Magnesium Silicate Honeycomb Structure on Attapulgite Clay Composite by Self-Template Method for Adsorption of Methylene Blue
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Materials and Method
2.2. Instrumentation
2.3. Adsorption Experiment
3. Results and Discussion
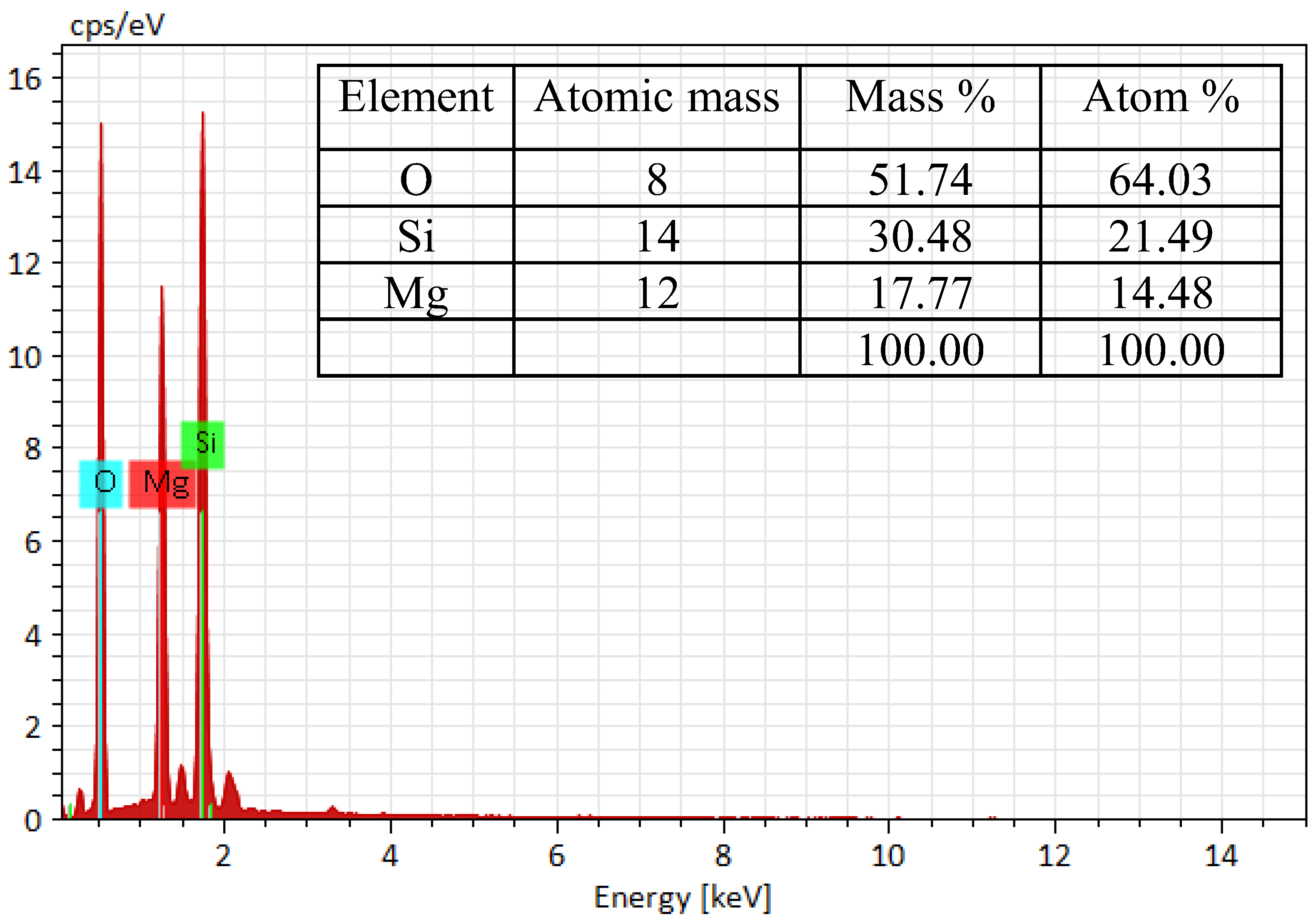
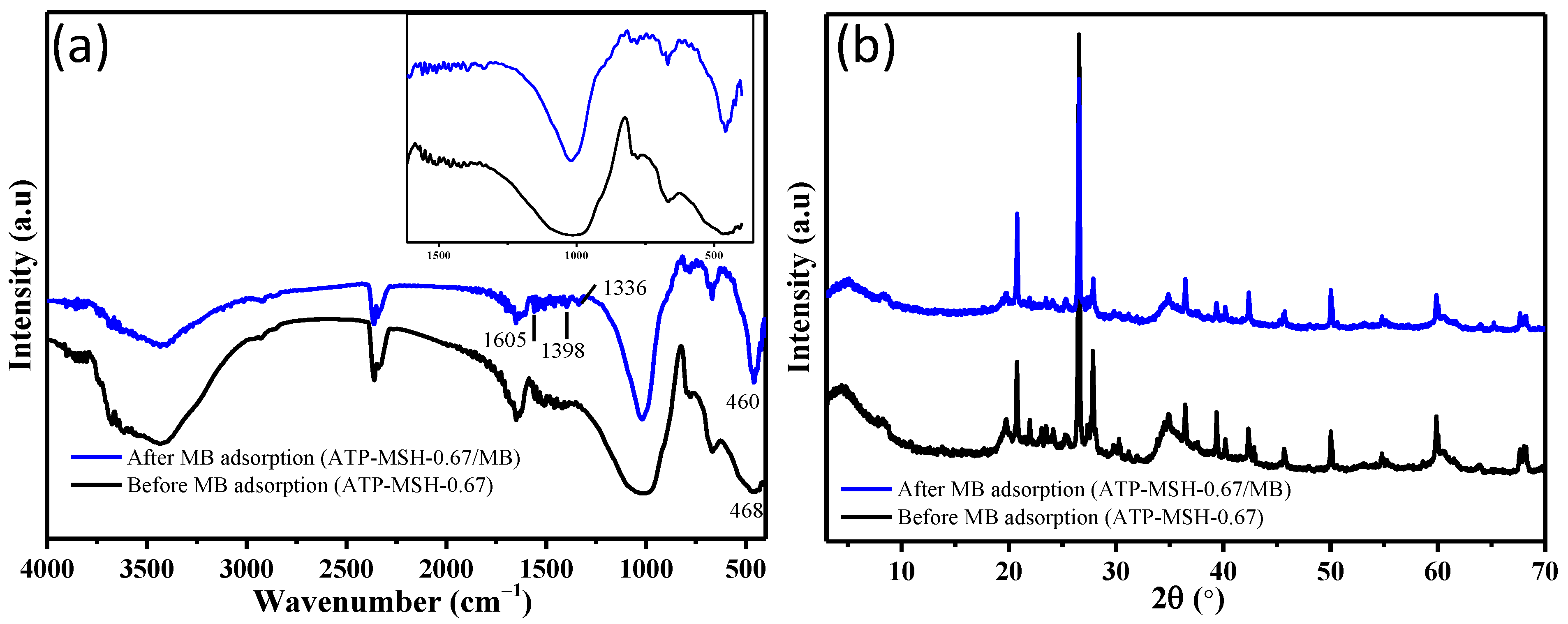
3.1. Structure and Chemical Composition
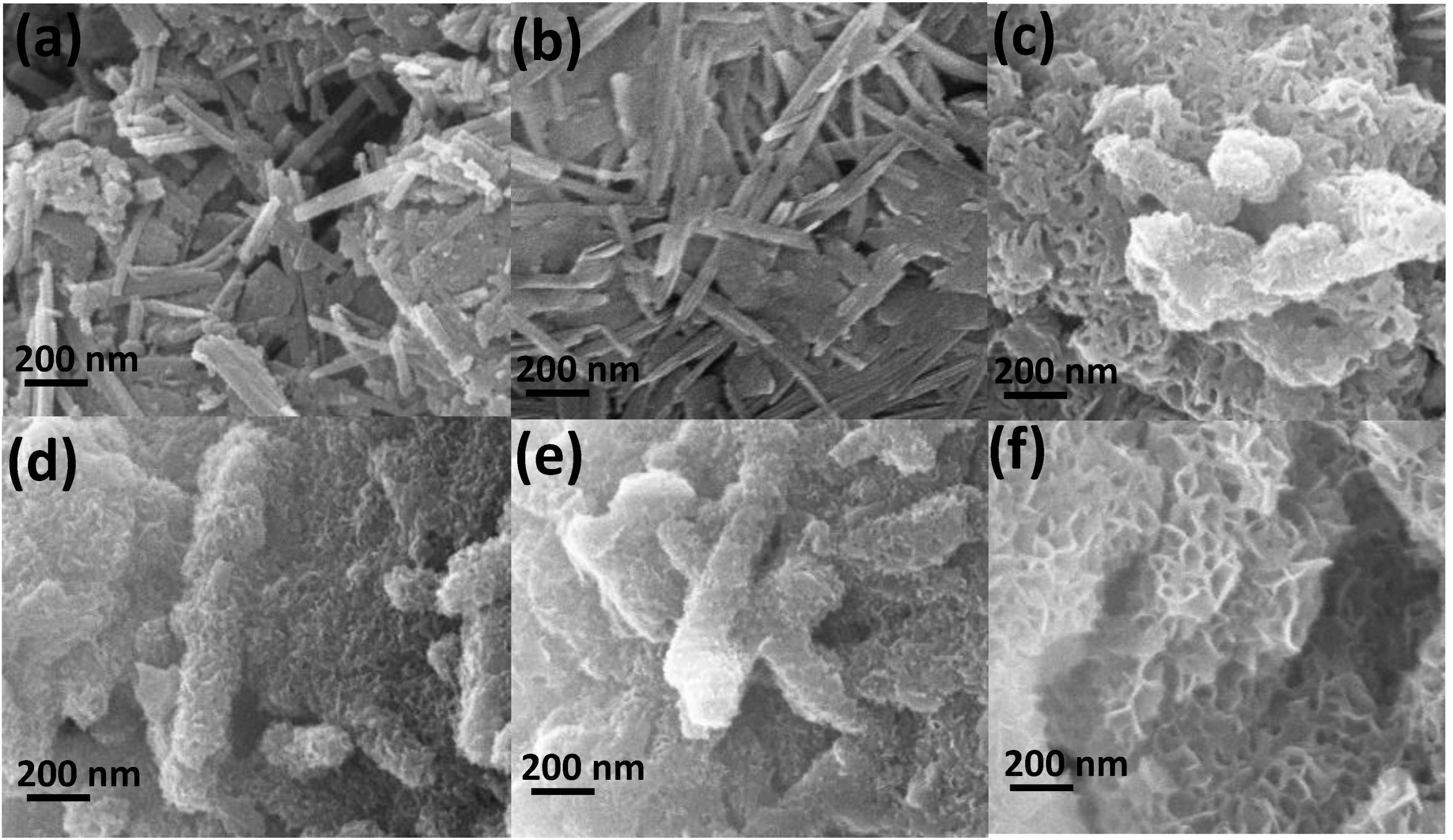
3.2. Surface Morphology
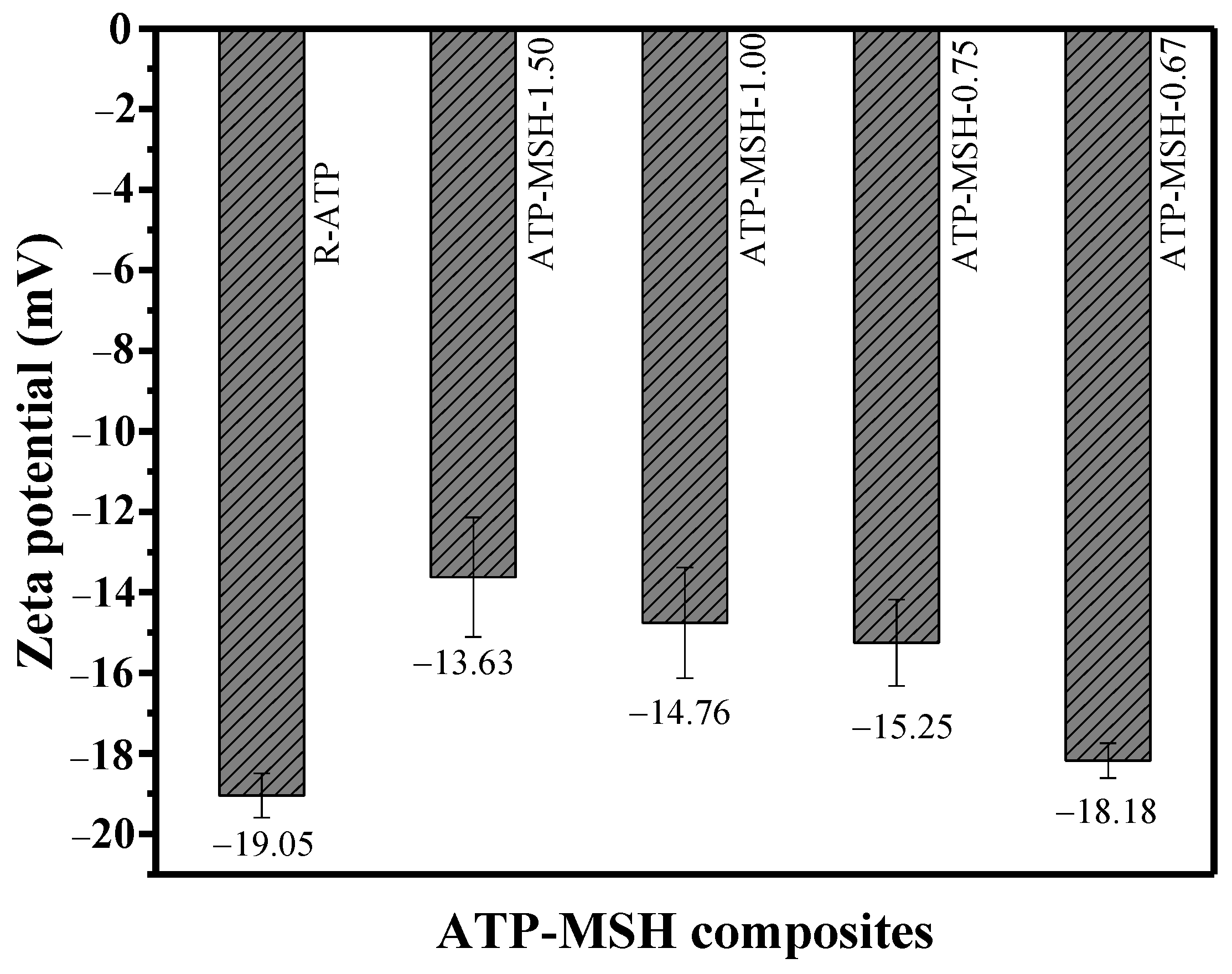
3.3. Zeta Potential Analysis
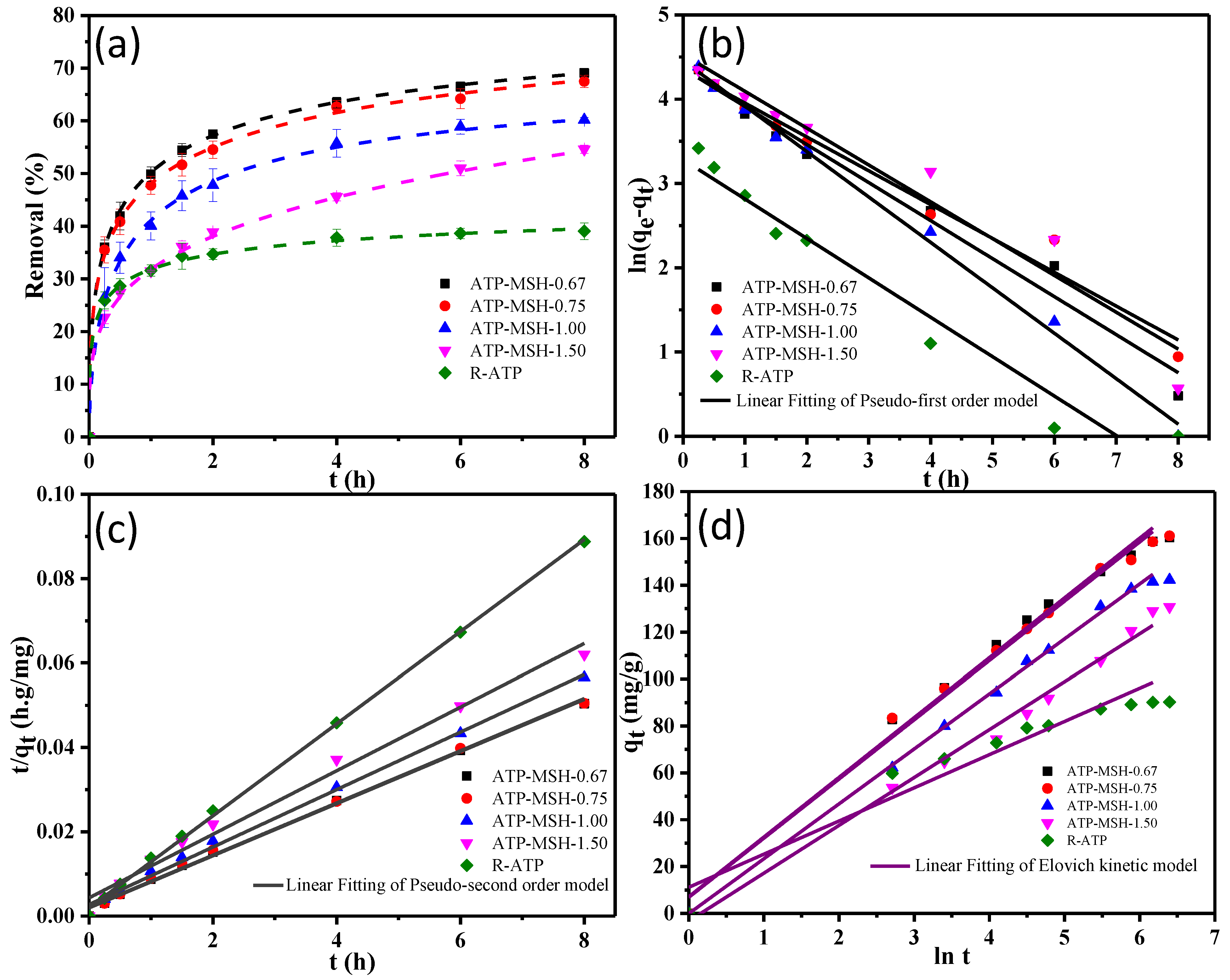
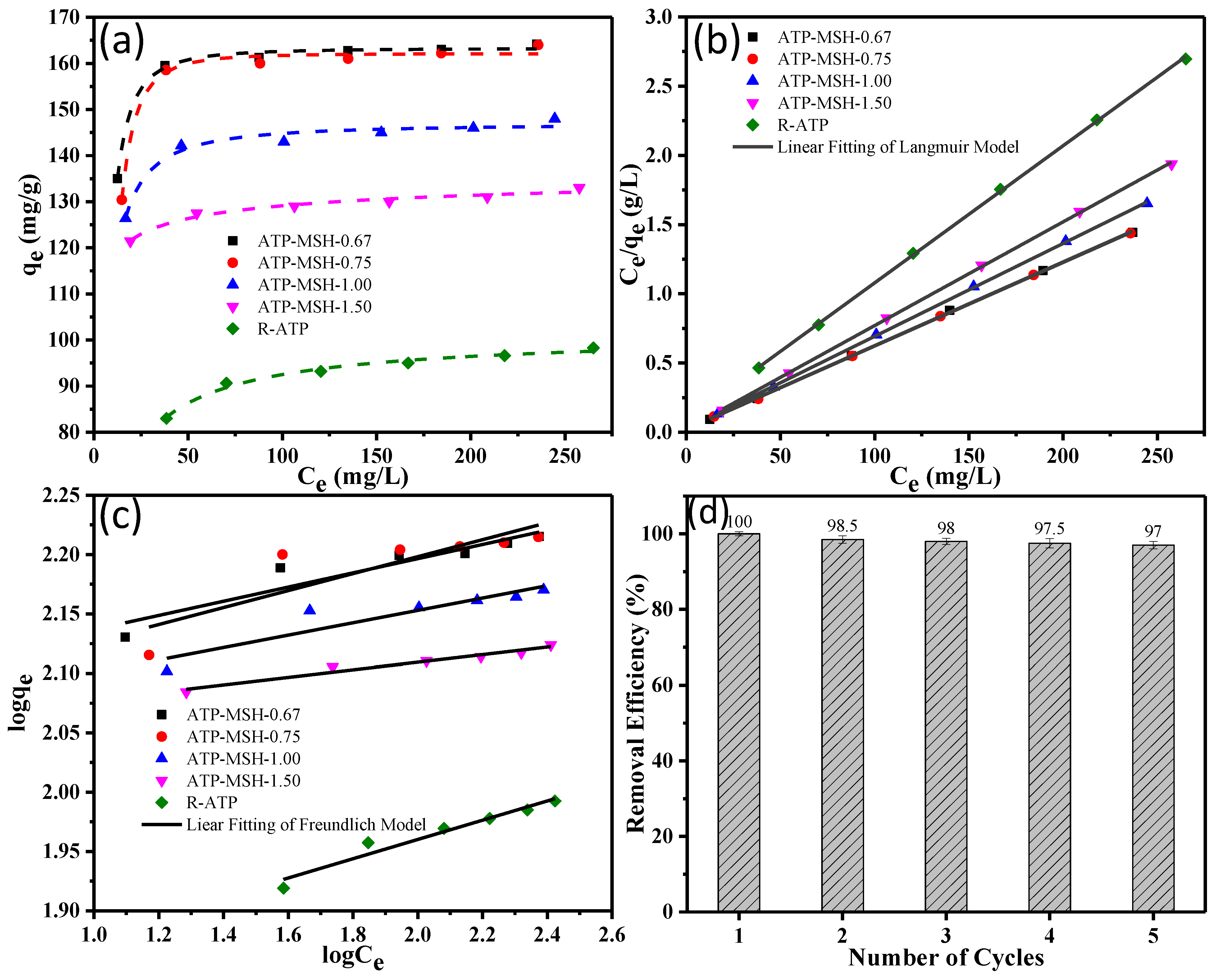
3.4. Adsorption of Methylene Blue
3.5. Adsorption Mechanism
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Metivier-Pignon, H.; Faur, C.; Le Cloirec, P. Adsorption of dyes onto activated carbon cloth: Using QSPRs as tools to approach adsorption mechanisms. Chemosphere 2007, 66, 887–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, N.; Shang, R.; Heijman, S.G.J.; Rietveld, L.C. High-silica zeolites for adsorption of organic micro-pollutants in water treatment: A review. Water Res. 2018, 144, 145–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Z.; Huang, D.; Duan, X.; Hong, W.; Liang, J. Functionalized nanoflower-like hydroxyl magnesium silicate for effective adsorption of aflatoxin B1. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 387, 121792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Wang, W.; Wang, A. Highly effective removal of methylene blue using functionalized attapulgite via hydrothermal process. J. Environ. Sci. 2015, 33, 106–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abu-Danso, E.; Peräniemi, S.; Leiviskä, T.; Kim, T.; Tripathi, K.M.; Bhatnagar, A. Synthesis of clay-cellulose biocomposite for the removal of toxic metal ions from aqueous medium. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 381, 120871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, I. Applied clay mineralogy: Occurrences, processing, and application of kaolins, bentonites, palygorskite-sepiolite, and common clays. Clays Clay Miner. 2007, 55, 644–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernard, E.; Lothenbach, B.; Chlique, C.; Wyrzykowski, M.; Dauzères, A.; Pochard, I.; Cau-dit-Coumes, C. Characterization of magnesium silicate hydrate (M-S-H). Cem. Concr. Res. 2018, 116, 309–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, G.; Tian, G.; Gong, L.; Tang, Q.; Li, M.; Meng, J.; Liang, J. Mesoporous zinc silicate composites derived from iron ore tailings for highly efficient dye removal: Structure and morphology evolution. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2020, 305, 110352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.; He, L.; Zhang, T.; Li, D.; Tang, P.; Zhao, Y.; Feng, Y. Fabrication and adsorption behavior of magnesium silicate hydrate nanoparticles towards methylene blue. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Weng, J.; Ding, J.; Zhao, Z.; Qin, L.; Xia, F. Effective conversion of saccharides into hydroxymethyl furfural catalyzed by a natural clay, attapulgite. Renew. Energy. 2020, 151, 829–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Wang, W.; Zhao, Y.; Bai, H.; Wen, T.; Kang, S.; Song, G.; Song, S.; Komarneni, S. Removal of heavy metals and dyes by clay-based adsorbents: From natural clays to 1D and 2D nano-composites. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 420, 127574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Xu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, X.; Chen, Y.; Kong, X. Effective removal of heavy metal ions by attapulgite supported sulfidized nanoscale zerovalent iron from aqueous solution. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2022, 640, 128192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Gui, W.; Wei, J.; Cui, Y.; Li, P.; Jia, Z.; Kong, P. Functionalized attapulgite for the adsorption of methylene blue: Synthesis, characterization, and adsorption mechanism. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 19586–19595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.; Xi, Y.; Lian, C.; Sun, Z.; Zheng, S. Simultaneous detoxification of polar aflatoxin B1 and weak polar zearalenone from simulated gastrointestinal tract by zwitterionic montmorillonites. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 364, 227–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farhadirad, M.; Najafi, H.; Sharifian, S.; Ebrahimian Pirbazari, A.; Asasian-Kolur, N.; Harasek, M. Enhanced levofloxacin degradation through Fenton-like process using Fe-silica pillared clay catalyst. Appl. Catal. O Open. 2024, 190, 206931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ugochukwu, U.C.; Fialips, C.I. Crude oil polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons removal via clay-microbe-oil interactions: Effect of acid activated clay minerals. Chemosphere 2017, 178, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roth, W.J.; Gil, B.; Makowski, W.; Marszalek, B.; Eliášová, P. Layer like porous materials with hierarchical structure. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2016, 45, 3400–3438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anirudhan, T.S.; Ramachandran, M. Adsorptive removal of basic dyes from aqueous solutions by surfactant modified bentonite clay (organoclay): Kinetic and competitive adsorption isotherm. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2015, 95, 215–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Tian, G.; Chen, B.; Liang, J. Self-templating construction of flower-like mesoporous magnesium silicate composites from sepiolite for high-efficiency adsorption of aflatoxin B1. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 291, 120953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Dong, W.; Tian, G.; Sun, L.; Wang, Q.; Hui, A.; Mu, B.; Wang, A. Highly efficient self-template synthesis of porous silica nanorods from natural palygorskite. Powder Technol. 2019, 354, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyawoo, T.; Karim, N.; Jiang, C.; Ahmed, S.; Tian, W.; Li, H.; Feng, Y. Facile formation of hierarchical magnesium silicate hydrate microspheres as an adsorbent for the textile dyes. Particuology 2024, 93, 99–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, L.; Wang, C.; Zhang, W.; Ma, B.; Deng, Y.; Li, W.; Zhao, D. Interfacial assembly and applications of functional mesoporous materials. Chem. Rev. 2021, 121, 14349–14429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghaedi, H.; Zhao, M. Review on Template removal techniques for synthesis of mesoporous silica materials. Energy Fuels 2022, 36, 2424–2446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Wang, W.; Goebl, J.; Yin, Y. Self-templated synthesis of hollow nanostructures. Nano Today 2009, 4, 494–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, L.; Tang, A.; Yan, P.; Wang, J.; Wang, Q.; Wen, X.; Cui, Y. Palygorskite-template amorphous carbon nanotubes as a superior adsorbent for removal of dyes from aqueous solutions. J. Colloid. Interface Sci. 2019, 537, 450–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gérardin, C.; Reboul, J.; Bonne, M.; Lebeau, B. Ecodesign of ordered mesoporous silica materials. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 4217–4255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Chen, T.; Chang, D.; Chen, D.; Qing, C.; Xie, J.; Frost, R. The difference of thermal stability between Fe-substituted palygorskite and Al-rich palygorskite. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2013, 111, 409–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Yin, Y.; Yao, C.; Zuo, S.; Lu, X.; Luo, S.; Ni, C. La1−xCexMnO3/attapulgite nanocomposites as catalysts for NO reduction with NH3 at low temperature. Particuology 2016, 26, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karim, N.; Kyawoo, T.; Jiang, C.; Ahmed, S.; Tian, W.; Li, H.; Feng, Y. Fenton-like degradation of methylene blue on attapulgite clay composite by loading of iron–oxide: Eco-friendly preparation and its catalytic activity. Materials 2024, 17, 2615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orrico, M.; Pota, G.; Venezia, V.; de Gennaro, B.; Landi, G.; Tescione, F.; Pezzella, A.; Luciani, G.; Silvestri, B. Phenolic driven decoration of silica with Ag nanoparticles: Towards sustainable water remediation. J. Water Process Eng. 2024, 59, 105079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamoto, K. Infrared and Raman spectra of inorganic and coordination compounds. In Handbook of Vibrational Spectroscopy; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2006; pp. 1872–1892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, T.-W.; Zhu, Y.-J.; Qi, C.; Chen, F.; Jiang, Y.-Y.; Zhang, Y.-G.; Wu, J.; Wu, C. Templated solvothermal synthesis of magnesium silicate hollow nanospheres with ultrahigh specific surface area and their application in high-performance protein adsorption and drug delivery. J. Mater. Chem. B 2016, 4, 3257–3268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Sun, J.; Yuan, J.; Wang, S.; Ding, Y.; Wu, Y.; Gao, C. A type of thiophene-bridged silica aerogel with a high adsorption capacity for organic solvents and oil pollutants. Inorg. Chem. Front. 2018, 5, 1894–1901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Y.L.; Yu, H.L.; Wang, H.M.; Ji, X.C.; Song, Z.Y.; Zhou, X.Y.; Wei, M.; Shi, P.J.; Zhang, W.; Zhao, C.F. Tribological behaviors of AZ91D magnesium alloy under the lubrication of oil suspended synthetic magnesium silicate hydroxide nanotubes. J. Magnes. Alloy. 2024, 13, 379–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Tian, G.; Zong, L.; Zhou, Y.; Kang, Y.; Wang, Q.; Wang, A. From illite/smectite clay to mesoporous silicate adsorbent for efficient removal of chlortetracycline from water. J. Environ. Sci. 2017, 51, 31–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Botella, E.; Valencia, S.; Rey, F. Zeolites in adsorption processes: State of the art and future prospects. Chem. Rev. 2022, 122, 17647–17695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, J.; Feng, Y.; Pan, Y.; Jiang, J. Adsorption of Co2+ and Cr3+ in industrial wastewater by magnesium silicate nanomaterials. Materials 2024, 17, 1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, S.; Pan, J.; Ashiq, M.N.; Li, D.; Tang, P.; Feng, Y. Ethylene glycol-assisted fabrication and superb adsorption capacity of hierarchical porous flower-like magnesium oxide microspheres for phosphate. Inorg. Chem. Front. 2019, 6, 1952–1961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S. CTAB-assisted fabrication of hierarchical flower-like magnesium oxide adsorbent for enhanced removal performance towards phosphate. J. Magnes. Alloy. 2023, 11, 3231–3240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, P.; Xu, L.; Jiang, X.; Zhang, H.; Zhu, W. Facile and Green one-pot hydrothermal formation of hierarchical porous magnesium silicate microspheres as excellent adsorbents for anionic organic dye removal. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2019, 58, 2945–2957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Nie, K.; Tang, Q.; Tian, G.; Liang, J. In-situ synthesis of duster-like hollow mesoporous copper silicate composites for high-efficiency adsorption of aflatoxin B1 from water. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2022, 346, 112317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.-C.; Tseng, R.-L.; Juang, R.-S. Characteristics of Elovich equation used for the analysis of adsorption kinetics in dye-chitosan systems. Chem. Eng. J. 2009, 150, 366–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Liu, Z.; Wang, W.; Peng, C.; Shi, K. Highly efficient macroporous adsorbents for toxic metal ions in water system based on polyvinyl alcohol-formaldehyde sponges. J. Mater. Chem. A 2016, 4, 2537–2549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, V.; Sillanpää, M. Synthesis of malachite@clay nanocomposite for rapid scavenging of cationic and anionic dyes from synthetic wastewater. J. Environ. Sci. 2017, 51, 97–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natrayan, L.; Niveditha, V.R.; Nadh, V.S.; Srinivas, C.; Dhanraj, J.A.; Saravanan, A. Application of response surface and artificial neural network optimization approaches for exploring methylene blue adsorption using luffa fiber treated with sodium chlorite. J. Water Process Eng. 2024, 58, 104778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abuhatab, S.; El-Qanni, A.; Marei, N.N.; Hmoudah, M.; El-Hamouz, A. Sustainable competitive adsorption of methylene blue and acid red 88 from synthetic wastewater using NiO and/or MgO silicate based nanosorbcats: Experimental and computational modeling studies. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 35483–35498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wawrzaszek, B.; Charmas, B.; Jedynak, K.; Skwarek, E. Impact of mechanochemical activation (MChA) on characteristics and dye adsorption behavior of sawdust-based biocarbons. Materials 2024, 17, 4458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, D.; Wu, C.; Adebajo, M.; Jin, G.; Yu, W.; Ji, S.; Zhou, C. Adsorption of methylene blue from aqueous solution onto porous cellulose-derived carbon/montmorillonite nanocomposites. Appl. Clay Sci. 2018, 161, 256–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Lin, Q.; Yang, T.; Bao, Y.c.; Liu, J. Preparation and characterization of ZSM-5 molecular sieve using coal gangue as a raw material via solvent-free method: Adsorption performance tests for heavy metal ions and methylene blue. Chemosphere 2023, 341, 139741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrero, F. Adsorption of methylene blue on magnesium silicate: Kinetics, equilibria and comparison with other adsorbents. J. Environ. Sci. 2010, 22, 467–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.-L.; Zaoui, A.; Sekkal, W. Adsorption efficiency of highly methylene blue dye concentrations with multilayer chitosan-modified clays for a precise nanofiltration performance of polluted water. J. Water Process Eng. 2024, 57, 104651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, R.; Li, Y.; Sun, B.; Chao, S.; Li, X.; Wang, C.; Zhu, G. Highly flexible magnesium silicate nanofibrous membranes for effective removal of methylene blue from aqueous solution. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 359, 1603–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

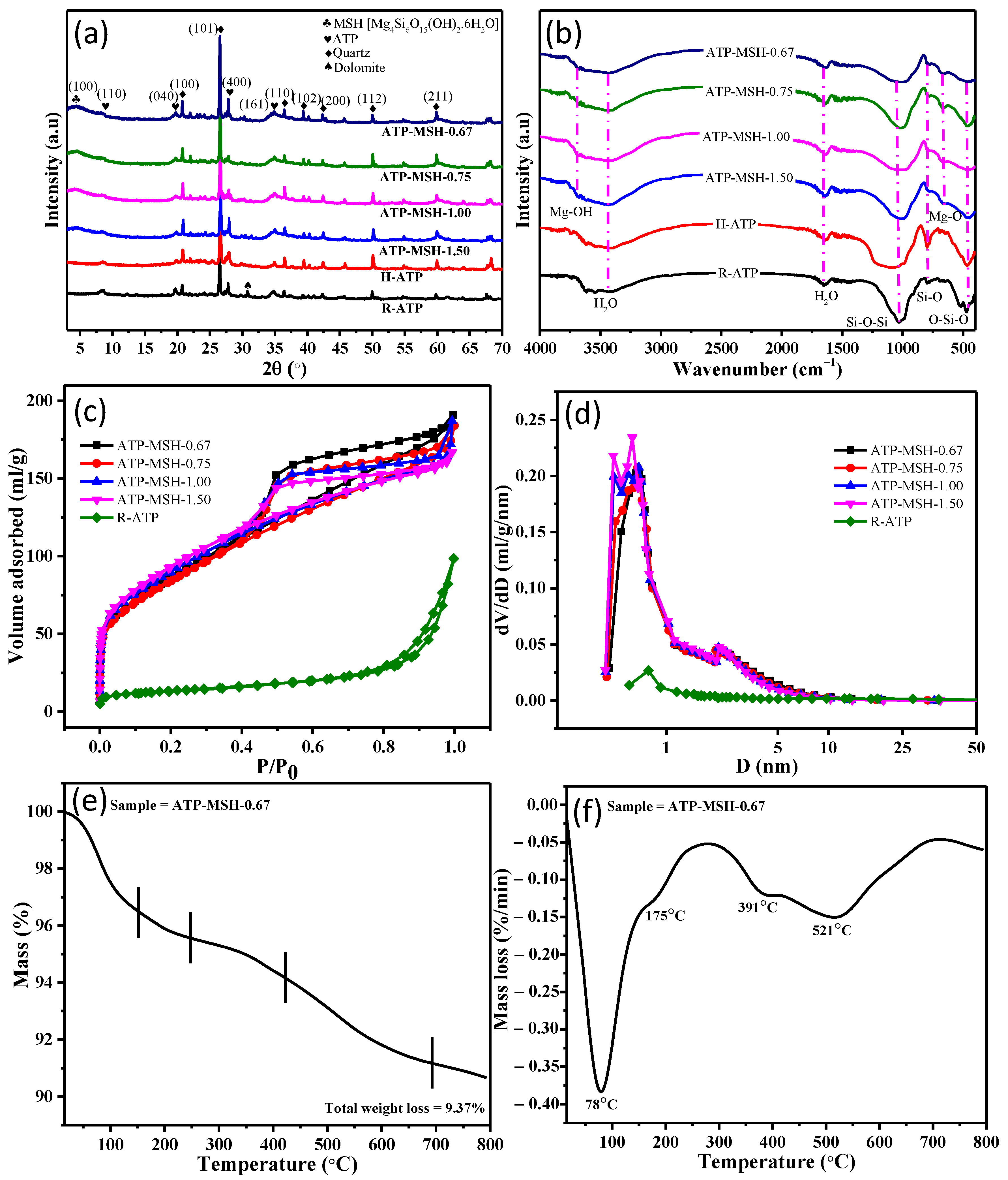
| Sample | Surface Area (m2/g) | Pore Volume (cm3/g) | Average Pore Diameter (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| ATP-MSH-0.67 | 310.41 | 0.29 | 3.74 |
| ATP-MSH-0.75 | 303.14 | 0.27 | 3.61 |
| ATP-MSH-1.00 | 322.48 | 0.27 | 3.54 |
| ATP-MSH-1.50 | 332.57 | 0.26 | 3.23 |
| R-ATP | 46.15 | 0.14 | 13.53 |
| Samples | qe,exp (mg/g) | Pseudo-First-Order | Pseudo-Second-Order | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| qe,cal (mg/g) | k1 (h−1) | R2 | qe,cal (mg/g) | k2 (h−1) | R2 | ||
| ATP-MSH-0.67 | 161.37 | 91.69 | 0.209 | 0.956 | 163.93 | 0.018 | 0.997 |
| ATP-MSH-0.75 | 161.10 | 91.10 | 0.187 | 0.949 | 163.93 | 0.017 | 0.996 |
| ATP-MSH-1.00 | 142.30 | 99.89 | 0.263 | 0.985 | 147.06 | 0.017 | 0.996 |
| ATP-MSH-1.50 | 130.76 | 89.51 | 0.159 | 0.953 | 136.99 | 0.012 | 0.987 |
| R-ATP | 90.28 | 40.36 | 0.276 | 0.966 | 91.74 | 0.059 | 0.999 |
| Samples | α (mgg−1min−1) | β (g mg−1) | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| ATP-MSH-0.67 | 35.304 | 0.040 | 0.986 |
| ATP-MSH-0.75 | 34.325 | 0.040 | 0.989 |
| ATP-MSH-1.00 | 24.126 | 0.044 | 0.996 |
| ATP-MSH-1.50 | 17.152 | 0.048 | 0.990 |
| R-ATP | 5.142 | 0.074 | 0.914 |
| Samples | Langmuir Model | Freundlich Model | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| qm (mg/g) | b (L/mg) | R2 | RL | K (mg/g) | n | R2 | |
| ATP-MSH-0.67 | 166.67 | 0.0001 | 0.999 | 0.96–0.99 | 119.37 | 16.72 | 0.887 |
| ATP-MSH-0.75 | 166.67 | 0.0001 | 0.999 | 0.96–0.99 | 113.55 | 13.99 | 0.747 |
| ATP-MSH-1.00 | 149.25 | 0.0001 | 0.999 | 0.95–0.99 | 111.89 | 19.19 | 0.873 |
| ATP-MSH-1.50 | 133.33 | 0.0002 | 0.999 | 0.95–0.98 | 111.12 | 31.45 | 0.963 |
| R-ATP | 101.01 | 0.0009 | 0.999 | 0.78–0.93 | 62.777 | 12.315 | 0.952 |
| Adsorbents | Adsorption Capacity (mg/g) | Refs. |
|---|---|---|
| Luffa fiber | 133.58 | [45] |
| NiO-MgO-SBNs | 94.7 | [46] |
| Sawdust-based biocarbon | 130.98 | [47] |
| Carbon/montmorillonite | 138.1 | [48] |
| ZSM-5 zeolite | 118.34 | [49] |
| Magnesium silicate | 149.3 | [50] |
| Chitosan/montmorillonite | 158.7 | [51] |
| ATP-MSH-0.67 | 166.67 | This work |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kyawoo, T.; Wei, T.; Karim, N.; Jiang, C.; Ahmed, S.; Li, H.; Feng, Y. Magnesium Silicate Honeycomb Structure on Attapulgite Clay Composite by Self-Template Method for Adsorption of Methylene Blue. Materials 2025, 18, 792. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18040792
Kyawoo T, Wei T, Karim N, Jiang C, Ahmed S, Li H, Feng Y. Magnesium Silicate Honeycomb Structure on Attapulgite Clay Composite by Self-Template Method for Adsorption of Methylene Blue. Materials. 2025; 18(4):792. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18040792
Chicago/Turabian StyleKyawoo, Tin, Tiefeng Wei, Naveed Karim, Chao Jiang, Saeed Ahmed, Huiyu Li, and Yongjun Feng. 2025. "Magnesium Silicate Honeycomb Structure on Attapulgite Clay Composite by Self-Template Method for Adsorption of Methylene Blue" Materials 18, no. 4: 792. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18040792
APA StyleKyawoo, T., Wei, T., Karim, N., Jiang, C., Ahmed, S., Li, H., & Feng, Y. (2025). Magnesium Silicate Honeycomb Structure on Attapulgite Clay Composite by Self-Template Method for Adsorption of Methylene Blue. Materials, 18(4), 792. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18040792







