Magnetic Biochar Prepared with Rosa roxburghii Residue as Adsorbents for Congo Red Removal
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents
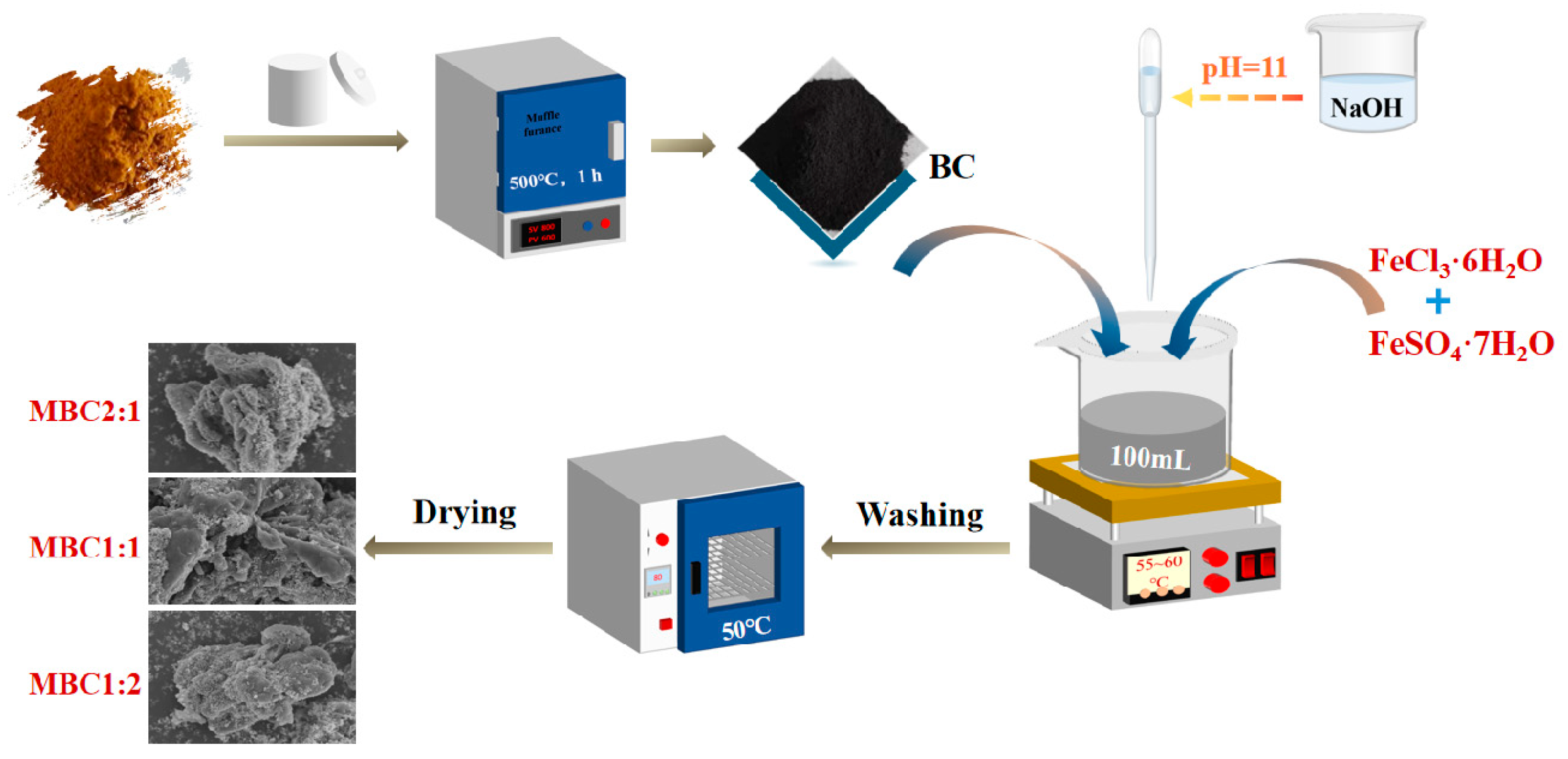
2.2. Magnetic Biochar Production
2.3. Characterization of Biochars
2.4. Adsorption Experiments
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Biochar Characterization
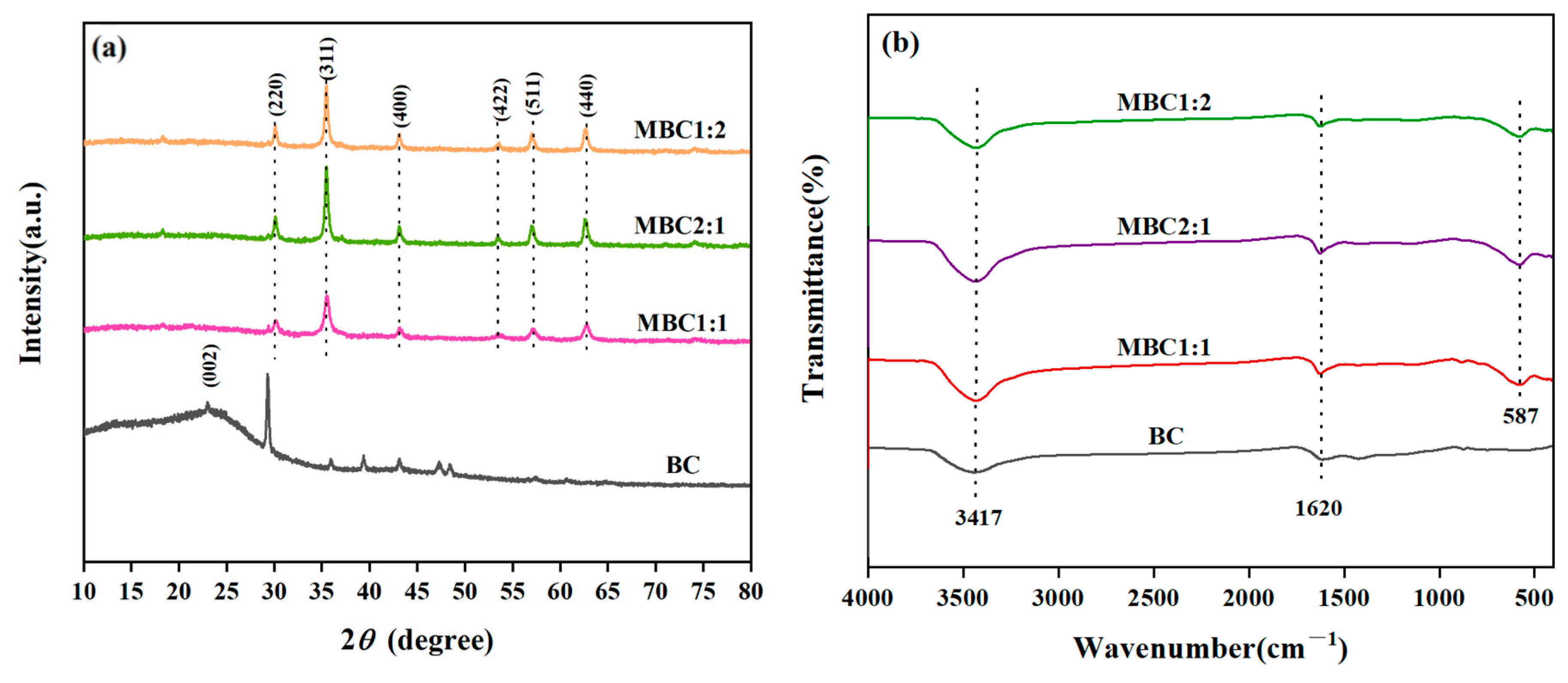
3.1.1. FTIR and XRD
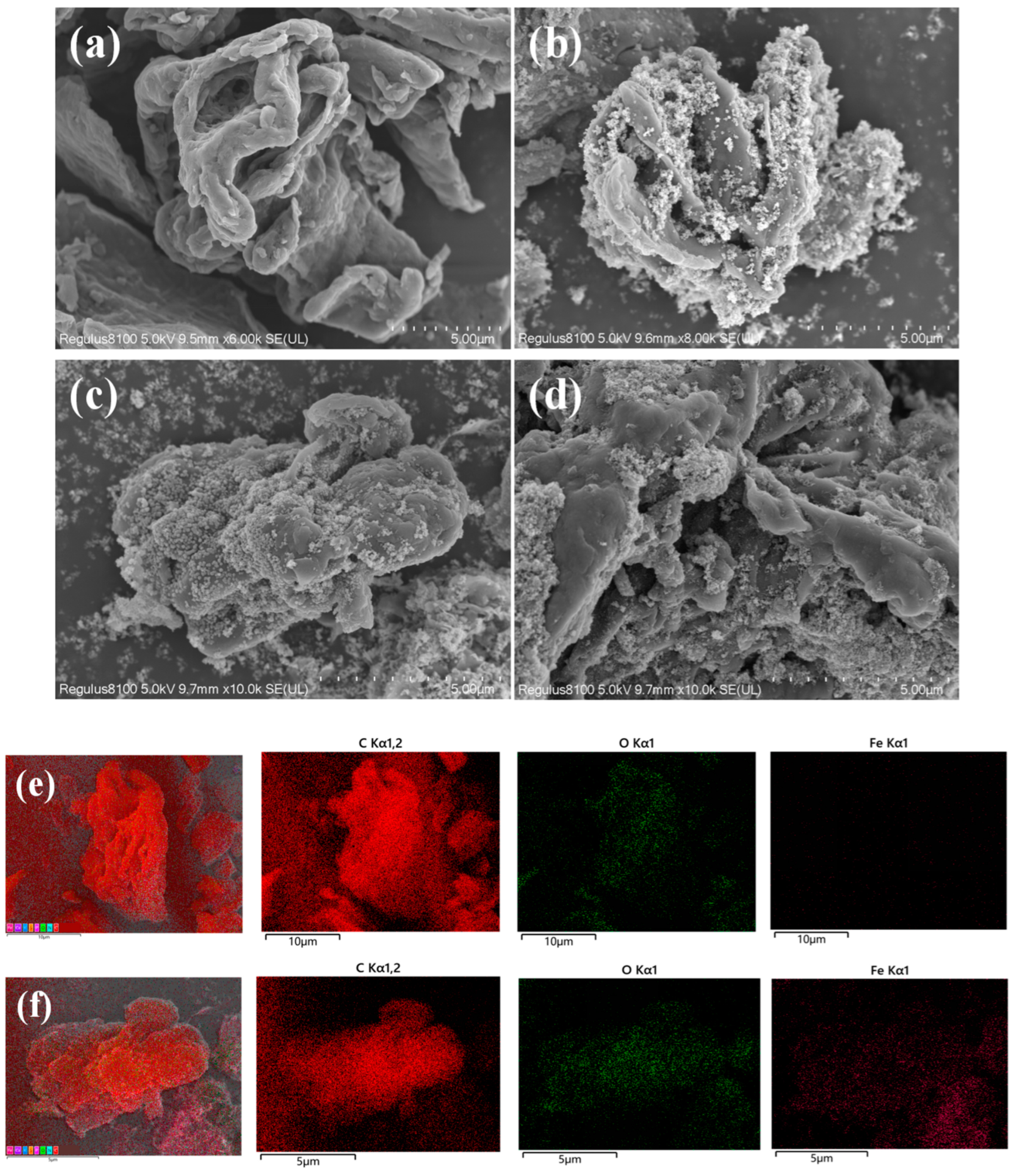
3.1.2. SEM-EDS
3.1.3. BET
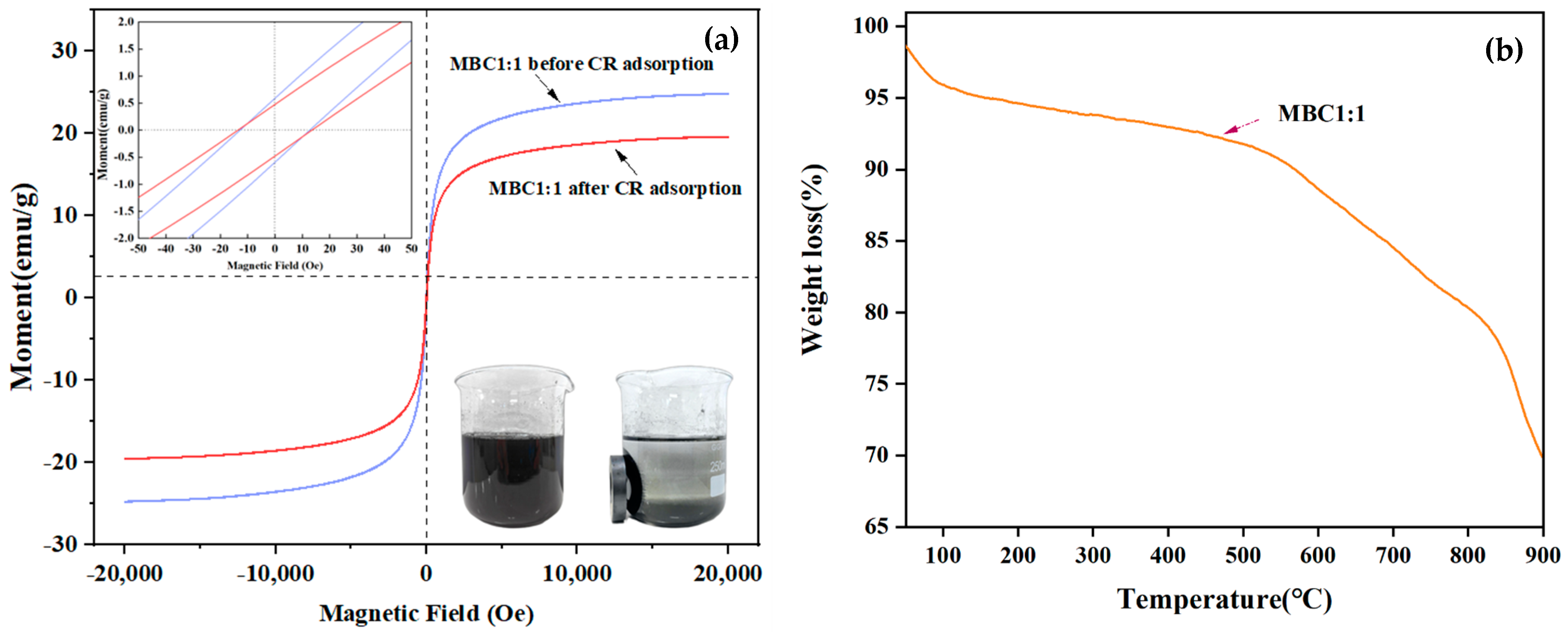
3.1.4. VSM
3.1.5. TGA
3.2. Adsorption Experiment
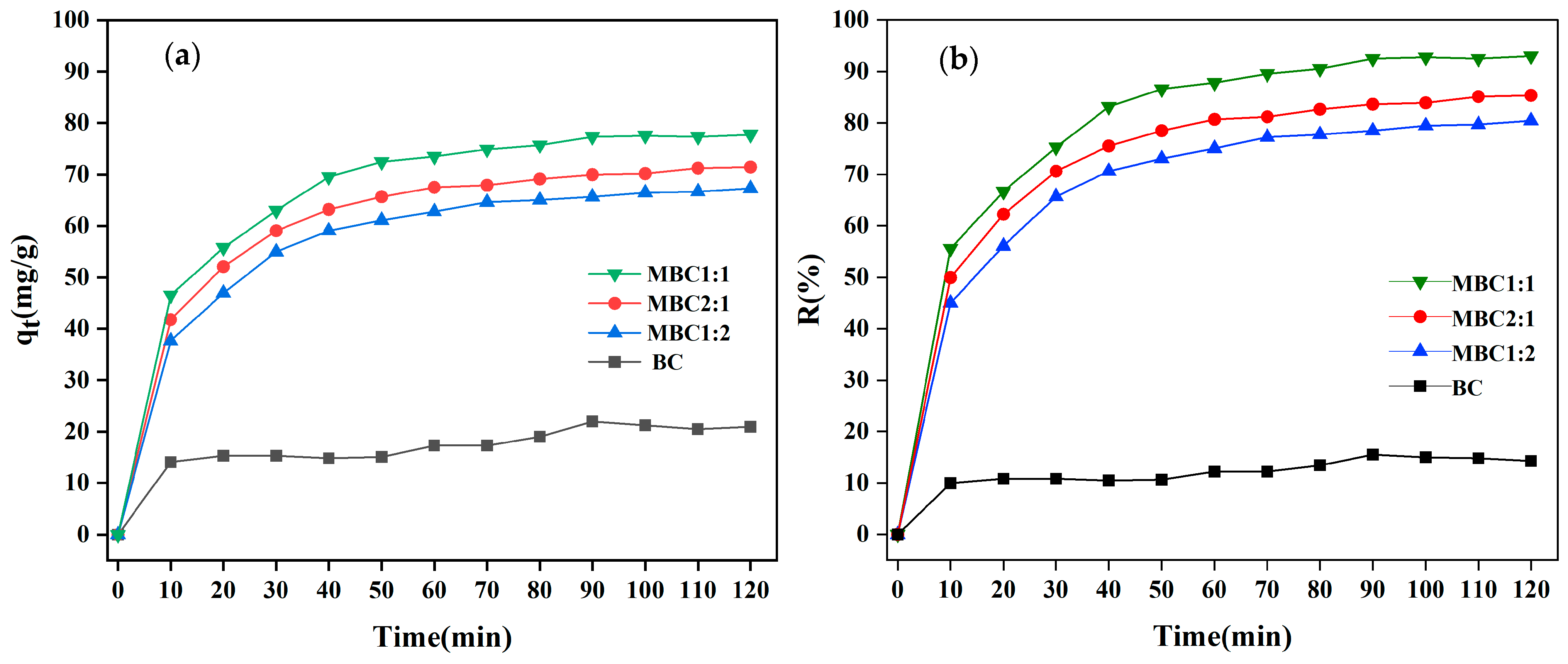
3.2.1. Effects of Different Biochars
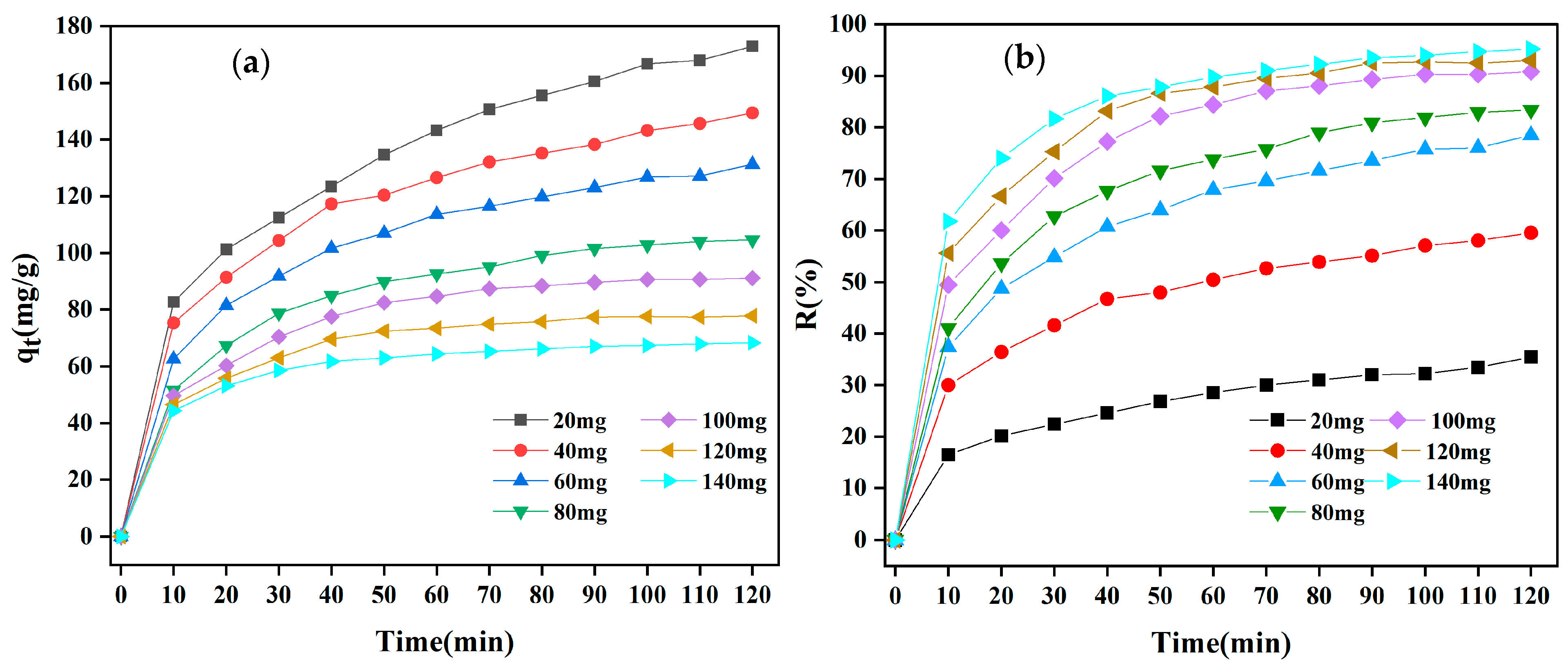
3.2.2. Influence of Adsorbent Dosage
3.2.3. Impact of CR Initial Concentration
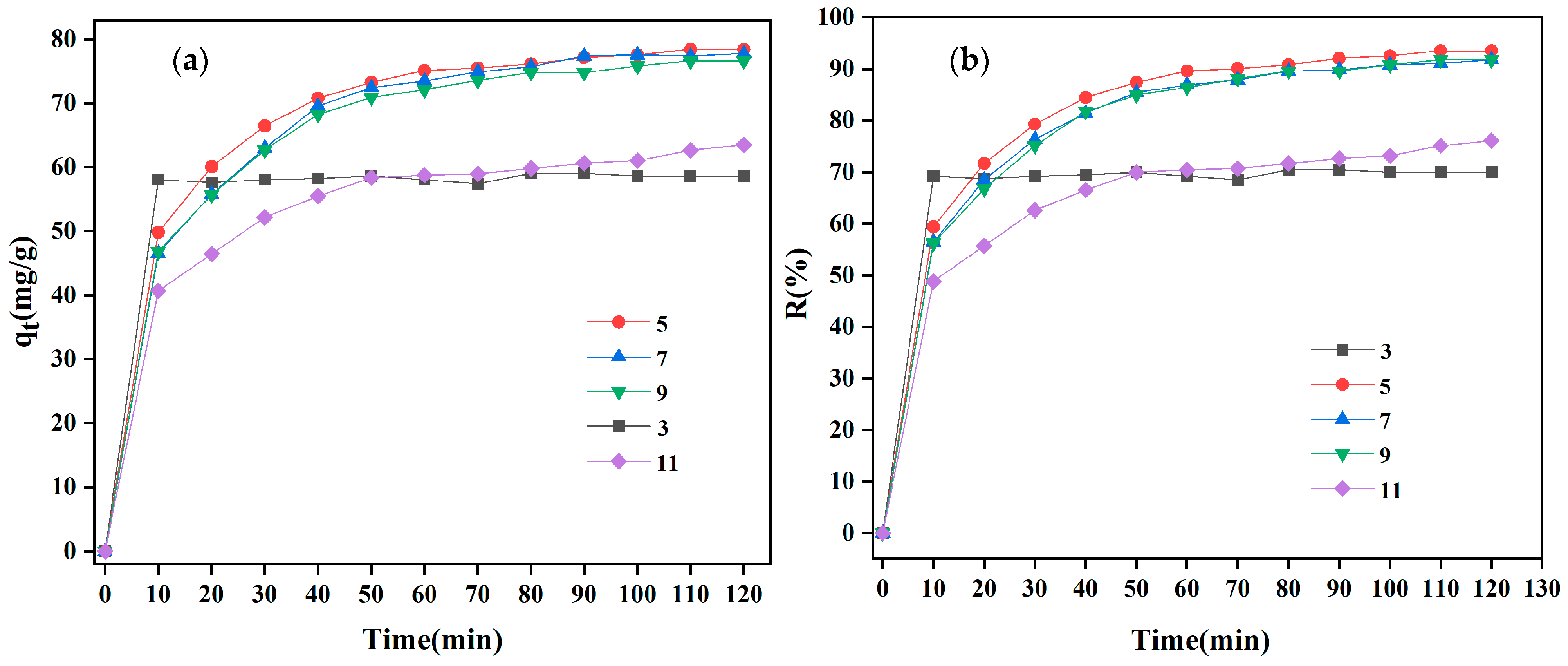
3.2.4. The Influence of pH Value
3.2.5. Effect of Different Ionics
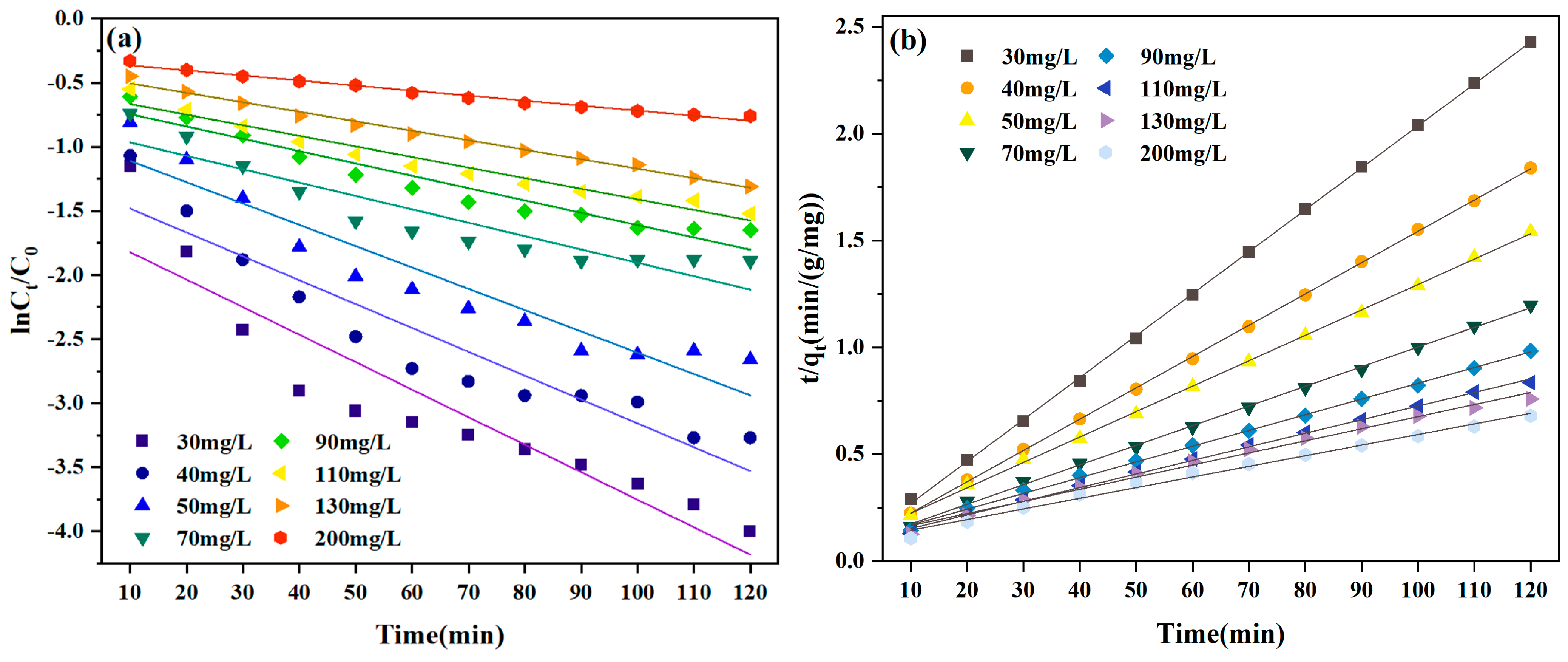
3.3. Adsorption Kinetics
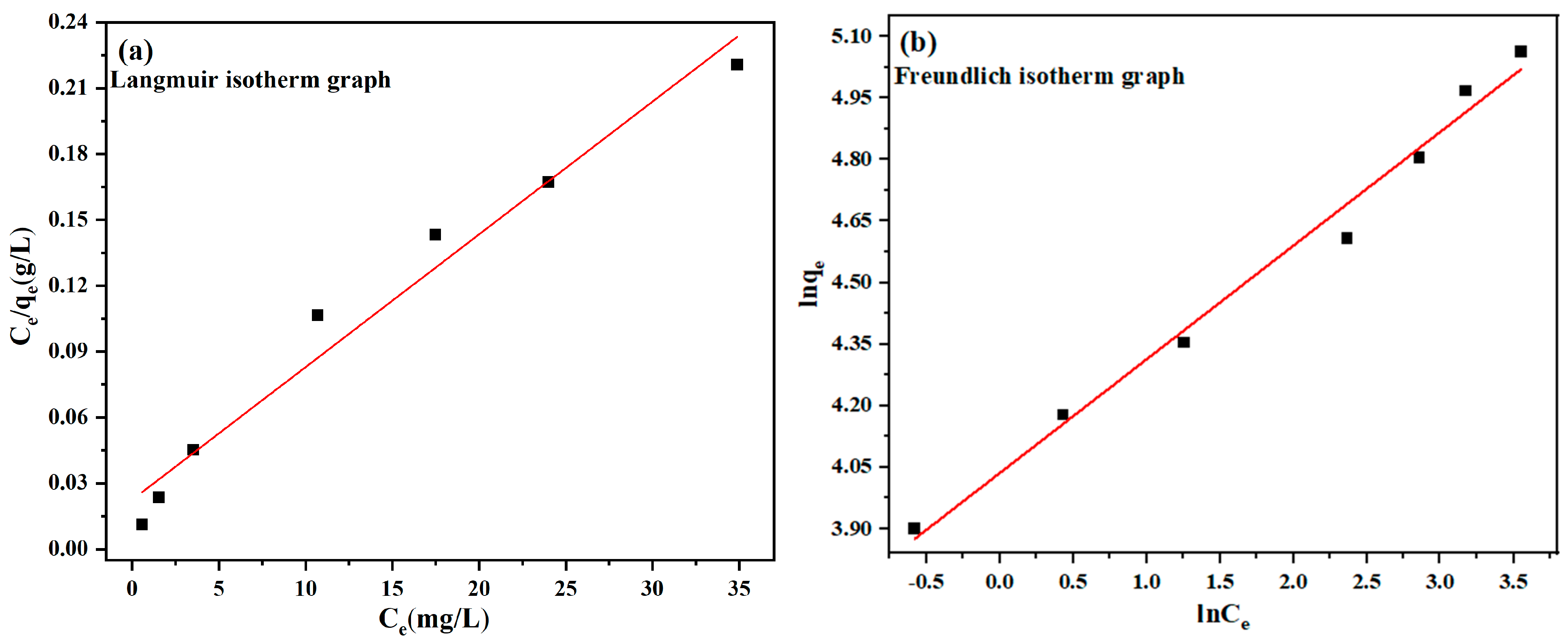
3.4. Adsorption Equilibrium
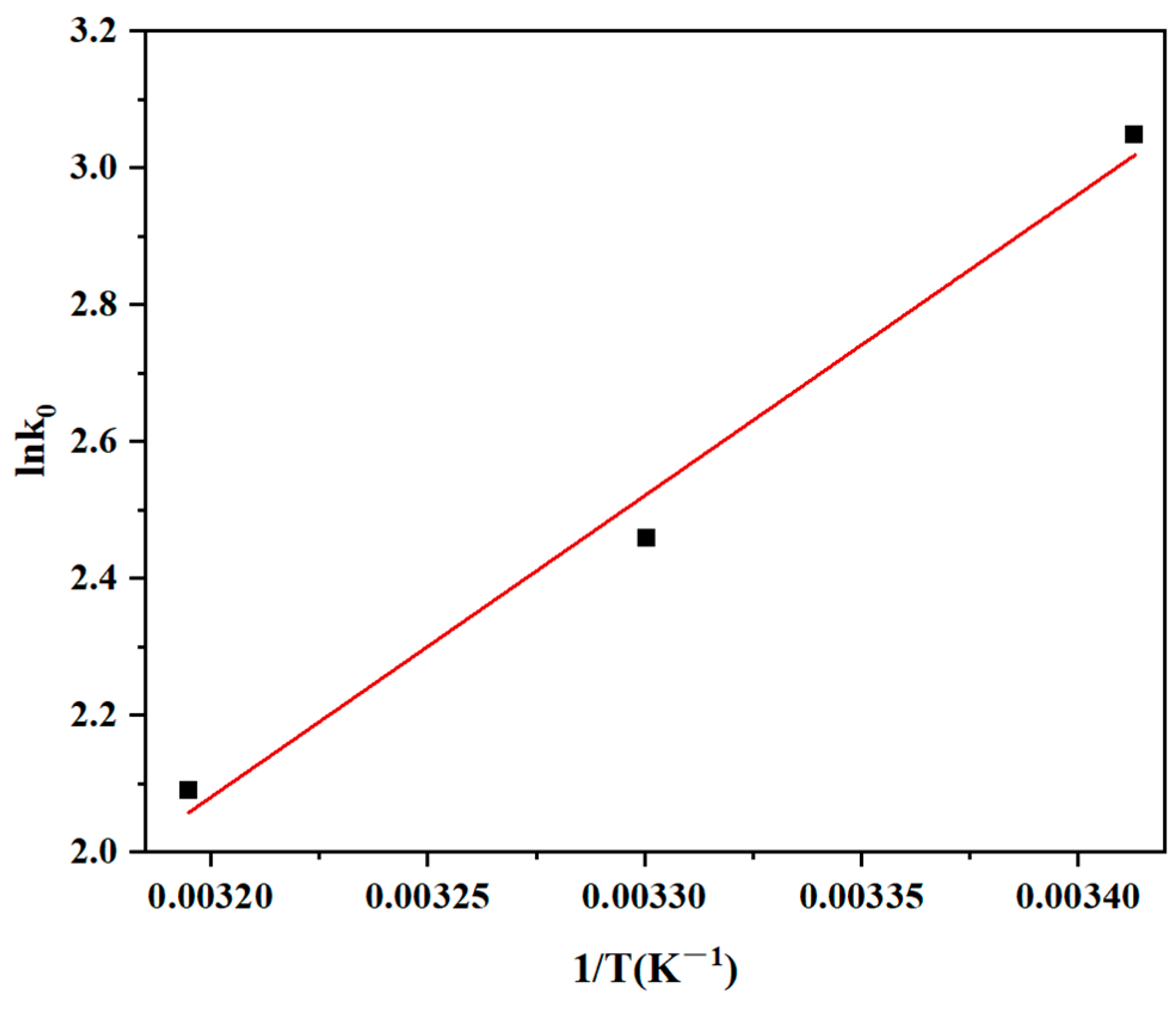
3.5. Adsorption Thermodynamics
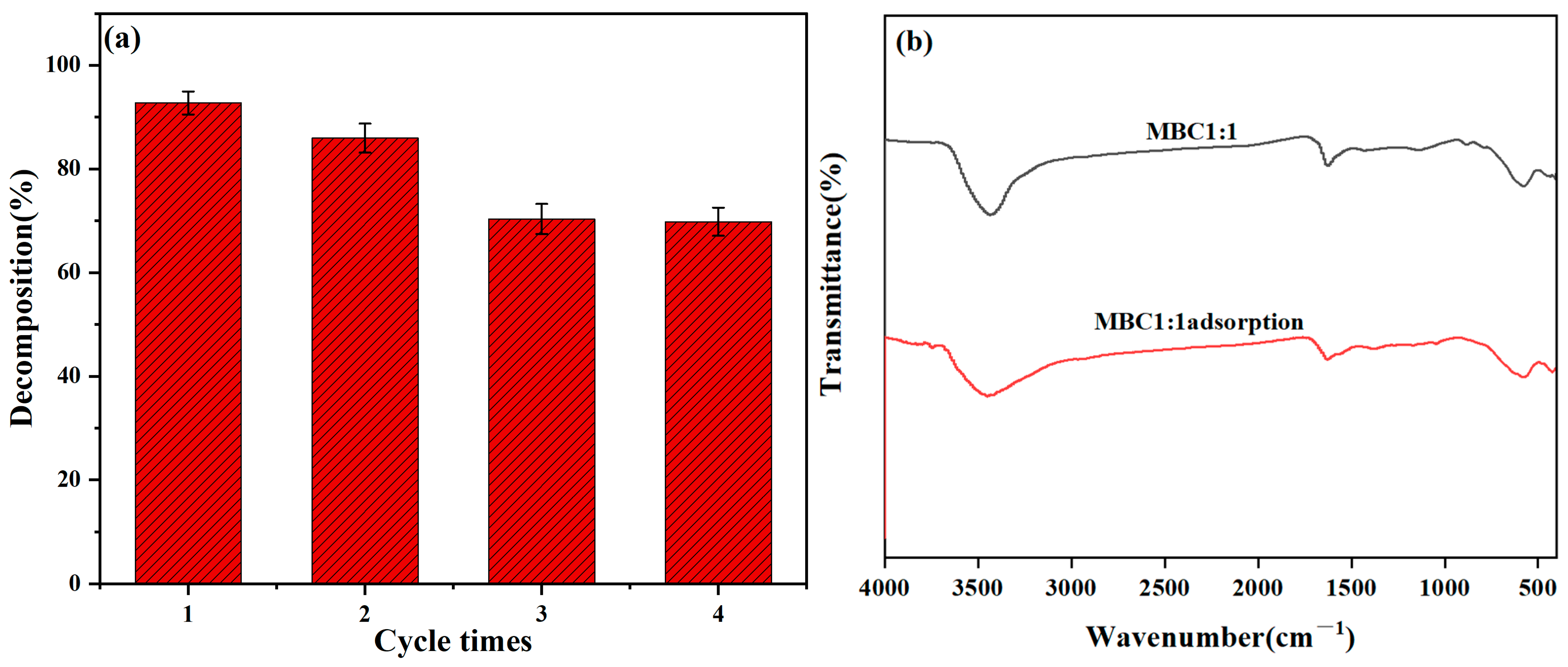
3.6. Recyclability and Regeneration of MBC1:1 Adsorbent
3.7. Adsorption of CR Dye by Various Adsorbents
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, X.J.; Cheng, W.W.; Wang, J.L.; Lei, Y.H.; Yang, X.Q.; Duan, Q.; Duan, W.; Zhang, Y.T. Study on adsorption characteristics of biochars and their modified biochars for removal of organic dyes from aqueous solution. Green Process. Synth. 2024, 13, 20240154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saravanan, A.; Kumar, P.S.; Yaashikaa, P.R.; Karishma, S.; Swetha, S. Mixed Biosorbent of Agro Waste and Bacterial Biomass for the Separation of Pb(II) Ions from Water System. Chemosphere 2021, 277, 130236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, M.F.; Khandake, S.; Sarker, F.; Islam, A.; Awual, M.R. Current treatment technologies and mechanisms for removal of indigo carmine dyes from wastewater: A review. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 318, 114061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fadillah, G.; Saleh, T.; Wahyuningsih, S.; Ninda Karlina Putri, E.; Febrianastuti, S. Electrochemical removal of methylene blue using alginate-modified graphene adsorbents. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 378, 122140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaniabadi, Y.O.; Basiri, H.; Nourmoradi, H.; Mohammadi, M.J.; Yari, A.R.; Sadeghi, S.; Amrane, A. Adsorption of Congo Red Dye from Aqueous Solutions by Montmorillonite as a Low-cost Adsorbent. Int. J. Chem. React. Eng. 2018, 16, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.Y.; Xie, F.R.; Wang, J.L.; Wang, T.Q.; Lei, J.; Li, W.H.; Cheng, J.S.; Zhang, Y.T. In-situ construction of Bi2O2CO3/MIL-101(Cr) nanosheet catalyst for enhanced photocatalytic degradation of organic dye molecules from water. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 2024, 38, aoc7614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Gong, J.L.; Zeng, G.M.; Zhang, P.; Song, B.; Cao, W.C.; Liu, H.Y.; Huan, S.Y. Zirconiumbased metal organic frameworks loaded on polyurethane foam membrane for simultaneous removal of dyes with different charges. J. Colloid. Interface Sci. 2018, 527, 267–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shu, Z.; Wu, H.; Lin, H.; Li, T.; Liu, Y.; Ye, F.; Mu, X.; Li, X.; Jiang, X.; Huang, J. Decolorization of Remazol Brilliant Blue R using a novel acyltransferase-ISCO (in situ chemical oxidation) coupled system. Biochem. Eng. J. 2016, 115, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.Y.; He, M.Z.; Wang, J.L.; He, S.J.; Deng, M.; Lei, Y.H.; Zhang, X.J.; Cheng, J.S.; Liu, Z.J.; Zhang, Y.T. In situ fabrication of AgI/MIL-101(Cr) nanocomposite catalyst with enhancing photocatalytic degradation of organic dye molecules from wastewater. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 2025, 39, e70037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, M.; Ying, H.; Cao, F.; Wang, Q.; Ai, N. Adsorption of Congo red on mesoporous activated carbon prepared by CO2 physical activation. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2020, 28, 1069–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, N.; Shang, R.; Heijman, S.G.J.; Rietveld, L.C. High-silica zeolites for adsorption of organic micro-pollutants in water treatment: A review. Water Res. 2018, 144, 145–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jain, M.; Khan, S.A.; Sahoo, A.; Dubey, P.; Pant, K.K.; Ziora, Z.M.; Blaskovich, M.A.T. Statistical evaluation of cow-dung derived activated biochar for phenol adsorption: Adsorption isotherms, kinetics, and thermodynamic studies. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 352, 127030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pang, X.; Sellaoui, L.; Franco, D.; Dotto, G.L.; Georgin, J.; Bajahzar, A.; Belmabrouk, H.; Lamine, A.B.; Bonilla-Petriciolet, A.; Li, Z. Adsorption of crystal violet on biomasses from pecan nutshell, para chestnut husk, araucaria bark and palm cactus: Experimental study and theoretical modeling via monolayer and double layer statistical physics models. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 378, 122101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astuti, W.; Sulistyaningsih, T.; Kusumastuti, E.; Thomas, G.; Kusnadi, R.Y. Thermal conversion of pineapple crown leaf waste to magnetized activated carbon for dye removal. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 287, 121426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bello, K.; Sarojini, B.K.; Narayana, B.; Rao, A.; Byrappa, K. A study on adsorption behavior of newly synthesized banana pseudo-stem derived superabsorbent hydrogels for cationic and anionic dye removal from effluents. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 181, 605–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, M.A.; Ahmed, N.A.B.; Adegoke, K.A.; Bello, O.S. Sorption studies of methyl red dye removal using lemon grass (Cymbopogon citratus). Chem. Data Collect. 2019, 22, 100249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oloo, C.M.; Onyari, J.M.; Wanyonyi, W.C.; Wabomba, J.N.; Muinde, V.M. Adsorptive removal of hazardous crystal violet dye form aqueous solution using Rhizophora mucronata stem-barks: Equilibrium and kinetics studies. Environ. Chem. Ecotoxicol. 2020, 2, 64–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheufele, F.B.; Staudt, J.; Ueda, M.H.; Ribeiro, C.; Steffen, V.; Borba, C.E.; Modenes, A.N.; Kroumov, A.D. Biosorption of direct black dye by cassava root husks: Kinetics, equilibrium, thermodynamics and mechanism assessment. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 103533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Lee, J.W.; Kim, J.E.; Kang, G.; Kim, H.J.; Choi, Y.K.; Lee, S.H. Adsorptive Behavior of Cu2+ and Benzene in Single and Binary Solutions onto Alginate Composite Hydrogel Beads Containing Pitch Pine-Based Biochar. Polymers 2022, 14, 3468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parlayici, S.; Pehlivan, E. An ecologically sustainable specific method using new magnetic alginate-biochar from acorn cups (Quercus coccifera L.) for decolorization of dyes. Polym. Bull. 2023, 80, 11167–11191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, N.A.; Hu, B.; Zheng, Z.Y.; Lu, H.Y.; Chen, J.W.; Zhang, X.M.; Jiang, X.Z.; Wu, Y.H.; Dolfing, J. Twice-milled magnetic biochar: A recyclable material for efficient removal of methylene blue from wastewater. Bioresour. Technol. 2023, 372, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Y.; Li, A.; Shi, W.; Zhao, L. Magnetic chitosan-functionalized waste carton biochar composites for efficient adsorption of anionic and cationic dyes. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 481, 148535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Tran, H.N.; Liu, Y.; Yang, C.; Zhang, T.; Guo, J.; Zhu, W.; Ahmad, M.; Xiao, H.; Song, J. Nitrogen-doped magnetic biochar made with K3[Fe(C2O4)3] to adsorb dyes: Experimental approach and density functional theory modeling. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 383, 135527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.R.; Jiang, M.Y.; Huang, Z.X.; Chen, L.X.; Wang, Y.P.; Zhao, A.J. Preparation of magnetic black algae biochar composite material andits adsorption of Cu2+ in water. New. Chem. Mater. 2021, 49, 186–190. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, X.; Yang, J.; Han, L.; Wang, D.; Yuan, G.; Fan, X.; Zhou, Y.; Guo, Z.; Hou, F. Preparation of chitosan supported magnetic walnut shell biochar and its adsorption properties on high concentration of Pb(II). China Nonferrous Metall. 2023, 5, 135–145. [Google Scholar]
- Rajput, S.; Pittman, C.U.; Mohan, D. Magnetic magnetite(Fe3O4) nanoparticle synthesis and applications for lead(Pb2+) and chromium (Cr6+) removal from water. J. Colloid. Interf. Sci. 2016, 468, 334–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.S.; Zhang, M.M.; Sheng, G.H.; Tian, Y.P.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, H.J.; Liu, Y.X. Adsorption mechanism of methyl orange by using the magnetic biochar-Based on density functional theory and batch adsorption experiment study. China Environ. Sci. 2023, 43, 4596–4605. [Google Scholar]
- Habibi, M.H.; Parhizkar, H.J. FTIR and UV-vis diffuse reflectance spectroscopy studies of the wet chemical (WC) route synthesized nano-structure CoFe2O4 from CoCl2 and FeCl3. Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2014, 127, 102–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, B.; Luo, Z.; Du, S.; Yang, J.; Zhi, D.; Zhou, Y. Magnetic MgFe2O4/biochar derived from pomelo peel as a persulfate activator for levofloxacin degradation: Effects and mechanistic consideration. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 346, 126547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Wang, X.; Yao, J.; Zhan, S.; Li, H.; Zhang, J.; Qiu, Z. Synthesis of polyethyleneimine modified CoFe2O4-loaded porous biochar for selective adsorption properties towards dyes and exploration of interaction mechanisms. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 277, 119474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Z.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, F.; Zhu, K.; Shen, Z.; Liang, H.; Xie, Y.; Yu, C.; Bao, Y.; Feng, B.; et al. The adsorption mechanisms of oriental plane tree biochar toward bisphenol S: A combined thermodynamic evidence, spectroscopic analysis and theoretical calculations. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 310, 119819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melliti, E.; Touati, K.; Bruggen, B.V.D.; Elfil, H. Effect of Fe2+ ions on gypsum precipitation during bulk crystallization of reverse osmosis concentrates. Chemosphere 2021, 263, 127866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, J.; Song, Y.; Li, H.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, L.K.; Sun, P.; Fan, J.; Li, Y.M. Preparation of novel magnetic porous biochar and its adsorption mechanism on cerium in rare earth wastewater. Ceram. Int. 2023, 49, 9901–9908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakhtouna, H.; Benzeid, H.; Zari, N.; Qaiss, A.E.K.; Bouhfid, R. Functional CoFe2O4-modified biochar derived from banana pseudostem as an efficient adsorbent for the removal of amoxicillin from water. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 266, 118592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Sun, C.; Huang, Q.X.; Chi, Y.; Yan, J.H. Adsorption and thermal degradation of microplastics from aqueous solutions by Mg/Zn modified magnetic biochars. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 419, 126486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Hao, R.; Wang, Z.; Xu, P.; Luo, Y.; Zhao, Y. Nanoscale CuFe2O4 monodispersedly anchored on reduced graphene oxide as excellent peroxydisulfate catalyst for removal of gaseous elemental mercury. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 401, 126101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Liu, Y.; Tan, X.; Li, M.; Liu, S.; Hu, X.; Zhang, P.; Dai, M.; Xu, W.; Wen, J. Synthesis a graphene-like magnetic biochar by potassium ferrate for 17β-estradiol removal: Effects of Al2O3 nanoparticles and microplastics. Sci. Total. Environ. 2020, 715, 136723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, L.P.; Cui, J.L.; Zhang, F.; Li, H.Y.; Cui, J.G.; Wei, L.Y. Removal of Rhodamine B from aqueous solutions by magnetic biochar activated persulfate. China Environ. Sci. 2023, 43, 1672–1687. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, X.; Yang, N.; Qi, X.; Chen, L.; Zhao, Y. Adsorptive removal of cholesterol by biodegradable zein-graft-β-cyclodextrin film. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 155, 293–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.B.; Do, Q.H.; Chen, C.W.; Chen, W.H.; Bui, X.T.; Dong, C.D. Pyrolysis temperature effect on biochar-derived cow manure: Physicochemical properties and adsorption behavior toward organic dyes. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2024, 164, 105675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.S.; Li, X.L.; Yang, M.; He, J.M. Preparation of Chitosan Modified Biochar Composites and Their Adsorption Properties for Pb2+. Chem. Reag. 2023, 45, 66–71. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Hu, L.S.; Yao, Y.J.; Su, Z.Q.; Hu, S.Q. Construction of composite chitosan-glucose hydrogel for adsorption of Co2+ ions. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 139, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jayaramudu, T.; Pyarasani, R.D.; Akbari-Fakhrabadi, A.; Abril-Milan, D.; Amalraj, J. Synthesis of Gum Acacia Capped Polyaniline-Based Nanocomposite Hydrogel for the Removal of Methylene Blue Dye. J. Polym. Environ. 2021, 29, 2447–2462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Z.; Huang, K.P.; Niu, Y.; Yao, Y.; Wang, S.; Cao, Z.F.; Zhong, H. Kinetic study of ultrasonic-assisted uranium adsorption by anion exchange resin. Colloids Surf. A 2020, 585, 124021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.; Wang, X.M.; Zhao, L.L.; Li, M.; Yang, W. Effective Removal of Dyes from Aqueous Solutions by a Gelatin Hydrogel. J. Polym. Environ. 2021, 29, 3497–3508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Xu, R.; Sun, D.; Shi, X.; Xu, W.; Li, M. Preparation of nitrogen-doped biochar and its adsorption properties for methylene blue. Inorg. Chem. Ind. 2024, 56, 117–127. [Google Scholar]
- Li, K.; Wu, J.; Li, X.; Zhou, B.; Li, D. Preparation of porous composite hydrogel with ultra-high dye adsorption capacity based on biochar: Adsorption behaviors and mechanisms. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2024, 295, 120115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Zhu, W.; Chen, F.; Song, Y.; Yu, Y.; Zhuang, H. Modifed biochar prepared from Retinervus luffae fructus for dyes adsorption and aerobic sludge granulation. Chemosphere 2023, 322, 138088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, H.M.; Kan, E. Engineered biochar from agricultural waste for removal of tetracycline in water. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 284, 437–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, F.; Gong, J.; Ren, Q.; Yu, X.; Wang, Y.; Chen, H.; Liang, Z. Preparation of Zn/Zr-MOFs by microwave-assisted ball milling and adsorption of lomefloxacin hydrochloride and levofloxacin hydrochloride in wastewater. Environ. Res. 2024, 252, 118941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.D.; Bi, F.K.; Zhao, Z.Y.; Yang, Y.; Li, Y.T.; Song, L.; Liu, N.; Cui, L. Boosting toluene oxidation by the regulation of Pd species on UiO-66: Synergistic effect of Pd species. J. Catal. 2022, 413, 59–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Q.X.; Rao, R.Z.; Bi, F.K.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, W.M.; Yang, Y.Q.; Liu, N.; Zhang, X. Preparation of modified zirconium-based metal-organic frameworks (Zr-MOFs) supported metals and recent application in environment: A review and perspectives. Surf. Interfaces 2022, 28, 101647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Ghouti, M.A.; Da’ana, D.A. Guidelines for the use and interpretation of adsorption isotherm models: A review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 393, 122383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malik, A.; Khan, A.; Anwar, N.; Naeem, M. A comparative study of the adsorption of congo red dye on rice husk, rice husk char and chemically modified rice husk char from aqueous media. Bull. Chem. Soc. Ethiop. 2020, 34, 41–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, K.; Hu, Y.; Khan, I.; He, S.; Fatehi, P. Recent advances in the synthesis and application of magnetic biochar for wastewater treatment. Bioresour. Technol. 2023, 390, 129786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wang, N.; Zhang, H.; Baeyens, J. Adsorption of Congo red dye on FexCo(3−x)O4 nanoparticles. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 238, 473–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, P.R.; Ansari, K. Comparative study for adsorption of congo red and methylene blue dye on chitosan modified hybrid nanocomposite. Process. Biochem. 2021, 108, 90–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Guo, J.; Wang, C.; Wang, X.; Zheng, B. Adsorptive Removal of Congo Red from Water by Iron-Modified Cattail Biochar. Chem. Reag. 2024, 46, 81–90. [Google Scholar]
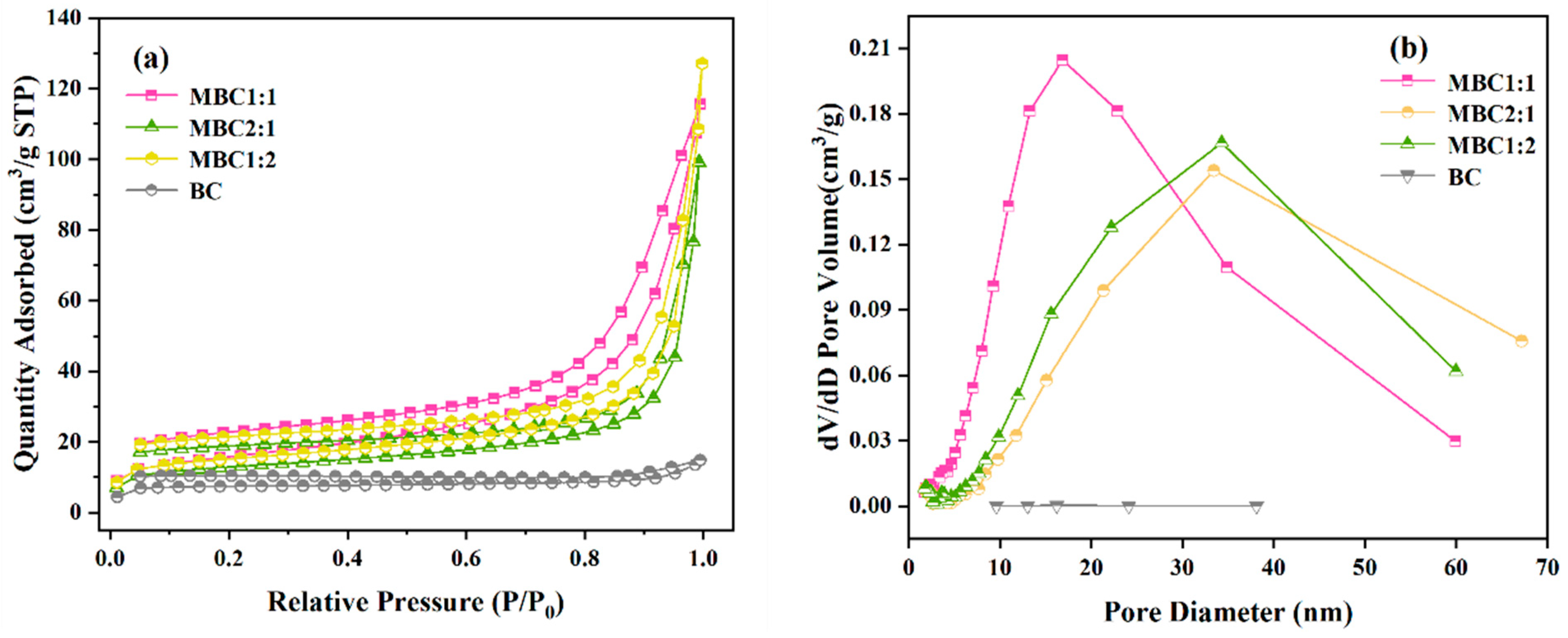


| Thermophysical Properties | BC | MBC1:1 | MBC2:1 | MBC1:2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BET surface area (m2/g) | 30.8006 | 56.3398 | 46.9072 | 55.7369 |
| Total pore volume (cm3/g) | 0.01978 | 0.1564 | 0.1087 | 0.1280 |
| Micropore volume (cm3/g) | 0.007515 | 0.002823 | 0.008833 | 0.010611 |
| Micropore area (m2/g) | 21.1302 | 7.8049 | 21.5450 | 25.9734 |
| Average pore size (nm) | 2.9758 | 12.7016 | 13.0753 | 14.1040 |
| Mass (mg) | Concentration (mg/L) | PSO Model | PFO Model | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| k2 (g/(mg·min)) | R2 | k1 (L/min) | R2 | qe,exp (mg/g) | ||
| 120 | 30 | 0.0196 | 0.9997 | 0.0215 | 0.8509 | 49.39 |
| 40 | 0.0146 | 0.9998 | 0.0186 | 0.8883 | 65.23 | |
| 50 | 0.0119 | 0.9994 | 0.1663 | 0.8989 | 77.79 | |
| 70 | 0.0092 | 0.9989 | 0.0104 | 0.8448 | 100.20 | |
| 90 | 0.0074 | 0.9983 | 0.0096 | 0.9299 | 122.02 | |
| 110 | 0.0064 | 0.9976 | 0.0083 | 0.9569 | 143.63 | |
| 130 | 0.0057 | 0.9901 | 0.0074 | 0.9902 | 158.02 | |
| 200 | 0.0050 | 0.9898 | 0.0039 | 0.9803 | 176.55 | |
| Langmuir Isotherm | Freundlich Isotherm | |||
| Adsorbent | 1/qm | R2 | 1/n | R2 |
| MBC1:1 | 0.0060 | 0.9665 | 0.2770 | 0.9845 |
| Van’t Hoff Equation | Temperature (°C) | ∆G° (kJ/mol) | ∆H° (kJ/mol) | ∆S° (J/(mol·K)) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Y = 4408x − 12.0 | 20 | −7.4 | −36.6 | −99.8 |
| 30 | −6.2 | |||
| 40 | −5.4 |
| Adsorbent | Adsorbent Dosage | Dye Concentration | Adsorption Time | Adsorption Capacity | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FexCo3−xO4 nanoparticle | 0.05 g/500 mL | 20 mg/L | 240 min | 128.6 mg/g | [56] |
| Activated carbon | 0.8 g/L | 200 mg/L | 180 min | 234 mg/g | [10] |
| (Chit/AILP-Kao) nanocomposite | 150 mg/20 mL | 20 mg/L | 240 min | 104.7 mg/g | [57] |
| Fe-BC | 40 mg/20 mL | 100 mg/L | 90 min | 45.96 mg/g | [58] |
| Magnetic self-nitrogen-doped biochar | 20 mg/200 mL | 1000 mg/L | 500 min | 1360 mg/g | [23] |
| magnetic biochar (MBC1:1) | 20 mg/200 mL | 50 mg/L | 120 min | 172.88 mg/g | This study |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, X.; Yang, X.; Xie, F.; Chen, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Q. Magnetic Biochar Prepared with Rosa roxburghii Residue as Adsorbents for Congo Red Removal. Materials 2025, 18, 1306. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18061306
Zhang X, Yang X, Xie F, Chen X, Zhang Y, Zhang Q. Magnetic Biochar Prepared with Rosa roxburghii Residue as Adsorbents for Congo Red Removal. Materials. 2025; 18(6):1306. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18061306
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Xiaojuan, Xueqin Yang, Feiran Xie, Xianglan Chen, Yutao Zhang, and Qiuyun Zhang. 2025. "Magnetic Biochar Prepared with Rosa roxburghii Residue as Adsorbents for Congo Red Removal" Materials 18, no. 6: 1306. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18061306
APA StyleZhang, X., Yang, X., Xie, F., Chen, X., Zhang, Y., & Zhang, Q. (2025). Magnetic Biochar Prepared with Rosa roxburghii Residue as Adsorbents for Congo Red Removal. Materials, 18(6), 1306. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18061306







