Atomic-Scale Fabrication of Micro/Nano Fe-Cu Galvanic Couples for Efficient Phenol Degradation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
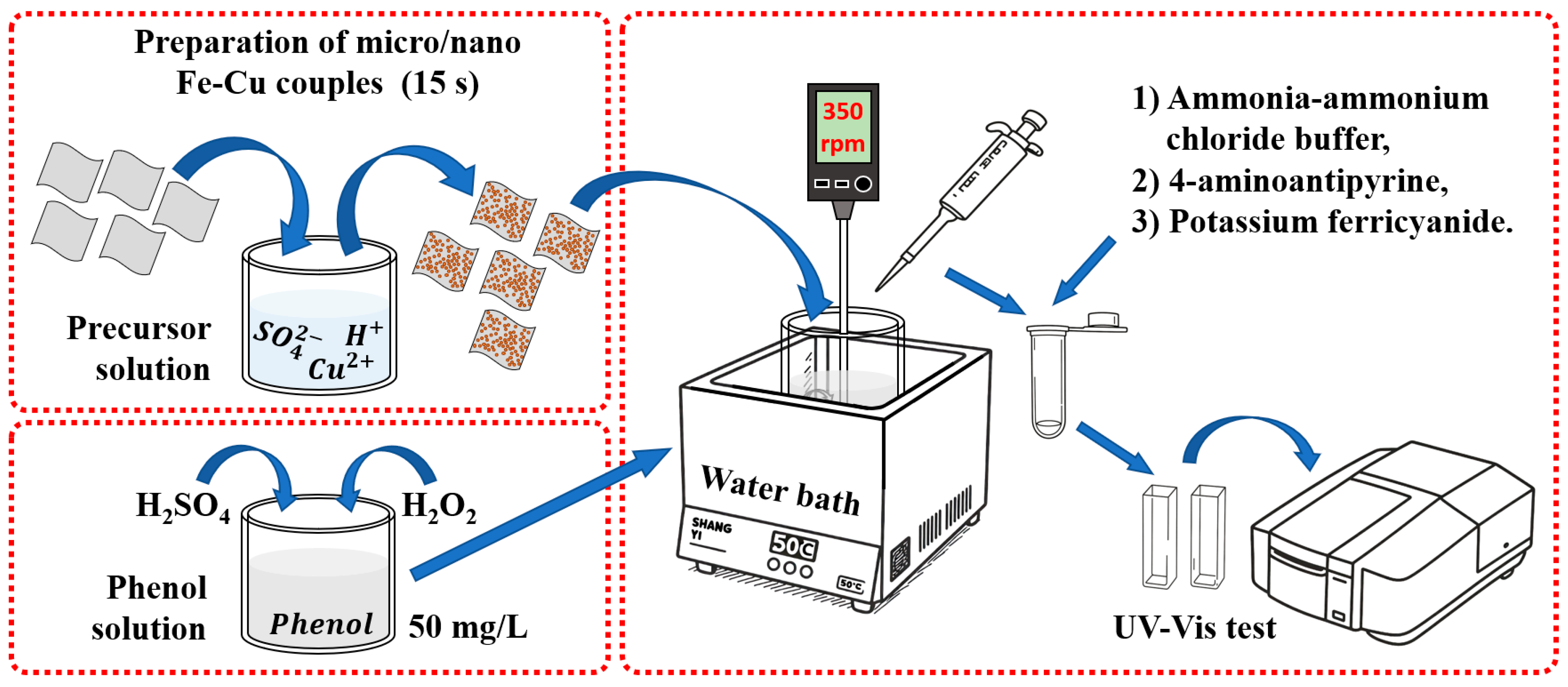
2.1. Materials and Fabrication of Micro/Nano Fe-Cu Couples
2.2. Microstructure Characterization
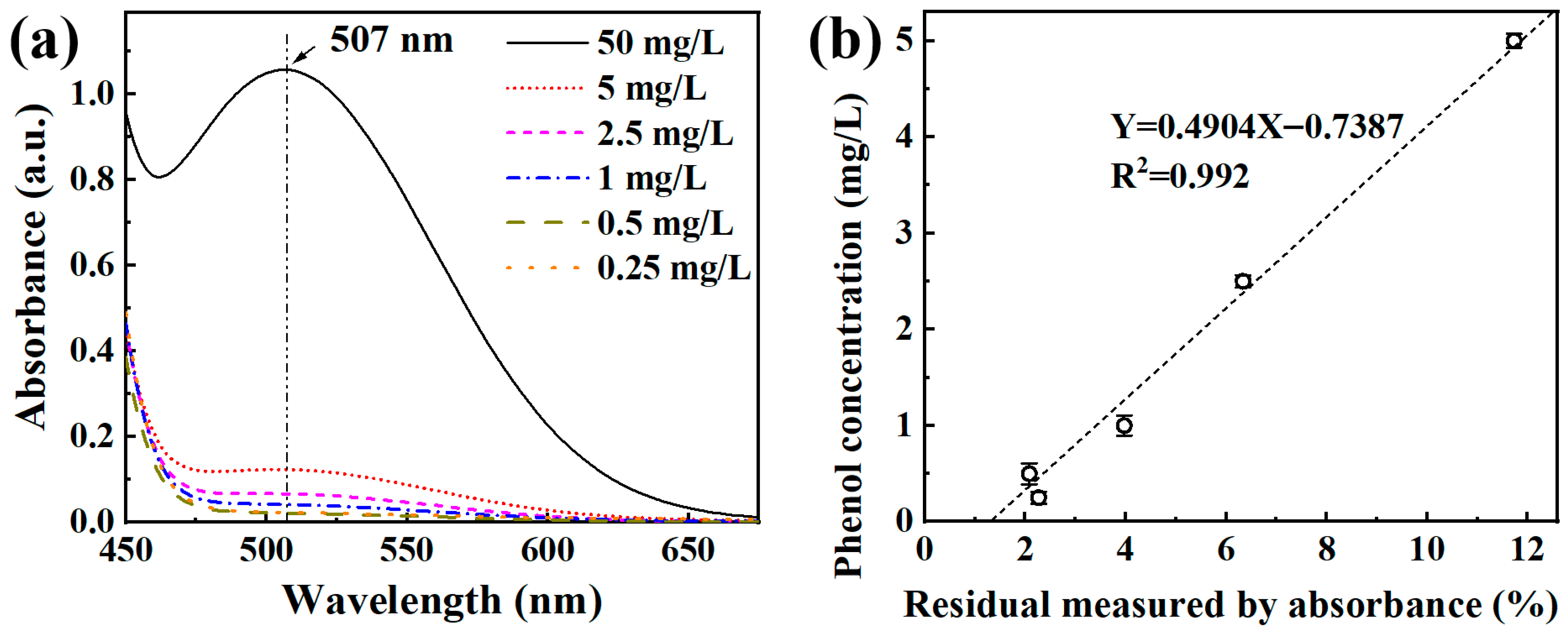
2.3. Phenol Degradation Experiments
3. Results
3.1. The Intrinsic Catalytic Performance of Fe73.5Si13.5B9Cu1Nb3
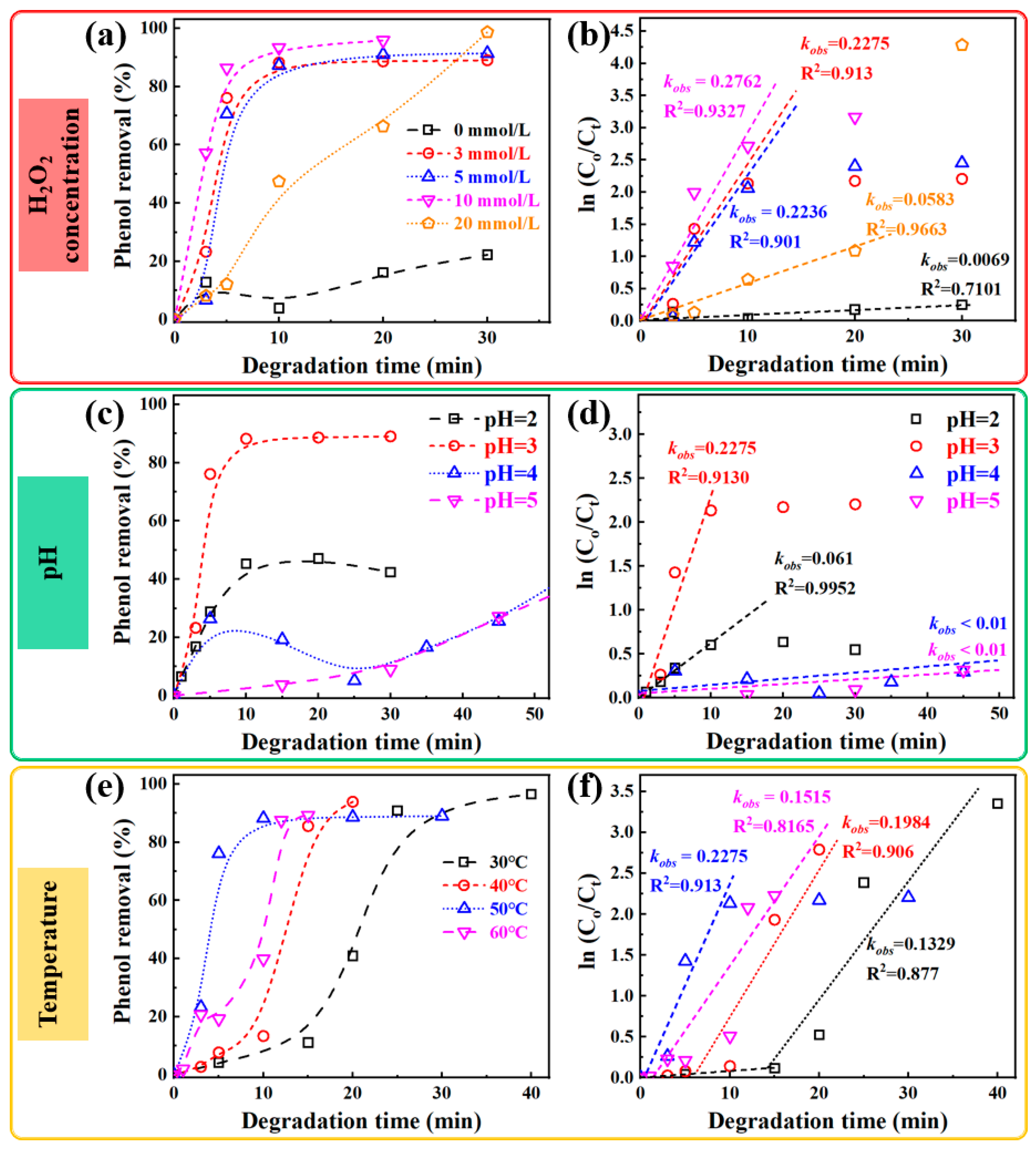
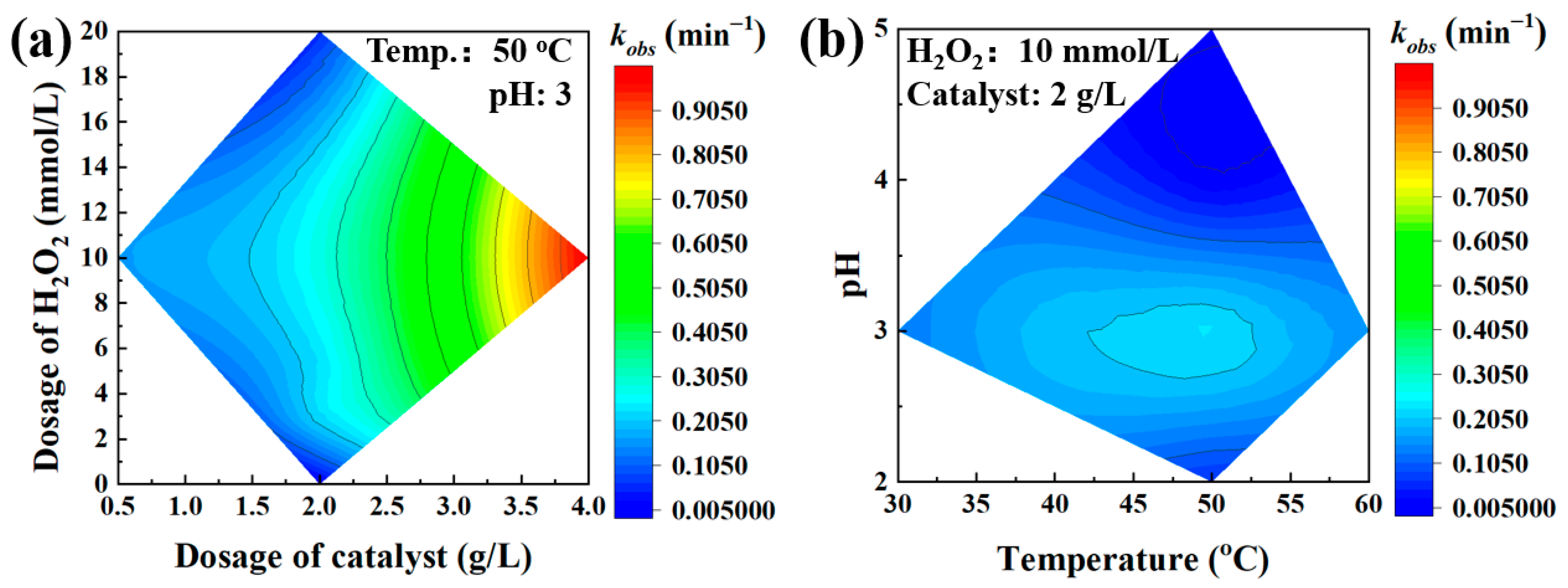
3.2. The Effect of Environmental Factors on Degradation of Phenol
- Effect of H2O2 concentration on phenol degradation
- Effect of pH on phenol degradation
- Effect of reaction temperature on phenol degradation
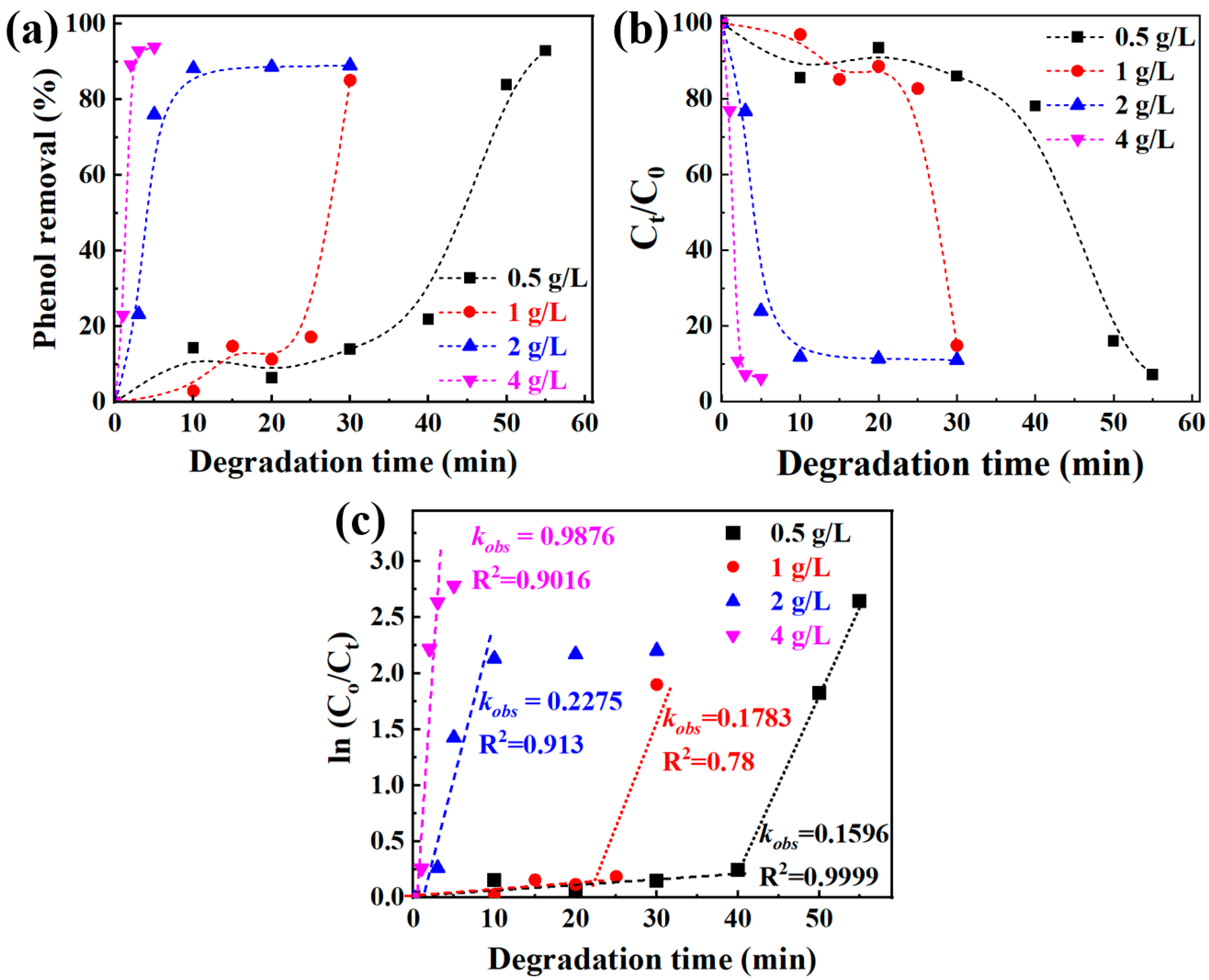
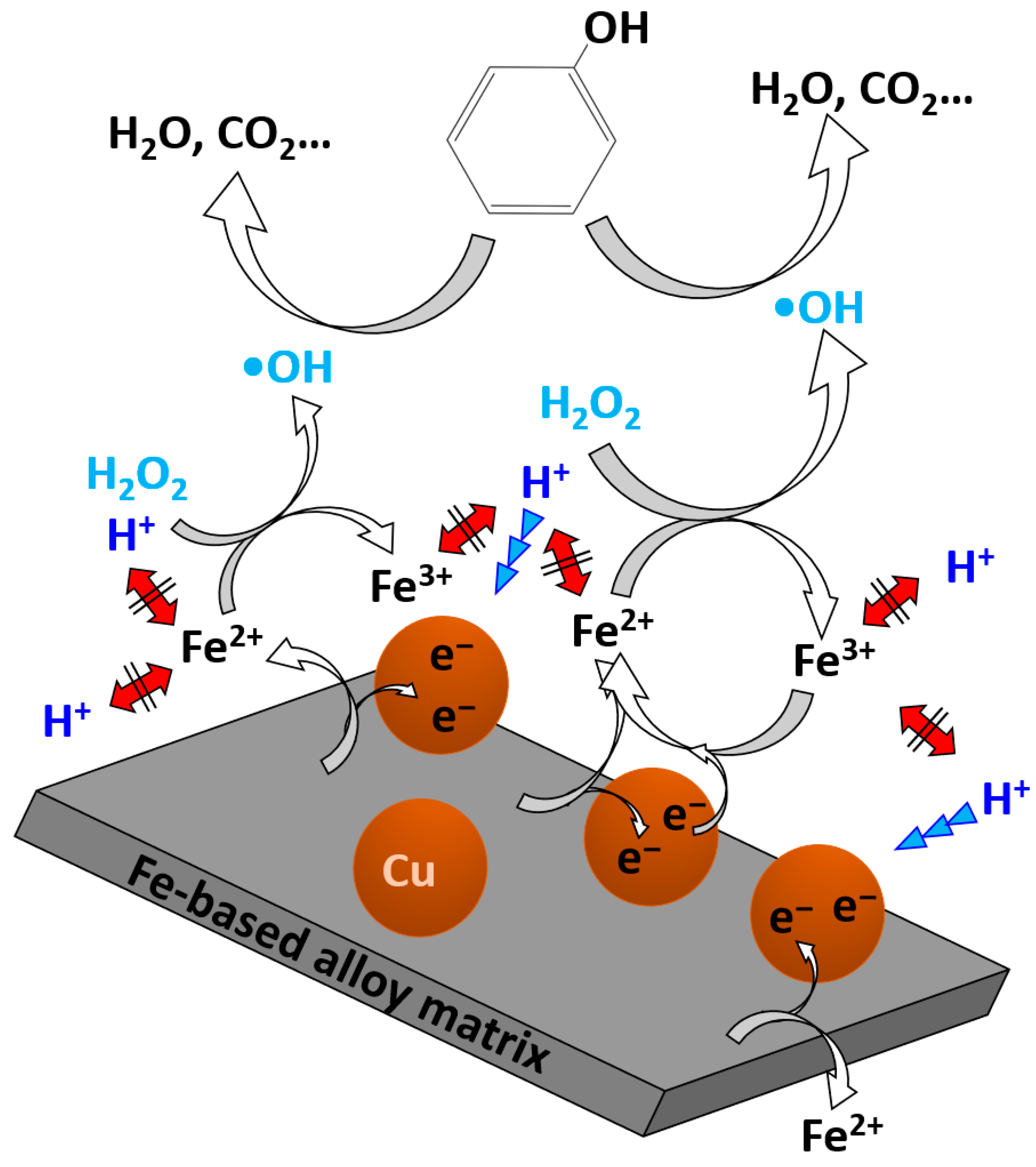
3.3. The Fabrication of Micro/Nano Fe-Cu Galvanic Couples and Its Effect on Phenol Degradation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tang, Y.; Zhong, G.; Li, X.; Gao, X.; Zhu, W.; Luo, Y. Synthesis of low-cost Fe/C catalysts from cold-rolled sludge for efficient phenol degradation via peroxodisulfate activation. J. Water Process Eng. 2025, 74, 107843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Li, M.; Wu, Y.; Zhao, N.; Jin, Z. A novel palladium decorated graphdiyne regulating d band center enhanced the ability of square meter scale and coal chemical wastewater for efficient hydrogen production. Appl. Catal. B Environ. Energy 2024, 359, 124488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, S.C.; Li, L.; Huang, G.X.; Pan, X.Q.; Yu, H.Q. Heterogeneous Fenton water purification catalyzed by iron phosphide (FeP). Water Res. 2023, 241, 120151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Hu, C.; Meng, X.; Sun, Y.; Zhao, B.; Lin, Z. Metal covalent organic frameworks-based laccase-like nanozyme for oxidative degradation and identification of phenolic pollutants. J. Hazard. Mater. 2025, 487, 137142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Liu, H.S.; Zhang, X.; Ma, L.; Yang, W.M. Simultaneously improved kinetic rate and reusability in phenol degradation by laser processing on Fe-based amorphous ribbon. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2025, 669, 123812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Dai, Y.; Wang, H.; Miao, S.; Deng, Z.; Yin, L. Activation of peroxymonosulfate by Fe based metal organic framework for selective degradation of phenol in water. J. Water Process Eng. 2024, 68, 106454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mihaylova, D.; Dimitrova-Dimova, M.; Popova, A. Dietary Phenolic compounds—Wellbeing and perspective applications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 4769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, B.; Zhang, S.; Jin, X.; Huang, H.; Du, Y.; Pan, C.; Song, H.; Gai, H. Review on progress of phenols−ammonia recovery process in coal chemical wastewater. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2025, 223, 115979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, Y.; Cheng, H.; Sun, D.W.; Huang, L.; He, Q.; Shi, B. Food nanozymology: Nanozyme engineering toward future food. Adv. Mater. 2025, 37, 2505552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Guo, X.; Yang, H.; Zhang, D.; Jiang, X. Construction of bio-TiO2/algae complex and synergetic mechanism of the acceleration of phenol biodegradation. Materials 2023, 16, 3882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathee, P.; Sehrawat, R.; Rathee, P.; Khatkar, A.; Akkol, E.K.; Khatkar, S.; Redhu, N.; Türkcanoğlu, G.; Sobarzo-Sánchez, E. Polyphenols: Natural preservatives with promising applications in food, cosmetics and pharma industries; problems and toxicity associated with synthetic preservatives; impact of misleading advertisements; recent trends in preservation and legislation. Materials 2023, 16, 4793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, L.; Li, Y. Organophosphorus pesticides management strategies: Prohibition and restriction multi-category multi-class models, environmental transformation risks, and special attention list. Toxics 2025, 13, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Z.L.; Gao, Y.C.; Qin, B.; Ma, Z.Y.; Yu, S.H. Revitalizing traditional phenolic resin toward a versatile platform for advanced materials. Accounts Mater. Res. 2024, 5, 146–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmaruzzaman, M.; Mishra, S.R.; Gadore, V.; Yadav, G.; Roy, S.; Bhattacharjee, B.; Bhuyan, A.; Hazarika, B.; Darabdhara, J.; Kumari, K. Phenolic compounds in water: From toxicity and source to sustainable solutions—An integrated review of removal methods, advanced technologies, cost analysis, and future prospects. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 112964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Sun, X.; Yang, H.; Cui, J.; Wang, J.; Kang, Y.; Deng, J.; Huang, G. Degradation of aqueous phenol by combined ultraviolet and electrochemical oxidation treatment. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 436, 140672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Li, L. VOC emitted by biopharmaceutical industries: Source profiles, health risks, and secondary pollution. J. Environ. Sci. 2024, 135, 570–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, S.; Jiang, J.; Xiong, K.; Chen, Y.; Yao, Y.; Liu, L.; Liu, H.; Li, X. Enzyme engineering: Performance optimization, novel sources, and applications in the food industry. Food 2024, 13, 3846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Z.; Wang, P.; Liu, X.; Liang, X.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, Z.; Zheng, Z.; Cheng, H.; Liu, Y.; Dai, Y.; et al. Design and synthesis of BiVO4@CuOx as a photo assisted Fenton-like catalyst for efficient degradation of tetracycline. Surf. Interfaces 2021, 26, 101380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valdes, C.; Alzate-Morales, J.; Osorio, E.; Villasenor, J.; Navarro-Retamal, C. A characterization of the two-step reaction mechanism of phenol decomposition by a Fenton reaction. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2015, 640, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalali, H.M. Simulation of degradation of the organic contaminants ethylene glycol and phenol by iron nanoparticles using the kinetic Monte Carlo method. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 32928–32933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.Z.; He, Z.C.; Chen, T.; Yan, A.; Huang, Z.Y.; Yan, Y.Q.; Ke, H.B.; Wang, W.H.; Yang, C. Improved soft magnetic properties of Fe-based amorphous powder cores by softening phenolic resin shell. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2024, 636, 123013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Song, Y.J.; Liu, H.S.; Xiong, X.; Yang, W.M.; Han, C.K. High-temperature oxidation and crystallization mechanism of Fe73.5Si13.5B9Cu1Nb3 amorphous alloy. Acta Phys. Sin. 2025, 74, 088101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.S.; Yang, D.F.; Jiang, Q.; Jiang, Y.Y.; Yang, W.M.; Liu, L.; Zhang, L.C. Additive manufacturing of metallic glasses and high-entropy alloys: Significance, unsettled issues, and future directions. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2023, 140, 79–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Bian, X.F.; Li, Y.X. Catalytic oxidation of phenol in wastewater-a new application of the amorphous Fe78Si9B13 alloy. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2012, 57, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Song, Y.J.; Xiong, X.; Li, Z.Y.; Yang, W.M.; Liu, H.S. A new insight into surface oxidation of Fe-based metallic glass for azo dye degradation. J. Water Process Eng. 2025, 76, 108170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, B.Y.; Zhao, Z.K. Evolution and performance of porous structure on the surface of Fe76Si7.2B9.6P7.2 amorphous ribbon. Mater. Sci. Forum 2017, 898, 653–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Sun, G.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Peng, J.; Jiang, F.; Li, J.; Tao, S.; Liu, Y.; Pan, Y. Structural design of single-atom catalysts for enhancing petrochemical catalytic reaction process. Adv. Mater. 2024, 36, 2313661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, Y.K.; Shaz, M.A.; Mukhopadhyay, N.K.; Yadav, T.P. High entropy alloys synthesized by mechanical alloying: A review. J. Alloys Metall. Syst. 2025, 9, 100170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Yu, X.D.; Liu, H.S.; Yang, W.M.; Xiong, X.; Chen, C.; Xie, Y. Ultrafast degradation of azo dye using surface-activated Fe-based metallic glass. Surf. Interfaces 2025, 59, 105938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, J.; Lu, S.; Luan, H.; Tong, T.; Wang, J.; Xu, G.; Lv, J.; Yao, K. Minor Cu modification endows inactive industrial FeSiBNbCu metallic glass with robust azo dye degradation activity. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2025, 689, 162511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Li, Z.; Song, Y.; Liu, H.; Xiong, X.; Fang, M. Surface modification of FeSi6.5 powders for additively manufactured catalysts with enhanced azo dye degradation. J. Water Process Eng. 2025, 79, 108942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Yan, Z.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, L.C.; Ma, H.; Wang, W.; Wang, W. High MB solution degradation efficiency of FeSiBZr amorphous ribbon with surface tunnels. Materials 2020, 13, 3694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Laat, J.; Gallard, H. Catalytic Decomposition of hydrogen peroxide by Fe(III) in homogeneous aqueous solution: Mechanism and kinetic modeling. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1999, 33, 2726–2732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anikin, O.V.; Bolotov, A.V.; Minkhanov, I.F.; Varfolomeev, M.A.; Tazeev, A.R. Factors influencing hydrogen peroxide decomposition dynamics for thermochemical treatment of bottomhole zone. J. Pet. Explor. Prod. Technol. 2022, 12, 2587–2598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Yang, S.; Li, Q.; Wang, M.; Xue, Y.; Zhao, D. Iron (II) sulfate crystals assisted mechanochemical modification of microscale zero-valent aluminum (mZVAl) for oxidative degradation of phenol in water. Chemosphere 2021, 274, 129767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Wang, P.; Bian, X. Phenol degradation property of Fe-based amorphous alloys with different composition. In Proceedings of the 2013 International Conference on Materials for Renewable Energy and Environment, Chengdu, China, 19–21 August 2013; Volume 2, pp. 621–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, J.; Lin, H.; Wang, L.; Xu, J. Synergistic Fe single-atom/amorphous Fe oxide on carbon nitride directs efficient peroxymonosulfate activation for non-radical phenolic pollutants degradation. Chem. Eng. J. 2025, 526, 170915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, B.; Cui, Y.; Du, Y.; Yu, Z.; Zhang, L.; Ning, Z.; Sun, X.; Li, J.; Tang, X.; et al. Catalytic mechanism of nanocrystalline and amorphous matrix in Fe-based microwires for advanced oxidation. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2025, 35, 2425912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

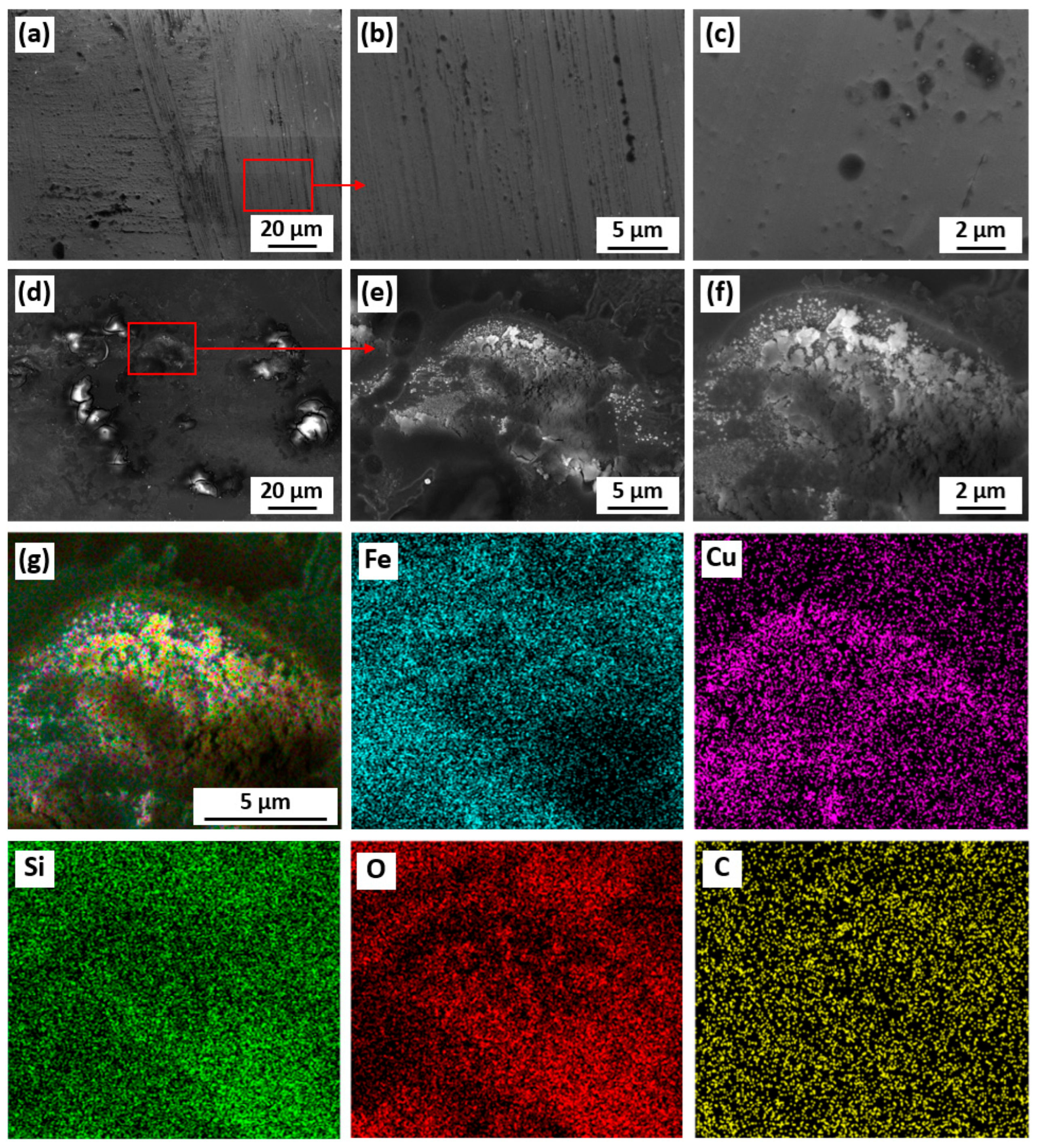
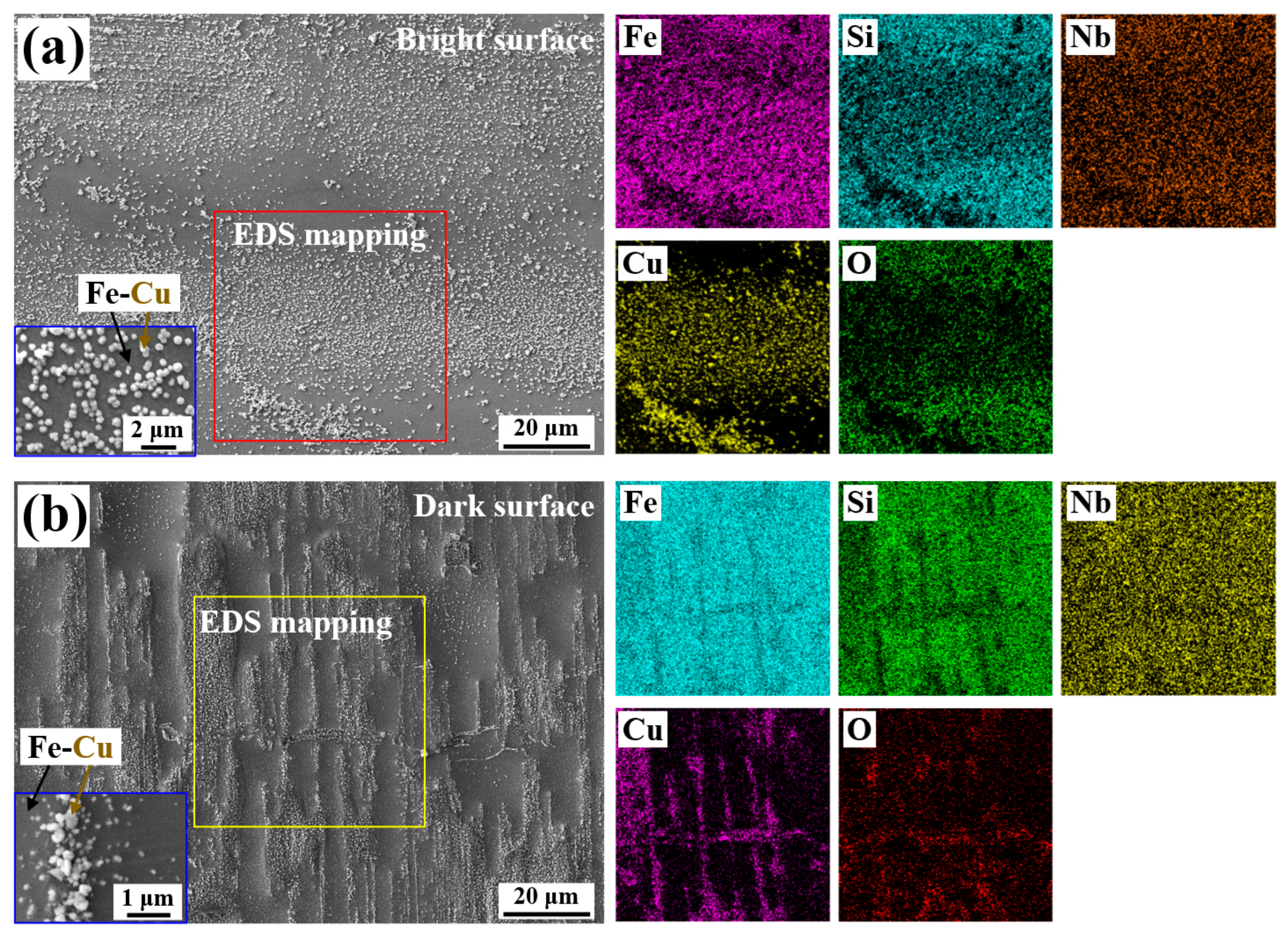


| Elements (at. %) | Fe | Si | B | Cu | Nb | O | C | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fe-Si-B-Cu-Nb | Before degradation | 84.05 | 8.85 | 0 | 1.97 | 5.13 | - | - |
| After degradation | 41.92 | 11.97 | 5.53 | 8.06 | 0.28 | 16.2 | 0.29 |
| Catalysts | Organic Conc. (mg/L) | Catalyst Dosage (g/L) | pH | Kobs (min−1) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fe-mZVAlbm | 20 | 3 | 2.5 | 0.04 | [35] |
| Fe73.5Si13.5B9Cu1Nb3 | 1000 | - | - | 0.05287 | [36] |
| Fe78Si9B13 | 1000 | - | - | 0.33173 | [36] |
| Fe78Si9B13 | 50 | 0.5 | 3 | 0.643 | [5] |
| Laser processed Fe78Si9B13 | 50 | 0.5 | 3 | 0.821 | [5] |
| Fe and FeOx | 20 (p-chlorophenol) | 0.2 | 5.6 | 0.268 | [37] |
| Fe78Si9B13 microwires | 25 (Rhodamine B) | 0.5 | 3 | ~3.7 | [38] |
| Surface activated Fe73.5Si13.5B9Cu1Nb3 | 20 (Orange II) | 0.5 | 3 | 1.4–3.2 | [29] |
| Fe73.5Si13.5B9Cu1Nb3 powder/Cu | 20 (Orange II) | 5 | 6.2 | ~0.0698 | [30] |
| Pure Fe | 50 | 0.5 | 3 | 0.30 | This work |
| Fe73.5Si13.5B9Cu1Nb3 | 50 | 0.5 | 3 | 0.16–0.24 | |
| Pure Fe with Fe-Cu couples | 50 | 0.5 | 3 | 1.4–1.56 | |
| Fe73.5Si13.5B9Cu1Nb3 with Fe-Cu couples | 50 | 0.5 | 3 | 0.94–2.36 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, X.; Yu, X.; Li, Z.; Liu, H.; Xiong, X.; Chen, C.; Yang, W. Atomic-Scale Fabrication of Micro/Nano Fe-Cu Galvanic Couples for Efficient Phenol Degradation. Materials 2025, 18, 5362. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18235362
Zhang X, Yu X, Li Z, Liu H, Xiong X, Chen C, Yang W. Atomic-Scale Fabrication of Micro/Nano Fe-Cu Galvanic Couples for Efficient Phenol Degradation. Materials. 2025; 18(23):5362. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18235362
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Xiang, Xiudong Yu, Zhaoyang Li, Haishun Liu, Xiang Xiong, Changjiu Chen, and Weiming Yang. 2025. "Atomic-Scale Fabrication of Micro/Nano Fe-Cu Galvanic Couples for Efficient Phenol Degradation" Materials 18, no. 23: 5362. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18235362
APA StyleZhang, X., Yu, X., Li, Z., Liu, H., Xiong, X., Chen, C., & Yang, W. (2025). Atomic-Scale Fabrication of Micro/Nano Fe-Cu Galvanic Couples for Efficient Phenol Degradation. Materials, 18(23), 5362. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18235362








