Kenaf Fiber-Reinforced Biocomposites for Marine Applications: A Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
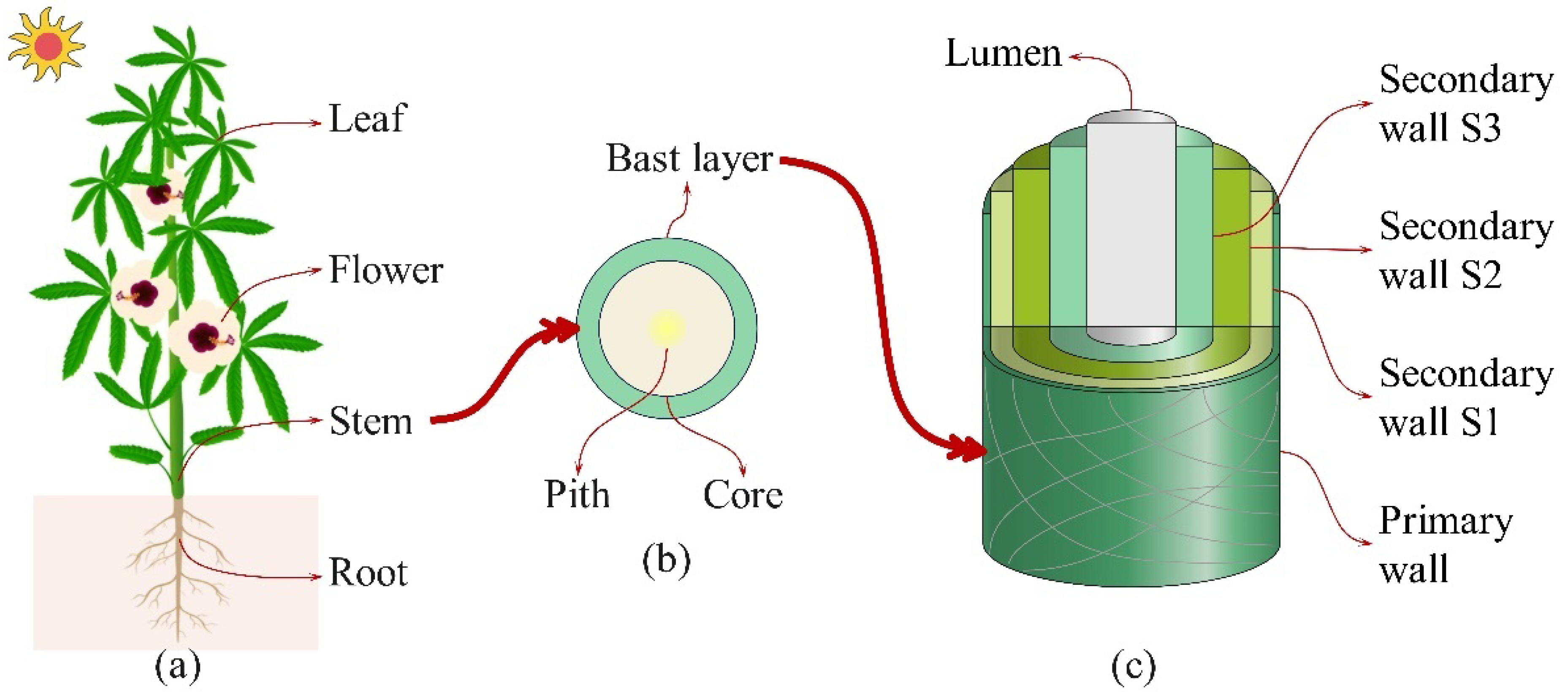
2. Kenaf Fiber
2.1. Structural and Chemical Composition of Kenaf Fiber
2.2. Physical and Mechanical Properties of Kenaf Fiber
2.3. Extraction Methods for Kenaf Fiber
3. Characteristics of Kenaf Fiber-Reinforced Biocomposites
4. Composites Testing Using ASTM Standards
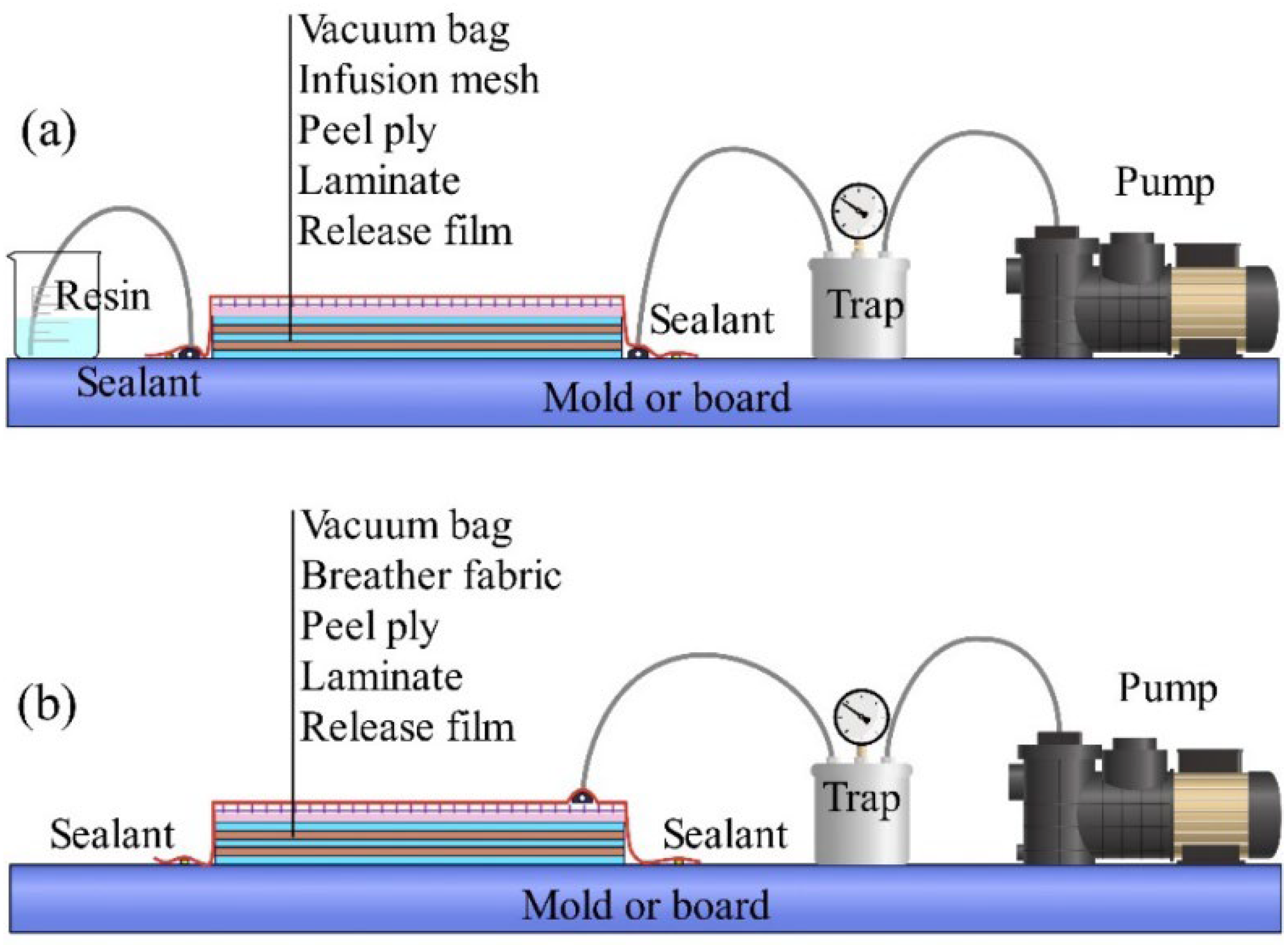
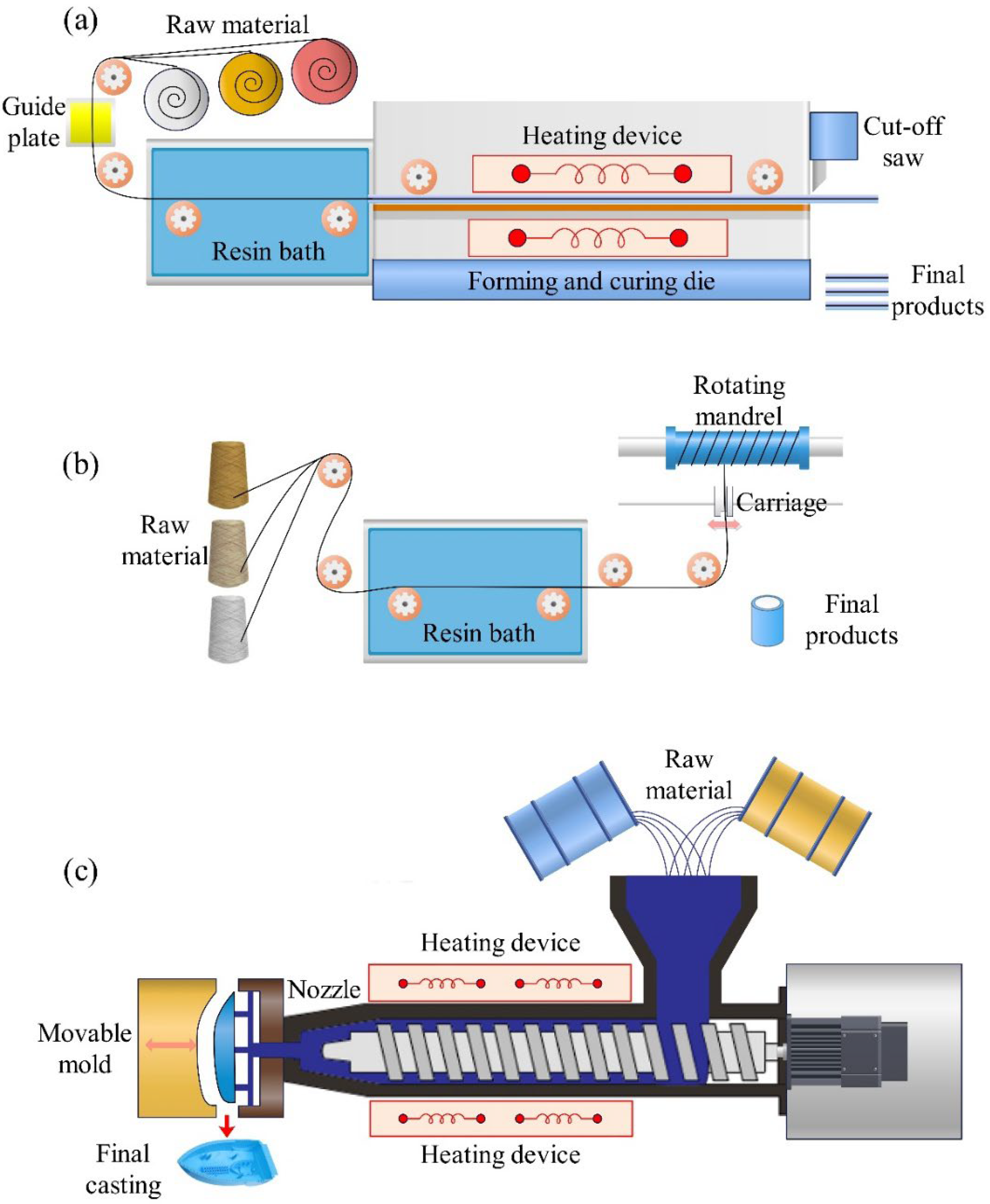
5. Manufacturing and Properties of Kenaf-Based Biocomposites
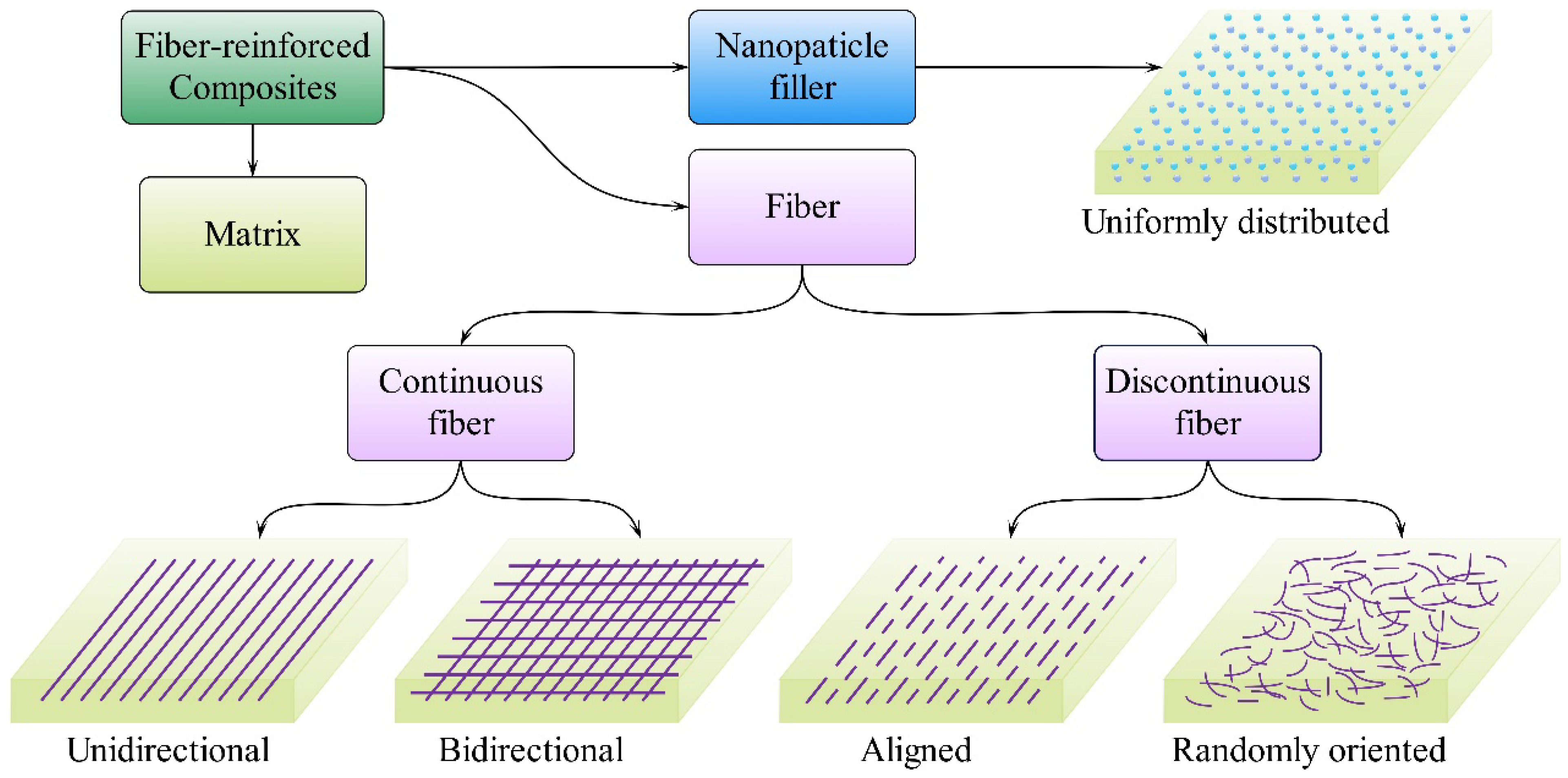
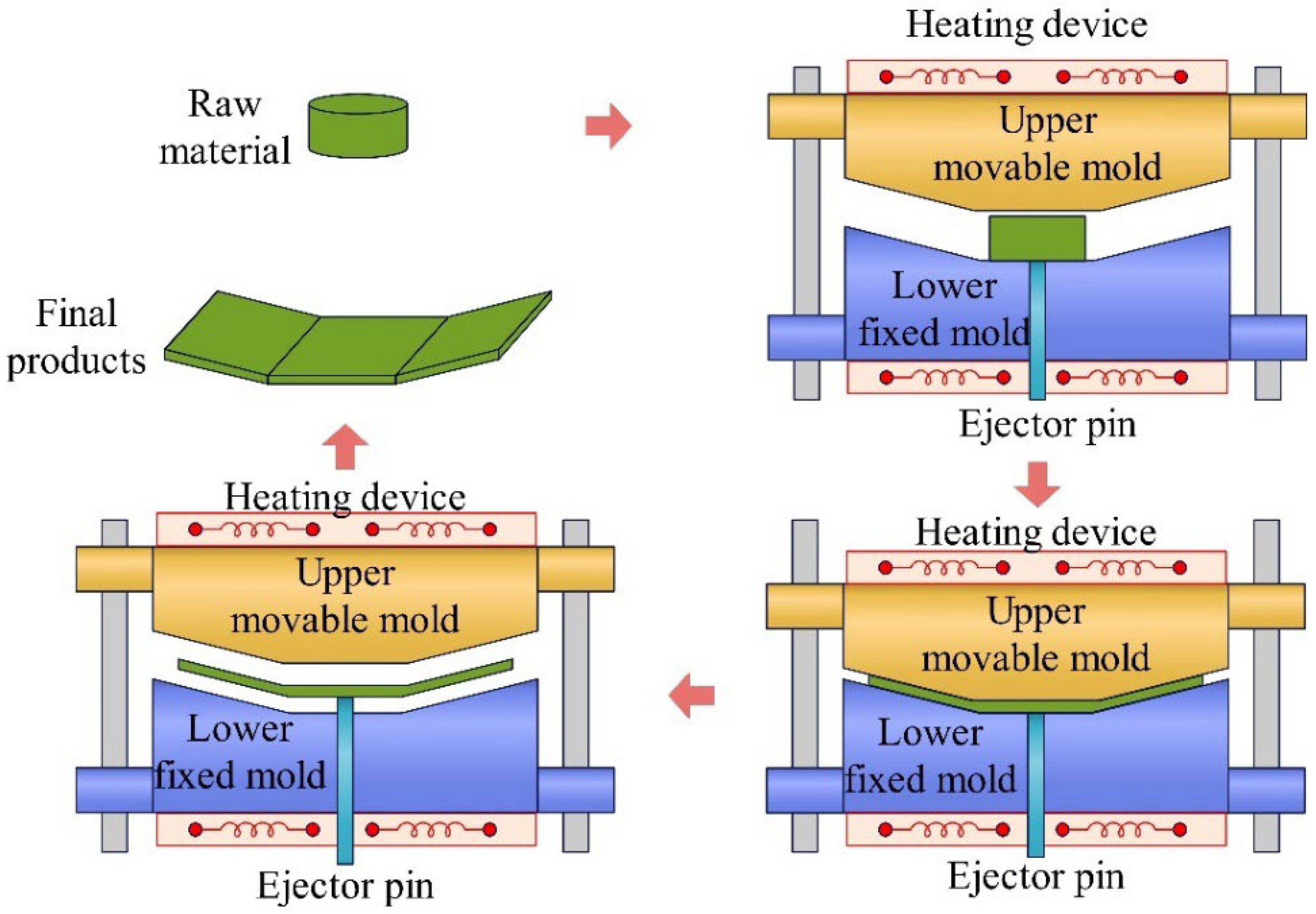
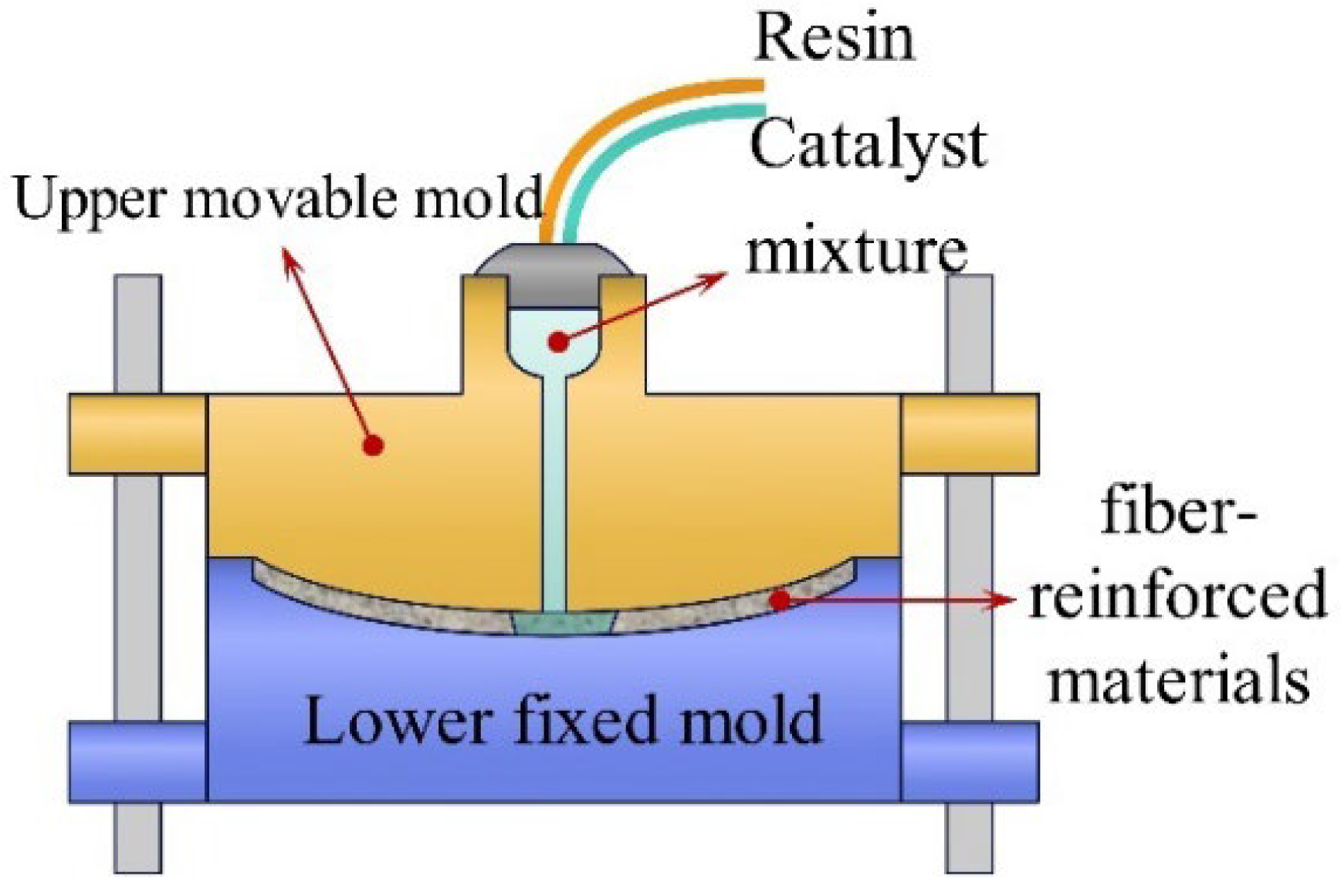
5.1. Manufacturing Methods for Fiber-Reinforced Composites
5.2. Properties of Kenaf Fiber-Reinforced Biocomposites
| Reinforcement | Matrix | Stacking Sequence | Fiber Ratio | Method | TS (MPa) | TM (GPa) | FS (MPa) | FM (GPa) | EA | WA (%) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kenaf (K)/ Glass (G) | Epoxy | G4KG4 | - | Hand lay-up | 94.92 | - | - | - | - | - | [108] |
| Kenaf (K) | PLA | - | 30 wt.% | Compression molding | 30.25 | 3.41 | 71.42 | 2.85 | 45.23 J/m | - | [143] |
| Kenaf (K) | Epoxy | K5 | - | Vacuum infusion method | 79.68 | 2.21 | 61.29 | 4.5 | - | - | [144] |
| Kenaf (K)/ Carbon (C) | Epoxy | CKCKC | - | Vacuum infusion method | 210.49 | 10.6 | 221.7 | 30.81 | - | - | [144] |
| Kenaf (K)/ Carbon (C) | Epoxy | KCKCK | - | Vacuum infusion method | 134.65 | 7.95 | 130 | 14.02 | - | - | [144] |
| Kenaf (K)/ Carbon (C) | Epoxy | C2KC2 | - | Vacuum infusion method | 202.77 | 10.49 | 299.31 | 32.67 | - | - | [144] |
| Kenaf (K) | PLA | - | 35 vol% | Compression molding | 65.158 | 3.29 | 86.956 | 7.99 | - | - | [131] |
| Kenaf (K) | Unsaturated polyester | K4 | 25.8 wt.% | Hand lay-up | 35.78 | - | 42.91 | - | - | - | [145] |
| Kenaf (K)/ Glass (G) | Unsaturated polyester | KGKG | K:9.63 wt.% G:12.04 wt.% | Hand lay-up | 85 | - | 69.96 | - | - | - | [145] |
| Kenaf (K)/ Glass (G) | Unsaturated polyester | KG2K | K:9.94 wt.% G:12.42 wt.% | Hand lay-up | 58.75 | - | 55.62 | - | - | - | [145] |
| Kenaf (K)/ Glass (G) | Unsaturated polyester | GK2G | K:9.35 wt.% G:11.70 wt.% | Hand lay-up | 77.98 | - | 59.37 | - | - | - | [145] |
| Kenaf (K) | Epoxy | K5 | 35.4 vol% | Vacuum infusion molding | 58.6 ± 5.7 | 5.2 | 100.1 ± 2.7 | 5.7 | - | 8.0 | [146] |
| Kenaf (K)/ Carbon (C) | Epoxy | KCKCK | K:28.2 vol% C:9.0 vol% | Vacuum infusion molding | 178.3 ± 9.1 | 13.3 | 188.3 ± 9.9 | 6.2 | - | 6.5 | [146] |
| Kenaf (K)/ Carbon (C) fibers | Epoxy | CKCKCKCKC | K:24.6 vol% C:15.8 vol% | Vacuum infusion molding | 294.1 ± 10.8 | 22.4 | 369.3 ± 9.4 | 20.0 | - | 4.2 | [146] |
| Kenaf (K)/ Carbon (C) | Epoxy | KC2KC2K | K:23.9 V% C:15.4 vol% | Vacuum infusion molding | 265.5 ± 7.3 | 21.0 | 267.2 ± 9.8 | 9.2 | - | 5.7 | [146] |
| Kenaf (K)/ Carbon (C) | Epoxy | C2K3C2 | K:25.9 vol% C:16.6 vol% | Vacuum infusion molding | 261.8 ± 8.6 | 18.0 | 401.0 ± 11.5 | 29.3 | - | 4.3 | [146] |
| Kenaf (K) fiber | Epoxy | - | 35.9 vol% | Vacuum infusion molding | 55.6 | 8.4 | 111.9 | 5.4 | - | 5.2 | [138] |
| Kenaf (K)/ UD-Glass (G) | Unsaturated polyester | KGKGKGK | - | Hand lay-up and Compression molding | 404.54 | 25.54 | - | - | - | - | [130] |
| Kenaf (K)/ UD-Glass (G) | Unsaturated polyester | KGKGKGK | - | Pultruded method | 410.6 | 26 | - | - | 260 kJ/m2 | - | [147] |
| Kenaf (K) | Unsaturated polyester | - | 6% | Hand lay-up | 40.6 | - | 54.02 | 2.25 | 44.95 kJ/m2 | - | [57] |
| Kenaf (K)/ Glass (G) | Epoxy | GKGKG | 30% | Hand lay-up | 147.64 | 3.9 | 188.99 | 10.9 | [148] | ||
| Kenaf (K)/ Glass (G) | Epoxy | KGKGK | 30% | Hand lay-up | 121.45 | 2.96 | 155.22 | 5.74 | [148] | ||
| Kenaf (K)/ Glass (G)/ Tea leaf (T) | Epoxy | GKGTGKG | K:25% G:10% T:5% | Compression molding | 70.81 | - | 181.08 | - | 96 kJ/m2 | - | [149] |
| Kenaf (K) | Epoxy | K5 | 21.91% | Hand lay-up | 31.9 | 2.87 | 43.1 | 3.85 | 3 J | - | [125] |
| Kenaf (K)/ Areca (A) | Epoxy | AKAKA | 28.45% | Hand lay-up | 8.76 | 0.47 | 15.7 | 1.35 | 15 J | - | [125] |
| Kenaf (K)/ Areca (A) | Epoxy | KAKAK | 27.28 | Hand lay-up | 13.98 | 1.39 | 26.9 | 4.21 | 8 J | - | [125] |
| Kenaf (K) | PLA | K5 | 40% | Hot compression process | 61 | 5.4 | 62 | 2.7 | 49 kJ/m2 | - | [150] |
| Kenaf (K)/ Polyester (P) | PLA | PK3P | K:23.5% P:16.5% | Hot compression process | 36 | 5.4 | 89 | 5.4 | 63 kJ/m2 | - | [150] |
| Kenaf (K)/ Polyester (P) | PLA | P2KP2 | K:7.7% P:32.3% | Hot compression process | 103 | 0.7 | 80 | 5.5 | 83.6 kJ/m2 | - | [150] |
| Kenaf (K) | Epoxy | - | 30% | Vacuum infusion molding | 70.96 | 2.09 | 59.04 | 3.77 | - | 25.49 | [132] |
| Kenaf (K) | Epoxy | - | 40% | Vacuum infusion molding | 76.67 | 2.31 | 61.24 | 4.2 | - | 30.46 | [132] |
| Kenaf (K)/ Flax (F) | Epoxy | FKF | - | Hand lay-up | 41.06 ± 1.83 | 2.6 ± 0.2 | 64.13 ± 6.29 | 3.80 ± 0.2 | - | - | [151] |
| Kenaf (K)/ Flax (F) | Epoxy | KFK | - | Hand lay-up | 44.4 ± 1.83 | 2.39 ± 0.1 | 64.94 ± 7.68 | 4.44 ± 0.3 | - | - | [151] |
| Kenaf (K)/ Jute (J) | Epoxy | JKJ | - | Hand lay-up | 40.66 | 3.27 | 57.2 | 3.24 | - | - | [129] |
| Kenaf (K)/ Jute (J) | Epoxy | KJK | - | Hand lay-up | 43.21 | 3.60 | 75.57 | 4.62 | - | - | [129] |
| Kenaf (K)/ Glass (G) | Epoxy | G2K2G2 | - | Vacuum-bagging process | 42.69 | - | 158.42 | - | - | - | [152] |
| Kenaf (K)/ Glass (G) | Epoxy | KG4K | - | Vacuum-bagging process | 88.08 | - | 71.63 | - | - | - | [152] |
| Kenaf (K)/ Jute (J)/ Glass (G) | Epoxy | K2JKG2 | - | Vacuum-bagging process | 41.613 | - | 243.86 | - | - | - | [152] |
6. Exploring Kenaf Fiber Composites for Marine Applications
| Fiber-Matrix | Applied Methods | Results | Ref. |
| Abaca (A)/Kenaf (K)/Carbon (C)-Epoxy |
|
| [156] |
| Kenaf (K)-Epoxy |
|
| [132] |
| Kenaf (K)/Glass (G)-Epoxy |
|
| [157] |
| Kenaf (K) fiber |
|
| [158] |
| Kenaf (K)-PLA |
|
| [159] |

7. Conclusions
- The impact of seawater absorption and UV radiation on the mechanical, thermal, physical, and chemical properties of the composites;
- The debonding effects of interfacial bonding between kenaf fibers and matrix materials in seawater environments;
- The long-term effects of seawater exposure on the degradation, corrosion, and durability of kenaf fiber-based composites.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kujoana, T.C.; Weeks, W.J.; Van der Westhuizen, M.M.; Mabelebele, M.; Sebola, N.A. Potential Significance of Kenaf (Hibiscus cannabinus L.) to Global Food and Feed Industries. Cogent Food Agric. 2023, 9, 2184014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramesh, M. Kenaf (Hibiscus cannabinus L.) Fibre Based Bio-Materials: A Review on Processing and Properties. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2016, 78–79, 1–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Tao, A.; Qi, J.; Wang, Y. 4—Bast Fibres: Kenaf. In Handbook of Natural Fibres, 2nd ed.; Kozłowski, R.M., Mackiewicz-Talarczyk, M., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing Series in Textiles; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2020; pp. 71–92. ISBN 978-0-12-818398-4. [Google Scholar]
- Austin, C.C.; Mondell, C.N.; Clark, D.G.; Wilkie, A.C. Kenaf: Opportunities for an Ancient Fiber Crop. Agronomy 2024, 14, 1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aizat Norhisham, D.; Md Saad, N.; Ahmad Usuldin, S.R.; Vayabari, D.A.G.; Ilham, Z.; Ibrahim, M.F.; Show, P.-L.; Wan-Mohtar, W.A.A.Q.I. Performance of Malaysian Kenaf Hibiscus cannabinus Callus Biomass and Exopolysaccharide Production in a Novel Liquid Culture. Bioengineered 2023, 14, 2262203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Mamun, M.; Rafii, M.Y.; Misran, A.B.; Berahim, Z.; Ahmad, Z.; Khan, M.M.H.; Oladosu, Y.; Arolu, F. Kenaf (Hibiscus cannabinus L.): A Promising Fiber Crop with Potential for Genetic Improvement Utilizing Both Conventional and Molecular Approaches. J. Nat. Fibers 2023, 20, 2145410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adole, A.M.; Yatim, J.M.; Ramli, S.A.; Othman, A.; Mizal, N.A. Kenaf Fibre and Its Bio-Based Composites: A Conspectus. Pertanika J. Sci. Technol. 2019, 27, 297–329. [Google Scholar]
- An, X.; Jin, G.; Zhang, J.; Ma, G.; Dai, L.; Jin, L.; Luo, X.; Chen, C.; Shi, X.; Zhou, J.; et al. Research Progress on Tissue Culture and Genetic Transformation of Kenaf (Hibiscus cannabinus). Open Life Sci. 2017, 12, 465–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yosr, B.M.; Mounir, J.; Slah, M. Study of the Kenaf Fibres Spinnability: Influence of the Percentage of Kenaf Cotton Mixture on the Yarn Properties. J. Nat. Fibers 2023, 20, 2166187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayadi, R.; Hanana, M.; Mzid, R.; Hamrouni, L.; Khouja, M.L.; Hanachi, A.S. Hibiscus cannabinus L.—Kenaf: A Review Paper. J. Nat. Fibers 2017, 14, 466–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahar, F.S.; Hameed Sultan, M.T.; Safri, S.N.A.; Jawaid, M.; Abu Talib, A.R.; Basri, A.A.; Md Shah, A.U. Fatigue and Impact Properties of 3D Printed PLA Reinforced with Kenaf Particles. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2022, 16, 461–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vayabari, D.A.G.; Ilham, Z.; Md Saad, N.; Usuldin, S.R.A.; Norhisham, D.A.; Abd Rahim, M.H.; Wan-Mohtar, W.A.A.Q.I. Cultivation Strategies of Kenaf (Hibiscus cannabinus L.) as a Future Approach in Malaysian Agriculture Industry. Horticulturae 2023, 9, 925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paridah, M.T.; Abdelrhman, A.H.; Shahwahid, M. Cost Benefit Analysis of Kenaf Cultivation for Producing Fiber in Malaysia. Arab. J. Bus. Manag. Rev. 2017, 7, 1000310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernando, A.L. Environmental Aspects of Kenaf Production and Use. In Kenaf: A Multi-Purpose Crop for Several Industrial Applications; Monti, A., Alexopoulou, E., Eds.; Green Energy and Technology; Springer: London, UK, 2013; pp. 83–104. ISBN 978-1-4471-5066-4. [Google Scholar]
- Akil, H.M.; Omar, M.F.; Mazuki, A.A.M.; Safiee, S.; Ishak, Z.A.M.; Abu Bakar, A. Kenaf Fiber Reinforced Composites: A Review. Mater. Des. 2011, 32, 4107–4121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.M.; Mohd Ishak, Z.A.; Mat Taib, R.; Law, T.T.; Ahmad Thirmizir, M.Z. Mechanical, Thermal and Water Absorption Properties of Kenaf-Fiber-Based Polypropylene and Poly (Butylene Succinate) Composites. J. Polym. Environ. 2013, 21, 293–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sreenivas, H.T.; Krishnamurthy, N.; Arpitha, G.R. A Comprehensive Review on Light Weight Kenaf Fiber for Automobiles. Int. J. Lightweight Mater. Manuf. 2020, 3, 328–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.H.; Khalina, A.; Nurazzi, N.M.; Norli, A.; Harussani, M.M.; Rafiqah, S.A.; Aisyah, H.A.; Ramli, N. The Challenges and Future Perspective of Woven Kenaf Reinforcement in Thermoset Polymer Composites in Malaysia: A Review. Polymers 2021, 13, 1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansingh, B.B.; Binoj, J.S.; Manikandan, N.; Sai, N.P.; Siengchin, S.; Mavinkere Rangappa, S.; Bharath, K.N.; Indran, S. Kenaf Fibers, Their Composites and Applications. In Plant Fibers, Their Composites, and Applications; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2022; pp. 283–304. ISBN 978-0-12-824528-6. [Google Scholar]
- Arunachalam, S.J.; Saravanan, R.; Sathish, T.; Parthiban, A. Effect of Nano-Particle Weight Percent on the Flexural Strength of Jute/Kenaf/Glass Fiber Composite Using RSM. Hyperfine Interact. 2024, 245, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, K.; Ahmad, F.; Yunus, N.A.; Gunister, E.; Ali, S.; Raza, A. Physical and Mechanical Properties of Kenaf/Flax Hybrid Composites. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2023, 140, e53421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owen, M.M.; Achukwu, E.O.; Romli, A.Z.; Md Akil, H. Recent Advances on Improving the Mechanical and Thermal Properties of Kenaf Fibers/Engineering Thermoplastic Composites Using Novel Coating Techniques: A Review. Compos. Interfaces 2023, 30, 849–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Fang, Y.; Gao, H. Effect of SiO2 Nano-Interphase on the Water Absorption Mechanism of Natural Fiber Reinforced Composites: A Multi-Scale Study. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2023, 637, 157942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seydibeyoğlu, M.Ö.; Dogru, A.; Wang, J.; Rencheck, M.; Han, Y.; Wang, L.; Seydibeyoğlu, E.A.; Zhao, X.; Ong, K.; Shatkin, J.A.; et al. Review on Hybrid Reinforced Polymer Matrix Composites with Nanocellulose, Nanomaterials, and Other Fibers. Polymers 2023, 15, 984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mokhena, T.C.; Mtibe, A.; Mokhothu, T.H.; Mochane, M.J.; John, M.J. A Review on Bast-Fibre-Reinforced Hybrid Composites and Their Applications. Polymers 2023, 15, 3414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsissou, R.; Seghiri, R.; Benzekri, Z.; Hilali, M.; Rafik, M.; Elharfi, A. Polymer Composite Materials: A Comprehensive Review. Compos. Struct. 2021, 262, 113640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baye, B.; Tesfaye, T. The New Generation Fibers: A Review of High Performance and Specialty Fibers. Polym. Bull. 2022, 79, 9221–9235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellano, J.; Marrero, M.D.; Ortega, Z. Opuntia Fiber and Its Potential to Obtain Sustainable Materials in the Composites Field: A Review. J. Nat. Fibers 2022, 19, 10053–10067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Sultan, M.T.H.; Shahar, F.S.; Grzejda, R.; Łukaszewicz, A. Hybrid Fiber-Reinforced Biocomposites for Marine Applications: A Review. J. Compos. Sci. 2024, 8, 430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiore, V.; Di Bella, G.; Valenza, A. Glass–Basalt/Epoxy Hybrid Composites for Marine Applications. Mater. Des. 2011, 32, 2091–2099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, W.; Zhang, H.-P.; Xu, X.; Tang, Y. Hybrid Enhancements by Polydopamine and Nanosilica on Carbon Fibre Reinforced Polymer Laminates under Marine Environment. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2018, 112, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acharya, S.; Rumi, S.S.; Hu, Y.; Abidi, N. Microfibers from Synthetic Textiles as a Major Source of Microplastics in the Environment: A Review. Text. Res. J. 2021, 91, 2136–2156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gowda, T.G.Y.; Vinod, A.; Madhu, P.; Sanjay, M.R.; Siengchin, S.; Jawaid, M. Areca/Synthetic Fibers Reinforced Based Epoxy Hybrid Composites for Semi-Structural Applications. Polym. Compos. 2022, 43, 5222–5234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Hawary, O.; Boccarusso, L.; Ansell, M.P.; Durante, M.; Pinto, F. An Overview of Natural Fiber Composites for Marine Applications. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2023, 11, 1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crupi, V.; Epasto, G.; Napolitano, F.; Palomba, G.; Papa, I.; Russo, P. Green Composites for Maritime Engineering: A Review. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2023, 11, 599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amiandamhen, S.O.; Meincken, M.; Tyhoda, L. Natural Fibre Modification and Its Influence on Fibre-Matrix Interfacial Properties in Biocomposite Materials. Fibers Polym. 2020, 21, 677–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, K.; Ahmad, F.; Gunister, E. A Review on the Kenaf Fiber Reinforced Thermoset Composites. Appl. Compos. Mater. 2021, 28, 491–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad Nadzri, S.N.Z.; Hameed Sultan, M.T.; Md Shah, A.U.; Safri, S.N.A.; Basri, A.A. A Review on the Kenaf/Glass Hybrid Composites with Limitations on Mechanical and Low Velocity Impact Properties. Polymers 2020, 12, 1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, S.; Parashar, V. Experimental Analysis of Duo-Fiber Interaction on the Tensile Strength of Surface-Modified Flax–Kenaf-Reinforced Epoxy Composite. Polym. Bull. 2023, 80, 13159–13179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salman, S.D.; Leman, Z.; Sultan, M.T.H.; Ishak, M.R.; Cardona, F. Kenaf/Synthetic and Kevlar®/Cellulosic Fiber-Reinforced Hybrid Composites: A Review. BioRes 2015, 10, 8580–8603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, Y. The Plant Cell Wall: Biosynthesis, Construction, and Functions. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2021, 63, 251–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayala Soto, F.E.; Serna Saldívar, S.O. Architecture, Structure and Chemistry of Plant Cell Walls and Their Constituents. In Science and Technology of Fibers in Food Systems; Welti-Chanes, J., Serna-Saldívar, S.O., Campanella, O., Tejada-Ortigoza, V., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 3–14. ISBN 978-3-030-38654-2. [Google Scholar]
- Agarwal, U.P.; Ralph, S.A. Raman Spectra of Delignified Plant Fibers: Exploring the Impact of Xylan’s Presence on the Spectral Features of Cellulose. Fibers 2024, 12, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chibrikov, V.; Pieczywek, P.M.; Cybulska, J.; Zdunek, A. Coarse-Grained Molecular Dynamics Model to Evaluate the Mechanical Properties of Bacterial Cellulose–Hemicellulose Composites. Carbohydr. Polym. 2024, 330, 121827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalia, S.; Dufresne, A.; Cherian, B.M.; Kaith, B.S.; Avérous, L.; Njuguna, J.; Nassiopoulos, E. Cellulose-Based Bio- and Nanocomposites: A Review. Int. J. Polym. Sci. 2011, 2011, 837875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimah, A.; Ridho, M.R.; Munawar, S.S.; Adi, D.S.; Ismadi; Damayanti, R.; Subiyanto, B.; Fatriasari, W.; Fudholi, A. A Review on Natural Fibers for Development of Eco-Friendly Bio-Composite: Characteristics, and Utilizations. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2021, 13, 2442–2458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, M.Z.; Zhang, M.Q.; Liu, Y.; Yang, G.C.; Zeng, H.M. The Effect of Fiber Treatment on the Mechanical Properties of Unidirectional Sisal-Reinforced Epoxy Composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2001, 61, 1437–1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Bai, S.; Yue, X.; Long, B.; Choo-Smith, L.-P. Relationship between Chemical Composition, Crystallinity, Orientation and Tensile Strength of Kenaf Fiber. Fibers Polym. 2016, 17, 1757–1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palanisamy, S.; Kalimuthu, M.; Santulli, C.; Nagarajan, R.; Karuppiah, G. Effect of Extraction Methods on the Properties of Bast Fibres. In Bast Fibers and Their Composites: Processing, Properties and Applications; Rajeshkumar, G., Devnani, G.L., Sinha, S., Sanjay, M.R., Siengchin, S., Eds.; Springer Nature: Singapore, 2022; pp. 17–37. ISBN 978-981-19-4866-4. [Google Scholar]
- Ben Mlik, Y.; Jaoudi, M.; Khoffi, F.; Slah, M.; Durand, B. Study the Effect of Chemical and Enzymatic Extraction Methods on the Kenaf Fibers Properties. J. Nat. Fibers 2022, 19, 1168–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asim, M.; Jawaid, M.; Abdan, K.; Ishak, M.R. Effect of Pineapple Leaf Fibre and Kenaf Fibre Treatment on Mechanical Performance of Phenolic Hybrid Composites. Fibers Polym. 2017, 18, 940–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koohestani, B.; Darban, A.K.; Mokhtari, P.; Yilmaz, E.; Darezereshki, E. Comparison of Different Natural Fiber Treatments: A Literature Review. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 16, 629–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safwan, A.; Jawaid, M.; Sultan, M.T.H.; Hassan, A. Preliminary Study on Tensile and Impact Properties of Kenaf/Bamboo Fiber Reinforced Epoxy Composites. J. Renew. Mater. 2018, 6, 529–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chokshi, S.; Parmar, V.; Gohil, P.; Chaudhary, V. Chemical Composition and Mechanical Properties of Natural Fibers. J. Nat. Fibers 2022, 19, 3942–3953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özturk, S. Effect of Fiber Loading on the Mechanical Properties of Kenaf and Fiberfrax Fiber-Reinforced Phenol-Formaldehyde Composites. J. Compos. Mater. 2010, 44, 2265–2288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazrol, M.D.; Sapuan, S.M.; Ilyas, R.A.; Zainudin, E.S.; Zuhri, M.Y.M.; Abdul, N.I. Effect of Corn Husk Fibre Loading on Thermal and Biodegradable Properties of Kenaf/Cornhusk Fibre Reinforced Corn Starch-Based Hybrid Composites. Heliyon 2023, 9, e15153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhambure, S.S.; Rao, A.S.; Senthilkumar, T. Analysis of Mechanical Properties of Kenaf and Kapok Fiber Reinforced Hybrid Polyester Composite. J. Nat. Fibers 2023, 20, 2156964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ugochukwu, S.; Ridzuan, M.J.M.; Majid, M.S.A.; Cheng, E.M.; Razlan, Z.M.; Marsi, N. Effect of Thermal Ageing on the Scratch Resistance of Natural-Fibre-Reinforced Epoxy Composites. Compos. Struct. 2021, 261, 113586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saw, S.K.; Akhtar, K.; Yadav, N.; Singh, A.K. Hybrid Composites Made from Jute/Coir Fibers: Water Absorption, Thickness Swelling, Density, Morphology, and Mechanical Properties. J. Nat. Fibers 2014, 11, 39–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunne, R.; Desai, D.; Sadiku, R.; Jayaramudu, J. A Review of Natural Fibres, Their Sustainability and Automotive Applications. J. Reinf. Plast. Compos. 2016, 35, 1041–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sathyanarayana, K.; Puttegowda, M.; Rangappa, S.M.; Siengchin, S.; Shivanna, P.; Nagaraju, S.B.; Somashekara, M.K.; Girijashankar, P.B.; Girijappa, Y.G.T. 3—Metallic Lightweight Materials: Properties and Their Applications. In Lightweight and Sustainable Composite Materials; Rangappa, S.M., Doddamani, S.M., Siengchin, S., Doddamani, M., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2023; pp. 47–67. ISBN 978-0-323-95189-0. [Google Scholar]
- Stochioiu, C.; Ciolcă, M.; Deca, A.-L. Mechanical Characterization of Flax and Hemp Fibers Cultivated in Romania. Materials 2024, 17, 4871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuravkov, M.; Lyu, Y.; Starovoitov, E. Material and Solid Mechanical Characteristics (Properties). In Mechanics of Solid Deformable Body; Springer Nature: Singapore, 2023; pp. 51–62. ISBN 978-981-19-8409-9. [Google Scholar]
- Mahjoub, R.; Yatim, J.M.; Mohd Sam, A.R.; Hashemi, S.H. Tensile Properties of Kenaf Fiber Due to Various Conditions of Chemical Fiber Surface Modifications. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 55, 103–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virk, A.S.; Hall, W.; Summerscales, J. Failure Strain as the Key Design Criterion for Fracture of Natural Fibre Composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2010, 70, 995–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiore, V.; Di Bella, G.; Valenza, A. The Effect of Alkaline Treatment on Mechanical Properties of Kenaf Fibers and Their Epoxy Composites. Compos. Part B Eng. 2015, 68, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahar, F.S.; Sultan, M.T.H.; Shah, A.U.M.; Safri, S.N.A. A Short Review on the Extraction of Kenaf Fibers and the Mechanical Properties of Kenaf Powder Composites; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2019; p. 012028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rassmann, S.; Reid, R.G.; Paskaramoorthy, R. Effects of Processing Conditions on the Mechanical and Water Absorption Properties of Resin Transfer Moulded Kenaf Fibre Reinforced Polyester Composite Laminates. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2010, 41, 1612–1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajak, D.K.; Pagar, D.D.; Menezes, P.L.; Linul, E. Fiber-Reinforced Polymer Composites: Manufacturing, Properties, and Applications. Polymers 2019, 11, 1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Popov, R.A. Increasing the Efficiency of the High-Stem Bast Crops Harvesting Process. Agrar. Sci. J. 2024, 6, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayorinde, T.A.; Owolarafe, O.K. Effect of Operational Parameters on the Performance of a Kenaf Harvester. Span. J. Agric. Res. 2023, 21, e0209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawahara, Y.; Tadokoro, K.; Endo, R.; Shioya, M.; Sugimura, Y.; Furusawa, T. Chemically Retted Kenaf Fibers. Sen’i Gakkaishi 2005, 61, 115–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Yu, C. Study on Microbe Retting of Kenaf Fiber. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2007, 40, 1806–1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Yu, C. Influence of Various Retting Methods on Properties of Kenaf Fiber. J. Text. Inst. 2010, 101, 452–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.M.; Siddiquee, S.; Kumar, V. Water Sources Derived Bio Retting Effect on Kenaf Fiber Compositions. J. Nat. Fibers 2022, 19, 9396–9409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahayu, F.; Wani, A.K.; Murianingrum, M.; Marjani; Suhara, C.; Hariyono, B. Studies on Dew Retting Process of Kenaf by Formulation of Indigenous Consortium Bacteria; AIP Publishing: College Park, MD, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anuar, A.; Ahmad, M.R.; Yahya, M.F. Linear Density and Surface Morphology of Kenaf Fibres from Different Extraction Methods. Adv. Mater. Res. 2016, 1134, 103–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amel, B.A.; Paridah, M.T.; Sudin, R.; Anwar, U.M.K.; Hussein, A.S. Effect of Fiber Extraction Methods on Some Properties of Kenaf Bast Fiber. Ind. Crops Prod. 2013, 46, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.H.; Khalina, A.; Lee, S.H.; Liu, M. A Comprehensive Review on Bast Fibre Retting Process for Optimal Performance in Fibre-Reinforced Polymer Composites. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 2020, 6074063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozyanty, A.R.; Zhafer, S.F.; Shayfull, Z.; Nainggolan, I.; Musa, L.; Zheing, L.T. Effect of Water and Mechanical Retting Process on Mechanical and Physical Properties of Kenaf Bast Fiber Reinforced Unsaturated Polyester Composites. Compos. Struct. 2021, 257, 113384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soatthiyanon, N.; Crosky, A. Characterisation of Elementary Kenaf Fibres Extracted Using HNO3 and H2O2/CH3COOH. Fibers 2022, 10, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sathish, S.; Karthi, N.; Prabhu, L.; Gokulkumar, S.; Balaji, D.; Vigneshkumar, N.; Ajeem Farhan, T.S.; AkilKumar, A.; Dinesh, V.P. A Review of Natural Fiber Composites: Extraction Methods, Chemical Treatments and Applications. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 45, 8017–8023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balasubramanian, M. Introduction to Composite Materials. In Fibrous and Textile Materials for Composite Applications; Rana, S., Fangueiro, R., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2016; pp. 1–38. ISBN 978-981-10-0234-2. [Google Scholar]
- Yi, X.-S. An Introduction to Composite Materials. In Composite Materials Engineering, Volume 1: Fundamentals of Composite Materials; Yi, X.-S., Du, S., Zhang, L., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2018; pp. 1–61. ISBN 978-981-10-5696-3. [Google Scholar]
- Egbo, M.K. A Fundamental Review on Composite Materials and Some of Their Applications in Biomedical Engineering. J. King Saud Univ. Eng. Sci. 2021, 33, 557–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajak, D.K.; Wagh, P.H.; Linul, E. A Review on Synthetic Fibers for Polymer Matrix Composites: Performance, Failure Modes and Applications. Materials 2022, 15, 4790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krauklis, A.E.; Karl, C.W.; Gagani, A.I.; Jørgensen, J.K. Composite Material Recycling Technology—State-of-the-Art and Sustainable Development for the 2020s. J. Compos. Sci. 2021, 5, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, K.M.F.; Horváth, P.G.; Alpár, T. Potential Natural Fiber Polymeric Nanobiocomposites: A Review. Polymers 2020, 12, 1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akter, M.; Uddin, M.H.; Tania, I.S. Biocomposites Based on Natural Fibers and Polymers: A Review on Properties and Potential Applications. J. Reinf. Plast. Compos. 2022, 41, 705–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohd Bakhori, S.N.; Hassan, M.Z.; Mohd Bakhori, N.; Jamaludin, K.R.; Ramlie, F.; Md Daud, M.Y.; Abdul Aziz, S. Physical, Mechanical and Perforation Resistance of Natural-Synthetic Fiber Interply Laminate Hybrid Composites. Polymers 2022, 14, 1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Dang, R.; Manna, A.; Dhiman, N.K.; Sharma, S.; Dwivedi, S.P.; Kumar, A.; Li, C.; Tag-Eldin, E.M.; Abbas, M. Optimization of Chemical Treatment Process Parameters for Enhancement of Mechanical Properties of Kenaf Fiber-Reinforced Polylactic Acid Composites: A Comparative Study of Mechanical, Morphological and Microstructural Analysis. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2023, 26, 8366–8387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yusuff, I.; Sarifuddin, N.; Ali, A.M. A Review on Kenaf Fiber Hybrid Composites: Mechanical Properties, Potentials, and Challenges in Engineering Applications. Prog. Rubber Plast. Recycl. Technol. 2021, 37, 66–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvaraj, V.K.; Subramanian, J.; Suyambulingam, I.; Viswanath, S.; Jayamani, E.; Siengchin, S. Influence of Bio-Based Kenaf Polymer Composites on Mechanical and Acoustic Properties for Futuristic Applications: An Initiative towards Net-Zero Carbon Emissions. Polym. Test. 2024, 134, 108409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcuello, C.; Chabbert, B.; Berzin, F.; Bercu, N.B.; Molinari, M.; Aguié-Béghin, V. Influence of Surface Chemistry of Fiber and Lignocellulosic Materials on Adhesion Properties with Polybutylene Succinate at Nanoscale. Materials 2023, 16, 2440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obermeier, F.; Karlinger, P.; Schemme, M.; Altstädt, V. Thermoplastic Hybrid Composites with Wood Fibers: Bond Strength of Back-Injected Structures. Materials 2022, 15, 2473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nadzri, S.N.Z.A.; Shah, A.U.M.; Sultan, M.T.H.; Safri, S.N.A.; Shahar, F.S.; Basri, A.A. Failure Mechanisms of Kenaf/Glass Sandwich Laminates Subjected to Low Velocity Impact Loading. J. Ind. Text. 2022, 51, 4167S–4183S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, J.S.; Song, K.H.; Kim, S.H. Biodegradable Acetylated Kenaf Fiber Composites. Fibers Polym. 2021, 22, 3437–3443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, R.; Hamid, R.; Osman, S.A. Physical and Chemical Modifications of Plant Fibres for Reinforcement in Cementitious Composites. Adv. Civ. Eng. 2019, 2019, e5185806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alarifi, I.M. Investigation the Conductivity of Carbon Fiber Composites Focusing on Measurement Techniques under Dynamic and Static Loads. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2019, 8, 4863–4893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubino, F.; Nisticò, A.; Tucci, F.; Carlone, P. Marine Application of Fiber Reinforced Composites: A Review. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2020, 8, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abidin, N.M.Z.; Sultan, M.T.H.; Hua, L.S.; Basri, A.A.; Md Shah, A.U.; Safri, S.N.A. A Brief Review of Computational Analysis and Experimental Models of Composite Materials for Aerospace Applications. J. Reinf. Plast. Compos. 2019, 38, 1031–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhari, P.; Kulkarni, V.; Khandal, S. Review on Efforts to Improve the Mechanical Performance of Fiber-Reinforced Polymer (FRP) Composites Under the Marine Environment. J. Inst. Eng. Ser. C 2024, 105, 241–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwuozor, K.O.; Micheal, T.T.; Micheal, K.T.; Emmanuel, S.S.; Emenike, E.C.; Adeniyi, A.G. Plant Biomass-Based Composites in the Maritime Industry: A Review. Mar. Struct. 2024, 96, 103609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saba, N.; Jawaid, M.; Sultan, M.T.H. 1—An Overview of Mechanical and Physical Testing of Composite Materials. In Mechanical and Physical Testing of Biocomposites, Fibre-Reinforced Composites and Hybrid Composites; Jawaid, M., Thariq, M., Saba, N., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing Series in Composites Science and Engineering; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2019; pp. 1–12. ISBN 978-0-08-102292-4. [Google Scholar]
- ASTM International—Standards Worldwide. Available online: https://www.astm.org/ (accessed on 10 November 2024).
- Composites Market Size to Worth Around USD 191.36 Bn by 2032. Available online: https://www.precedenceresearch.com/composites-market (accessed on 17 November 2024).
- Manral, A.; Radhakrishnan, S.; Dwivedi, S.P.; Sharma, B.; Gupta, P.; Chaudhary, V. Effect of Water Ageing on Mechanical Performance of Kenaf/PLA Bio-Composites. Biomass Conv. Bioref. 2024, 14, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamidon, M.H.; Sultan, M.T.H.; Ariffin, A.H. 7—Investigation of Mechanical Testing on Hybrid Composite Materials. In Failure Analysis in Biocomposites, Fibre-Reinforced Composites and Hybrid Composites; Jawaid, M., Thariq, M., Saba, N., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing Series in Composites Science and Engineering; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2019; pp. 133–156. ISBN 978-0-08-102293-1. [Google Scholar]
- Prem Kumar, R.; Muthukrishnan, M.; Felix Sahayaraj, A. Effect of Hybridization on Natural Fiber Reinforced Polymer Composite Materials—A Review. Polym. Compos. 2023, 44, 4459–4479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palanisamy, S.; Vijayananth, K.; Murugesan, T.M.; Palaniappan, M.; Santulli, C. The Prospects of Natural Fiber Composites: A Brief Review. Int. J. Lightweight Mater. Manuf. 2024, 7, 496–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaysar, M.A.; Ahmed, S.J.; Jamil, A.T.M.K.; Habib, M.; Dayan, A.R.; Rashid, M.O.; Gafur, A. Impact of NaOH Treatment on the Chemical, Structural, Physico-Mechanical, and Thermal Characteristics of Jute Species. Fibers Polym. 2024, 25, 1765–1777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvi, S.T.; Banu, A.J.; Sunitha, R.; Ayyanar, C.B.; Prakash, C. Effect of Chemical and Biological Treatments on Agave Americana Yarn Braid Reinforced Composite Structures. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2023, 296, 127236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latif, R.; Wakeel, S.; Zaman Khan, N.; Noor Siddiquee, A.; Lal Verma, S.; Akhtar Khan, Z. Surface Treatments of Plant Fibers and Their Effects on Mechanical Properties of Fiber-Reinforced Composites: A Review. J. Reinf. Plast. Compos. 2019, 38, 15–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenned, J.J.; Sankaranarayanasamy, K.; Kumar, C.S. Chemical, Biological, and Nanoclay Treatments for Natural Plant Fiber-Reinforced Polymer Composites: A Review. Polym. Polym. Compos. 2021, 29, 1011–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasidi, I.N.; Ismail, L.H.; Samsudin, E.; Jaffar, M.I. Effects of Kenaf Fiber Strand Treatment by Sodium Hydroxide On Sound Absorption. J. Nat. Fibers 2022, 19, 6727–6736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, N.F.; Mohd Radzuan, N.A.; Sulong, A.B.; Muhamad, N.; Che Haron, C.H. The Effect of Alkali Treatment on Physical, Mechanical and Thermal Properties of Kenaf Fiber and Polymer Epoxy Composites. Polymers 2021, 13, 2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verma, R.; Shukla, M.; Shukla, D.K. Effect of Glass Fiber Hybridization on the Mechanical Properties of Unidirectional, Alkali-treated Kenaf-epoxy Composites. Polym. Compos. 2022, 43, 7483–7499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tay, C.H.; Mazlan, N.; Sultan, M.T.H.; Abdan, K.; Lee, C.H. Mechanical Performance of Hybrid Glass/Kenaf Epoxy Composite Filled with Organomodified Nanoclay. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2021, 15, 4415–4426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samaei, S.E.; Mahabadi, H.A.; Mousavi, S.M.; Khavanin, A.; Faridan, M.; Taban, E. The Influence of Alkaline Treatment on Acoustical, Morphological, Tensile and Thermal Properties of Kenaf Natural Fibers. J. Ind. Text. 2022, 51, 8601S–8625S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muralidharan, D. Mechanical Characteristics Study of Chemically Modified Kenaf Fiber Reinforced Epoxy Composites. J. Nat. Fibers 2022, 19, 2457–2467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lunetto, V.; Galati, M.; Settineri, L.; Iuliano, L. Sustainability in the Manufacturing of Composite Materials: A Literature Review and Directions for Future Research. J. Manuf. Process. 2023, 85, 858–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaghloul, M.M.Y. Developments in Polyester Composite Materials—An in-Depth Review on Natural Fibres and Nano Fillers. Compos. Struct. 2021, 278, 114698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sujon, M.A.S.; Habib, M.A.; Abedin, M.Z. Experimental Investigation of the Mechanical and Water Absorption Properties on Fiber Stacking Sequence and Orientation of Jute/Carbon Epoxy Hybrid Composites. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2020, 9, 10970–10981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashim, M.K.R.; Majid, M.S.A.; Jamir, M.R.M.; Kasim, F.H.; Sultan, M.T.H. The Effect of Stacking Sequence and Ply Orientation on the Mechanical Properties of Pineapple Leaf Fibre (Palf)/Carbon Hybrid Laminate Composites. Polymers 2021, 13, 455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sathyaseelan, P.; Sellamuthu, P.; Palanimuthu, L. Influence of Stacking Sequence on Mechanical Properties of Areca-Kenaf Fiber- Reinforced Polymer Hybrid Composite. J. Nat. Fibers 2022, 19, 369–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukanto, H.; Raharjo, W.W.; Ariawan, D.; Triyono, J.; Kaavesina, M. Epoxy Resins Thermosetting for Mechanical Engineering. Open Eng. 2021, 11, 797–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, T.; Haq, F.; Farid, A.; Cheng, L.; Chuah, L.F.; Bokhari, A.; Mubashir, M.; Tang, D.Y.Y.; Show, P.L. The Epoxy Resin System: Function and Role of Curing Agents. Carbon Lett. 2024, 34, 477–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cakiroglu, C.; Bekdaş, G. Buckling Analysis and Stacking Sequence Optimization of Symmetric Laminated Composite Plates. In Advances in Structural Engineering—Optimization; Nigdeli, S.M., Bekdaş, G., Kayabekir, A.E., Yucel, M., Eds.; Studies in Systems, Decision and Control; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; Volume 326, pp. 237–248. ISBN 978-3-030-61847-6. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, T.; Sultan, M.T.H.; Shah, A.U.M.; Ariffin, A.H.; Jawaid, M. The Effects of Stacking Sequence on the Tensile and Flexural Properties of Kenaf/Jute Fibre Hybrid Composites. J. Nat. Fibers 2021, 18, 452–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balakrishnan, T.S.; Sultan, M.T.H.; Shahar, F.S.; Nayak, S.Y.; Shah, A.U.M.; Sebaey, T.A.; Basri, A.A. Hybridization of Woven Kenaf and Unidirectional Glass Fibre Roving for Unsaturated Polyester Composite. Iran Polym. J. 2024, 33, 1231–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, J.I.P.; Sharma, V.; Singh, S.; Dhawan, V.; Belaadi, A.; Kumar, R.; Sharma, S.; Kumar, A.; Awwad, F.A.; Khan, M.I.; et al. Impact of Molding Temperature, Fiber Loading and Chemical Modifications on the Physicomechanical, and Microstructural Morphology Properties of Woven Kenaf Fiber/PLA Composites for Non-Structural Applications. J. Nat. Fibers 2024, 21, 2326586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yusuff, I.; Sarifuddin, N.; Badari, S.N.M.; Ali, A.M. Mechanical Properties, Water Absorption, and Failure Analyses of Kenaf Fiber Reinforced Epoxy Matrix Composites. IIUM Eng. J. 2021, 22, 316–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jasti, A.; Biswas, S. Effect of Ocean Water Absorption on Flexural Properties of Cannabis Sativa L. Hemp Fibre Reinforced Polymer Composites for Marine Applications. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part C J. Mech. Eng. Sci. 2023, 237, 3894–3907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kattaguri, R.; Fulmali, A.O.; Prusty, R.K.; Ray, B.C. Effects of Acid, Alkaline, and Seawater Aging on the Mechanical and Thermomechanical Properties of Glass Fiber/Epoxy Composites Filled with Carbon Nanofibers. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2020, 137, 48434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caldwell, K.B.; Berg, J.C. Nanoparticles as Interphase Modifiers in Fiber Reinforced Polymeric Composites: A Critical Review. In Progress in Adhesion and Adhesives; Mittal, K.L., Ed.; Wiley: Austin, TX, USA, 2018; pp. 1–51. ISBN 978-1-119-52629-2. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, J.; Chen, C.; Zhang, S.; Zhong, T.; Xu, Q.; Su, Z.; Jiang, M.; Liu, P. Enhancing the Interfacial Adhesion between Continuous Basalt Fibers and Epoxy Resin by Depositing Silicon Dioxide Nanonparticles. J. Ind. Text. 2022, 51, 3309S–3329S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taj, A.; RP, S.; Naik, K.; KN, B. Physical Effects of Nanoaluminum Oxide and Nanographene on Kenaf Epoxy Composite; Vacuum Bagging Process. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2023, 140, e53374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, K.; Ahmad, F.; Dawood, M.S.; Islam, M.S.; Ali, S.; Raza, A.; Shahed, C.A. Mechanical Property Enhancement of Graphene-Kenaf-Epoxy Multiphase Composites for Automotive Applications. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2024, 177, 107916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esnaola, A.; Tena, I.; Aurrekoetxea, J.; Gallego, I.; Ulacia, I. Effect of Fibre Volume Fraction on Energy Absorption Capabilities of E-Glass/Polyester Automotive Crash Structures. Compos. Part B Eng. 2016, 85, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahrom, M.F.; Awang, M.K.; Mustapa, M.S.; Ismail, A.E.; Jaafar, J.; Al-Moayed, O.M.; Kareem, A.K. Crushing Performances of Kenaf Fibre Reinforce Composite Tubes. J. Adv. Res. Appl. Mech. 2024, 116, 130–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radzi, F.S.M.; Bakar, A.A.; Asyraf, M.A.; Abdullah, N.A.N.; Suriani, M.J. Manufacturing Defects and Interfacial Adhesion of Arenga Pinnata and Kenaf Fibre Reinforced Fibreglass/Kevlar Hybrid Composite in Boat Construction Application. Phys. Sci. Rev. 2023, 8, 5165–5173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Futalan, C.M.; Choi, A.E.S.; Soriano, H.G.O.; Cabacungan, M.K.B.; Millare, J.C. Modification Strategies of Kapok Fiber Composites and Its Application in the Adsorption of Heavy Metal Ions and Dyes from Aqueous Solutions: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 2703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manral, A.; Bajpai, P.K. Static and Dynamic Mechanical Analysis of Geometrically Different Kenaf/PLA Green Composite Laminates. Polym. Compos. 2020, 41, 691–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yusuff, I.; Sarifuddin, N.; Norbahiyah, S.; Ali, A.M.; Ismail, H. Tensile and Flexural Properties of Woven Carbon-Kenaf Fiber Reinforced Epoxy Matrix Hybrid Composite: Effect of Hybridization and Stacking Sequences. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Postgraduate Conference on Materials, Minerals & Polymer (MAMIP), Penang, Malaysia, 31 October–1 November 2020; p. 020026. [Google Scholar]
- Mishra, C.; Mohapatra, D.K.; Deo, C.R.; Mishra, P.; Ekka, K.K. Erosion Wear Behaviour of Kenaf/Glass Hybrid Polymer Composites. J. Harbin Inst. Technol. 2024, 31, 78–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, K.; Ahmad, F.; Yunus, N.A.; Gunister, E.; Shahed, C.A. Mechanical Investigation of Kenaf/Carbon Hybrid Composites for Building and Construction Applications. J. Compos. Constr. 2024, 28, 04023066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balakrishnan, T.S.; Sultan, M.T.H.; Shahar, F.S.; Basri, A.A.; Shah, A.U.M.; Sebaey, T.A.; Łukaszewicz, A.; Józwik, J.; Grzejda, R. Fatigue and Impact Properties of Kenaf/Glass-Reinforced Hybrid Pultruded Composites for Structural Applications. Materials 2024, 17, 302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abidin, N.M.Z.; Sultan, M.T.H.; Md Shah, A.U.; Shahar, F.S.; Najeeb, M.I.; Ali, M.R.; Basri, A.A.; Baloor, S.S.; Gaff, M.; Hui, D. The Evaluation of the Mechanical Properties of Glass, Kenaf, and Honeycomb Fiber-Reinforced Composite. Rev. Adv. Mater. Sci. 2023, 62, 20220299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabhu, L.; Krishnaraj, V.; Gokulkumar, S.; Sathish, S.; Sanjay, M.; Siengchin, S. Mechanical, Chemical and Sound Absorption Properties of Glass/Kenaf/Waste Tea Leaf Fiber-Reinforced Hybrid Epoxy Composites. J. Ind. Text. 2022, 51, 1674–1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azlin, M.N.M.; Sapuan, S.M.; Zuhri, M.Y.M.; Zainudin, E.S. Effect of Stacking Sequence and Fiber Content on Mechanical and Morphological Properties of Woven Kenaf/Polyester Fiber Reinforced Polylactic Acid (PLA) Hybrid Laminated Composites. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2022, 16, 1190–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razali, N.; Sultan, M.T.H.; Jawaid, M.; Md Shah, A.U.; Safri, S.N.A. Mechanical Properties of Flax/Kenaf Hybrid Composites. In Structural Health Monitoring System for Synthetic, Hybrid and Natural Fiber Composites; Jawaid, M., Hamdan, A., Hameed Sultan, M.T., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2021; pp. 177–194. ISBN 978-981-15-8840-2. [Google Scholar]
- Chethan, N.; Nagesh, S.N.; Sunith Babu, L. Mechanical Behaviour of Kenaf-Jute-E-Glass Reinforced Hybrid Polymer Composites. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 46, 4454–4459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suriani, M.J.; Ilyas, R.A.; Zuhri, M.Y.M.; Khalina, A.; Sultan, M.T.H.; Sapuan, S.M.; Ruzaidi, C.M.; Wan, F.N.; Zulkifli, F.; Harussani, M.M.; et al. Critical Review of Natural Fiber Reinforced Hybrid Composites: Processing, Properties, Applications and Cost. Polymers 2021, 13, 3514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zwawi, M. A Review on Natural Fiber Bio-Composites, Surface Modifications and Applications. Molecules 2021, 26, 404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voutetaki, M.E.; Mpalaskas, A.C. Natural Fiber-Reinforced Mycelium Composite for Innovative and Sustainable Construction Materials. Fibers 2024, 12, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatasudhahar, M.; Ravichandran, A.T.; Dilipraja, N. Effect of Stacking Sequence on Mechanical and Moisture Absorption Properties of Abaca-Kenaf-Carbon Fiber Reinforced Hybrid Composites. J. Nat. Fibers 2022, 19, 7229–7240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babu, T.N.; Singh, S.; Prabha, D.R.; Mishra, S.; Pandey, V. Mechanical, Machinability and Water Absorption Properties of Novel Kenaf Fiber, Glass Fiber and Graphene Composites Reinforced with Epoxy. Sci Rep. 2024, 14, 29955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogunbode, B.E.; Nyakuma, B.B.; Lawal, T.A.; Yatim, J.M.; Abdul, A.; Ayoosu, M.I. Morphological, Microstructure, Tensile and Water-Sorption Characteristics of Surface Modified Kenaf Fibre for Sustainable Biocomposite Reinforcement. J. Nat. Fibers 2022, 19, 7174–7185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramesh, P.; Prasad, B.D.; Narayana, K.L. Influence of Montmorillonite Clay Content on Thermal, Mechanical, Water Absorption and Biodegradability Properties of Treated Kenaf Fiber/PLA-Hybrid Biocomposites. Silicon 2021, 13, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elfaleh, I.; Abbassi, F.; Habibi, M.; Ahmad, F.; Guedri, M.; Nasri, M.; Garnier, C. A Comprehensive Review of Natural Fibers and Their Composites: An Eco-Friendly Alternative to Conventional Materials. Results Eng. 2023, 19, 101271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khurchania, G.S.; Bhavsar, D.; Rao, A.K. Characterization of Composite Materials Using Natural and Synthetic Fiber: A Review. In Advances in Manufacturing and Processing of Materials; Apple Academic Press: Palm Bay, FL, USA, 2024; ISBN 978-1-003-40834-5. [Google Scholar]
- Prakoso, M.W.; Baroroh, D.N.; Setswalo, K. Water Absorption Rate of Kenaf Fiber (KF)/ Hydroxiteapatite (HA) in Simulated Sea Water. Mech. Explor. Mater. Innov. 2024, 1, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhuvaneswari, V.; Devarajan, B.; Arulmurugan, B.; Mahendran, R.; Rajkumar, S.; Sharma, S.; Mausam, K.; Li, C.; Eldin, E.T. A Critical Review on Hygrothermal and Sound Absorption Behavior of Natural-Fiber-Reinforced Polymer Composites. Polymers 2022, 14, 4727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kenaf Fiber Boat Testing by Kenaf Tech Master Resources (KTMR). 2024. Available online: https://www.lktn.gov.my/lktn/?p=6624&lang=en (accessed on 19 January 2025).
- Abdurohman, K.; Adhitya, M. Effect of Water and Seawater on Mechanical Properties of Fiber Reinforced Polymer Composites: A Review for Amphibious Aircraft Float Development; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayandi, K.; Rajini, N.; Ayrilmis, N.; Indira Devi, M.P.; Siengchin, S.; Mohammad, F.; Al-Lohedan, H.A. An Overview of Endurance and Ageing Performance under Various Environmental Conditions of Hybrid Polymer Composites. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2020, 9, 15962–15988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, M.K.; Zafar, S.; Rangappa, S.M.; Siengchin, S. Mechanical Performance Study of Kenaf/HDPE Composite for Structural Applications under Wet or Outdoor Environments. J. Nat. Fibers 2022, 19, 14115–14130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, M.K.; Zafar, S. Wettability, Absorption and Degradation Behavior of Microwave-Assisted Compression Molded Kenaf/HDPE Composite Tank under Various Environments. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2021, 185, 109500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jawaid, M.; Chee, S.S.; Asim, M.; Saba, N.; Kalia, S. Sustainable Kenaf/Bamboo Fibers/Clay Hybrid Nanocomposites: Properties, Environmental Aspects and Applications. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 330, 129938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guchait, A.; Saxena, A.; Chattopadhyay, S.; Mondal, T. Influence of Nanofillers on Adhesion Properties of Polymeric Composites. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 3844–3859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raj, R.R.; Sathish, S.; Mansadevi, T.L.D.; Supriya, R.; Sekar, S.; Patil, P.P.; Tonmoy, M.M. Effect of Graphene Fillers on the Water Absorption and Mechanical Properties of NaOH-Treated Kenaf Fiber-Reinforced Epoxy Composites. J. Nanomater. 2022, 2022, 1748121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmiyanto, M.H.; Surojo, E.; Ariawan, D.; Imaduddin, F. E-Glass/Kenaf Fibre Reinforced Thermoset Composites Fiiled with MCC and Immersion in a Different Fluid. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 20332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawaz, H.; Umar, M.; Maryam, R.; Nawaz, I.; Razzaq, H.; Malik, T.; Liu, X. Polymer Nanocomposites Based on TiO2 as a Reinforcing Agent: An Overview. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2022, 24, 2200844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambekar, A.M.; Muralishwara, K.; Hindi, J.; Acharya, S.; Naik, N.; Gurumurthy, B.M.; Hiremath, P.; Kasip, K. Effect of Seawater Absorption on Mechanical and Flexural Properties of Pineapple Leaf Fiber Reinforced Epoxy Nanoclay Composites. ES Mater. Manuf. 2023, 22, 1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elamvazhudi, B.; Gopalakannan, S. Long-Term Behavior of Nanoclay/TiO2 Nanoparticles Modified Carbon/Glass Fiber–Reinforced Hybrid Composites. J. Test. Eval. 2023, 51, 2468–2489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Location | 2017/18 | 2018/19 | 2019/20 | 2020/21 | 2021/22 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I. Developing countries | 202.6 | 198.6 | 204.6 | 200.3 | 195.7 |
| a. Far East | 155.3 | 151.3 | 157.7 | 150.2 | 146.7 |
| 1. India | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| 2. China | 50 | 45.97 | 52.37 | 45.03 | 41.43 |
| 3. Indonesia | 3.3 | 3.3 | 3.4 | 3.3 | 3.3 |
| 4. Pakistan | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 5. Vietnam | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.3 | 0.4 |
| 6. Thailand | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.3 | 0.3 |
| 7. Cambodia | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.3 | 0.3 |
| b. Latin America and the Caribbean | 26 | 26.1 | 25.6 | 28.5 | 27.3 |
| 1. Cuba | 11.9 | 12 | 11.8 | 11.8 | 11.8 |
| 2. Brazil | 2.8 | 2.9 | 2.6 | 5.5 | 4.4 |
| 3. Other | 11.3 | 11.2 | 11.2 | 11.2 | 11.1 |
| c. Africa | 15.5 | 15.4 | 15.5 | 15.6 | 15.7 |
| d. Near East | 5.7 | 5.7 | 5.8 | 6 | 6 |
| II. Developed countries | 6.8 | 6.8 | 6.9 | 6.8 | 6.8 |
| Total (I + II) | 209.4 | 205.4 | 211.5 | 207.1 | 202.5 |
| No. | Cellulose (%) | Hemicellulose (%) | Lignin (%) | Pectin (%) | Moisture (%) | Wax (%) | Ash (%) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 44–57 | 21 | 15–19 | 2 | - | - | - | [3] |
| 2 | 45–57 | 21.5 | 8–13 | - | - | - | - | [4] |
| 3 | 66.9 | 14.98 | 6.85 | [37,51] | ||||
| 4 | 31–57 | 21.5–23 | 15.0–19 | 3–5 | - | - | - | [37,52] |
| 5 | 65.7 | 17.8 | 6.0 | - | - | - | - | [37,53] |
| 6 | 45–57 | 8.0–13.0 | 21.5 | 0.6 | 6.2–12 | 0.8 | 2–5 | [54] |
| 7 | 53–57 | 15–19 | - | 5.9–9.3 | 7–10 | - | - | [55] |
| 8 | 69.2 | 27.2 | 2.8 | - | 8–12 | - | 0.8 | [56] |
| 9 | 44–57 | 22–23 | 15–19 | - | - | - | 0.8 | [57] |
| 10 | 72 | 20.3 | 9 | - | - | - | - | [58] |
| Range | 31–72 | 13.59–23 | 2.8–20.1 | 0.6–9.3 | 6.2–12 | 0.8 | 0.8–5 |
| S. No. | Tensile Strength (MPa) | Tensile Modulus (GPa) | Elongation at Break (%) | Density (g/cm3) | Diameter (μm) | Specific Strength (N·m/g) | Specific Stiffness (N·m/g) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 223 | 15 | 5.7 | - | 140 | - | - | [55] |
| 2 | 350–600 | 40 | 2.5–3.5 | 1.2 | 50–60 | 291.7–500 | 2083.3–2916.7 | [66] |
| 3 | 284–930 | 21–60 | 1.6 | 1.45 | - | 195.9–641.4 | 1103.4 | [67] |
| 4 | 284–800 | 21–60 | 1.6 | 1.4 | - | 202.9–571.4 | 1142.9 | [37,64] |
| 5 | 350–600 | 40 | 2.5–3.5 | 1.5 | - | 233.3–400 | 1666.7–2333.3 | [37,68] |
| 6 | - | - | 1.9–4.8 | - | 80–144.8 | - | - | [50] |
| 7 | - | - | - | 1.4 | - | - | - | [56] |
| 8 | 223–1191 | 11–60 | 1.6–4.3 | 1.5 | - | 148.7–794 | 1066.7–2866.7 | [69] |
| 9 | 290–950 | 50 | - | 1.2 | - | 241.7–791.7 | [57] | |
| Range | 223–1191 | 11–60 | 1.6–5.7 | 1.2–1.5 | 50–144.8 | 148.7–794 | 1066.7–2916.7 |
| Retting Method | Principle | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mechanical | Separates fibers from bast layers via mechanical force. |
|
|
| Chemical | Dissolves lignin and pectin using acids, alkalis, or other chemical solutions. |
|
|
| Biological | Uses microbes or enzymes to degrade lignin and pectin. |
|
|
| Physical | Separates fibers from bast layers in natural circumstances. |
|
|
| S. No. | Test Item | ASTM Standard | Brief Description of the Test | Results Data |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Tensile test | D3039 |
|
|
| 2 | Tensile test | D638 |
|
|
| 3 | Flexural test | D790 |
|
|
| 4 | Flexural test | D6272 |
|
|
| 5 | Flexural test | D7264 |
|
|
| 6 | Compression test | D695 |
|
|
| 7 | Compression test | D3410/D3410M |
|
|
| 8 | Compression test | D6641/D6641M |
|
|
| 9 | Water absorption test | D570 |
|
|
| 10 | Density and specific gravity | D792 |
|
|
| 11 | Apparent density test | D1895 |
|
|
| 12 | Void content of reinforced plastics | D2734 |
|
|
| 13 | Izod Pendulum Impact Resistance | D256 |
|
|
| 14 | Charpy Impact Resistance | D6110 |
|
|
| 15 | Damage Resistance of Fiber-Reinforced Polymer Matrix Composites | D7136/D7136M |
|
|
| Fiber-Matrix | Alkali Solution | Treatment Parameters | Highlight RESULTS | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kenaf-Epoxy | 5%(w/v) NaOH | 24 h 28°C |
| [117] |
| Kenaf-Epoxy | 6 wt.% NaOH | 24 h room temperature |
| [116] |
| Kenaf/Glass-Epoxy | 2 M NaOH | 4 h room temperature |
| [118] |
| Kenaf fiber | 6 wt.% NaOH | 4 h room temperature |
| [119] |
| Kenaf-Epoxy | 6 wt.% NaOH 6 wt.% KOH | 8 h |
| [120] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, Y.; Sultan, M.T.H.; Shahar, F.S.; Łukaszewicz, A.; Oksiuta, Z.; Grzejda, R. Kenaf Fiber-Reinforced Biocomposites for Marine Applications: A Review. Materials 2025, 18, 999. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18050999
Huang Y, Sultan MTH, Shahar FS, Łukaszewicz A, Oksiuta Z, Grzejda R. Kenaf Fiber-Reinforced Biocomposites for Marine Applications: A Review. Materials. 2025; 18(5):999. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18050999
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Yang, Mohamed Thariq Hameed Sultan, Farah Syazwani Shahar, Andrzej Łukaszewicz, Zbigniew Oksiuta, and Rafał Grzejda. 2025. "Kenaf Fiber-Reinforced Biocomposites for Marine Applications: A Review" Materials 18, no. 5: 999. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18050999
APA StyleHuang, Y., Sultan, M. T. H., Shahar, F. S., Łukaszewicz, A., Oksiuta, Z., & Grzejda, R. (2025). Kenaf Fiber-Reinforced Biocomposites for Marine Applications: A Review. Materials, 18(5), 999. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18050999










