Fabrication and Wear Behavior of TiCN-Based Cermets with Nano-Diamond Addition
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation
2.2. Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
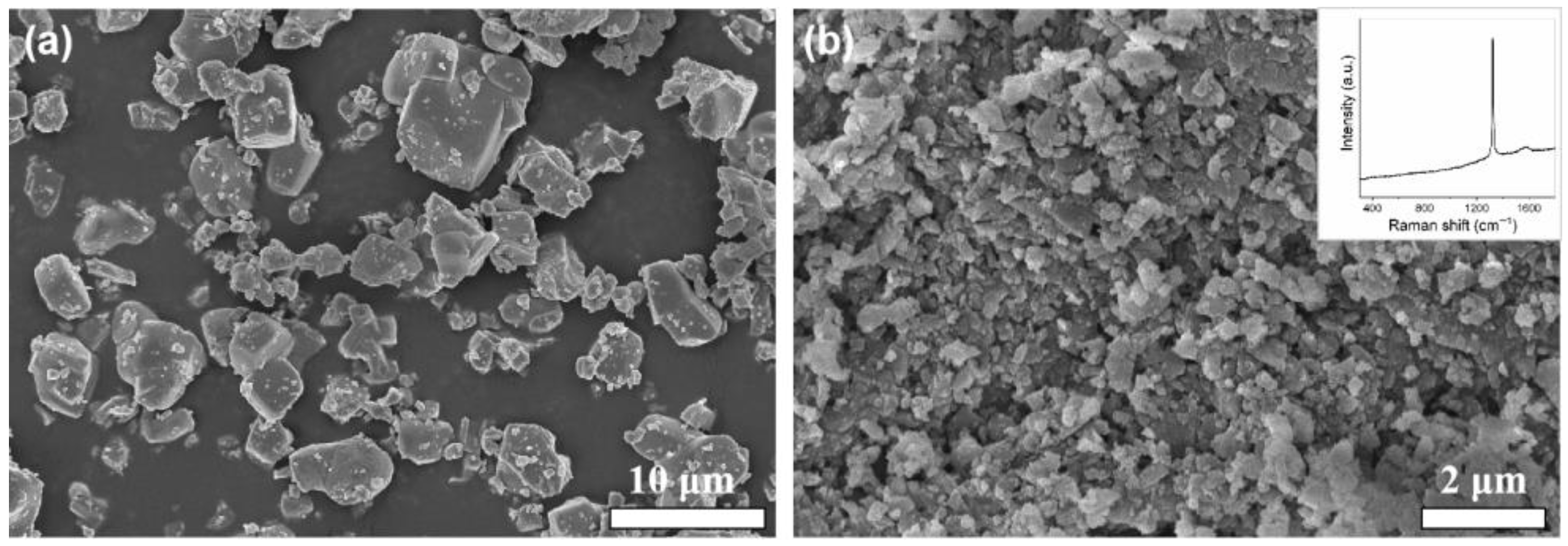
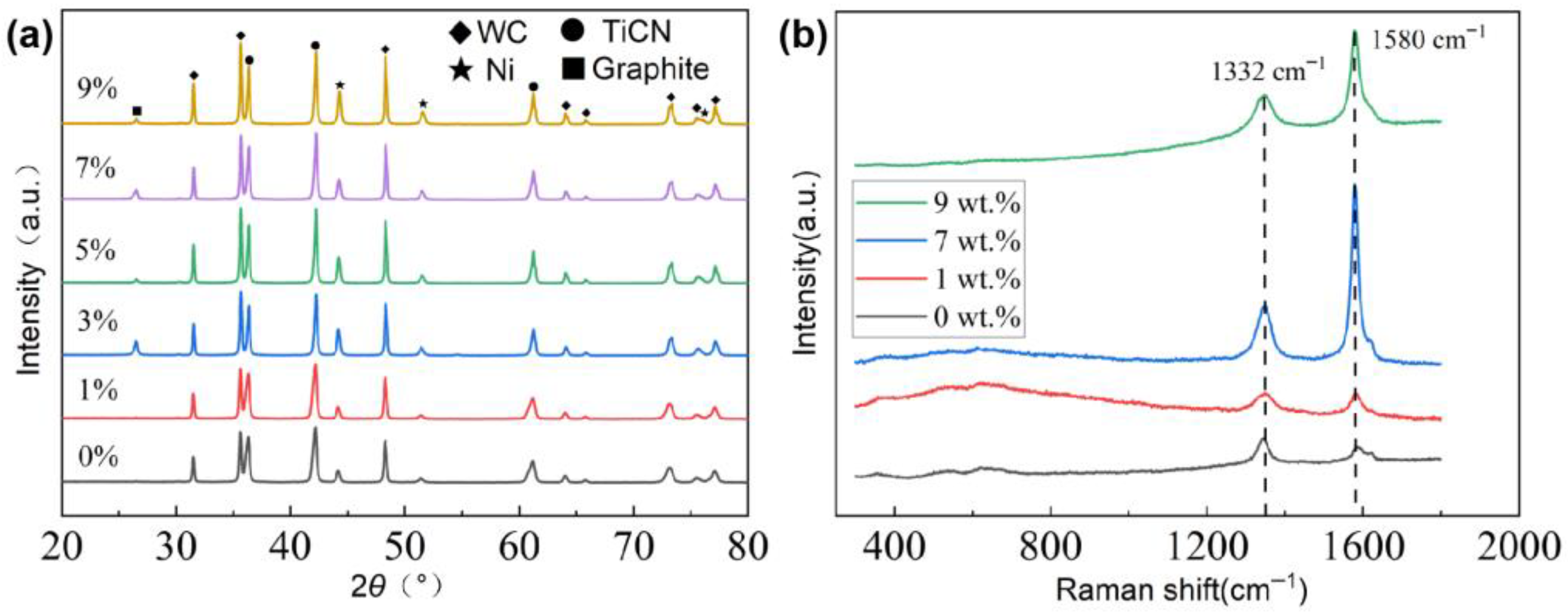
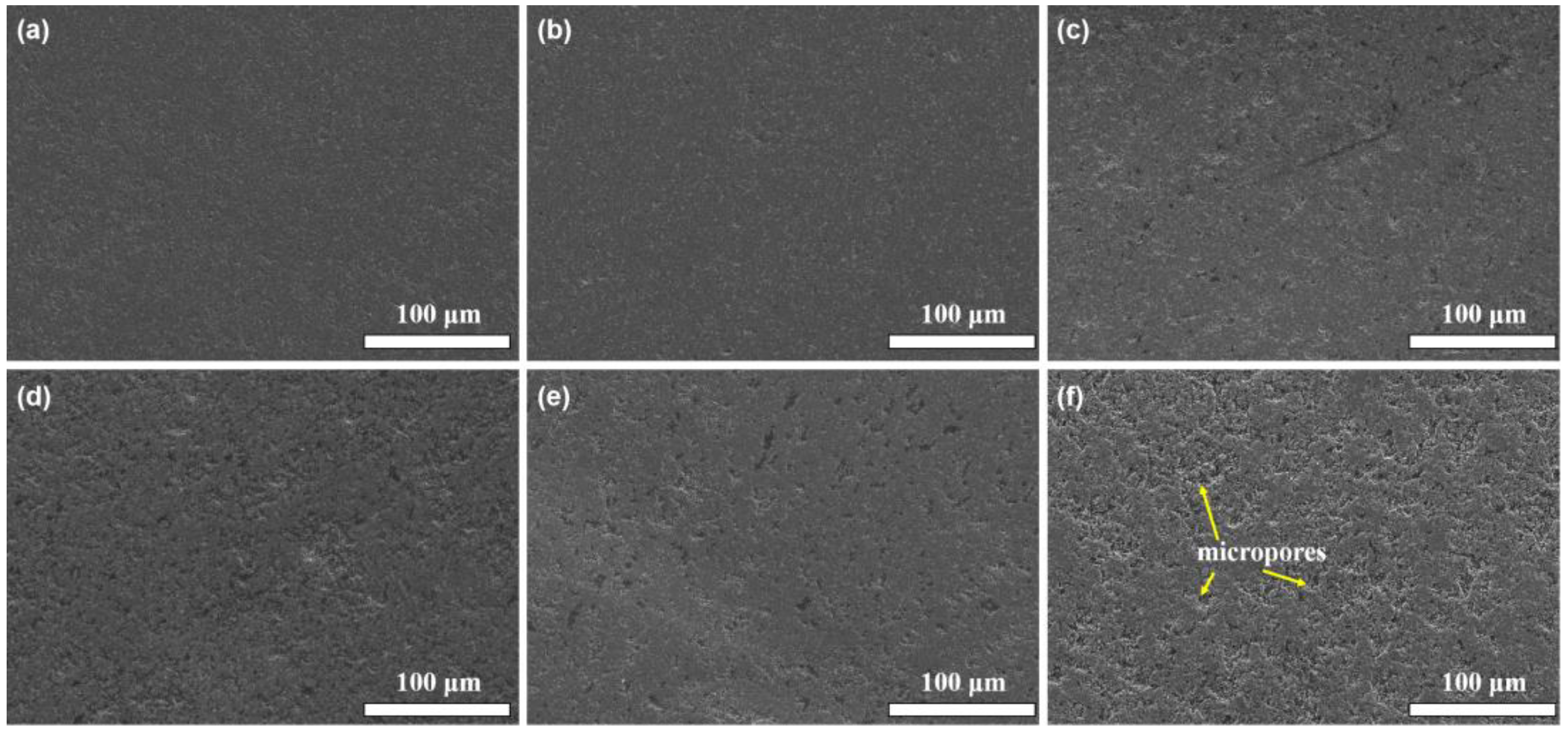
3.1. Phase Composition and Microstructure
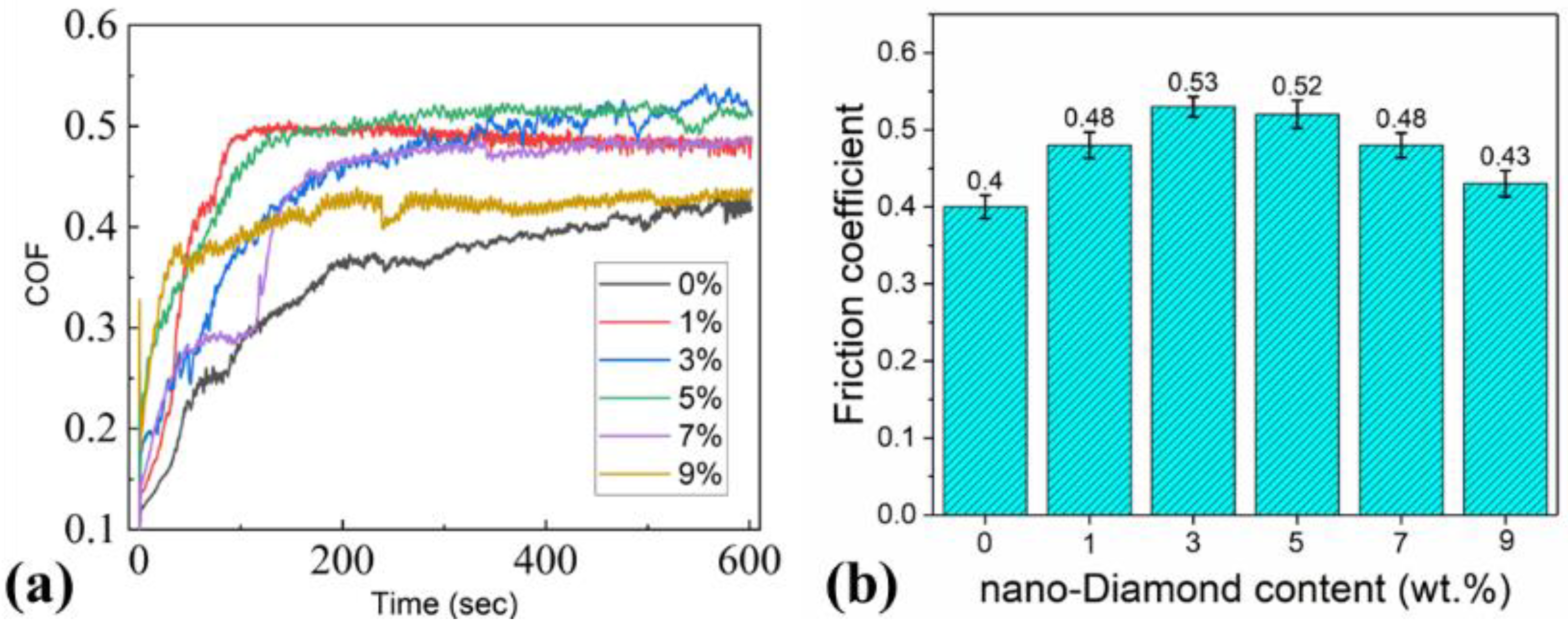
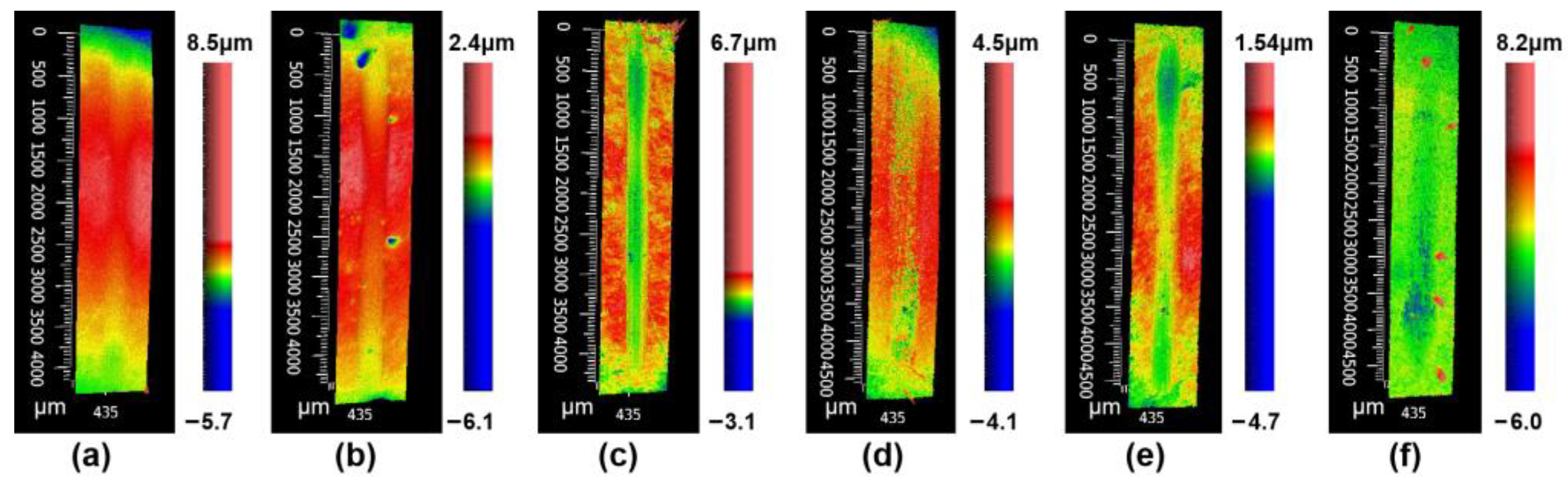
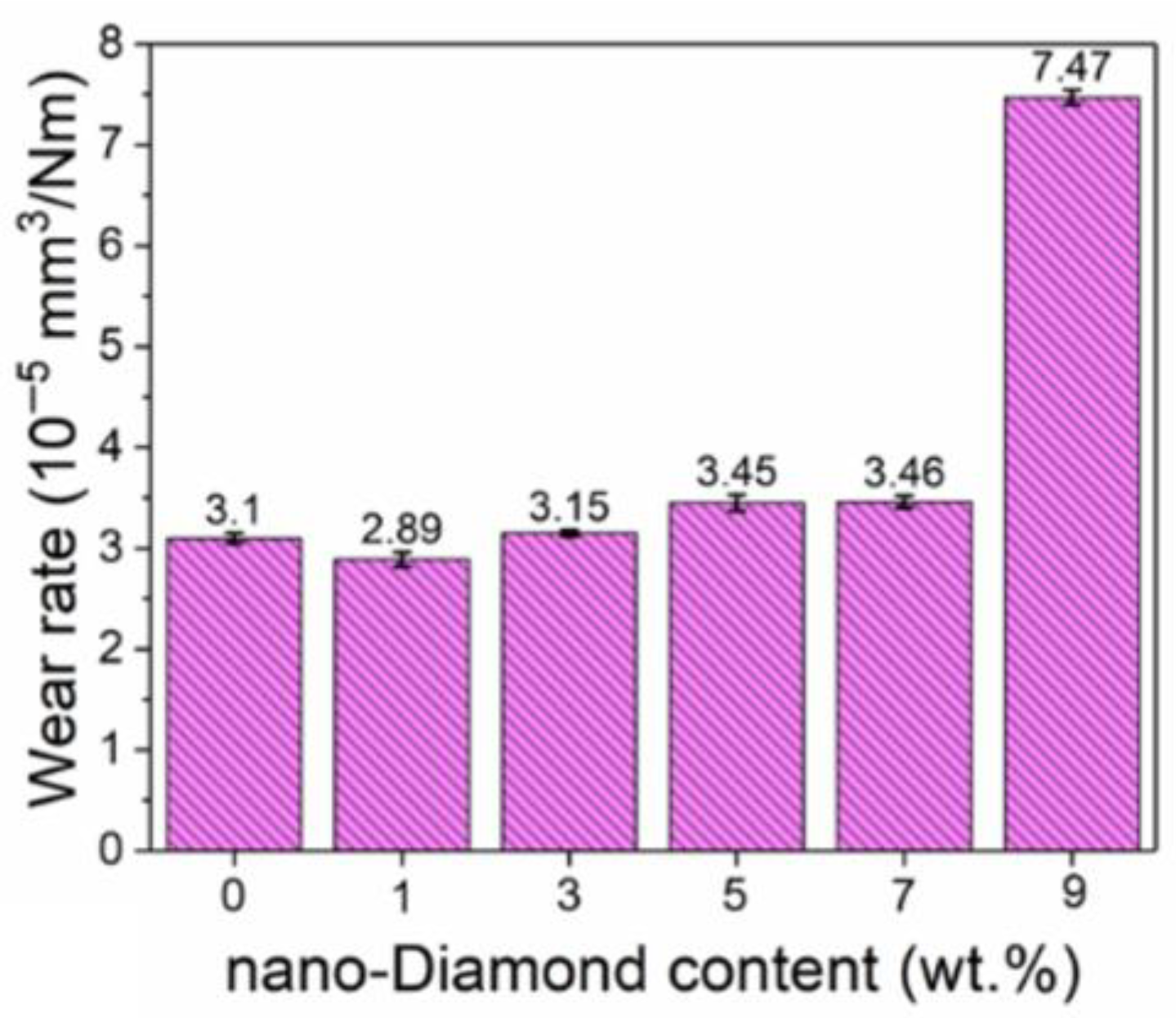
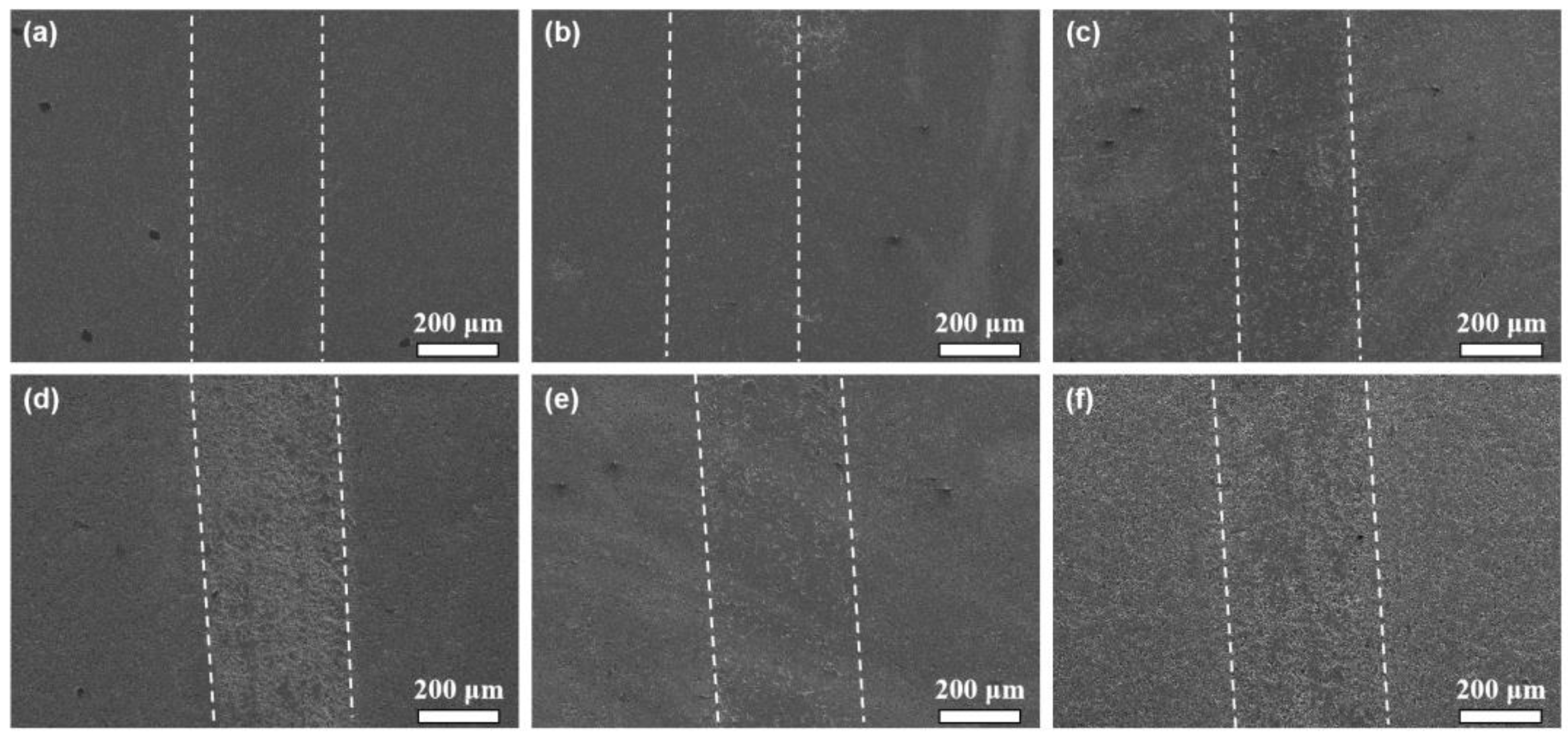
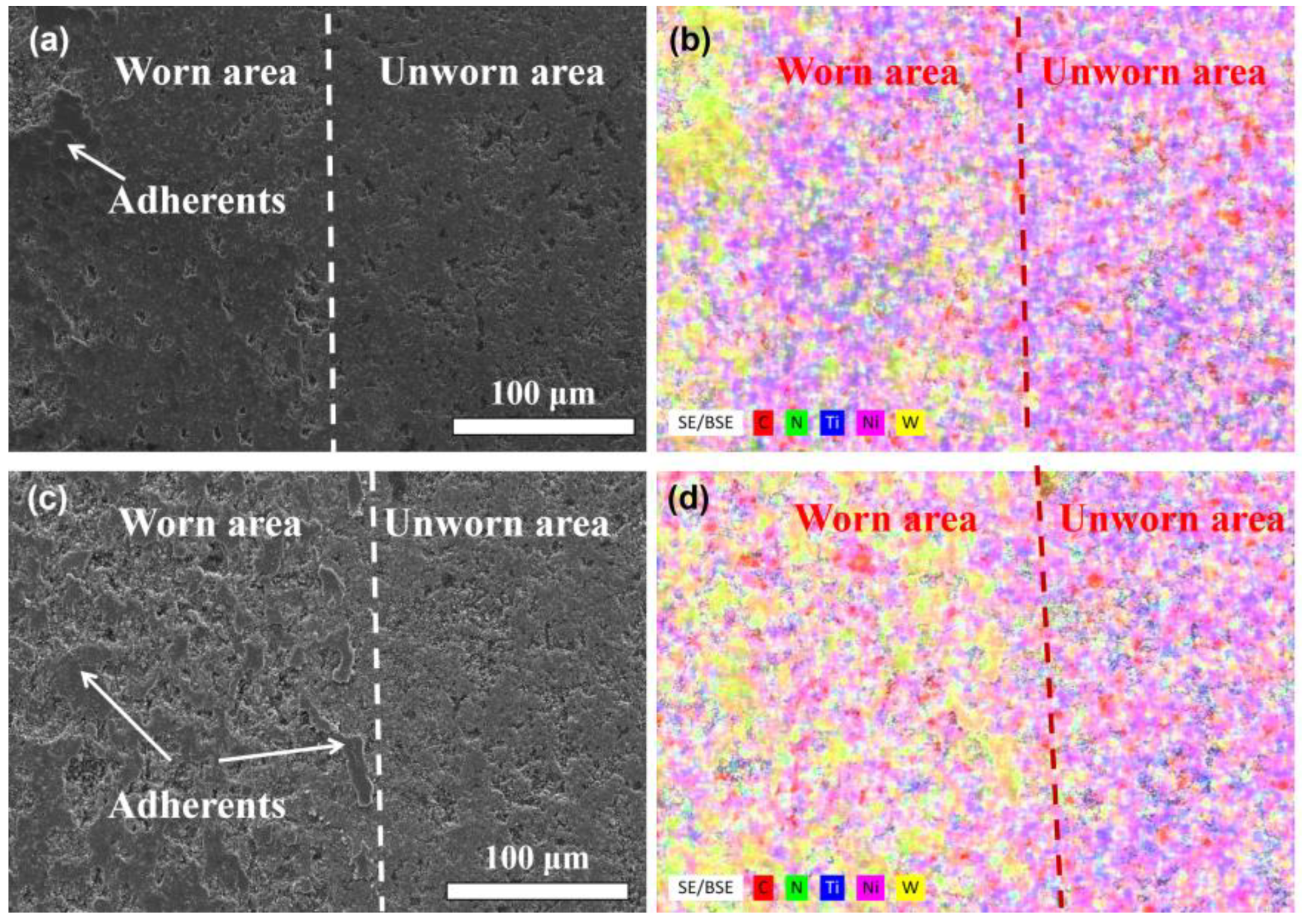
3.2. Tribological Properties
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- During the sintering process, a large fraction of the added nano-diamonds was transformed into graphite. With the increase in the added amount of nano-diamond, the aggregation of the graphite became serious.
- (2)
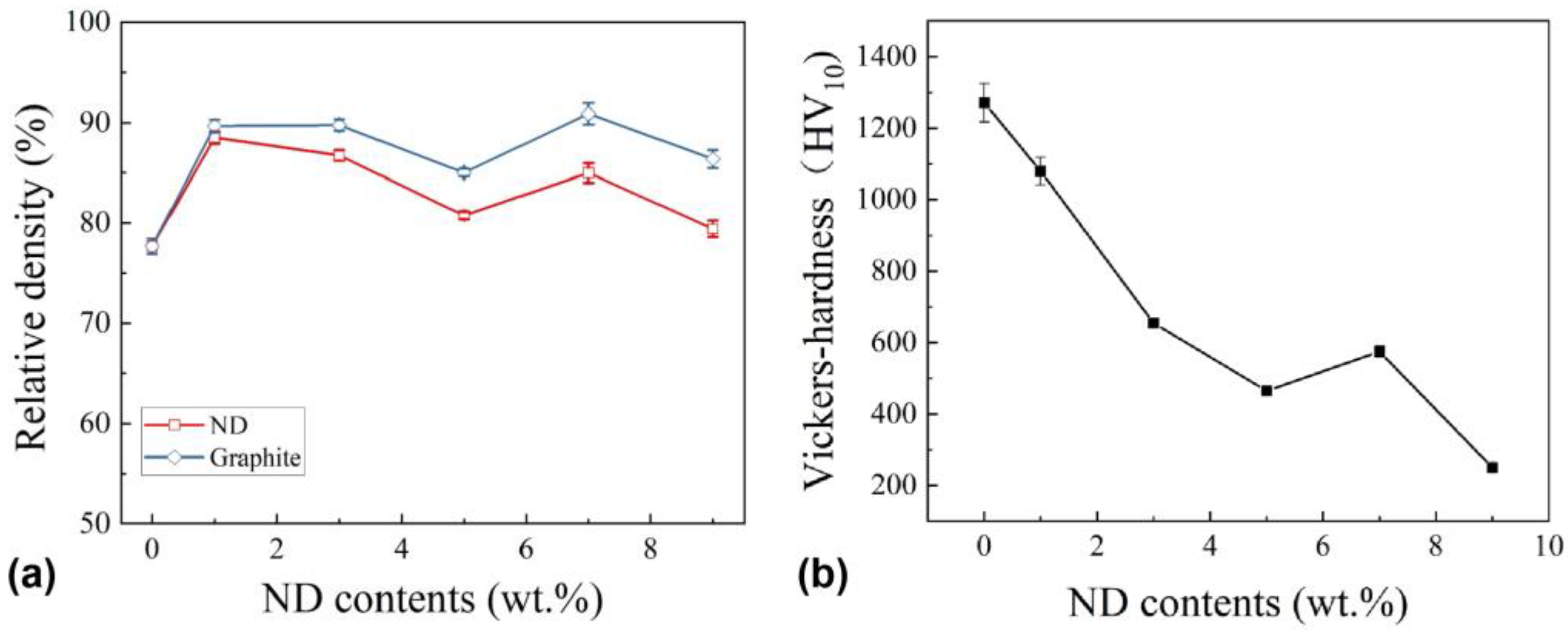
- The relative densities of the added nano-diamond samples were approximately 87%, and the compactness needs to be further improved. The hardness decreases with the increase in the added amount of nano-diamond.
- (3)
- Using Si3N4 as the friction pair, the average coefficient of the friction of the samples ranged from 0.4 to 0.5. The coefficient of friction did not show a significant decrease after adding the nano-diamond. The wear rate of the samples with less than 7 wt.% of added nano-diamond was similar to that of the samples without added nano-diamond. However, when the added amount of nano-diamond was further increased, the wear rate of the samples increased sharply. The graphitization of nano-diamond during sintering is the main cause of the deterioration of the mechanical properties of composite materials.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Peng, Y.; Miao, H.; Peng, Z. Development of TiCN-based cermets: Mechanical properties and wear mechanism. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 2013, 39, 78–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, J.; Lu, J.; Wang, J.; Yang, S. Tribological behavior of TiCN-based cermets at elevated temperatures. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2006, 418, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Yan, H.; Zhang, X.; Tang, S. Properties of titanium carbonitride matrix cermets. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 2006, 24, 236–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Ye, J.; Ying, L.; Yang, D.; Yu, H. Study on the Formation of Core–Rim Structure in Ti(CN)-Based Cermets. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard 2012, 35, 27–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sembulingam, S.S.; Soundaraj, P.V.; Shanmugavel, B.P. Enhanced thermal stability and wear resistance of TiCN-SiC-TiN-Cr3C2-Co cermet modified by B4C for cutting tool application. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 2020, 93, 105352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Zhang, M.; Cao, M.; Zhang, W.; Wang, F.; Liu, H. Effect of Co content on microstructure and properties of TiCN-TiB2 cermets prepared by spark plasma sintering from a TiCN-B4C-Ti-Co system. Ceram. Int. 2025, 51, 1782–1792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angerer, P.; Yu, L.; Khor, K.A.; Korb, G.; Zalite, I. Spark-plasma-sintering (SPS) of nanostructured titanium carbonitride powders. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2005, 25, 1919–1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagos, M.A.; Agote, I.; Atxaga, G.; Adarraga, O.; Pambaguian, L. Fabrication and characterisation of titanium matrix composites obtained using a combination of self propagating high temperature synthesis and spark plasma sintering. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2016, 655, 44–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joardar, J.; Kim, S.W.; Kang, S. Effect of nanocrystalline binder on the microstructure and mechanical properties of ultrafine Ti(CN) cermets. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2003, 360, 385–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Zhuang, Q.; Lin, N.; He, Y. Improvement in microstructure and mechanical properties of Ti(C,N)-Fe cermets with the carbon additions. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 701, 408–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, S.Y.; Kang, S. Formation of core/rim structures in Ti(C,N)-WC-Ni cermets via a dissolution and precipitation process. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2010, 83, 1489–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Archana, M.S.; Srikanth, V.S.; Joshi, S.V.; Joardar, J. Influence of applied pressure during field-assisted sintering of Ti(C,N)-WC-FeAl based nanocomposite. Ceram. Int. 2015, 41, 1986–1993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, M.; Wan, W.; Guo, Z.; Xiong, J.; Dong, G.; Zheng, X.; Chen, Y.; Liu, P. Erosion–corrosion behavior of Ti(C,N)-based cermets with different TiN contents. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 2014, 43, 322–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, X.; Nan, L.; He, Y.; Zhang, M. Influence of ZrC addition on the microstructure, mechanical properties and oxidation resistance of Ti(C,N)-based cermets. Ceram. Int. 2018, 4, 11151–11159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Zheng, Y.; Ke, Z.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, Y.; Lu, X. Effect of WC content on the microstructure and mechanical properties of Ti (C,N)-based cermets fabricated by in situ carbothermal reduction of TiO2. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2019, 761, 138024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, W.; Xiong, J.; Yang, M.; Guo, Z.; Dong, G.; Yi, C. Effects of Cr3C2 addition on the corrosion behavior of Ti(C, N)-based cermets. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 2012, 31, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Lin, N.; He, Y. Influence of Mo2C and TaC additions on the microstructure and mechanical properties of Ti(C, N)-based cermets. Ceram. Int. 2016, 42, 3569–3574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Liu, N.; Zhang, X.; Rong, C. Effect of WC content on the microstructure and mechanical properties of (Ti,W)(C,N)–Co cermets. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 2008, 26, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Liu, Y.; Feng, Y.; Ye, J.; Tu, M. Effect of NbC on the microstructure and sinterability of Ti(C0.7N0.3)-based cermets. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 2009, 27, 549–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Liu, Z.; Lu, J.; Shen, X.; Wang, F.; Wang, Y. The sintering mechanism in spark plasma sintering proof of the occurrence of spark discharge. Scr. Mater. 2014, 81, 56–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shankar, E.; Prabu, S.B.; Padmanabhan, K.A. Mechanical properties and microstructures of TiCN/nano-TiB2/TiN cermets prepared by spark plasma sintering. Ceram. Int. 2018, 44, 9384–9394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Zheng, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Ma, Y.; Xiong, W. Microstructure characterization and mechanical properties of Ti(C, N)-based cermets with AlN addition. Ceram. Int. 2015, 41, 5010–5016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Liu, Y.; Jin, Y.; Ye, J. Effect of secondary carbides addition on the microstructure and mechanical properties of (Ti,W,Mo,V)(C,N)-based cermets. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 2011, 29, 586–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Liu, S.; Zhao, P.; Liu, T.; Sun, J. Titanium/nanodiamond nanocomposites: Effect of nanodiamond on microstructure and mechanical properties of titanium. Mater. Des. 2017, 131, 144–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saba, F.; Zhang, F.; Liu, S.; Liu, T. Tribological properties, thermal conductivity and corrosion resistance of titanium/nanodiamond nanocomposites. Compos. Commun. 2018, 10, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, X.; She, D.; Peng, Z. Fabrication of diamond enhanced WC-Ni composites by spark plasma sintering. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 2022, 102, 105732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.; Liu, S.C.; Jiang, X.R. Effect of multi-walled carbon nanotube addition on the microstructures and mechanical properties of Ti(C,N)-based cermets. J. Adv. Ceram. 2018, 7, 58–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Zhang, Z.; Sun, Y.; Liu, Y.; Hu, Z.; Wang, H.; Korznikov, A.V.; Korznikova, E.; Liu, Z.; Osamu, S. Rapid and low temperature spark plasma sintering synthesis of novel carbon nanotube reinforced titanium matrix composites. Carbon 2015, 95, 396–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munir, K.S.; Zheng, Y.; Zhang, D.; Lin, J.; Li, Y.; Wen, C. Microstructure and mechanical properties of carbon nanotubes reinforced titanium matrix composites fabricated via spark plasma sintering. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2017, 688, 505–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Yun, Q.; Chen, C. Substrate modification for high performance CrAl/CrAlBN multilayers coated TiCN-based cermet through plasma nitriding. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 2025, 126, 106930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Zhang, M.; Cao, M. In-situ fabrication TiB2 reinforced TiCN-based cermets from TiCN-B4C-Ti-Co system by spark plasma sintering. Ceram. Int. 2024, 50, 33018–33026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Cermets | TiCN | WC | Ni | Nano-Diamond |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0% | 60 | 20 | 20 | - |
| 1% | 59 | 20 | 20 | 1 |
| 3% | 57 | 20 | 20 | 3 |
| 5% | 55 | 20 | 20 | 5 |
| 7% | 53 | 20 | 20 | 7 |
| 9% | 51 | 20 | 20 | 9 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ren, X.; Leng, X.; Deng, H.; Yin, G. Fabrication and Wear Behavior of TiCN-Based Cermets with Nano-Diamond Addition. Materials 2025, 18, 5448. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18235448
Ren X, Leng X, Deng H, Yin G. Fabrication and Wear Behavior of TiCN-Based Cermets with Nano-Diamond Addition. Materials. 2025; 18(23):5448. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18235448
Chicago/Turabian StyleRen, Xiaoyong, Xuyang Leng, Hong Deng, and Guangxuan Yin. 2025. "Fabrication and Wear Behavior of TiCN-Based Cermets with Nano-Diamond Addition" Materials 18, no. 23: 5448. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18235448
APA StyleRen, X., Leng, X., Deng, H., & Yin, G. (2025). Fabrication and Wear Behavior of TiCN-Based Cermets with Nano-Diamond Addition. Materials, 18(23), 5448. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18235448








