Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Dynamics of LiTFSI–Pyrazole Eutectic Solvents
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
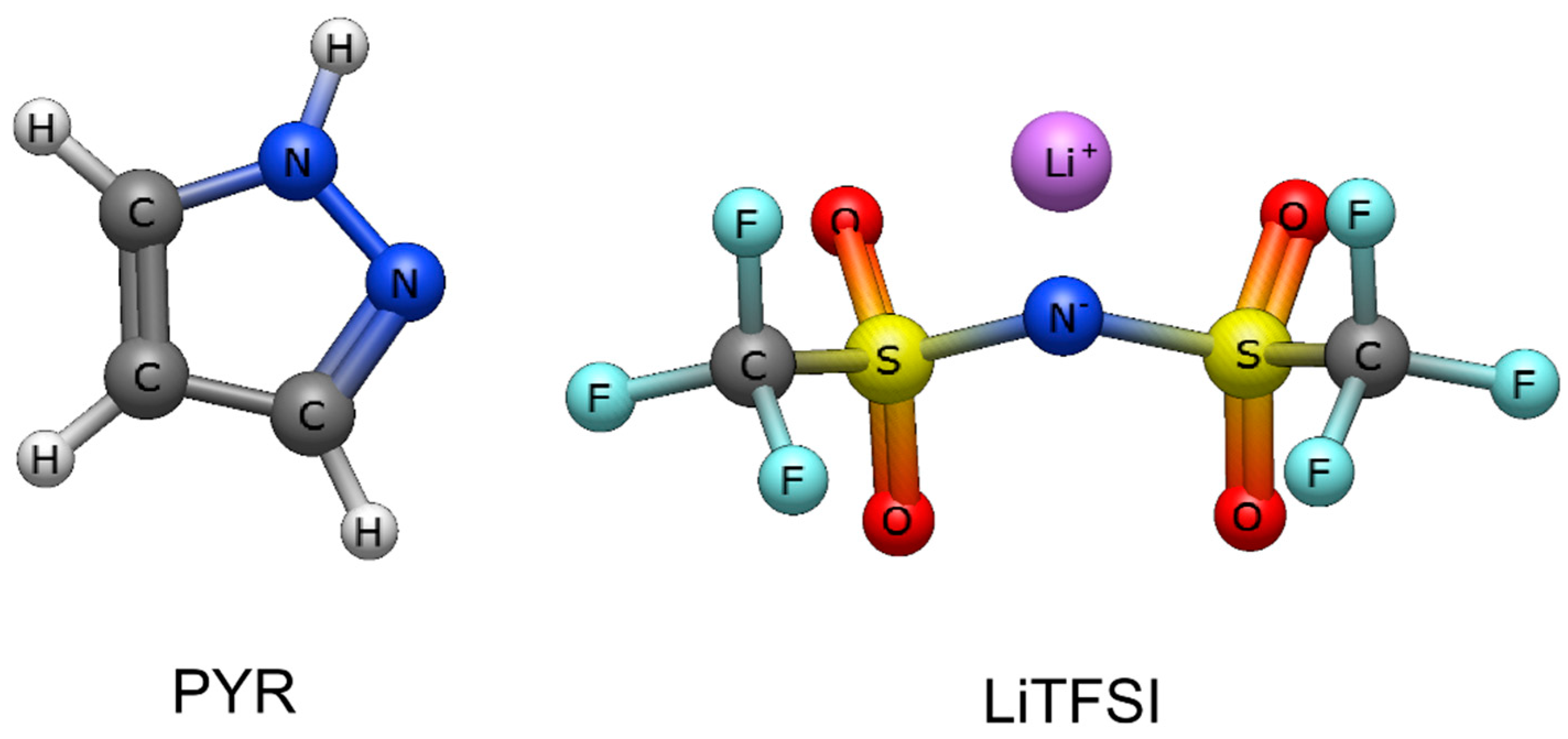
2.1. Sample Preparation
2.2. Diffusion NMR
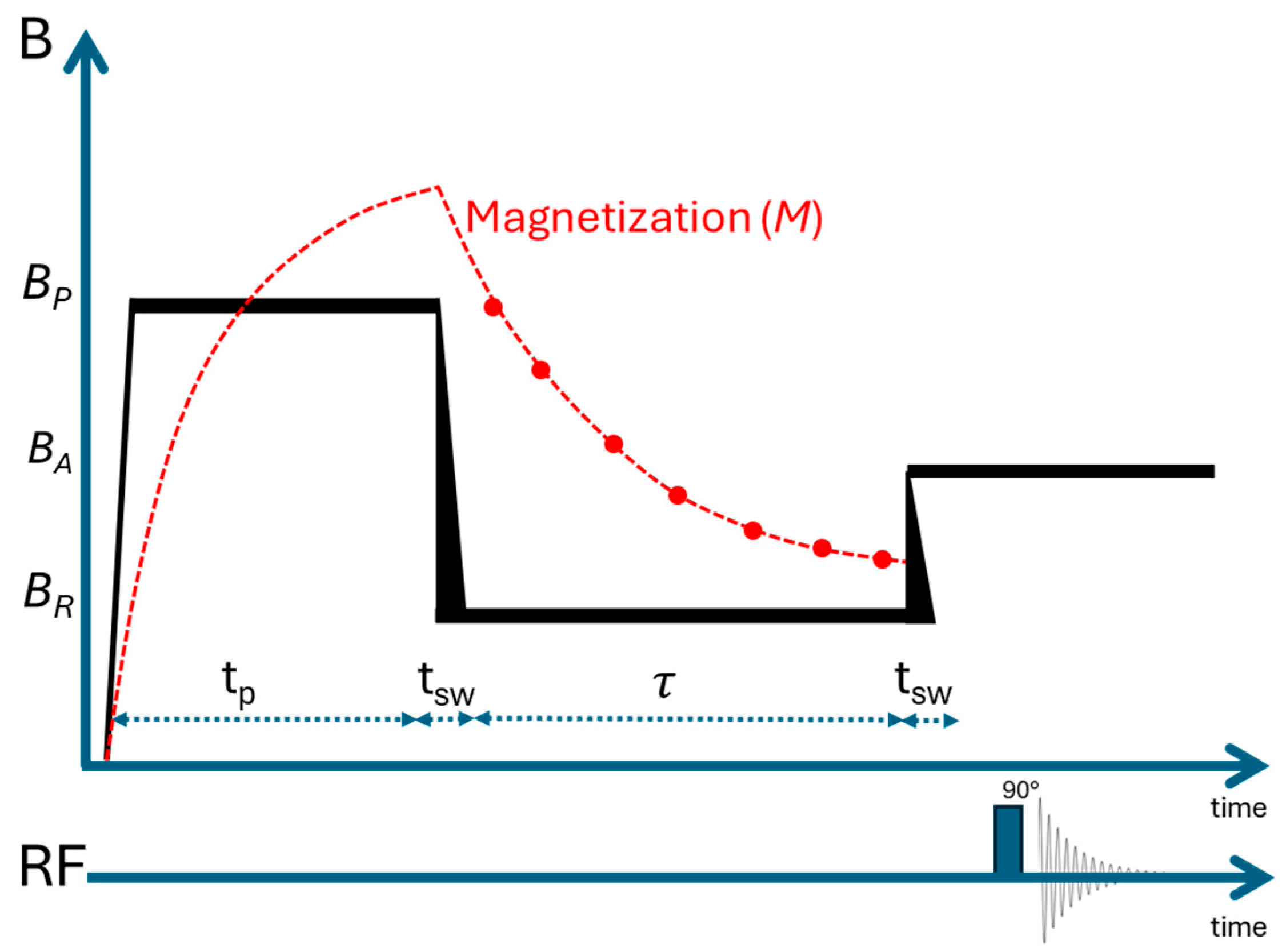
2.3. Longitudinal Relaxation NMR
2.4. Relaxation Models
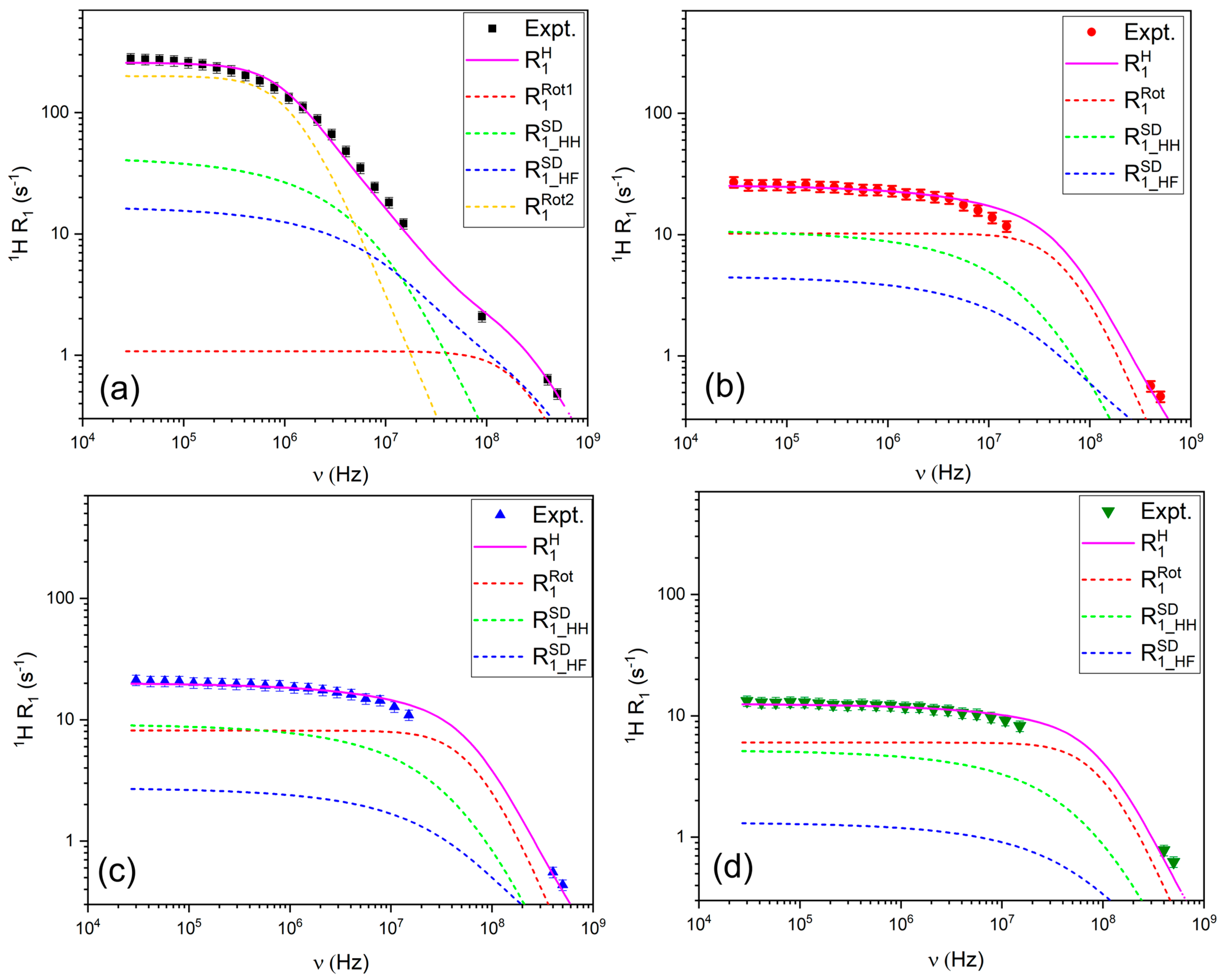
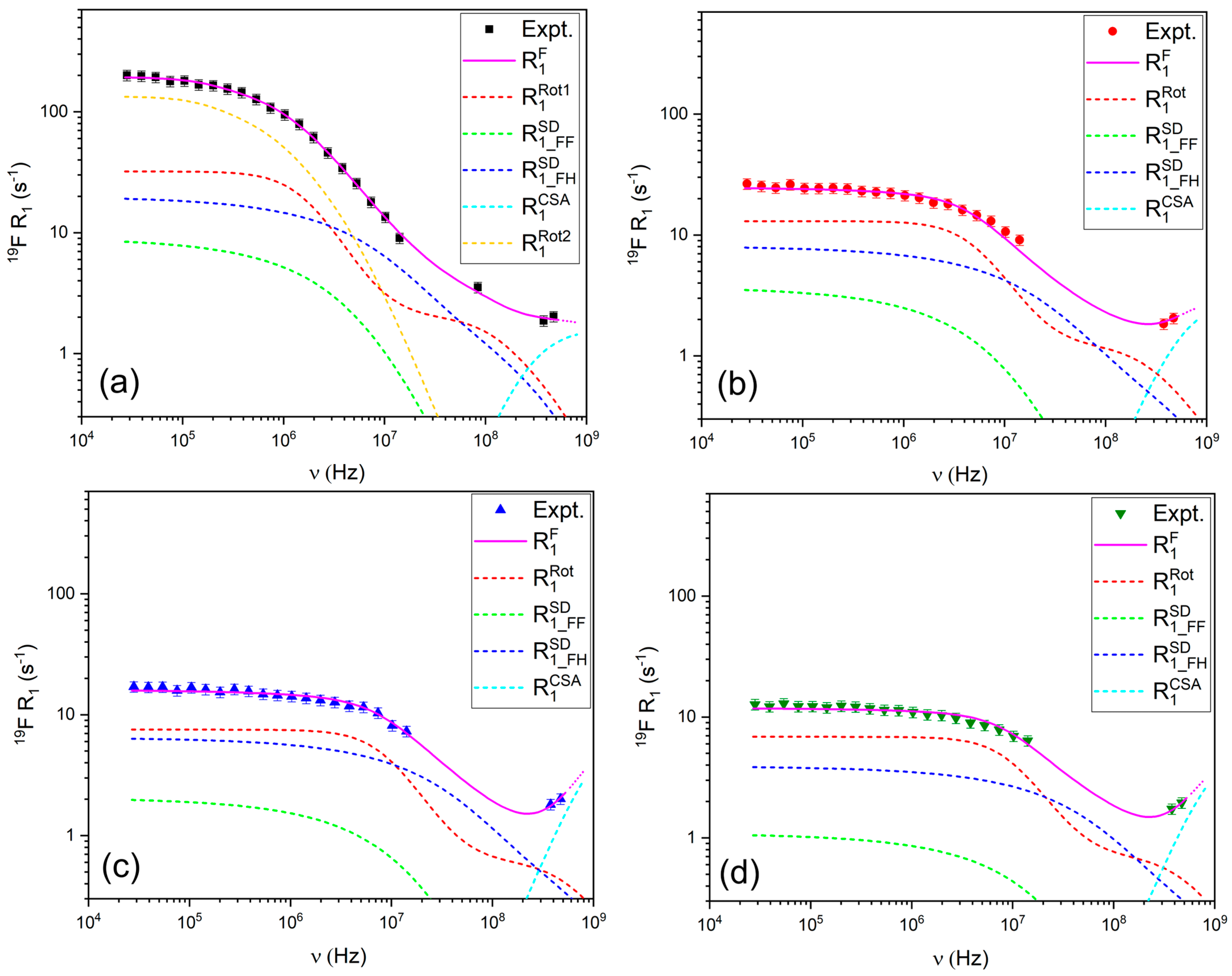
2.4.1. Relaxation Due to Intermolecular Contributions ()
2.4.2. Relaxation Due to Intramolecular Contributions ()
2.4.3. Relaxation Due to Chemical Shift Anisotropy ()
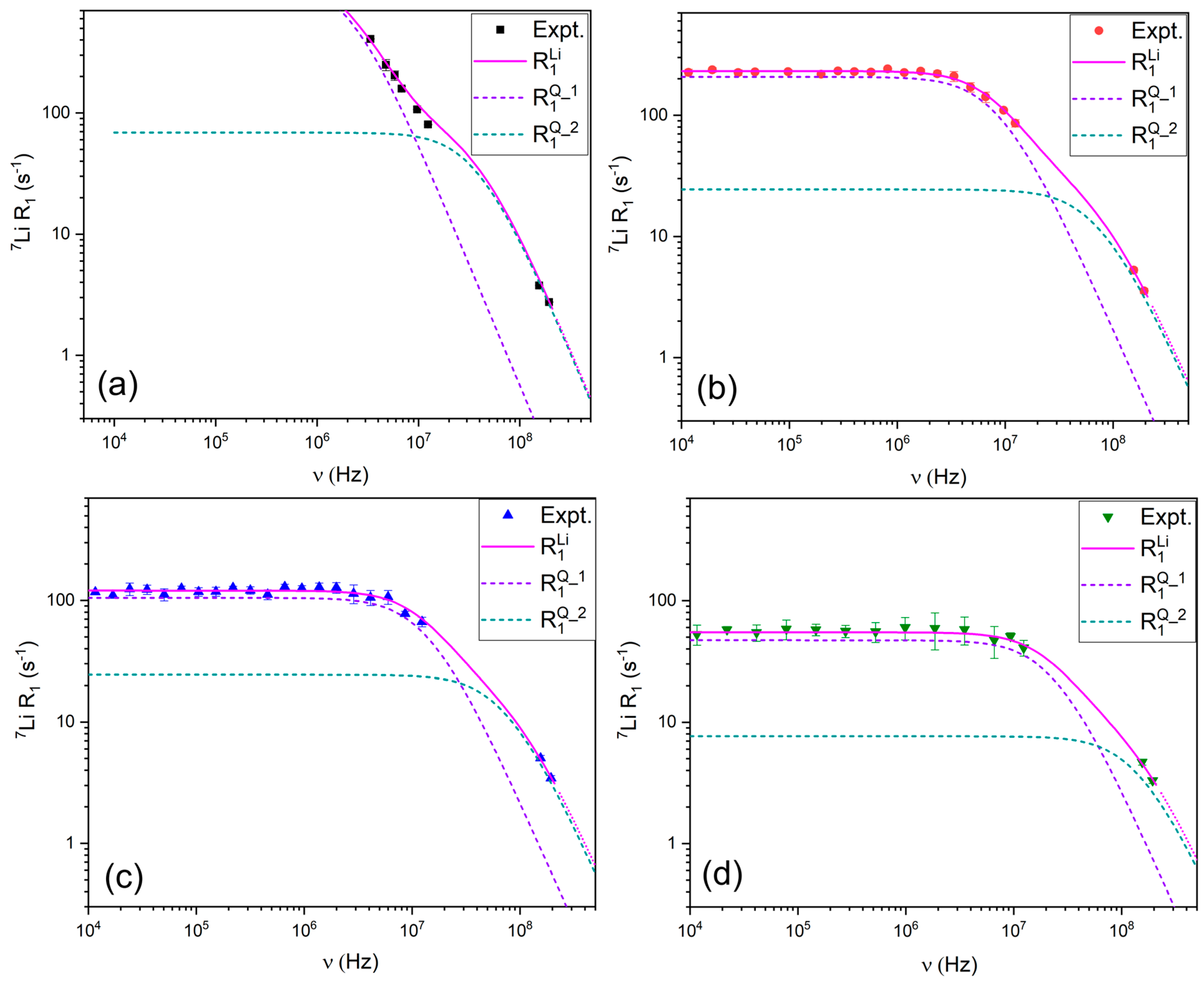
2.4.4. Relaxation Due to the Quadrupolar Mechanism ()
2.5. Viscosity and Conductivity
3. Results and Discussion
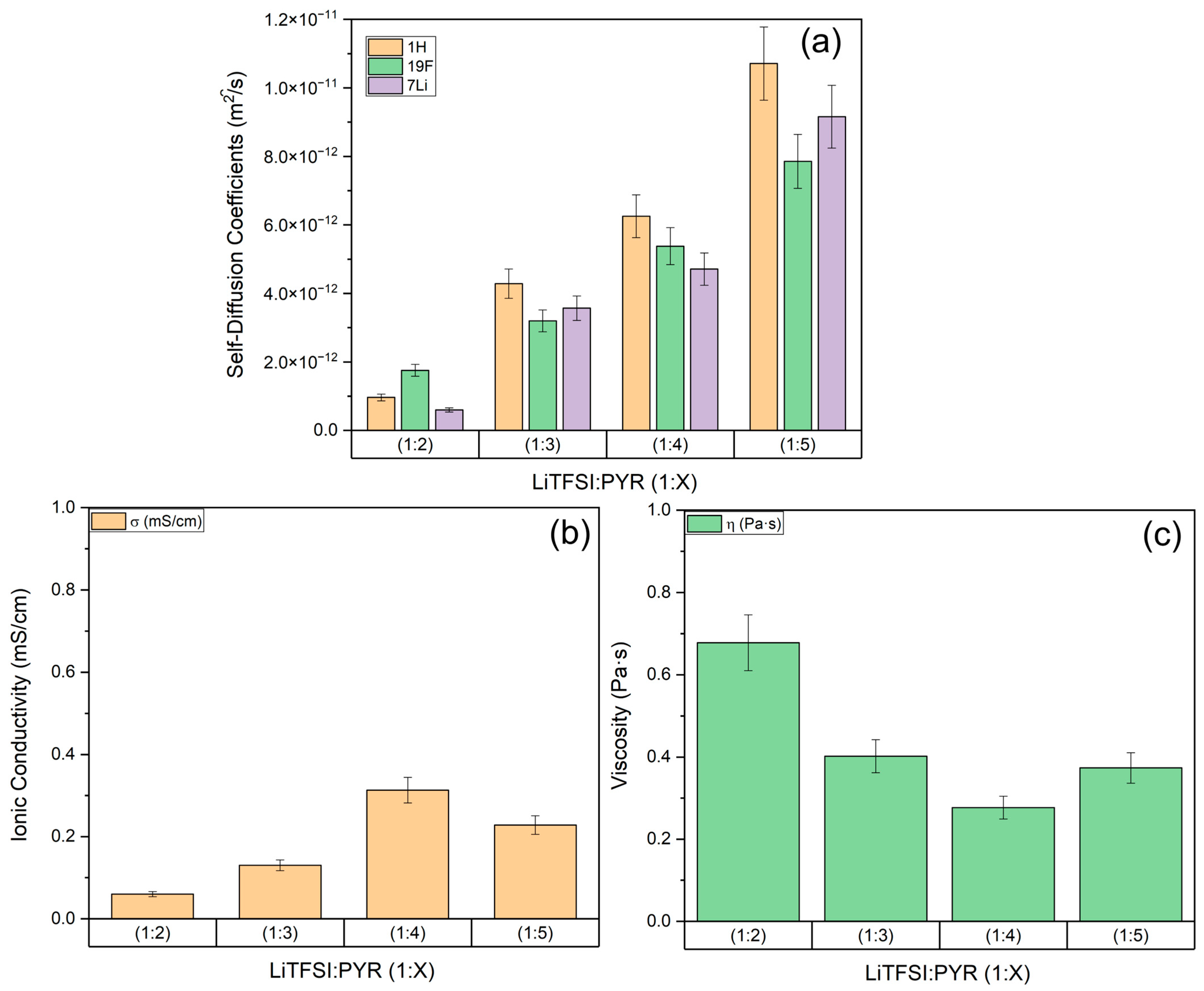
3.1. Transport Properties
3.2. Local Dynamics
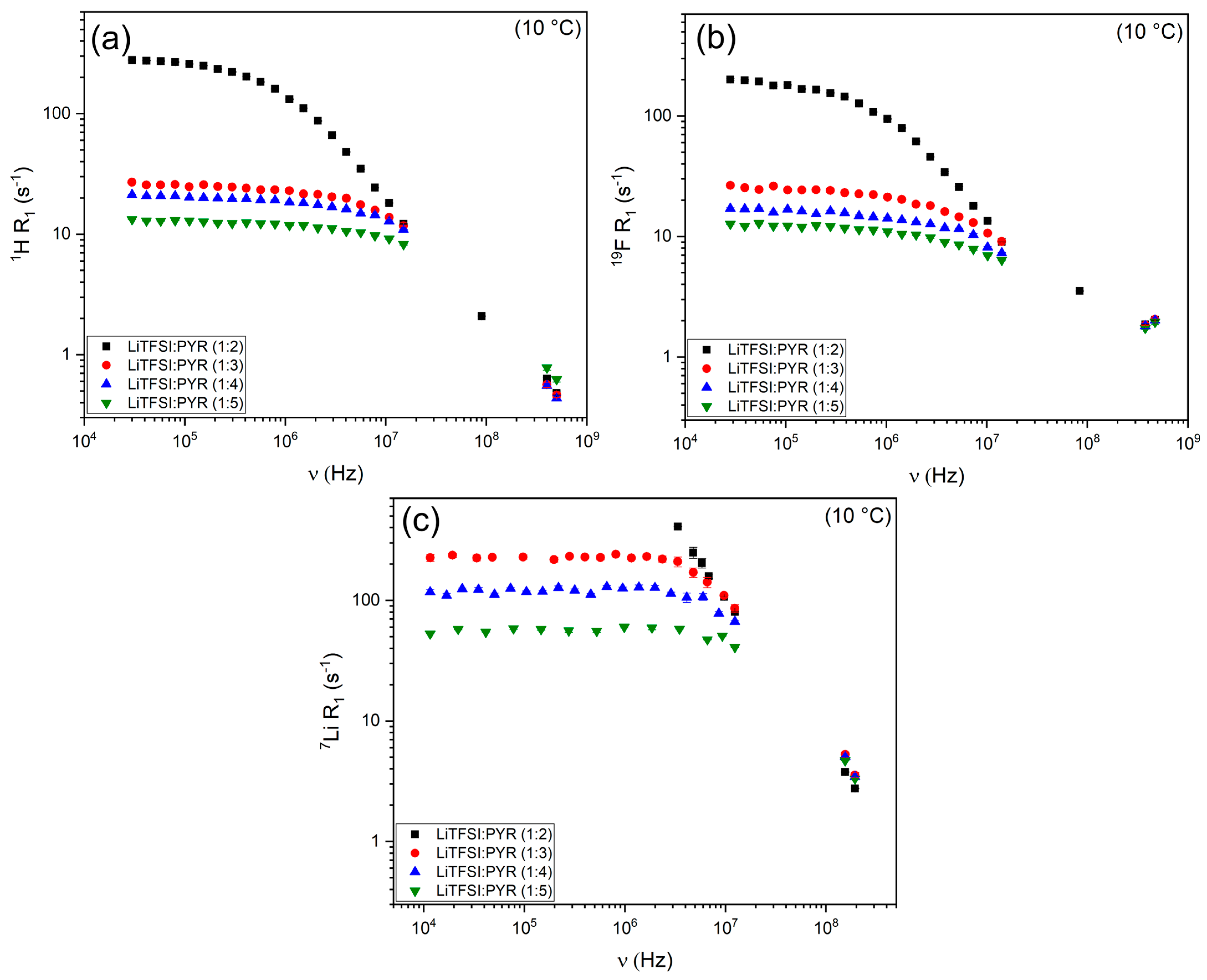
3.2.1. 1H and 19F Relaxation Mechanisms
3.2.2. 7Li Relaxation Mechanisms
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, M.; Lu, J.; Chen, Z.; Amine, K. 30 Years of Lithium-Ion Batteries. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1800561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whittingham, M.S. Lithium Batteries: 50 Years of Advances to Address the Next 20 Years of Climate Issues. Nano Lett. 2020, 20, 8435–8437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dahbi, M.; Ghamouss, F.; Tran-Van, F.; Lemordant, D.; Anouti, M. Comparative Study of EC/DMC LiTFSI and LiPF6 Electrolytes for Electrochemical Storage. J. Power Sources 2011, 196, 9743–9750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flamme, B.; Rodriguez Garcia, G.; Weil, M.; Haddad, M.; Phansavath, P.; Ratovelomanana-Vidal, V.; Chagnes, A. Guidelines to Design Organic Electrolytes for Lithium-Ion Batteries: Environmental Impact, Physicochemical and Electrochemical Properties. Green. Chem. 2017, 19, 1828–1849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Kang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, L.; Liu, J.; Li, Y.; Liang, Z.; He, X.; Li, X.; Tavajohi, N.; et al. A Review of Lithium-Ion Battery Safety Concerns: The Issues, Strategies, and Testing Standards. J. Energy Chem. 2021, 59, 83–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsson, F.; Andersson, P.; Blomqvist, P.; Mellander, B.E. Toxic Fluoride Gas Emissions from Lithium-Ion Battery Fires. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 10018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarra, M.A. Ionic Liquids as Safe Electrolyte Components for Li-Metal and Li-Ion Batteries. MRS Bull. 2013, 38, 548–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Lv, S.; Jiang, K.; Zhou, G.; Liu, X. Recent Development of Ionic Liquid-Based Electrolytes in Lithium-Ion Batteries. J. Power Sources 2022, 542, 231792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Jesus, S.S.; Maciel Filho, R. Are Ionic Liquids Eco-Friendly? Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2022, 157, 112039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shivani; Thakur, R.C.; Thakur, A.; Sharma, A.; Sharma, R. Unravelling the Prospects of Electrolytes Containing Ionic Liquids and Deep Eutectic Solvents for next Generation Lithium Batteries. J. Energy Chem. 2025, 105, 482–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florindo, C.; Branco, L.C.; Marrucho, I.M. Quest for Green-Solvent Design: From Hydrophilic to Hydrophobic (Deep) Eutectic Solvents. ChemSusChem 2019, 12, 1549–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.-L.; Yang, W.; Wang, Q.; Du, X.; Hu, B.; Chen, Y.; Wang, D.-Y. Azole Derived Deep Eutectic Electrolyte for High Performance Lithium Metal-Free Full Batteries. Ceram. Int. 2024, 50, 8178–8184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramalingam, L.P.; Ramalingam, B.; Rathnasamy, S.; Kathirvelu, P. Deep Eutectic Solvent-Based Sustainable Electrochemical Lithium Batteries—Prospects, Challenges, and Life Cycle Engineering. Sustain. Energy Technol. Assess. 2025, 73, 104136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimmich, R.; Anoardo, E. Field-Cycling NMR Relaxometry. Prog. Nucl. Magn. Reson. Spectrosc. 2004, 44, 257–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anoardo, E.; Galli, G.; Ferrante, G. Fast-Field-Cycling NMR: Applications and Instrumentation. Appl. Magn. Reson. 2001, 20, 365–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gogoi, B.J.; Murugesan, M.; Nallamuthu, N.; Devendran, P.; Murugan, A.; Blange, R.; Shellaiah, M. Investigation into PVDF-HFP and PVP Polymer Blend Electrolytes with Lithium Ions for Energy Storage Application. Polymers 2025, 17, 1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stejskal, E.O.; Tanner, J.E. Spin Diffusion Measurements: Spin Echoes in the Presence of a Time-Dependent Field Gradient. J. Chem. Phys. 1965, 42, 288–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimmich, R. Field-Cycling NMR Relaxometry; Royal Society of Chemistry: Cambridge, UK, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Di Pietro, M.E.; Goloviznina, K.; van den Bruinhorst, A.; de Araujo Lima e Souza, G.; Costa Gomes, M.; Padua, A.A.H.; Mele, A. Lithium Salt Effects on the Liquid Structure of Choline Chloride–Urea Deep Eutectic Solvent. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 11835–11845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Araujo Lima e Souza, G.; Di Pietro, M.E.; Castiglione, F.; Vanoli, V.; Mele, A. Insights into the Effect of Lithium Doping on the Deep Eutectic Solvent Choline Chloride:Urea. Materials 2022, 15, 7459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraenza, C.C.; Elgammal, R.A.; Garaga, M.N.; Bhattacharyya, S.; Zawodzinski, T.A.; Greenbaum, S.G. Dynamics of Glyceline and Interactions of Constituents: A Multitechnique NMR Study. J. Phys. Chem. B 2022, 126, 890–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triolo, A.; Di Pietro, M.E.; Mele, A.; Lo Celso, F.; Brehm, M.; Di Lisio, V.; Martinelli, A.; Chater, P.; Russina, O. Liquid Structure and Dynamics in the Choline Acetate:Urea 1:2 Deep Eutectic Solvent. J. Chem. Phys. 2021, 154, 244501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfurayj, I.; Fraenza, C.C.; Zhang, Y.; Pandian, R.; Spittle, S.; Hansen, B.; Dean, W.; Gurkan, B.; Savinell, R.; Greenbaum, S.; et al. Solvation Dynamics of Wet Ethaline: Water Is the Magic Component. J. Phys. Chem. B 2021, 125, 8888–8901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinz, Y.; Böhmer, R. 2H and 13C Nuclear Spin Relaxation Unravels Dynamic Heterogeneities in Deep Eutectic Solvents of Ethylene Glycol, Glycerol, or Urea with Choline Chloride. J. Chem. Phys. 2023, 159, 224502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paterno, D.; Rock, E.; Forbes, A.; Iqbal, R.; Mohammad, N.; Suarez, S. Aluminum Ions Speciation and Transport in Acidic Deep Eutectic AlCl3 Amide Electrolytes. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 319, 114118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajbangshi, J.; Mukherjee, K.; Biswas, R. Heterogeneous Orientational Relaxations and Translation–Rotation Decoupling in (Choline Chloride + Urea) Deep Eutectic Solvents: Investigation through Molecular Dynamics Simulations and Dielectric Relaxation Measurements. J. Phys. Chem. B 2021, 125, 5920–5936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kruk, D.; Florek-Wojciechowska, M. Recent Development in 1H NMR Relaxometry. In Annual Reports on NMR Spectroscopy; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2020; pp. 119–184. [Google Scholar]
- Jayakody, N.K.; Fraenza, C.C.; Greenbaum, S.G.; Ashby, D.; Dunn, B.S. NMR Relaxometry and Diffusometry Analysis of Dynamics in Ionic Liquids and Ionogels for Use in Lithium-Ion Batteries. J. Phys. Chem. B 2020, 124, 6843–6856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abragam, A. Principles of Nuclear Magnetism; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1961. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, R.Y. NMR Relaxation Rates. In Encyclopedia of Spectroscopy and Spectrometry; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 209–215. [Google Scholar]
- De Araujo Lima e Souza, G.d.A.L.; Acero, M.; Pelegano-Titmuss, E.; Stallworth, P.; Thomas, C.M.; Hersam, M.C.; Oliveira Sebastião, P.J.; Greenbaum, S. Ion Dynamics in Hexagonal Boron Nitride Ionogel Electrolytes. J. Chem. Phys. 2025, 162, 214706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sebastião, P.J.; Beira, M.J.; Cordeiro, R.; Kumar, A.; Fernandes, J.C.; Ferraz, A.; Gonçalves, L.N. The Art of Fitting Ordinary Differential Equations Models to Experimental Results. Eur. J. Phys. 2022, 43, 035807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sebastião, P.J. The Art of Model Fitting to Experimental Results. Eur. J. Phys. 2014, 35, 015017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meier, R.; Kruk, D.; Gmeiner, J.; Rössler, E.A. Intermolecular Relaxation in Glycerol as Revealed by Field Cycling 1H NMR Relaxometry Dilution Experiments. J. Chem. Phys. 2012, 136, 034508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, L.P.; Freed, J.H. Dynamic Effects of Pair Correlation Functions on Spin Relaxation by Translational Diffusion in Liquids. J. Chem. Phys. 1975, 63, 4017–4025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, R.Y. Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy of Liquid Crystals; World Scientific: Singapore, 2009; ISBN 978-981-4273-66-4. [Google Scholar]
- Vilfan, M.; Apih, T.; Sebastião, P.J.; Lahajnar, G.; Žumer, S. Liquid Crystal 8CB in Random Porous Glass: NMR Relaxometry Study of Molecular Diffusion and Director Fluctuations. Phys. Rev. E 2007, 76, 051708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knapkiewicz, M.; Rachocki, A.; Bielejewski, M.; Sebastião, P.J. NMR Studies of Molecular Ordering and Molecular Dynamics in a Chiral Liquid Crystal with the SmCα∗ Phase. Phys. Rev. E 2020, 101, 052708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sebastião, P.J. NMR Relaxometry in Liquid Crystals: Molecular Organization and Molecular Dynamics Interrelation. In Field-cycling NMR Relaxometry: Instrumentation, Model Theories and Applications; Royal Society of Chemistry: Cambridge, UK, 2018; Chapter 11; pp. 255–302. [Google Scholar]
- Bloembergen, N.; Purcell, E.M.; Pound, R.V. Relaxation Effects in Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Absorption. Phys. Rev. 1948, 73, 679–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nordio, P.L.; Segre, U. Magnetic Relaxation from First-Rank Interactions. J. Magn. Reson. (1969) 1977, 27, 465–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerig, J.T. Fluorine NMR. In Biophysics Textbook Online; Biophysical Society: Rockville, MD, USA, 2001; pp. 1–35. [Google Scholar]
- Hull, W.E.; Sykes, B.D. Fluorotyrosine Alkaline Phosphatase: Internal Mobility of Individual Tyrosines and the Role of Chemical Shift Anisotropy as a 19F Nuclear Spin Relaxation Mechanism in Proteins. J. Mol. Biol. 1975, 98, 121–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Araujo Lima e Souza, G.; Brandwein, E.; Pelegano-Titmuss, E.; Stallworth, P.; Zhang, Y.; Oliveira Sebastião, P.J.; Greenbaum, S. Expanded View of NMR Spin–Lattice Relaxation in Fluorine-Containing Ionic Liquids. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2025, 16, 7622–7629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitawala, J.; Martinelli, A.; Johansson, P.; Jacobsson, P.; Matic, A. Coordination and Interactions in a Li-Salt Doped Ionic Liquid. J. Non Cryst. Solids 2015, 407, 318–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castiglione, F.; Ragg, E.; Mele, A.; Appetecchi, G.B.; Montanino, M.; Passerini, S. Molecular Environment and Enhanced Diffusivity of Li+ Ions in Lithium-Salt-Doped Ionic Liquid Electrolytes. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2011, 2, 153–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasan, H.; Sharma, V.K.; Mukhopadhyay, R.; Mitra, S. Solvation and Transport of Lithium Ions in Deep Eutectic Solvents. J. Chem. Phys. 2020, 153, 104505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Pedersen, C.M.; Zhang, J.; Liu, R.; Zhang, Z.; Hou, X.; Wang, Y. Ternary Deep Eutectic Solvents Catalyzed D-Glucosamine Self-Condensation to Deoxyfructosazine: NMR Study. Green. Energy Environ. 2021, 6, 261–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appetecchi, G.B.; Montanino, M.; Balducci, A.; Lux, S.F.; Winterb, M.; Passerini, S. Lithium Insertion in Graphite from Ternary Ionic Liquid-Lithium Salt ElectrolytesI. Electrochemical Characterization of the Electrolytes. J. Power Sources 2009, 192, 599–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, M.; Simonetti, E.; Appetecchi, G.B.; Carewska, M.; Montanino, M.; Kim, G.-T.; Loeffler, N.; Passerini, S. Ionic Liquid Electrolytes for Safer Lithium Batteries. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2017, 164, A6026–A6031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brinkkötter, M.; Giffin, G.A.; Moretti, A.; Jeong, S.; Passerini, S.; Schönhoff, M. Relevance of Ion Clusters for Li Transport at Elevated Salt Concentrations in [Pyr12O1][FTFSI] Ionic Liquid-Based Electrolytes. Chem. Commun. 2018, 54, 4278–4281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wettstein, A.; Diddens, D.; Heuer, A. Controlling Li+ Transport in Ionic Liquid Electrolytes through Salt Content and Anion Asymmetry: A Mechanistic Understanding Gained from Molecular Dynamics Simulations. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2022, 24, 6072–6086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokuda, H.; Tsuzuki, S.; Susan, M.d.A.B.H.; Hayamizu, K.; Watanabe, M. How Ionic Are Room-Temperature Ionic Liquids? An Indicator of the Physicochemical Properties. J. Phys. Chem. B 2006, 110, 19593–19600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davidowski, S.K.; Thompson, F.; Huang, W.; Hasani, M.; Amin, S.A.; Angell, C.A.; Yarger, J.L. NMR Characterization of Ionicity and Transport Properties for a Series of Diethylmethylamine Based Protic Ionic Liquids. J. Phys. Chem. B 2016, 120, 4279–4285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacFarlane, D.R.; Forsyth, M.; Izgorodina, E.I.; Abbott, A.P.; Annat, G.; Fraser, K. On the Concept of Ionicity in Ionic Liquids. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2009, 11, 4962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Squire, H.; Gurkan, B.; Maginn, E.J. Refined Classical Force Field for Choline Chloride and Ethylene Glycol Mixtures over Wide Composition Range. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2022, 67, 1864–1871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Araujo Lima e Souza, G.; Pelegano-Titmuss, E.; Muñoz, M.; Gurkan, B.; di Pietro, M.E.; Mele, A.; Stallworth, P.; Greenbaum, S. Probing the Potential of Type V Deep Eutectic Solvents as Sustainable Electrolytes. J. Mol. Liq. 2024, 416, 126526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gajardo-Parra, N.F.; Cotroneo-Figueroa, V.P.; Aravena, P.; Vesovic, V.; Canales, R.I. Viscosity of Choline Chloride-Based Deep Eutectic Solvents: Experiments and Modeling. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2020, 65, 5581–5592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Pietro, M.E.; Mele, A. Deep Eutectics and Analogues as Electrolytes in Batteries. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 338, 116597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, K.R. Scaling the Transport Properties of Molecular and Ionic Liquids. J. Mol. Liq. 2016, 222, 520–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fragiadakis, D.; Roland, C.M. Dynamic Correlations and Heterogeneity in the Primary and Secondary Relaxations of a Model Molecular Liquid. Phys. Rev. E 2014, 89, 052304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hon, J.F.; Bray, P.J. Nuclear Quadrupole Coupling Constants of Li7 in Lithium Compounds. Phys. Rev. 1958, 110, 624–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gouverneur, M.; Jeremias, S.; Schönhoff, M. 7Li Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Studies of Dynamics in a Ternary Gel Polymer Electrolyte Based on Polymeric Ionic Liquids. Electrochim. Acta 2015, 175, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marinos, C.; Plesko, S.; Jonas, J.; Conard, J.; Guerard, D. Pressure Effects on the Quadrupole Coupling Constant of 7Li in First Stage Lithium Graphite. Solid. State Commun. 1983, 47, 645–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plimpton, S. Fast Parallel Algorithms for Short-Range Molecular Dynamics. J. Comput. Phys. 1995, 117, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez, J.M.; Martínez, L. Packing Optimization for Automated Generation of Complex System’s Initial Configurations for Molecular Dynamics and Docking. J. Comput. Chem. 2003, 24, 819–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez, L.; Andrade, R.; Birgin, E.G.; Martínez, J.M. Software News and Update Packmol: A Package for Building Initial Configurations for Molecular Dynamics Simulations. J. Comput. Chem. 2009, 30, 2157–2164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoover, W.G. Canonical Dynamics: Equilibrium Phase-Space Distributions. Phys. Rev. A 1985, 31, 1695–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinoda, W.; Shiga, M.; Mikami, M. Rapid Estimation of Elastic Constants by Molecular Dynamics Simulation under Constant Stress. Phys. Rev. B 2004, 69, 134103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorgensen, W.L.; Maxwell, D.S.; Tirado-Rives, J. Development and Testing of the OPLS All-Atom Force Field on Conformational Energetics and Properties of Organic Liquids. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1996, 118, 11225–11236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wolf, R.M.; Caldwell, J.W.; Kollman, P.A.; Case, D.A. Development and Testing of a General Amber Force Field. J. Comput. Chem. 2004, 25, 1157–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frisch, M.J.; Trucks, G.W.; Schlegel, H.B.; Scuseria, G.E.; Robb, M.A.; Cheeseman, J.R.; Scalmani, G.; Barone, V.; Petersson, G.A.; Nakatsuji, H.; et al. Gaussian 16 Revision C.01; Gaussian: Wallingford, CT, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Bayly, C.I.; Cieplak, P.; Cornell, W.; Kollman, P.A. A Well-Behaved Electrostatic Potential Based Method Using Charge Restraints for Deriving Atomic Charges: The RESP Model. J. Phys. Chem. 1993, 97, 10269–10280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Maginn, E.J. A Simple AIMD Approach to Derive Atomic Charges for Condensed Phase Simulation of Ionic Liquids. J. Phys. Chem. B 2012, 116, 10036–10048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hockney, R.; Eastwood, J. Computer Simulation Using Particles; Adam Hilger: New York, NY, USA, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, H. COMPASS: An Ab Initio Force-Field Optimized for Condensed-Phase Applications Overview with Details on Alkane and Benzene Compounds. J. Phys. Chem. B 1998, 102, 7338–7364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| LiTFSI:PYR (1:2) | LiTFSI:PYR (1:3) | LiTFSI:PYR (1:4) | LiTFSI:PYR (1:5) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fitting Parameters | 1H | 1H | 1H | 1H |
| τ (s) | 4.0 ± 0.1 × 10−10 7.9 ± 0.4 × 10−8 (w = 0.48 ± 0.05) | 1.6 ± 0.2 × 10−9 | 1.3 ± 0.2 × 10−9 | 9.4 ± 0.2 × 10−10 |
| Fitting Parameters | 19F | 19F | 19F | 19F |
| τz (s) | 3.4 ± 0.2 × 10−9 6.1 ± 0.1 × 10−7 (w = 0.20 ± 0.02) | 1.6 ± 0.1 × 10−9 | 6.9 ± 0.1 × 10−10 | 9.5 ± 0.1 × 10−10 |
| τx (s) | 2.9 ± 0.1 × 10−7 2.2 ± 0.1 × 10−6 (w = 0.20 ± 0.02) | 9.3 ± 0.4 × 10−8 | 5.4 ± 0.3 × 10−8 | 4.8 ± 0.1 × 10−8 |
| τF (s) | 5.7 ± 0.1 × 10−10 | 2.7 ± 0.2 × 10−10 | 1.4 ± 0.1 × 10−10 | 1.6 ± 0.2 × 10−10 |
| CSA (ppm) | 78 ± 5 | 75 ± 5 | 90 ± 6 | 83 ± 4 |
| Fitting Parameters | LiTFSI:PYR (1:2) | LiTFSI:PYR (1:3) | LiTFSI:PYR (1:4) | LiTFSI:PYR (1:5) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CQ (kHz) | 52 ± 1 | 44 ± 1 | 39 ± 1 | 34 ± 1 |
| r1 (Å) | 3.8 ± 0.02 | 4.9 ± 0.1 | 4.3 ± 0.1 | 4.1 ± 0.1 |
| r2 (Å) | 0.9 ± 0.1 | 1.7 ± 0.1 | 1.6 ± 0.1 | 1.6 ± 0.1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pelegano-Titmuss, E.; Arif, M.Z.; de Araujo Lima e Souza, G.; Stallworth, P.; Zhang, Y.; Imel, A.; Zawodzinski, T.; Greenbaum, S. Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Dynamics of LiTFSI–Pyrazole Eutectic Solvents. Materials 2025, 18, 5184. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18225184
Pelegano-Titmuss E, Arif MZ, de Araujo Lima e Souza G, Stallworth P, Zhang Y, Imel A, Zawodzinski T, Greenbaum S. Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Dynamics of LiTFSI–Pyrazole Eutectic Solvents. Materials. 2025; 18(22):5184. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18225184
Chicago/Turabian StylePelegano-Titmuss, Emilia, Muhammad Zulqarnain Arif, Giselle de Araujo Lima e Souza, Phillip Stallworth, Yong Zhang, Adam Imel, Thomas Zawodzinski, and Steven Greenbaum. 2025. "Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Dynamics of LiTFSI–Pyrazole Eutectic Solvents" Materials 18, no. 22: 5184. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18225184
APA StylePelegano-Titmuss, E., Arif, M. Z., de Araujo Lima e Souza, G., Stallworth, P., Zhang, Y., Imel, A., Zawodzinski, T., & Greenbaum, S. (2025). Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Dynamics of LiTFSI–Pyrazole Eutectic Solvents. Materials, 18(22), 5184. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18225184









