Analysis of the Effects of Rubber Dosage and Digestion Time on the Mechanical Properties of Low Dosage Crumb-Rubber-Modified Asphalt Concrete Mixtures
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Background
2.1. Asphalt Binder and Mixture Ageing
2.2. Crumb Rubber as an Asphalt Binder Modifier
2.3. Mechanical Properties of Asphalt
- Stiffness;
- Deformation resistance;
- Fatigue resistance;
- Fracture resistance;
- Moisture damage resistance.
3. Methods and Results
3.1. Materials
3.2. Methods
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Stiffness
4.2. Deformation Resistance
4.3. Fatigue Resistance
4.4. Fracture Resistance
4.5. Moisture Resistance
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, H. (Ed.) Asphalt and Asphalt Mixtures; Intechopen: London, UK, 2019; Available online: https://www.intechopen.com/books/8747 (accessed on 3 August 2021).
- Hunter, R.; Self, A.; Read, J. Shell Bitumen Handbook, 6th ed.; ICE Publishing: London, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Jamieson, S.; White, G.; Verstraten, L. Principles for incorporating recycled materials into airport pavement construction for more sustainable airport pavements. Sustainability 2024, 16, 7586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamshidi, A.; White, G. Evaluation of performance of challenges of use of waste materials in pavement construction: A critical review. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, G.; Kidd, A.; Shadforth, T. Effect of low dosage crumbed rubber on the mechanical properties of a dense graded asphalt mixture. Road Mater. Pavement Des. 2023, 24, 2464–2482. [Google Scholar]
- Jamieson, S.; White, G. Review of the performance and cost of asphalt mixture options for runway surfacing. In Proceedings of the 8th Eurasphalt and Eurobitume Congress, Budapest, Hungary, 19–21 June 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Van Den Heuvel, D.; White, G. Objective comparison of sustainable asphalt concrete solutions for airport pavement surfacing. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Sustainable Infrastructure, Virtual, 6–10 December 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Aswegen, E.; Latter, L. Transfer of Appropriate Crumb Rubber Modified Bitumen Technology to WA Stage 1: Open Graded Asphalt; Australian Roads Research Board, Report prepared for Main Roads Western Australia; Australian Roads Research Board: Perth, Australia, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Bressi, S.; Fiorentini, N.; Huang, J.; Losa, M. Crumb rubber modifier in road asphalt pavements: State of the art and statistics. Coatings 2019, 9, 384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo Presti, D.; Memon, N.; Airey, G. Influence of processing conditions on rheology of tyre rubber modified bitumens. In Proceedings of the 2012 Asphalt Rubber Conference, Munich, Germany, 23–26 October 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Hassan, N.; Airey, G.; Jaya, R.; Mashros, N.; Aziz, M. A Review of Crumb Rubber Modification in Dry Mixed Rubberised Asphalt Mixtures. J. Teknol. 2014, 70, 127–134. [Google Scholar]
- Hassan, N.; Almusawi, A.; Mahmud, M.; Abdullah, N.; Shukry, N.; Mashros, H.; Jaya, R.; Yusoff, N. Engineering properties of crumb rubber modified dense-graded asphalt mixtures using dry process. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2019, 220, 012009. [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez-Fernandex, I.; Cavalli, M.; Poulikakos, L.; Bueno, M. Recyclability of Asphalt Mixtures with Crumb Rubber Incorporated by Dry Process: A Laboratory Investigation. Materials 2020, 13, 2870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kidd, A.; White, G.; Stephenson, G. Estimating the cost and benefit of low dosage crumb rubber modification of dense graded asphalt mixtures for longer lasting local road surfaces. In Proceedings of the 19th AfPA International Flexible Pavements Conference, Brisbane, Australia, 30 October–1 November 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Mashaan, N.; Ali, A.; Karim, M.; Abdelaziz, M. An overview of crumb rubber modified asphalt. Int. J. Phys. Sci. 2011, 7, 166–170. [Google Scholar]
- Ghavibazoo, A.; Abdelrahman, M.; Ragab, M. Mechanism of Crumb Rubber Modifier Dissolution into Asphalt Matrix and Its Effect on Final Physical Properties of Crumb Rubber–Modified Binder. Transp. Res. Rec. J. Transp. Res. Board 2013, 2370, 92–101. [Google Scholar]
- Ibrahim, M.; Katman, H.; Karim, M.; Koting, S.; Mashaan, N. A Review on the Effect of Crumb Rubber Addition to the Rheology of Crumb Rubber Modified Bitumen. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2013, 2013, 415246. [Google Scholar]
- Subhy, A.; Lo Presti, D.; Airey, G. An investigation on using pre-treated tyre rubber as a replacement of synthetic polymers for bitumen modification. Road Mater. Pavement Des. 2015, 16, 245–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grobler, J.; Harrison, J.; Chen, S. Facilitating the Use of Crumb Rubber Modified Asphalt on Local Government Roads in South East Queensland; Tyre Stewardship Australia: Richmond, Australia; ARRB Transport Research: Brisbane, Australia, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Lyu, L.; Fini, E.; Pei, J.; Poulikakos, L. Aging Evolution and sustainability Implications of Crumb Rubberized Asphalt Binder: A State-of-the-Art. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 434, 140202. [Google Scholar]
- Jamal, M.; Giustozzi, F. Enhancing the asphalt binder’s performance against oxidative ageing and solar radiations by incorporating rubber from waste tyres. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 350, 128803. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, S.; Ren, X.; Wu, H.; Liu, H.; Xu, M.; Zhu, Z.; Ling, M. Effect of Ultraviolet Aging on Fundamental Properties of Polymer and Crumb Rubber Modified Asphalt and Asphalt Mixtures. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2024, 36, 05024005. [Google Scholar]
- Borinelli, J.; Enfrin, M.; Blom, J.; Giustozzi, F.; Vuye, C.; Hernando, D. Investigating thermal and UV ageing effects on crumb rubber modified bitumen enhanced with emission reduction agents and carbon black. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 449, 138452. [Google Scholar]
- Zadshir, M.; Ploger, S.; Yu, X.; Sangiorgi, C.; Yin, H. Chemical, thermophysical, rheological, and microscopic characterisation of rubber modified asphalt binder exposed to UV radiation. Road Mater. Pavement Des. 2020, 21 (Suppl. 1), S123–S139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamal, M.; Lanotte, M.; Giustozzi, F. Exposure of crumb rubber modified bitumen to UV radiation: A waste-based sunscreen for roads. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 348, 131372. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Liu, X.; Apostolidis, P.; van de Ven, M.; Erkens, S.; Skarpas, A. Effect of laboratory aging on chemistry and rheology of crumb rubber modified bitumen. Mater. Struct. 2020, 53, 26. [Google Scholar]
- Kidd, A.; Stephenson, G.; White, G. Towards the use of crumb rubber modified asphalt for local government roads. In Proceedings of the AfPA International Flexible Pavements Symposium, Virtual, 3–5 August 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Haroon, W.; Ahmad, N. Effect of low-content crumb rubber modification on the performance of bitumen and asphalt. Eng. Res. Express 2024, 6, 035116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asif, A.; Ahmad, N. Experimental investigation of impact of crumb rubber on modified bitumen. Aust. J. Civ. Eng. 2023, 21, 182–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, P.; Noojilla, S.; Reddy, M. Evaluation of fatigue characteristics of asphalt mixtures using Cracking Tolerance index (CTIndex). Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 342 Pt B, 128030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abouelsaad, A.; White, G. Review of asphalt mixture ravelling mechanisms, causes and testing. Int. J. Pavement Res. Technol. 2022, 15, 1448–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malinowski, S. Aromatisation process as part of bitumen ageing in the light of electronic structure and further oxidation of its components. Constr. Build. Mater. 2013, 366, 130198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.; Harvey, J.; Elkashef, M.; Jiao, L.; Jones, D. Characterizing the Aging and Performance of Asphalt Binder Blends Containing Recycled Materials. Adv. Civ. Eng. Mater. 2023, 12, 41–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqui, M.; Ali, M. Investigation of chemical transformations by NMR and GPC during the laboratory aging of Arabian asphalt. Fuel 1999, 78, 1407–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandoval, C.; Amaya, X.; Molano, E. Effect of aging on the properties of asphalt and asphalt mixtures. Ing. Y Univ. 2015, 19, 335–349. [Google Scholar]
- Hagos, E.T. The Effect of Aging on Binder Properties of Porous Asphalt Concrete. Master’s Thesis, Delft University of Technology, Delft, The Netherlands, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Abouelsaad, A.; White, G. Fretting and ravelling of asphalt surfaces for airport pavements: A load or environmental distress? In Proceedings of the Nineteenth Annual International Conference on Highways and Airport Pavement Engineering, Asphalt Technology, and Infrastructure, Liverpool, UK, 11–12 March 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Chowdhury, A.; Button, J.W. A Review of Warm Mix Asphalt; Report 473700-0080-1, December; Texas Transportation Institute: College Station, TX, USA, 2008. Available online: https://rosap.ntl.bts.gov/view/dot/16887 (accessed on 3 August 2021).
- Zaumanis, M.; Mallick, R.B.; Poulikakos, L.; Frank, R. Influence of six rejuvenators on the performance properties of reclaimed asphalt pavement (RAP) binder and 100% recycled asphalt mixtures. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 71, 538–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, B.; Kumar, P. Effect of polymer modification on the aging properties of asphalt binders: Chemical and morphological investigation. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 205, 633–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, G.; Hall, F.; Foster, D. Comparing binder modified with recycled plastic to conventional polymer modified binder. In Proceedings of the International Airfield and Highway Pavement Conference, Virtual, 8–10 June 2021. [Google Scholar]
- White, G. Early life asphalt surface rejuvenation. In Proceedings of the 7th Eurasphalt and Eurobitume Congress, Virtual, 15–17 June 2021. [Google Scholar]
- White, G.; Thompson, M. Australian airport asphalt surface treatments. In Proceedings of the 6th Eurasphalt & Eurobitume Congress, Prague, Czech Republic, 1–3 June 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Chavez, F.; Marcobal, J.; Gallego, J. Laboratory evaluation of the mechanical properties of asphalt mixtures with rubber incorporated by the wet, dry and semi-wet process. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 205, 164–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennert, T.; Maher, A.; Smith, J. Evaluation of Crumb Rubber in Hot Mix Asphalt; Research Report BAY RU9247, July; Center for Advanced Infrastructure and Transportation: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2004; Available online: https://cait.rutgers.edu/wp-content/uploads/2018/05/bay-ru9247.pdf (accessed on 3 August 2021).
- Pant, S.; Akentuna, M.; Mohammad, L.; Cooper, S.; Cooper, S. Long-Term Performance of Flexible Pavements Containing Crumb Rubber Modified Asphalt in Louisiana. Transp. Res. Rec. J. Transp. Res. Board 2024, 2678, 1610–1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghabchi, R.; Zaman, M.; Arshadi, A. Use of Ground Tire Rubber (GTR) in Asphalt Pavements: Literature Review and DOT Survey—Final Report; Report prepared for Oklahoma Department of Environmental Quality; Oklahoma Department of Environmental Quality: Oklahoma, OK, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Buttlar, W.; Rath, P. State of Knowledge Report on Rubber Modified Asphalt; Report prepared for U.S. Tire Manufacturers Association; U.S. Tire Manufacturers Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Austroads. Passenger Cars and Other Non-Truck Tyres Crumb Rubber in Asphalt: National Market Analysis, Review of Industry Practices and Technology Transfer; Report AP-R681-22; Austroads: Sydney, Australia, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Ghavibazoo, A.; Abdelrahman, M.; Ragab, M. Evaluation of Oxidation of Crumb Rubber-Modified Asphalt during Short-Term Aging. Transp. Res. Rec. J. Transp. Res. Board 2015, 2505, 84–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putman, B.; Amirkhanian, S. Crumb rubber modification of binders: Interaction and particle effects. In Proceedings of the 2006 Asphalt Rubber Conference, Palm Springs, CA, USA, 25–27 October 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, W.; Liu, S.; Cui, X.; Yu, X. Effect of Crumb Rubber Particle Size and Content on Properties of Crumb Rubber Modified (CRM) Asphalt. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2011, 99–100, 955–959. [Google Scholar]
- Guerrero-Bustamante, O.; Camargo, R.; Dawd, I.; Duque, J.; Polo-Mendoza, R.; Gálvis, J.; Díaz, J.; Daza, O.; Cucunuba, J.; Acosta, C. Implementation of Crumb Rubber (CR) in Road Pavements: A Comprehensive Literature Review. Infrastructures 2024, 9, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo Presti, D. Recycled Tyre Rubber Modified Bitumens for Road Asphalt Mixtures: A Literature Review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2013, 49, 863–881. [Google Scholar]
- Rice, Z.; Harrison, J. Investigation of the Use of Reclaimed Asphalt Pavement from Crumb Rubber Modified Asphalt—Stage 2; Report prepared for Western Australian Road Research and Innovation Program (WARRIP); Western Australian Road Research and Innovation Program (WARRIP): Perth, Australia, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Marais, H.I.J.; Botha, B.; Hosfink, W.; van Heeerden, J. Latest developments in crumb rubber modified bitumen for use in asphalt and seals—The South African Experience. In Proceedings of the 17th AAPA International Flexible Pavements Conference, Melbourne, VIC, Australia, 13–16 August 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Bahia, H.U.; Davies, R. Effect of crumb rubber modifiers (CRM) on performance-related properties of asphalt binders. Asph. Paving Technol. 1994, 63, 414–449. [Google Scholar]
- Lo Presti, D.; Airey, G. Tyre rubber-modified bitumens development: The effect of varying processing conditions. Road Mater. Pavement Des. 2013, 14, 888–900. [Google Scholar]
- Lv, Q.; Huang, W.; Zheng, M.; Hu, Y.; Yan, C.; Wang, J. Understanding the particle effects and interaction effects of crumb rubber modified asphalt regarding bonding properties. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 348, 128716. [Google Scholar]
- Denneman, E.; Lee, J.; Raymond, C.; Choi, Y.; Khoo, K.; Dias, M. Optimising the Use of Crumb Rubber Modified Bitumen in Seals and Asphalt; Report prepared for The Queensland Departments of Environment and Heritage Protection, and Transport and Main Roads; Queensland Departments of Environment and Heritage Protection, and Transport and Main Roads: Brisbane, Australia, 2015.
- Mohamed, A.; Cao, Z.; Xu, X.; Xiao, F.; Abdel-Wahed, T. Bonding, rheological, and physiochemical characteristics of reclaimed asphalt rejuvenated by crumb rubber modified binder. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 373, 133896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.Q.; Li, L.H. Factors affecting the viscosity of crumb rubber-modified asphalt. Pet. Sci. Technol. 2010, 28, 1555–1566. [Google Scholar]
- Mashaan, N.; Karim, M. Investigating the Rheological Properties of Crumb Rubber Modified Bitumen and its Correlation with Temperature Susceptibility. Mater. Res. 2013, 16, 116–127. [Google Scholar]
- Thives, L.; Pais, J.; Pereira, P.; Triches, G.; Amorim, S. Assessment of the digestion time of asphalt rubber binder based on microscopy analysis. Constr. Build. Mater. 2013, 47, 431–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, G.; Kidd, A. The volumetric challenge of crumbed rubber modified asphalt mixtures. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Road and Airfield Pavement Technology, Columbo, Sri Lanka, 14–15 July 2021; pp. 867–882. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.; Amirkhanian, S.; Putman, B.; Kim, K. Laboratory Study of the Effects of Compaction on the Volumetric and rutting Properties of CRM Asphalt Mixtures. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2007, 19, 1079–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.H. Pavement Analysis and Design, 2nd ed.; Pearson: London, UK, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Ariyapijati, R.; Hadiwardoyo, S.; Sumabrata, R. Contributions crumb rubber in hot mix asphalt to the resilient modulus. AIP Conf. Proc. 2017, 1855, 030005. [Google Scholar]
- Austroads. Improved Design Procedures for Asphalt Pavement; Report AP-R511-16; Austroads: Sydney, Australia, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Sousa, J.B.; Solaimanian, M.; Weissman, S.L. Development and Use of the Repeated Shear Test (Constant Height): An Optional Superpave Mix Design Tool; Report SHRP-A-698; Strategic Highway Research Program, National Research Council: Washington, DC, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Molenaar, A.A.A. Prediction of fatigue cracking in asphalt pavements: Do we follow the right approach? Transp. Res. Rec. J. Transp. Res. Board 2007, 2001, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirsayar, M.M. On the low temperature mixed mode fracture analysis of asphalt binder—Theories and experiments. Eng. Fract. Mech. 2017, 186, 181–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Solaimanian, M. Evaluating fracture properties of crumb rubber modified asphalt mixes. Int. J. Pavement Res. Technol. 2019, 12, 407–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, F.; Im, S.; Sun, L.; Scullion, T. Development of an IDEAL cracking test for asphalt mix design and QC/QA. Road Mater. Pavement Des. 2017, 18, 405–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kidd, A.; White, G. Anti-aging benefits for mechanical properties of low dose crumb rubber modified dense grade asphalt. In Proceedings of the International Airfield and Highway Pavements Conference, Glendale, AZ, USA, 8–11 June 2025. article-in-press. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, C.; Zhang, Y.; Bahia, H. Comparison between SCB-IFIT, un-nothced SCB-IFIT and IDEAL-CT for measuring cracking resistance of asphalt mixtures. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 252, 119060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandhal, P.S. Field and laboratory investigation of stripping in asphalt pavements: State of the art report. Transp. Res. Rec. J. Transp. Res. Board 1994, 1454, 35–46. [Google Scholar]
- Bhasin, A.; Little, D.N. Methods to quantify interfacial adhesion and debonding in bitumen-aggregate system in dry and wet conditions. In Proceedings of the Advanced Characterisation of Pavement and Soil Engineering Materials, Athens, Greece, 20–22 June 2007; pp. 689–699. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, L. (Ed.) Structural Behavior of Asphalt Pavements; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Gudimettla, J.M.; Cooley, A.L.; Brown, E.R. Workability of Hot Mix Asphalt; NCAT Report 03-03; National Center for Asphalt Technology: Auburn, AL, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- AS 2008; Bitumen for Pavements. Standards Australia: Sydney, Australia, 2013; last updated 18 November 2013.
- Brase, C.H.; Brase, C.P. Understanding Basis Statistics, 2nd ed.; Houghton Mifflin Company: Boston, MA, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- White, G. Potential Causes of Top-down cracking of Australian runway surfaces. In Proceedings of the 27th ARRB Conference, Melbourne, VIC, Australia, 16–18 November 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Kidd, A.; White, G. Effect of rubber content and digestion time on the properties of crumb rubber modified binder. In Proceedings of the 10th International Conference on Maintenance and Rehabilitation of Pavements, Guimaraes, Portugal, 24–26 July 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Chandrawal, M.; Verma, G.; Kushwah, K.; Sharma, V. An Experimental Study of Rutting on Dense Bituminous Macadam of Grading-I (Middle) using Crumb Rubber Modified Bitumen and Waste Plastic Coated Aggregates. Int. J. Res. Sci. Innov. 2016, 3, 99–107. [Google Scholar]
- Petho, L.; Lange, C.; Lyons, M.; Forbes, S. Dense Graded Crumb Rubber Asphalt Development for Sub-Tropical Climate. In Proceedings of the 7th Eurasphalt & Eurobitume Congress, Madrid, Spain, 15–17 June 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Sahebzamani, H.; Naderi, K.; Mahmoodinia, N.; Sousa, J. Laboratory Investigation of Reacted and Activated Rubber Modified Gap and Dense Grade Asphalt Mixtures. In Proceedings of the 7th Eurasphalt & Eurobitume Congress, Madrid, Spain, 15–17 June 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Wong, C.; Wong, W. Effect of crumb rubber modifiers on high temperature susceptibility of wearing course mixtures. Constr. Build. Mater. 2007, 21, 1741–1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaled, T.; Aboud, G.; Al-Hamd, R. Study the effect of adding crumb rubber on the performance of hot mix asphalt. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 737, 012129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhammad, I.; Yasir, A.; Sarfraz, A.; Imran, H. Performance Evaluation of Crumb Rubber-Modified Asphalt Mixtures Based on Laboratory and Field Investigations. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2018, 43, 1795–1806. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, D.; Liang, Y.; Harvey, J. Performance Based Specifications: Literature Review on Increasing Crumb Rubber Usage by Adding Small Amounts of Crumb Rubber Modifier in Hot Mix Asphalt; California Department of Transportation: Sacramento, CA, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- King, R.; Brown, W.; McArthur, R. Crumb Rubber in Asphalt Roads—Where the Rubber Hits the Road. In Proceedings of the International Public Works Conference, Hobart, Tasmania, 25–29 August 2019. [Google Scholar]
- White, G. Incorporating binder type into fatigue life characterisation of airport pavement surfaces. Int. J. Pavement Res. Technol. 2020, 13, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, P.; Huang, W.; Tang, N.; Xiao, F. Performance characteristics of Terminal Blend rubberized asphalt with SBS and polyphosphoric acid. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 141, 171–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riekstins, A.; Baumanis, J.; Barbars, J. Laboratory investigation of crumb rubber in dense graded asphalt by wet and dry processes. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 292, 123459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalid, H.; Artamendi, I. Characterisation of Fatigue Damage of Asphaltic Materials. In Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Bearing Capacity of Roads, Railways and Airfields, Trondheim, Norway, 25–27 June 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, Y.; Harvey, J.; Wu, R.; Jiao, L.; Jones, D. Fatigue and Fracture Properties of Asphalt Mixes Containing Low Content of Crumb-Rubber Modifier. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2020, 32, 04020280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joohari, I.; Giustozzi, F. Waste tyres crumb rubber as a sustainability enhancer for polymer-modified and hybrid polymer-modified bitumen. Int. J. Pavement Eng. 2021, 23, 4357–4371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peralta, J.; Silva, H.; Machado, A.; Pais, J.; Pereita, P.; Sousa, J. Changes in Rubber Due to its Interaction with Bitumen when Producing Asphalt Rubber. Road Mater. Pavement Des. 2010, 11, 1009–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badughaish, A.; Li, J.; Amirkhanian, S.; Xiao, F. Adhesion and segregation characteristics of crumb rubberized binders based on solution-soaked methods. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 354, 131762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Q.; Lu, J.; Tang, X.; Hu, Y.; Yan, C. Evaluation of the moisture resistance of rubberized asphalt using BBS/UTM bonding test, TSR and HWT test. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 340, 127831. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Liu, J.; Wang, Z.; Jing, H.; Yang, B. Investigations on Adhesion Characteristics between High-Content Rubberized Asphalt and Aggregates. Polymers 2022, 14, 5474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ziari, H.; Divandari, H.; Hajiloo, M.; Amini, S. Investigating the effect of amorphous carbon powder on the moisture sensitivity, fatigue performance and rutting resistance of rubberized asphalt concrete mixtures. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 217, 62–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.; Airey, G.; Collop, A. Moisture Susceptiblity of High and Low Compaction Dry Process Crumb Rubber-Modified Asphalt Mixtures. Transp. Res. Rec. J. Transp. Res. Board 2010, 2180, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziari, H.; Divandari, H.; Akbar, S.; Hosseinian, S. Investigation of the Effect of Crumb Rubber Powder and Warm Additives on Moisture Resistance of SMA Mixtures. Adv. Civ. Eng. 2021, 2021, 6653594. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, E.; Kandhal, P.; Roberts, F.; Kim, Y.; Lee, D.; Kennedy, T. Hot Mix Asphalt Materials, Mixture Design, and Construction, 3rd ed.; NAPA Research and Education Foundation: Greenbelt, MD, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
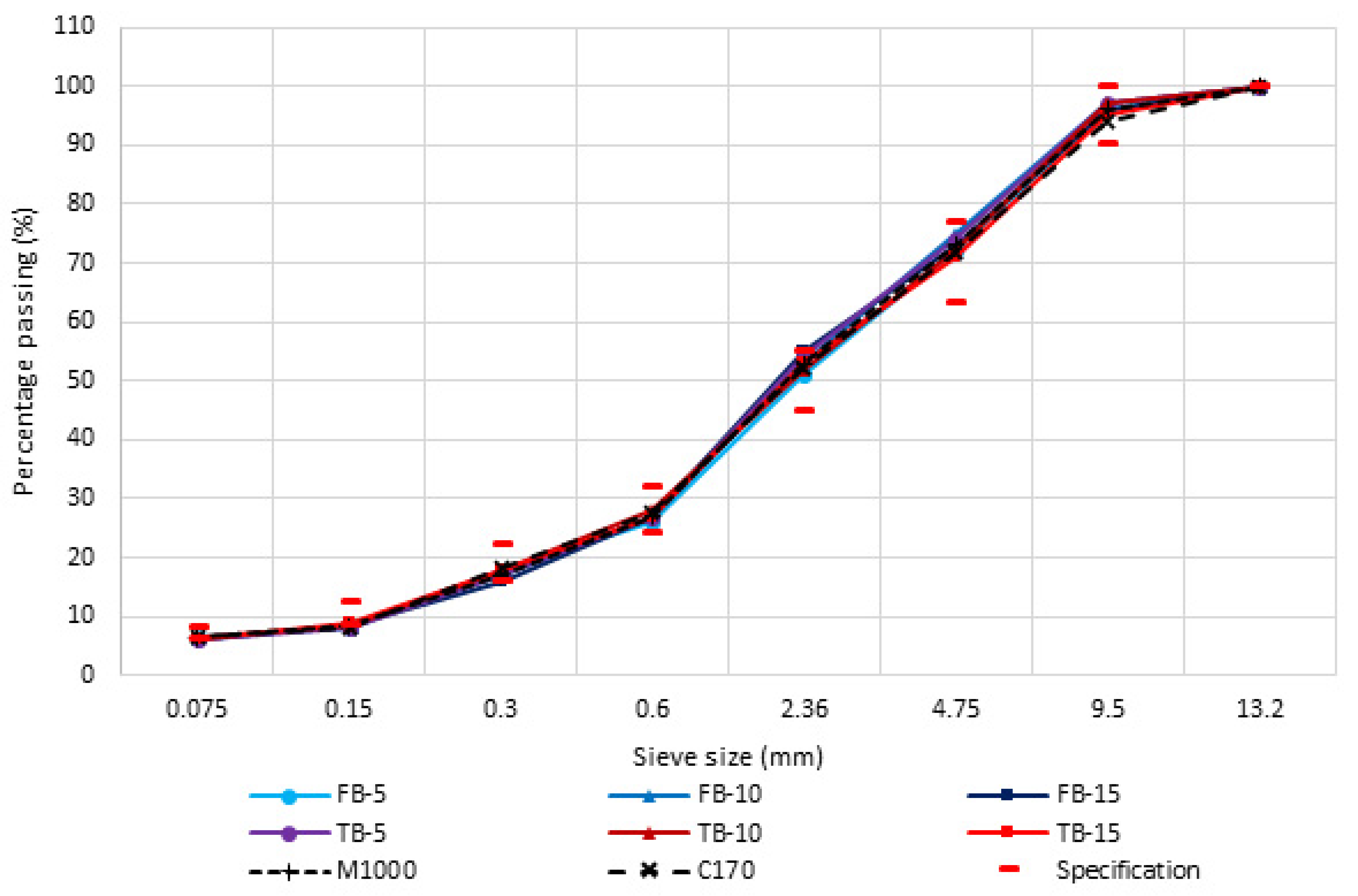
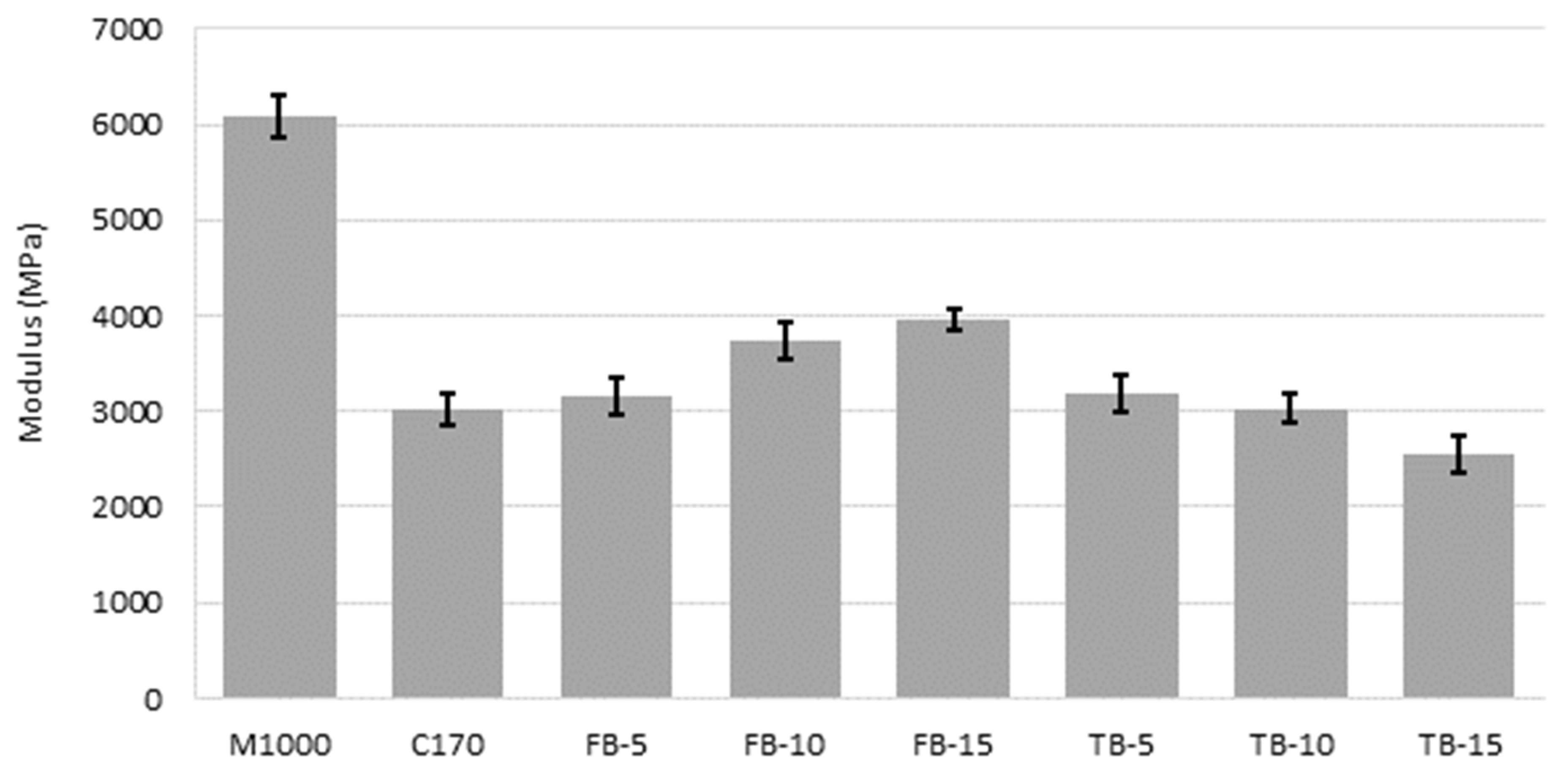

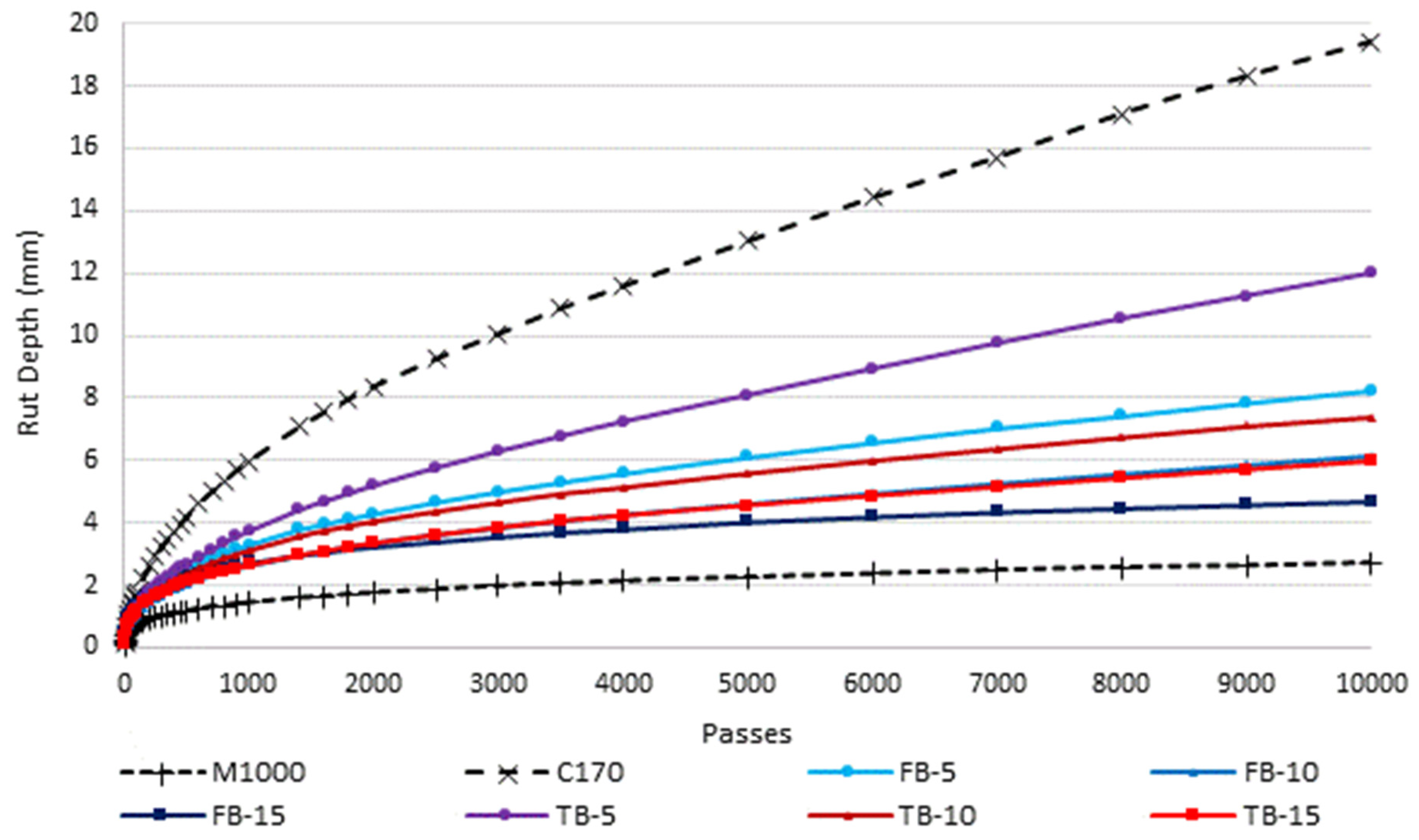

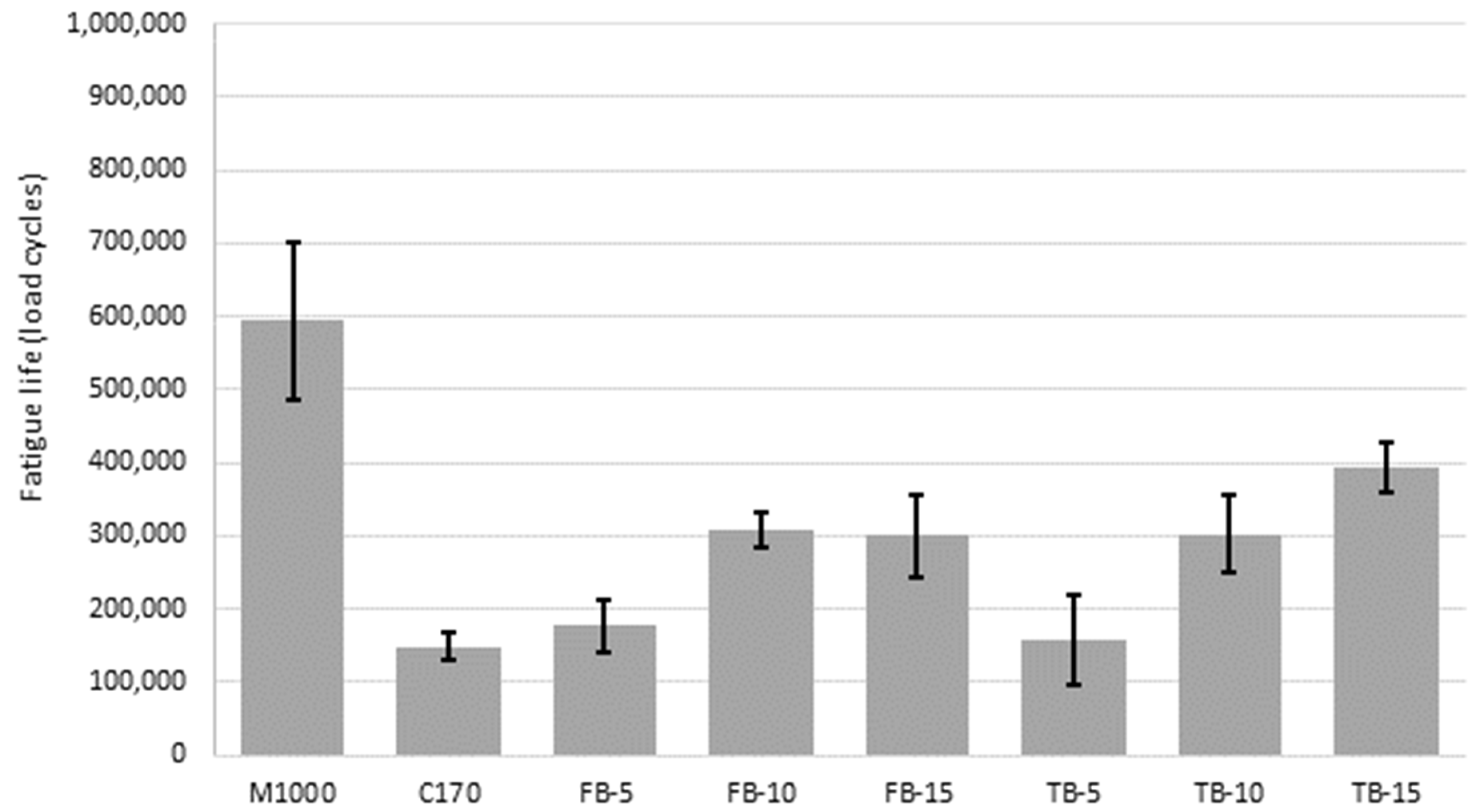
| Sample Description | Modified Binder Content (by Mass) |
|---|---|
| Control with M1000 bitumen | 5.9% |
| Control with C170 bitumen | 5.9% |
| Short-blended 5% crumb rubber | 6.1% |
| Short-blended 10% crumb rubber | 6.5% |
| Short-blended 15% crumb rubber | 7.0% |
| Long-blended 5% crumb rubber | 6.0% |
| Long-blended 10% crumb rubber | 6.4% |
| Long-blended 15% crumb rubber | 6.8% |
| Property | Torsional Recovery | Penetration | Softening Point | Viscosity at 60 °C | Segregation | Jnr3.2 at 60 °C (MSCR) (RTFO) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Units | (%) | (Units) | (°C) | (Pa.s) | (%) | (kPa−1) |
| Method | AGPT/T122 | AGPT/T108 | AGPT/T131 | AGPT/T131 | AGPT/T108 | AASHTO T350 |
| M1000 | 9 | 40.5 | 56.7 | 1354 | N/A | 0.126 |
| C170 | 4 | 65.7 | 48.3 | 203 | N/A | 2.101 |
| FB-5 | 14 | 60.7 | 51.2 | 474 | 6 | 1.268 |
| FB-10 | 21 | 54.7 | 57.8 | 947 | 8 | 0.568 |
| FB-15 | 41 | 50.4 | 62.4 | 1712 | 12 | 0.285 |
| TB-5 | 14 | 65.2 | 50.7 | 461 | 5 | 1.192 |
| TB-10 | 25 | 63.8 | 54.0 | 691 | 18 | 0.749 |
| TB-15 | 28 | 64.5 | 56.5 | 1116 | 18 | 0.468 |
| Designation | CR Content | CR Blending Duration |
|---|---|---|
| M1000 | Not applicable | Not applicable |
| C170 | Not applicable | Not applicable |
| FB-5 | 5% | Short |
| FB-10 | 10% | Short |
| FB-15 | 15% | Short |
| TB-5 | 5% | Long |
| TB-10 | 10% | Long |
| TB-15 | 15% | Long |
| Property | Method | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Resilient modulus | AS/NZS 2891.13.1 | Indirect tensile modulus at 25 °C, an indicator of relative material stiffness |
| Wheel tracking | AGPT/T231 | Cooper’s wheel tracker to 10,000 passes at 60 °C, an indicator of relative deformation resistance at high in-service temperatures |
| Fatigue life | AGPT/T274 | The number of four-point bending cycles at 20 °C and 200 µɛ sinusoidal until the modulus is reduced to 50% of the initial modulus, an indicator of relative fracture resistance at intermediate in-service temperatures |
| IDEAL-CT | ASTM D8225 | An energy-based index calculated from monotonic loading at 50 mm/min and 25 °C, an indicator of intermediate temperature crack resistance |
| Tensile strength ratio | AGPT/T232 | Modified Lottman test, as the ratio between the average unconditioned an indicator of moisture damage (stripping) resistance |
| Mixture | Resilient Modulus (MPa) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Specimen 1 | Specimen 2 | Specimen 3 | |
| M1000 | 5836 | 6142 | 6262 |
| C170 | 2850 | 3010 | 3180 |
| FB-5 | 2950 | 3240 | 3310 |
| FB-10 | 3692 | 3584 | 3947 |
| FB-15 | 4070 | 3880 | 3920 |
| TB-5 | 3015 | 3130 | 3384 |
| TB-10 | 2883 | 3194 | 3011 |
| TB-15 | 2340 | 2564 | 2742 |
| Mixture | Fatigue Life (Cycles to Failure) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Specimen 1 | Specimen 2 | Specimen 3 | |
| M1000 | 518,210 | 669,240 | 593,725 |
| C170 | 152,090 | 165,630 | 127,800 |
| FB-5 | 215,670 | 173,390 | 143,730 |
| FB-10 | 306,340 | 283,420 | 332,130 |
| FB-15 | 239,910 | 304,790 | 354,510 |
| TB-5 | 87,570 | 200,060 | 184,220 |
| TB-10 | 357,480 | 297,500 | 251,820 |
| TB-15 | 412,270 | 352,560 | 414,750 |
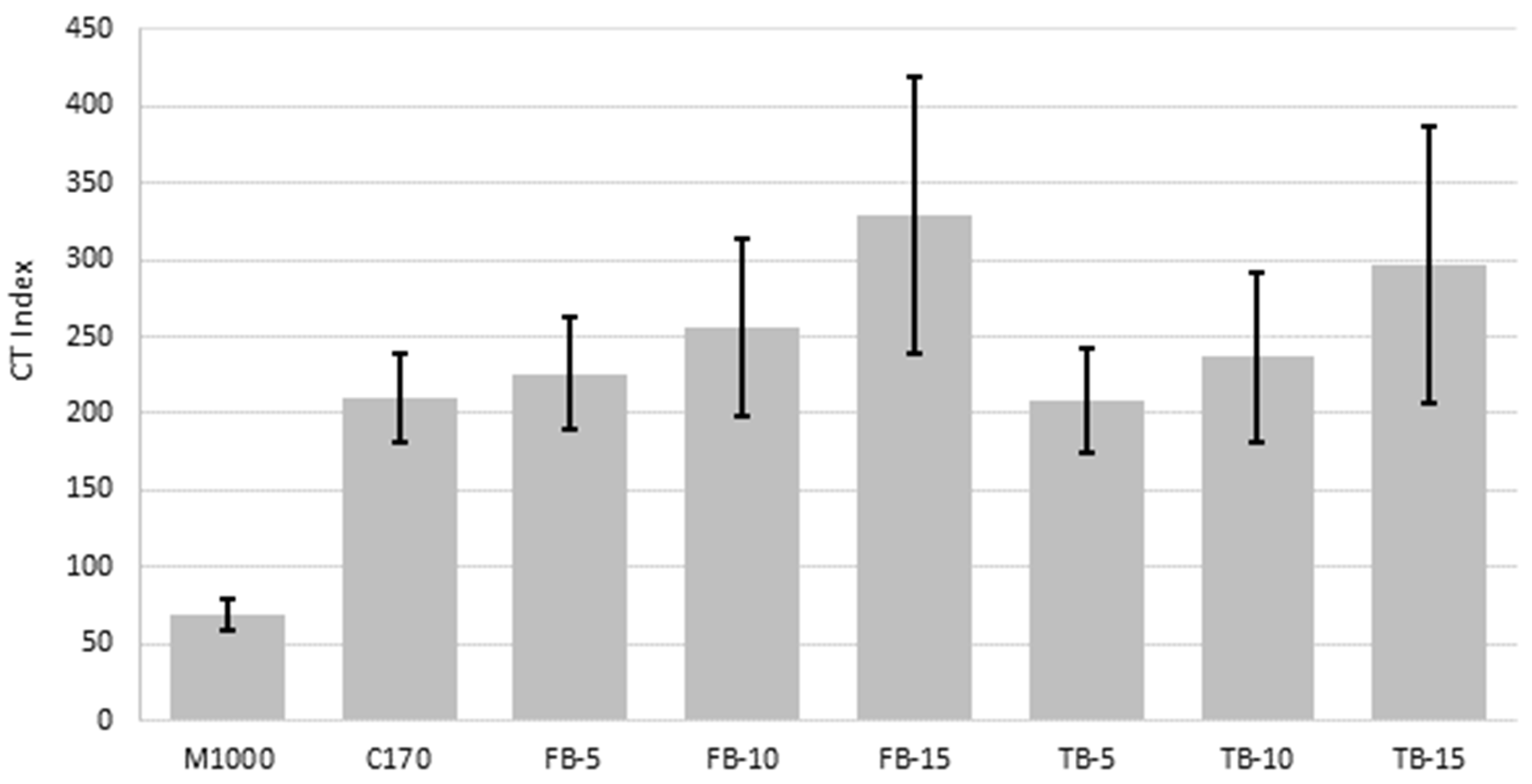
| Mixture | CT Index | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Specimen 1 | Specimen 2 | Specimen 3 | |
| M1000 | 65.4 | 60.3 | 79.9 |
| C170 | 239.8 | 182.6 | 205.5 |
| FB-5 | 184.3 | 248.9 | 263.5 |
| FB-10 | 245.6 | 317.3 | 203.8 |
| FB-15 | 272.7 | 432.2 | 281.0 |
| TB-5 | 177.1 | 244.2 | 203.1 |
| TB-10 | 297.4 | 188.7 | 224.6 |
| TB-15 | 243.9 | 245.8 | 401.4 |
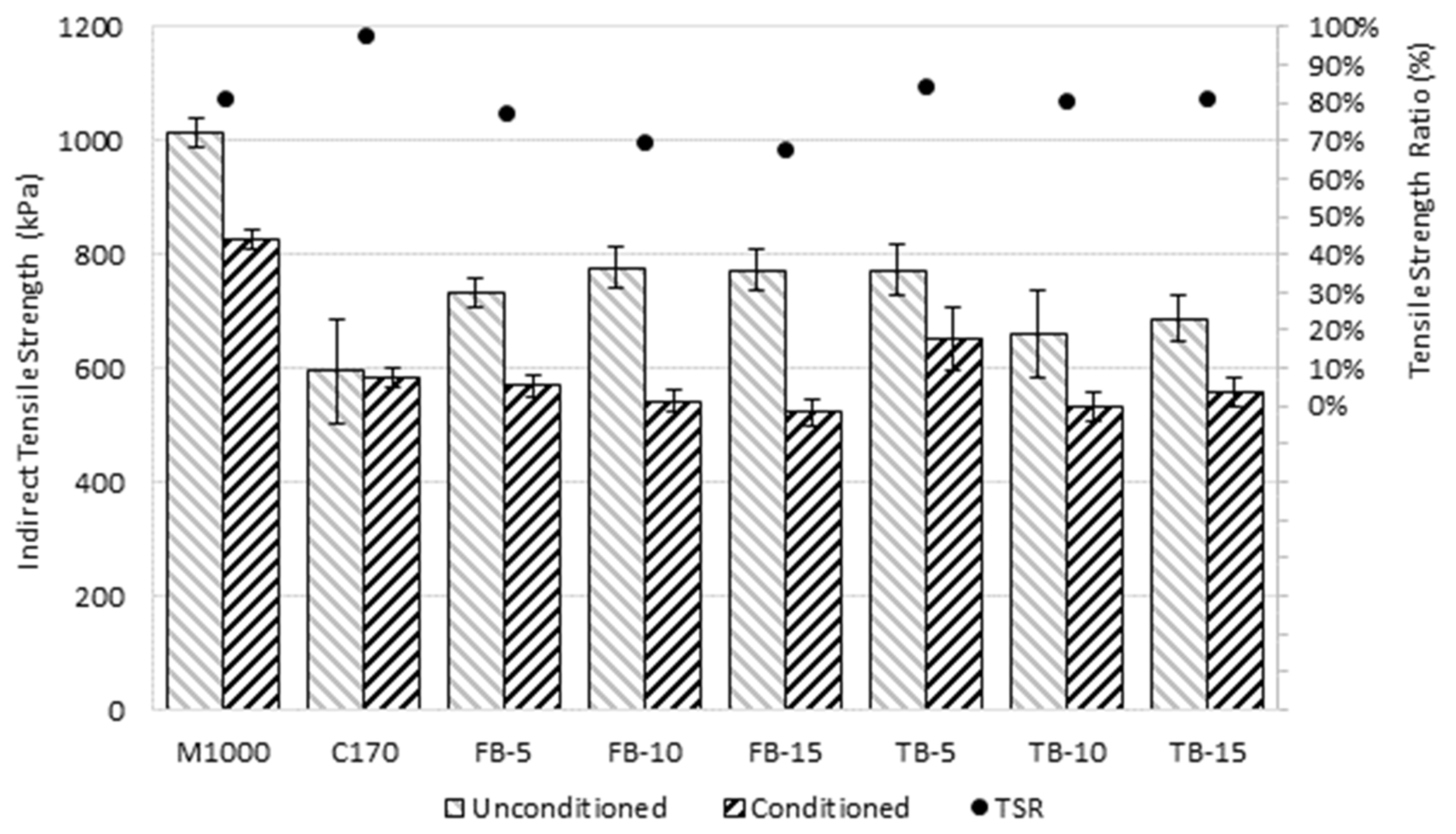
| Mixture | CT Index | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unconditioned Specimens | Conditioned Specimens | |||||
| Specimen 1 | Specimen 2 | Specimen 3 | Specimen 4 | Specimen 5 | Specimen 6 | |
| M1000 | 1025 | 985 | 1034 | 816 | 846 | 816 |
| C170 | 490 | 627 | 666 | 597 | 567 | 588 |
| FB-5 | 732 | 707 | 761 | 592 | 555 | 561 |
| FB-10 | 802 | 793 | 735 | 536 | 565 | 527 |
| FB-15 | 812 | 766 | 739 | 531 | 497 | 542 |
| TB-5 | 752 | 741 | 823 | 607 | 637 | 715 |
| TB-10 | 607 | 627 | 746 | 509 | 558 | 529 |
| TB-15 | 697 | 720 | 642 | 540 | 588 | 550 |
| Property | Short Duration (FB) | Long Duration (TB) |
|---|---|---|
| Stiffness | Improvement, increasing with increasing CR content | Comparable, but decreasing with increasing CR content |
| Deformation resistance | Significant improvement, increasing with increasing CR content | Significant improvement, increasing with increasing CR content |
| Fatigue resistance | Significant improvement at 10% and 15%, increasing with increasing CR content | Significant improvement at 10% and 15%, increasing with increasing CR content |
| Fracture resistance | Insignificant but consistent improvement, increasing with increasing CR content | Insignificant but consistent improvement, increasing with increasing CR content |
| Moisture resistance | Significant reduction | Insignificant average reduction |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
White, G.; Kidd, A. Analysis of the Effects of Rubber Dosage and Digestion Time on the Mechanical Properties of Low Dosage Crumb-Rubber-Modified Asphalt Concrete Mixtures. Materials 2025, 18, 1419. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18071419
White G, Kidd A. Analysis of the Effects of Rubber Dosage and Digestion Time on the Mechanical Properties of Low Dosage Crumb-Rubber-Modified Asphalt Concrete Mixtures. Materials. 2025; 18(7):1419. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18071419
Chicago/Turabian StyleWhite, Greg, and Andrew Kidd. 2025. "Analysis of the Effects of Rubber Dosage and Digestion Time on the Mechanical Properties of Low Dosage Crumb-Rubber-Modified Asphalt Concrete Mixtures" Materials 18, no. 7: 1419. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18071419
APA StyleWhite, G., & Kidd, A. (2025). Analysis of the Effects of Rubber Dosage and Digestion Time on the Mechanical Properties of Low Dosage Crumb-Rubber-Modified Asphalt Concrete Mixtures. Materials, 18(7), 1419. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18071419







