La/Fe-Bimetallic-Modified Red Brick Powder for Phosphate Removal from Wastewater: Characterization, Adsorption, and Mechanism
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Chemical Precursors
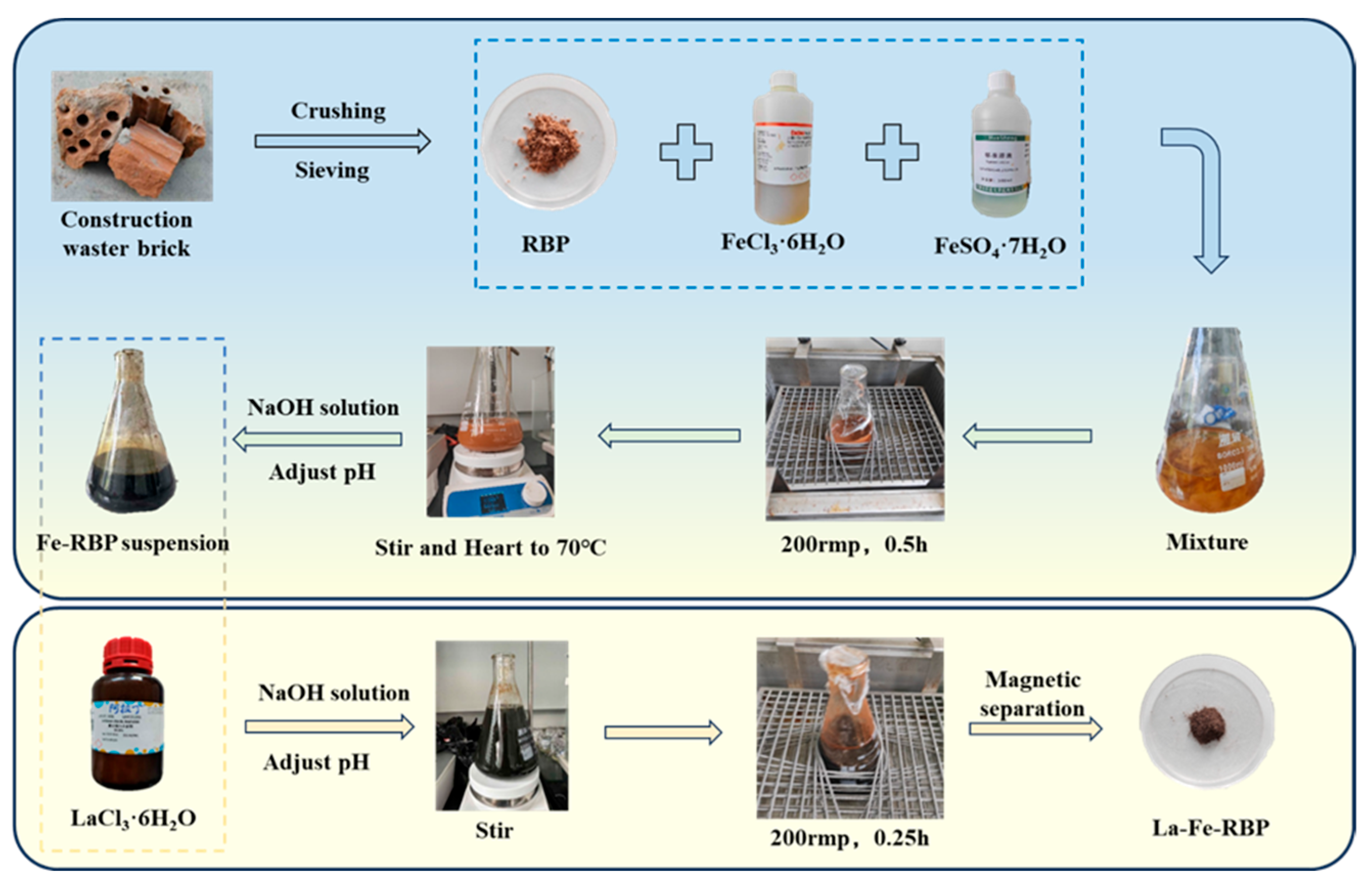
2.2. Synthesis of La-Fe-RBP
2.3. Material Properties
2.4. Adsorption Test
2.5. Recycling Capacity
2.6. Remove Phosphorus from Real Sewage
3. Results and Discussion
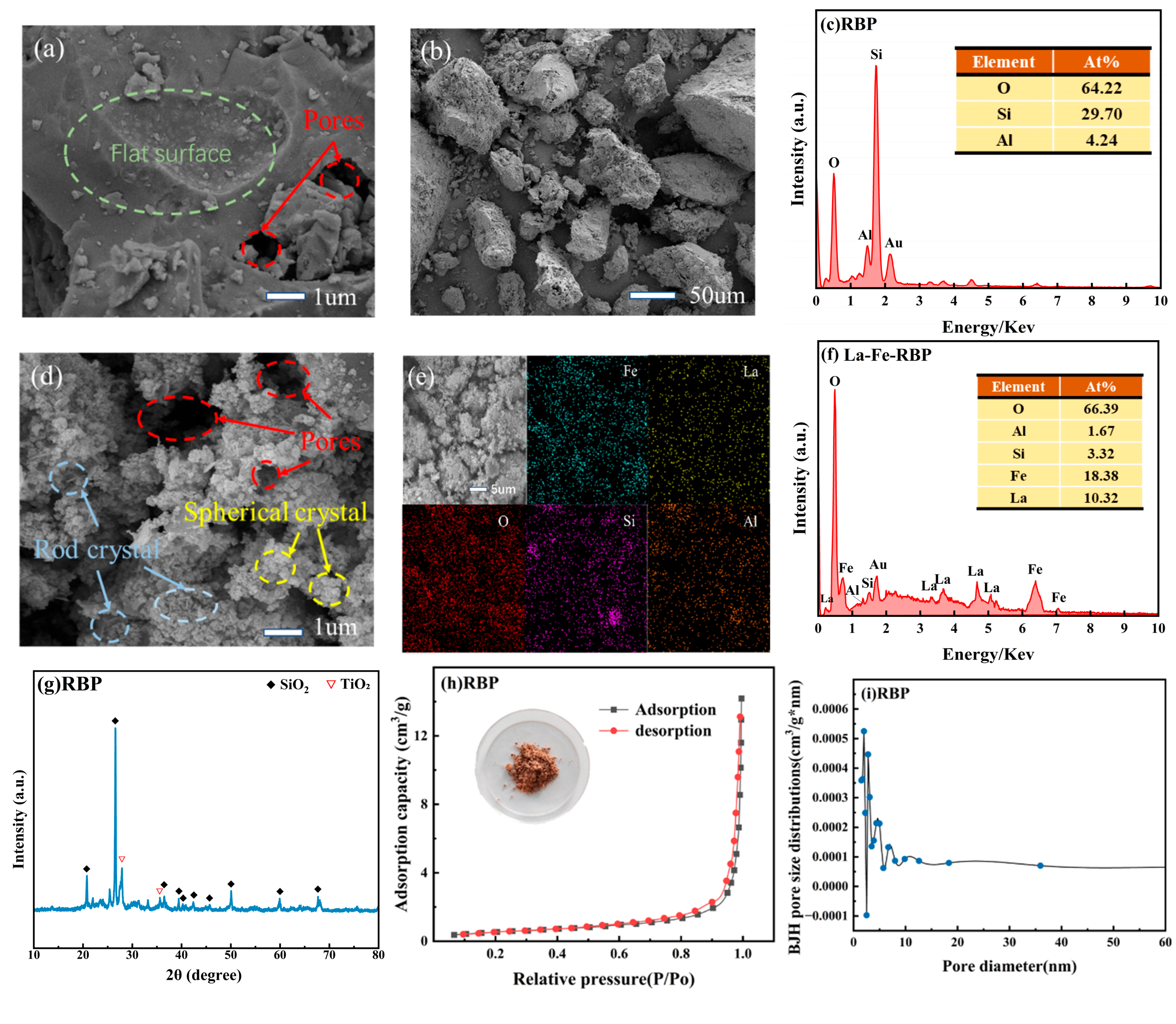
3.1. Material Characterization
3.2. Adsorption Kinetics
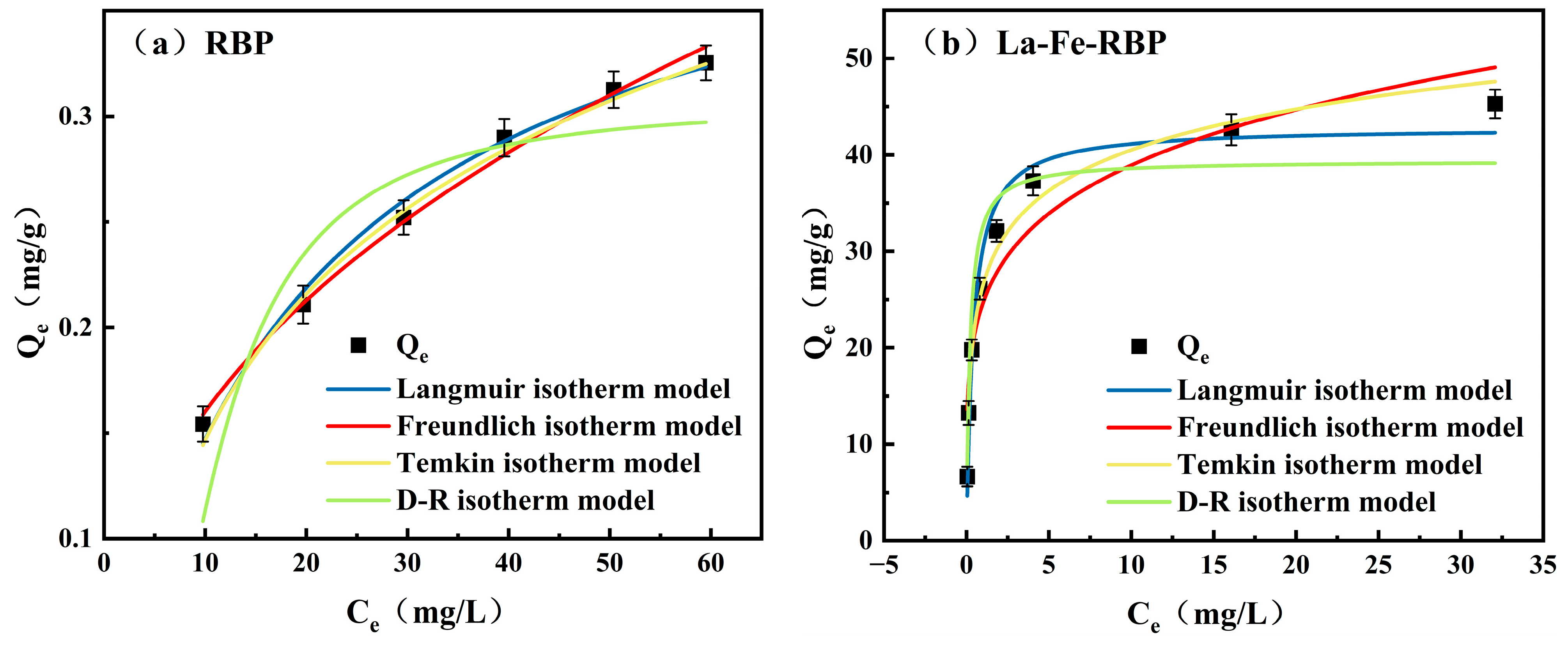
3.3. Adsorption Isotherm
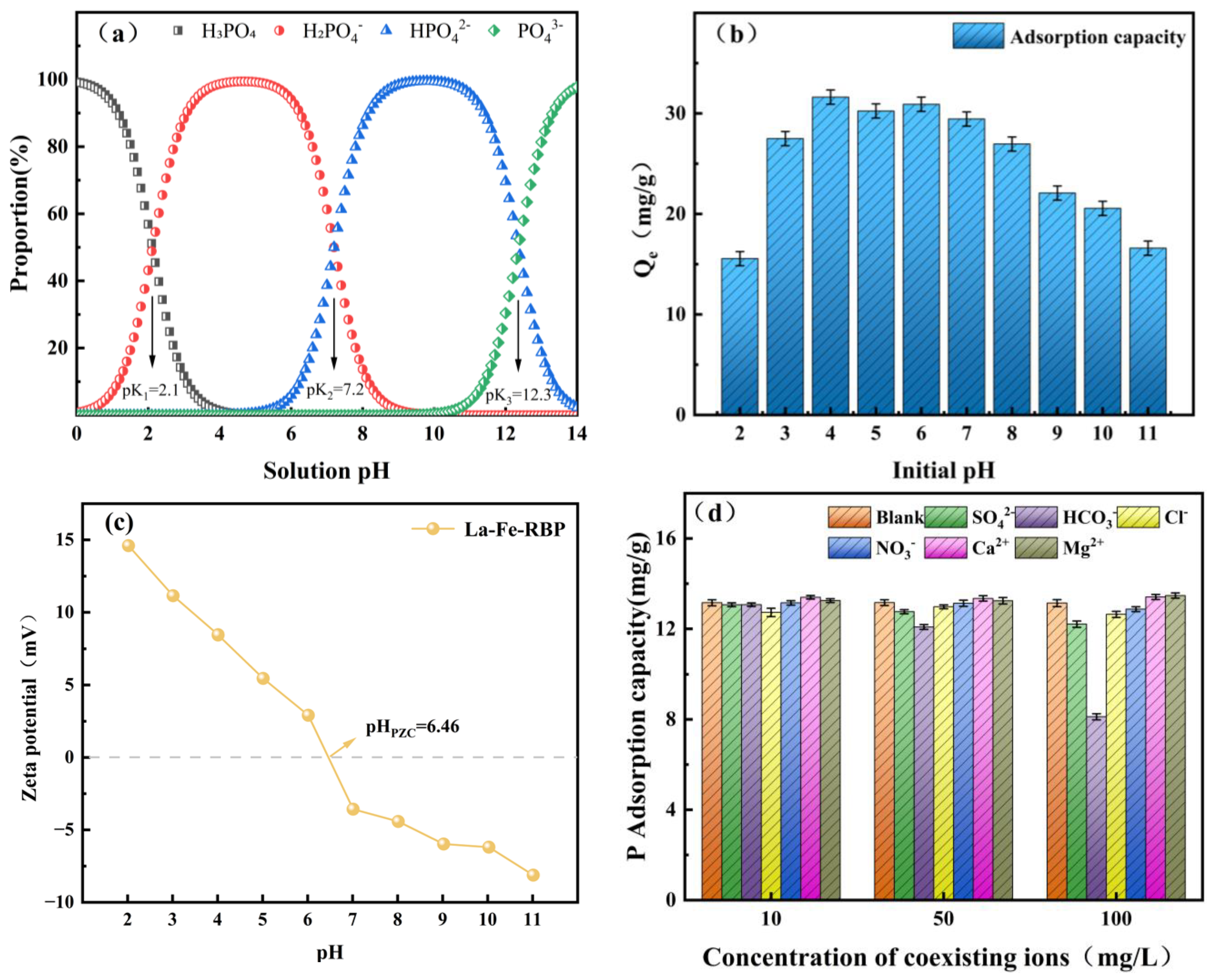
3.4. Impact of pH and Coexisting Ions
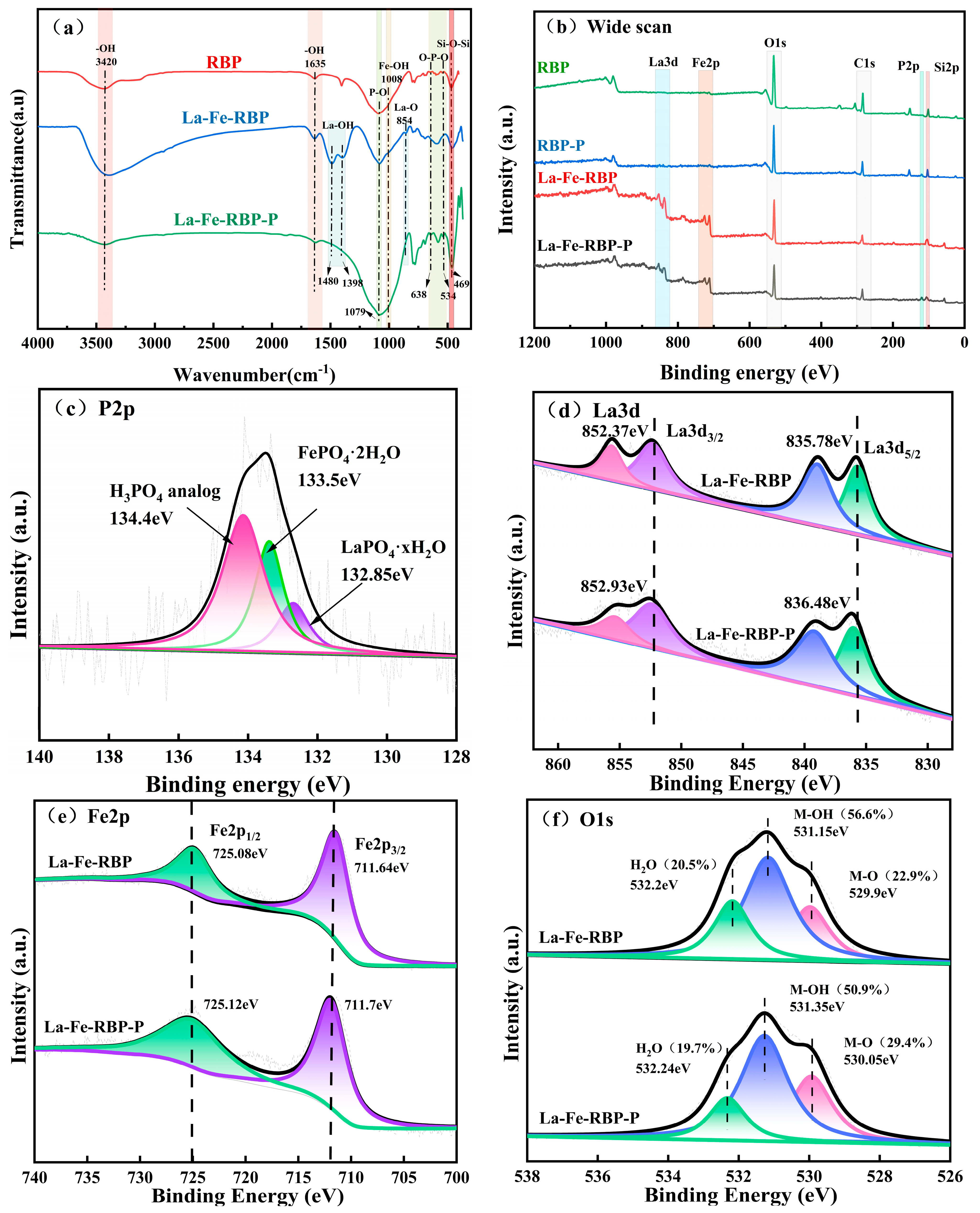
3.5. FTIR and XPS
3.6. The Recyclability of La-Fe-RBP
3.7. Real Sewage Treatment
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- Due to the incorporation of iron and lanthanum, La-Fe-RBP exhibits significant roughness, porosity, and magnetism. La-Fe-RBP demonstrates superior adsorption kinetics and capacity compared to RBP, reaching saturation in approximately 60 min. The PSO model can better describe the adsorption kinetics of the adsorbent, indicating that the adsorption process is primarily chemical adsorption. Isotherm studies show that the Langmuir model can effectively describe the phosphate loading behavior on La-Fe-RBP, with a maximum theoretical Q value of 42.835 mg/g;
- (2)
- Batch adsorption tests showed that La-Fe-RBP maintained a high value of Q across a wide range of pH values (3 to 8) and demonstrated high selectivity for phosphate, even in the presence of competing ions, with minimal interference at low concentrations. The results obtained from the XPS and FTIR characterizations proved that the adsorption mechanism involved ligand exchange and electrostatic attraction, forming a metal–O–P inner complex on the surface of La-Fe-RBP.
- (3)
- La-Fe-RBP can be successfully recovered magnetically and retains good phosphate adsorption efficiency even after five desorption/adsorption cycles. In the treatment of real wastewater, it still meets the Class IV surface water environmental quality standards of China.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cheng, H. Reuse research progress on waste clay brick. Procedia Environ. Sci. 2016, 31, 218–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, L.; Jin, Y.; Gong, Y.; Li, A.; Li, J.; Li, F. Recycled aggregates from construction and demolition waste as wetland substrates for pollutant removal. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 311, 127766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, Y. Research on the Phosphate Removal Performance of Runoff Water Used by Modified Demolition Grated Wasted Red Bricks. Master’s Thesis, Nanjing University of Information Science and Technology, Nanjing, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, D.; Liu, M.; Ma, Z. Properties of the foam concrete containing waste brick powder derived from construction and demolition waste. J. Build. Eng. 2020, 32, 101509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Zheng, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, T. Recycled brick powder from construction and demolition waste as waterborne coating filler with robust scrubbing resistance. Constr Build Mater. 2023, 385, 131494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Qi, T.; Zhu, C.A. Experimental Study on Solid Waste Combined with Cement to Solidify Dredged Silt. Gd. Archit. Civ. Eng. 2021, 28, 46–50. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Ding, L.; Li, F.; Peng, J. Recycled aggregates from construction and demolition wastes as alternative filling materials for highway subgrades in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 255, 120223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.; Sun, H.; Zhang, X.; He, T.; Wang, Y.; Mo, Q.; Zhuo, C. Degradation of trichloromethane by immobilized microspheres of modified red brick. Desalination Water Treat. 2023, 306, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Zhao, Y.; Zhan, Y.; Wang, Y. Control of internal phosphorus release from sediments using magnetic lanthanum/iron-modified bentonite as active capping material. Environ Pollut. 2020, 264, 114809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, R.; Ma, J.; Jiao, G.; Sun, R. Efficient removal of phosphate from aqueous media using magnetic bimetallic lanthanum-iron-modified sulfonylmethylated lignin biochar. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 247, 125809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, W.; Wang, J.; Zhou, X. Characteristics of Phosphorus Adsorption by Three Kinds of Fillers and Their Influence Factors. Wetland Sci. 2018, 16, 341–346. [Google Scholar]
- Lan, Y.; Gai, S.; Cheng, K.; Li, J.; Yang, F. Lanthanum carbonate hydroxide/magnetite nanoparticles functionalized porous biochar for phosphate adsorption and recovery: Advanced capacity and mechanisms study. Environ. Res. 2022, 214, 113783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, H.; Yang, Y.; Zhu, R.; Liu, J.; Usman, M.; Chen, Q.; He, H. Superior adsorption of phosphate by ferrihydrite-coated and lanthanum-decorated magnetite. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2018, 530, 704–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Tian, Q.; Chen, H.; He, M.; Qiu, F.; Zhang, T. Resourcing of building waste brick slags as a column packing material: Toward excellent phosphate removal performance for water treatment. J. Water Process. Eng. 2023, 51, 103344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Zhang, H.; Hu, X.; Chen, R.; Guo, W.; Wang, H.; Wang, C.; Yuan, J.; Chen, L.; Xia, S. Efficient phosphate elimination from aqueous media by La/Fe bimetallic modified bentonite: Adsorption behavior and inner mechanism. Chemosphere 2023, 312, 137149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB 11893-89; Water Quality-Determination of Total Phosphorus-Ammonium Molybdate Spectrophotometric Method. Ministry of Ecology and Environment: Beijing, China, 1989.
- Liu, Z.; Liang, Z.; Wu, S. Novel lanthanum and waste lye modified fly ash zeolite for nitrogen and phosphorus removal: Mechanisms and application in the constructed wetland. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2024, 208, 559–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Zhao, S.; Fan, F.; Zhang, B.-T.; Wang, S. Magnetically separable and recyclable lanthanum/iron co-modified attapulgite: A sustainable option to efficiently control phosphate loading. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 348, 131294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Zhao, Z.; Kang, H.; Guo, Y.; Peng, T.; Li, K.; Yan, L. Lanthanum-doped mesoporous magnetic carbon microspheres derived from Camellia oleifera shell biomass for phosphate removal from industrial wastewater. Sep. Purif. 2025, 356, 129887. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, J.; Xiang, C.; Zhang, G.; Wang, H.; Ji, Q.; Qu, J. Activation of lattice oxygen in LaFe (oxy) hydroxides for efficient phosphorus removal. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 9073–9080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Xu, R.; Li, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, J.; Chen, S.; Yin, H.; Zeng, Z. La(OH)3-modified magnetic CoFe2O4 nanocomposites: A novel adsorbent with highly efficient activity and reusability for phosphate removal. Colloids Surf. 2020, 599, 124870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhou, Q.; Liu, J.; Chang, N.; Wan, L.; Chen, J. Phosphate adsorption on lanthanum hydroxide-doped activated carbon fiber. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 185, 160–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Zhuang, Y.; Li, G.; Zou, T.; Wang, H.; Tan, W.; Yang, M. Selective adsorption and efficient removal of phosphate using lanthanum-modified mesoporous silica from aqueous solutions. Desalination Water Treat. 2021, 241, 159–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Xie, Y.; Lu, H.; Xin, Y.; Altaf, R.; Zhu, S.; Liu, D. Facile preparation of dual La-Zr modified magnetite adsorbents for efficient and selective phosphorus recovery. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 413, 127530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, W.-J.; Guo, L.-X.; Yu, L.-Q.; Zhang, Q.; Xiong, J.-R.; Zhu, X.-Y.; Wang, X.-C.; Huang, B.-C.; Jin, R.-C. Phosphorus removal from diluted wastewaters using a La/C nanocomposite-doped membrane with adsorption-filtration dual functions. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 405, 126924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, K.; Yang, W.; Song, P.; Fan, L.; Xu, S.; Li, B.; Feng, L. Lanthanum-modified magnetic oyster shell and its use for enhancing phosphate removal from water. Colloids Surf. 2022, 633, 127897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.; Wan, J.; Zhang, Y.; Pan, B.; Lo, I.M. Selective phosphate removal from water and wastewater using sorption: Process fundamentals and removal mechanisms. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 54, 50–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.; Zhao, H.; Teng, Z.; Guo, Y.; Ji, X.; Hu, W.; Li, M. Tuning microscopic structure of La-MOFs via ligand engineering effect towards enhancing phosphate adsorption. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 353, 120149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Lin, H.; Dong, Y.; Wang, L. Preferable adsorption of phosphate using lanthanum-incorporated porous zeolite: Characteristics and mechanism. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 426, 995–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Q.; Shi, C.; Shi, W.; Huang, X.; Ye, Y.; Jiang, W.; Kang, J.; Liu, D.; Ren, Y.; Li, D. Preferable phosphate removal by nano-La (III) hydroxides modified mesoporous rice husk biochars: Role of the host pore structure and point of zero charge. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 662, 511–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Luo, H.; Han, R.; Wu, W.; Yang, J.; Qin, T.; Chen, L.; Liu, M.; He, B.-J.; Jing, Z. Preparation of efficient and reusable lanthanum and iron co-modified soda residue for selective phosphate removal from domestic sewage. Sci Rep. 2025, 15, 3145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.; Yang, P.; Kong, M.; Li, W. Use of lanthanum/aluminum co-modified granulated attapulgite clay as a novel phosphorus (P) sorbent to immobilize P and stabilize surface sediment in shallow eutrophic lakes. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 385, 123395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Li, X.; Yang, Q.; Wang, D.; Xu, Q.; Yao, F.; Chen, F.; Tao, Z.; Huang, X. Hydrated lanthanum oxide-modified diatomite as highly efficient adsorbent for low-concentration phosphate removal from secondary effluents. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 231, 370–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, T.; Su, X.; Yu, X.; Song, H.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, Y. La(OH)3-modified magnetic pineapple biochar as novel adsorbents for efficient phosphate removal. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 263, 207–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, S.; Lo, I.M. Phosphate removal from river water using a highly efficient magnetically recyclable Fe3O4/La(OH)3 nanocomposite. Chemosphere 2020, 261, 128118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Huang, L.; Le, X.; Huang, R. Performance and mechanism on the phosphorus adsorption by magnetic lanthanum-loaded acidified vermiculite. KSCE J. Civ. Eng. 2024, 46, 197–205. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, Q.; Wei, J.; Guo, Z.; Song, Y. Adsorption and immobilization of phosphorus from water and sediments using a lanthanum-modified natural zeolite: Performance, mechanism and effect. Sep. Purif. 2024, 329, 125187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, H.; Wang, Y.; Shi, B. NaLa(CO3)2 hybridized with Fe3O4 for efficient phosphate removal: Synthesis and adsorption mechanistic study. Water Res. 2019, 155, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Index | pH | COD (mg/L) | TN (mg/L) | NH4+-N (mg/L) | TP (mg/L) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Value | 6.92 ± 0.2 | 382 ± 5 | 30.2 ± 0.2 | 16.7 ± 0.3 | 5.9 ± 0.1 |
| Samples | BET Surface Areas (m2/g) | Total Pore Volume (cm3/g) | Mean Pore Size (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| RBP | 1.855 | 0.019 | 8.855 |
| La-Fe-RBP | 67.59 | 0.399 | 22.687 |
| Adsorbents | T (°C) | PFO Model | PSO Model | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| K1 (1/min) | Qe (mg/g) | R2 | K2 (g/mg·min) | Qe (mg/g) | R2 | ||
| RBP | 25 | 0.0083 | 0.1180 | 0.9445 | 0.0991 | 0.1292 | 0.9621 |
| La-Fe-RBP | 25 | 0.3004 | 6.6527 | 0.8823 | 0.2839 | 6.6907 | 0.9584 |
| Adsorbents | T (°C) | Langmuir Model | Freundlich Model | Temkin Model | D-R Model | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Qm | KL | R2 | KF | 1/n | R2 | A | B | R2 | K | E | R2 | ||
| RBP | 25 | 0.426 | 0.053 | 0.988 | 0.062 | 0.410 | 0.991 | 0.435 | 0.100 | 0.991 | 86.42 | 0.076 | 0.911 |
| La-Fe-RBP | 25 | 42.83 | 2.417 | 0.966 | 24.63 | 0.199 | 0.896 | 77.01 | 6.094 | 0.987 | 0.0067 | 8.639 | 0.924 |
| Materials | Absorption Capacity (mg/g) | Experimental Conditions (Temperature, Dosage, P Initial Concentration) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| La-Fe-RBP | 42.84 | 25 °C; 1.5 g/L; 10–120 mg/L | This Work |
| Activated carbon fiber–La–OH | 15.3 | 25 °C; 2.5 g/L;10–70 mg/L | [22] |
| Mesoporous silica–La | 27.98 | 25 °C; 0.8 g/L; 5–80 mg/L | [23] |
| La–zeolite synthesized from fly ash | 21.48 | 25 °C; 10 g/L; 5–300 mg/L | [17] |
| La–Zr@Fe3O4 | 49.1 | 25 °C; 0.25 g/L; 0–50 mg/L | [24] |
| Magnetic lanthanum/iron-modified bentonite | 14.3 | 25 °C; 2 g/L; 2–40 mg/L | [9] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, Y.; Luo, H.; Han, R.; Tao, S.; Liu, M.; Tang, M.; Xing, J.; Chen, L.; He, B.-J. La/Fe-Bimetallic-Modified Red Brick Powder for Phosphate Removal from Wastewater: Characterization, Adsorption, and Mechanism. Materials 2025, 18, 1326. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18061326
Zhao Y, Luo H, Han R, Tao S, Liu M, Tang M, Xing J, Chen L, He B-J. La/Fe-Bimetallic-Modified Red Brick Powder for Phosphate Removal from Wastewater: Characterization, Adsorption, and Mechanism. Materials. 2025; 18(6):1326. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18061326
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Yunrui, Hui Luo, Rubin Han, Shiheng Tao, Meng Liu, Ming Tang, Jiayao Xing, Limin Chen, and Bao-Jie He. 2025. "La/Fe-Bimetallic-Modified Red Brick Powder for Phosphate Removal from Wastewater: Characterization, Adsorption, and Mechanism" Materials 18, no. 6: 1326. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18061326
APA StyleZhao, Y., Luo, H., Han, R., Tao, S., Liu, M., Tang, M., Xing, J., Chen, L., & He, B.-J. (2025). La/Fe-Bimetallic-Modified Red Brick Powder for Phosphate Removal from Wastewater: Characterization, Adsorption, and Mechanism. Materials, 18(6), 1326. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18061326








