Comparative Study on Intermediate-Temperature Deformation Mechanisms of Inconel 718 Alloys Fabricated by Additive Manufacturing and Conventional Forging
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Sample Preparation and Heat Treatment
2.3. Microstructure and Property Testing
3. Experimental Results and Discussions
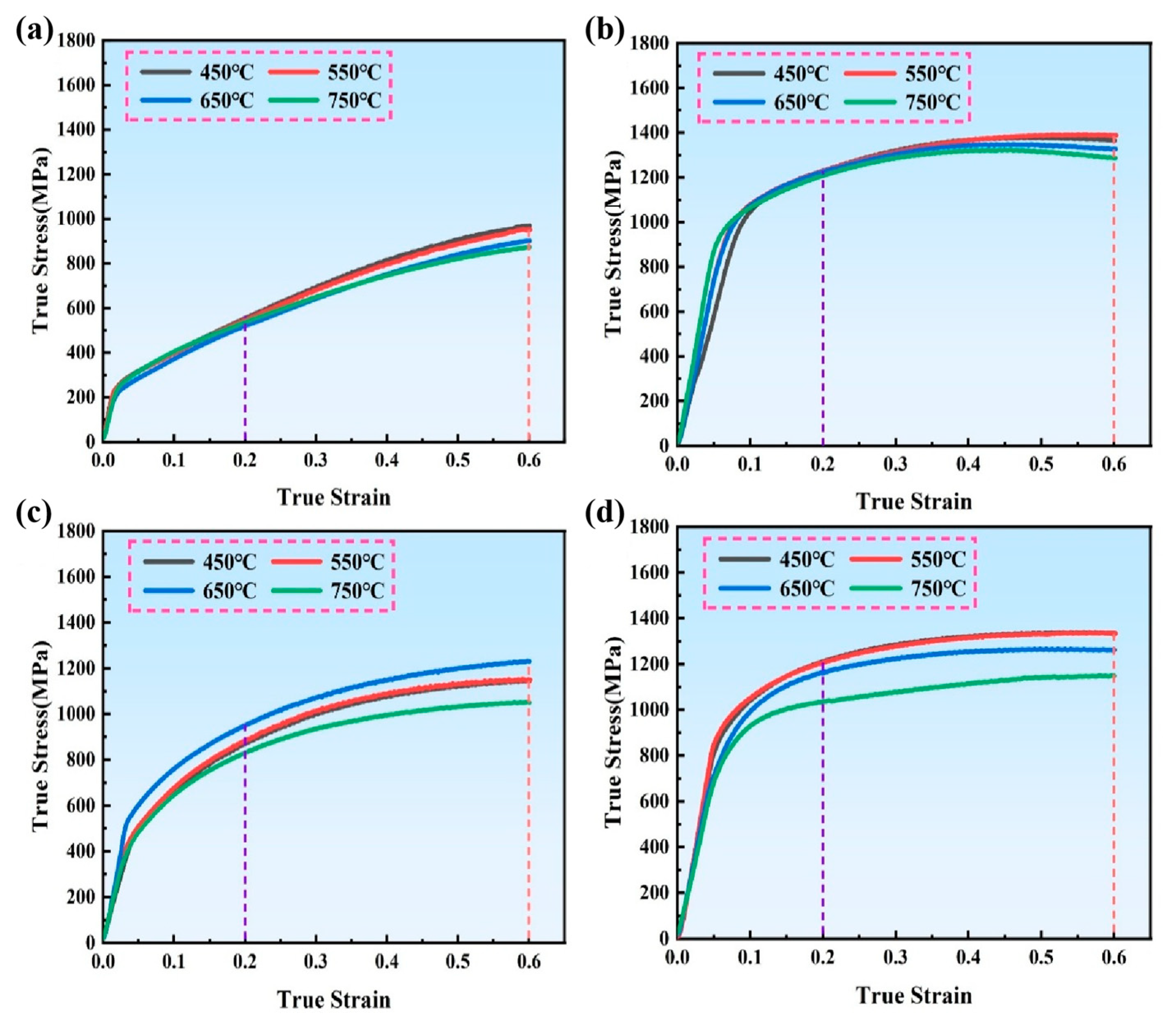
3.1. Mechanical Behaviors Under Different Deformation Conditions
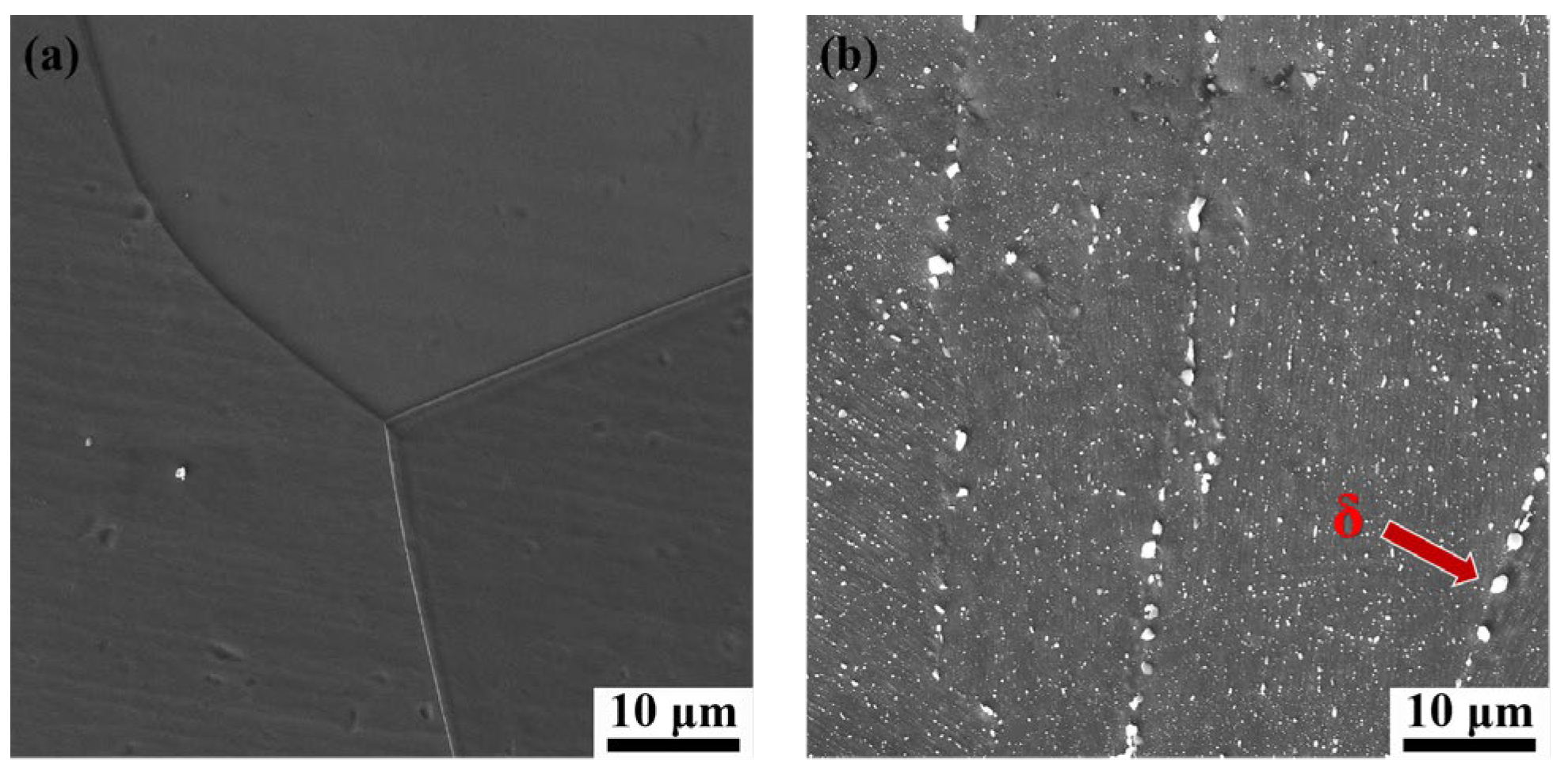
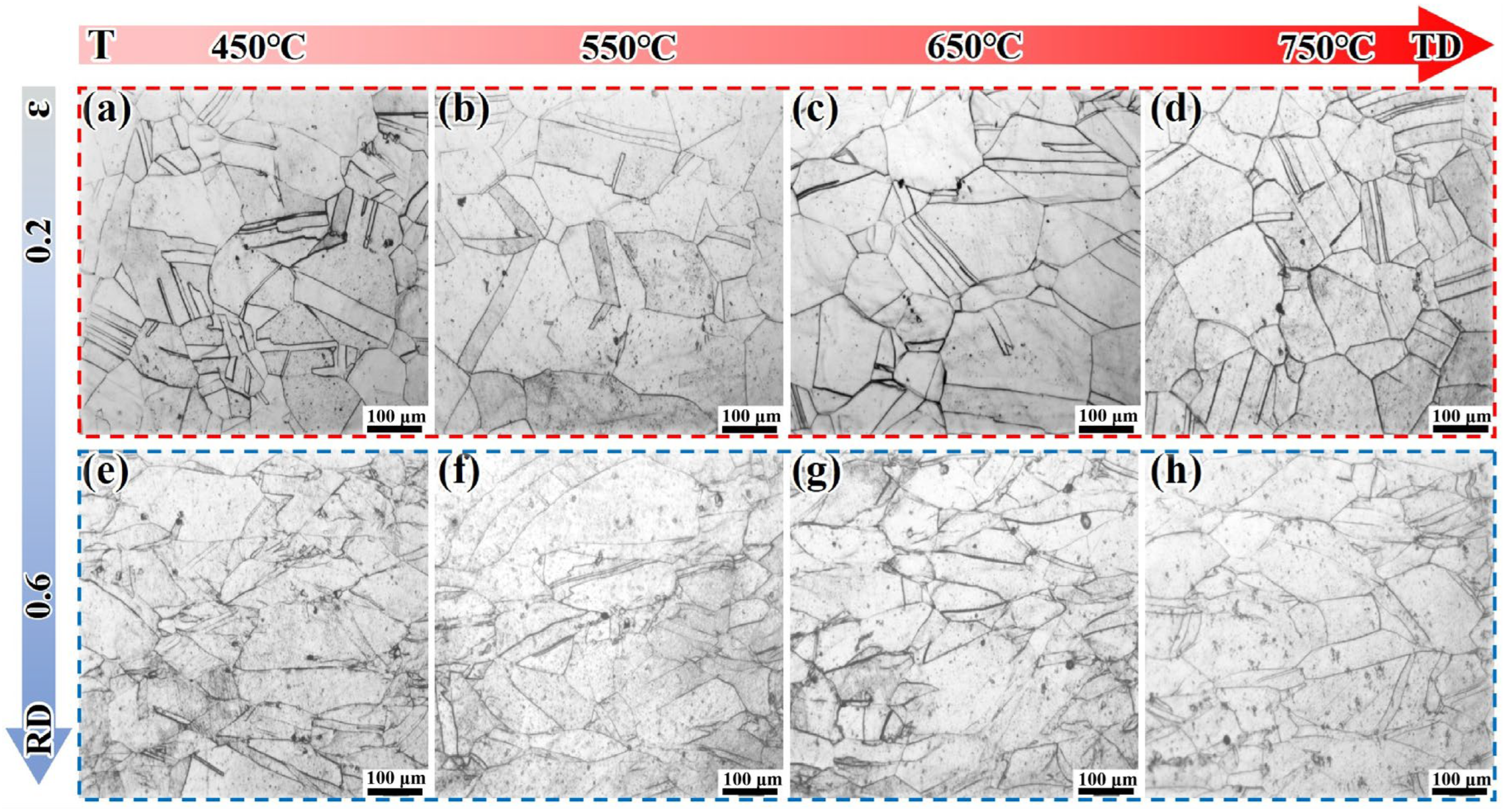
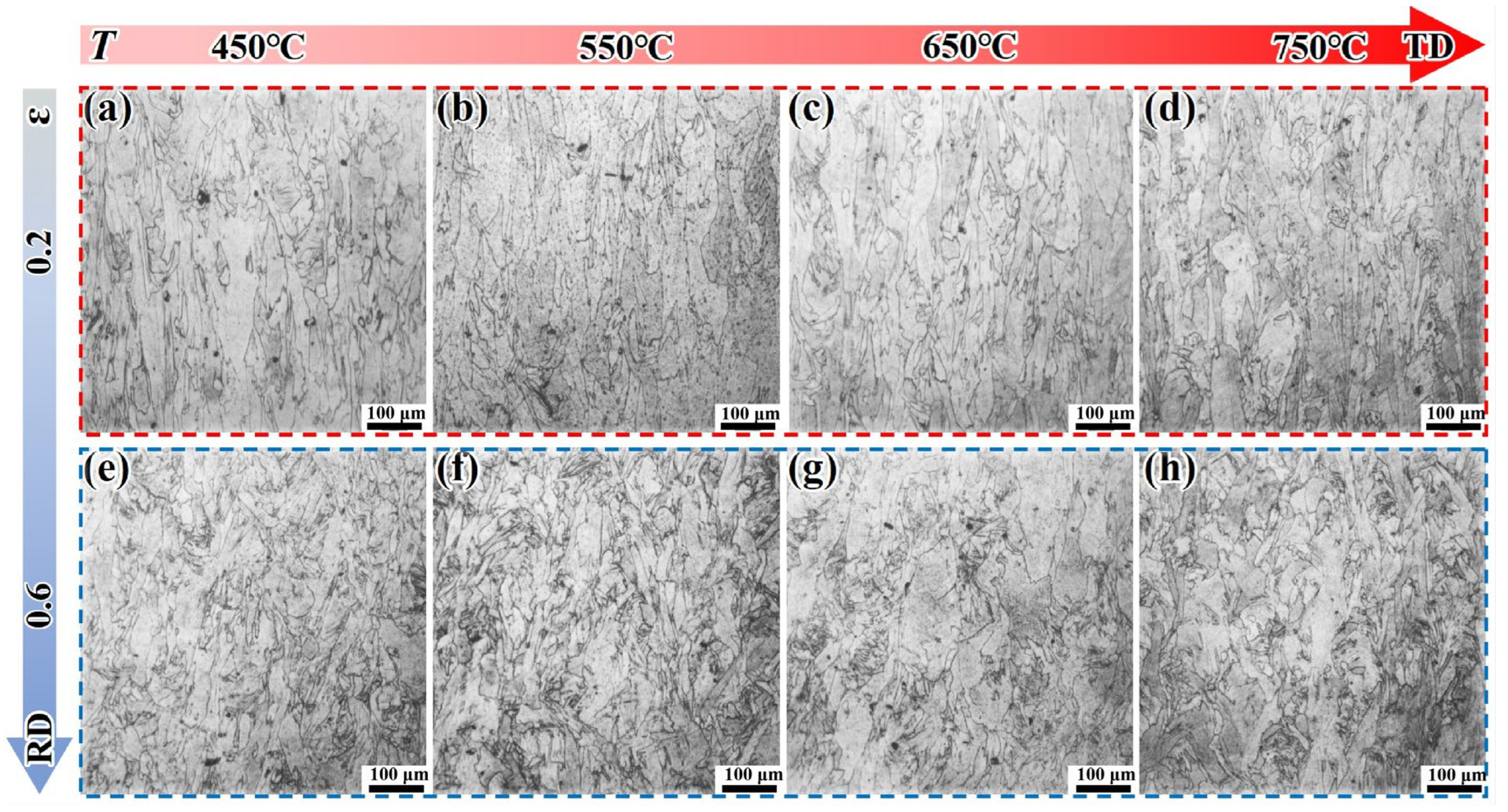
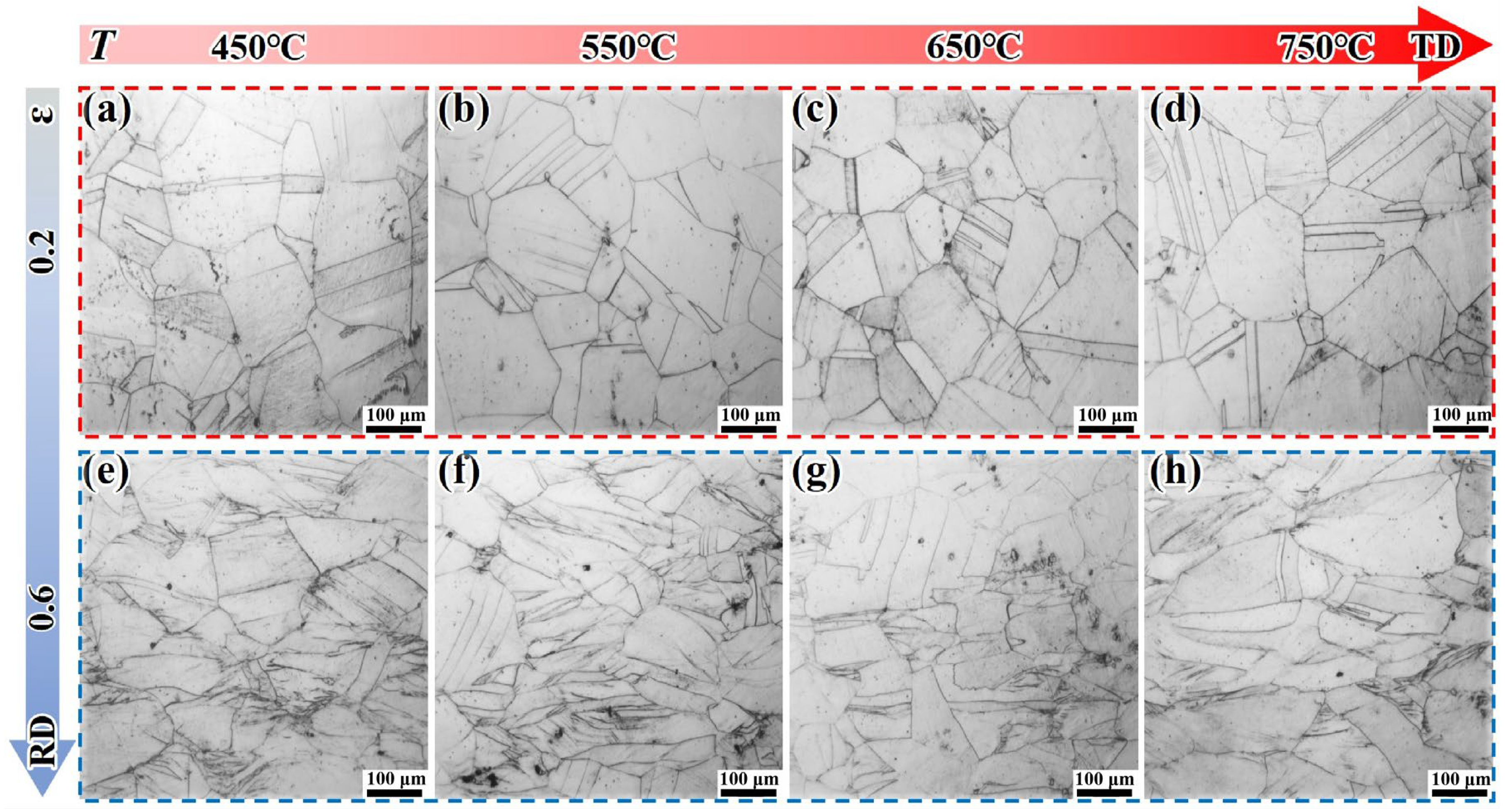
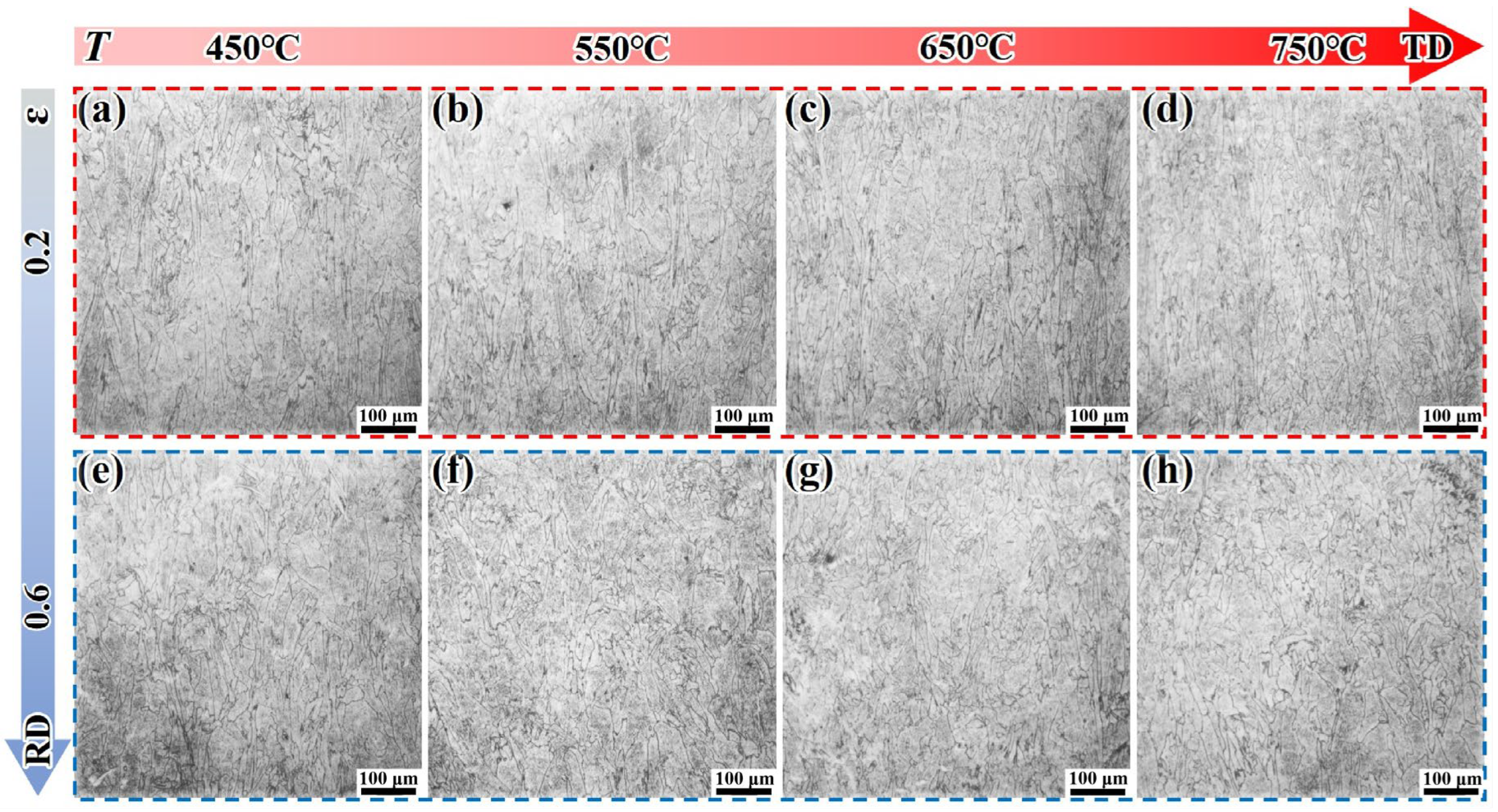
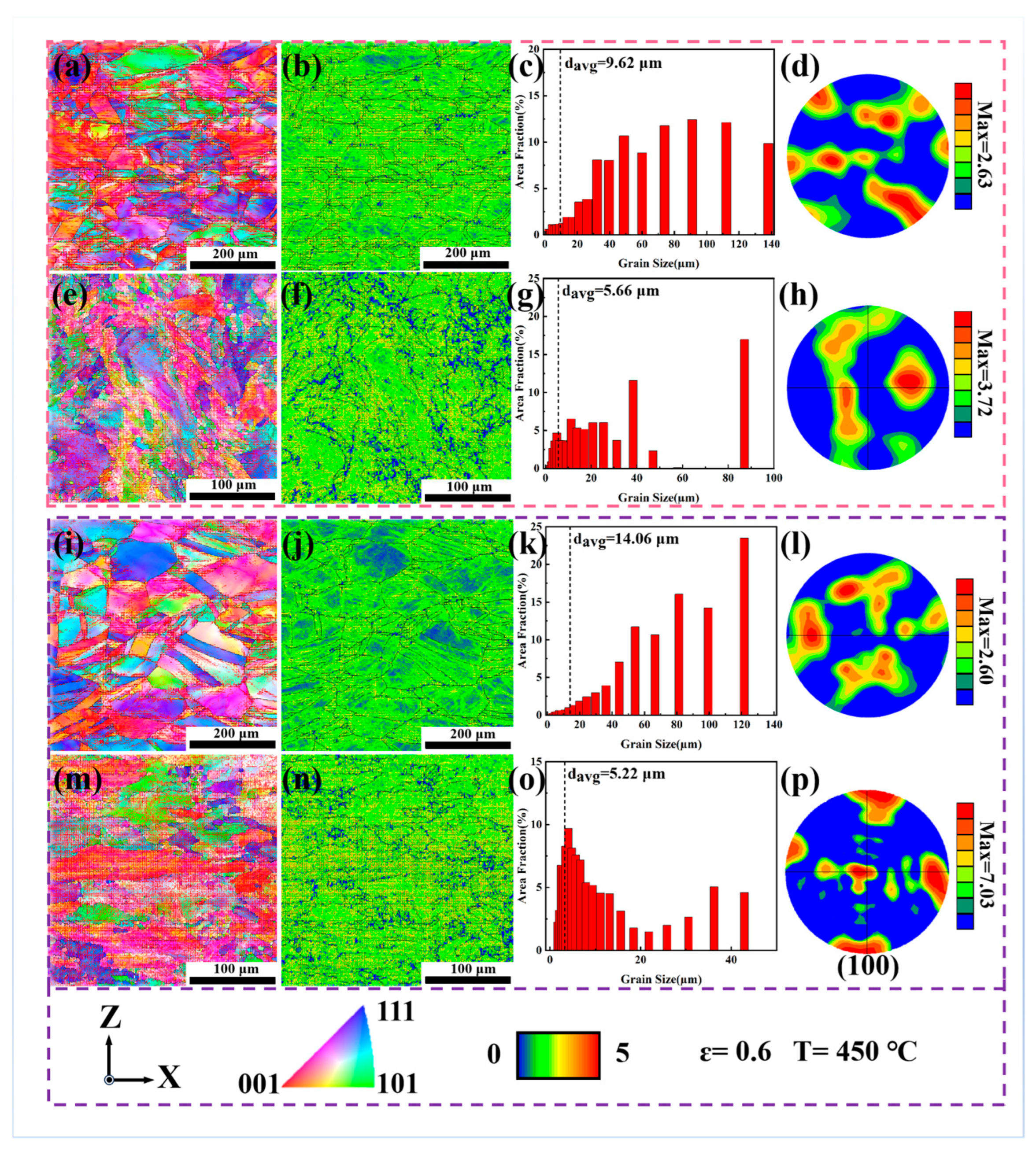
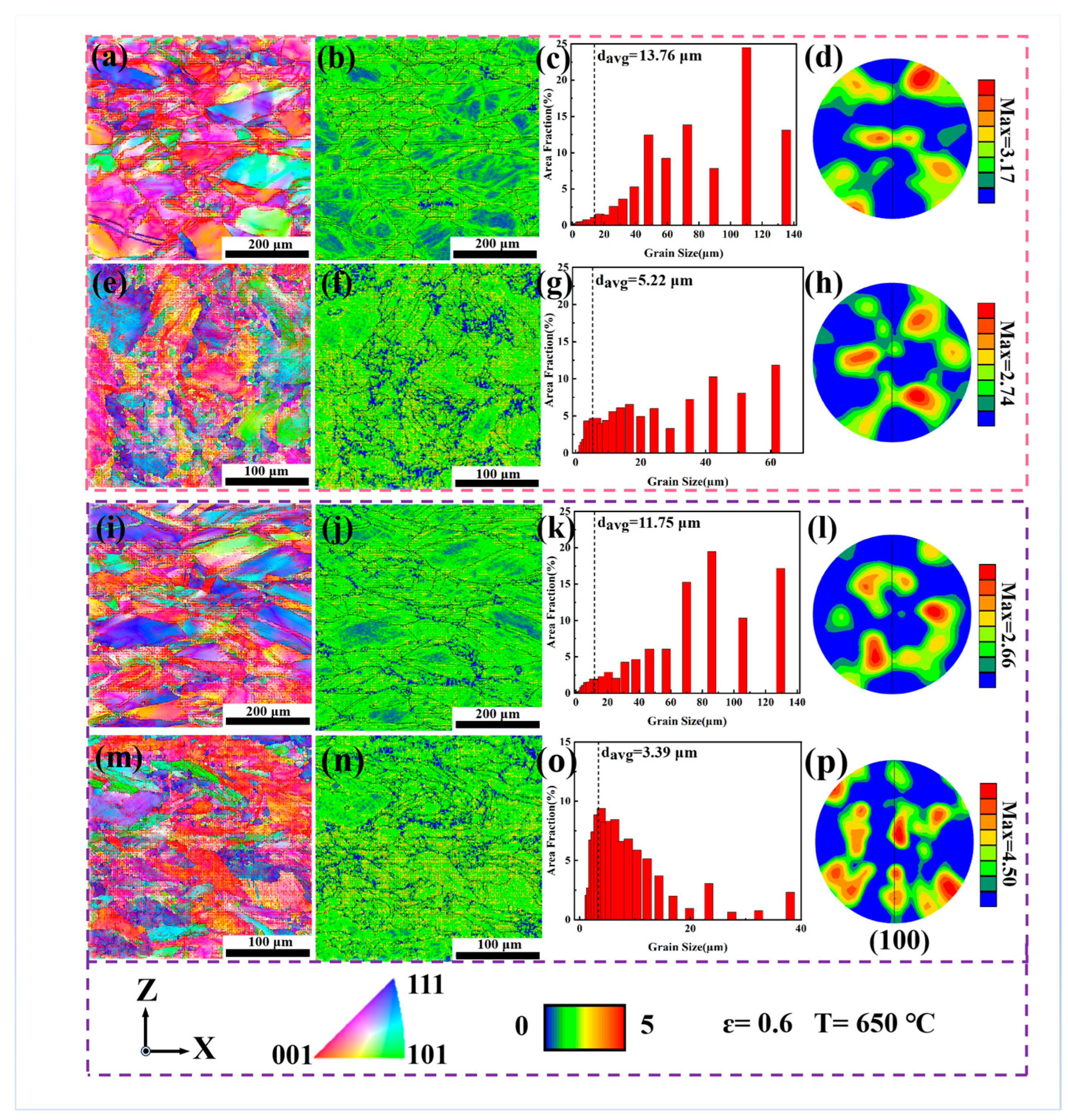
3.2. Metallographic Analysis and Grain Texture Evolution
3.3. TEM Microstructural Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- (1)
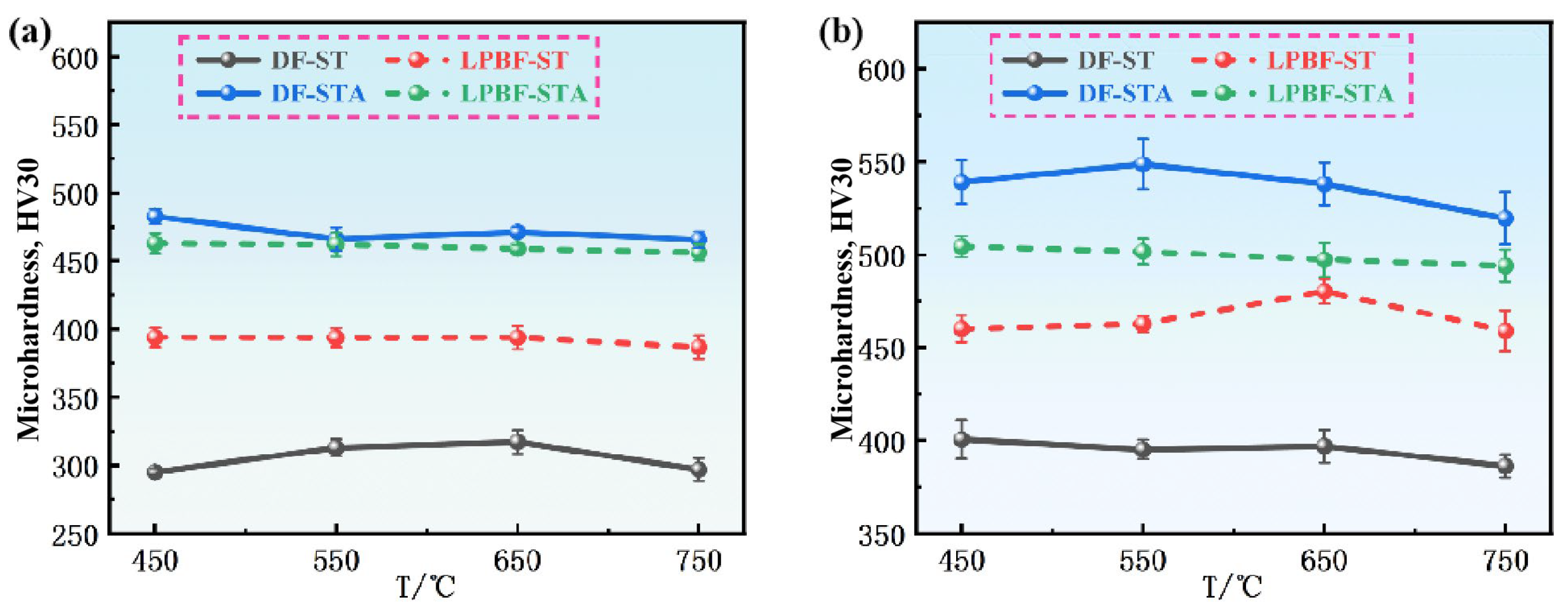
- After ST treatment, the DF-ST alloy only contains the γ matrix, while the LPBF-ST alloy retains the δ phase at the grain boundaries. Under the ST condition, the LPBF alloy shows higher intermediate-temperature compressive strength than the DF alloy, primarily owing to grain refinement and δ phase pinning at grain boundaries. After STA treatment, both alloys are significantly strengthened by the γ″ and γ′ precipitates. However, in the LPBF alloy, Nb consumption by δ phase formation reduces γ″/γ′ precipitates, resulting in a slightly lower strength compared to the DF-STA alloy.
- (2)
- The DF alloy shows a decreasing flow stress with increasing deformation temperature due to thermal activation and softening. However, the LPBF-ST alloy exhibits a peak in strength at around 650 °C, attributed to the temperature-induced precipitation of the γ″/γ′ phases within the matrix. EBSD and TEM analyses reveal that deformation in DF alloys is more homogeneous, while LPBF alloys exhibit localized dislocation accumulation and stress concentration arising from δ phase heterogeneity and microsegregation.
- (3)
- The distinct precipitation and deformation behaviors between LPBF and DF alloys originate from their different solidification microstructures and Nb segregation characteristics. Controlling δ phase precipitation and homogenization heat treatment is crucial for balancing strength and ductility in additively manufactured IN718 superalloys.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kennedy, R.L. Allvac® 718Plus™, superalloy for the next forty years. In Proceedings of the 6th International Symposium on Superalloys 718, 625, 706 and Derivatives, Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 2–5 October 2005; pp. 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Amanov, A.; Umarov, R.; Amanov, T. Increase in Strength and Fretting Resistance of Alloy 718 Using the Surface Modification Process. Materials 2018, 11, 1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.S.; Dong, J.X.; Zhang, M.C. Research and Development of Inconel 718 Type Superalloy. Mater. Sci. Forum 2007, 539–543, 262–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin-Hui, D.U.; Xu-Dong, L.U.; Deng, Q.; Zhong-Nan, B.I. Progress in the Research and Manufacture of GH4169 Alloy. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 2015, 22, 657–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzmán-Tapia, M.; Almaraz, G.M.D.; Tello, I.F.Z.; Martínez, A.G.; Juárez, J.C.V. Microstructural Characterization of Inconel 718 for Future Ultrasonic Fatigue Testing; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Wan, C.; Wang, B. Crystal Plasticity Modeling of Strain Hardening Induced by Coherent Precipitates in Inconel 718 Superalloy. Materials 2025, 18, 2436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaturvedi, M.; Han, Y.F. Strengthening mechanisms in Inconel 718 superalloy. Met. Sci. 1983, 17, 145–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sang, L.; Lu, J.; Cheng, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Z. In Situ EBSD Study of Deformation Behavior at Grain Scale of Inconel 718 Alloy During Tensile Test at 650 degrees C. Materials 2025, 18, 1934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, R.; Li, X.J.; Wan, M.; Han, J.Q.; Meng, B.; Cai, Z.Y. Fracture behavior of Inconel 718 sheet in thermal-aided deformation considering grain size effect and strain rate influence. Mater. Des. 2017, 130, 413–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Li, C.; Guo, Q.; Ma, Z.; Li, H.; Liu, Y. Improving creep resistance of nickel-based superalloy Inconel 718 by tailoring gamma double prime variants. Scr. Mater. 2019, 164, 66–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, S.; Tan, H.; Chen, J.; Zhong, C.; Li, Z.; Fan, W.; Gasser, A.; Huang, W. The influence of Laves phases on the room temperature tensile properties of Inconel 718 fabricated by powder feeding laser additive manufacturing. Pergamon 2019, 164, 413–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chicos, L.A.; Lancea, C.; Zaharia, S.M.; Cempura, G.; Kruk, A.; Pop, M.A. Effects of Homogenization Heat Treatment on Microstructure of Inconel 718 Lattice Structures Manufactured by Selective Laser Melting. Materials 2025, 18, 4149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sang, L.; Lu, J.; Wang, J.; Ullah, R.; Sun, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Z. In-situ SEM study of temperature-dependent tensile behavior of Inconel 718 superalloy. J. Mater. Sci. 2021, 56, 16097–16112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.N.; Guan, K.; Yang, Z.W.; Hu, Z.P.; Qian, Z.; Wang, H.; Ma, Z.Q. The effect of subsequent heat treatment on the evolution behavior of second phase particles and mechanical properties of the Inconel 718 superalloy manufactured by selective laser melting. Mater. Sci. Eng. A-Struct. Mater. Prop. Microstruct. Process. 2020, 794, 139931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azadian, S.; Wei, L.Y.; Warren, R. Delta phase precipitation in Inconel 718. Mater. Charact. 2004, 53, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulhameed, O.; Al-Ahmari, A.; Ameen, W.; Mian, S.H. Additive manufacturing: Challenges, trends, and applications. Adv. Mech. Eng. 2019, 11, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirchmayer, A.; Lyu, H.; Prbstle, M.; Houllé, F.; Neumeier, S. Combining Experiments and Atom Probe Tomography-informed Simulations on γ′ Precipitation Strengthening in the Polycrystalline Ni-base Superalloy A718Plus. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2020, 22, 2000149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tucho, W.M.; Ohm, B.A.; Canizalez, S.A.P.; Egeland, A.; Mildt, M.B.; Nedreberg, M.L.; Hansen, V.F. Effects of δ Phase and Annealing Twins on Mechanical Properties and Impact Toughness of L-PBF Inconel 718. J. Manuf. Mater. Process. 2024, 8, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, J.; Kujawski, D. Additively Manufactured Inconel 718 Low-Cycle Fatigue Performance. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadollahi, A.; Shamsaei, N. Additive manufacturing of fatigue resistant materials: Challenges and opportunities. Int. J. Fatigue 2017, 98, 14–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, J.; Chen, L.; Van Petegem, S.; Jiang, F.; Li, Q.; Luan, J.; Sing, S.L.; Wang, J.; Tan, C. Additive manufacturing metallurgy guided machine learning design of versatile alloys. Mater. Today 2025, 88, 240–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, J.; Jiang, F.; Tan, C.; Weng, F.; Ng, F.L.; Goh, M.H.; Xie, H.; Liu, J.; Chew, Y.; Teng, J. Additive manufacturing of fine-grained high-strength titanium alloy via multi-eutectoid elements alloying. Compos. Part B Eng. 2023, 249, 110399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, W.; Guo, H.; Wang, K.; Han, T.; Zhang, J.; Wu, M.; Wang, L. Radiation-synthesis of covalent bonding heterojunctions for selective solar-driven CO2 reduction. Mater. Today 2025, 84, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, J.; Li, Q.; Teng, J.; Ng, F.L.; Shen, Z.; Goh, M.H.; Jiang, F.; Sing, S.L.; Yang, T.; Tan, C. Programmable mechanical properties of additively manufactured novel steel. Int. J. Extrem. Manuf. 2024, 7, 015001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, J.; Mo, Y.; Shangguan, P.; Panwisawas, C.; Jiang, F.; Sing, S.L. Additive manufacturing-by-design for support structures: A critical review. Int. J. Extrem. Manuf. 2025, 7, 052002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frankiewicz, M.; Karoluk, M.; Dziedzic, R.; Gruber, K.; Stopyra, W. Static and Fatigue Properties of Rhenium-Alloyed Inconel 718 Produced by Powder Bed Fusion Additive Manufacturing. Materials 2025, 18, 692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.T.; Panwisawas, C.; Ghoussoub, J.N.; Gong, Y.; Clark, J.W.G.; Németh, A.A.N.; McCartney, D.G.; Reed, R.C. Alloys-by-design: Application to new superalloys for additive manufacturing. Acta Mater. 2021, 202, 417–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Sheng, J.; Wang, Z.; Meng, X.; Lu, J.; Hu, X.; Zhou, J. Finite element and experimental analysis of elevated-temperature fatigue behavior of IN718 alloy subjected to laser peening. Int. J. Fatigue 2020, 131, 105337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundararaman, M.; Mukhopadhyay, P.; Banerjee, S. Precipitation of the δ-Ni3Nb Phase in Two Nickel Base Superalloys. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 1988, 19, 453–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valle, L.C.M.; Araújo, L.S.; Gabriel, S.B.; Dille, J.; Almeida, L.H.D. The Effect of δ Phase on the Mechanical Properties of an Inconel 718 Superalloy. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2013, 22, 1512–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, N.Y.; Ni, Z.Y.; Fang, X.W.; Zhou, Y.; Tang, K.X.; Zhang, H.K.; Huang, K. Role of d-phase on Mechanical Behaviors of Additive Manufactured Inconel 718: Detailed Microstructure Analysis and Crystal Plasticity Modelling. Int. J. Plast. 2023, 168, 103708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaole, Z.; Yun, J.; Xiaoan, H.; Jia, H.; Yun, W. High-temperature mechanical properties of nickel-based superalloys manufactured by additive manufacturing. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2020, 36, 1523–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Tang, J.; Ke, Y.; Teng, J.; Jiang, F. On the Hardening and Softening Behaviors of Additively Manufactured and Forged Inconel 718 Alloys Under Non-Isothermal Heat Treatments. Materials 2025, 18, 5174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, Y.Q.; Huang, S.B.; Fu, M.W.; Dong, J. Microstructural characterization, formation mechanism and fracture behavior of the needle 6 phase in Fe-Ni-Cr type superalloys with high Nb content. Mater. Charact. 2015, 109, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kombaiah, B.; Murty, K.L. Coble, Orowan Strengthening, and Dislocation Climb Mechanisms in a Nb-Modified Zircaloy Cladding. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2015, 46, 4646–4660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
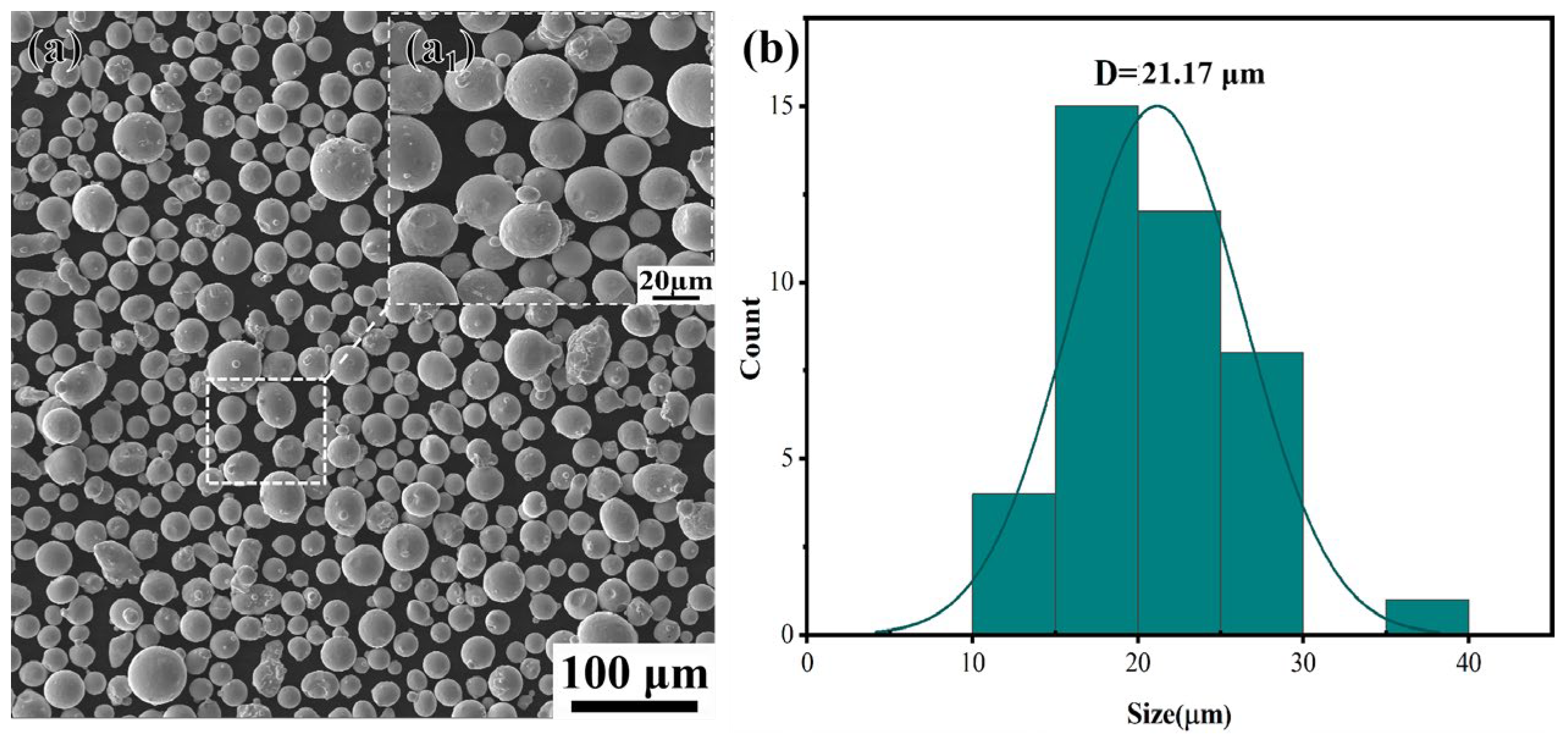

| Element | Ni | Cr | Fe | Nb | Ti | Mo | Co | Al | Mn | Others |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DF alloy | 53.89 | 17.75 | 17.27 | 5.48 | 1.01 | 2.96 | 0.27 | 0.50 | 0.06 | Bal. |
| LPBF alloy | 53.24 | 19.41 | 15.76 | 5.48 | 0.95 | 3.26 | 0.92 | 0.42 | 0.28 | Bal. |
| Deformation Temperature (°C) | Yield Strength (MPa) | Compressive Strength (MPa) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| DF-ST | 450 | 240 | 969 |
| LPBF-ST | 405 | 1146 | |
| DF-STA | 904 | 1390 | |
| LPBF-STA | 853 | 1336 | |
| DF-ST | 550 | 236 | 952 |
| LPBF-ST | 435 | 1152 | |
| DF-STA | 899 | 1390 | |
| LPBF-STA | 850 | 1336 | |
| DF-ST | 650 | 208 | 902 |
| LPBF-ST | 540 | 1231 | |
| DF-STA | 895 | 1347 | |
| LPBF-STA | 721 | 1265 | |
| DF-ST | 750 | 182 | 873 |
| LPBF-ST | 383 | 1050 | |
| DF-STA | 890 | 1321 | |
| LPBF-STA | 695 | 1150 |
| Alloy | Deformation Temperature (°C) | Grain Size (μm) | Texture Intensity | Grain Orientation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DF-ST | 450 | 9.62 | 2.63 | <001> <111> |
| DF-STA | 14.06 | 2.60 | <001> <111> | |
| LPBF-ST | 5.66 | 3.72 | <001> <111> | |
| LPBF-STA | 5.22 | 7.03 | <001> <101> | |
| DF-ST | 650 | 13.76 | 3.17 | <001> |
| DF-STA | 11.75 | 2.66 | <001> <111> | |
| LPBF-ST | 5.22 | 2.74 | <001> <111> | |
| LPBF-STA | 3.39 | 4.50 | <001> <111> |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, J.; Cheng, Y.; Su, J.; Ke, Y.; Teng, J.; Jiang, F. Comparative Study on Intermediate-Temperature Deformation Mechanisms of Inconel 718 Alloys Fabricated by Additive Manufacturing and Conventional Forging. Materials 2025, 18, 5354. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18235354
Wu J, Cheng Y, Su J, Ke Y, Teng J, Jiang F. Comparative Study on Intermediate-Temperature Deformation Mechanisms of Inconel 718 Alloys Fabricated by Additive Manufacturing and Conventional Forging. Materials. 2025; 18(23):5354. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18235354
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Jin, Yetao Cheng, Jinlong Su, Yubin Ke, Jie Teng, and Fulin Jiang. 2025. "Comparative Study on Intermediate-Temperature Deformation Mechanisms of Inconel 718 Alloys Fabricated by Additive Manufacturing and Conventional Forging" Materials 18, no. 23: 5354. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18235354
APA StyleWu, J., Cheng, Y., Su, J., Ke, Y., Teng, J., & Jiang, F. (2025). Comparative Study on Intermediate-Temperature Deformation Mechanisms of Inconel 718 Alloys Fabricated by Additive Manufacturing and Conventional Forging. Materials, 18(23), 5354. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18235354







