Evaluation of the Self-Healing Capacity of Asphalt Concrete with Polymer Capsules Containing Rejuvenator Under Various Cyclic Load Conditions
Abstract
1. Introduction
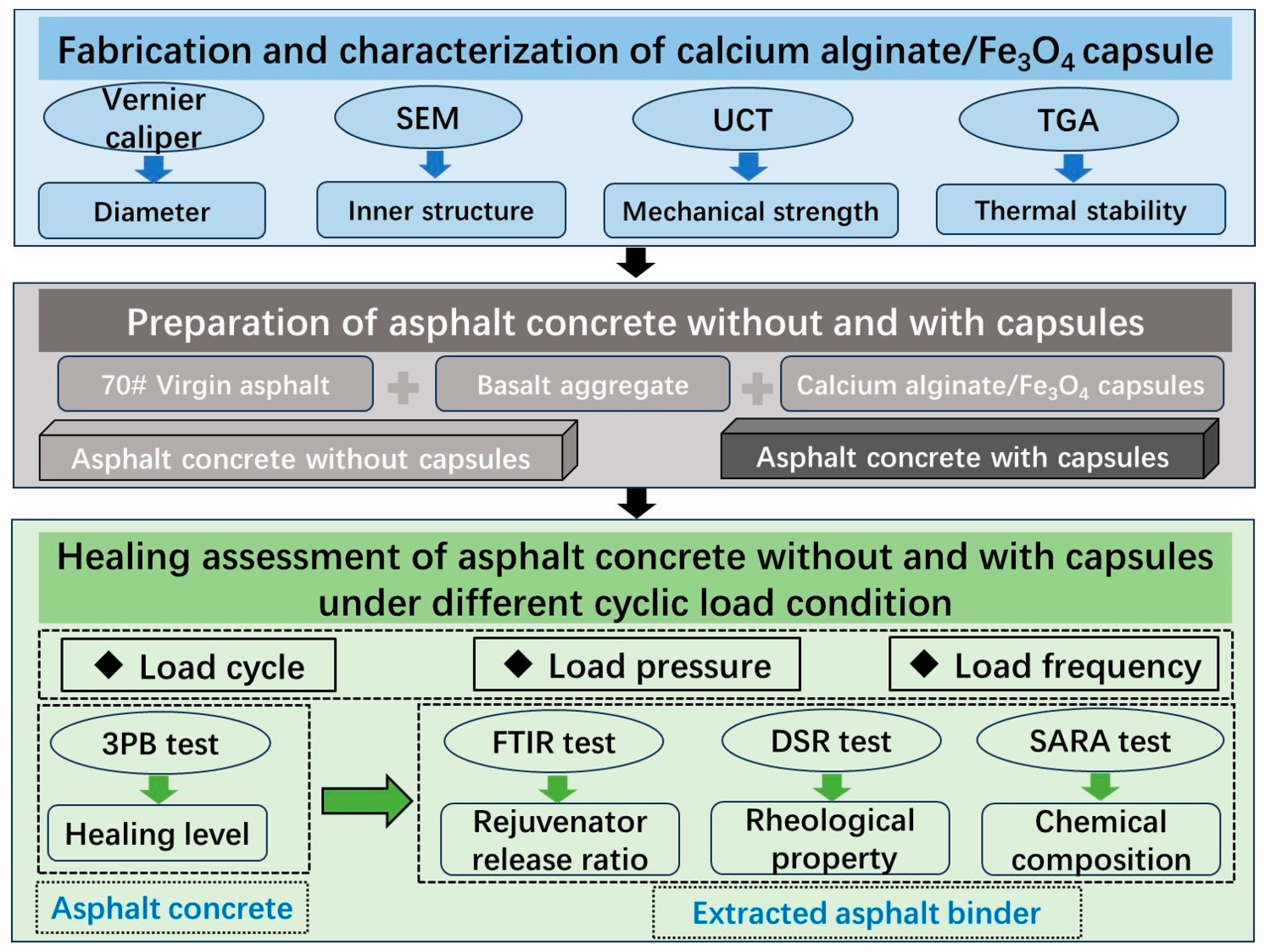
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Raw Materials
2.2. Preparation of Ca-Alginate/Fe3O4 Capsules via Ionic Gelation
2.3. Performance Evaluation of Capsules
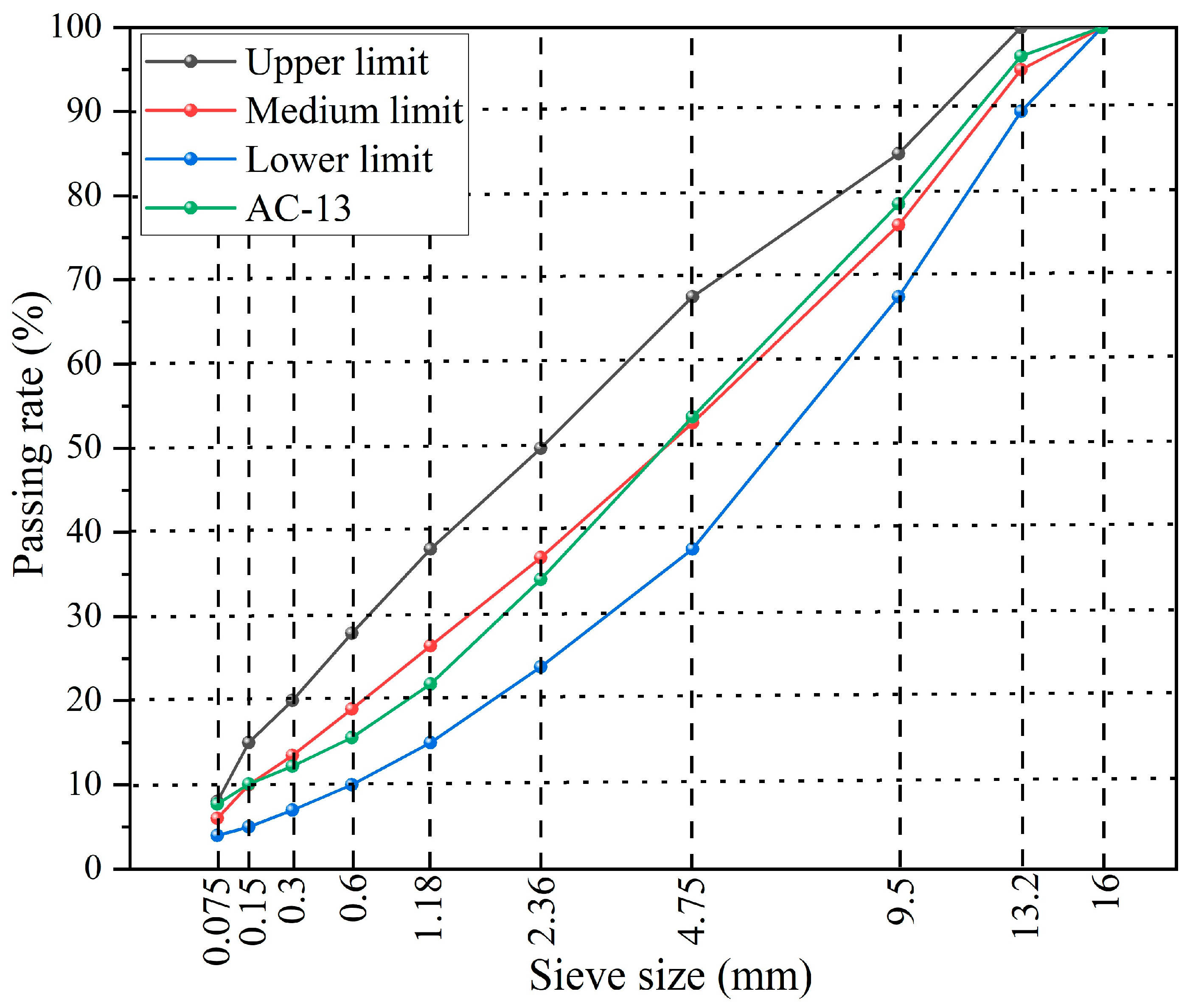
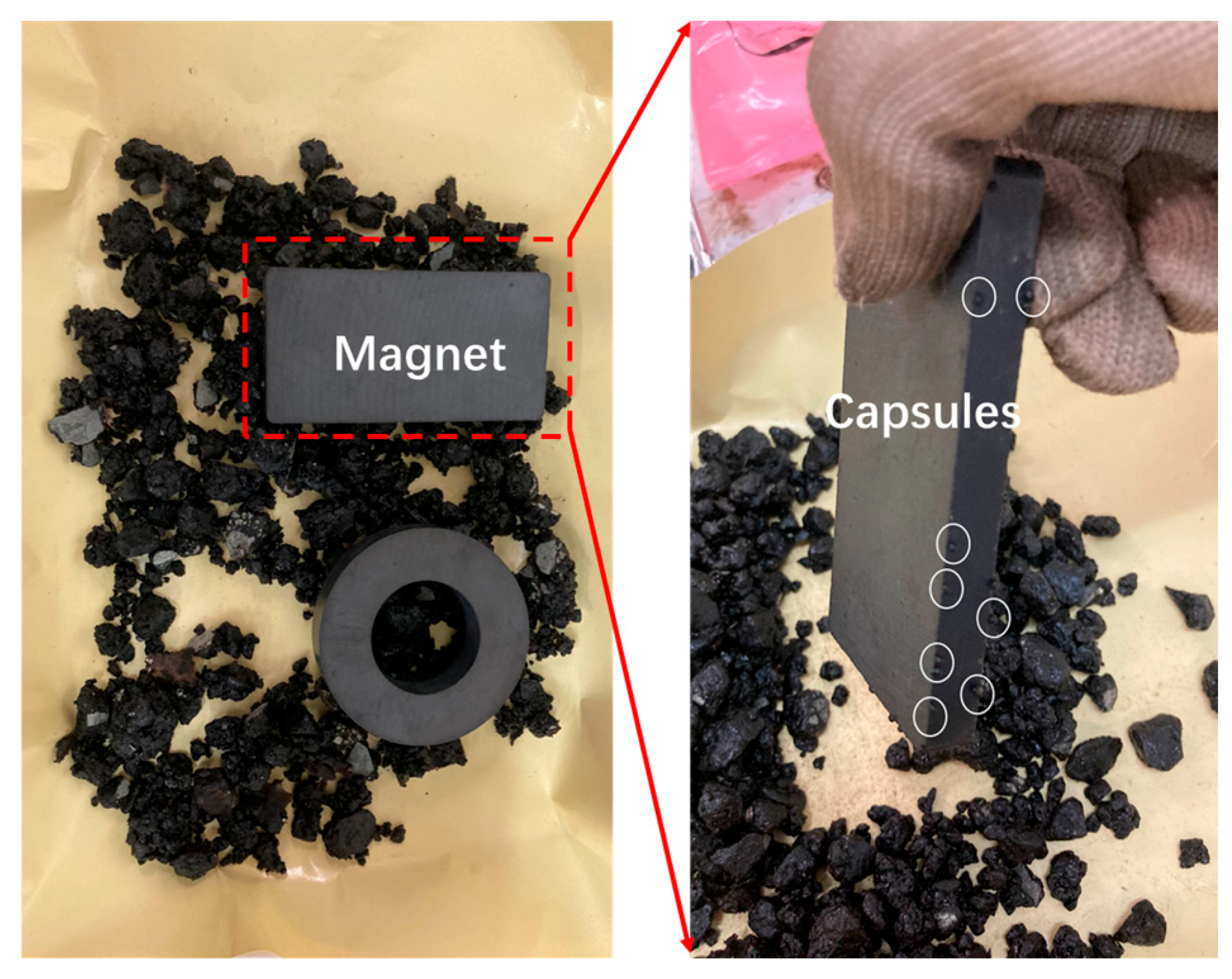
2.4. Preparation of Asphalt Mixtures Incorporating Capsules
2.5. Healing Assessment of Asphalt Concrete Under Different Cyclic Load Conditions
2.6. Characterization of Rejuvenator Release from Capsules in Asphalt Concrete After Cyclic Load
- (1)
- The relation establishment between absorption peak index I1745cm−1 and oil concentration in asphalt
- (2)
- The extraction of asphalt from asphalt concrete incorporating capsules after load
2.7. Rheological Characteristics of Asphalt Binder Under Different Load Scenarios
2.8. Chemical Composition Characteristics of Extracted Asphalt Binder After Various Cyclic Load Treatments
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Basic Performance of Capsules
3.2. Assessment of Asphalt Concrete Self-Healing Under Various Cyclic Load Conditions
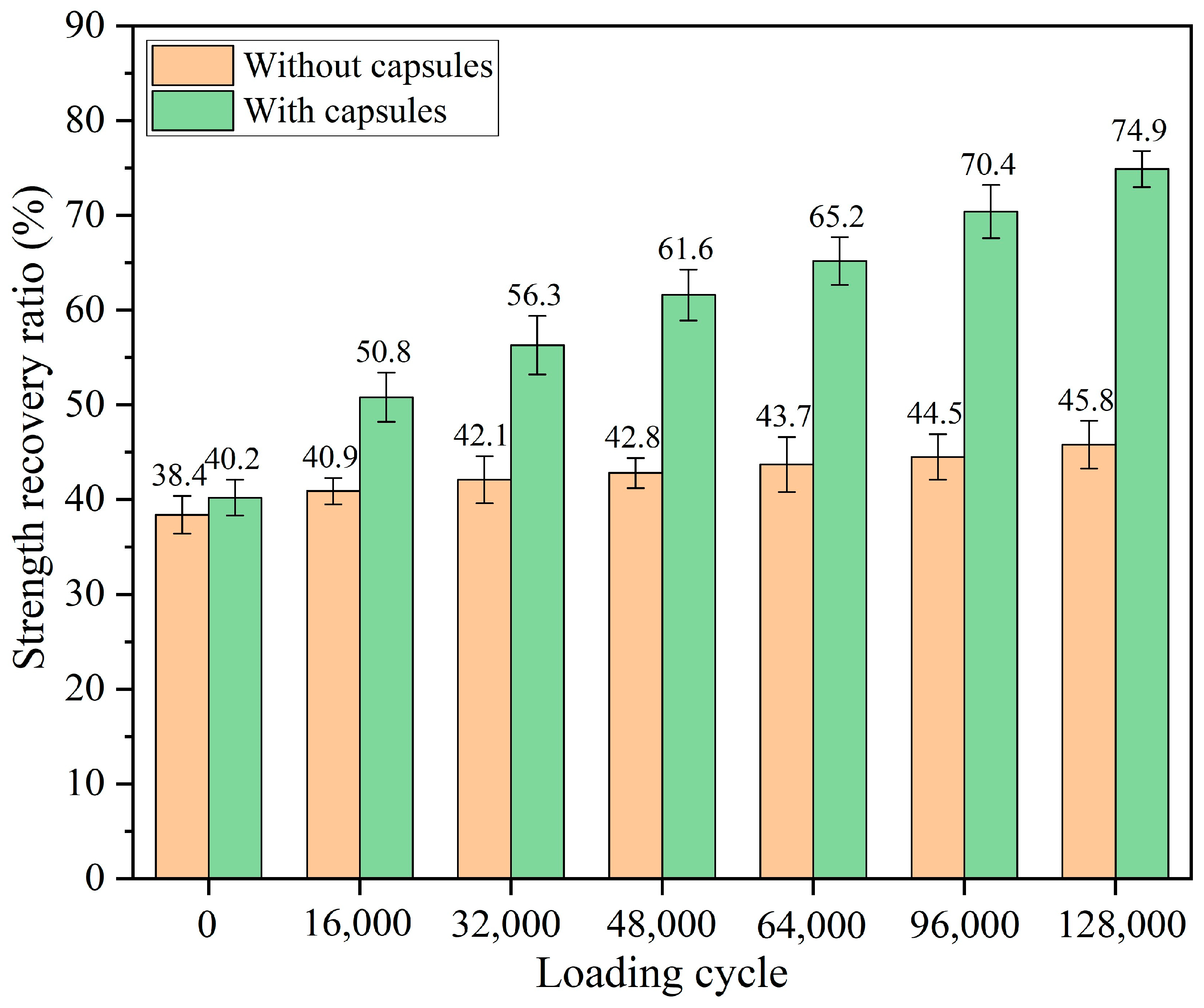
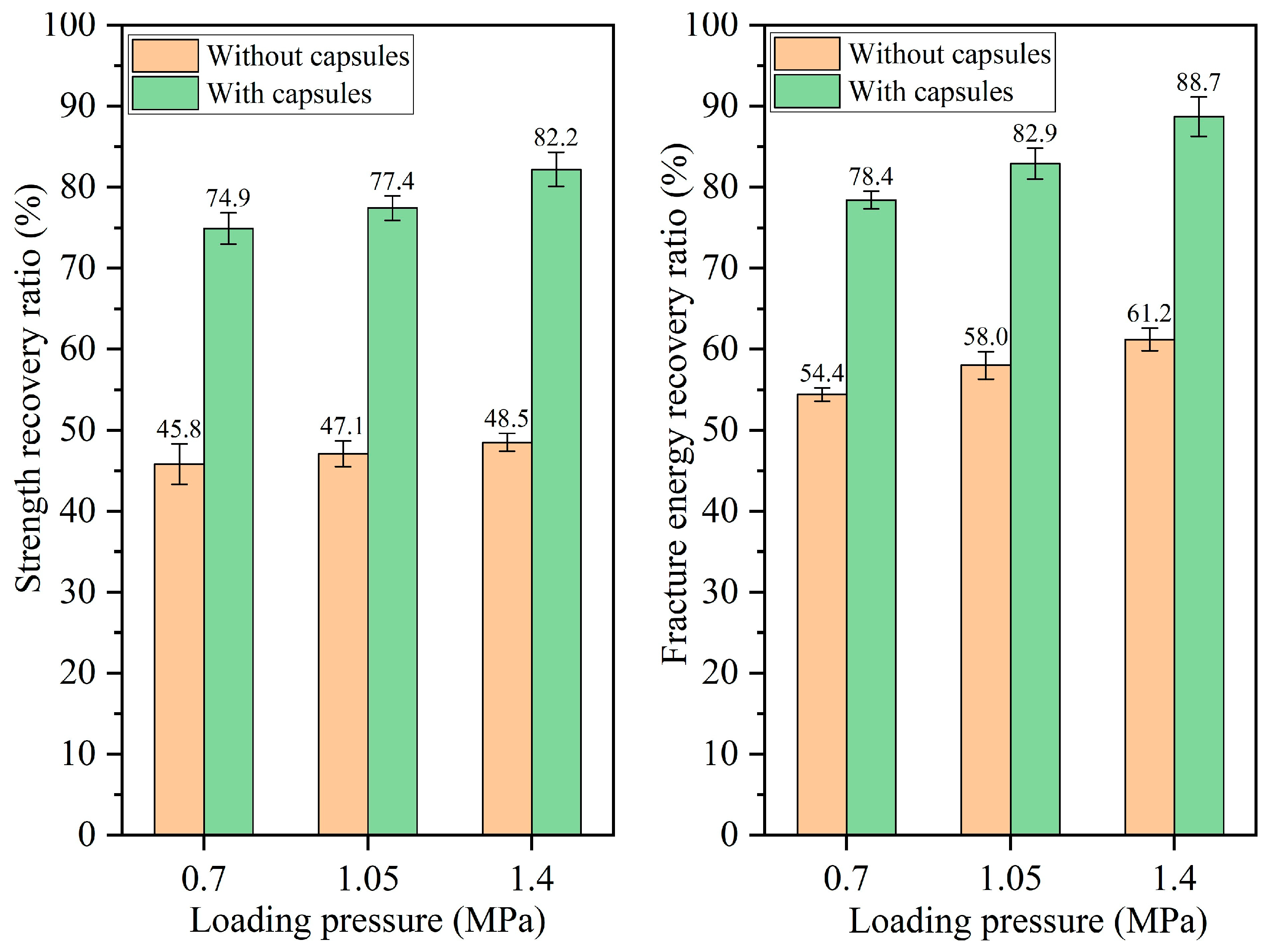
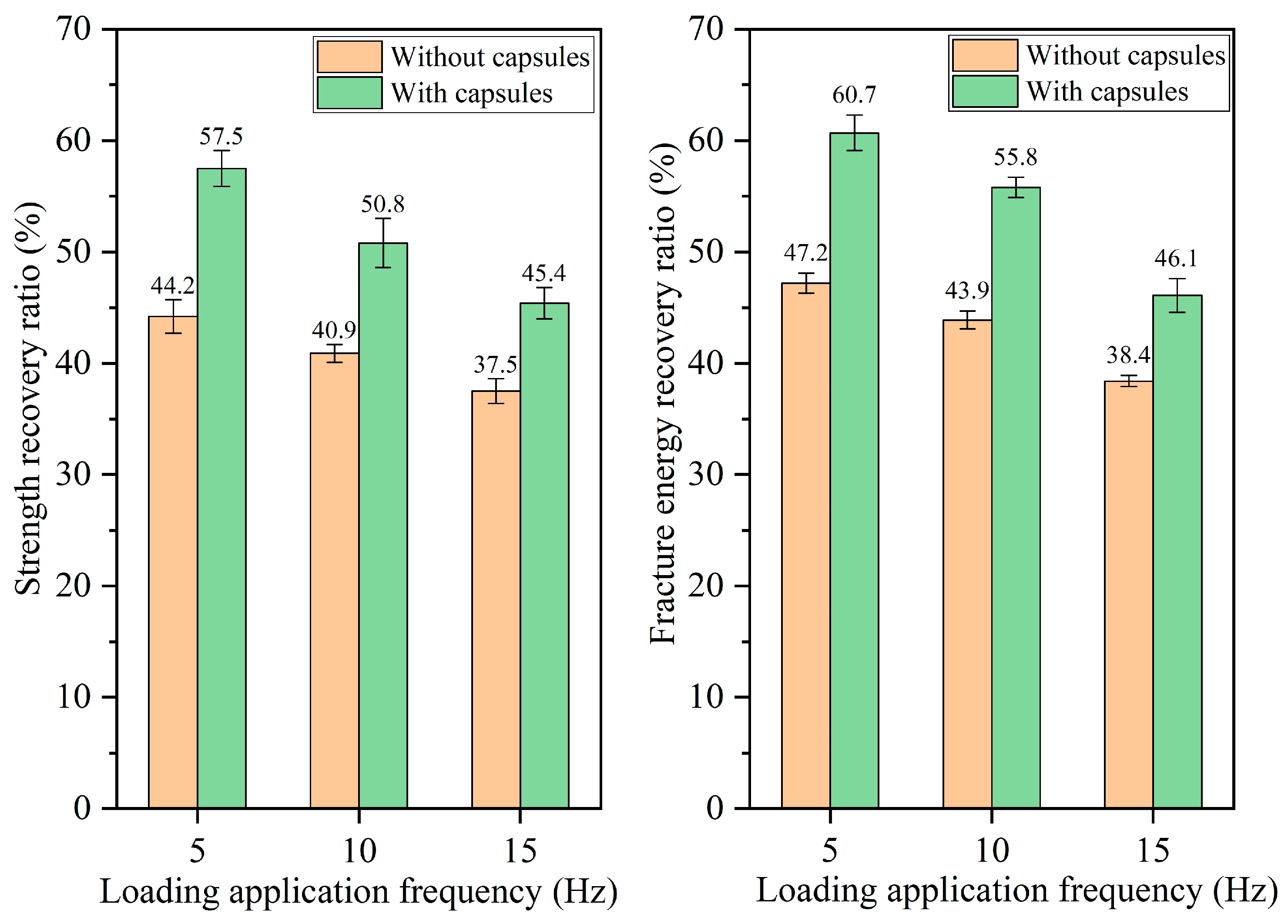
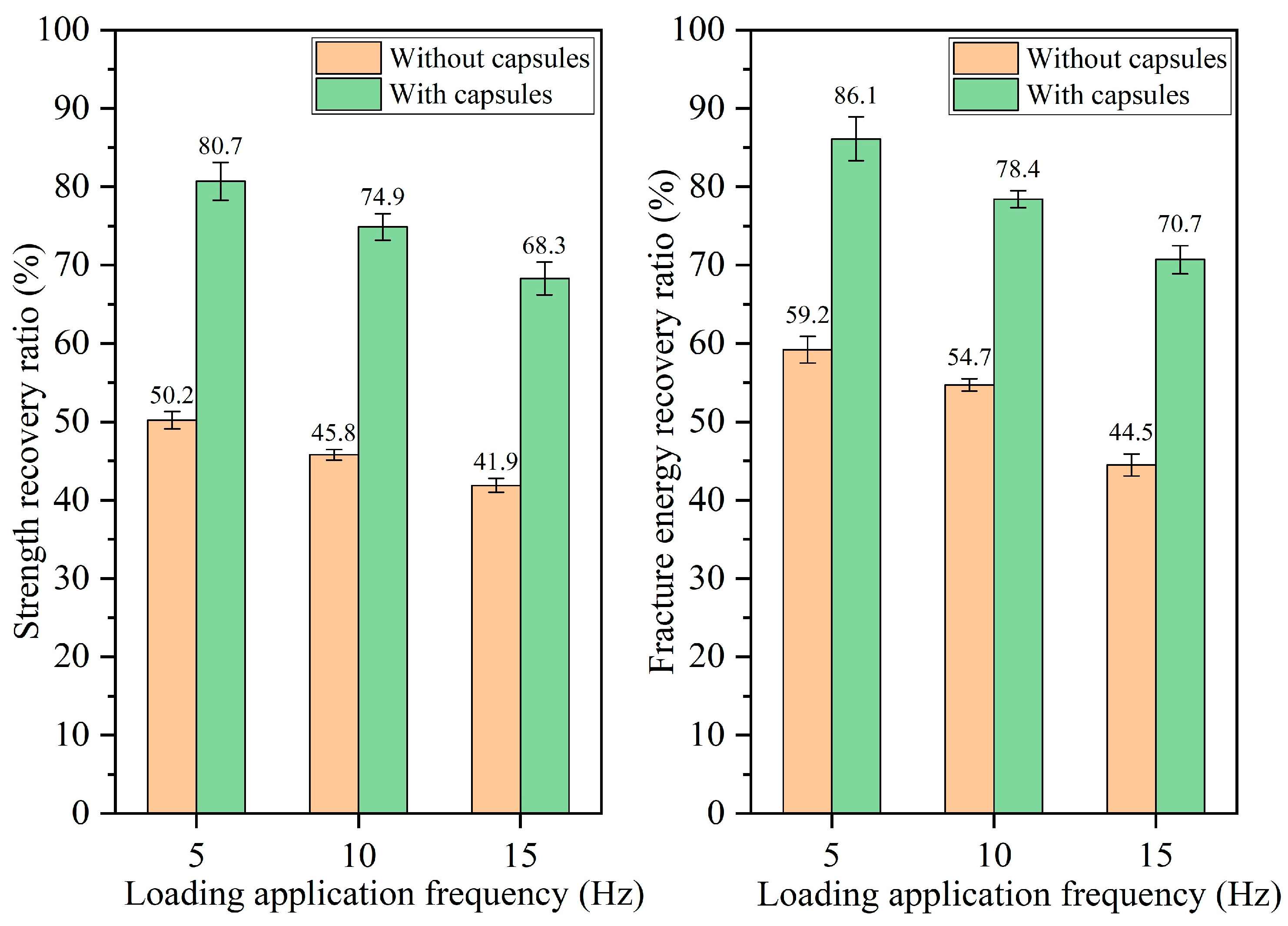
3.2.1. Healing Performance of Test Beams After Various Load Cycles
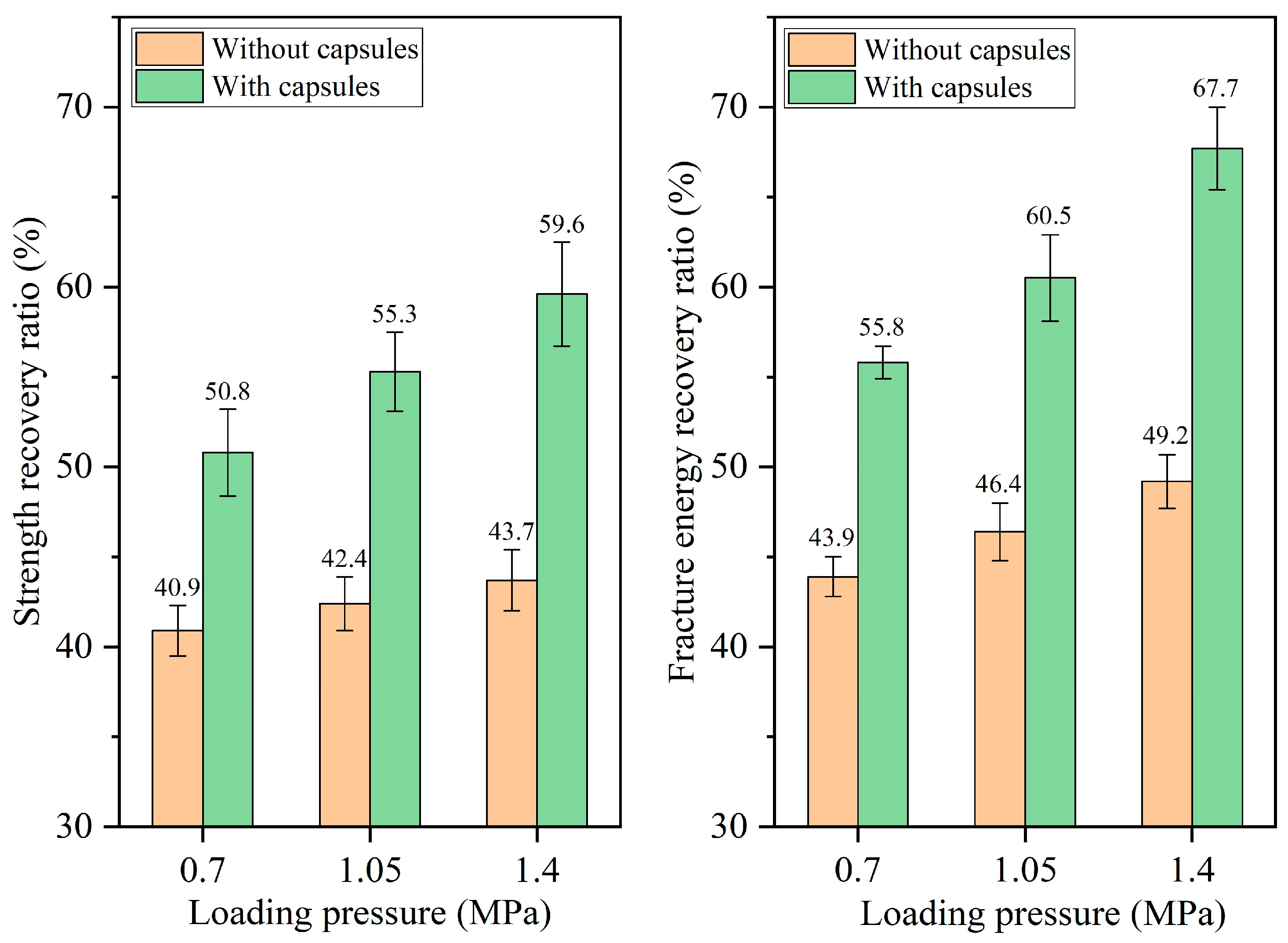
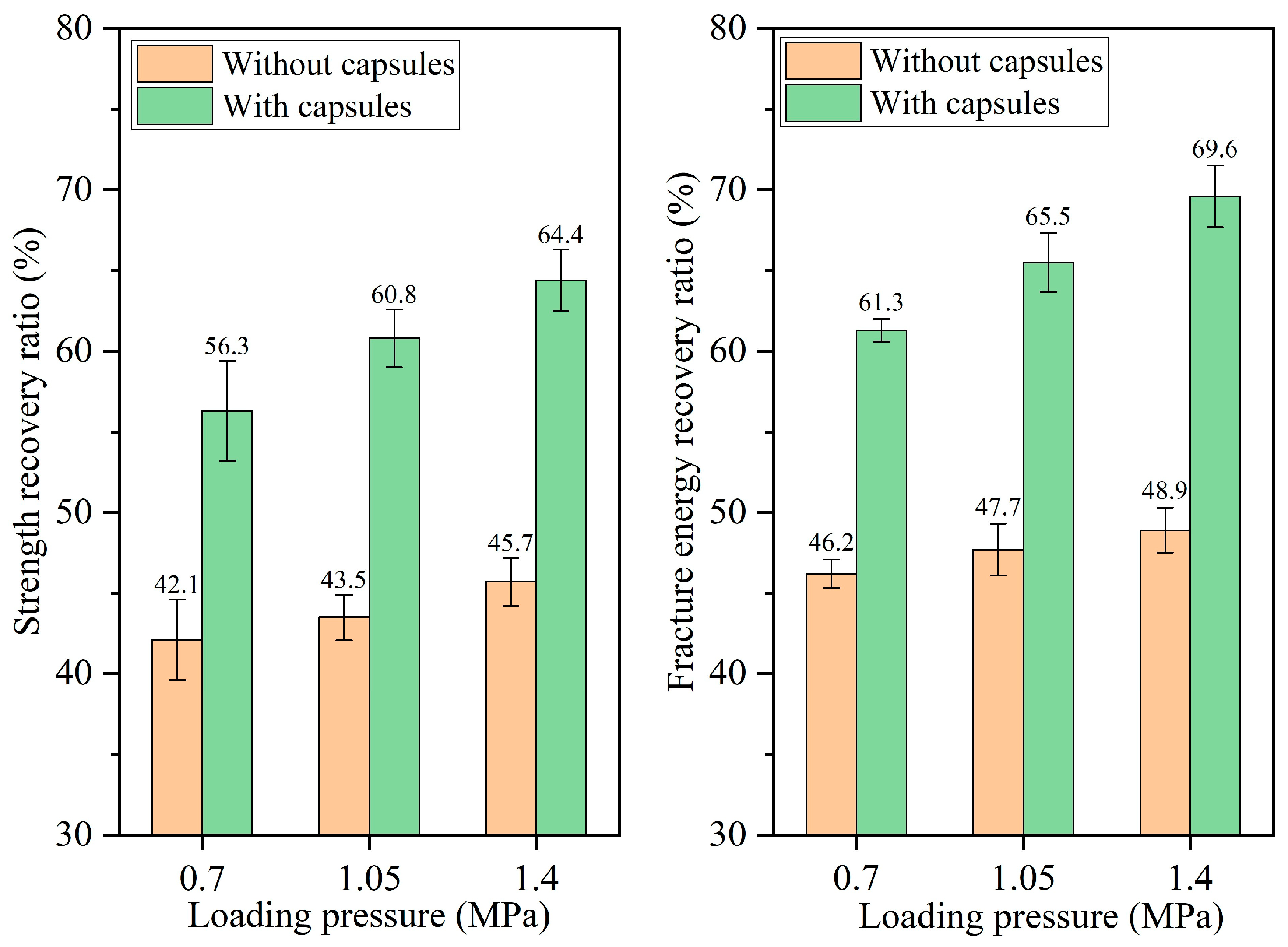
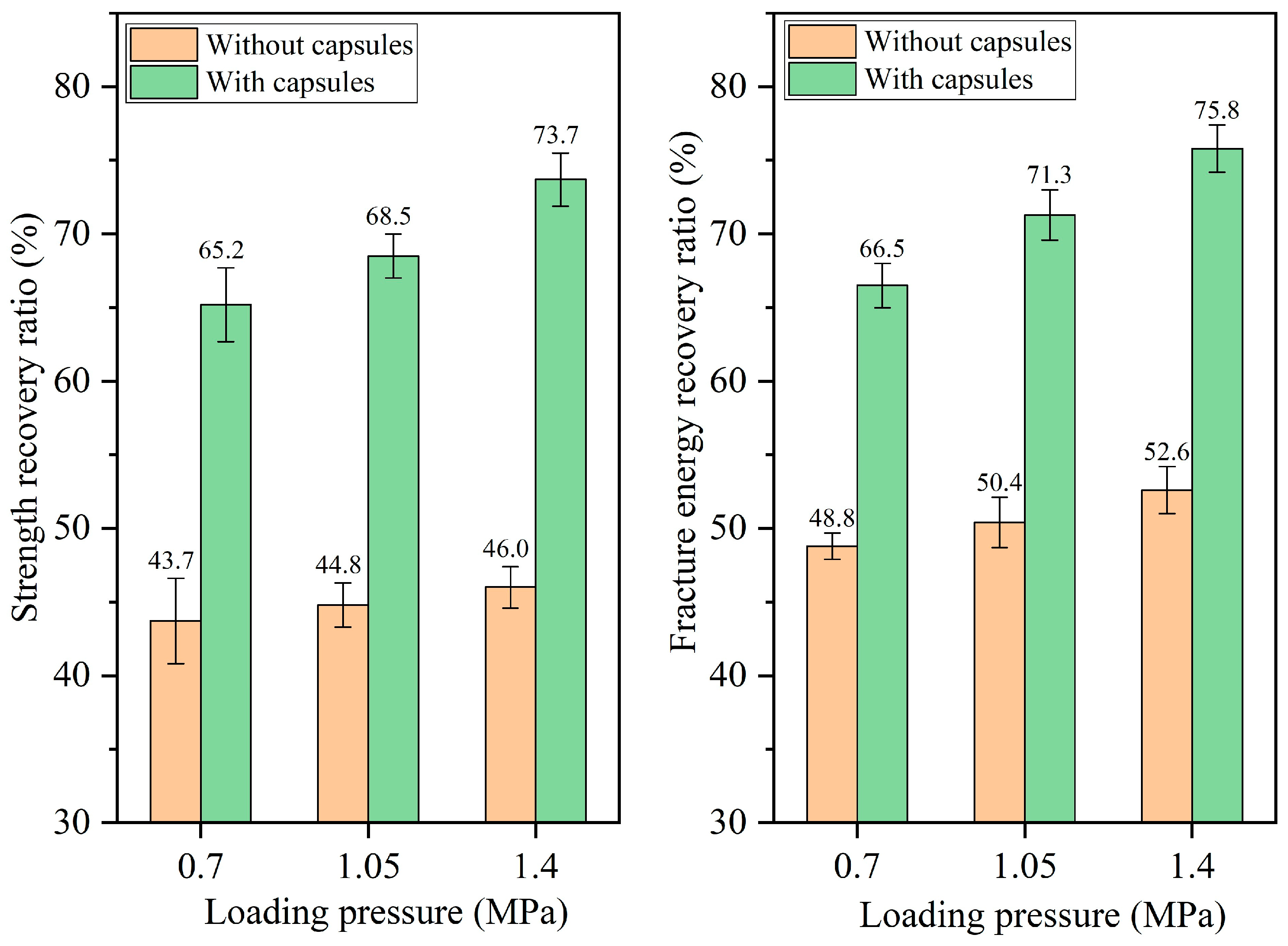
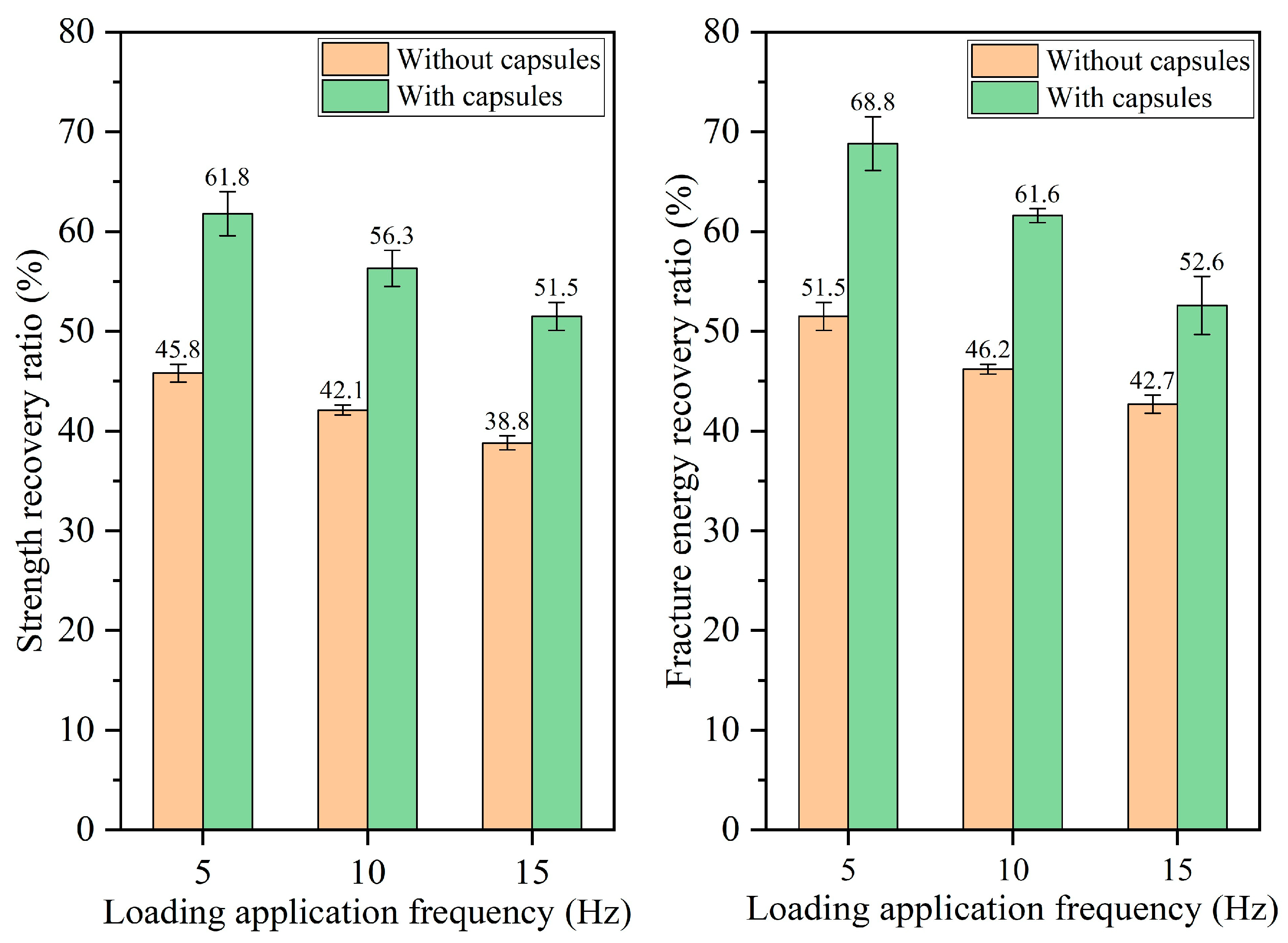
3.2.2. Healing Performance of Test Beams Under Different Load Pressures
3.2.3. Healing Performance of Beams Following Different Load Frequencies
3.3. Rejuvenator Release Evaluation of Capsules After Cyclic Load
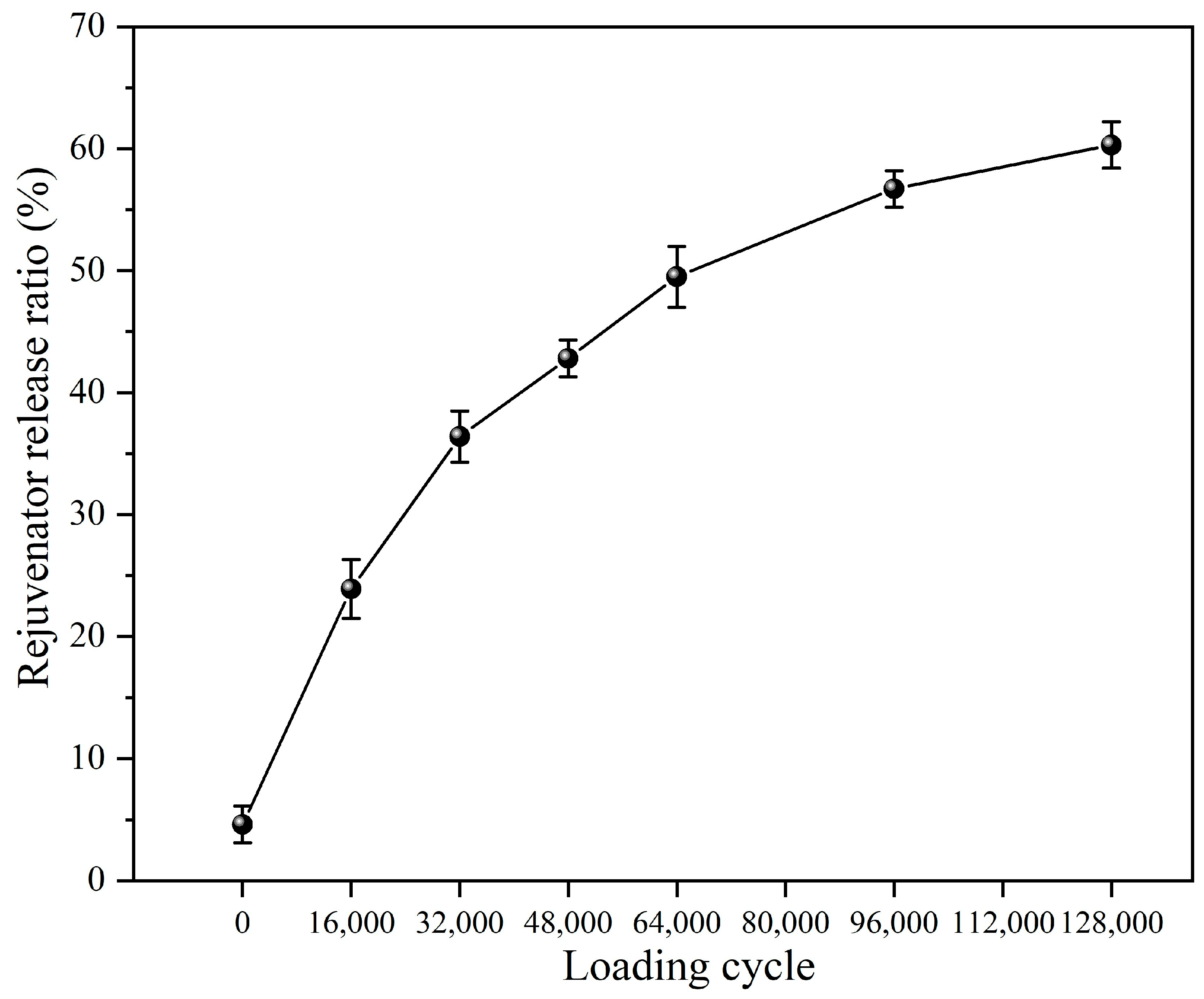
3.3.1. Rejuvenator Release Ratio of Capsules After Different Cycles of Load
3.3.2. Rejuvenator Release Ratio of Capsules Following Different Load Pressures
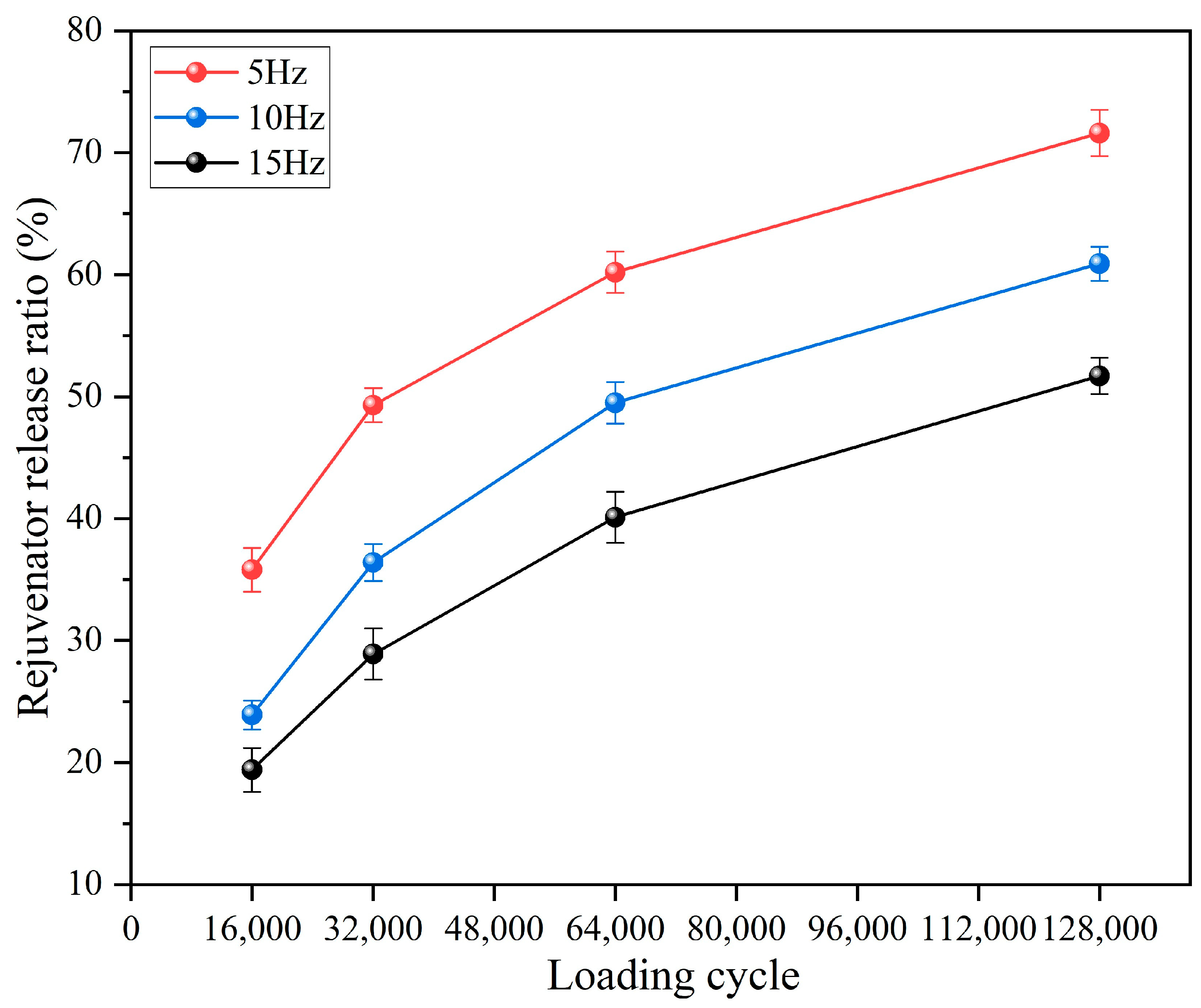
3.3.3. Rejuvenator Release Ratio of Capsules Following Different Load Application Frequencies
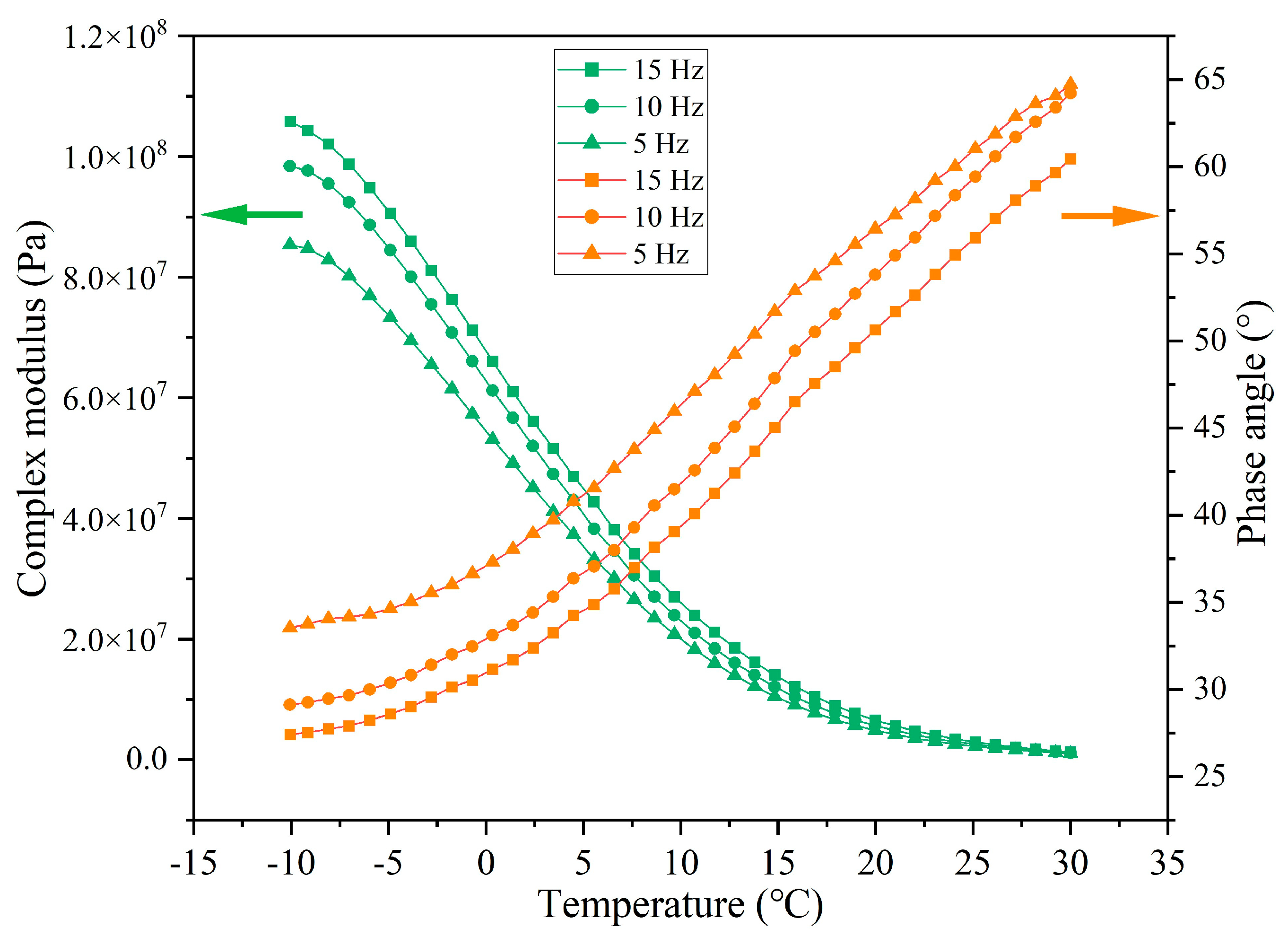
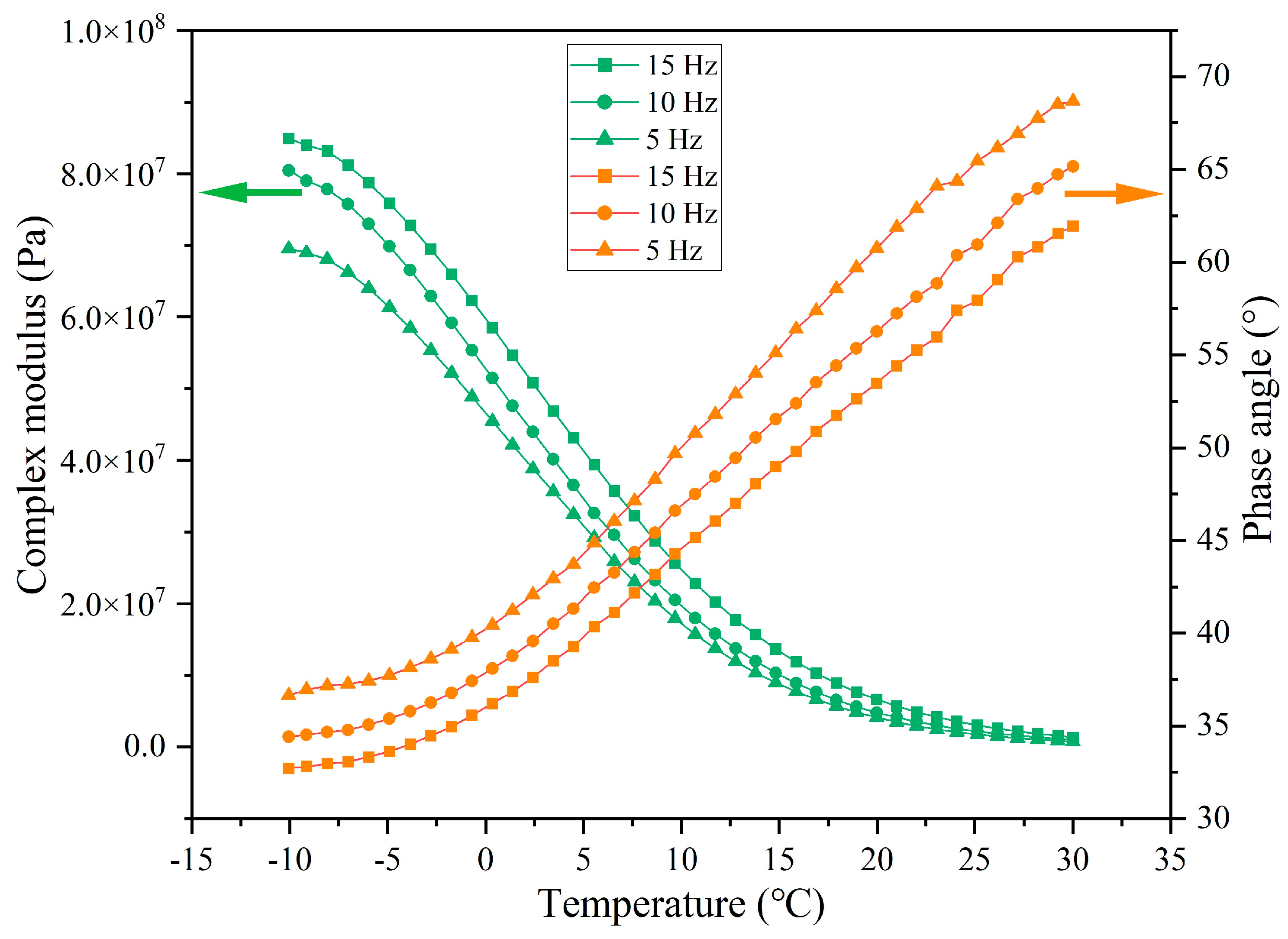
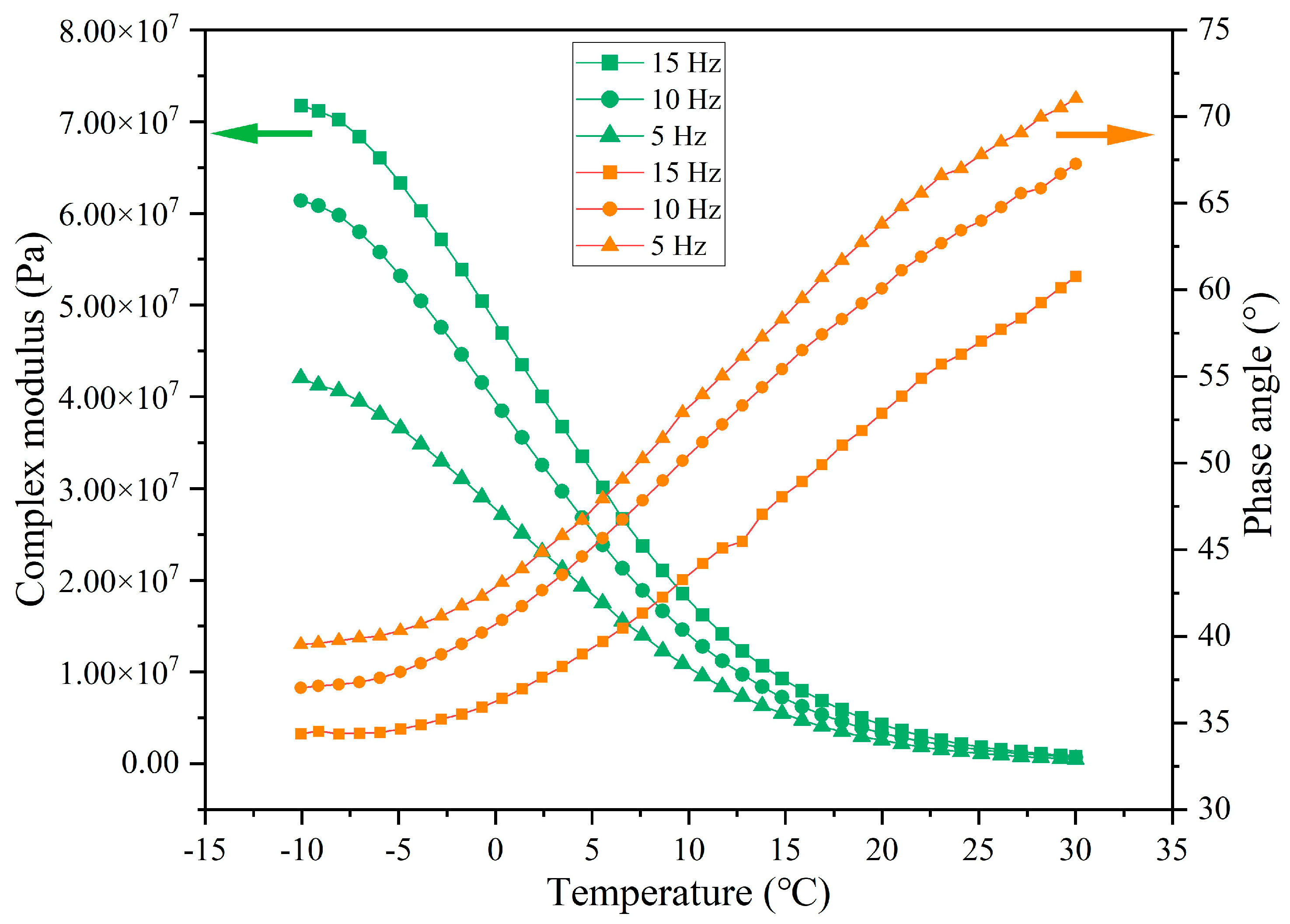
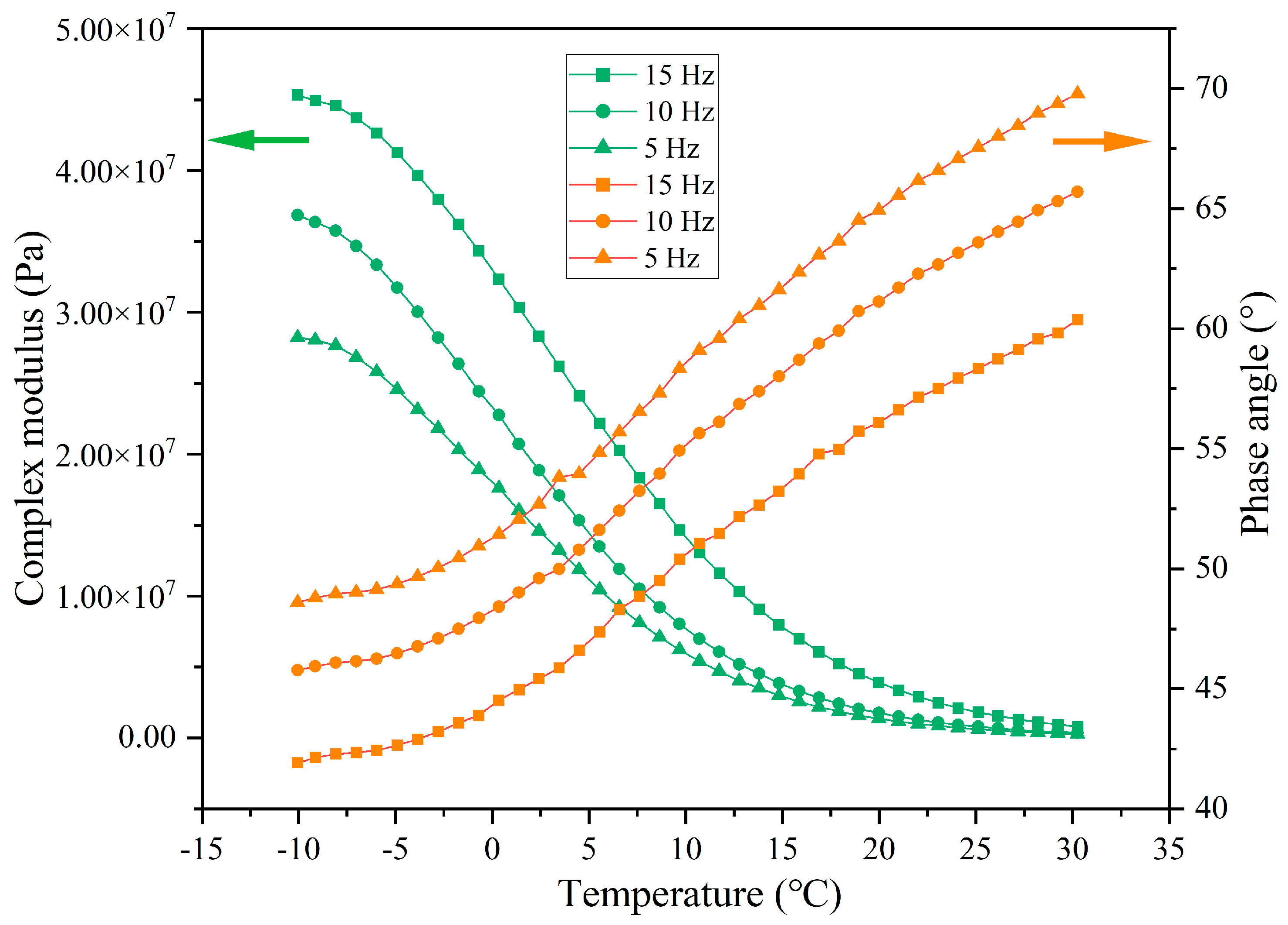
3.4. Rheological Characteristics of Asphalt Binder Following Cyclic Load
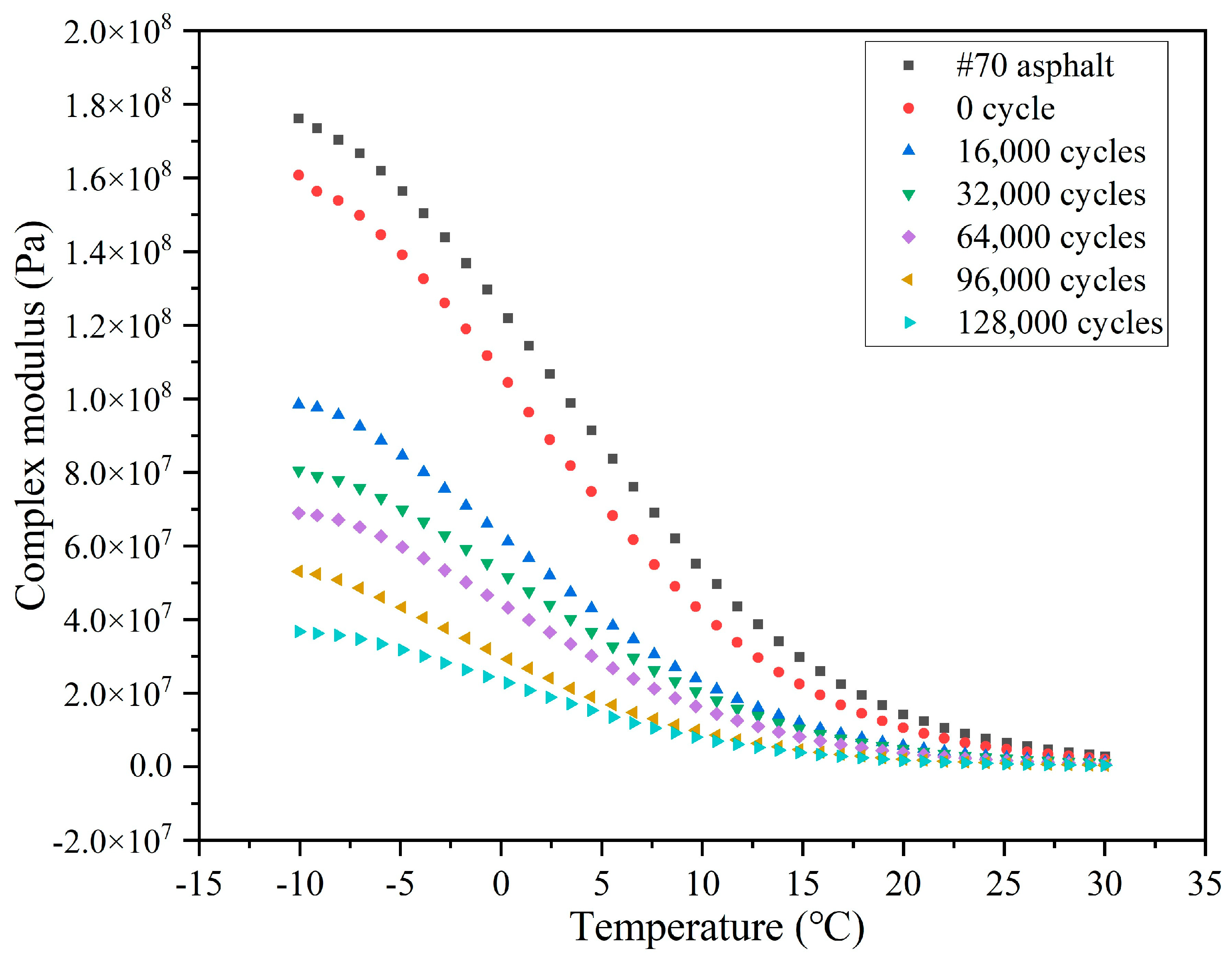
3.4.1. Rheological Property of Asphalt Under Different Cycles of Load
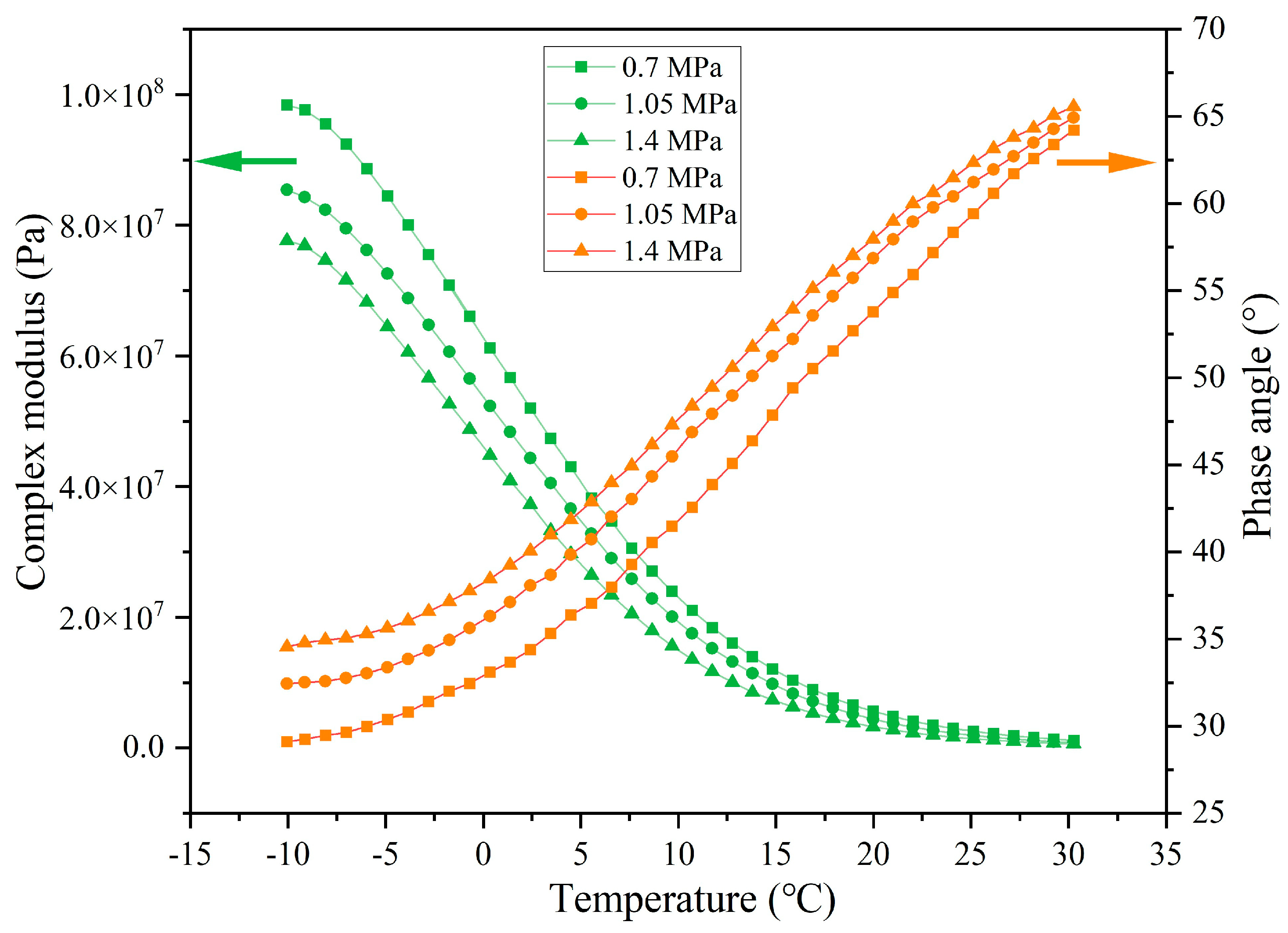
3.4.2. Rheological Property of Asphalt Binder Following Different Load Pressures
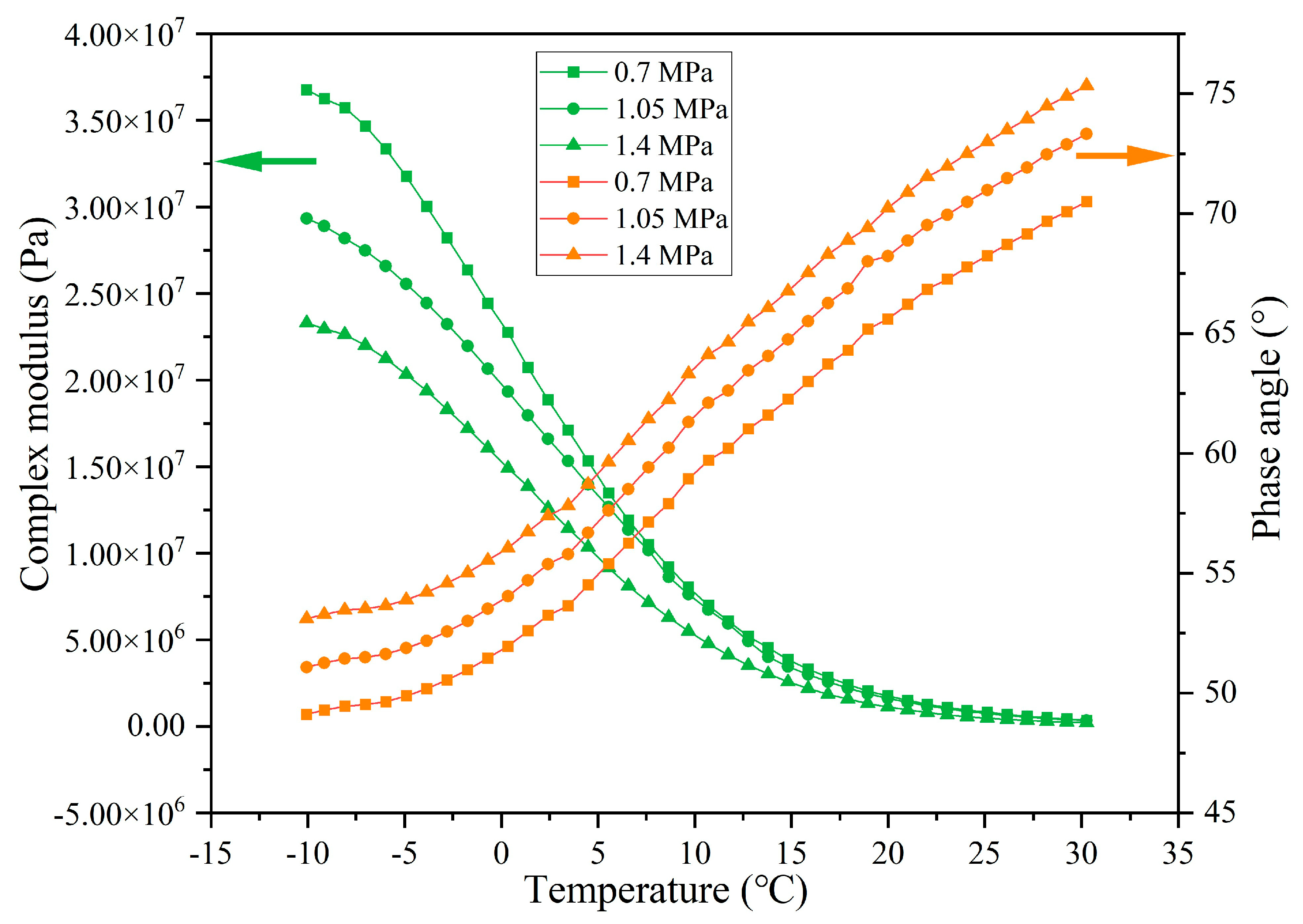
3.4.3. Rheological Property of Asphalt Binder Under Different Load Application Frequencies
3.5. SARA Fractions of Extracted Asphalt Binder After Cyclic Load
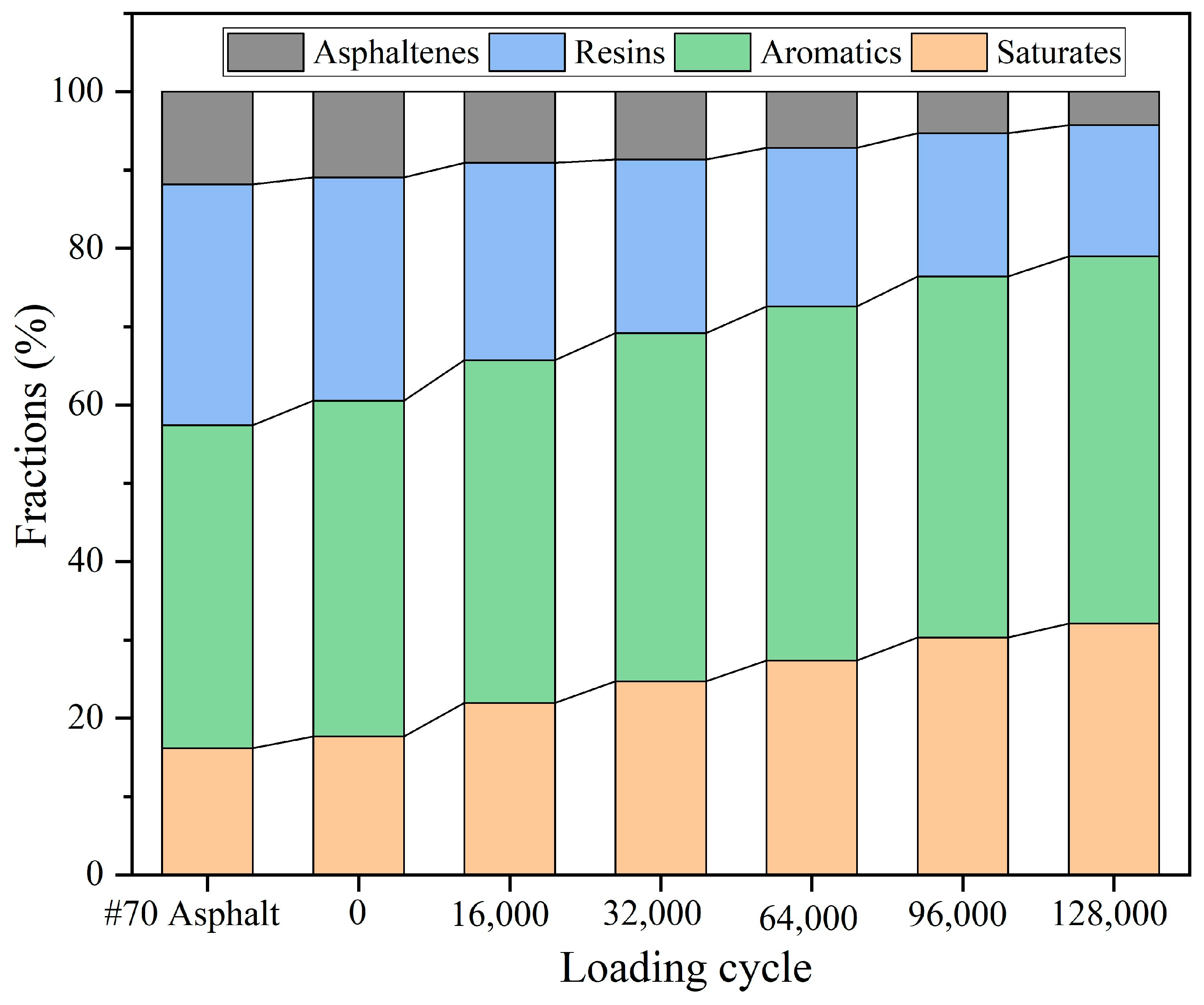
3.5.1. SARA Fractions of Asphalt After Different Load Cycles
3.5.2. SARA Fractions of Extracted Asphalt Binder Under Different Load Pressures
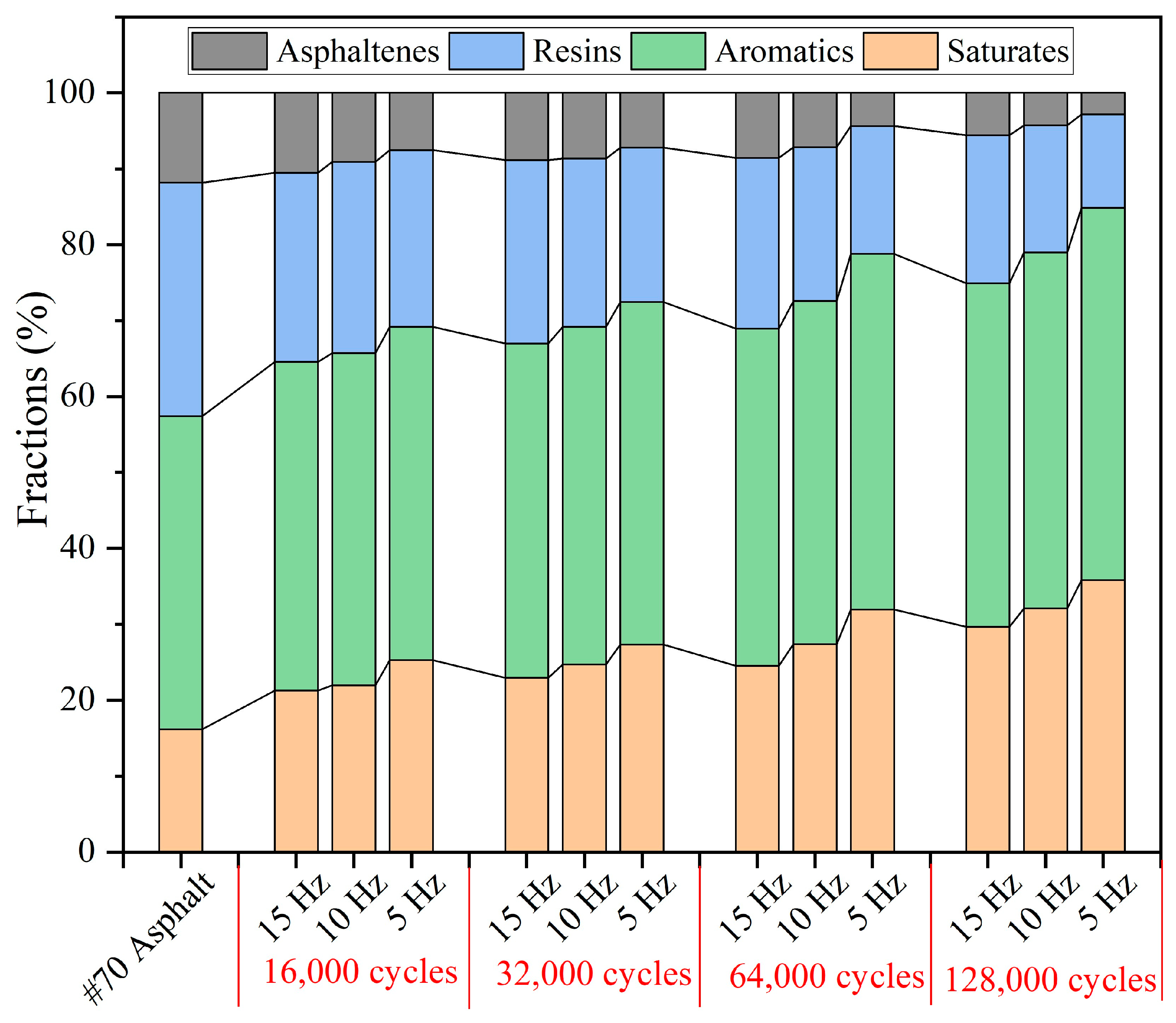
3.5.3. SARA Fractions of Extracted Asphalt Binder After Different Load Frequencies
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- The healing ratio of normal asphalt concrete exhibits minimal fluctuations with the load cycle, pressure, and frequency. The healing ratio of capsule-modified asphalt concrete increases as the load cycle and intensity increase and decreases as the load frequency increases. Overloading and speeding accelerate crack formation in asphalt pavements; the incorporation of capsules may mitigate this phenomenon.
- (2)
- The rejuvenator in the capsules shows a gradual release feature. After 16,000, 32,000, 48,000, 64,000, 96,000, and 128,000 cycles of load (0.7 MPa), the rejuvenator release ratios of the capsules are 23.9%, 36.4%, 44.8%, 49.5%, 56.7%, and 60.3%, respectively. The long-lasting sustained release characteristics of the capsules support the realization of sustainable healing for asphalt pavement. Under fixed load cycles, the rejuvenator release ratio of the capsules increases with the increase in load pressure and decreases with the increase in load frequency. Overloading and speeding accelerate the release of rejuvenating agents, which may expedite crack closure and repair, thereby mitigating damage to asphalt pavements under severe traffic loading conditions.
- (3)
- The released rejuvenator modifies the rheological properties of asphalt. The complex modulus and phase angle of asphalt decline and rise, respectively, with the increase in the rejuvenator release ratio. Meanwhile, the released rejuvenator can balance the component content of asphalt and improve the light components content of the asphalt, which realizes the regeneration of aged asphalt. The incorporation of capsules delays the aging of asphalt pavements, promising to extend their service life and enhance the resilience of road infrastructure.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, T.; Yang, S.; Liao, B.; Yang, E.; Jiang, X. Contribution of climate change and traffic load on asphalt pavement carbon emissions. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 434, 140553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, S.; Xiao, F.; Luan, D.; Cui, Q. Study on curing degree of emulsified asphalt chip seal based on the comprehensive electrical properties index. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 418, 135401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Peng, W.; Mao, J.; Yan, X.; Liu, Z.; Kong, L. Airport pavement performance evaluation of pavement fog seal based on optimized test technology. Front. Mater. 2023, 10, 1231461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Cheng, M.; Yi, J.; Yang, G. Research on the Influence of Material Composition and Construction Process on the Properties of Emulsified Sand Asphalt Fog Seal. In Proceedings of the 13th International Conference on Road and Airfield Pavement Technology (ICPT), Beijing, China, 6–8 July 2023; pp. 500–511. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Liu, K.; Chong, D.; Niu, D.; Lin, P.; Liu, X.; Niu, Y.; Jing, R. Evaluation of photocatalytic micro-surfacing mixture: Road performance, vehicle exhaust gas degradation capacity and environmental impacts. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 345, 128367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.; Zheng, M.; Gao, Y.; Ding, X.; Zhang, W.; Chen, W. Study of long-term skid and wear resistance of waterborne epoxy resin-SBR compound modified emulsified asphalt microsurfacing. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2024, 141, e54937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Montero, T.; Martinez, A.H.; Miro, R.; Subarroca, M.; Bobis, A. Characterising the bonding between asphalt ultra-thin layers applying a new cyclic shear test. Int. J. Fatigue 2023, 177, 107953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Feng, Z.; Chen, Y.; Yu, H.; Korolev, E.; Obukhova, S.; Zou, G.; Zhang, Y. Investigation of cracking resistance of cold asphalt mixture designed for ultra-thin asphalt layer. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 414, 134941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, P.; Wu, S.; Zhang, L.; Liu, Q.; Xu, S.; Wang, J. A novel combined healing system for sustainable asphalt concrete based on loading-microwave dual responsive capsules. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 450, 141927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabette, M.; Pais, J.; Micaelo, R. Extrinsic healing of asphalt mixtures: A review. Road Mater. Pavement Des. 2023, 25, 1145–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Hoff, I.; Zhang, X.; Liu, J.; Yang, C.; Wang, F. A Methodological Review on Development of Crack Healing Technologies of Asphalt Pavement. Sustainability 2023, 15, 9659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nalbandian, K.M.; Carpio, M.; González, Á. Analysis of the scientific evolution of self-healing asphalt pavements: Toward sustainable road materials. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 293, 126107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, K.; Ahmad, W.; Amin, M.N.; Khan, S.A.; Deifalla, A.F.; Younes, M.Y.M. Research evolution on self-healing asphalt: A scientometric review for knowledge mapping. Rev. Adv. Mater. Sci. 2023, 62, 20220331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, P.; Wu, S.; Liu, Q.; Wang, H.; Gong, X.; Zhao, Z.; Xu, S.; Jiang, J.; Fan, L.; Tu, L. Extrinsic self-healing asphalt materials: A mini review. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 425, 138910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, X.; Xiao, Z.; He, C.; Li, W.; Lin, P.; Meng, Y.; Hu, C. Roles of waste carbon fibers on the efficiency of multiple induction heating healing behavior in asphalt mixture for sustainable infrastructure. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 423, 138694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahanbakhsh, H.; Nejad, F.M.; Khodaii, A.; Karimi, M.M. Induction heating and induced healing evaluation of the asphalt concretes incorporating conductive aggregates exposed to microwave radiation. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 416, 135126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Liu, Q.; Wang, J.; Wu, S. Study on induction healing properties of OGFC asphalt mixture with high elasticity and high viscosity modifier. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 411, 134317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Yu, J.; Wu, S.; Liu, Q.; Li, B.; Li, Y.; Wu, Y. Study on the gradient heating and healing behaviors of asphalt concrete induced by induction heating. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 208, 638–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Zou, Y.; Wu, S.; Li, H.; Xu, S.; Zhao, Y.; Lv, Y. Research on gradient characteristics and its prediction method of induction heating asphalt concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 309, 124920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trigos, L.; Escavy, J.I.; Gallego, J.; Gulisano, F. Natural factors related to the differential heating of aggregates exposed to microwaves. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 314, 125654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, D.; Jiang, X.; Leng, Z.; Zhang, S.; Wang, D.; Zhong, J. Dual responsive microwave heating-healing system in asphalt concrete incorporating coal gangue and functional aggregate. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 422, 138648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Zheng, L.; Cheng, Y.; Chi, F.; Liu, K.; Zhu, T. Research on maintenance equipment and maintenance technology of steel fiber modified asphalt pavement with microwave heating. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2023, 18, 730–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, B.; Sha, A.; Barbieri, D.M.; Zhang, X.; Chen, H.; Hoff, I. Evaluation of microwave aging impact on asphalt mixtures. Road Mater. Pavement Des. 2022, 24, 730–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, T.; Hofko, B.; Sun, D.; Mirwald, J.; Eberhardsteiner, L.; Hu, M. Microscopic and rheologic characterization of third generation self-repairing microcapsule modified asphalt. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 400, 132841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, X.; Xu, T. Fatigue fracture and self-healing behaviors of cold recycled emulsified asphalt mixture containing microcapsules based on semicircular bending test. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 410, 137171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, J.-F.; Schlangen, E. Synthesis and physicochemical properties of high compact microcapsules containing rejuvenator applied in asphalt. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 198–199, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Zheng, M.; Li, P.; Zhang, J.; Qiao, R.; Cheng, C.; Xu, H. Preparation and characterization of self-healing microcapsules of asphalt. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 263, 120174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Zhou, T.; Pei, J. Design, preparation and properties of microcapsules containing rejuvenator for asphalt. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 99, 143–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.; Pang, Q.; Zhu, X.; Tian, Y.; Lu, T.; Yang, Y. Enhanced Self-Healing Process of Sustainable Asphalt Materials Containing Microcapsules. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 9881–9893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Micaelo, R.; Al-Mansoori, T.; Garcia, A. Study of the mechanical properties and self-healing ability of asphalt mixture containing calcium-alginate capsules. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 123, 734–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Mansoori, T.; Micaelo, R.; Artamendi, I.; Norambuena-Contreras, J.; Garcia, A. Microcapsules for self-healing of asphalt mixture without compromising mechanical performance. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 155, 1091–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Mansoori, T.; Norambuena-Contreras, J.; Garcia, A. Effect of capsule addition and healing temperature on the self-healing potential of asphalt mixtures. Mater. Struct. 2018, 51, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Mansoori, T.; Norambuena-Contreras, J.; Micaelo, R.; Garcia, A. Self-healing of asphalt mastic by the action of polymeric capsules containing rejuvenators. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 161, 330–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Liu, Q.; Li, H.; Norambuena-Contreras, J.; Wu, S.; Bao, S.; Shu, B. Synthesis and characterization of multi-cavity Ca-alginate capsules used for self-healing in asphalt mixtures. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 211, 298–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Hoff, I.; Zhang, X.; Yang, C. Investigation of the self-healing and rejuvenating properties of aged asphalt mixture containing multi-cavity Ca-alginate capsules. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 361, 129685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, S.; Liu, Q.; Rao, W.; Yu, X.; Zhang, L. Synthesis and characterization of calcium alginate-attapulgite composite capsules for long term asphalt self-healing. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 265, 120779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, S.; Liu, Q.; Li, H.; Zhang, L.; Barbieri, D.M. Investigation of the Release and Self-Healing Properties of Calcium Alginate Capsules in Asphalt Concrete under Cyclic Compression Loading. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2021, 33, 04020401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, N.; Wang, H.; Wang, H.; Kazemi, M.; Fini, E. Research progress on resource utilization of waste cooking oil in asphalt materials: A state-of-the-art review. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 385, 135427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, J.; Yao, H.; Suo, Z.; You, Z.; Li, H.; Xu, S.; Sun, L. Effectiveness of Vegetable Oils as Rejuvenators for Aged Asphalt Binders. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2017, 29, D4016003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Liu, Q.; Wan, P.; Song, J.; Wang, H.; Zhao, F.; Wang, Y.; Wu, J. Effect of Ageing on Self-Healing Properties of Asphalt Concrete Containing Calcium Alginate/Attapulgite Composite Capsules. Materials 2022, 15, 1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaç, Ö.E.; Yilmaz, M.; Yalçın, E.; Kök, B.V.; Norambuena-Contreras, J.; Garcia, A. Self-healing of asphalt mastic using capsules containing waste oils. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 270, 121417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Riancho, N.; Saadoon, T.; Garcia, A.; Grossegger, D.; Hudson-Griffiths, R. Optimisation of self-healing properties for asphalts containing encapsulated oil to mitigate reflective cracking and maximize skid and rutting resistance. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 300, 123879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, P.; Wu, S.; Liu, Q.; Xu, H.; Wang, H.; Peng, Z.; Rao, W.; Zou, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Chen, S. Self-healing properties of asphalt concrete containing responsive calcium alginate/nano-Fe3O4 composite capsules via microwave irradiation. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 310, 125258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, P.; Wu, S.; Liu, Q.; Wang, H.; Zhao, F.; Wu, J.; Niu, Y.; Ye, Q. Sustained-release calcium alginate/diatomite capsules for sustainable self-healing asphalt concrete. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 372, 133639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, P.; Liu, Q.; Wu, S.; Zhao, Z.; Chen, S.; Zou, Y.; Rao, W.; Yu, X. A novel microwave induced oil release pattern of calcium alginate/nano-Fe3O4 composite capsules for asphalt self-healing. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 297, 126721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, W.; Liu, Q.; Yu, X.; Wan, P.; Wang, H.; Song, J.; Ye, Q. Efficient preparation and characterization of calcium alginate-attapulgite composite capsules for asphalt self-healing. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 299, 123931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, A.; Schlangen, E.; van de Ven, M.; Sierra-Beltran, G. Preparation of capsules containing rejuvenators for their use in asphalt concrete. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 184, 603–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, P.; Liu, Q.; Wu, S.; Zou, Y.; Zhao, F.; Wang, H.; Niu, Y.; Ye, Q. Dual responsive self-healing system based on calcium alginate/Fe3O4 capsules for asphalt mixtures. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 360, 129585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]











| Raw Material | Purity | Manufacturer |
|---|---|---|
| Sodium alginate | CP | Sinopharm Chemical Reagent (Beijing, China) |
| Anhydrous calcium chloride | CP | Sinopharm Chemical Reagent (Beijing, China) |
| Nano-Fe3O4 (50 nm) | 99.9% | Chaowei nanomaterials Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China. |
| Sunflower oil | Food grade | Arowana Group Co., Ltd., Hangzhou, China. |
| Tween 80 | AR | Sinopharm Chemical Reagent (Beijing, China) |
| Item | Value |
|---|---|
| Appearance | Light yellow liquid |
| Density (15 °C) | 0.935 g/cm3 |
| Viscosity (60 °C) | 0.285 Pa·s |
| Flash point | 230 °C |
| Design Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Service life of pavement (years) | 15 |
| Traffic volume cumulative equivalent axle times (times/lane) | 1 × 107 |
| Lane coefficient | 0.4 |
| Distribution coefficient of wheel grinding | 0.5 |
| Equivalent car axle load conversion factor | 0.12 |
| Speed (km/h) | Load Action Frequency (Hz) | Load Action Time (ms) | Rest Time (ms) | Load Cycle Time (ms) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 30 | 5 | 200 | 800 | 1000 |
| 60 | 10 | 100 | 900 | 1000 |
| 90 | 15 | 66.67 | 933.33 | 1000 |
| Performance | Value |
|---|---|
| Average diameter (mm) | 1.8 |
| Rejuvenator content (%mass) | 58.1% |
| Compressive strength (N) | 11.8 |
| Mass loss (%) at | |
| 160 °C | 2.8 |
| 200 °C | 3.9 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wan, P.; Ma, Z.; Lin, Z.; Zhong, P.; Zou, X.; Shen, Y.; Lin, N.; Chen, H.; Wang, J.; Wu, S.; et al. Evaluation of the Self-Healing Capacity of Asphalt Concrete with Polymer Capsules Containing Rejuvenator Under Various Cyclic Load Conditions. Materials 2025, 18, 5201. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18225201
Wan P, Ma Z, Lin Z, Zhong P, Zou X, Shen Y, Lin N, Chen H, Wang J, Wu S, et al. Evaluation of the Self-Healing Capacity of Asphalt Concrete with Polymer Capsules Containing Rejuvenator Under Various Cyclic Load Conditions. Materials. 2025; 18(22):5201. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18225201
Chicago/Turabian StyleWan, Pei, Zirong Ma, Zhiming Lin, Peixin Zhong, Xiaobin Zou, Yilun Shen, Niecheng Lin, Hang Chen, Jiazhu Wang, Shaopeng Wu, and et al. 2025. "Evaluation of the Self-Healing Capacity of Asphalt Concrete with Polymer Capsules Containing Rejuvenator Under Various Cyclic Load Conditions" Materials 18, no. 22: 5201. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18225201
APA StyleWan, P., Ma, Z., Lin, Z., Zhong, P., Zou, X., Shen, Y., Lin, N., Chen, H., Wang, J., Wu, S., Liu, Q., Zhang, L., & Gong, X. (2025). Evaluation of the Self-Healing Capacity of Asphalt Concrete with Polymer Capsules Containing Rejuvenator Under Various Cyclic Load Conditions. Materials, 18(22), 5201. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18225201









