The Inhibitory Effect of Hafnium Oxide on Grain Growth in Yttrium Aluminum Garnet Composite Fiber
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Materials
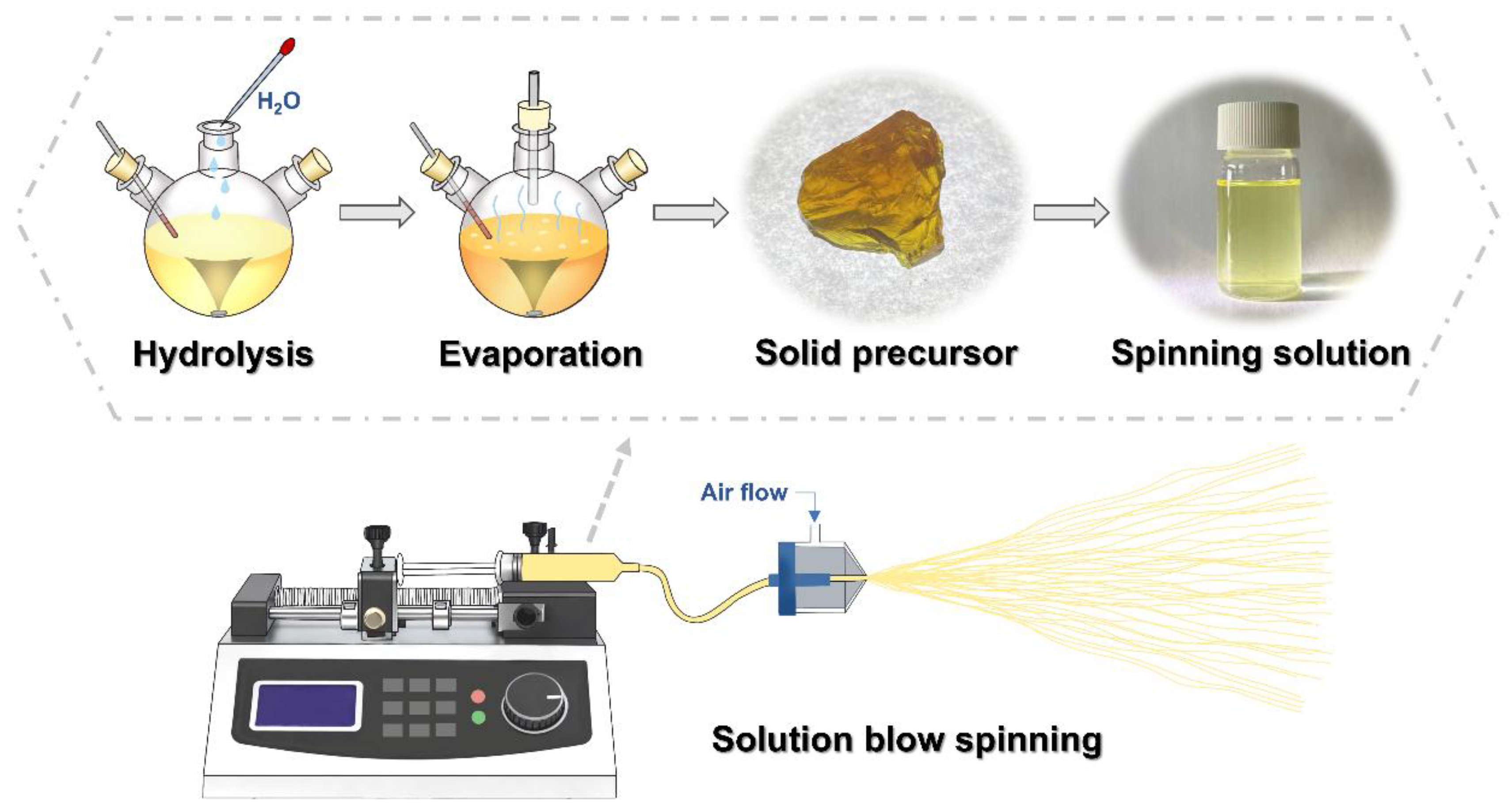
2.2. Preparation of YAG-HfO2 Precursor and Fiber
2.3. Characterization
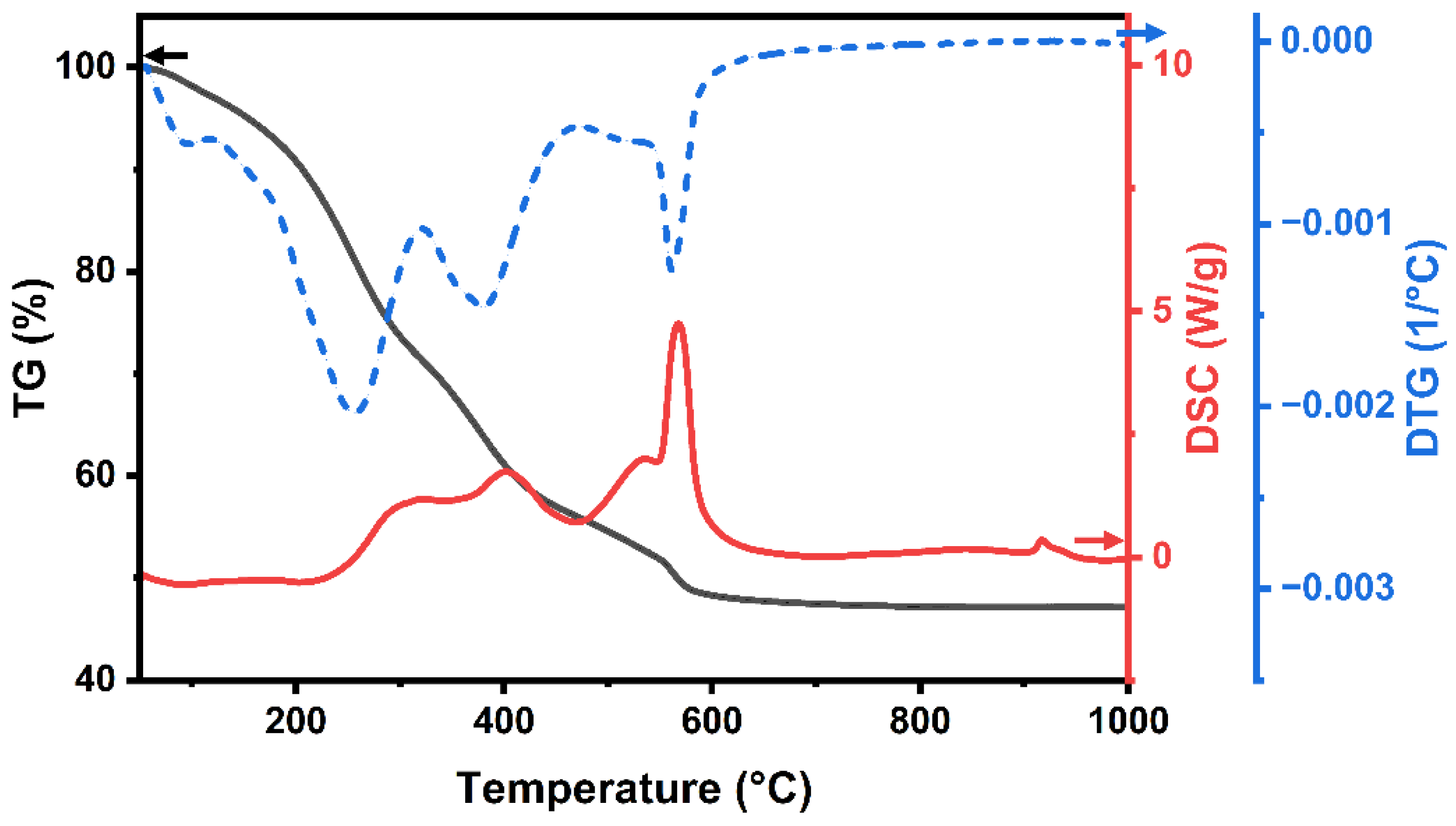
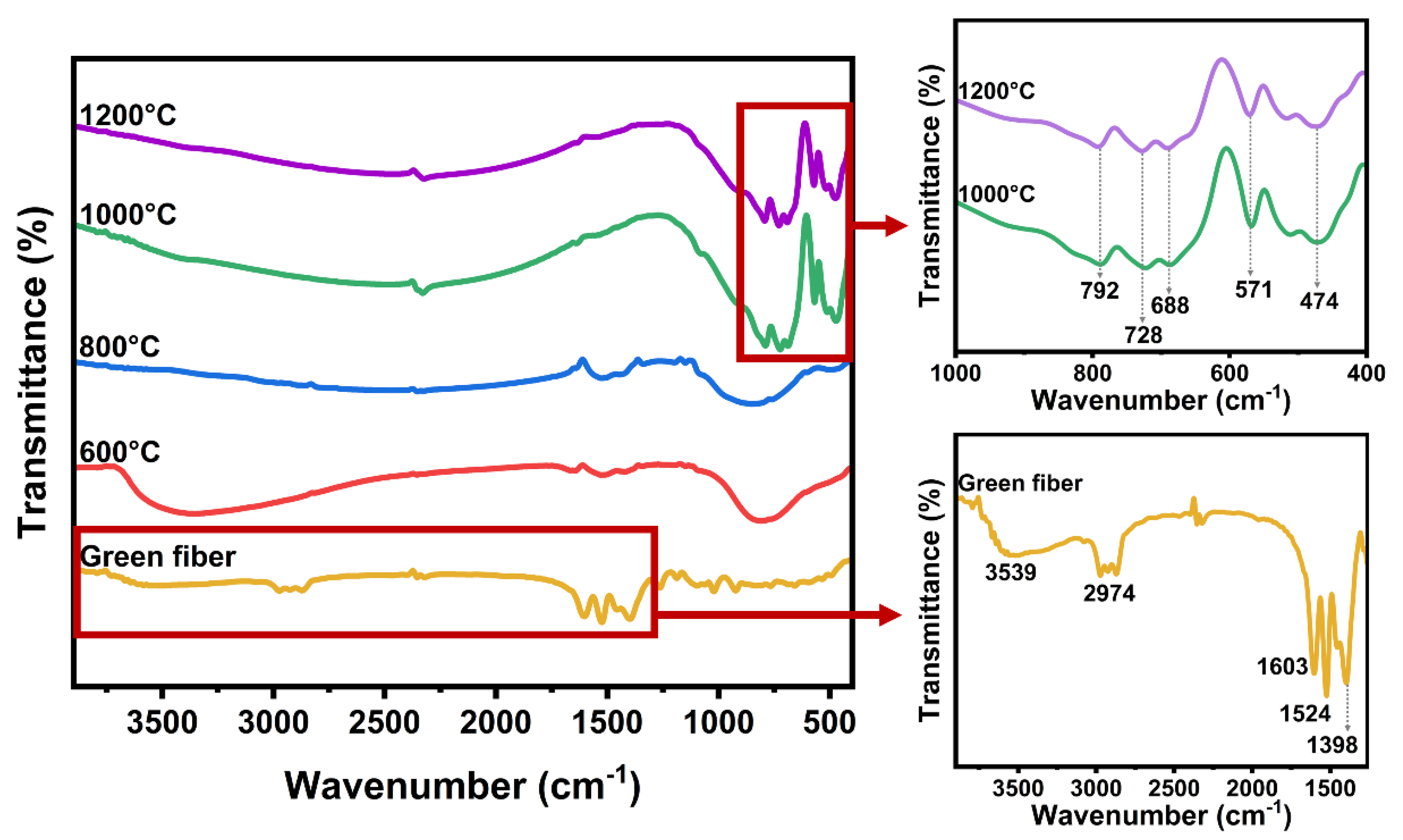
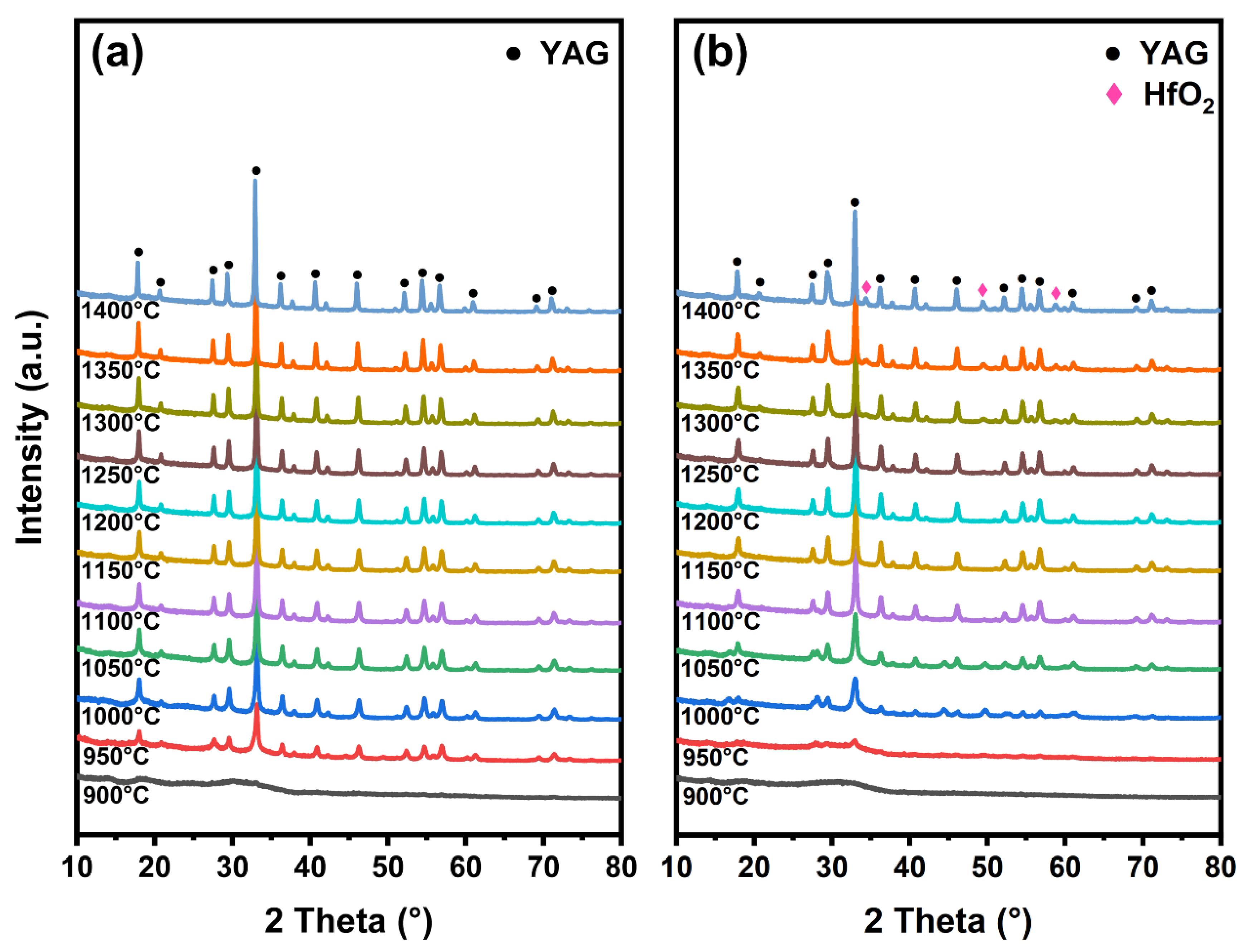
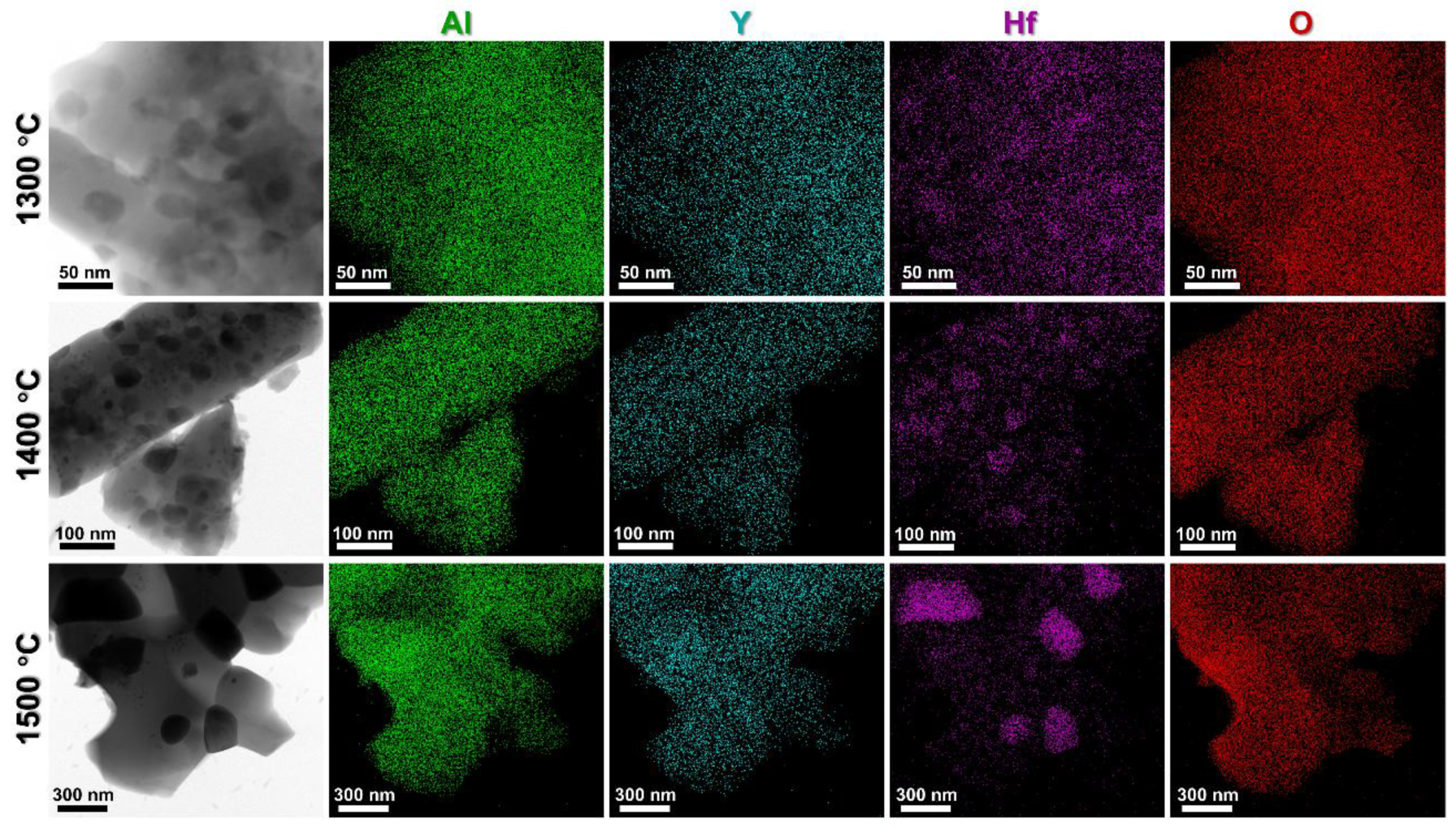
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
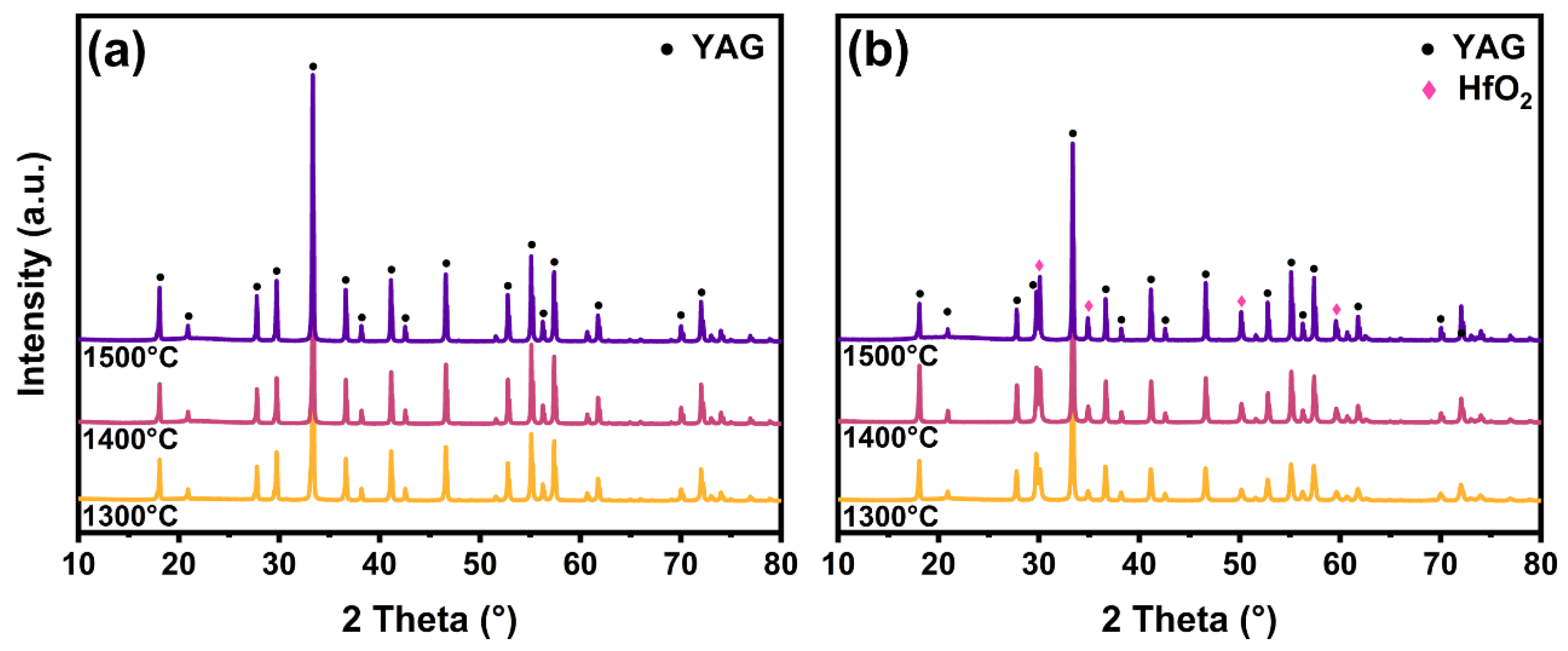
- Compared with pure YAG fiber without HfO2, the introduction of HfO2 delayed the crystal phase transformation of the YAG-HfO2 fibers, increasing the crystallization temperature of the YAG phase from 900 °C to 950 °C.
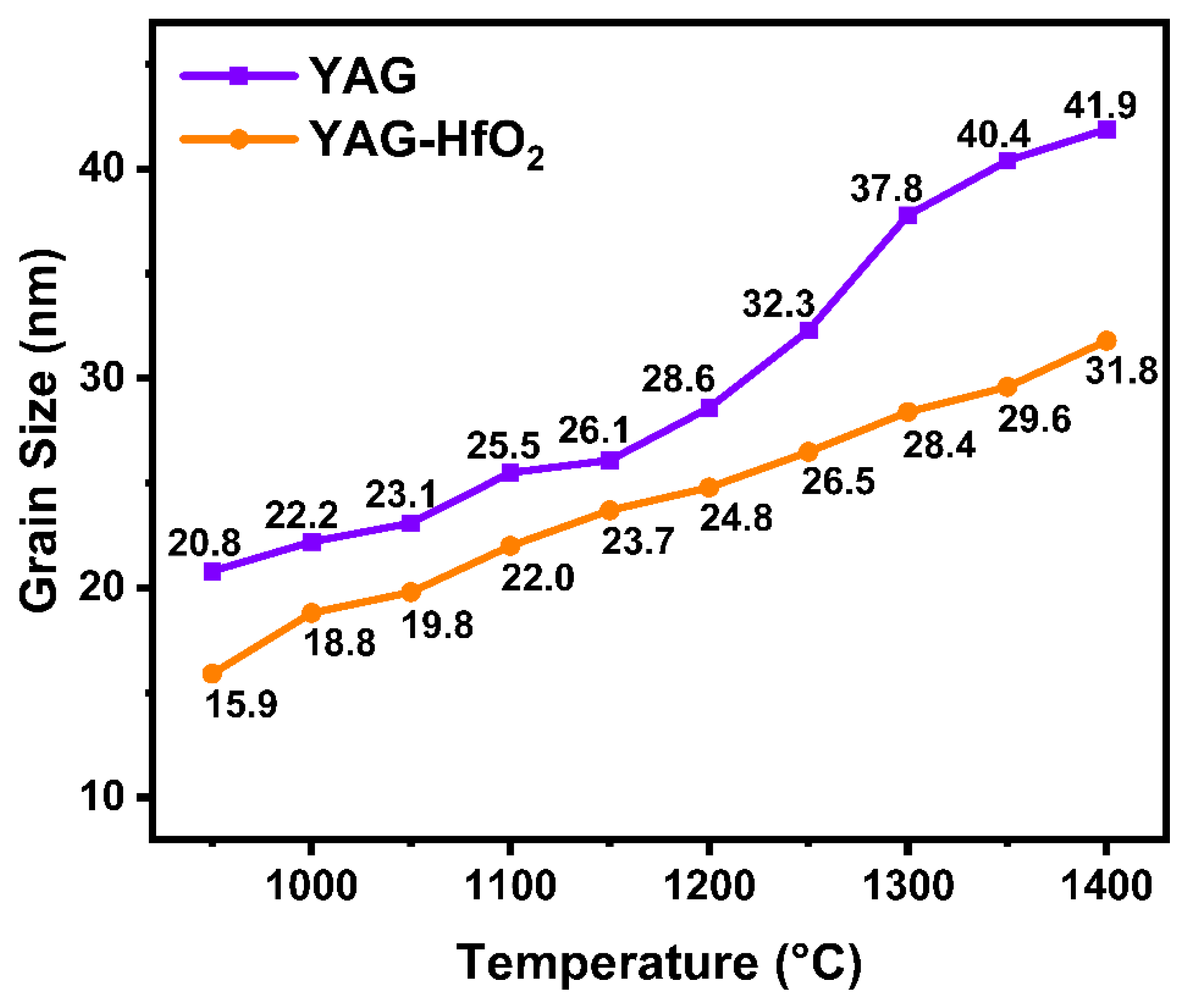
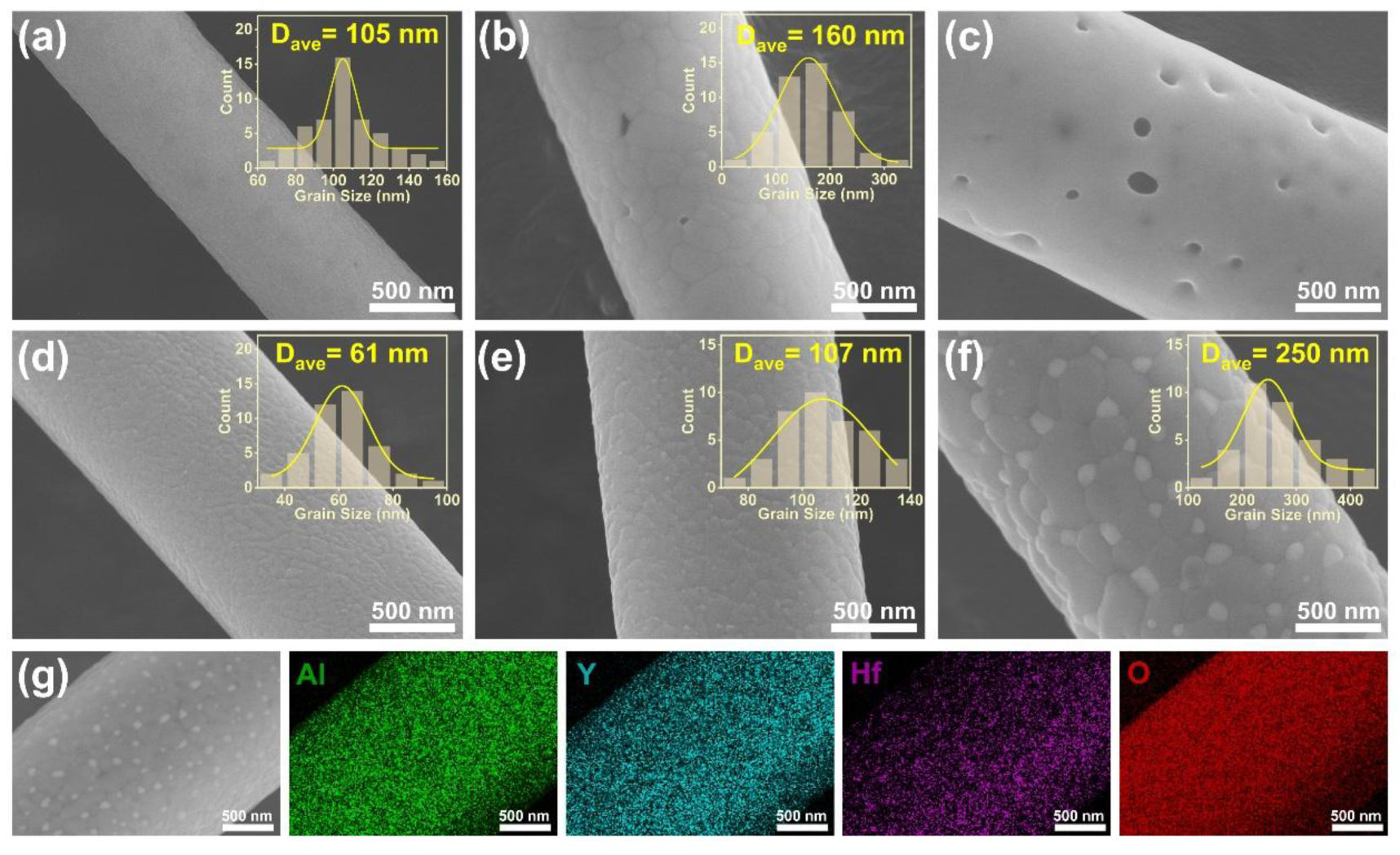
- The grain growth in YAG-HfO2 fibers was consistently suppressed, resulting in a steadier and finer microstructure. The crystal size of YAG-HfO2 fiber was only 31.8 nm at 1400 °C, notably smaller than the 41.9 nm in pure YAG fibers.
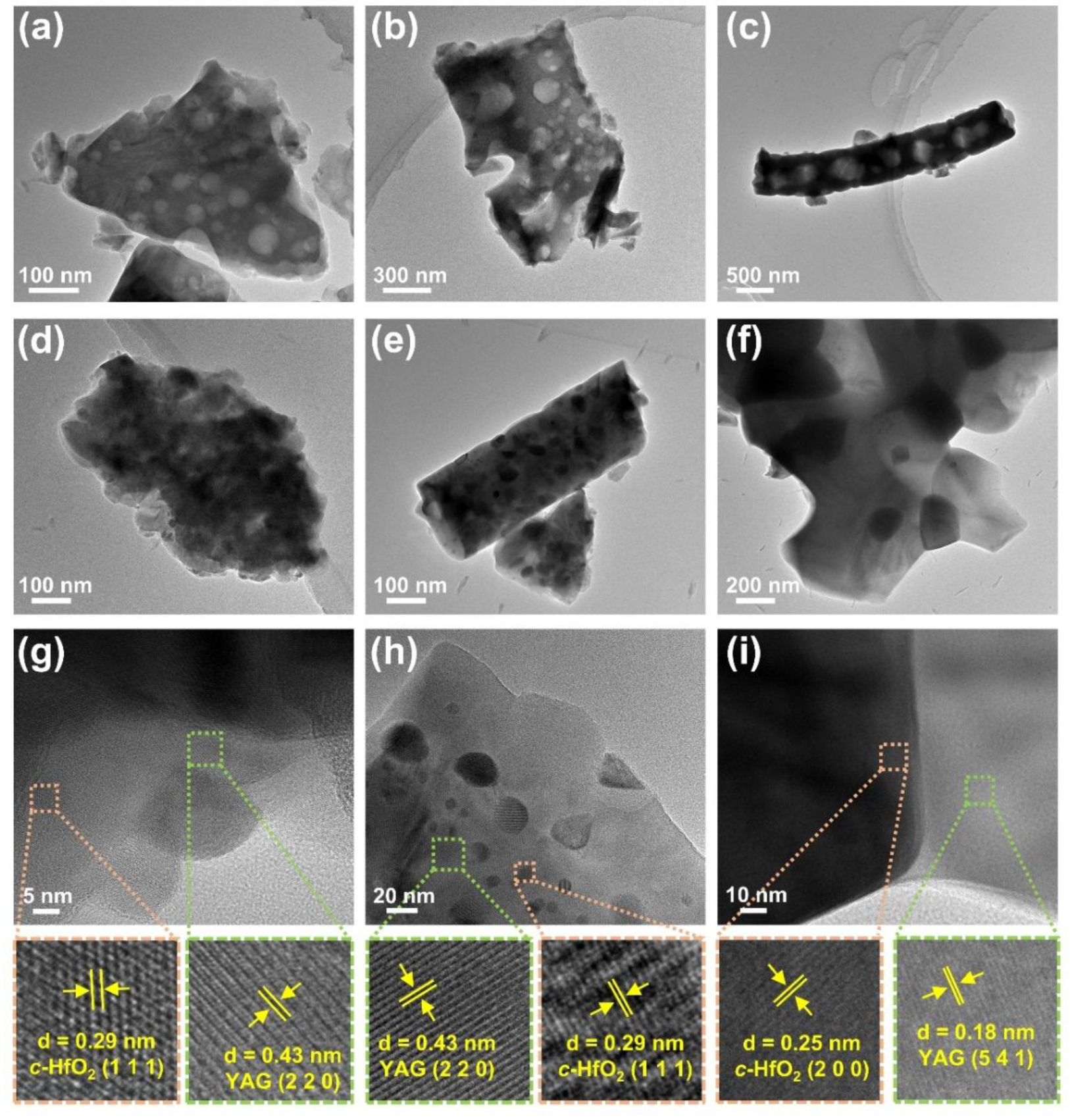
- The suppression mechanism was identified as Zener pinning, where HfO2 particles located at YAG grain boundaries effectively impeded grain coarsening. YAG-HfO2 fibers had an average grain size of ~250 nm at 1500 °C, demonstrating exceptional microstructural stability at high temperatures.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Khalil, K.A.; Almajid, A.A.; El-Danaf, E.A.; El Rayes, M.M.; Sherif, E.-S.M. Direct fabrication of yttrium aluminium garnet nanofibers by electrospinning. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2012, 7, 12218–12226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Peng, Y.; Ma, D.; Liu, W.; Deng, Z.; Zhu, L.; Zhang, G.; Wang, X. Lightweight, high-strength, flexible YAG fibrous membrane for efficient heat insulation. J. Alloys Compd. 2021, 876, 159978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Tian, J.; Pan, G.; Xie, Y.; Yao, Q. Preparation of the flexible green body of YAG ceramic fiber by melt spinning. Polymers 2022, 14, 2096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shojaie-Bahaabad, M.; Taheri-Nassaj, E.; Naghizadeh, R. Effect of yttria on crystallization and microstructure of an alumina-YAG fiber prepared by aqueous sol-gel process. Ceram. Int. 2009, 35, 391–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutyin, A.M.; Rostokina, E.Y.; Gavrishchuk, E.M.; Drobotenko, V.V.; Plekhovich, A.D.; Yunin, P.A. Kinetics and formation mechanism of yttrium aluminum garnet from an amorphous phase prepared by the sol-gel method. Ceram. Int. 2015, 41, 10616–10623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Wang, C.; Tan, H.; Nan, J.; Lv, Z. Preparation and crystal activation energy of long yttrium aluminum garnet gel fibers. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 2016, 80, 226–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfeifer, S.; Bischoff, M.; Niewa, R.; Clauß, B.; Buchmeiser, M.R. Structure formation in yttrium aluminum garnet (YAG) fibers. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2014, 34, 1321–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.J.; Fair, G.E.; Hart, A.M.; Potticary, S.A.; Usechak, N.G.; Corns, R.G.; Hay, R.S. Development of polycrystalline yttrium aluminum garnet (YAG) fibers. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2015, 35, 4251–4258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pullar, R.C.; Taylor, M.D.; Bhattacharya, A.K. Effect of sodium on the creep resistance of yttrium aluminium garnet (YAG) fibres. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2006, 26, 1577–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Wang, L.; Ma, D.; Peng, Y.; Zhu, L.; Wang, X.; Zhang, G.; Wang, T.; Jia, Z.; Zhang, J. Preparation, mechanical properties, and diffuse reflectance of YAG continuous fibers and nanofibers. Ceram. Int. 2019, 45, 21213–21219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Zhang, Y.; Gong, H.; Zhang, J.; Nie, L. Preparation, microstructure and properties of yttrium aluminum garnet fibers prepared by sol-gel method. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2009, 113, 31–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Towata, A.; Hwang, H.J.; Yasuokaa, M.; Sandoa, M.; Niiharab, K. Preparation of polycrystalline YAG/alumina composite fibers and YAG fiber by sol-gel method. Compos. Part A 2001, 32, 1127–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, D.M.; Visser, L.R. High performance oxide fibers for metal and ceramic composites. Compos. Part A 2001, 32, 1143–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hay, R.S.; Armani, C.J.; Ruggles-Wrenn, M.B.; Fair, G.E. Creep mechanisms and microstructure evolution of Nextel™ 610 fiber in air and steam. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2014, 34, 2413–2426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunsell, A.R.; Berger, M.-H. Fine diameter ceramic fibres. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2000, 20, 2249–2260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kniec, K.; Marciniak, L. The influence of grain size and vanadium concentration on the spectroscopic properties of YAG: V3+,V5+ and YAG: V, Ln3+ (Ln3+ = Eu3+, Dy3+, Nd3+) nanocrystalline luminescent thermometers. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 264, 382–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, H.; Ma, X.; Lu, J.; Li, K. Effect of zirconia on crystallization of yttrium aluminum garnet precursor gel fibers. Ceram. Silikáty 2014, 58, 118–122. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, X.; Lv, Z.; Tan, H.; Nan, J.; Wang, C. Preparation and grain-growth of magnesia-alumina spinel/yttrium aluminum garnet composite fibers. Ceram. Silik. 2018, 62, 279–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Qiu, X.; Zhang, B.; Zhong, G.; Shen, M.; Liu, X.; Ou-Yang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, B.; Yang, X.; et al. Effect of calcination temperatures on HfO2 fibers via electrospinning. Ceram. Int. 2021, 47, 9048–9054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, D.; Bae, W.J.; Joo, Y.L.; Ober, C.K.; Frey, M.W. Properties of PVA/HfO2 hybrid electrospun fibers and calcined inorganic HfO2 fibers. J. Phys. Chem. C 2011, 115, 5535–5544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gai, K.; Guan, B.; Liang, L.; Li, J.; Wang, Q.; Zhao, T. Continuous aluminum oxide-mullite-hafnium oxide composite ceramic fibers with high strength and thermal stability by melt-spinning from polymer precursor. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2022, 42, 5911–5921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gai, K.; Wang, Q.; Zhao, T. Effect of hafnium oxide on continuous aluminum oxide-mullite-hafnium oxide composite ceramic fibers. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2023, 43, 6225–6233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gai, K.; Wang, Q.; Li, J.; Lu, B.; Liang, L.; Tai, J.; Cheng, Y.; Guan, B.; Zhao, T. Studies on the crystallization behavior of Al2O3-HfO2 ceramic fibers prepared by melt-spinning of polymer precursors. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2023, 43, 5587–5595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, B.; Gai, K.; Wang, Q.; Zhao, T. Continuous yttrium aluminum garnet ceramic fiber with high tensile strength by melt-spinning from polymer precursor. Ceram. Int. 2023, 49, 32318–32323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Sun, Y.N.; Zhang, T.Z.; Chen, F.H.; Ye, L.; Zhao, T. Polymer-derived Ta4HfC5 nanoscale ultrahigh-temperature ceramics: Synthesis, microstructure and properties. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2019, 39, 205–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abe, Y.; Tomioka, H.; Gunji, T.; Nagao, Y.; Misono, T. A one-pot sunthesis of polyzirconoxane as a precursor for continous zirconia fibers. J. Mater. Sci. Lett. 1994, 13, 960–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.Y.; Yu, G.; Qin, W.W.; Wang, X.Q.; Xu, D. Preparation, morphology and specific surface area of CeO2-ZrO2 and CeO2-ZrO2-Al2O3 fine fibers via precursor sol-gel technique. J. Alloys Compd. 2010, 492, 456–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Lv, Z.; Tan, H.; Wang, C.; Li, L.; Wang, Y. Preparation of YAG nano-fibers using polyvinyl butyral from nitrate solution. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 2019, 130, 276–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, H.; Ma, X.; Lu, J.; Li, K. Preparation of yttrium aluminum garnet fibers by the sol-gel method. Ceram. Silikaty 2012, 56, 186–190. [Google Scholar]
- He, L.; Cao, S.; Li, W.; Dong, Q.; Sun, W.; Dong, Q.; Sun, W. YAG/Al2O3/ZrO2 composite fibers of core-shell structure prepared by electrospinning. J. Asian Ceram. Soc. 2021, 9, 1046–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gai, K.; Wang, Q.; Guan, K.; Li, X.; Liu, W.; Li, Y.; Zhao, H.; Zhao, T. The Inhibitory Effect of Hafnium Oxide on Grain Growth in Yttrium Aluminum Garnet Composite Fiber. Materials 2025, 18, 5272. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18235272
Gai K, Wang Q, Guan K, Li X, Liu W, Li Y, Zhao H, Zhao T. The Inhibitory Effect of Hafnium Oxide on Grain Growth in Yttrium Aluminum Garnet Composite Fiber. Materials. 2025; 18(23):5272. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18235272
Chicago/Turabian StyleGai, Ke, Qian Wang, Ketian Guan, Xiaohu Li, Weisen Liu, Yuan Li, Hongwei Zhao, and Tong Zhao. 2025. "The Inhibitory Effect of Hafnium Oxide on Grain Growth in Yttrium Aluminum Garnet Composite Fiber" Materials 18, no. 23: 5272. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18235272
APA StyleGai, K., Wang, Q., Guan, K., Li, X., Liu, W., Li, Y., Zhao, H., & Zhao, T. (2025). The Inhibitory Effect of Hafnium Oxide on Grain Growth in Yttrium Aluminum Garnet Composite Fiber. Materials, 18(23), 5272. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18235272





