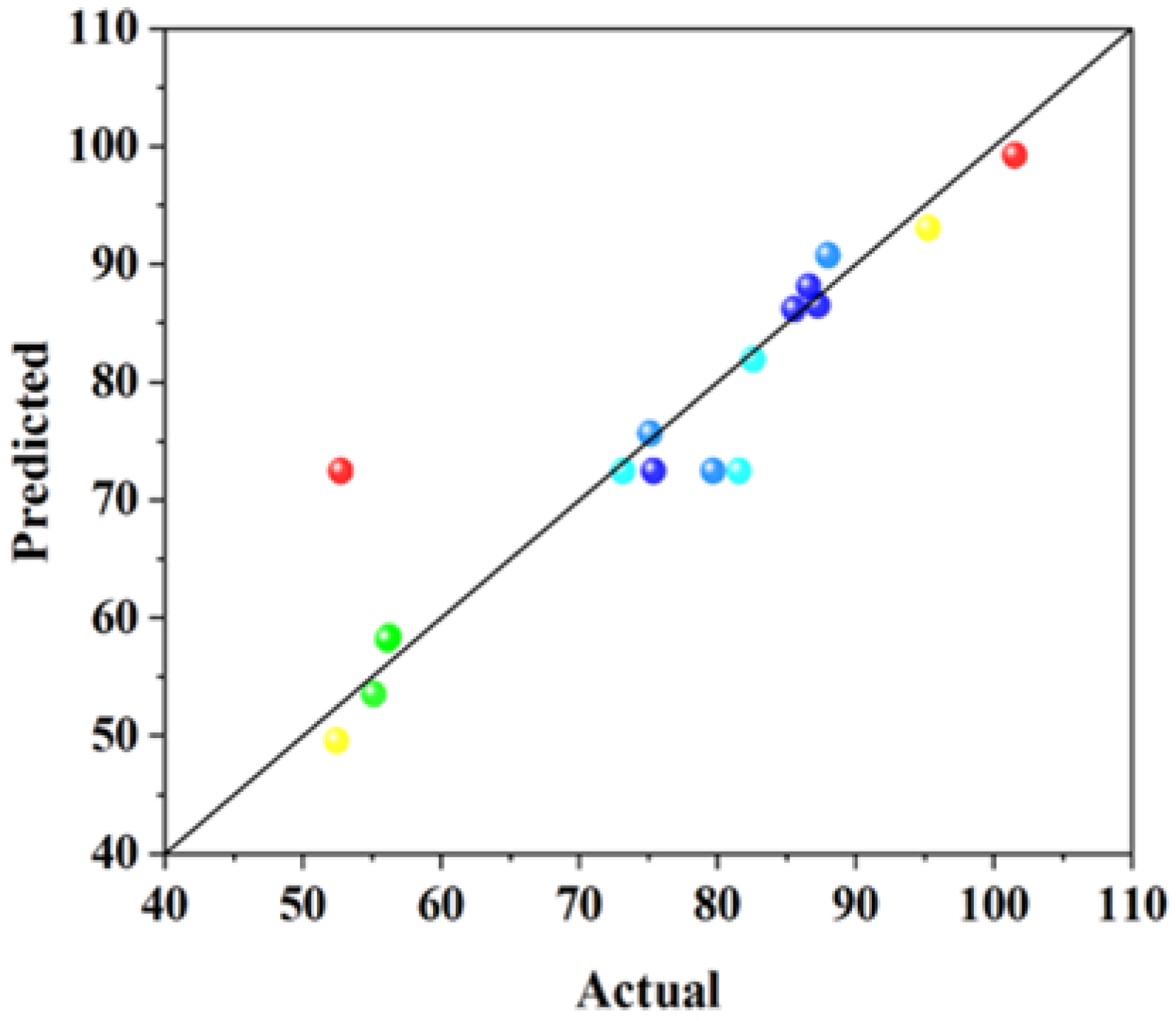
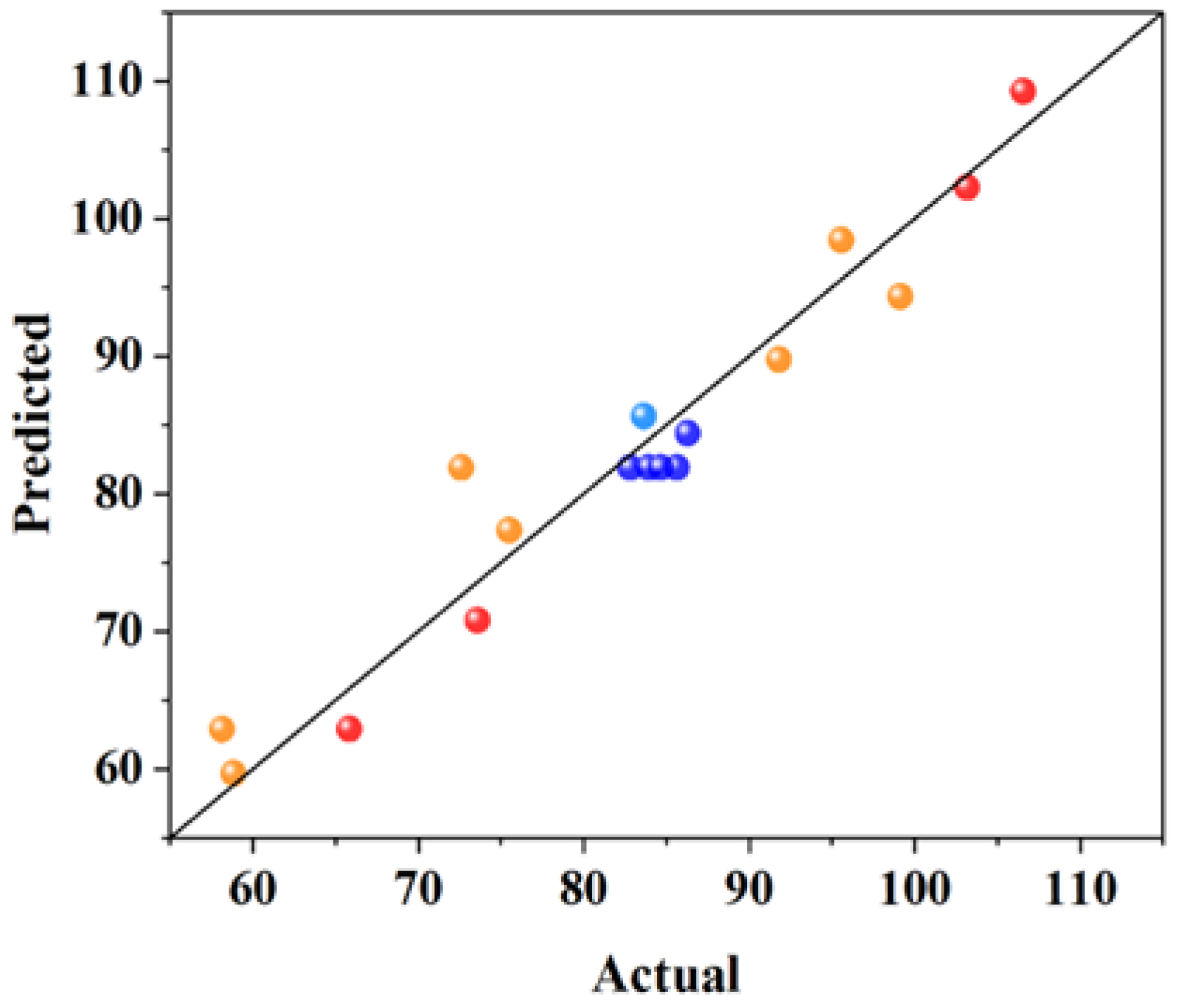
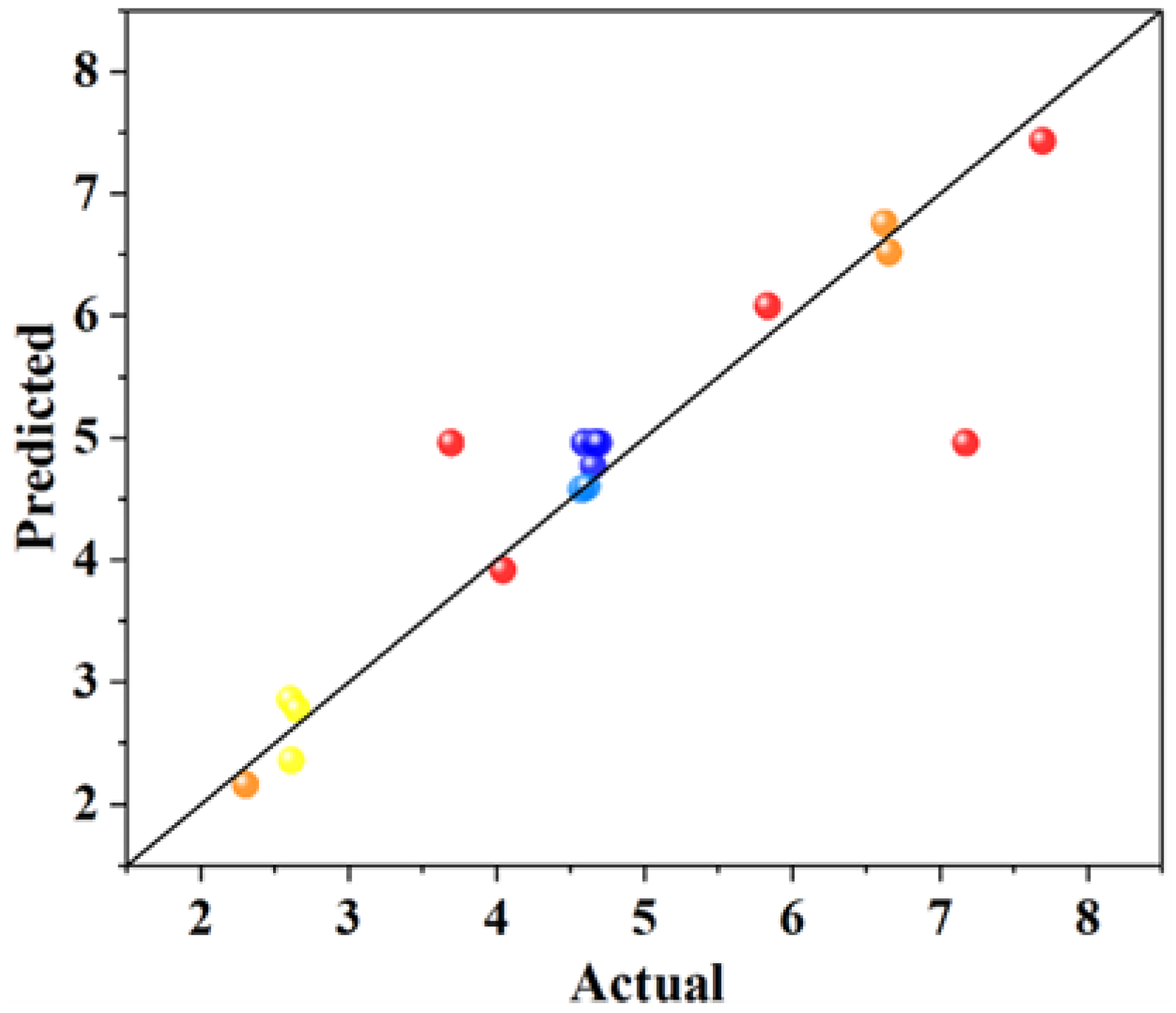
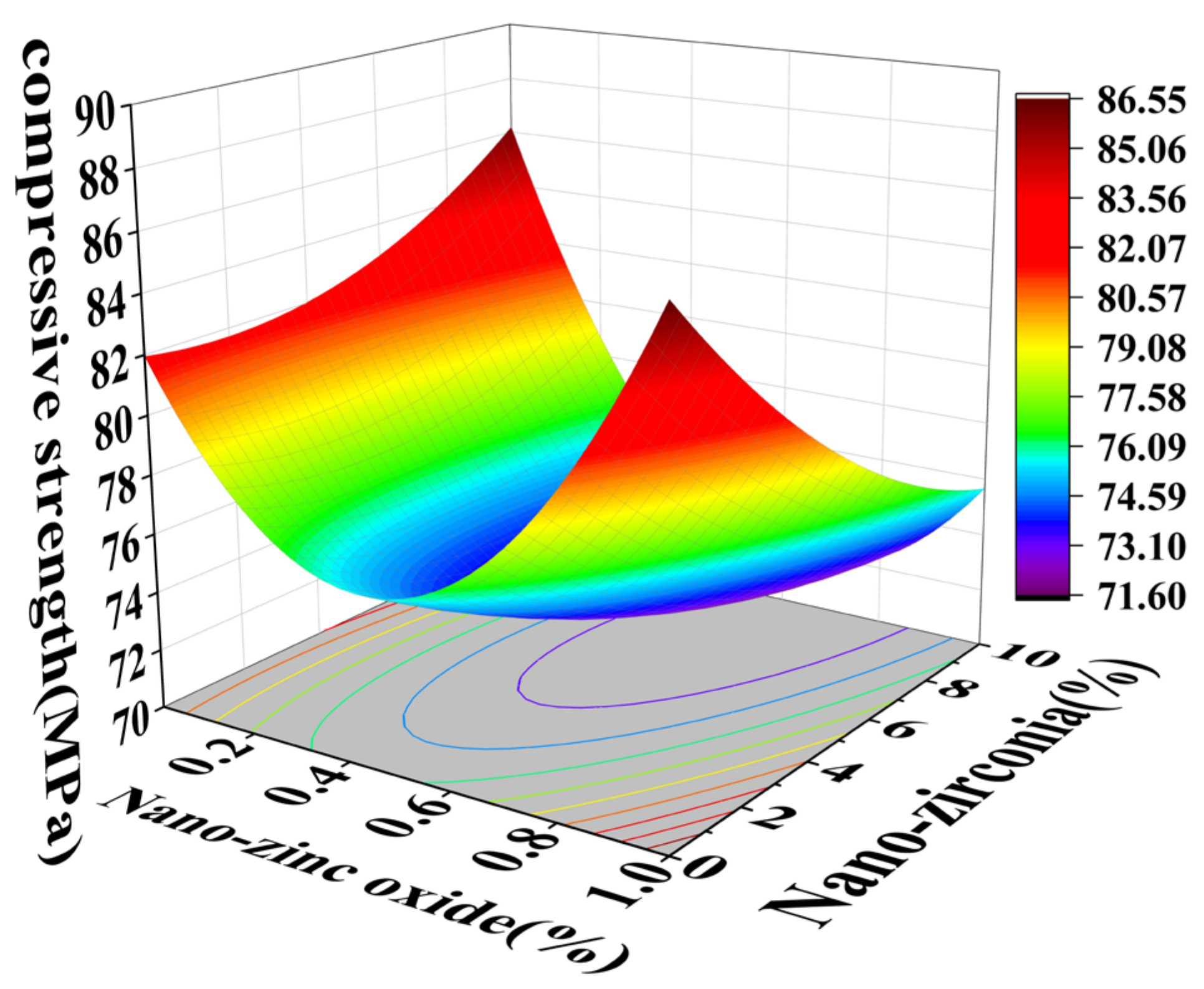
3. Experimental Results and Analysis
BC + 8.43 × A2 + 1.69 × B2 − 3.65 × C2
− 1.59 × A2 + 3.97 × B2 − 0.5167 × C2
0.2475 × BC − 0.525 × A2 + 0.0325 × B2 − 0.095 × C2
× BC + 0.089 × A2 + 0.139 × B2 + 0.1090 × C2
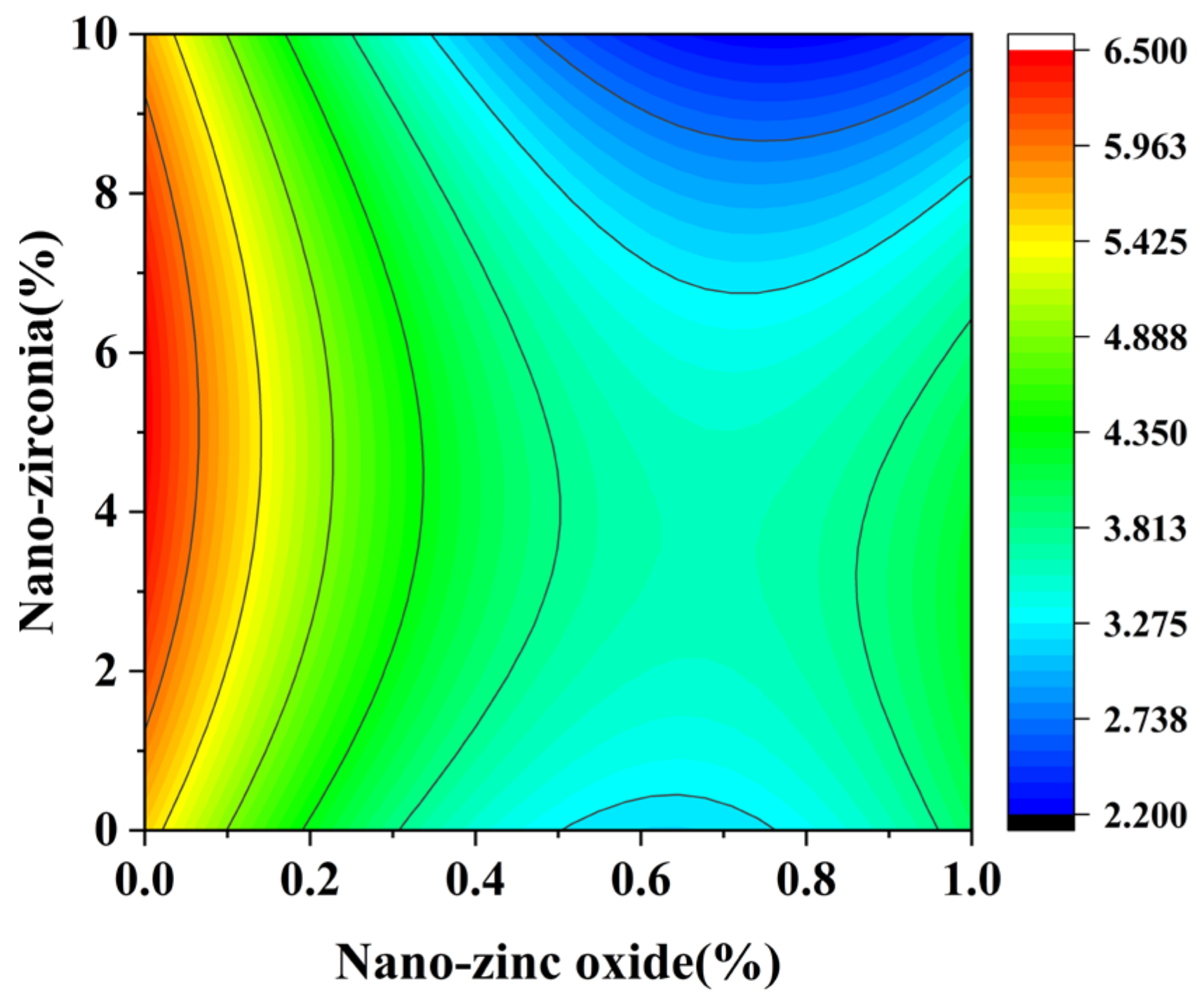
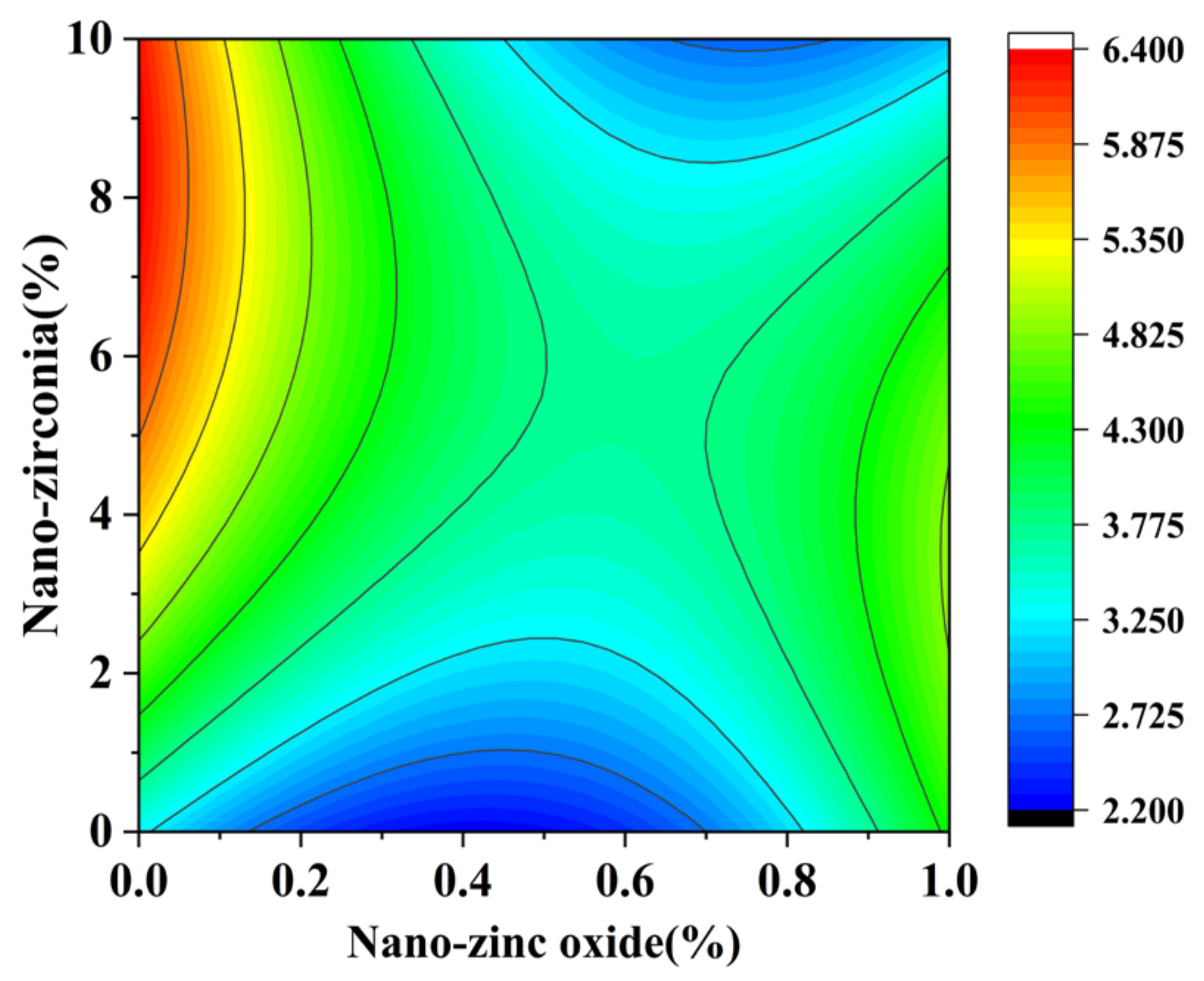
3.1. Compressive Strength Analysis
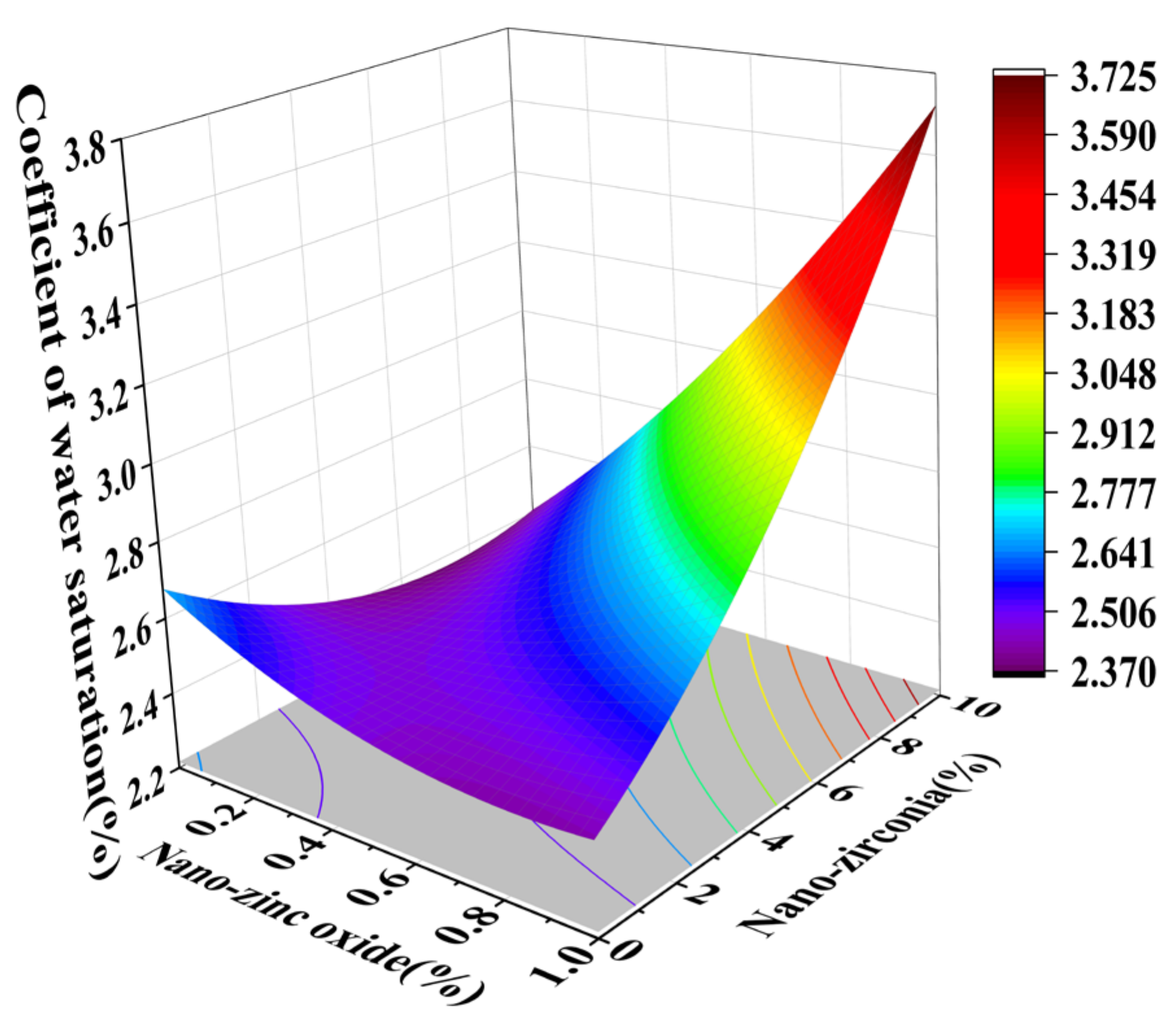
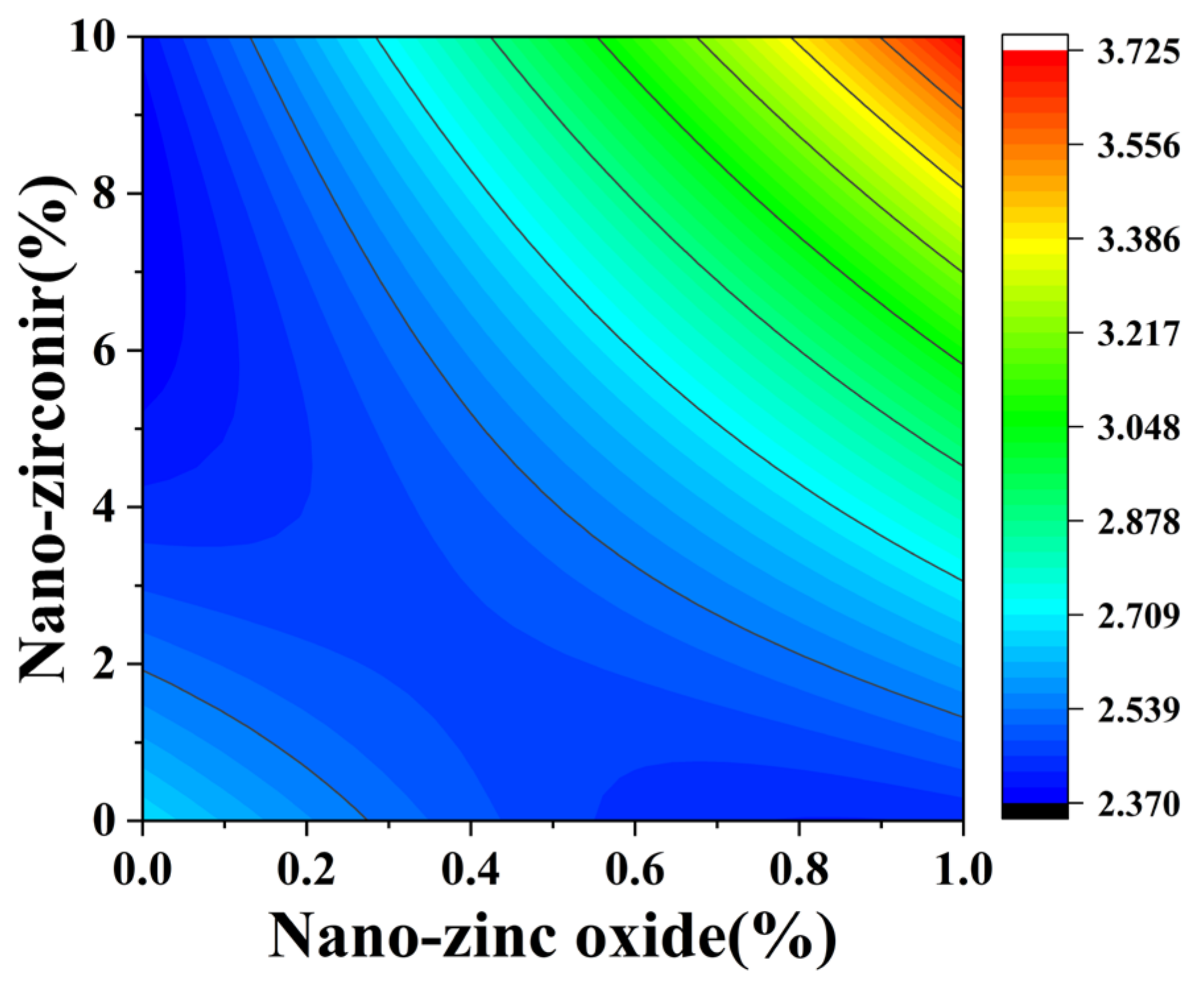
3.2. Coefficient of Water Saturation Analysis
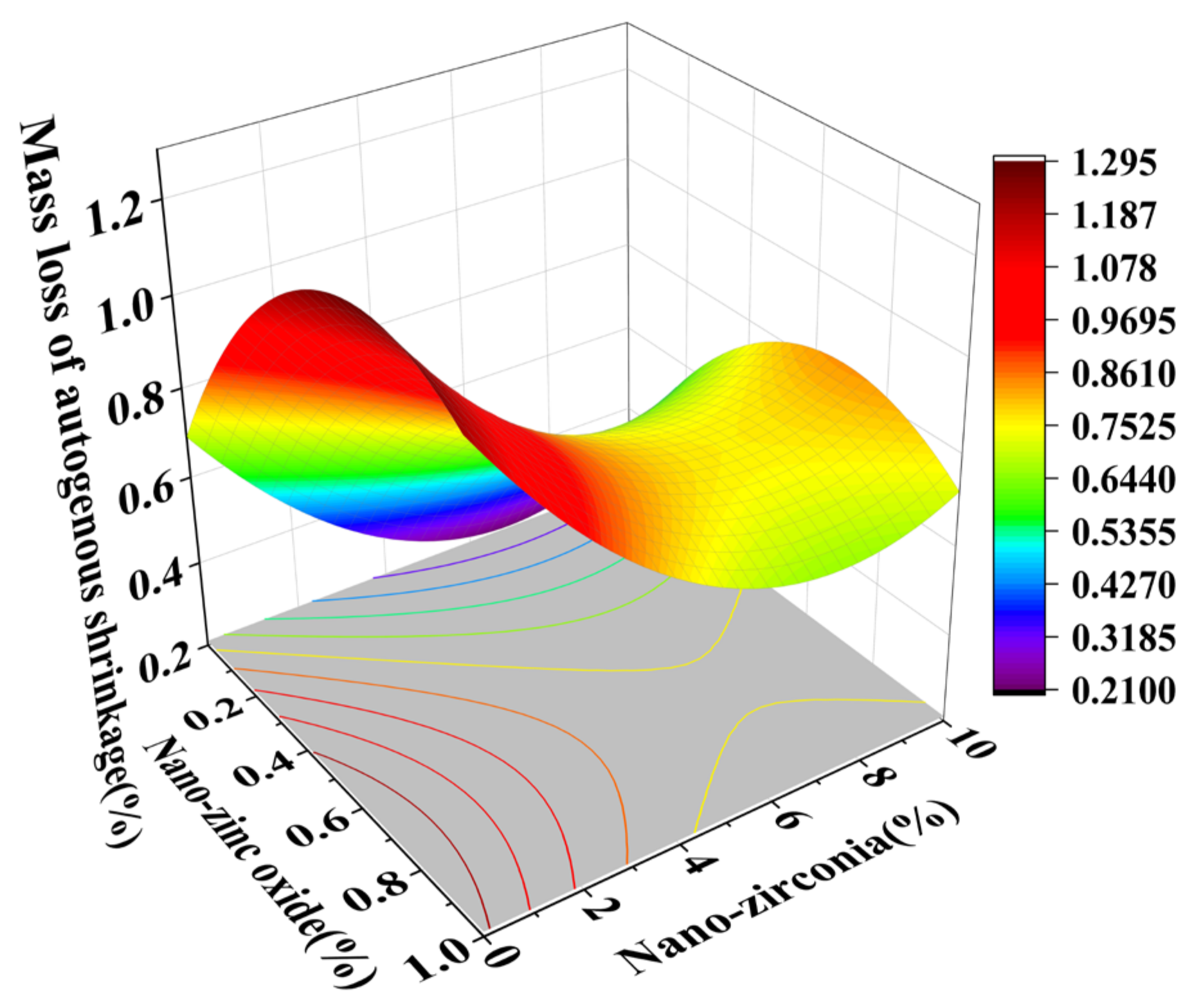
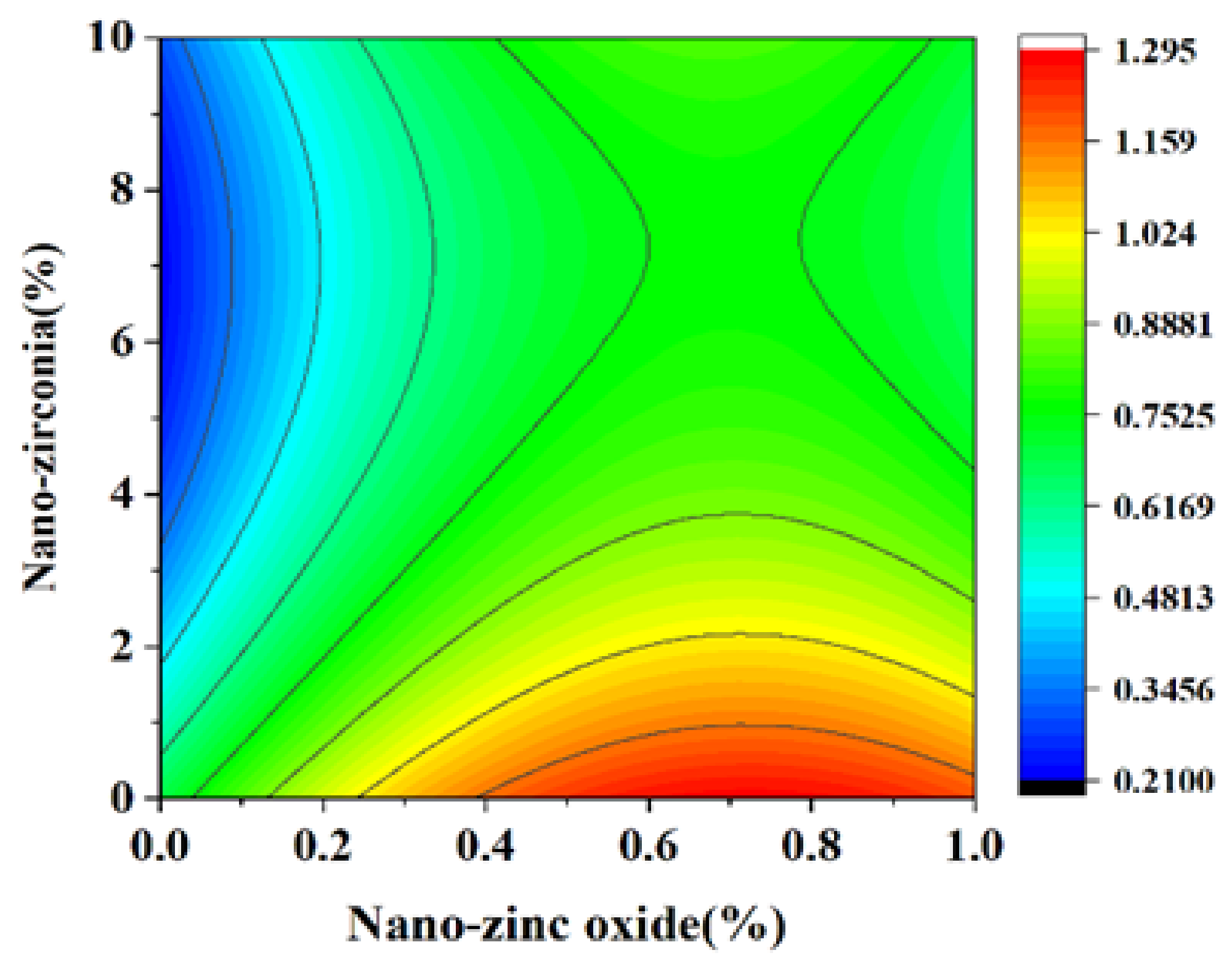
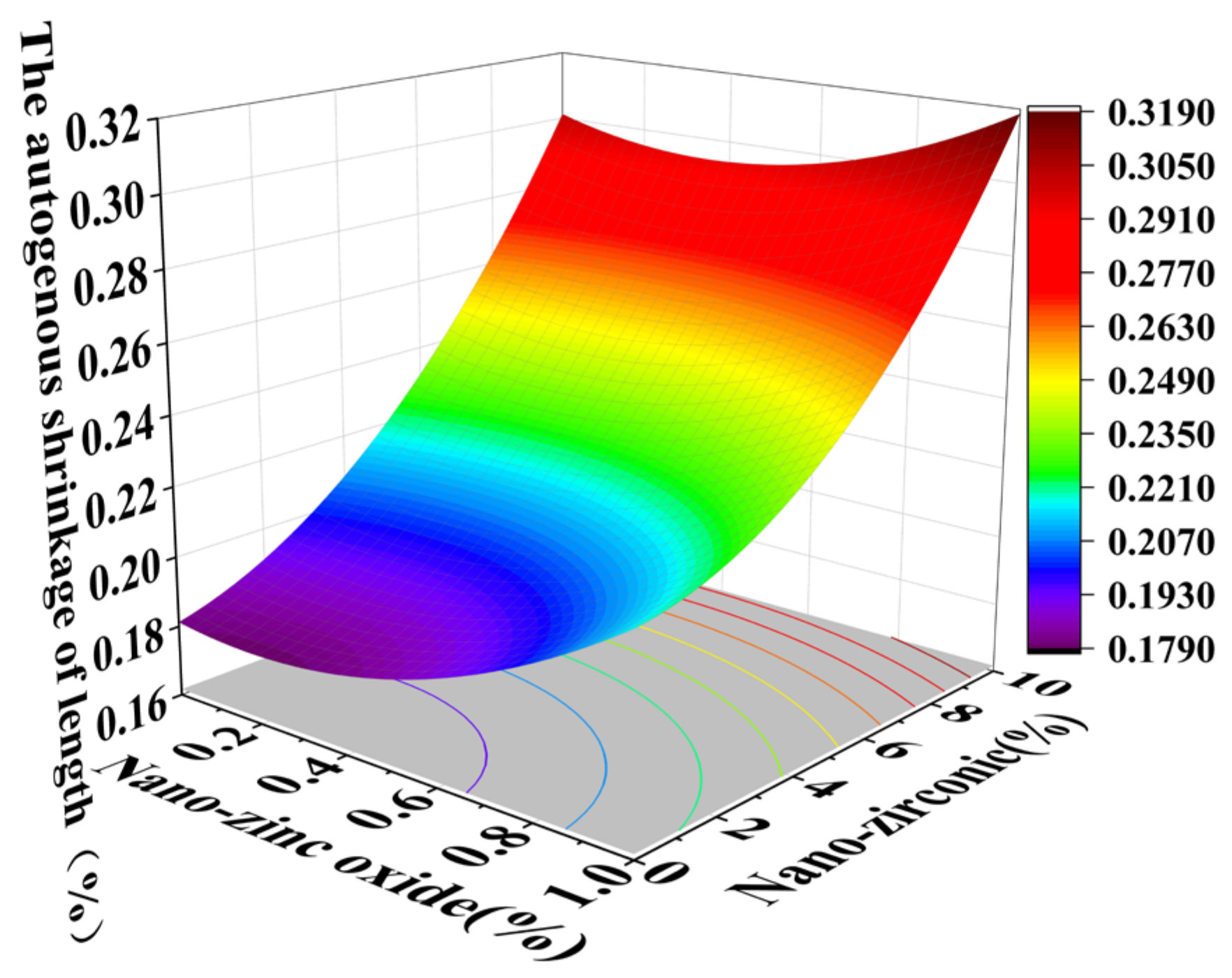
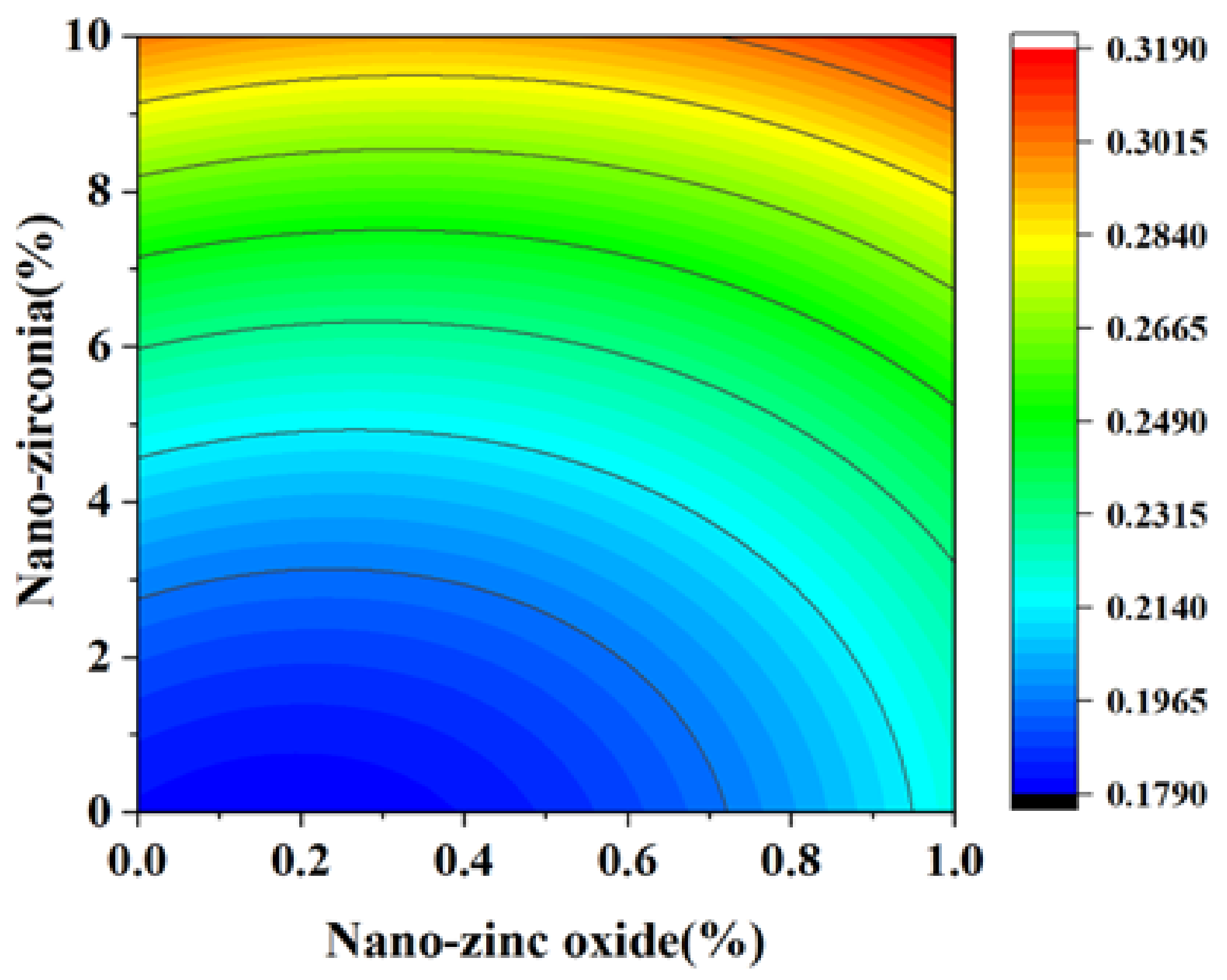
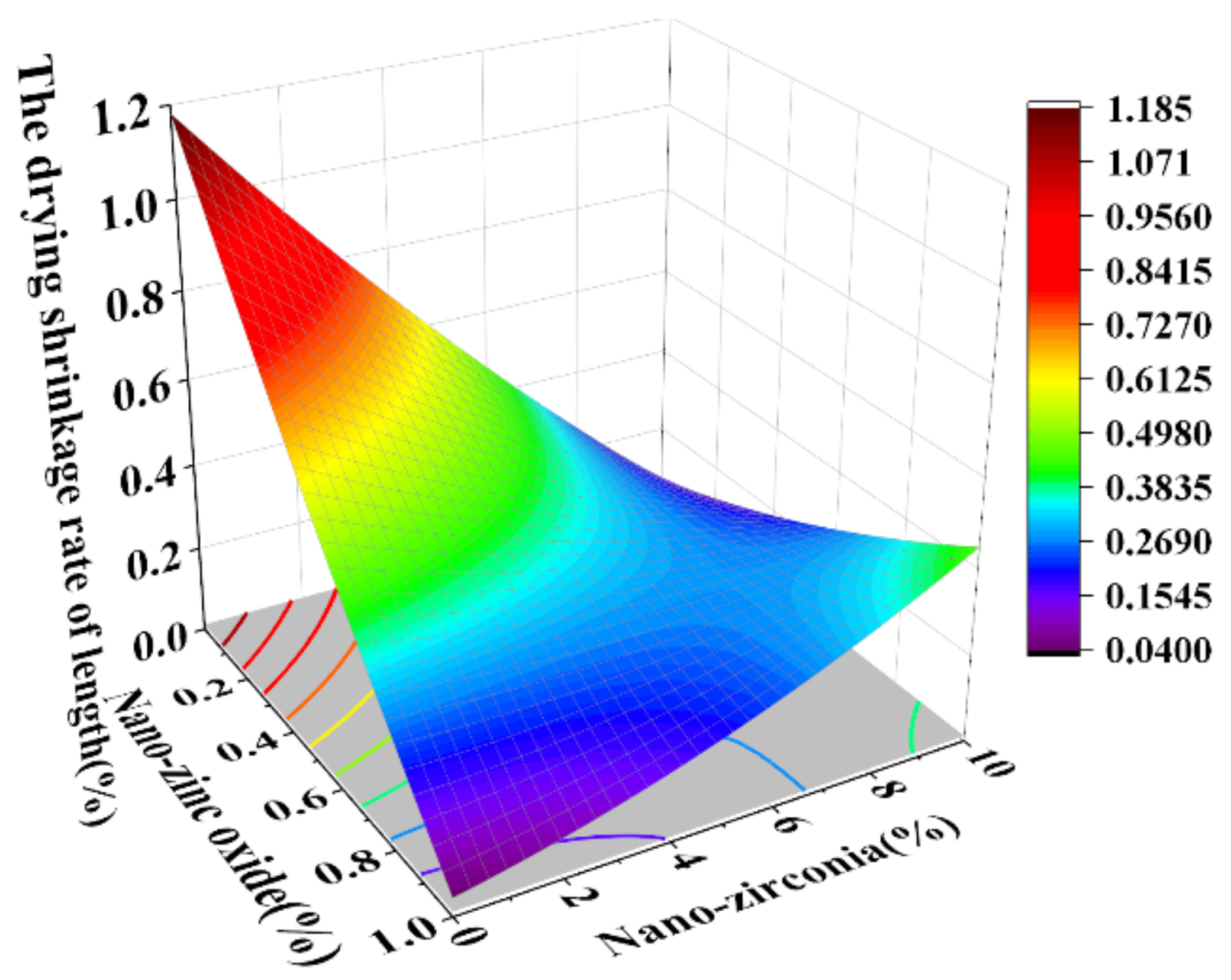
3.3. Shrinkage Performance Analysis
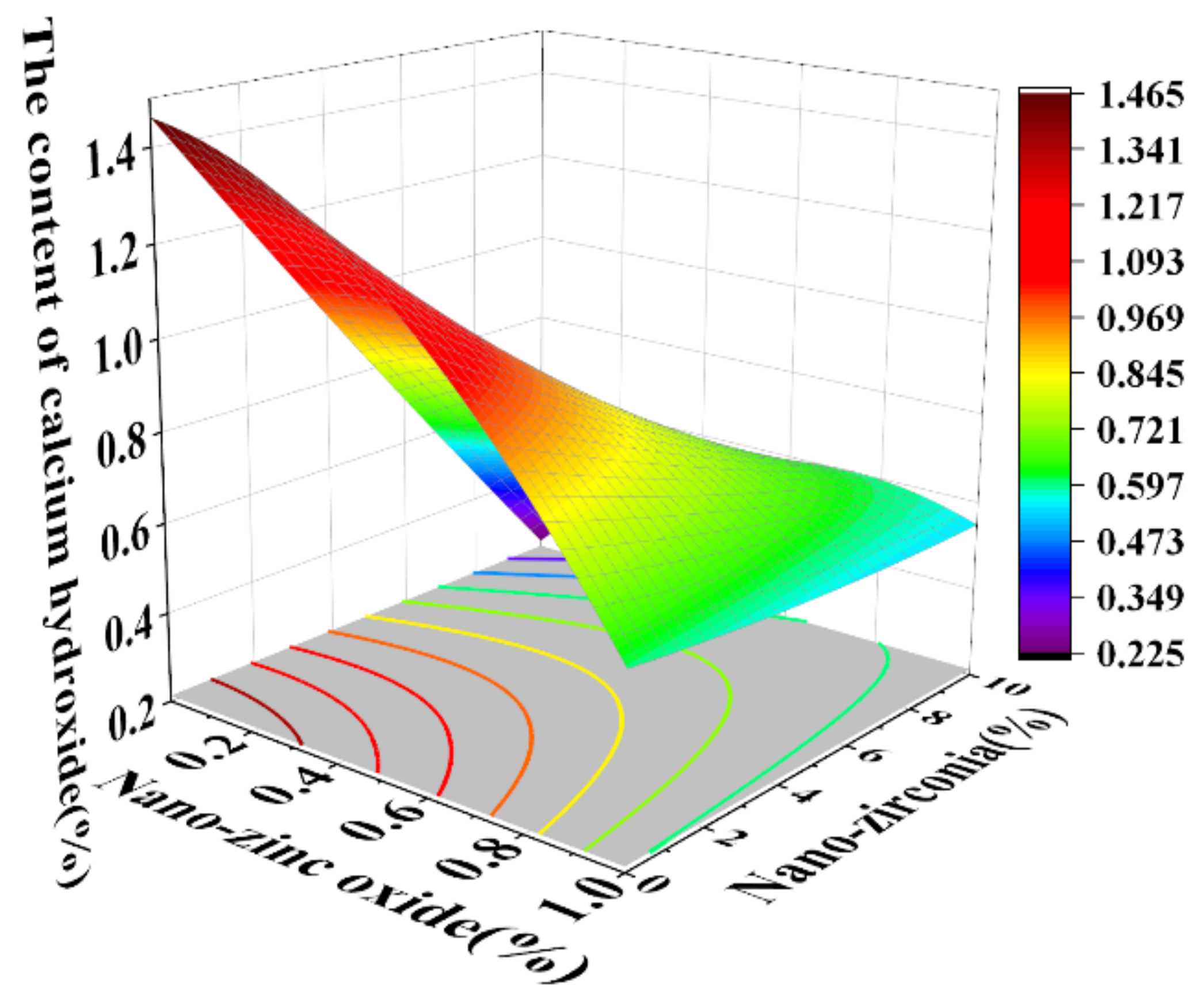
3.4. The Content of Calcium Hydroxide (CH) and Calcium Silicate Hydrate (CSH)
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wickramanayake, N.D.; Jayalath, J.A.C.D.; Kulatunga, U.; Siriwardhana, S.D. Limitations of traditional building materials for sustainable construction in Sri Lanka. FARU J. 2024, 11, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devi, S.; Khan, R. Effect of graphene oxide on mechanical and durability performance of concrete. J. Build. Eng. 2020, 27, 101007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Yang, J.; Thomas, B.S.; Li, L.; Li, H.; Nazar, S. Hybrid graphene oxide/carbon nanotubes reinforced cement paste: An investigation on hybrid ratio. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 261, 119815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Chen, K.; Lu, Z.; Lin, S.; Yuan, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, J.; Wen, Z. Nonmetallic high-entropy engineered nanocarbons for advanced ORR electrocatalysis. Angew. Chem. (Int. Ed. Engl.) 2025, e202501290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, M.; Huang, Z.; Bao, Z.; Ou, Y.; Zou, S.; Liu, G. Gold nanoparticles incorporated liquid metal for wearable sensors and wound healing. Chem. Eng. J. 2025, 508, 161120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Li, Y.; Wang, F.; Liu, Z.; Jiang, J. A novel energy-saving and emission-reduction strategy based on facile preparation of thermal insulation coatings doped with modified vacuum ceramic microbeads for concrete protection. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2024, 33, 5299–5310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arunothayan, R.A.; Ramesh, A.; Sanjayan, G.J. Fire resistance of 3D printed ultra-high performance concrete panels. J. Build. Eng. 2024, 98, 111100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lessa, F.P.; Jr, O.L.; Margalho, É.; Pinheiro, C.; Segundo, I.R.; Carneiro, J.O. Application of nano-TiO2 and micro-ZnO on cementitious surfaces for self-cleaning façades by spray coating and dip coating: A comparative study. J. Build. Pathol. Rehabil. 2024, 10, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Hou, D.; Ma, H.; Wang, P. Nanomodified cement-based materials: Review (2015–2020) of molecular dynamics studies. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2022, 34, 03121002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chilmon, K.; Kalinowski, M.; Jackiewicz-Rek, W. Predictive modeling of air purification efficiency in nano-TiO2-Modified photocatalytic cementitious composites using high-resolution EDS mapping and mercury intrusion porosimetry. Purification 2025, 1, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freitas, D.R.A.; Schmitz, A.T.; Eduarda, P.D.M.; Santos, G.T.; Luís, R.H.; Antunes, B.E.; Teixeira, C.S.; Garcia, L.F.R. Physicochemical properties of a calcium aluminate cement containing nanoparticles of zinc oxide. Restor. Dent. Endod. 2023, 48, e3. [Google Scholar]
- Abbas, B.; Mahmoud, G.; Navid, G. Experimental investigation of nano-ZnO effect on mechanical properties of cemented clayey sand. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2022, 81, 73. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.Z.; Yong, M.J.; Tan, V.Y.; Kong, S.L.S.; Elnawawy, H.M.A.; Yahya, N.A.; Kutty, M.G.; Ahmed, H.M.A. The effect of a setting accelerator on the physical and mechanical properties of a fast-set white portland cement mixed with nano-zirconium oxide. Eur. Endod. J. 2023, 8, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ElKemary Baraa, M.; ElBorady Ola, M.; Abdel Gaber Sara, A.; Beltagy Talat, M. Role of nano-zirconia in the mechanical properties improvement of resin cement used for tooth fragment reattachment. Polym. Compos. 2021, 42, 3307–3319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qudoos, A.; Jakhrani, S.H.; Kim, H.G.; Ryou, J.S. Influence of nano-silica on the leaching attack upon photocatalytic cement mortars. Int. J. Concr. Struct. Mater. 2019, 13, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Vaid, U.; Balwinder, L. Effect on concrete strength and durability with partial replacement of cement by nano-titanium dioxide (nano-TiO2) and ground granulated blast furnace slag (GGBS): A Review Summary. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2024, 1326, 012046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, N.; Kumar, B.; Usman, U.L.; Susan, A.B.H. Nano revolution: Exploring the frontiers of nanomaterials in science, technology, and society. Nano Struct. Nano Objects 2024, 39, 101299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB175-2023; Common Portland Cement. China Standard Press: Beijing, China, 2023.
- Abdalla, J.A.; Thomas, B.S.; Hawileh, R.A.; Kabeer, K.S.A. Influence of nanomaterials on the water absorption and chloride penetration of cement-based concrete. Mater. Today Proc. 2022, 65, 2066–2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Aslani, F. Piezoresistivity performance of cementitious composites containing activated carbon powder, nano zinc oxide and carbon fibre. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 278, 122375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, C.; Qu, C. Macro-mechanics and microstructure of nanomaterial-modified geopolymer concrete: A comprehensive review. J. Wuhan Univ. Technol. Mater. Sci. Ed. 2025, 40, 204–214. [Google Scholar]
- Behnia, B.; Anvari, A.A.; Safardoust-Hojaghan, H.; Salavati-Niasari, M. Positive effects of novel nano-zirconia on flexural and compressive strength of portland cement paste. Polyhedron 2020, 177, 114317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahdy, M.G.; Ali-Eldin, A.M.; Hamza, A.; Kandil, M.A. Optimizing mix proportioning of high-performance concrete using genetic algorithm. Innov. Infrastruct. Solut. 2025, 10, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, K.R.; Mishra, K.A. Machine learning based prediction model for the compressive strength of fly ash reinforced concrete: An exploration of varying cement replacements and water-cement ratios. Asian J. Civ. Eng. 2025, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haque, S.M.; Rahman, H.; Rahman, N.; Azmi, S.N.H.; Ashwaq, O.; Wabaidur, S.M.; Siddiqui, M.R.; Alam, M. Application of Box-Behnken design combined response surface methodology to optimize HPLC and spectrophotometric techniques for quantifying febuxostat in pharmaceutical formulations and spiked wastewater samples. Microchem. J. 2023, 184, 108191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- JGJ 55-2011; Specification for Mix Proportion Design of Ordinary Concrete. China Standard Press: Beijing, China, 2011.
- Zhang, Q.; Dong, S.; Wu, F.; Cai, Y.; Xie, L.; Huang, C.; Zhao, J.; Yang, S.; Xu, F.; Zhu, H.; et al. Investigation of the macro performance and mechanism of biochar modified ultra-high-performance concrete. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2024, 21, e03595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christoph, S.; Tim, K. Comparison of the calcium carbide method and Darr drying to quantify the amount of chemically bound water in early age concrete. Materials 2022, 15, 8422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsimbe, J.; Dinka, M.; Olukanni, D.; Musonda, I. Durability properties of ambient-cured fly ash-phosphogypsum blended geopolymer mortar in terms of water absorption, porosity, and sulfate resistance. Discov. Sustain. 2024, 5, 330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, R.; Kim, H.; Lee, N.K.; Park, J.J.; Jang, J.G. Microstructural characteristics and CO2 uptake of calcium sulfoaluminate cement by carbonation curing at different water-to-cement ratios. Cem. Concr. Res. 2023, 163, 107012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.; Yang, B.; Luo, P.; Dong, S.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Q.; Huang, Z.; Jiang, J.; Cai, Y.; Yang, S.; et al. Improving the performance of mortar under carbonization curing by adjusting the composition of ternary binders. Materials 2024, 17, 5037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afshar, S.; Baniasadi, H. Investigation the effect of graphene oxide and gelatin/starch weight ratio on the properties of starch/gelatin/GO nanocomposite films: The RSM study. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 109, 1019–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, H.; Jin, C.; Shen, J. The study of effect of carbon nanotubes on the compressive strength of cement-based materials based on machine learning. Constr. Build Mater. 2022, 358, 129435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahish, H.A.; Almutairi, A.D. Compressive strength prediction models for concrete containing nano materials and exposed to elevated temperatures. Results Eng. 2025, 25, 103975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, B.V.; Surendra, B.V. Strength and water absorption characteristics of cement stabilized masonry blocks using brick masonry waste. Adv. Sustain. Constr. Mater. 2020, 68, 131–143. [Google Scholar]
- Du, P.; Yang, J.; Chu, H.; Lu, X.; Cheng, X. Influence of additional components on mechanical and shrinkage properties of high-performance cementitious grouting materials. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2024, 21, 3425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Fang, T.; Zuo, J. Effect of nano-materials on autogenous shrinkage properties of cement-based materials. Symmetry 2019, 11, 1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Y.; Hadigheh, S. Enhancing the strength, microstructural integrity, and shrinkage performance of cement-based mortar using pulverised carbon and glass FRP composite waste. J. Build. Eng. 2024, 94, 110053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awoyera, P.O.; Thomas, C.; Kirgiz, M.S. (Eds.) The Structural Integrity of Recycled Aggregate Concrete Produced with Fillers and Pozzolans; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Kong, X.; Lu, Z.; Lu, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Dong, B.; Xing, F. Influence of triethanolamine on the hydration product of portlandite in cement paste and the mechanism. Cem. Concr. Res. 2016, 87, 64–76. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Ding, S.; Du, F.; Tang, J.; Liao, J.; Deng, L.; Hu, Z.; Liu, J. Interaction between calcium hydroxide and calcium-alumino-silicate-hydrate on micromechanical properties. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 449, 138321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jun, Y.; Hilario, J.H.P.; Kang, I.K.; Park, C.K.; Lee, H.; Kim, J.H. Properties of cement-based materials incorporating byproduct colloidal nanosilica. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 453, 139055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, B.; Zhang, L.; Zeng, S.; Dong, S.; Yu, X.; Yang, R.; Ou, J. Nano-core effect in nano-engineered cementitious composites. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci Manuf. 2017, 95, 100–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhi, F.; Yang, J.; Yang, G.; Zhang, L.; Li, W.; Jiang, L. Investigation on the calcium leaching behaviors of cellulose ethers containing cement pastes. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2024, 154, 105797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, C.; Zhang, Z.; Zhu, Y. Effect of field’s metal particles coated with PVA, nano-SiO2 and PVA@nano-SiO2 on the performance of cement pastes. Compos. Part B 2024, 287, 111823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Z.; Huang, S.; Li, Z.; Su, D.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, B.; Yang, Y. Carboxyl carbon nano-tubes modified calcium silicate hydrate (C-S-H-PCE/CNTs) to enhance the CO2 corrosion resistance of oil well cement. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 452, 138894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, S.; Shi, Z.; Ouyang, X. Comparison of the effects of carbon-based and inorganic nanomaterials on early cement hydration. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 421, 135705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyal, A.; Palaia, I.; Ioannidou, K.; Ulm, F.J.; van Damme, H.; Pellenq, R.J.M.; Trizac, E.; Del Gado, E. The physics of cement cohesion. Sci. Adv. 2021, 7, eabg5882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






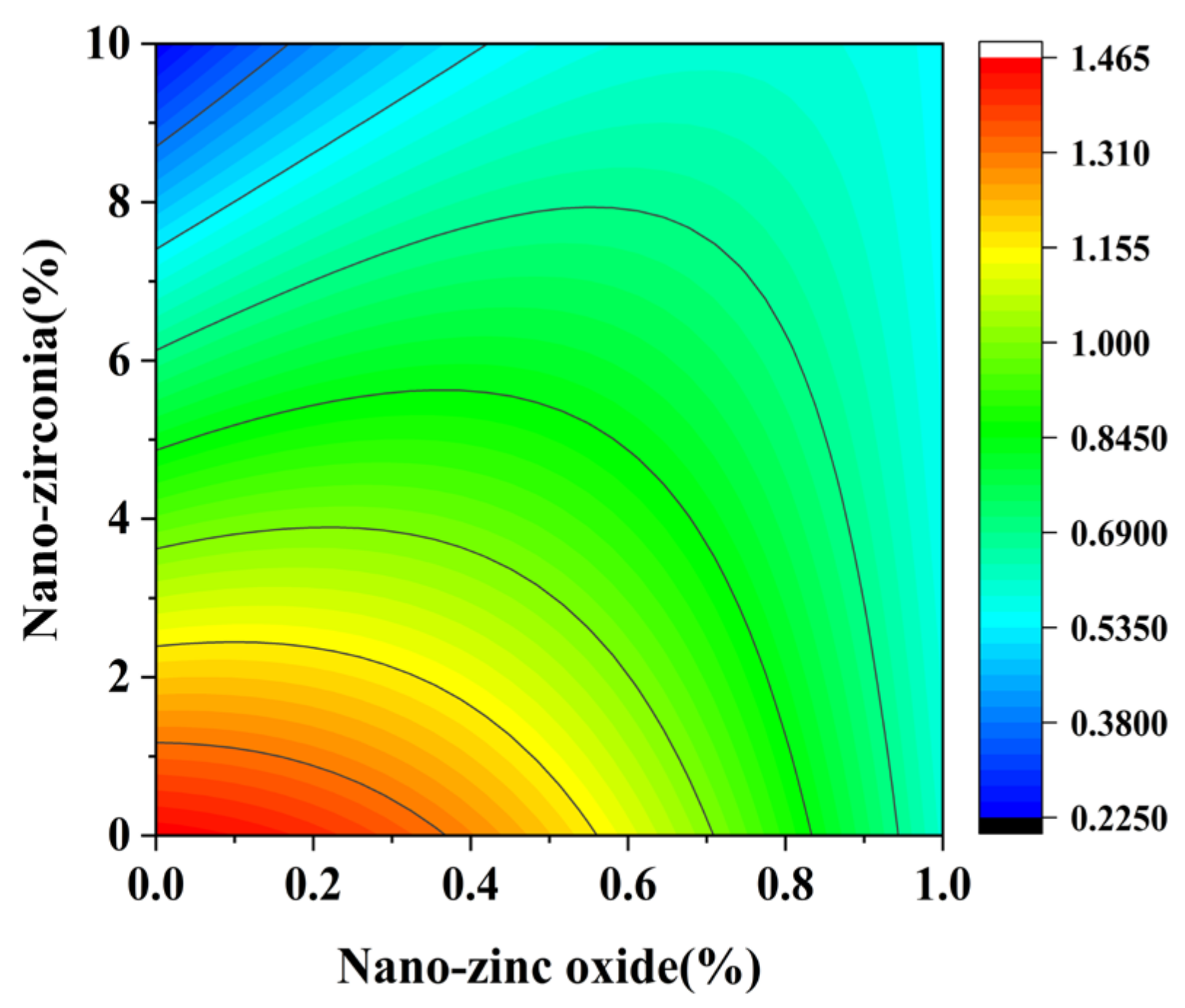
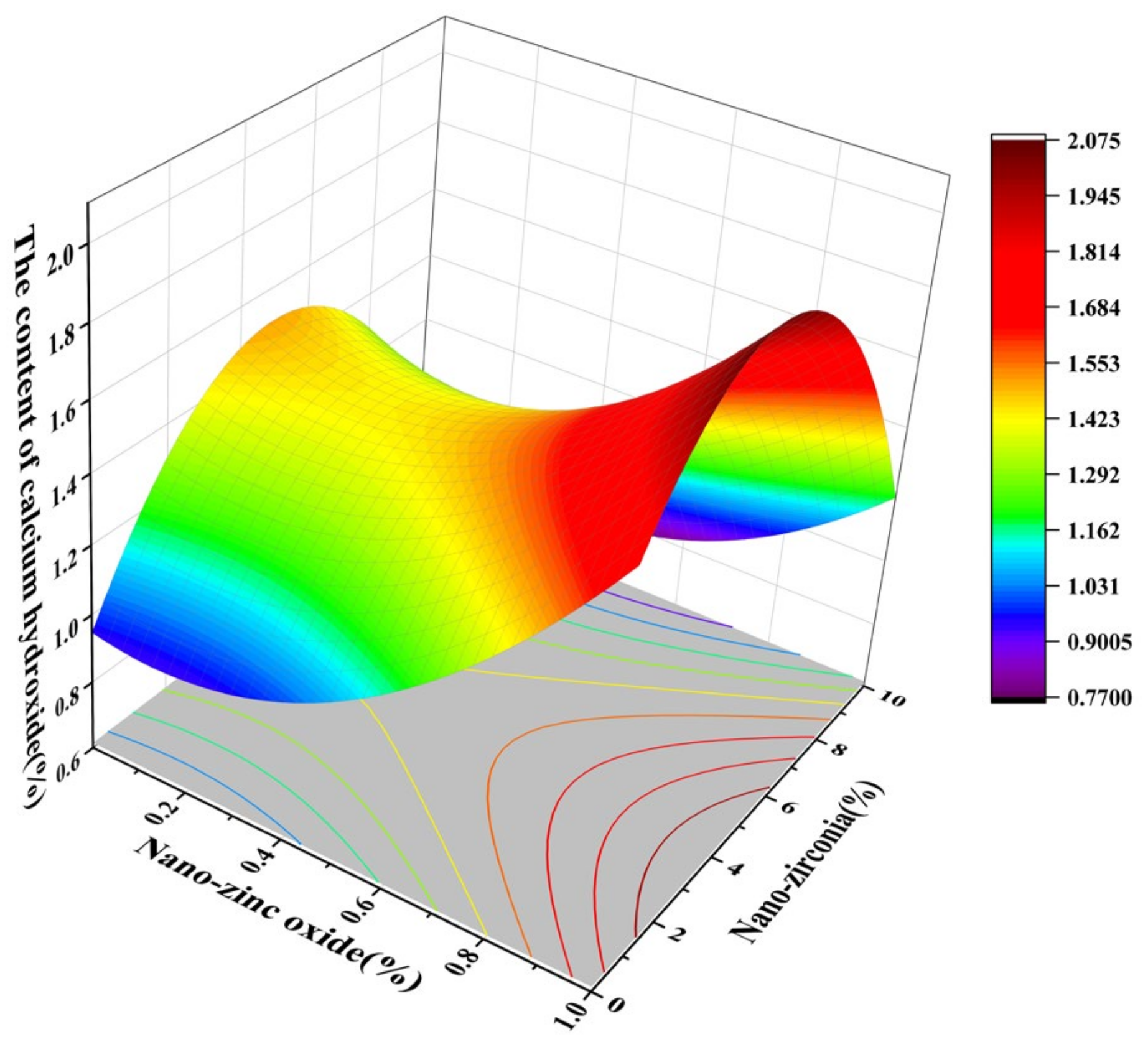
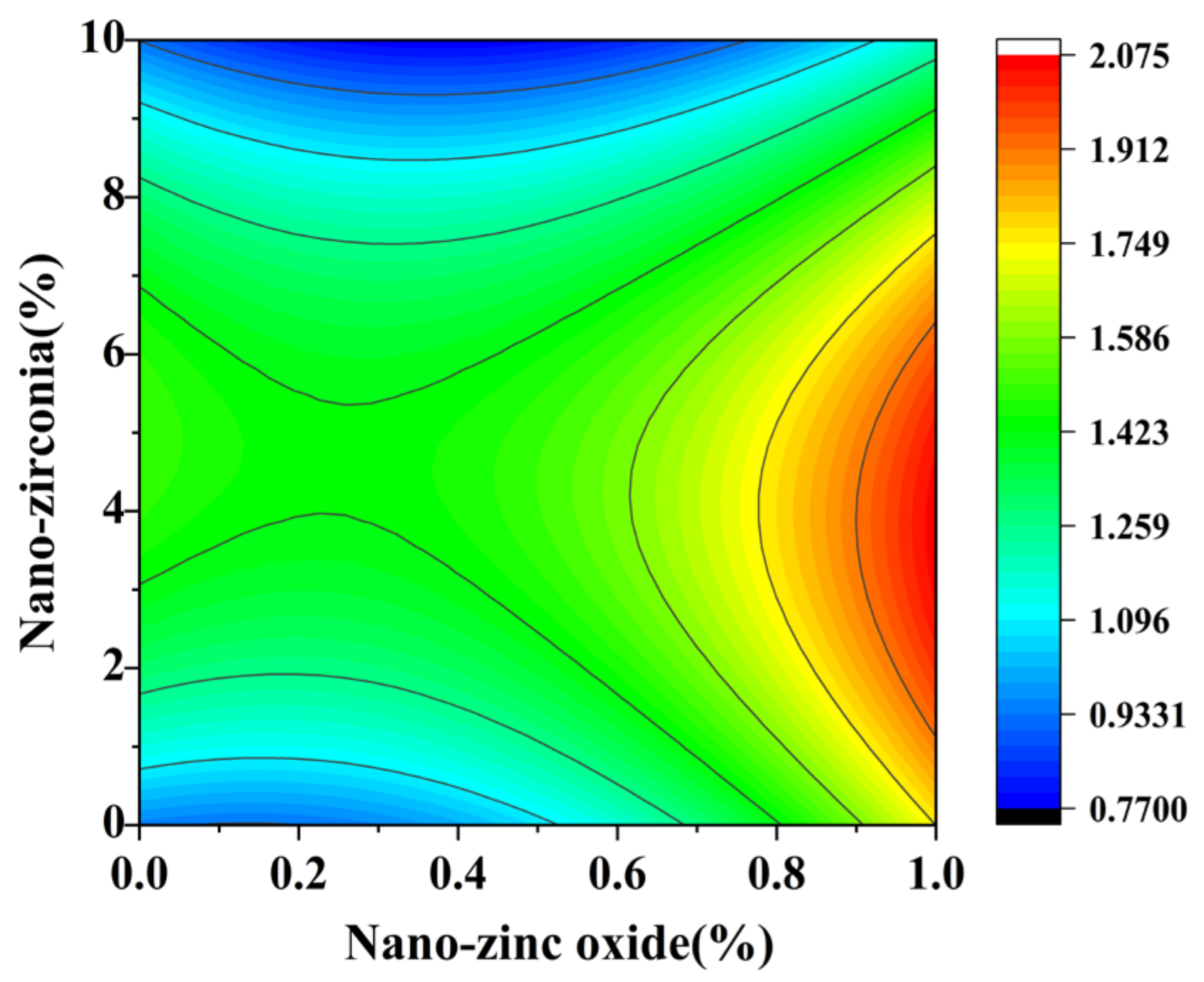
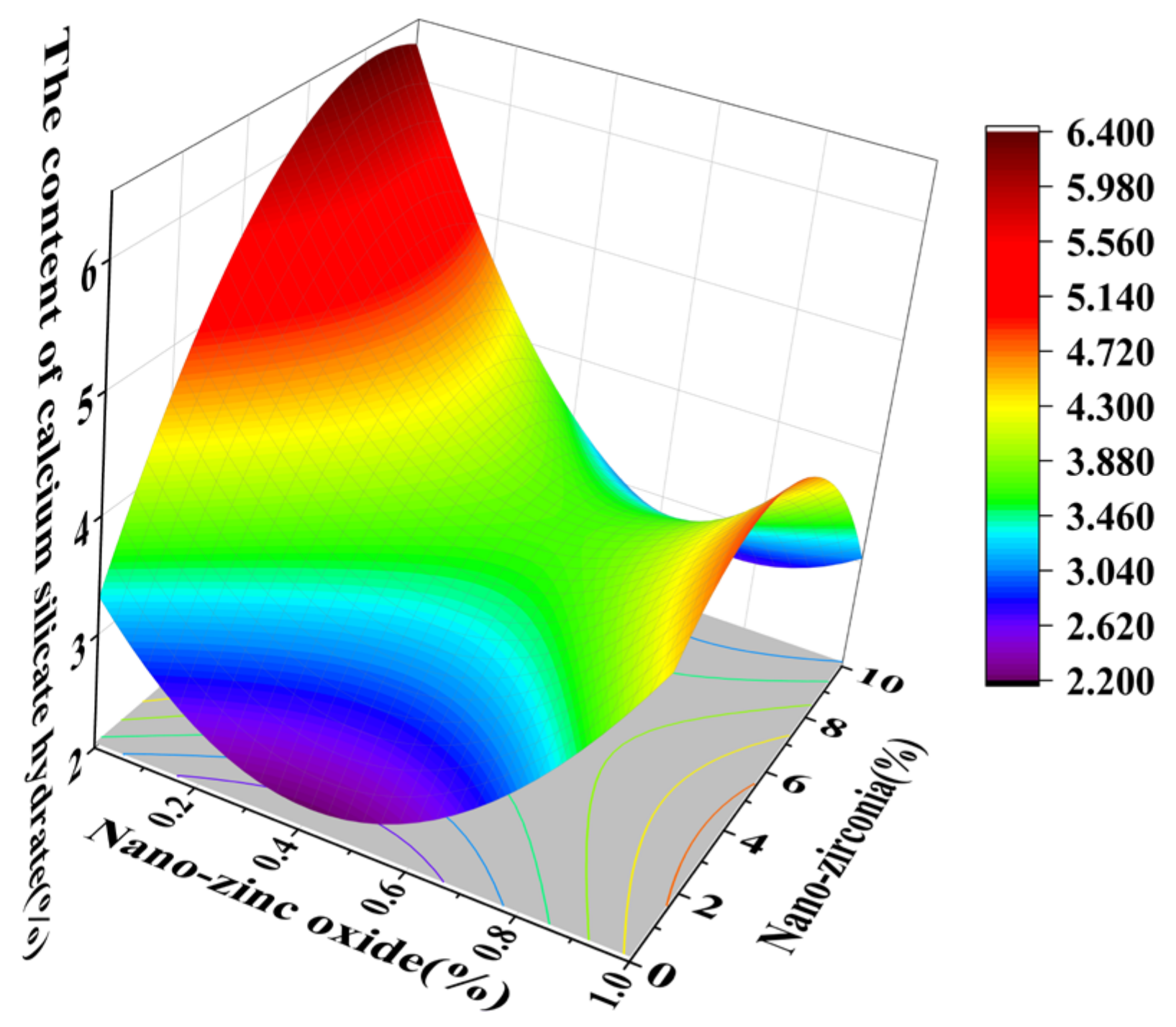

| Name | Mean Diameter (nm) | Purity (%) | Specific Surface Area (m2/g) | Volume Density (g/cm3) | Density (g/cm3) | Crystal Form | Color |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nano-zinc oxide | 20 | 99.99 | 100 | 0.41 | 5.6 | Globular | White |
| Nano-zirconia | 20 | 99.99 | 95 | 1.98 | 6.0 | Monoclinic | White |
| Serial Number | Influence Factor | Response Value | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | B | C | Y1/MPa | Y2/MPa | Y3/% | Y4/% | |
| 1 | 0 | −1 | 1 | 55.0842 | 65.8202 | 6.65 | 3.98 |
| 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 75.3317 | 85.6096 | 7.17 | 2.43 |
| 3 | 0 | 1 | −1 | 86.5781 | 95.5268 | 2.65 | 2.33 |
| 4 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 56.2102 | 58.123 | 6.62 | 4.23 |
| 5 | −1 | 1 | 0 | 85.5009 | 75.484 | 4.57 | 2.46 |
| 6 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 79.65 | 72.5788 | 3.69 | 2.06 |
| 7 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 73.119 | 82.7936 | 4.59 | 2.71 |
| 8 | 1 | −1 | 0 | 87.2233 | 86.2618 | 4.61 | 2.38 |
| 9 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 81.5281 | 83.9072 | 4.69 | 2.31 |
| 10 | −1 | −1 | 0 | 82.5387 | 83.5948 | 4.04 | 2.84 |
| 11 | −1 | 0 | 1 | 56.0825 | 58.8089 | 5.83 | 3.87 |
| 12 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 52.3926 | 73.5458 | 7.69 | 3.95 |
| 13 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 75.0862 | 91.7801 | 4.65 | 3.56 |
| 14 | 0 | −1 | −1 | 87.9653 | 106.525 | 2.6 | 1.06 |
| 15 | −1 | 0 | −1 | 101.475 | 99.1047 | 2.3 | 0.94 |
| 16 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 52.7044 | 84.6178 | 4.66 | 3.4 |
| 17 | 1 | 0 | −1 | 95.198 | 103.138 | 2.61 | 2.08 |
| Source | Y1 | Y2 | Y3 | Y4 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F | P | F | P | F | P | F | P | |
| Model | 4.52 | 0.0297 | 11.32 | 0.0021 | 4.01 | 0.0403 | 9.03 | 0.0042 |
| A | 0.2152 | 0.6568 | 2.10 | 0.1906 | 0.3745 | 0.5599 | 3.32 | 0.1114 |
| B | 0.2680 | 0.6207 | 0.1451 | 0.7145 | 0.3369 | 0.5798 | 3.01 | 0.1261 |
| C | 34.99 | 0.0006 | 92.41 | <0.0001 | 33.81 | 0.0007 | 67.02 | <0.0001 |
| AB | 0.6955 | 0.4318 | 1.57 | 0.2508 | 0.0587 | 0.8155 | 3.52 | 0.1025 |
| AC | 0.1251 | 0.7340 | 0.1880 | 0.6777 | 0.0563 | 0.8192 | 0.8812 | 0.3791 |
| BC | 0.0052 | 0.9446 | 2.96 | 0.1291 | 0.2397 | 0.6394 | 2.45 | 0.1617 |
| A2 | 3.65 | 0.0977 | 0.3597 | 0.5676 | 1.14 | 0.3220 | 0.1932 | 0.6735 |
| B2 | 0.1471 | 0.7127 | 2.24 | 0.1782 | 0.0044 | 0.9493 | 0.4713 | 0.5145 |
| C2 | 0.6859 | 0.4349 | 0.0379 | 0.8511 | 0.0372 | 0.8526 | 0.2898 | 0.6070 |
| Lack of Fit | 0.1019 | 0.9547 | 1.12 | 0.4411 | 0.0705 | 0.9727 | 0.1938 | 0.8958 |
| Response Value | R2 | Adjusted R2 | Predicted R2 | Adeq Precision | C.V./% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Y1 | 0.7440 | 0.6849 | 0.6071 | 9.6776 | 11.62 |
| Y2 | 0.9357 | 0.8531 | 0.4766 | 11.8772 | 6.58 |
| Y3 | 0.8375 | 0.6286 | 0.6283 | 6.7942 | 21.59 |
| Y4 | 0.9207 | 0.8187 | 0.7310 | 9.5878 | 15.16 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hu, H.; Wu, F.; Chen, J.; Guan, S.; Qu, P.; Zhang, H.; Chen, Y.; Xu, Z.; Huang, C.; Pu, S. Experimental Study on Cement-Based Materials Modified by Nano-Zinc Oxide and Nano-Zirconia Based on Response Surface Optimization Design. Materials 2025, 18, 1515. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18071515
Hu H, Wu F, Chen J, Guan S, Qu P, Zhang H, Chen Y, Xu Z, Huang C, Pu S. Experimental Study on Cement-Based Materials Modified by Nano-Zinc Oxide and Nano-Zirconia Based on Response Surface Optimization Design. Materials. 2025; 18(7):1515. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18071515
Chicago/Turabian StyleHu, Hongyin, Fufei Wu, Jiao Chen, Shuangshuang Guan, Peng Qu, Hongqin Zhang, Yuyi Chen, Zirun Xu, Chuanteng Huang, and Shuang Pu. 2025. "Experimental Study on Cement-Based Materials Modified by Nano-Zinc Oxide and Nano-Zirconia Based on Response Surface Optimization Design" Materials 18, no. 7: 1515. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18071515
APA StyleHu, H., Wu, F., Chen, J., Guan, S., Qu, P., Zhang, H., Chen, Y., Xu, Z., Huang, C., & Pu, S. (2025). Experimental Study on Cement-Based Materials Modified by Nano-Zinc Oxide and Nano-Zirconia Based on Response Surface Optimization Design. Materials, 18(7), 1515. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18071515








