Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Fe-30Mn-10Al-3.3Si-1C Light-Weight Steel
Abstract
1. Introduction
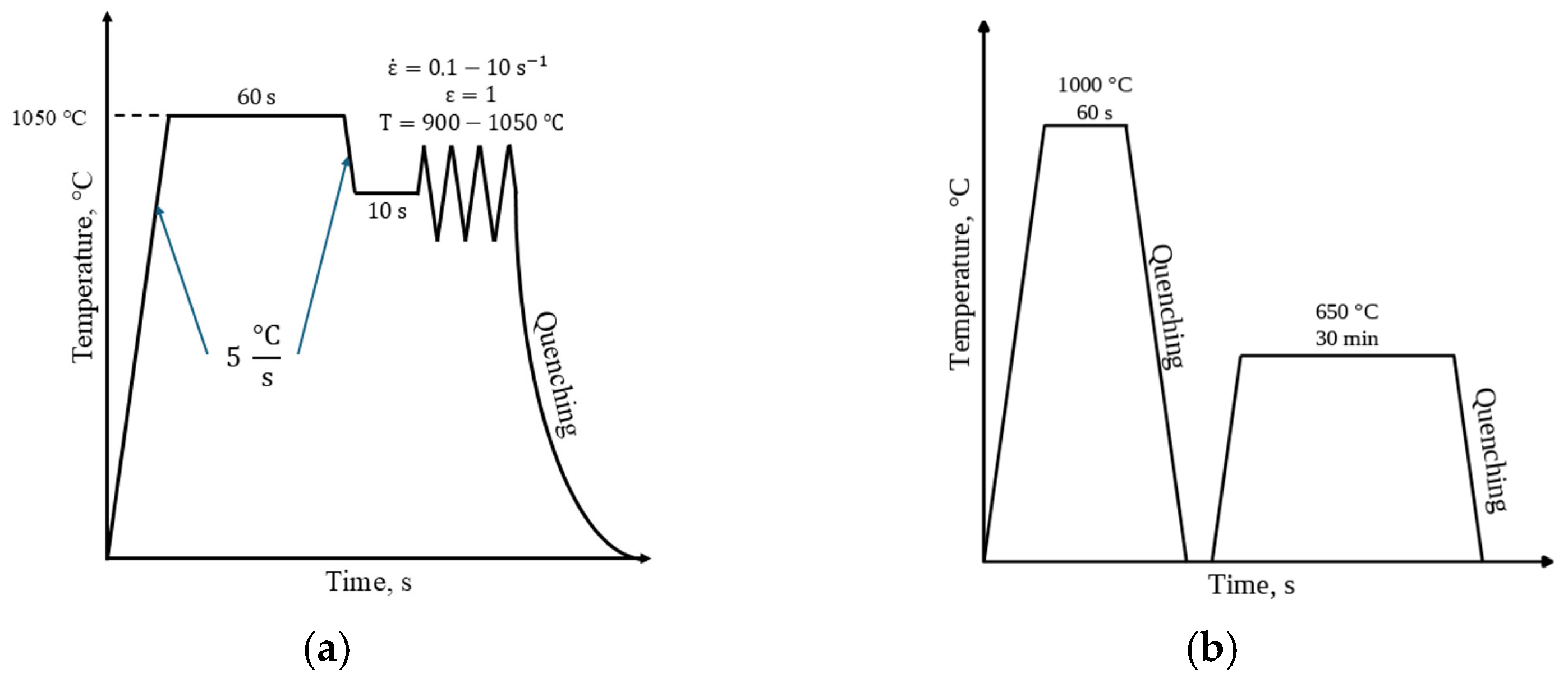
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
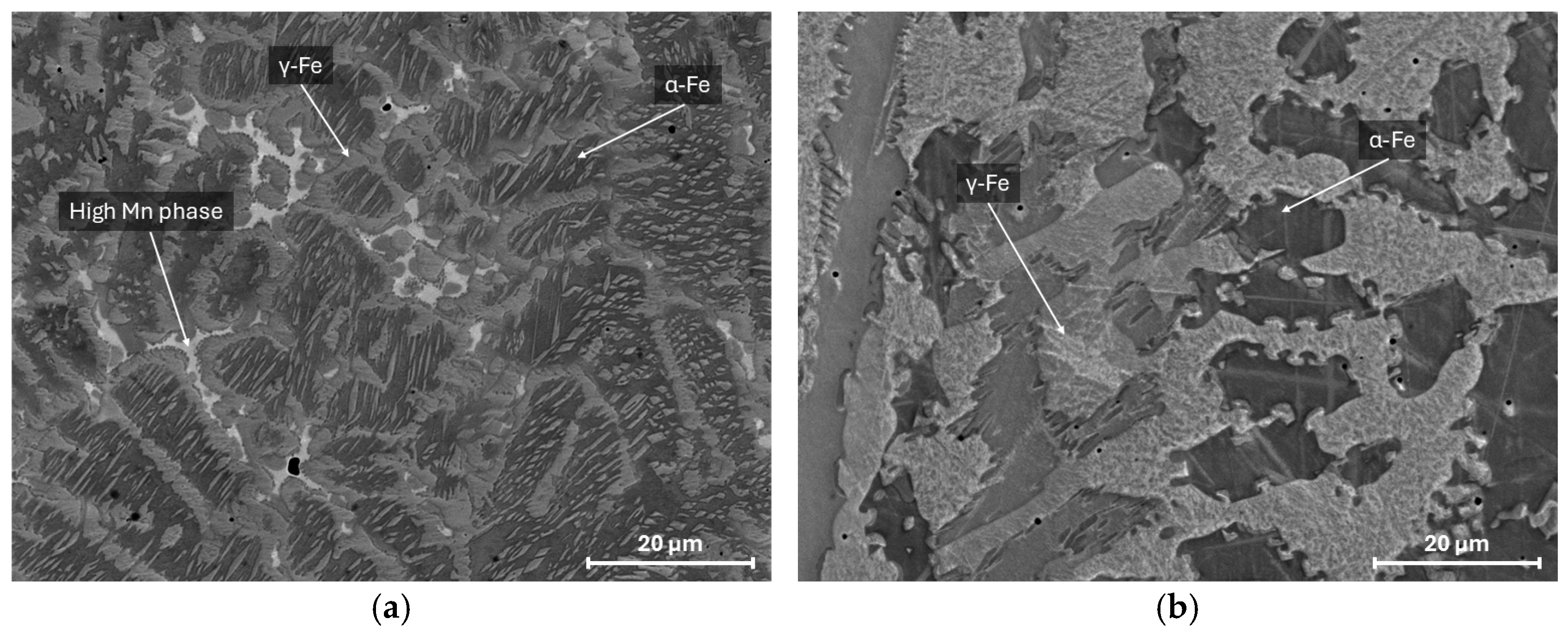
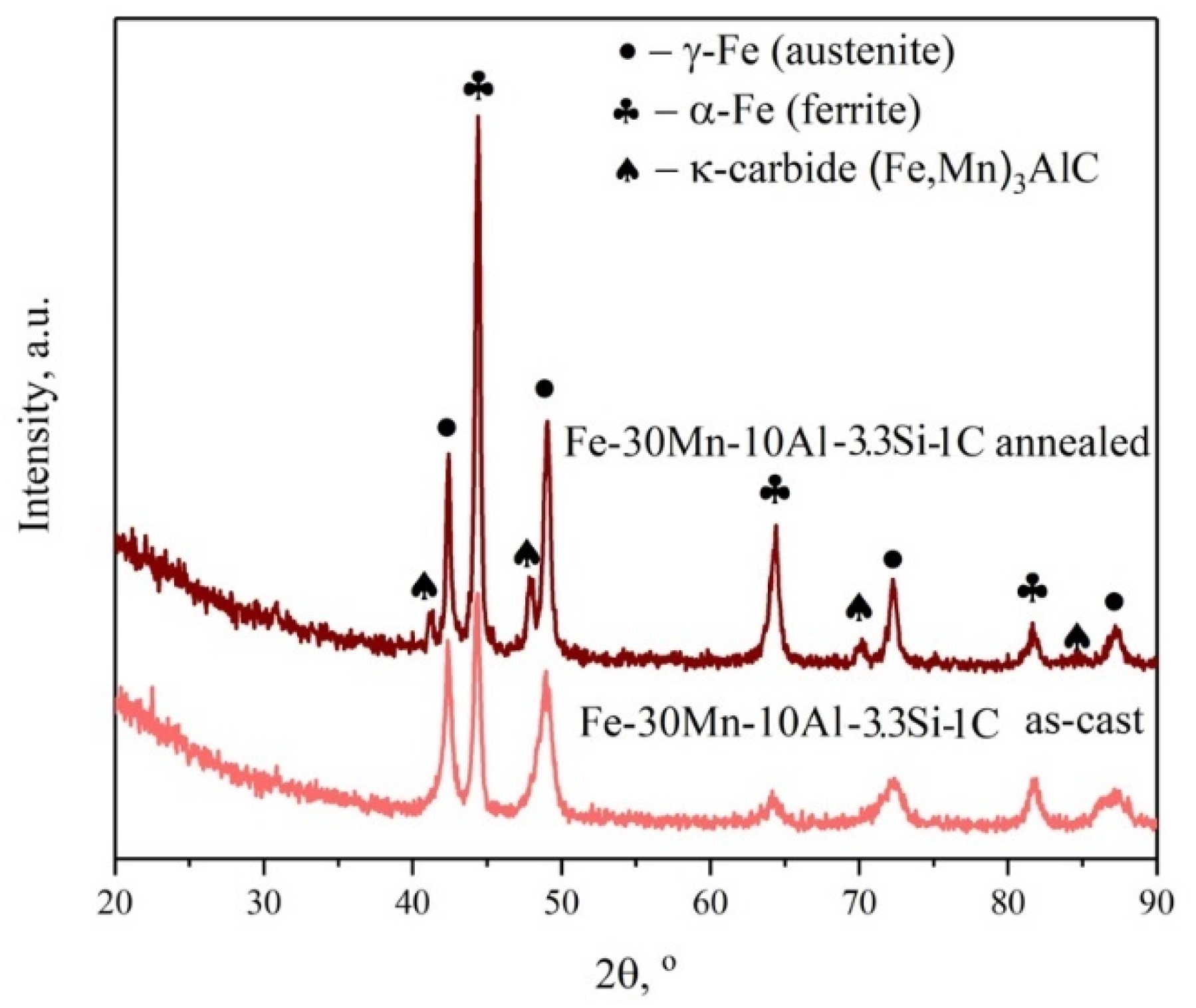
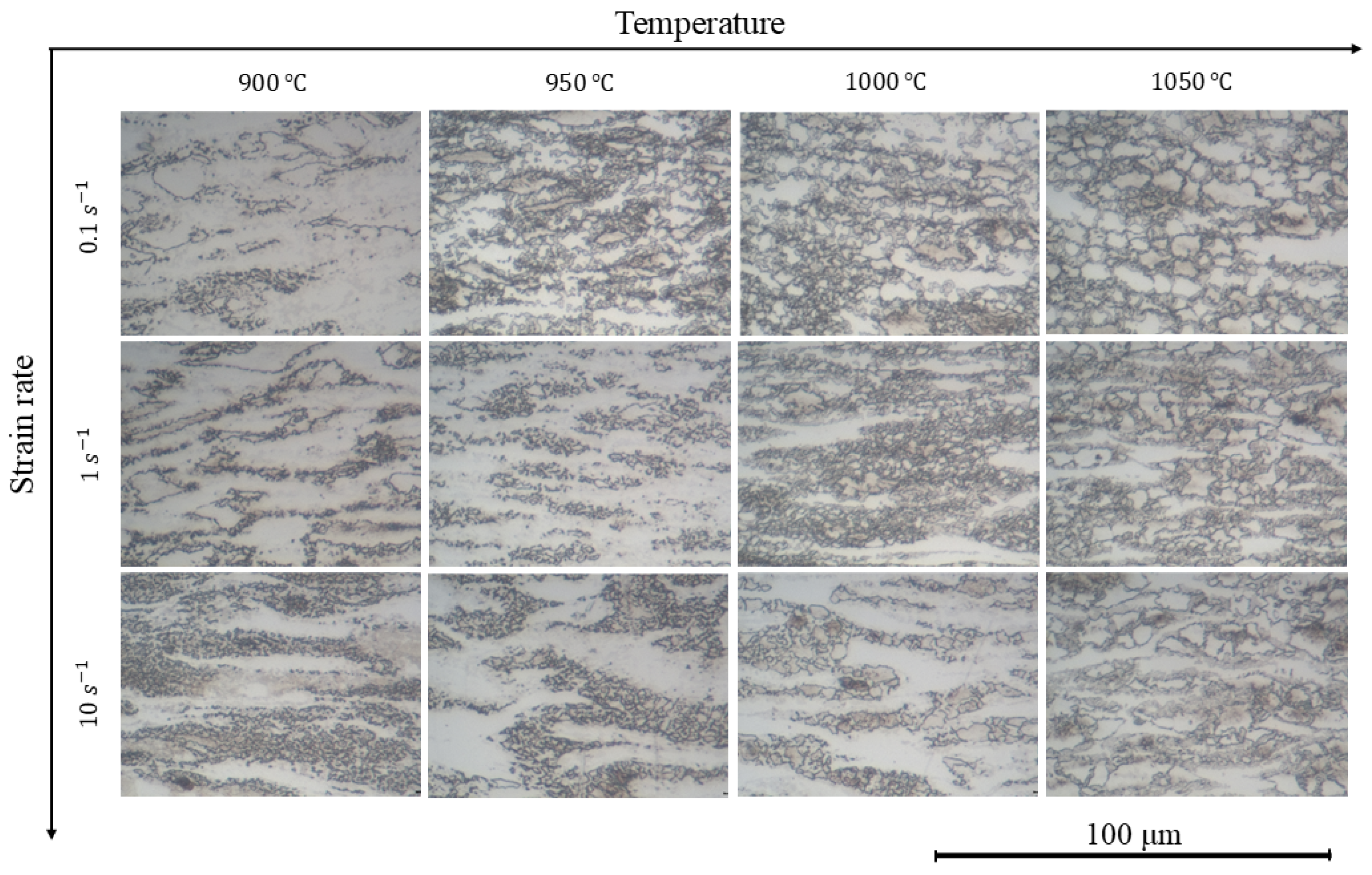
3.1. Microstructure and Phase Composition
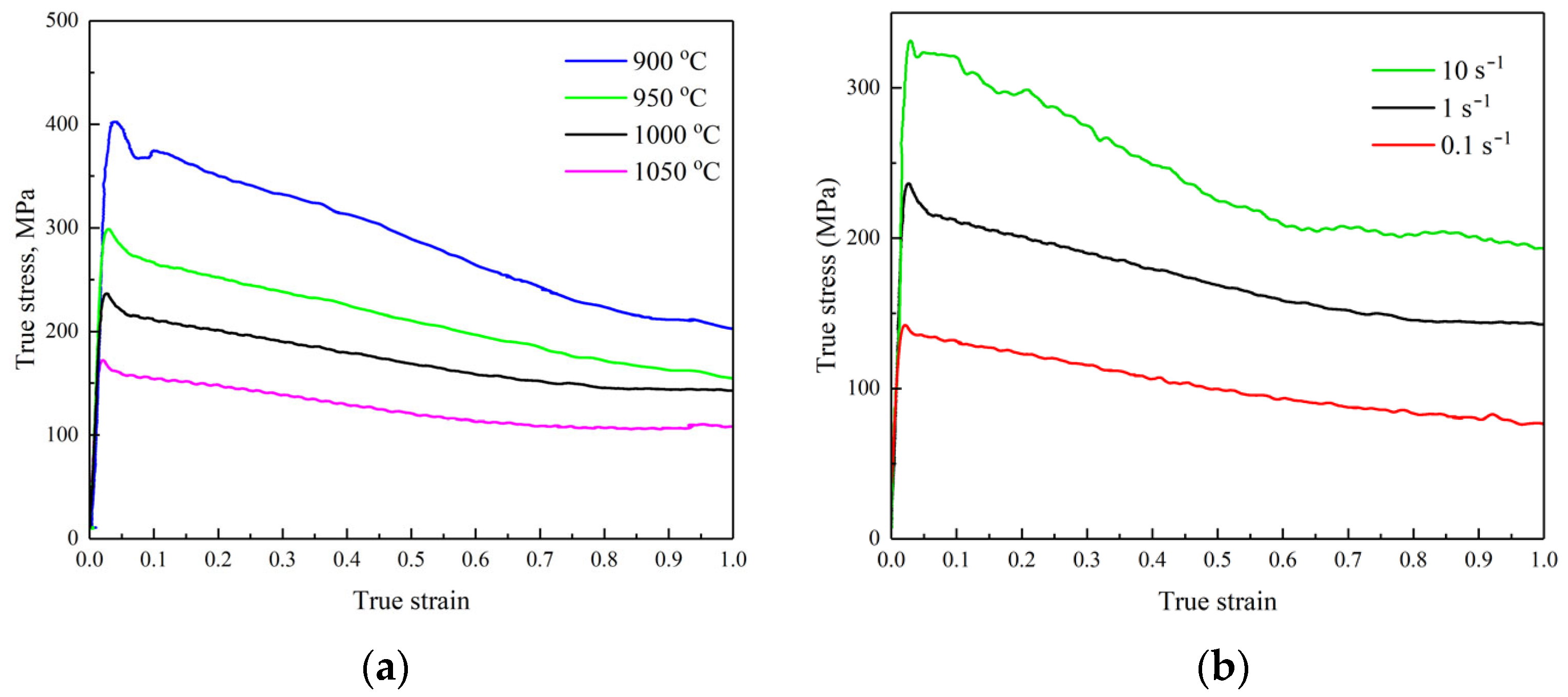
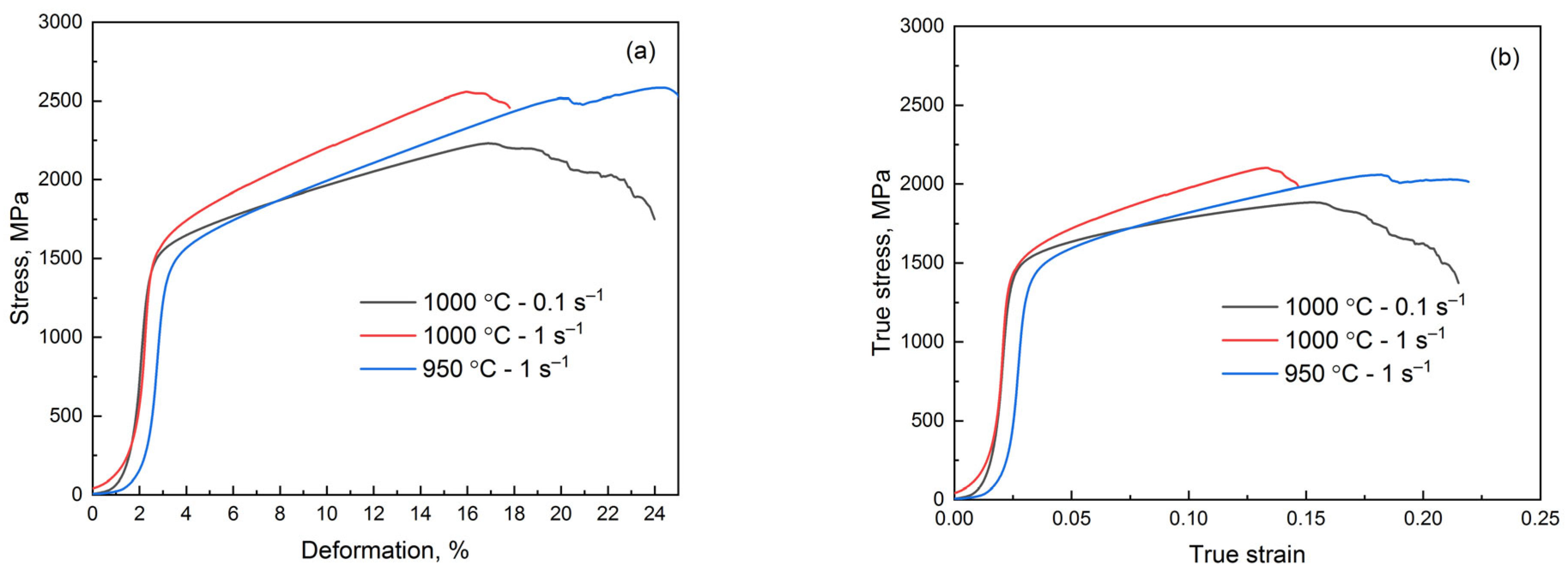
3.2. Hot Deformation
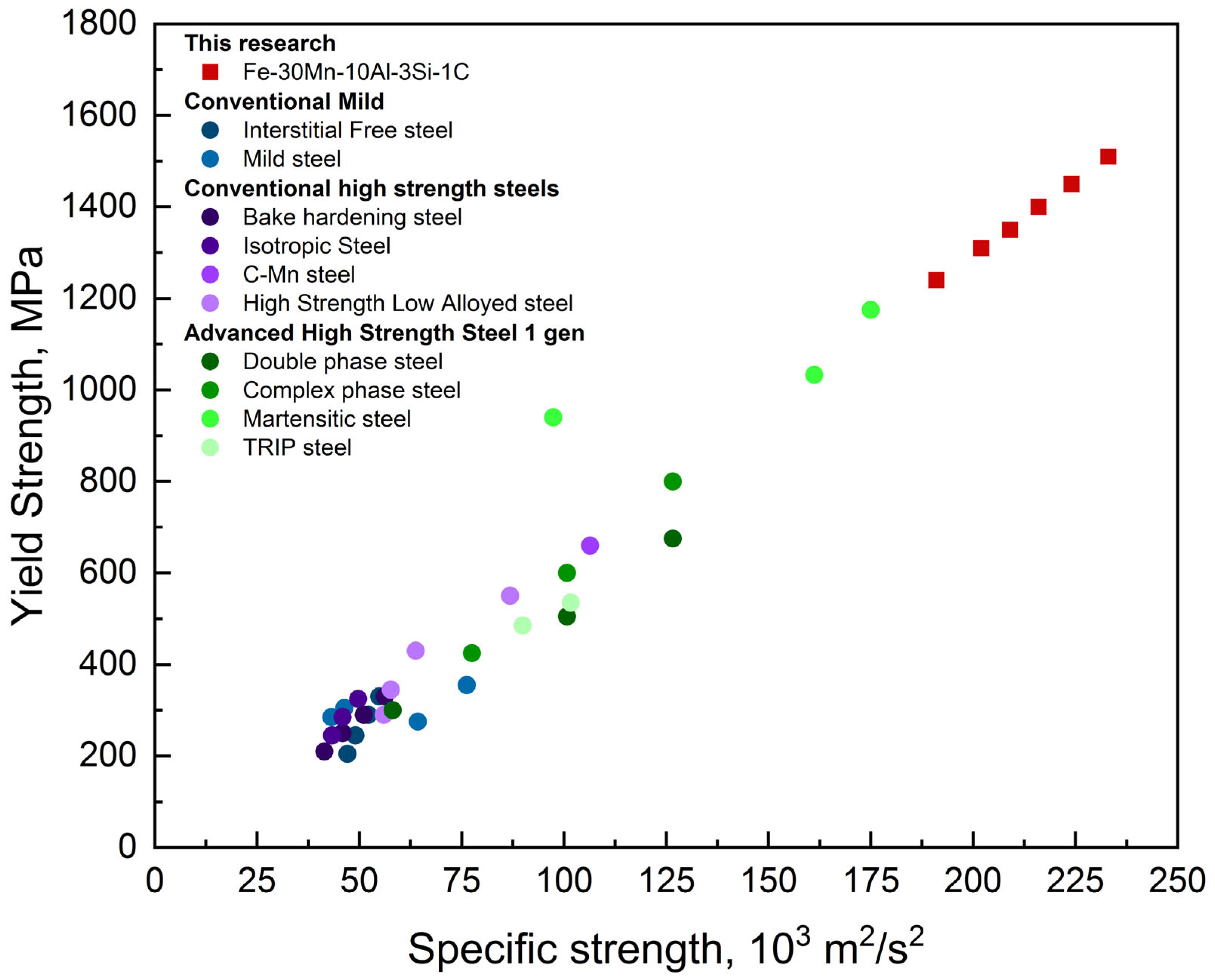
3.3. Mechanical Properties
4. Conclusions
- The microstructure and mechanical properties of the Fe-30Mn-10Al-3.3Si-1C steel in as-cast, quenched, aged, and hot-deformed states were investigated. Austenite, ferrite, and κ-carbides are present in the steel in an as-cast state. It was shown that annealing at a temperature of 1050 °C leads to full dissolution of κ-carbides.
- A constitutive model of the hot deformation behavior of the investigated material was constructed:
- 3.
- The hardness of the steel has values in the range of 500–580 HV, with a maximum after the hot deformation at a high strain rate and low temperatures. The minimum hardness in the temperature dependence for a 0.1 s−1 strain rate may be described by the competitive processes of phase transformation and dynamic softening.
- 4.
- Compression tests showed an increase in strength and ductility after the hot deformation. The specific strength of the steel has values of 202,000–233,000 m2/s2, which is higher than currently used automotive steels.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bian, X.; Ma, K.; Liu, Z.Y.; Xiao, B.L.; Wang, Q.Z.; Ma, Z.Y. Hot Deformation Behavior Analysis of CNT/2009Al Composite with Bimodal Heterostructure via Constructing a New Processing Map. Mater. Charact. 2024, 212, 113979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, X.; Wang, X.; Lan, A.; Qiao, J. Synergistic Effect of Al and Ni on Microstructure Evolutions and Mechanical Properties of Fe-Mn-Al-C Low-Density Steels. Metals 2024, 14, 495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Chen, R.; Wang, Y.; Gao, L.; Li, X. Tailoring Strength and Ductility of an Fe–Mn–Al–C Low-Density Duplex Steel by Controlling the Cooling Path after Hot Rolling. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2024, 26, 2301595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voron, M.; Semenko, A.; Shemet, V. Microstructure, Mechanical and High Temperature Properties of Cast High Mn Low-Density Steels Alloying by Small Lanthanum Additions. Mater. Lett. 2024, 355, 135421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Chen, P.; Wang, P.; Li, X. Achieving Well-Balanced Strength and Ductility in Warm-Rolled Fe–30.5Mn–8Al–1.0C Lightweight Austenitic Steels via Aging Treatment. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2024, 26, 2401797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Chen, G.; Hu, H.; Zheng, W.; Wan, X.; Xue, Z.; Xu, G. Temperature Dependence of the Deformation Behavior and Mechanical Properties of a Fe–Mn–Al–C Low-Density Steel for Cryogenic Application. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2024, 33, 3418–3426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Xie, T.; Xie, Y.; Xiao, L.; Lin, Y. Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Fe–30Mn–9Al–C–3Ni Low-Density Steel Manufactured by Selective Laser Melting. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2024, 33, 4280–4289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Lin, Z.; Jiang, A.; Chen, G. Use of High Strength Steel Sheet for Lightweight and Crashworthy Car Body. Mater. Des. 2003, 24, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabłońska, M.B.; Kowalczyk, K. Microstructural Aspects of Energy Absorption of High Manganese Steels. Procedia Manuf. 2019, 27, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Rana, R.; Haldar, A.; Ray, R.K. Current State of Fe-Mn-Al-C Low Density Steels. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2017, 89, 345–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tjong, S.C. Electron Microscope Observations of Phase Decompositions in an Austenitic Fe-8.7AI-29.7Mn-1.04C Alloy. Mater. Charact. 1990, 24, 275–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, W.C.; Cheng, C.Y.; Hsu, C.W.; Laughlin, D.E. Phase Transformation of the L12 Phase to Kappa-Carbide after Spinodal Decomposition and Ordering in an Fe–C–Mn–Al Austenitic Steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2015, 642, 128–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.P.; Song, R.B.; Wen, E.D.; Yang, F.Q. Hot Deformation and Dynamic Recrystallization Behavior of Austenite-Based Low-Density Fe-Mn-Al-C Steel. Acta Metall. Sin. (Engl. Lett.) 2016, 29, 441–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamada, A.S.; Karjalainen, L.P.; Somani, M.C. The Influence of Aluminum on Hot Deformation Behavior and Tensile Properties of High-Mn TWIP Steels. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2007, 467, 114–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamada, A.S.; Karjalainen, L.P.; Somani, M.C.; Ramadan, R.M. Deformation Mechanisms in High-Al Bearing High-Mn TWIP Steels in Hot Compression and in Tension at Low Temperatures. Mater. Sci. Forum 2007, 550, 217–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutierrez-Urrutia, I.; Raabe, D. High Strength and Ductile Low Density Austenitic FeMnAlC Steels: Simplex and Alloys Strengthened by Nanoscale Ordered Carbides. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2014, 30, 1099–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howell, R.A.; Van Aken, D.C. A Literature Review of Age Hardening Fe-Mn-Al-C Alloys; Missouri University of Science and Technology: Rolla, MO, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Welsch, E.; Ponge, D.; Hafez Haghighat, S.M.; Sandlöbes, S.; Choi, P.; Herbig, M.; Zaefferer, S.; Raabe, D. Strain Hardening by Dynamic Slip Band Refinement in a High-Mn Lightweight Steel. Acta Mater. 2016, 116, 188–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, M.J.; Welsch, E.; Ponge, D.; Haghighat, S.M.H.; Sandlöbes, S.; Choi, P.; Herbig, M.; Bleskov, I.; Hickel, T.; Lipinska-Chwalek, M.; et al. Strengthening and Strain Hardening Mechanisms in a Precipitation-Hardened High-Mn Lightweight Steel. Acta Mater. 2017, 140, 258–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Springer, H.; Raabe, D. Rapid Alloy Prototyping: Compositional and Thermo-Mechanical High Throughput Bulk Combinatorial Design of Structural Materials Based on the Example of 30Mn–1.2C–X Al Triplex Steels. Acta Mater. 2012, 60, 4950–4959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frommeyer, G.; Brüx, U. Microstructures and Mechanical Properties of High-Strength Fe-Mn-Al-C Light-Weight TRIPLEX Steels. Steel Res. Int. 2006, 77, 627–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Lu, W.; Zhao, H.; He, J.; Wang, K.; Zhou, B.; Ponge, D.; Raabe, D.; Li, Z. Formation Mechanism of κ-Carbides and Deformation Behavior in Si-Alloyed FeMnAlC Lightweight Steels. Acta Mater. 2020, 198, 258–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Churyumov, A.Y.; Khomutov, M.G.; Tsar’Kov, A.A.; Pozdnyakov, A.V.; Solonin, A.N.; Efimov, V.M.; Mukhanov, E.L. Study of the Structure and Mechanical Properties of Corrosion-Resistant Steel with a High Concentration of Boron at Elevated Temperatures. Phys. Met. Metallogr. 2014, 115, 809–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hull, D.; Bacon, D.J. Introduction to Dislocations; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2011; Volume 37, ISBN 008096673X. [Google Scholar]
- Mishra, B.; Singh, V.; Sarkar, R.; Mukhopadhyay, A.; Gopinath, K.; Madhu, V.; Prasad, M.J.N.V. Dynamic Restoration Activities in Austenite Matrix and Secondary B2 Phase during Hot Deformation of Austenitic Low-Density Steels. Mat Sci Eng A. 2022, 842, 143095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Churyumov, A.Y.; Kazakova, A.A. Prediction of True Stress at Hot Deformation of High Manganese Steel by Artificial Neural Network Modeling. Materials 2023, 16, 1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Churyumov, A.Y.; Kazakova, A.A.; Pozdniakov, A.V.; Churyumova, T.A.; Prosviryakov, A.S. Investigation of Hot Deformation Behavior and Microstructure Evolution of Lightweight Fe-35Mn-10Al-1C Steel. Metals 2022, 12, 831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Gao, Z.; Shi, Z.; Xu, H.; Zhang, L.; Wu, G.; Wang, C.; Wang, C.; Weng, Y.; Cao, W. High Temperature Deformation Behavior and Microstructure Evolution of Low-Density Steel Fe30Mn11Al1C Micro-Alloyed with Nb and V. Materials 2021, 14, 6555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, P.; Yu, H.; Li, F.; Gao, P.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, Z. Hot Deformation Behaviors and Process Parameters Optimization of Low-Density High-Strength Fe–Mn–Al–C Alloy Steel. Met. Mater. Int. 2022, 28, 2498–2512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Yan, L.; Shang, X.; Li, G.; Qi, X.; Liu, P.; Li, B.; Wang, X.; Xu, X.; Shang, C. Dynamic Recrystallization Behavior and Microstructure Evolution of High-Mn Austenitic Steel for Application in a Liquefied Natural Gas Carrier. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2023, 27, 5479–5488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Li, L.; Zhang, K.; Fu, X.; Cao, Y.; Zhang, X.; Li, Z. Comprehensive Analysis of Austenitic Fe-Mn-Al-C Lightweight Steel: Hot Deformation Behavior, Dynamic Recrystallization Mechanisms and Numerical Simulation. Vacuum 2025, 234, 114012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Wu, Y.; Hu, D.; Cai, Y.; Liu, Y.; Chen, H. Study of Microstructure and Mechanical Properties and Residual Stresses of 24CrNiMo Steel Prepared by Selective Laser Melting and Laser Melting Deposition. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2024, 28, 4764–4777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, S.; Chen, Y.; Liu, X.; Lu, H.; Bai, P.; Li, D.; Huang, Z.; Li, J. Research Status and Development Prospect of Fe–Mn–C–Al System Low-Density Steels. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2023, 25, 1537–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BS EN 10025-1:2004; Hot Rolled Products of Structural Steels—General Technical Delivery Conditions. British Standard: London, UK, 2004.


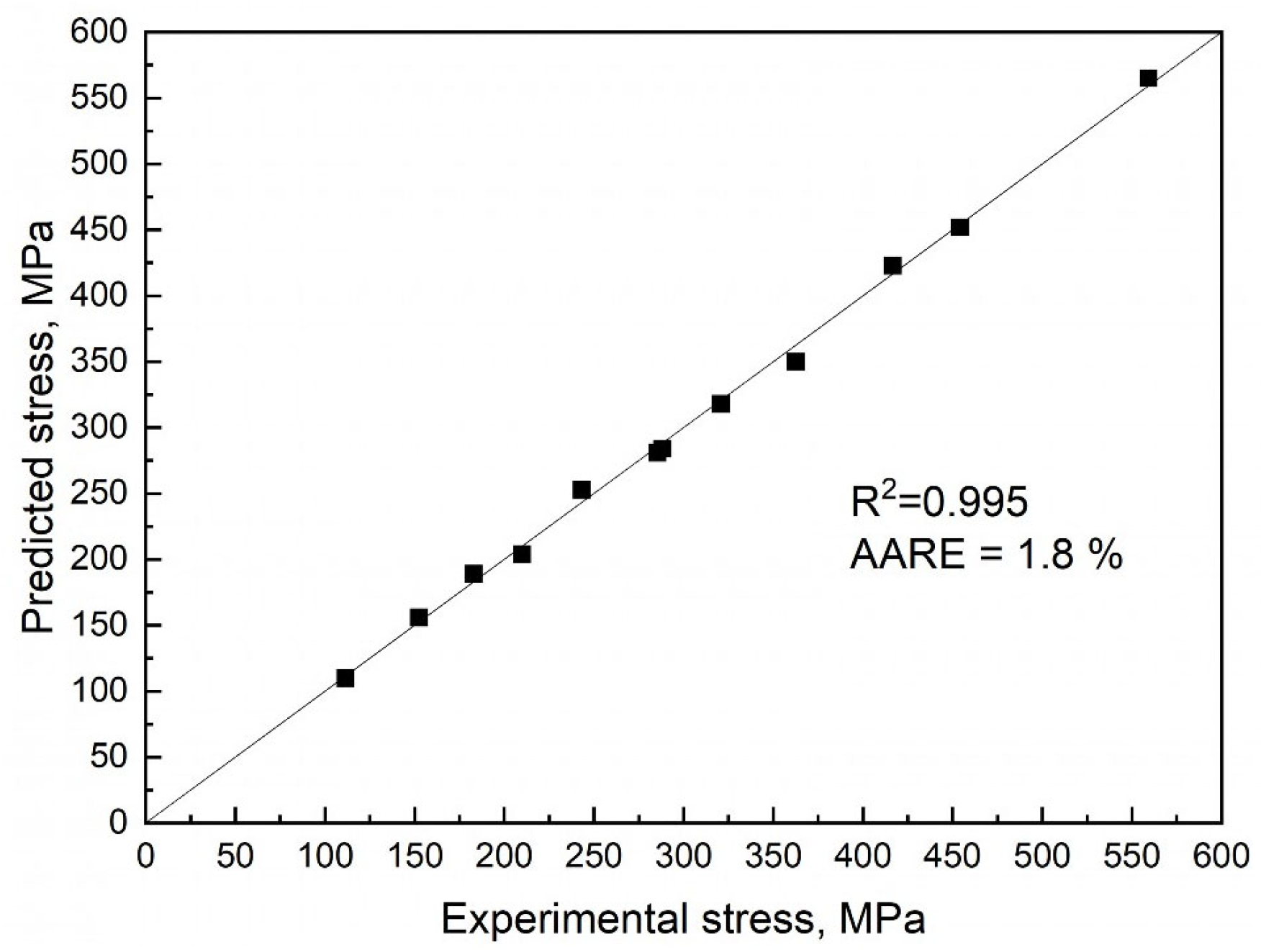
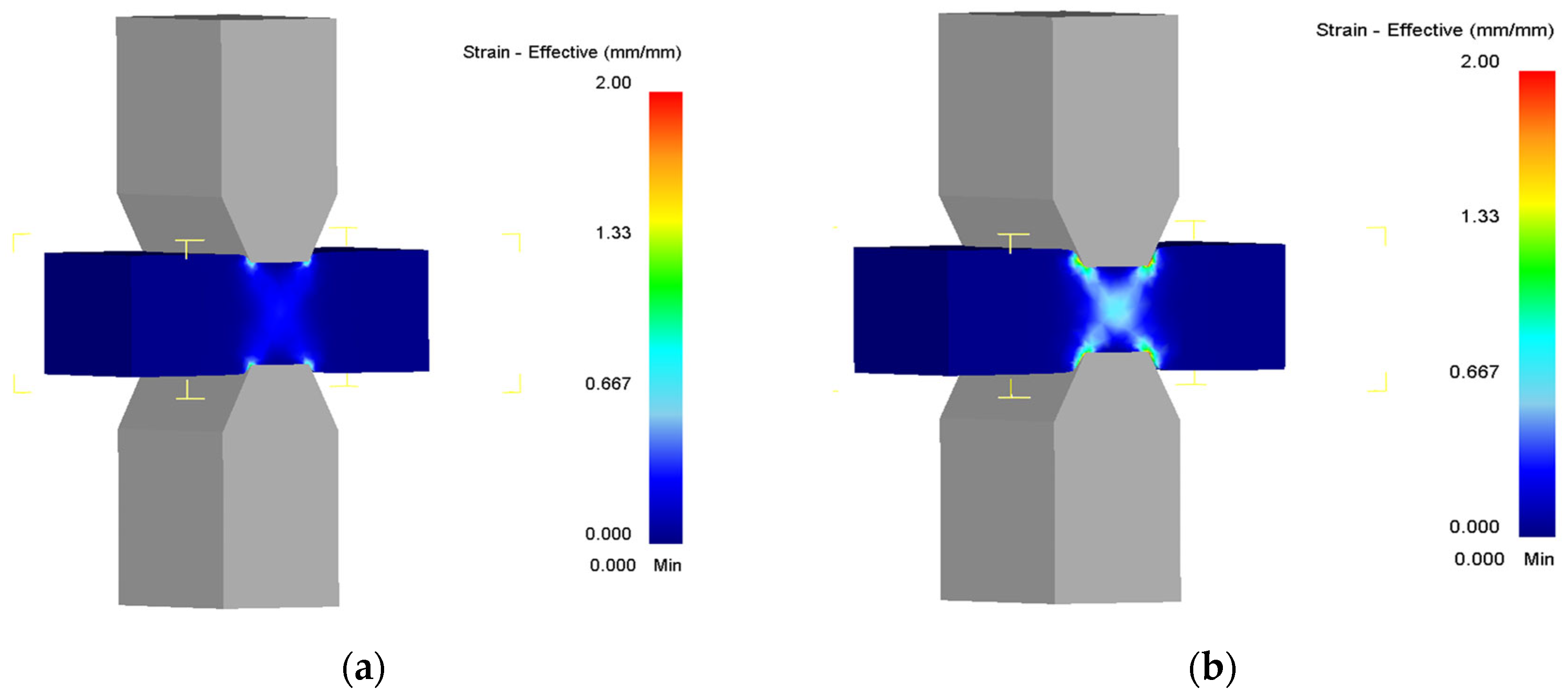
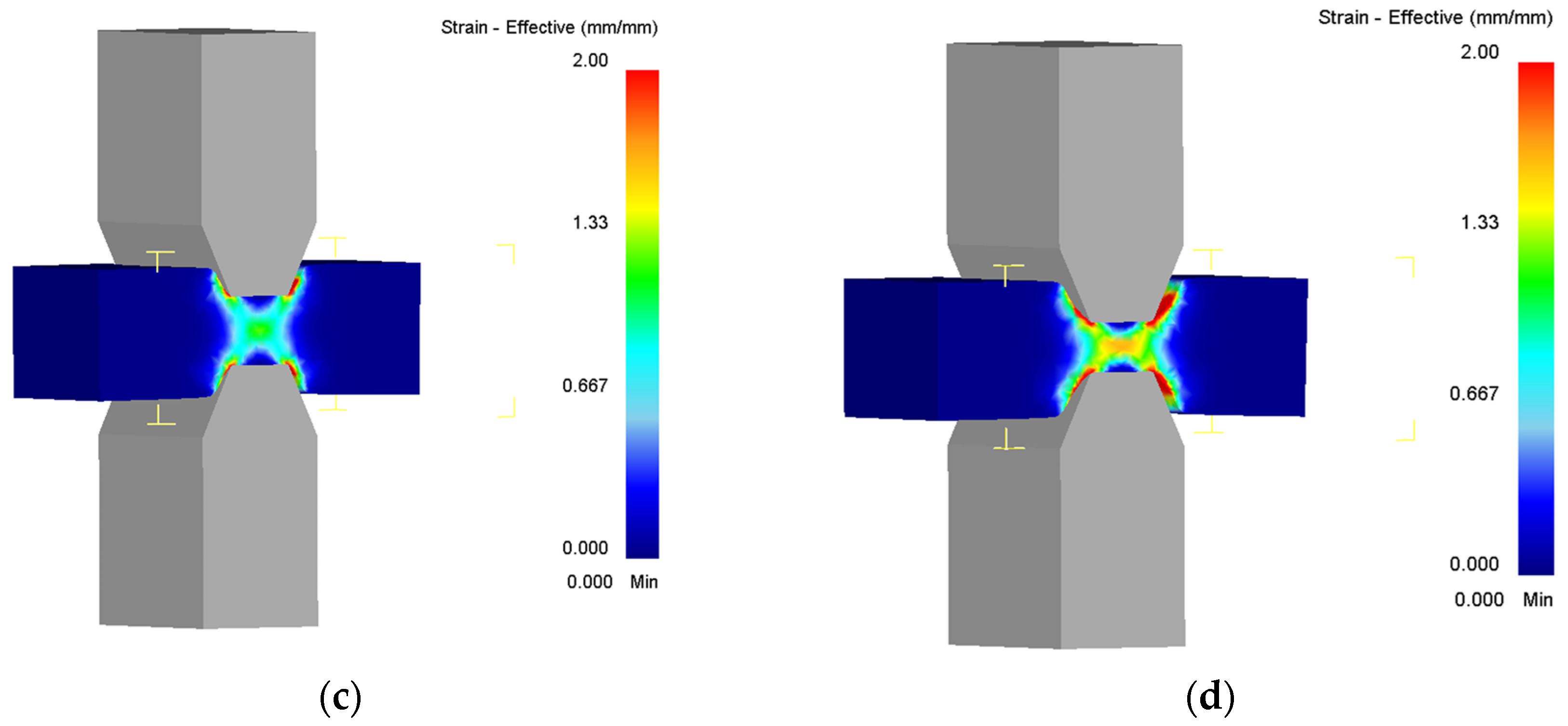
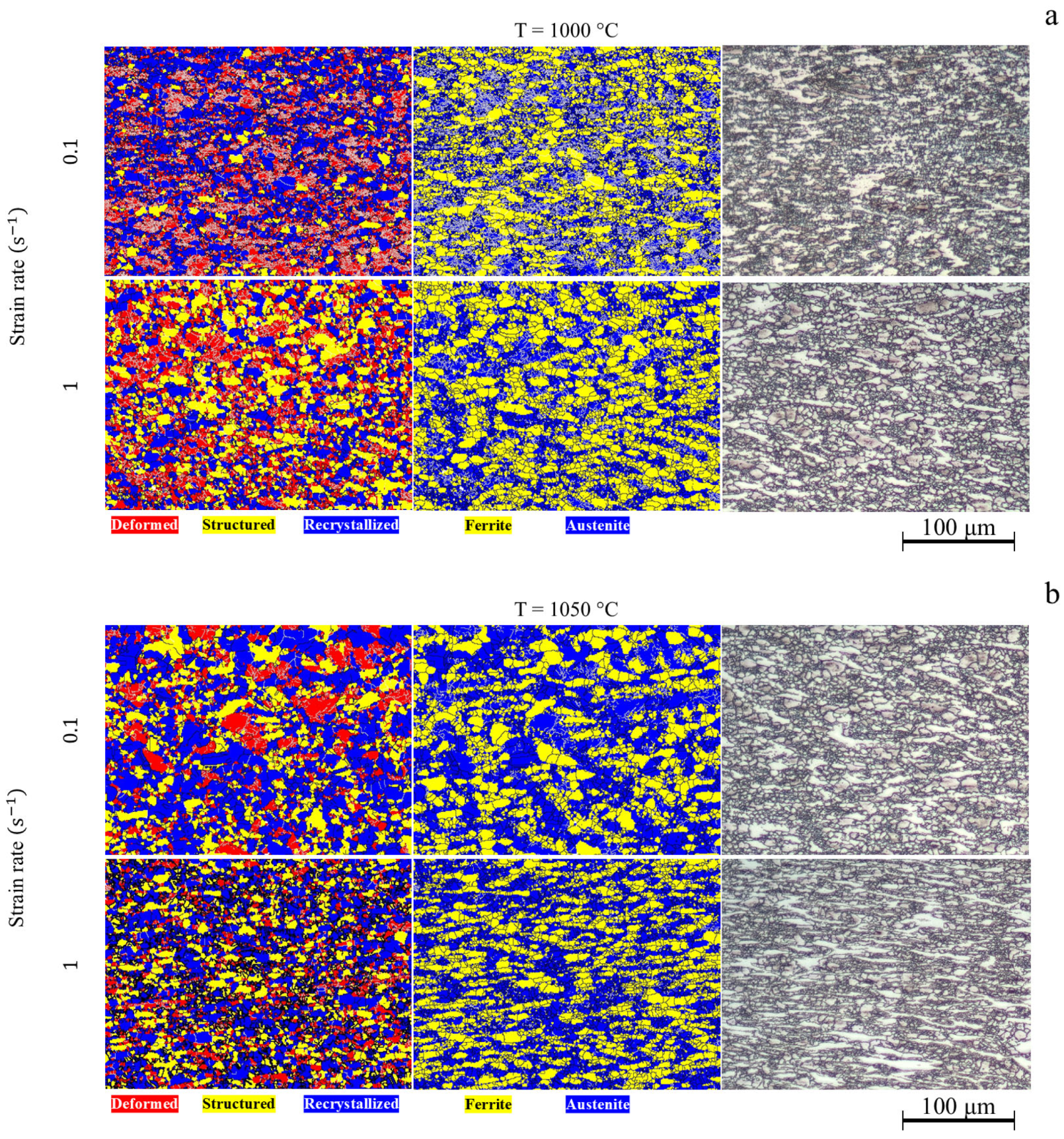
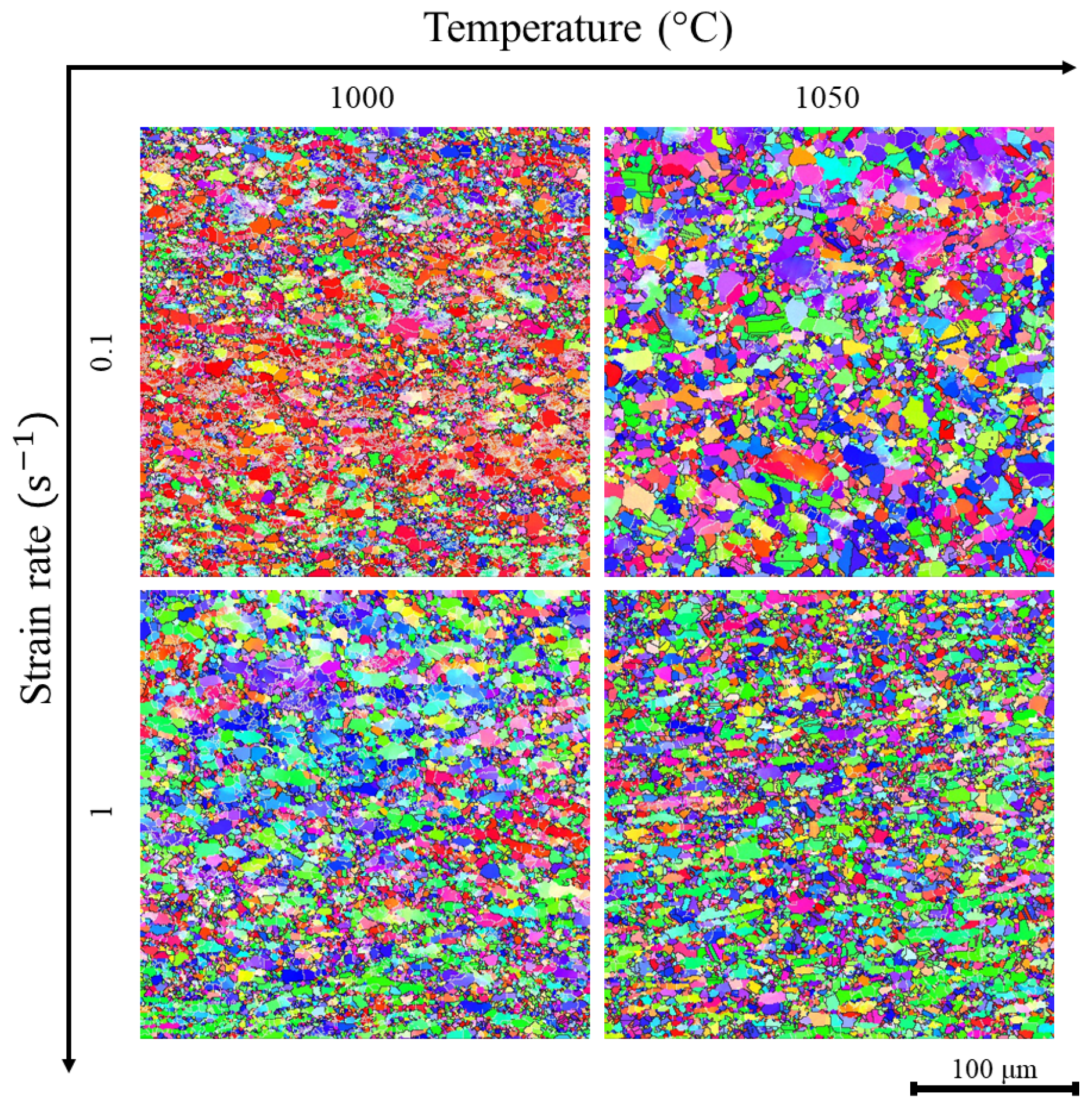
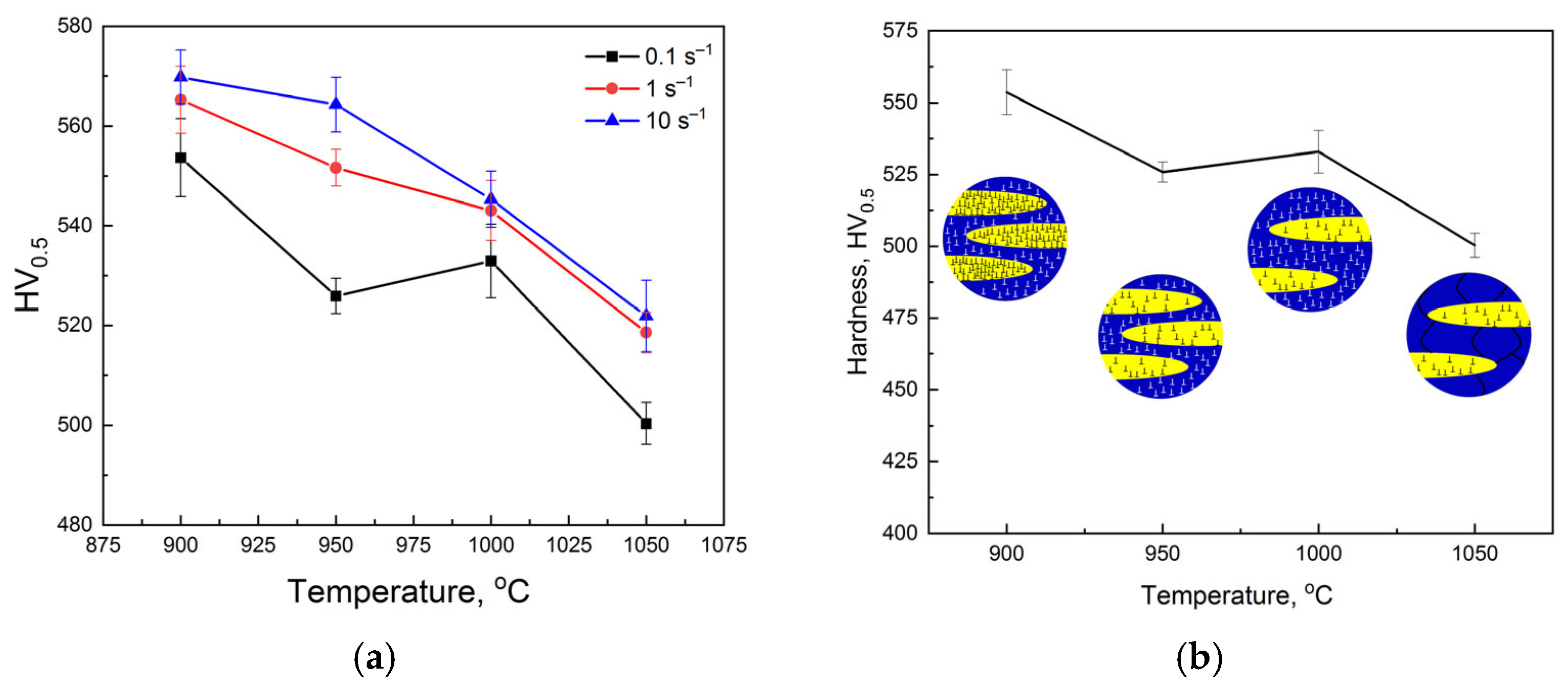
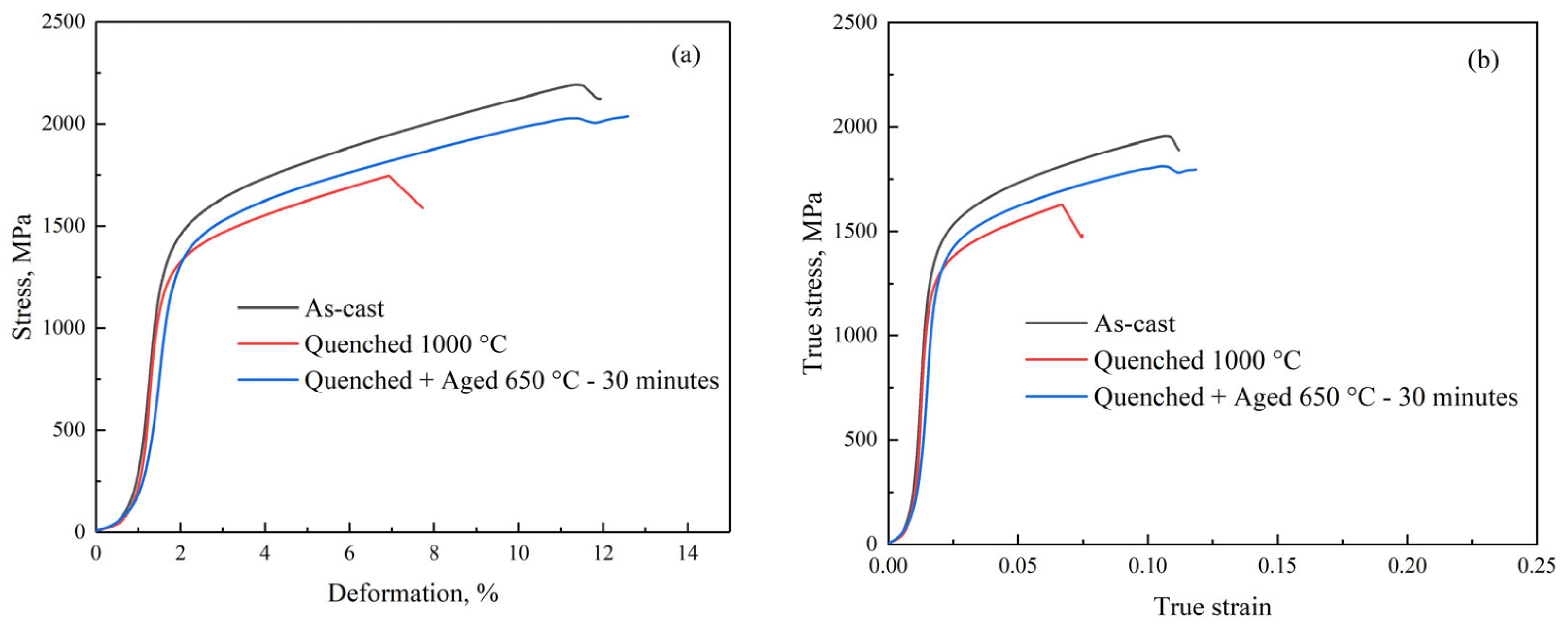
| Steel | Phase Composition at Deformation Temperatures | Effective Activation Energy of Hot Deformation |
|---|---|---|
| Fe-30Mn-10Al-3.3Si-1C [this work] | Austenite/Ferrite | 400 ± 13 kJ/mol |
| Fe-28Mn-8.8Al-0.9C [25] | Austenite | 394 kJ/mol |
| Fe-28Mn-8Al-1C [26] | Austenite | 385 kJ/mol |
| Fe-35Mn-10Al-1C [27] | Austenite | 432 kJ/mol |
| Fe-30Mn-11Al-1C-0.1Nb-0.1V [28] | Austenite | 389 kJ/mol |
| Fe-25Mn-10Al-1.5C-0.053Nb [29] | Austenite | 513 kJ/mol |
| State | Yield Strength, MPa | True Compressive Strength, MPa | Deformation to Fracture, % | Specific Strength, σ0.2/ρ, 103 m2/s2 | Vickers Hardness, HV0.5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| As-cast | 1350 ± 32 | 1960 ± 45 | 8 ± 2 | 209 ± 5 | 508 ± 3 |
| Quenched at 1000 °C | 1350 ± 35 | 1620 ± 41 | 5 ± 1 | 209 ± 5 | 530 ± 16 |
| Quenched at 1000 °C + aging at 650 for 30 min | 1310 ± 25 | 1810 ± 35 | 8 ± 1 | 202 ± 4 | 550 ± 17 |
| State | Yield Strength, MPa | True Compressive Strength, MPa | Deformation to Fracture, % | Specific Strength, σ0.2/ρ, 103 m2/s2 | Vickers Hardness, HV0.5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1000 °C—0.1 s−1 | 1450 ± 41 | 1880 ± 52 | 13 ± 2 | 224 ± 6 | 532 ± 12 |
| 1000 °C—1 s−1 | 1510 ± 38 | 2100 ± 45 | 13 ± 2 | 233 ± 6 | 543 ± 10 |
| 950 °C—0.1 s−1 | 1400 ± 35 | 2060 ± 54 | 16 ± 3 | 216 ± 5 | 526 ± 8 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kazakova, A.A.; Churyumov, A.Y. Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Fe-30Mn-10Al-3.3Si-1C Light-Weight Steel. Materials 2025, 18, 1258. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18061258
Kazakova AA, Churyumov AY. Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Fe-30Mn-10Al-3.3Si-1C Light-Weight Steel. Materials. 2025; 18(6):1258. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18061258
Chicago/Turabian StyleKazakova, Alena A., and Alexander Yu. Churyumov. 2025. "Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Fe-30Mn-10Al-3.3Si-1C Light-Weight Steel" Materials 18, no. 6: 1258. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18061258
APA StyleKazakova, A. A., & Churyumov, A. Y. (2025). Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Fe-30Mn-10Al-3.3Si-1C Light-Weight Steel. Materials, 18(6), 1258. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18061258







