The Influence of Basil and Cinnamon Essential Oils on Bioactive Sponge Composites of Collagen Reinforced with Hydroxyapatite
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of Biopolymeric Samples
2.2. Fourier-Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR)
2.3. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
2.4. Water Absorption
2.5. Enzymatic Degradation
2.6. Compression Test
2.7. Shore C Hardness
2.8. Roughness
2.9. Antimicrobial Activity
3. Results and Discussion
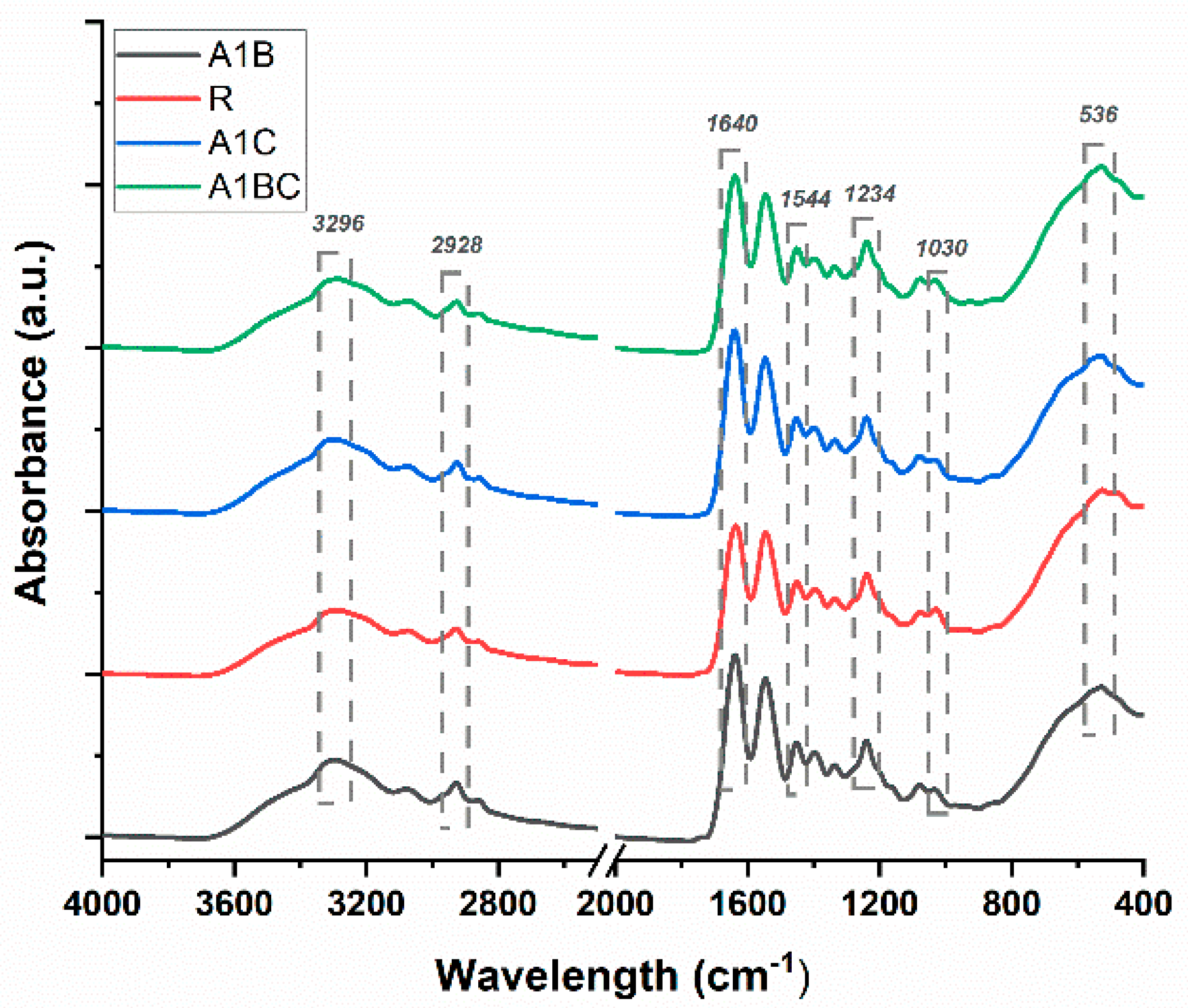
3.1. Fourier-Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR)
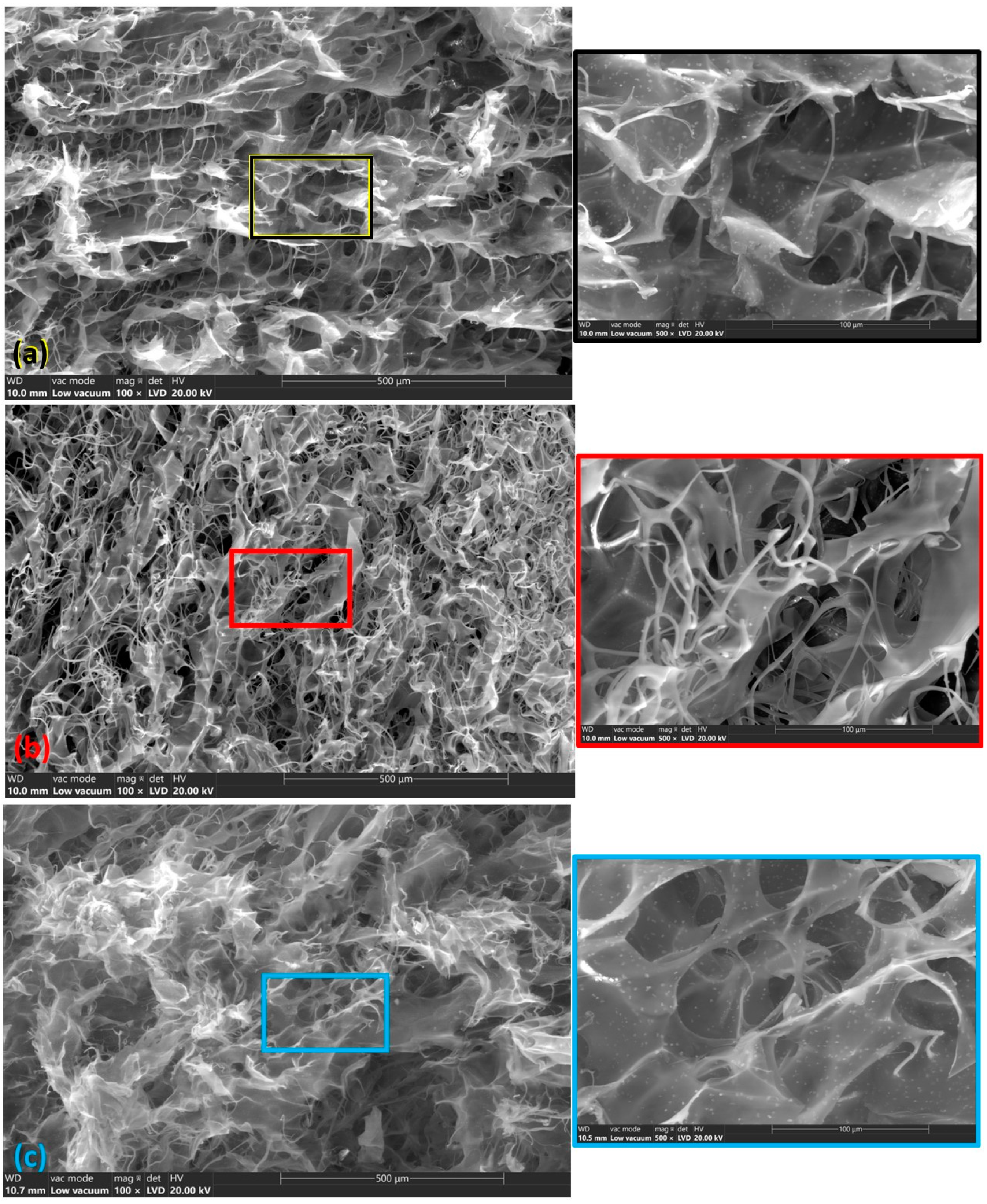
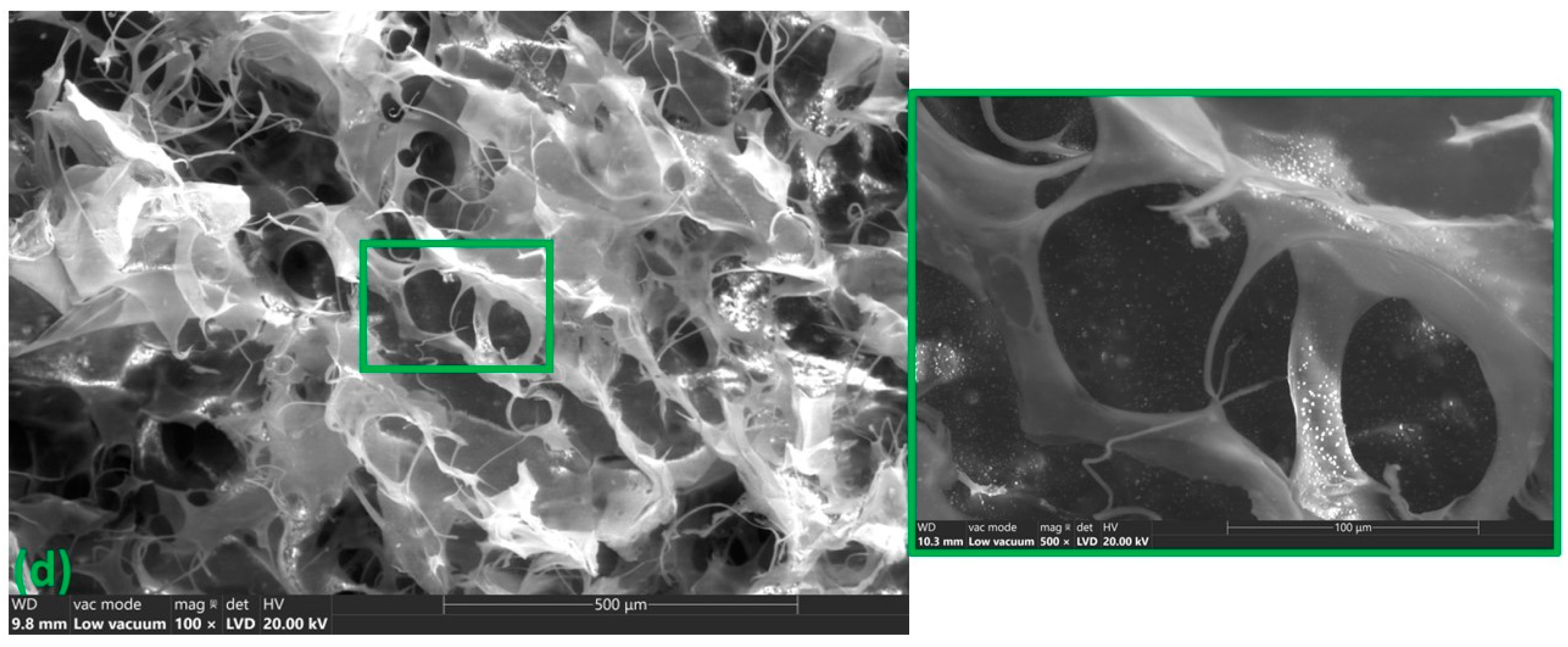
3.2. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
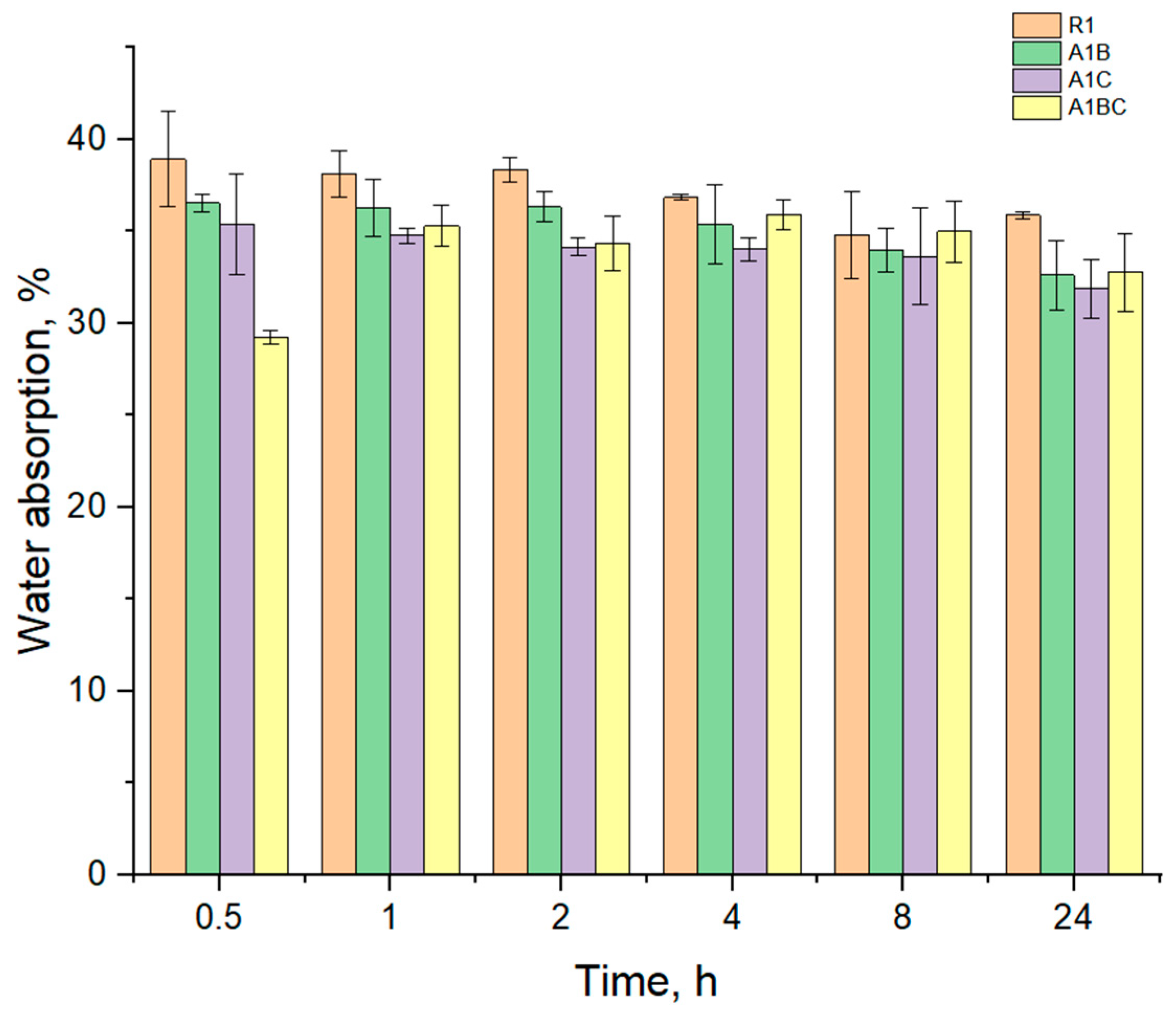
3.3. Water Absorption
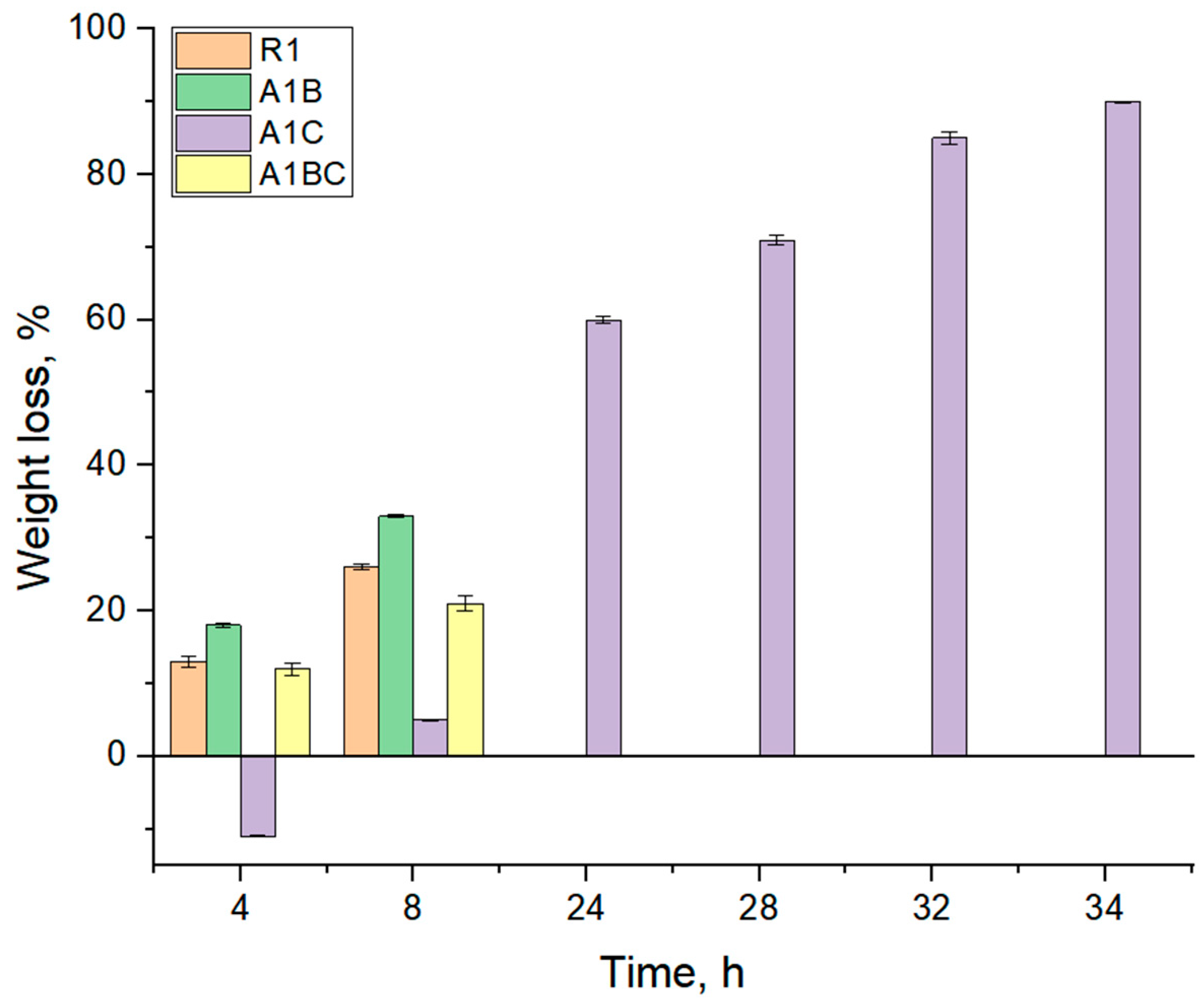
3.4. Enzymatic Degradation
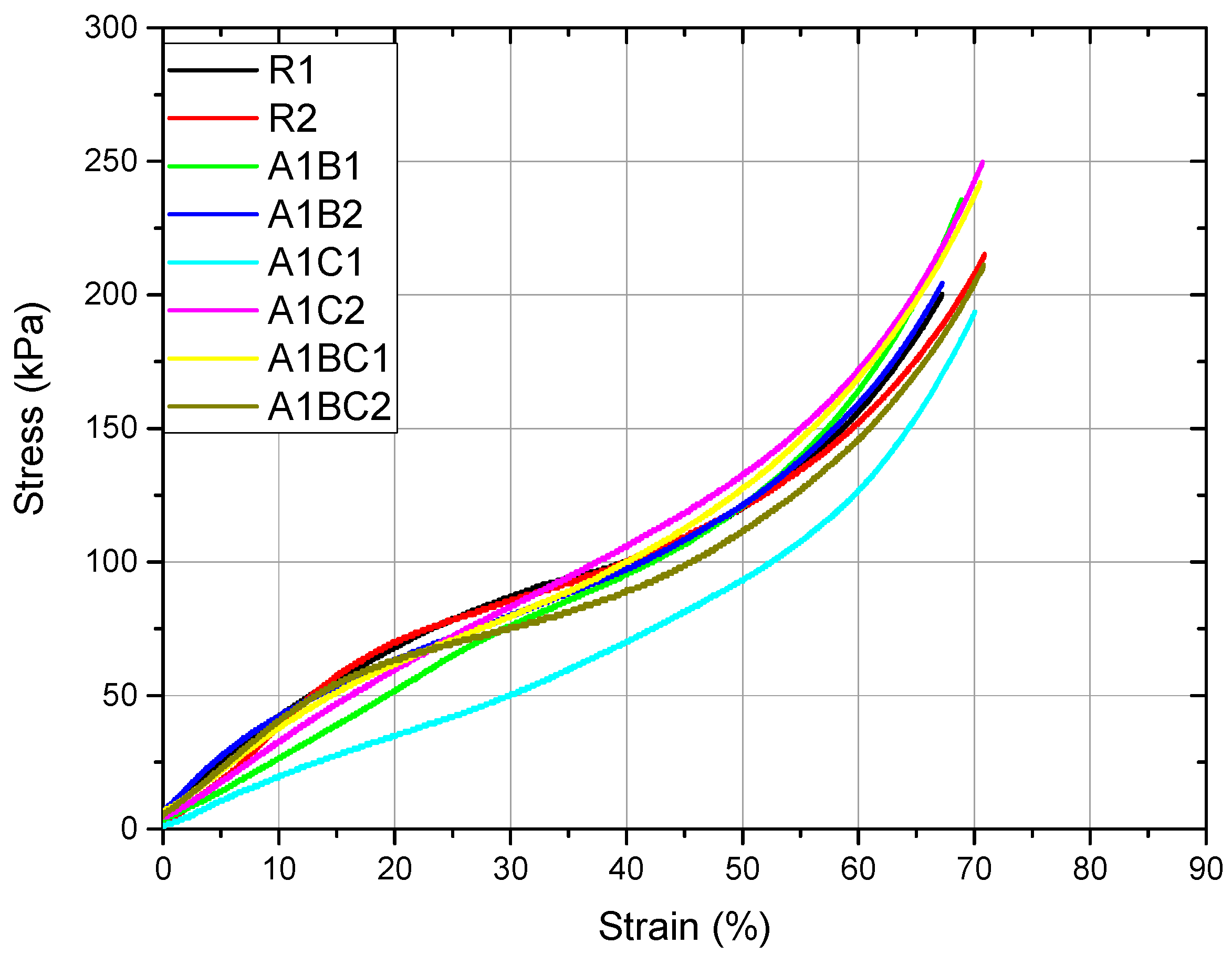
3.5. Compression Test
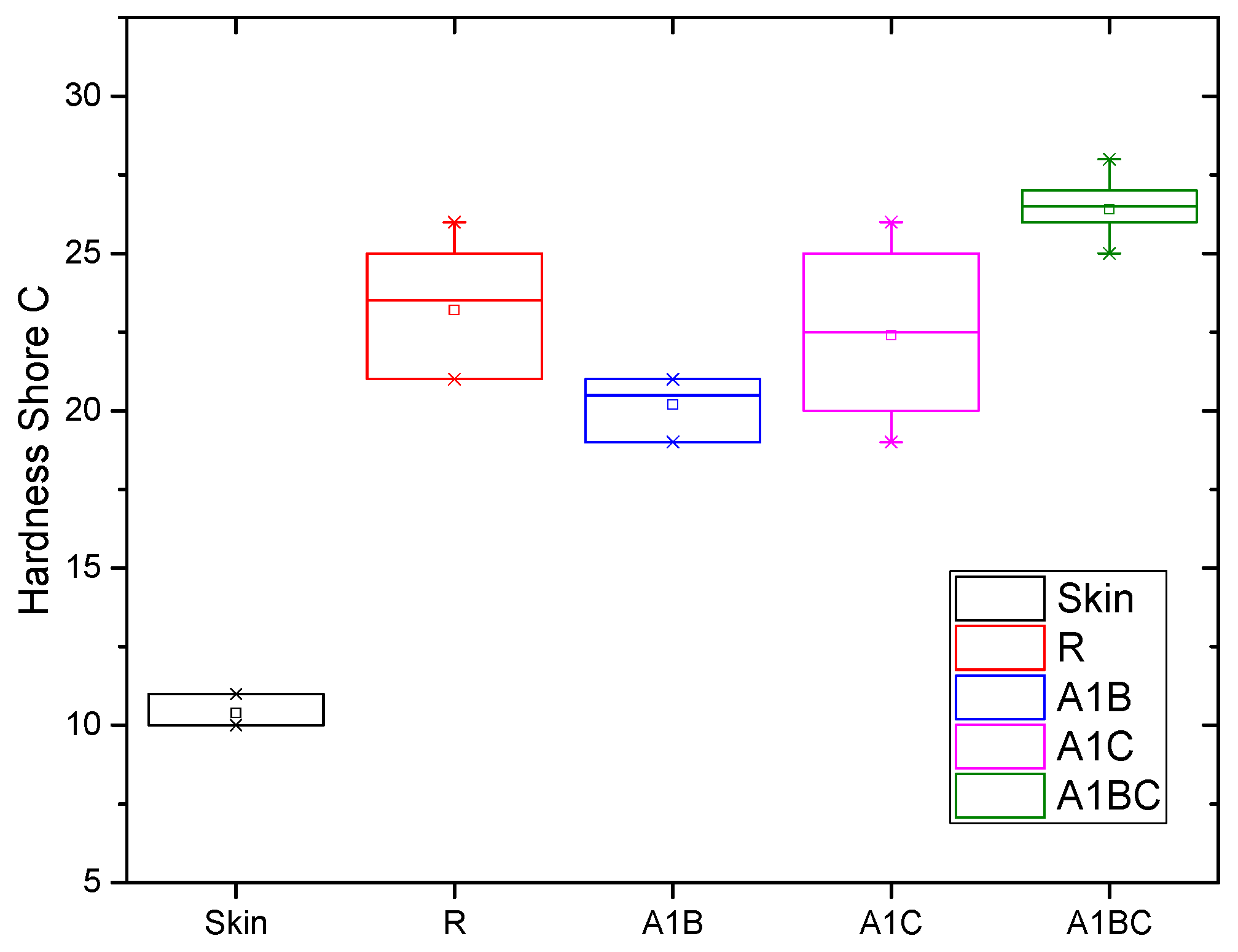
3.6. Shore C Hardness
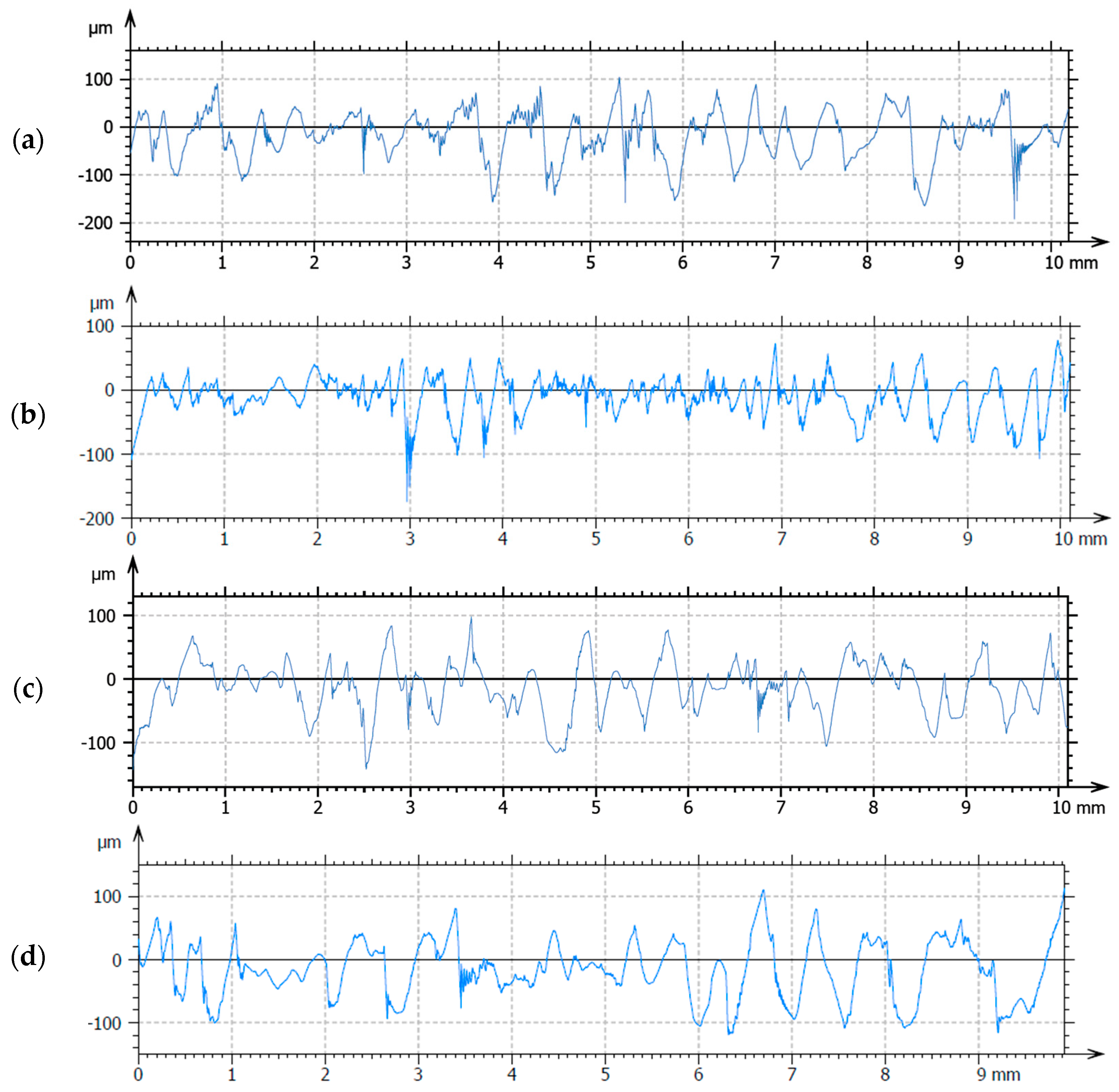
3.7. Roughness
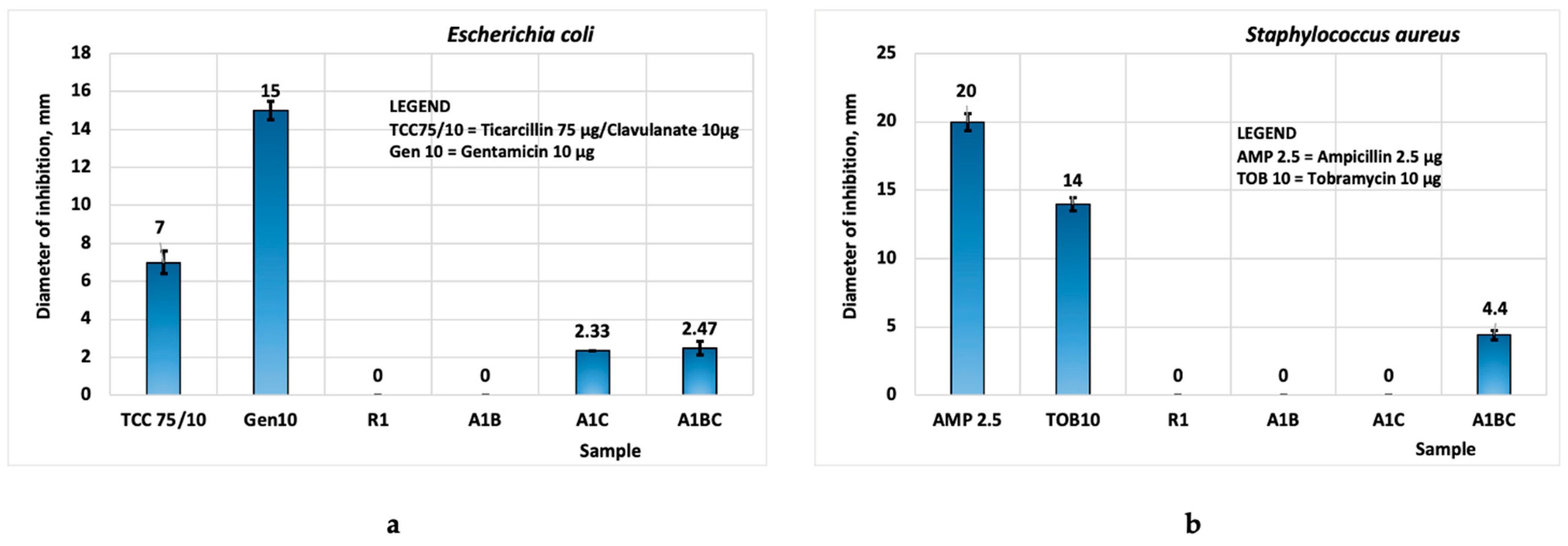
3.8. Antimicrobial Activity
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yousefian, F.; Hesari, R.; Jensen, T.; Obagi, S.; Rgeai, A.; Damiani, G.; Bunick, C.G.; Grada, A. Antimicrobial Wound Dressings: A Concise Review for Clinicians. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selem, E.; Mekky, A.F.; Hassanein, W.A.; Reda, F.M.; Selim, Y.A. Antibacterial and Antibiofilm Effects of Silver Nanoparticles against the Uropathogen Escherichia Coli U12. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2022, 29, 103457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gheorghita, D.; Robu, A.; Antoniac, A.; Antoniac, I.; Ditu, L.M.; Raiciu, A.-D.; Tomescu, J.; Grosu, E.; Saceleanu, A. In Vitro Antibacterial Activity of Some Plant Essential Oils against Four Different Microbial Strains. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 9482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gheorghiță, D.; Moldovan, H.; Robu, A.; Bița, A.-I.; Grosu, E.; Antoniac, A.; Corneschi, I.; Antoniac, I.; Bodog, A.D.; Băcilă, C.I. Chitosan-Based Biomaterials for Hemostatic Applications: A Review of Recent Advances. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 10540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gheorghita, D.; Grosu, E.; Robu, A.; Ditu, L.M.; Deleanu, I.M.; Gradisteanu Pircalabioru, G.; Raiciu, A.D.; Bita, A.I.; Antoniac, A.; Antoniac, V.I. Essential Oils as Antimicrobial Active Substances in Wound Dressings. Materials 2022, 15, 6923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parenteau-Bareil, R.; Gauvin, R.; Berthod, F. Collagen-Based Biomaterials for Tissue Engineering Applications. Materials 2010, 3, 1863–1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albu, M.G.; Vladkova, T.G.; Ivanova, I.A.; Shalaby, A.S.A.; Moskova-Doumanova, V.S.; Staneva, A.D.; Dimitriev, Y.B.; Kostadinova, A.S.; Topouzova-Hristova, T.I. Preparation and Biological Activity of New Collagen Composites, Part I: Collagen/Zinc Titanate Nanocomposites. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2016, 180, 177–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boateng, J.S.; Matthews, K.H.; Stevens, H.N.E.; Eccleston, G.M. Wound Healing Dressings and Drug Delivery Systems: A Review. J. Pharm. Sci. 2008, 97, 2892–2923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pitterou, I.; Kalogeropoulou, F.; Tzani, A.; Tsiantas, K.; Gatou, M.A.; Pavlatou, E.; Batrinou, A.; Fountzoula, C.; Kriebardis, A.; Zoumpoulakis, P.; et al. Development of Alginate Hydrogels Incorporating Essential Oils Loaded in Chitosan Nanoparticles for Biomedical Applications. Molecules 2024, 29, 5318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulvirenti, A.; Boccia, A.C.; Constantin, C.; Surcel, M.; Munteanu, A.; Peteu, V.E.; Neagu, M. Single-Component Starch-Based Hydrogels for Therapeutic Delivery. Molecules 2024, 29, 5463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, X.; Yang, B.; Hou, Z. In Situ Crosslinked Biodegradable Hydrogels Based on Poly(Ethylene Glycol) and Poly(ε-Lysine) for Medical Application. Molecules 2024, 29, 5435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansari, M.; Darvishi, A. A Review of the Current State of Natural Biomaterials in Wound Healing Applications. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2024, 12, 1309541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robu, A.; Antoniac, A.; Ciocoiu, R.; Grosu, E.; Rau, J.V.; Fosca, M.; Krasnyuk, I.I.; Pircalabioru, G.G.; Manescu (Paltanea), V.; Antoniac, I.; et al. Effect of the Antimicrobial Agents Peppermint Essential Oil and Silver Nanoparticles on Bone Cement Properties. Biomimetics 2022, 7, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlík, V.; Sobotka, L.; Pejchal, J.; Čepa, M.; Nešporová, K.; Arenbergerová, M.; Mrózková, A.; Velebný, V. Silver Distribution in Chronic Wounds and the Healing Dynamics of Chronic Wounds Treated with Dressings Containing Silver and Octenidine. FASEB J. 2021, 35, e21580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, A.; Bankar, N.; Nagore, D.; Kothapalli, L.; Chitlange, S. Herbal Oils for Treatment of Chronic and Diabetic Wounds: A Systematic Review. Curr. Diabetes Rev. 2022, 18, 52–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- do Nascimento, A.S.; Tamiasso, R.S.S.; Morais, S.F.M.; Rizzo Gnatta, J.; Turrini, R.N.T.; Calache, A.L.S.C.; de Brito Poveda, V. Essential Oils for Healing and/or Preventing Infection of Surgical Wounds: A Systematic Review. Rev. Esc. Enferm. USP 2022, 56, e20210442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alven, S.; Peter, S.; Aderibigbe, B.A. Polymer-Based Hydrogels Enriched with Essential Oils: A Promising Approach for the Treatment of Infected Wounds. Polymers 2022, 14, 3772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasile, B.S.; Oprea, O.; Voicu, G.; Ficai, A.; Andronescu, E.; Teodorescu, A.; Holban, A. Synthesis and Characterization of a Novel Controlled Release Zinc Oxide/Gentamicin–Chitosan Composite with Potential Applications in Wounds Care. Int. J. Pharm. 2014, 463, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Homaeigohar, S.; Boccaccini, A.R. Antibacterial Biohybrid Nanofibers for Wound Dressings. Acta Biomater. 2020, 107, 25–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Chang, J.; Wu, C. Bioactive Inorganic/Organic Nanocomposites for Wound Healing. Appl. Mater. Today 2018, 11, 308–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, N.N.; de Faria Lopes, L.; Ferreira, D.F.; de Prado, E.M.L.; Severi, J.A.; Resende, J.A.; de Paula Careta, F.; Ferreira, M.C.P.; Carreira, L.G.; de Souza, S.O.L.; et al. Polymeric Films Containing Pomegranate Peel Extract Based on PVA/Starch/PAA Blends for Use as Wound Dressing: In Vitro Analysis and Physicochemical Evaluation. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2020, 109, 110643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tudoroiu, E.E.; Dinu-Pîrvu, C.E.; Kaya, M.G.A.; Popa, L.; Anuța, V.; Prisada, R.M.; Ghica, M.V. An Overview of Cellulose Derivatives-Based Dressings for Wound-Healing Management. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koehler, J.; Brandl, F.P.; Goepferich, A.M. Hydrogel Wound Dressings for Bioactive Treatment of Acute and Chronic Wounds. Eur. Polym. J. 2018, 100, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santamaria, N.; Woo, K.; Beeckman, D.; Alves, P.; Cullen, B.; Gefen, A.; Lázaro-Martínez, J.L.; Lev-Tov, H.; Najafi, B.; Sharpe, A.; et al. Clinical Performance Characteristics for Bordered Foam Dressings in the Treatment of Complex Wounds: An International Wound Dressing Technology Expert Panel Review. Int. Wound J. 2023, 20, 3467–3473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zare-Gachi, M.; Daemi, H.; Mohammadi, J.; Baei, P.; Bazgir, F.; Hosseini-Salekdeh, S.; Baharvand, H. Improving Anti-Hemolytic, Antibacterial and Wound Healing Properties of Alginate Fibrous Wound Dressings by Exchanging Counter-Cation for Infected Full-Thickness Skin Wounds. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2020, 107, 110321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Luca, I.; Pedram, P.; Moeini, A.; Cerruti, P.; Peluso, G.; Di Salle, A.; Germann, N. Nanotechnology Development for Formulating Essential Oils in Wound Dressing Materials to Promote the Wound-Healing Process: A Review. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezvani Ghomi, E.; Khalili, S.; Nouri Khorasani, S.; Esmaeely Neisiany, R.; Ramakrishna, S. Wound Dressings: Current Advances and Future Directions. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2019, 136, 47738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dursun, N.; Liman, N.; Özyazgan, İ.; Güneş, I.; Saraymen, R. Role of Thymus Oil in Burn Wound Healing. J. Burn. Care Rehabil. 2003, 24, 395–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khansa, I.; Schoenbrunner, A.R.; Kraft, C.T.; Janis, J.E. Silver in Wound Care—Friend or Foe?: A Comprehensive Review. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. Glob. Open 2019, 7, e2390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.; Lee, S. Electrospun Nanofibrous Membranes with Essential Oils for Wound Dressing Applications. Fibers Polym. 2020, 21, 999–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maver, T.; Kurečič, M.; Maja Smrke, D.; Stana Kleinschek, K.; Maver, U. Plant-Derived Medicines with Potential Use in Wound Treatment. In Herbal Medicine; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Nešporová, K.; Pavlík, V.; Šafránková, B.; Vágnerová, H.; Odráška, P.; Žídek, O.; Císařová, N.; Skoroplyas, S.; Kubala, L.; Velebný, V. Effects of Wound Dressings Containing Silver on Skin and Immune Cells. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 15216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yammine, J.; Chihib, N.-E.; Gharsallaoui, A.; Dumas, E.; Ismail, A.; Karam, L. Essential Oils and Their Active Components Applied as: Free, Encapsulated and in Hurdle Technology to Fight Microbial Contaminations. A Review. Heliyon 2022, 8, e12472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nazzaro, F.; Fratianni, F.; De Martino, L.; Coppola, R.; De Feo, V. Effect of Essential Oils on Pathogenic Bacteria. Pharmaceuticals 2013, 6, 1451–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aelenei, P.; Miron, A.; Trifan, A.; Bujor, A.; Gille, E.; Aprotosoaie, A. Essential Oils and Their Components as Modulators of Antibiotic Activity against Gram-Negative Bacteria. Medicines 2016, 3, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.-K.; Tan, N.-P.; Chong, C.-W.; Abushelaibi, A.; Lim, S.-H.-E.; Lai, K.-S. The Missing Piece: Recent Approaches Investigating the Antimicrobial Mode of Action of Essential Oils. Evol. Bioinform. 2021, 17, 117693432093839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ojah, E.O. Exploring Essential Oils as Prospective Therapy against the Ravaging Coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2). Iberoam. J. Med. 2020, 4, 322–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fachriyah, E.; Wibawa, P.J.; Awaliyah, A. Antibacterial Activity of Basil Oil (Ocimum basilicum L.) and Basil Oil Nanoemulsion. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2020, 1524, 012060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brdjanin, S.; Bogdanovic, N.; Kolundzic, M.; Milenkovic, M.; Golic, N.; Kojic, M.; Kundakovic, T. Antimicrobial Activity of Oregano (Origanum vulgare L.): And Basil (Ocimum basilicum L.): Extracts. Adv. Technol. 2015, 4, 5–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Abbasy, D.W.; Pathare, N.; Al-Sabahi, J.N.; Khan, S.A. Chemical Composition and Antibacterial Activity of Essential Oil Isolated from Omani Basil (Ocimum basilicum Linn.). Asian Pac. J. Trop. Dis. 2015, 5, 645–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalkhorani, N.M.; Dadgar, M.; Rezaee, M.B.; Mahboubi, A.; HeroAbad, F. Essential Oils Composition of Ocimum Basilicum Var. Purpurascens FromDifferent Ecological Zone in Iran and Antimicrobial Activity against Different Bacterial Species. J. Med. Plants By-Prod. 2017, 2, 117–123. [Google Scholar]
- Miguel, M.G. Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Activities of Essential Oils: A Short Review. Molecules 2010, 15, 9252–9287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Zhang, C.; Chen, X.; Cui, H.; Lin, L. The Interference Mechanism of Basil Essential Oil on the Cell Membrane Barrier and Respiratory Metabolism of Listeria Monocytogenes. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 855905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamelnia, E.; Mohebbati, R.; Kamelnia, R.; El-Seedi, H.R.; Boskabady, M.H. Anti-Inflammatory, Immunomodulatory and Anti-Oxidant Effects of Ocimum basilicum L. and Its Main Constituents: A Review. Iran. J. Basic. Med. Sci. 2023, 26, 617–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadi, M.; Moghtadaei-Khorasgani, E.; Etesamnia, M.H. The Influence of Basil Seed Hydroethanolic Extract on the Skin Wound Healing in Diabetic Male Rats. World’s Vet. J. 2021, 11, 377–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonescu, I.A.; Antonescu, A.; Miere, F.; Fritea, L.; Teușdea, A.C.; Vicaș, L.; Vicaș, S.I.; Brihan, I.; Domuța, M.; Zdrinca, M.; et al. Evaluation of Wound Healing Potential of Novel Hydrogel Based on Ocimum Basilicum and Trifolium Pratense Extracts. Processes 2021, 9, 2096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, L.; Hassanzadeh Khankahdani, H.; Tanaka, F.; Tanaka, F. Effect of Aloe Vera Gel Combined with Basil (Ocimum basilicum L.) Essential Oil as a Natural Coating on Maintaining Post-Harvest Quality of Peach (Prunus persica L.) during Storage. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2020, 594, 012008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bejeshk, M.A.; Aminizadeh, A.H.; Rajizadeh, M.A.; Khaksari, M.; Lashkarizadeh, M.; Shahrokhi, N.; Zahedi, M.J.; Azimi, M. The Effect of Combining Basil Seeds and Gum Arabic on the Healing Process of Experimental Acetic Acid-Induced Ulcerative Colitis in Rats. J. Tradit. Complement. Med. 2022, 12, 599–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonescu (Mintas), A.-I.; Miere (Groza), F.; Fritea, L.; Ganea, M.; Zdrinca, M.; Dobjanschi, L.; Antonescu, A.; Vicas, S.I.; Bodog, F.; Sindhu, R.K.; et al. Perspectives on the Combined Effects of Ocimum basilicum and Trifolium pratense Extracts in Terms of Phytochemical Profile and Pharmacological Effects. Plants 2021, 10, 1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhakipbekov, K.; Turgumbayeva, A.; Akhelova, S.; Bekmuratova, K.; Blinova, O.; Utegenova, G.; Shertaeva, K.; Sadykov, N.; Tastambek, K.; Saginbazarova, A.; et al. Antimicrobial and Other Pharmacological Properties of Ocimum basilicum, Lamiaceae. Molecules 2024, 29, 388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doyle, A.A.; Stephens, J.C. A Review of Cinnamaldehyde and Its Derivatives as Antibacterial Agents. Fitoterapia 2019, 139, 104405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasconcelos, N.G.; Croda, J.; Simionatto, S. Antibacterial Mechanisms of Cinnamon and Its Constituents: A Review. Microb. Pathog. 2018, 120, 198–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, S.-T.; Chen, P.-F.; Chang, S.-C. Antibacterial Activity of Leaf Essential Oils and Their Constituents from Cinnamomum Osmophloeum. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2001, 77, 123–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raeisi, M.; Tajik, H.; Yarahmadi, A.; Sanginabadi, S. Antimicrobial Effect of Cinnamon Essential Oil Against Escherichia Coli and Staphylococcus Aureus. Health Scope 2015, 4, e21808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayaud, L.; Carricajo, A.; Zhiri, A.; Aubert, G. Comparison of Bacteriostatic and Bactericidal Activity of 13 Essential Oils against Strains with Varying Sensitivity to Antibiotics. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2008, 47, 167–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noura, E.; Kamilia, A.M.A. The Antibacterial Activity of Nano-Encapsulated Basil and Cinnamon Essential Oils against Certain Multidrug-Resistant Bacteria Recovered from Infected Wounds. Nov. Res. Microbiol. J. 2021, 5, 1447–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López, P.; Sánchez, C.; Batlle, R.; Nerín, C. Solid- and Vapor-Phase Antimicrobial Activities of Six Essential Oils: Susceptibility of Selected Foodborne Bacterial and Fungal Strains. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 6939–6946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Atki, Y.; Aouam, I.; El Kamari, F.; Taroq, A.; Nayme, K.; Timinouni, M.; Lyoussi, B.; Abdellaoui, A. Antibacterial Activity of Cinnamon Essential Oils and Their Synergistic Potential with Antibiotics. J. Adv. Pharm. Technol. Res. 2019, 10, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buriti, B.M.A.D.B.; Figueiredo, P.L.B.; Passos, M.F.; da Silva, J.K.R. Polymer-Based Wound Dressings Loaded with Essential Oil for the Treatment of Wounds: A Review. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vranceanu, M.D.; Antoniac, I.V.; Miculescu, F.; Vrânceanu, M.D.; Şaban, R.; Antoniac, I.; Albu, M. Development and Characterization of Novel Porous Collagen Based Biocomposite for Bone Tissue Regeneration. Bull. Ser. B 2012, 74, 145–156. [Google Scholar]
- Popescu, F.; Titorencu, I.; Albu Kaya, M.; Miculescu, F.; Tutuianu, R.; Coman, A.E.; Danila, E.; Marin, M.M.; Ancuta, D.-L.; Coman, C.; et al. Development of Innovative Biocomposites with Collagen, Keratin and Hydroxyapatite for Bone Tissue Engineering. Biomimetics 2024, 9, 428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mederle, N.; Marin, S.; Marin, M.M.; Danila, E.; Mederle, O.; Albu Kaya, M.G.; Ghica, M.V. Innovative Biomaterials Based on Collagen-Hydroxyapatite and Doxycycline for Bone Regeneration. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2016, 2016, 3452171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Yuan, Y.; Hays, M.P.; Hardwidge, P.R.; Kim, J. Surface Characteristics Influencing Bacterial Adhesion to Polymeric Substrates. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 14254–14261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, L.; Levänen, E. Superhydrophobic Surfaces for the Reduction of Bacterial Adhesion. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 12003–12020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stallard, C.P.; McDonnell, K.A.; Onayemi, O.D.; O’Gara, J.P.; Dowling, D.P. Evaluation of Protein Adsorption on Atmospheric Plasma Deposited Coatings Exhibiting Superhydrophilic to Superhydrophobic Properties. Biointerphases 2012, 7, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seyed Ahmadi, S.G.; Farahpour, M.R.; Hamishehkar, H. Topical Application of Cinnamon Verum Essential Oil Accelerates Infected Wound Healing Process by Increasing Tissue Antioxidant Capacity and Keratin Biosynthesis. Kaohsiung J. Med. Sci. 2019, 35, 686–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breijyeh, Z.; Karaman, R. Antibacterial Activity of Medicinal Plants and Their Role in Wound Healing. Futur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2024, 10, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcut, L.; Manescu, V.; Antoniac, A.; Paltanea, G.; Robu, A.; Mohan, A.G.; Grosu, E.; Corneschi, I.; Bodog, A.D. Antimicrobial Solutions for Endotracheal Tubes in Prevention of Ventilator-Associated Pneumonia. Materials 2023, 16, 5034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albu, M.G. Collagen Gels and Matrices for Biomedical Applications: The Obtaining and Characterization of Collagen-Based Biomaterials as Support for Local Release; LAP LAMBERT Academic Publishing: London, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- ASTM D570; International Standard. ASTM International (ASTM): West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2022.
- ISO 62, Third Edition 2008-02-15; Plastics–Determination of Water Absorption. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2008. Available online: https://standards.iteh.ai/catalog/standards/sist/2b2d1778-aa01-4c95-8144-ade41e59b9fa/iso-62-2008 (accessed on 15 December 2024).
- ASTM D695; International Standard. ASTM International (ASTM): West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2015.
- Standard Test Method for Rubber Property-Durometer Hardness D2240-00. Available online: https://www.plantech.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/05/ASTM-D2240-Durometer-Hardness.pdf (accessed on 15 December 2024).
- Chang, M.C.; Tanaka, J. FT-IR Study for Hydroxyapatite/Collagen Nanocomposite Cross-Linked by Glutaraldehyde. Biomaterials 2002, 23, 4811–4818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takallu, S.; Mirzaei, E.; Azadi, A.; Karimizade, A.; Tavakol, S. Plate-shape Carbonated Hydroxyapatite/Collagen Nanocomposite Hydrogel via in Situ Mineralization of Hydroxyapatite Concurrent with Gelation of Collagen at PH = 7.4 and 37 °C. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2019, 107, 1920–1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antoniac, I.V.; Antoniac, A.; Vasile, E.; Tecu, C.; Fosca, M.; Yankova, V.G.; Rau, J.V. In Vitro Characterization of Novel Nanostructured Collagen-Hydroxyapatite Composite Scaffolds Doped with Magnesium with Improved Biodegradation Rate for Hard Tissue Regeneration. Bioact. Mater. 2021, 6, 3383–3395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendes, L.C.; Ribeiro, G.L.; Marques, R.C. In Situ Hydroxyapatite Synthesis: Influence of Collagen on Its Structural and Morphological Characteristic. Mater. Sci. Appl. 2012, 3, 580–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Plepis, A.M.G.; Rodrigues, F.T.; Martins, V.C.A. Porcine Skin as a Source of Biodegradable Matrices: Alkaline Treatment and Glutaraldehyde Crosslinking. Polímeros 2010, 20, 92–97. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, X.; Shao, Z.; Li, C.; Yu, L.; Raja, M.A.; Liu, C. Isolation, Characterization and Evaluation of Collagen from Jellyfish Rhopilema Esculentum Kishinouye for Use in Hemostatic Applications. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0169731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Huang, C.; Ke, Q.; He, C.; Wang, H.; Mo, X. Preparation and Characterization of Coaxial Electrospun Thermoplastic Polyurethane/Collagen Compound Nanofibers for Tissue Engineering Applications. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2010, 79, 315–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szychlinska, M.A.; Calabrese, G.; Ravalli, S.; Dolcimascolo, A.; Castrogiovanni, P.; Fabbi, C.; Puglisi, C.; Lauretta, G.; Di Rosa, M.; Castorina, A.; et al. Evaluation of a Cell-Free Collagen Type i-Based Scaffold for Articular Cartilage Regeneration in an Orthotopic Rat Model. Materials 2020, 13, 2369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fathima, N.N.; Madhan, B.; Rao, J.R.; Nair, B.U.; Ramasami, T. Interaction of Aldehydes with Collagen: Effect on Thermal, Enzymatic and Conformational Stability. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2004, 34, 241–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraternale, D.; Flamini, G.; Ascrizzi, R. In Vitro Anticollagenase and Antielastase Activities of Essential Oil of Helichrysum Italicum Subsp. Italicum (Roth) G. Don. J. Med. Food 2019, 22, 1041–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Sun, X.; Lei, Y.; Sun, B.; Xie, P.; Liu, X. Effects of Chitosan/Collagen Peptides/Cinnamon Bark Essential Oil Composite Coating on the Quality of Dry-Aged Beef. Foods 2022, 11, 3638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takasao, N.; Tsuji-Naito, K.; Ishikura, S.; Tamura, A.; Akagawa, M. Cinnamon Extract Promotes Type i Collagen Biosynthesis via Activation of IGF-I Signaling in Human Dermal Fibroblasts. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 1193–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, H.; Park, J.; Pei, D. Peptidyl Aldehydes as Reversible Covalent Inhibitors of Protein Tyrosine Phosphatases. Biochemistry 2002, 41, 10700–10709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berechet, M.D.; Gaidau, C.; Miletic, A.; Pilic, B.; Râpă, M.; Stanca, M.; Ditu, L.M.; Constantinescu, R.; Lazea-Stoyanova, A. Bioactive Properties of Nanofibres Based on Concentrated Collagen Hydrolysate Loaded with Thyme and Oregano Essential Oils. Materials 2020, 13, 1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalra, A.; Lowe, A. Mechanical Behaviour of Skin: A Review. J. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2016, 5, 1000254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eswaramoorthy, N.; McKenzie, D.R. Plasma Treatments of Dressings for Wound Healing: A Review. Biophys. Rev. 2017, 9, 895–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ficai, A.; Andronescu, E.; Voicu, G.; Ficai, D. Advances in Collagen/Hydroxyapatite Composite Materials. In Advances in Composite Materials for Medicine and Nanotechnology; InTech: London, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Wu, T.-H.; Hu, X.; Liu, J.; Wu, D.; Miguez, P.A.; Wright, J.T.; Zhang, S.; Chi, J.-T.; Tseng, H.C.; et al. Biomimetic Polydopamine-Laced Hydroxyapatite Collagen Material Orients Osteoclast Behavior to an Anti-Resorptive Pattern without Compromising Osteoclasts’ Coupling to Osteoblasts. Biomater. Sci. 2021, 9, 7565–7574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moharam, L.M.; Sadony, D.M.; Adel, M.M.; Montasser, K. Evaluation of Surface Roughness and Vickers Microhardness of Various Nano-Herbal Extracts on Demineralized Dentin and Their Bactericidal Efficacy with 970-Nm Wavelength Diode Laser Irradiation. Bull. Natl. Res. Cent. 2021, 45, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miwa, M.; Nakajima, A.; Fujishima, A.; Hashimoto, K.; Watanabe, T. Effects of the Surface Roughness on Sliding Angles of Water Droplets on Superhydrophobic Surfaces. Langmuir 2000, 16, 5754–5760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanojevic, L.P.; Marjanovic-Balaban, Z.R.; Kalaba, V.D.; Stanojevic, J.S.; Cvetkovic, D.J.; Cakic, M.D. Chemical Composition, Antioxidant and Antimicrobial Activity of Basil (Ocimum basilicum L.) Essential Oil. J. Essent. Oil Bear. Plants 2017, 20, 1557–1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Sample | Coll (wt.%) | HAp % | Basil EO % | Cinnamon EO % |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| R1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| A1B | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| A1C | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| A1BC | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Samples | R | A1B | A1C | A1BC |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| E[kPa]Average | 360.70 | 440.30 | 299.50 | 346.80 |
| Standard deviation | 22.03 | 5.08 | 7.03 | 17.93 |
| Rc0.2[kPa]Average | 56.00 | 46.06 | 56.61 | 56.82 |
| Standard deviation | 3.55 | 4.78 | 3.17 | 0.38 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Robu, A.; Kaya, M.G.A.; Antoniac, A.; Kaya, D.A.; Coman, A.E.; Marin, M.-M.; Ciocoiu, R.; Constantinescu, R.R.; Antoniac, I. The Influence of Basil and Cinnamon Essential Oils on Bioactive Sponge Composites of Collagen Reinforced with Hydroxyapatite. Materials 2025, 18, 626. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18030626
Robu A, Kaya MGA, Antoniac A, Kaya DA, Coman AE, Marin M-M, Ciocoiu R, Constantinescu RR, Antoniac I. The Influence of Basil and Cinnamon Essential Oils on Bioactive Sponge Composites of Collagen Reinforced with Hydroxyapatite. Materials. 2025; 18(3):626. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18030626
Chicago/Turabian StyleRobu, Alina, Madalina Georgiana Albu Kaya, Aurora Antoniac, Durmuș Alpaslan Kaya, Alina Elena Coman, Maria-Minodora Marin, Robert Ciocoiu, Rodica Roxana Constantinescu, and Iulian Antoniac. 2025. "The Influence of Basil and Cinnamon Essential Oils on Bioactive Sponge Composites of Collagen Reinforced with Hydroxyapatite" Materials 18, no. 3: 626. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18030626
APA StyleRobu, A., Kaya, M. G. A., Antoniac, A., Kaya, D. A., Coman, A. E., Marin, M.-M., Ciocoiu, R., Constantinescu, R. R., & Antoniac, I. (2025). The Influence of Basil and Cinnamon Essential Oils on Bioactive Sponge Composites of Collagen Reinforced with Hydroxyapatite. Materials, 18(3), 626. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18030626









