Effect of Initial Relative Density on Liquid-Phase Sintering Behaviors of Al Powder Using Al–Cu Eutectic Alloy Aid: In Situ Observations Using Tomography and Microscopy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Procedure
2.1. Experiment Overview
2.2. Investigation of Sintering Behaviors of Green Bodies with Different Initial Relative Densities
2.3. In Situ X-Ray CT Observation
2.4. In Situ SEM Observation
2.5. In Situ Optical Microscopy
3. Results
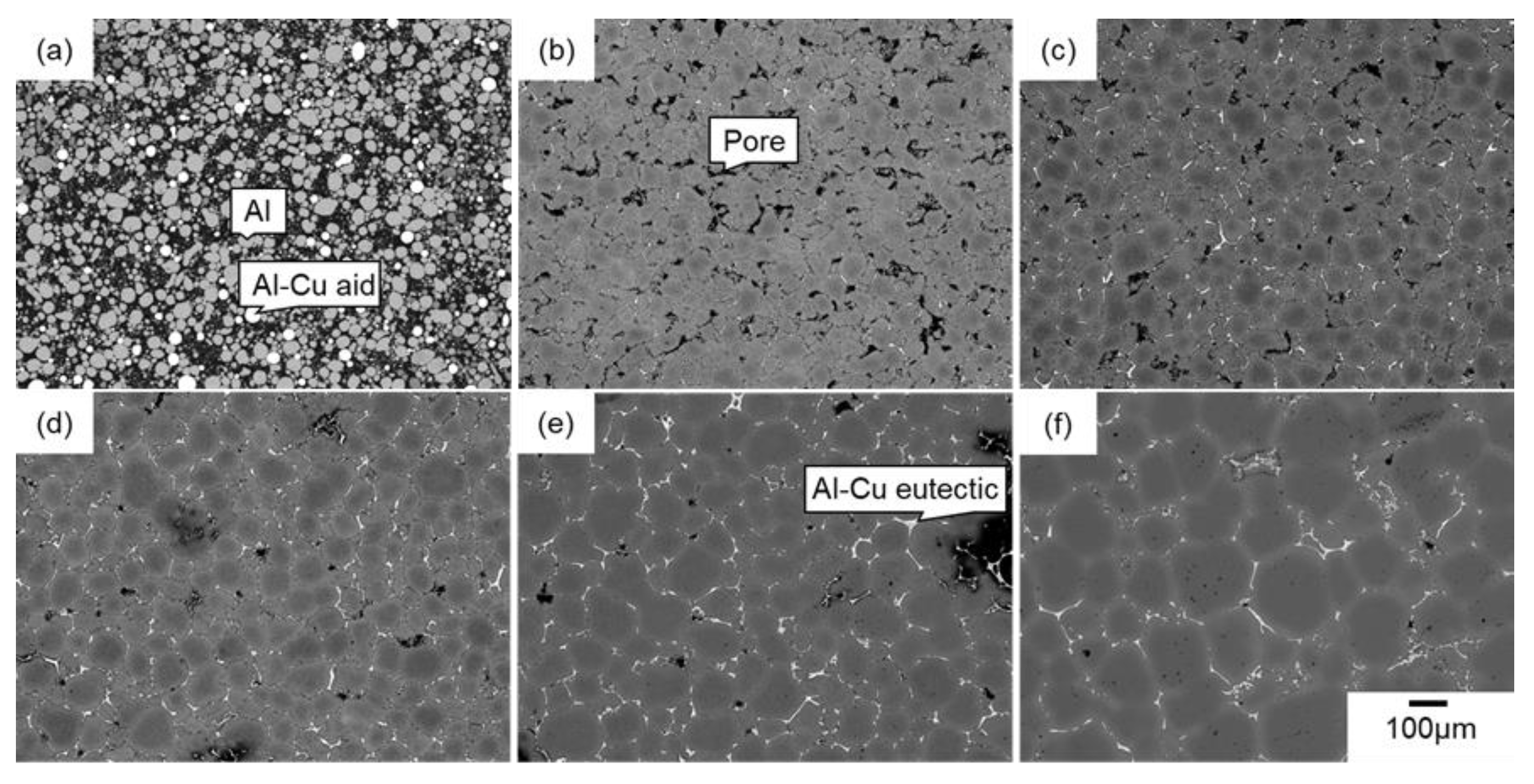
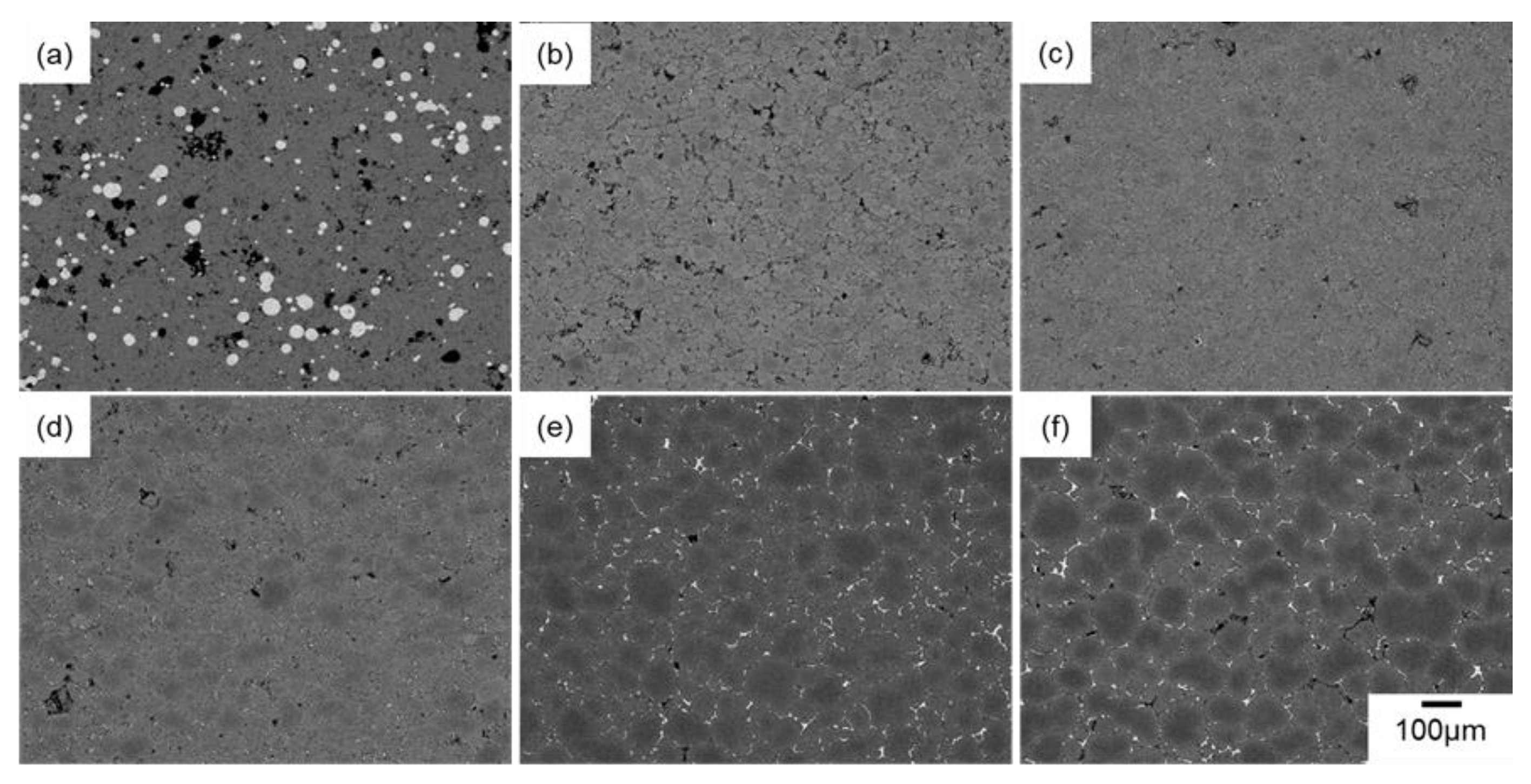
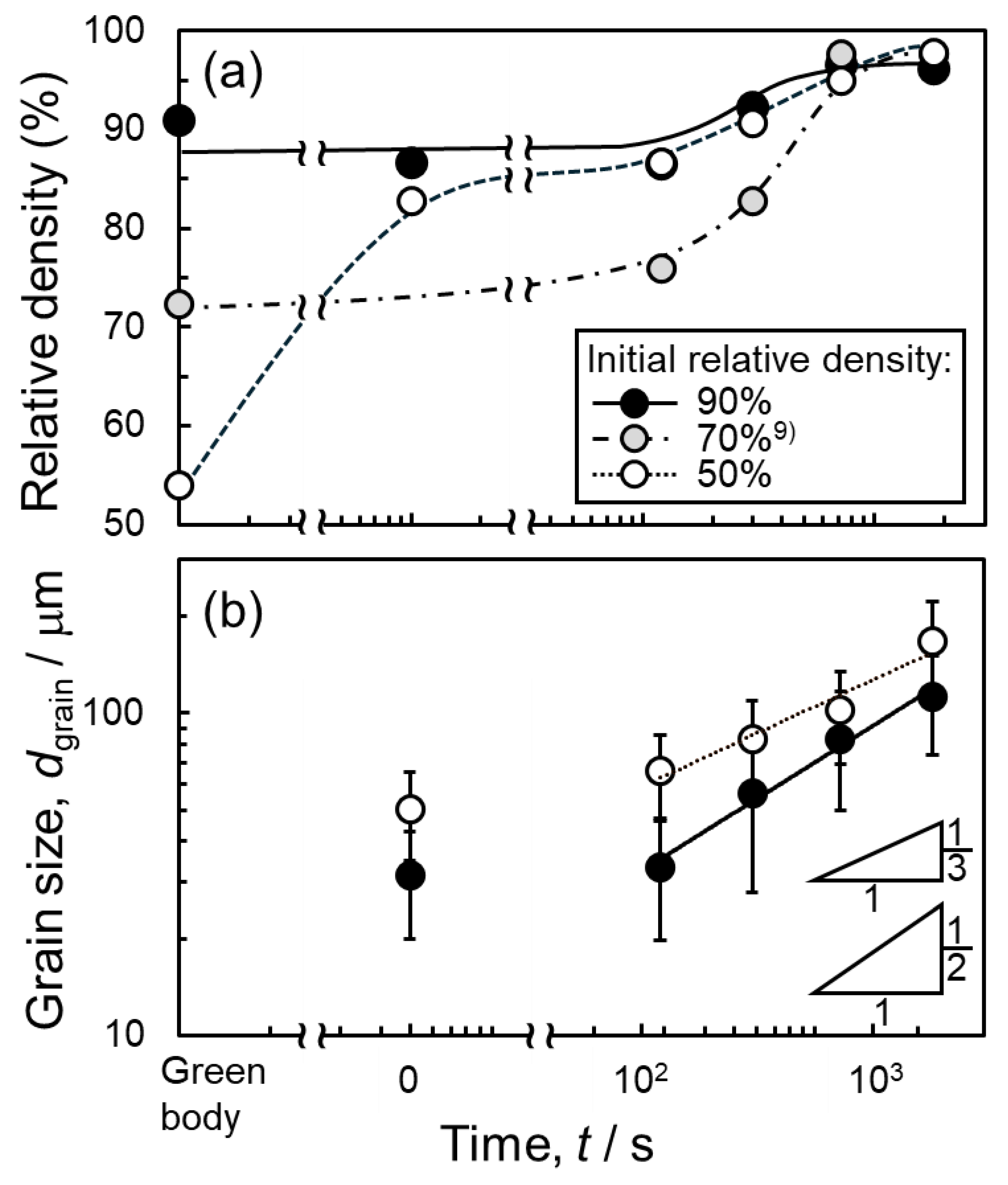
3.1. Sintering Behaviors of Green Bodies with Different Initial Relative Densities
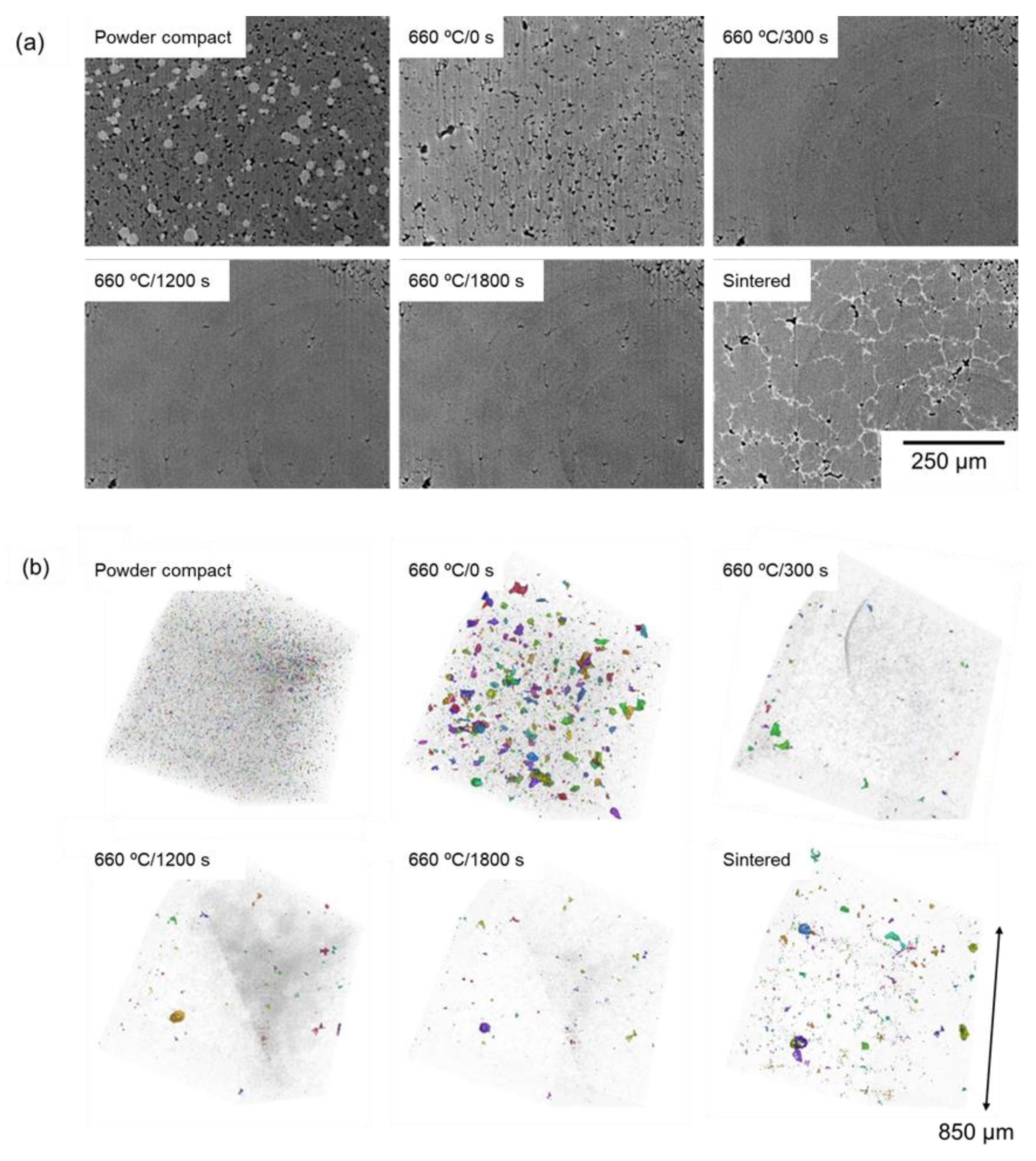
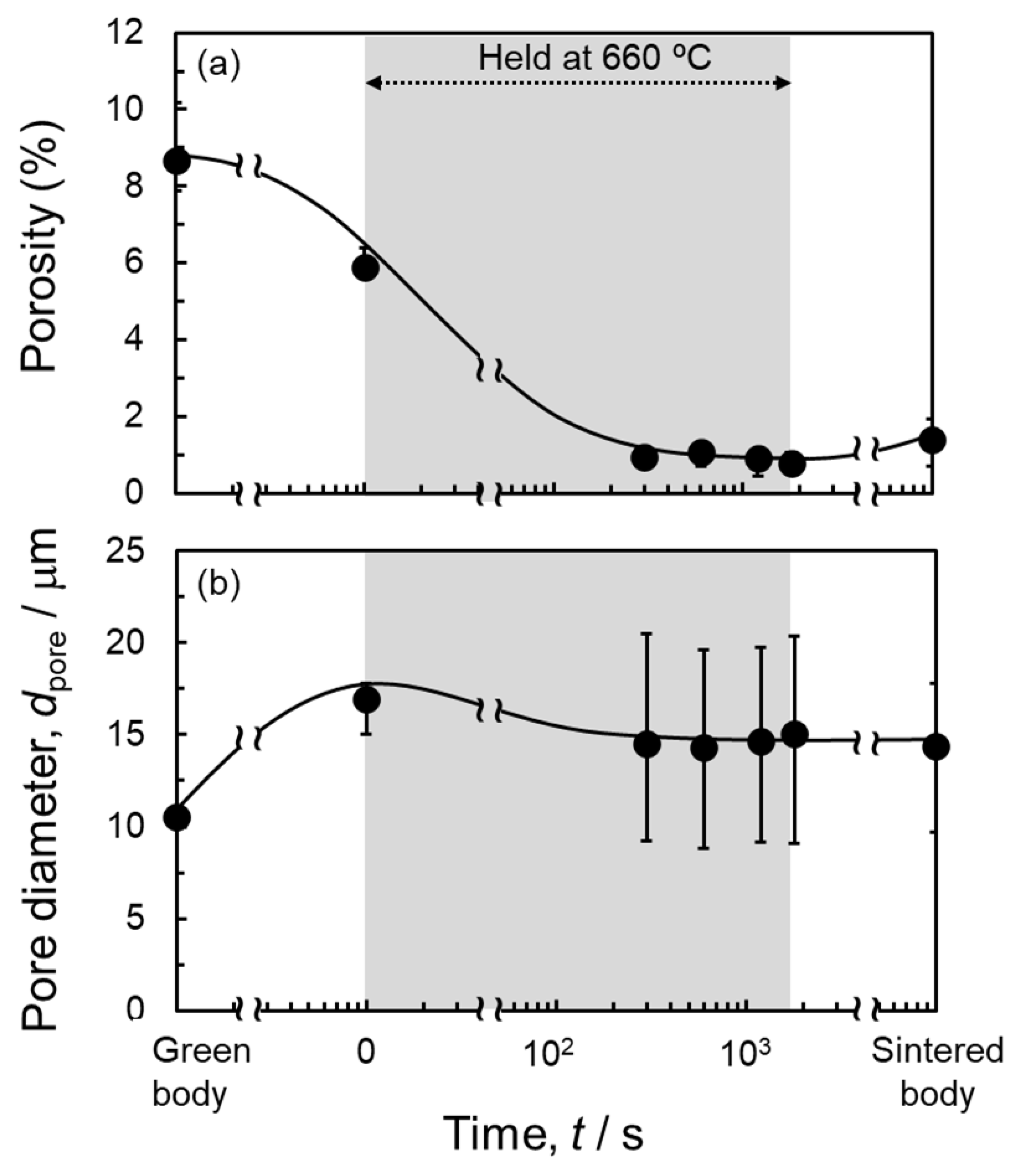
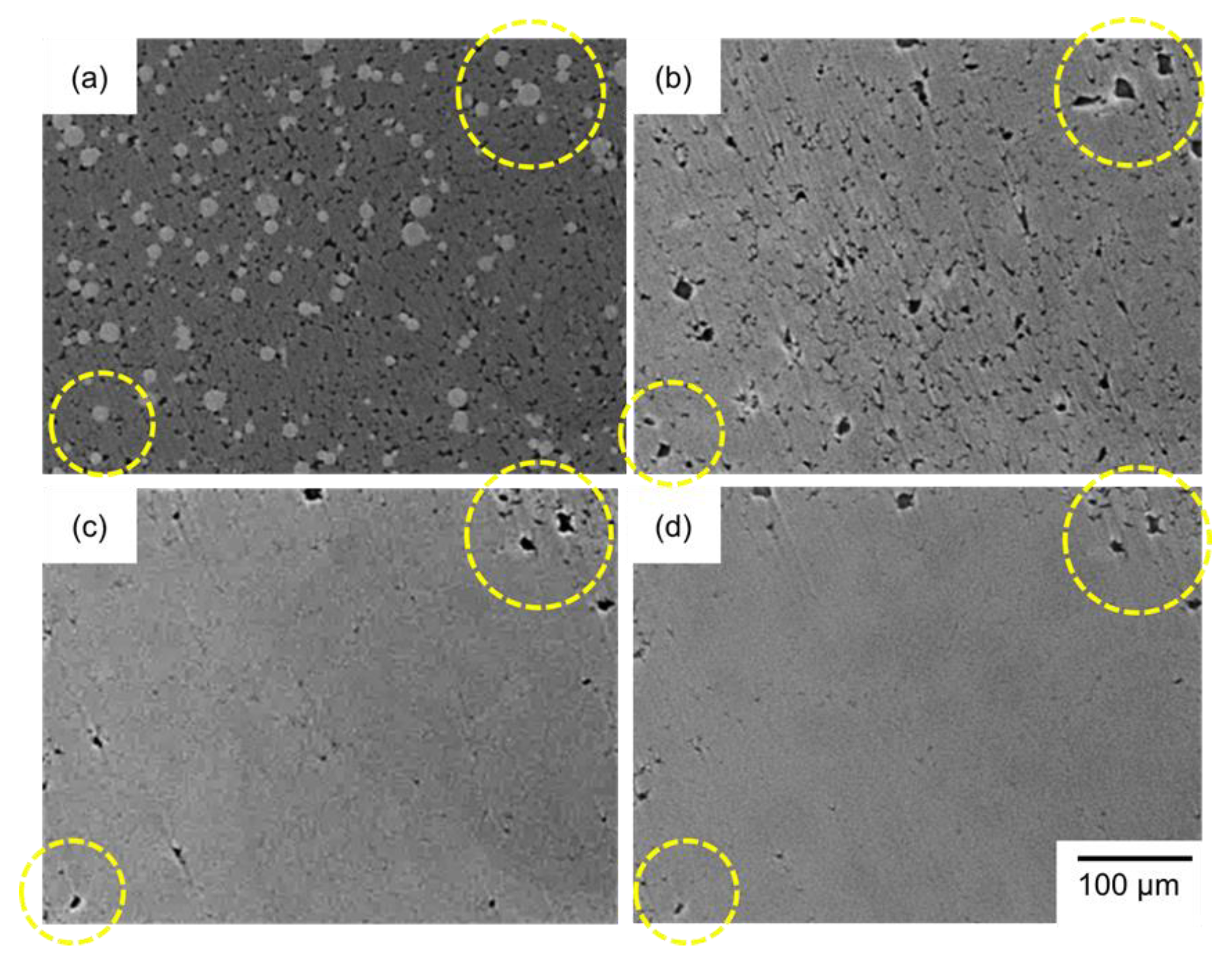
3.2. In Situ Synchrotron Radiation X-Ray CT Observation
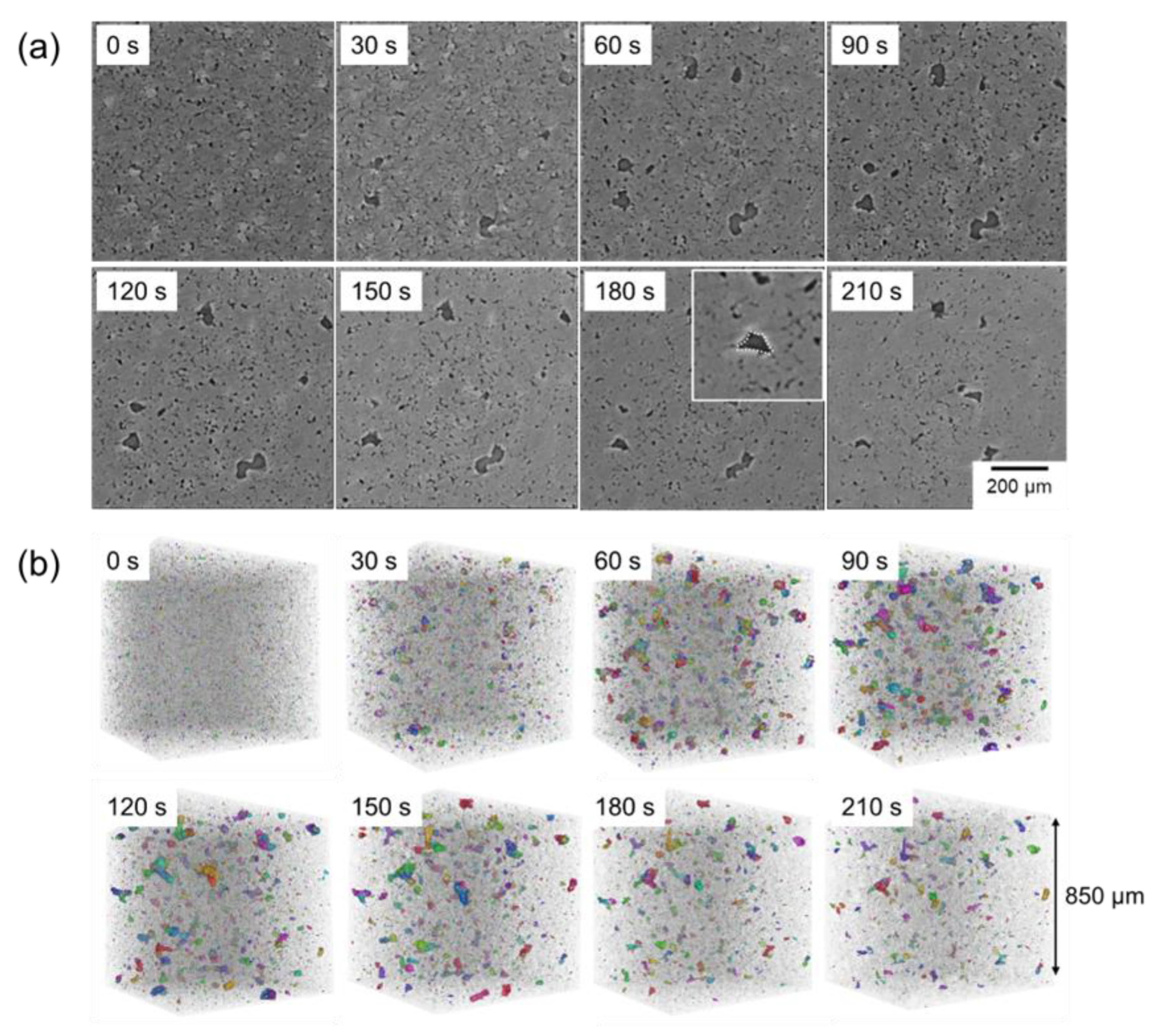
3.3. In Situ Microscopy Observations
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- Even when the initial relative density was varied in the range of 50–90%, the liquid-phase sintering at 630 °C for 1800 s achieved a high final relative density of 96–97%. The final relative density was less affected by the initial relative density in the case of this liquid-phase sintering.
- The pores tended to remain in the sample sintered using a dense green body with an initial relative density of approximately 90%. In situ observation using synchrotron radiation X-ray computed tomography (CT) revealed that large pores formed early in sintering, and some of these pores remained after sintering for 1800 s. The large pores were formed due to the infiltration of the Al–Cu melt into fine pores.
- The powder mixture with a low initial relative density of 50% was densified significantly at the early stage of sintering. In situ observation using optical microscopy revealed a significant rearrangement of Al powder at the early sintering stage, which promoted the densification.
- This study suggests that the liquid-phase sintering of Al powder using Al–Cu aids is suitable for BJT additive manufacturing, which requires the sintering of green bodies with a low relative density of 40–60%.
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ngo, T.D.; Kashani, A.; Imbalzano, G.; Nguyen, K.T.Q.; Hui, D. Additive Manufacturing (3D Printing): A Review of Materials, Methods, Applications and Challenges. Compos. Part B Eng. 2018, 143, 172–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziaee, M.; Crane, N.B. Binder Jetting: A Review of Process, Materials, and Methods. Addit. Manuf. 2019, 28, 781–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Du, W.; Elwany, A.; Pei, Z.; Ma, C. Metal Binder Jetting Additive Manufacturing: A Literature Review. J. Manuf. Sci. Eng. 2020, 142, 090801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Yu, Z.; Liu, C.; Ma, Y.; Huang, Y.; Wang, T.; Yang, L.; Yan, H.; Liu, W. Microstructure and Tensile Properties of Aluminum Powder Metallurgy Alloy Prepared by a Novel Low-Pressure Sintering. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2021, 14, 1419–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaffer, G.B.; Sercombe, T.B.; Lumley, R.N. Liquid-phase sintering of Aluminium Alloys. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2001, 67, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lumley, R.N.; Sercombe, T.B.; Schaffer, G.M. Surface Oxide and the Role of Magnesium during the Sintering of Aluminum. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 1999, 30, 457–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- German, R.M. Supersolidus Liquid-Phase Sintering of Prealloyed Powders. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 1997, 28, 1553–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sucgang, A.T.; Cuzacq, L.; Bobet, J.-L.; Lu, Y.; Silvain, J.-F. Pressure-Less Liquid-Phase Sintering of Aluminum-Based Materials. J. Manuf. Mater. Process. 2025, 9, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusunoki, R.; Hayashi, H.; Matsumoto, E.; Suzuki, A.; Takata, N.; Kobashi, M.; Yoshida, A.; Hamada, T.; Mekata, M. Liquid-phase sintering of Al Powder Using Al-X (X=Cu, Ca, Mg) Eutectic Alloy Powders: Effect of Alloy Elements and Oxide Film Thickness. Materials 2025, 18, 1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Chen, W.; Chen, L.; Zhu, D.; Chen, Q.; Fu, Z. Influence of initial relative densities on the sintering behavior and mechanical behavior of 316L stainless steel fabricated by binder jet 3D printing. Mater. Today Commun. 2022, 31, 103369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savttskii, A.P.; Kim, E.S.; Martsunova, L.S. Compact Shrinkage during Liquid-Phase Sintering. Powder Metall. Met. Ceram. 1980, 19, 593–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatesh, A.M.; Bouvard, D.; Lhuissier, P.; Villanova, J.; Rajon, C. In-Situ 3D X-Ray Investigation of Ceramic Powder Sintering at the Particle Length-Scale. Ceram. Int. 2024, 50, 4715–4728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oya, N.; Sato, T.; Yamaguchi, D. In Situ Scanning Electron Microscopy Observation of Sintering Process of Aluminum Alloy. Mater. Trans. 2023, 64, 1946–1951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, D.; Oya, N. In Situ Visualization of Aluminum Sintering for Binder Jetting by X-Ray Transmission. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2022, 121, 3965–3975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tikare, V.; Cawley, J.D. Numerical Simulation of Grain Growth in Liquid Phase Sintered Materials-I. Model. Acta Mater. 1998, 46, 1333–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- German, R.M.; Olevsky, E.A. Modeling Grain Growth Dependence on the Liquid Content in Liquid-Phase-Sintered Materials. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 1998, 29, 3057–3067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bordia, R.K.; Kang, S.-J.L.; Olevsky, E.A. Current Understanding and Future Research Directions at the Onset of the next Century of Sintering Science and Technology. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2017, 100, 2314–2352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leitner, M.; Leitner, T.; Schmon, A.; Aziz, K.; Pottlacher, G. Thermophysical Properties of Liquid Aluminum. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2017, 48, 3036–3045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- German, R.M.; Suri, P.; Park, S.J. Review: Liquid-phase sintering. J. Mater. Sci. 2009, 44, 1–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, P.; Xu, X.; Yi, W.; German, R.M. Porosity Effect on Densification and Shape Distortion in Liquid-phase sintering. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2001, 318, 111–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- German, R.M.; Churn, K.S. Sintering Atmosphere Effects on the Ductility of W- Ni- Fe Heavy Metals. Metall. Trans. A 1984, 15, 747–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turriff, D.M.; Corbin, S.F. Modelling the Influences of Solid-State Interdiffusion and Dissolution on Transient Liquid-phase sintering Kinetics in a Binary Isomorphous System. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2006, 37, 1645–1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeurgens, L.P.H.; Sloof, W.G.; Tichelaar, F.D.; Mittemeijer, E.J. Structure and Morphology of Aluminium-Oxide Films Formed by Thermal Oxidation of Aluminium. Thin Solid Film. 2002, 418, 89–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, P.; Fujii, H.; Matsumoto, T.; Nogi, K. Critical Factors Affecting the Wettability of α-Alumina by Molten Aluminum. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2004, 87, 2151–2159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobczak, N.; Ksiazek, M.; Radziwill, W.; Asthana, R.; Mikulowski, B. The Effect of Temperature, Matrix Alloying and Substrate Coatings on Wettability and Shear Strength of Al/Al2O3 Couples. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2004, 35, 911–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klinter, A.J.; Leon-Patiño, C.A.; Drew, R.A.L. Wetting Phenomena of Al–Cu Alloys on Sapphire below 800 °C. Acta Mater. 2010, 58, 1350–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasani, S.; Panjepour, M.; Shamanian, M. The Oxidation Mechanism of Pure Aluminum Powder Particles. Oxid. Met. 2012, 78, 179–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Zuo, Y.; Tang, Y.; Zhao, X. The Cracking Behavior of Anodic Films on Cast Aluminum Alloy after Heating in the Temperature Range up to 300 °C. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2008, 202, 4183–4188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Shang, H.; Ma, B.; Guo, X.; Li, R.; Li, G. The Effect of Temperature and Sputtered Particles on the Wettability of Al/Al2O3. Materials 2021, 14, 2110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paladino, A.E.; Kingery, W.D. Aluminum Ion Diffusion in Aluminum Oxide. J. Chem. Phys. 1962, 37, 957–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doremus, R.H. Diffusion in Alumina. J. Appl. Phys. 2006, 100, 101301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, L.; Li, J.; Zakharov, D.; Stach, E.A.; Zhou, G. In Situ Atomic-Scale Imaging of the Metal/Oxide Interfacial Transformation. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, Y.; Williams, C.B. An Exploration of Binder Jetting of Copper. Rapid Prototyp. J. 2015, 21, 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, X.; Zu, Y.; Ma, Q.; Hu, J. State of the Art of Metal Powder Bonded Binder Jetting Printing Technology. Discov. Mater. 2023, 3, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

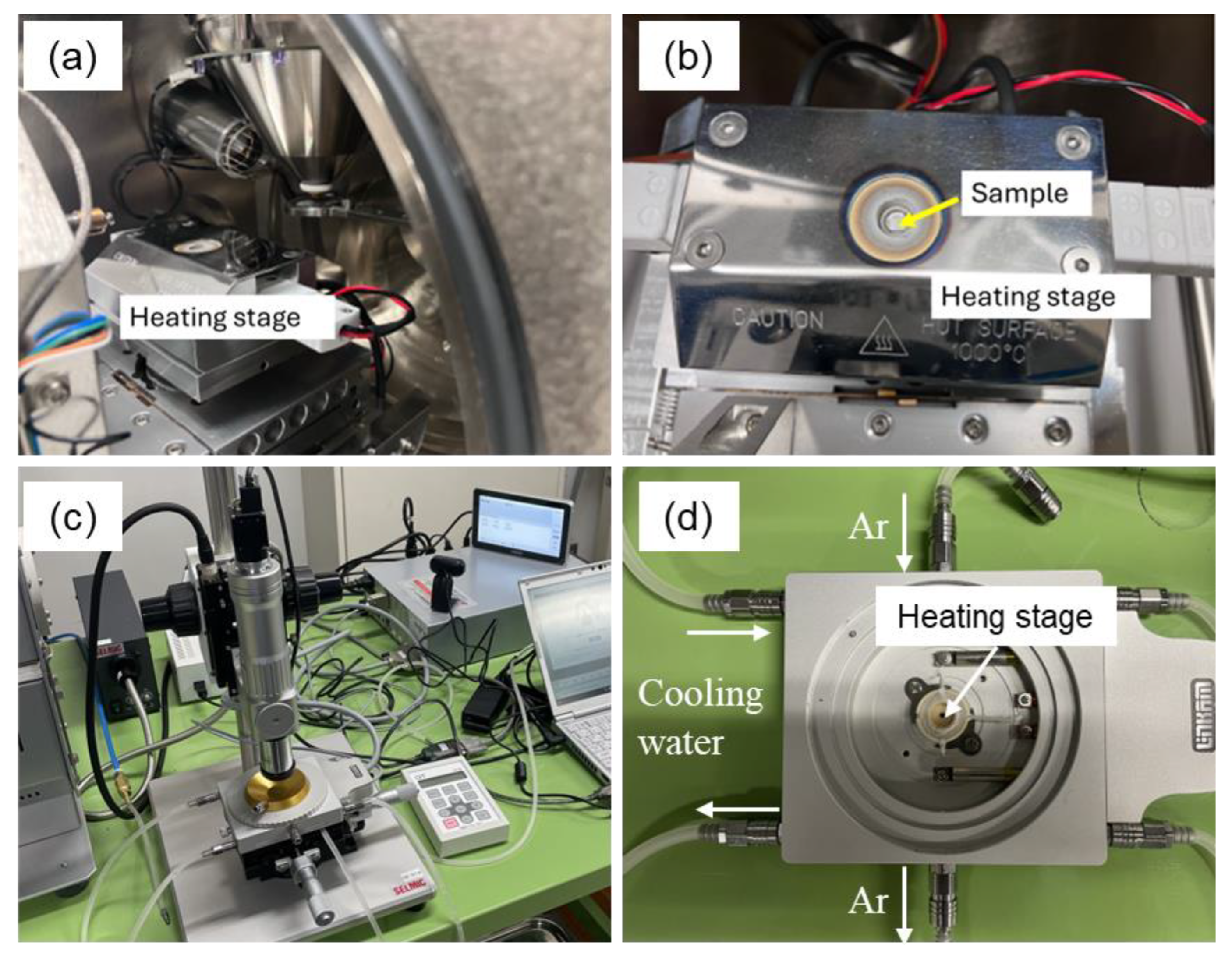




| Ex Situ/In Situ | Methods | Conditions |
|---|---|---|
| Ex situ sintering tests |
| Initial relative density: 50%, 90% Temperature: 630 °C Time: 0–1800 s Atmosphere: Ar (0.05 MPa) |
| In situ observations | Synchrotron X-ray computed tomography (CT) | Initial relative density: 90% Temperature: 660 °C Time: 0–1800 s Atmosphere: N2 flow |
| Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) | Initial relative density: 90% Temperature: 630 °C Time: 0–1800 s Atmosphere: Ar (50 Pa) | |
| Optical microscopy (OM) | Initial relative density: 50% Temperature: 630 °C Time: 0–1800 s Atmosphere: Ar flow |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kusunoki, R.; Matsumoto, E.; Higaki, T.; Suzuki, A.; Kobashi, M.; Ozaki, Y.; Hoshino, M.; Uesugi, M. Effect of Initial Relative Density on Liquid-Phase Sintering Behaviors of Al Powder Using Al–Cu Eutectic Alloy Aid: In Situ Observations Using Tomography and Microscopy. Materials 2025, 18, 5499. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18245499
Kusunoki R, Matsumoto E, Higaki T, Suzuki A, Kobashi M, Ozaki Y, Hoshino M, Uesugi M. Effect of Initial Relative Density on Liquid-Phase Sintering Behaviors of Al Powder Using Al–Cu Eutectic Alloy Aid: In Situ Observations Using Tomography and Microscopy. Materials. 2025; 18(24):5499. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18245499
Chicago/Turabian StyleKusunoki, Ryotaro, Erika Matsumoto, Takeshi Higaki, Asuka Suzuki, Makoto Kobashi, Yukiko Ozaki, Masato Hoshino, and Masayuki Uesugi. 2025. "Effect of Initial Relative Density on Liquid-Phase Sintering Behaviors of Al Powder Using Al–Cu Eutectic Alloy Aid: In Situ Observations Using Tomography and Microscopy" Materials 18, no. 24: 5499. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18245499
APA StyleKusunoki, R., Matsumoto, E., Higaki, T., Suzuki, A., Kobashi, M., Ozaki, Y., Hoshino, M., & Uesugi, M. (2025). Effect of Initial Relative Density on Liquid-Phase Sintering Behaviors of Al Powder Using Al–Cu Eutectic Alloy Aid: In Situ Observations Using Tomography and Microscopy. Materials, 18(24), 5499. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18245499








