A Review of Guerbet Alcohols and Their Esters: Synthesis, Applications, and Future Perspectives
Abstract
1. Introduction
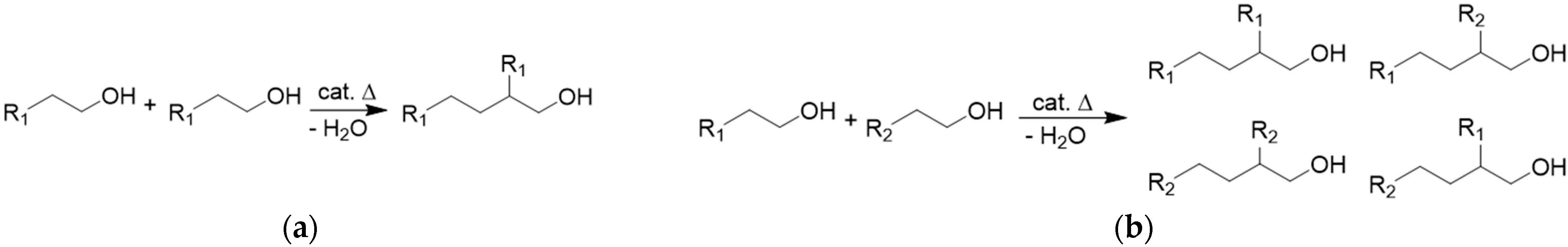
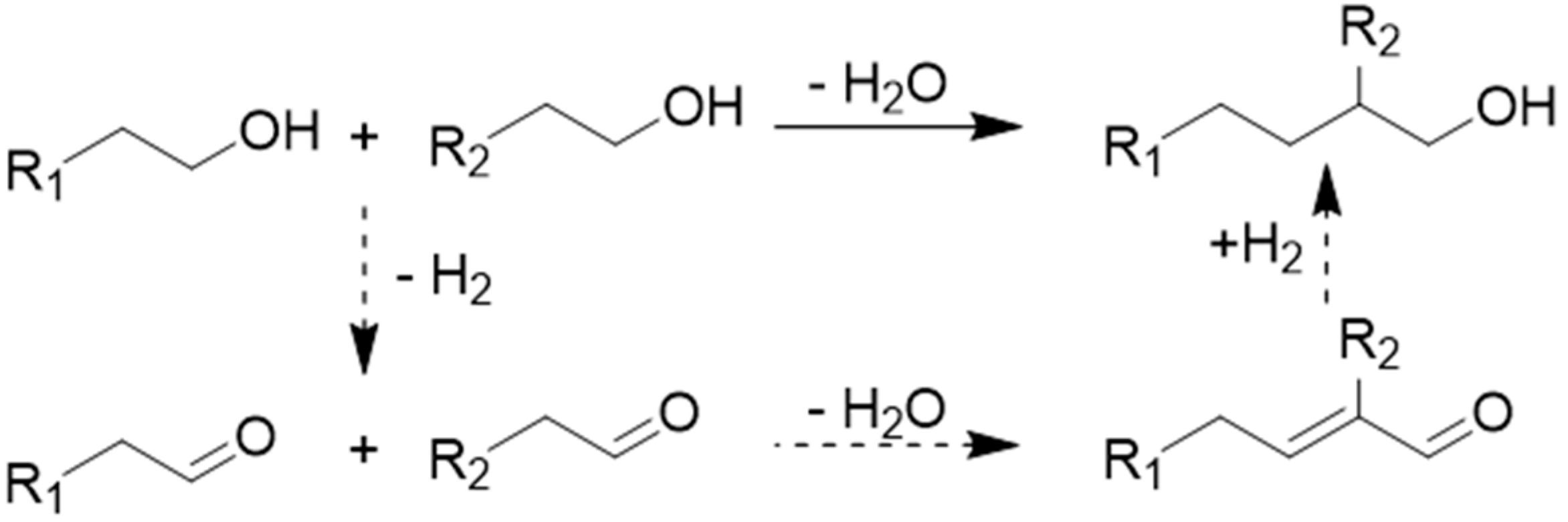
2. Guerbet Alcohols
3. Guerbet Alcohol Esters
4. State of the Art and Future Perspectives
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CAGR | Compound Annual Growth rate |
| EU | European Union |
| INCI | International Nomenclature of Cosmetic Ingredients |
| PBT | Persistent, bioaccumulative, and toxic |
| PTSA | p-Toluenesulfonic acid |
| SDGs | Sustainable Development Goals |
| USD | United States Dollar |
| VI | Viscosity Index |
| WOS | Web of Science |
References
- Haßelberg, J.; Behr, A. Saturated Branched Fatty Compounds: Proven Industrial Processes and New Alternatives. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2016, 118, 36–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirsam, R.; Hansora, D.; Usmani, G.A. A Mini-Review on Solid Acid Catalysts for Esterification Reactions. J. Inst. Eng. India Ser. 2016, 97, 167–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega-Requena, S.; Montiel, C.; Máximo, F.; Gómez, M.; Murcia, M.D.; Bastida, J. Esters in the Food and Cosmetic Industries: An Overview of the Reactors Used in Their Biocatalytic Synthesis. Materials 2024, 17, 268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Lenick, A.J. Guerbet Chemistry. J. Surfactants Deterg. 2001, 4, 311–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waykole, C.; Bhowmick, D.N.; Pratap, A. Synthetic Base Stock Based on Guerbet Alcohols. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2014, 91, 1407–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Lenick, A.J.; Parkinson, J.K. The Effect of Branching and Unsaturation upon Some Properties of Polyoxyethylene Glycol Diesters. J. Surfactants Deterg. 1998, 1, 529–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerbet, M. Action de L’alcool Amylique de Fermentation Dérivé Sodé. C. R. Acad. Sci. 1899, 128, 511–513. [Google Scholar]
- Markownikoff, W.; Zuboff, P. Ueber die Condensation höherer Alkohole: Tricaprylalkohol. Chem. Ber. 1901, 34, 3246–3249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knothe, G.; Carlson, K.D. Synthesis, Mass Spectrometry, and Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Characterization of Di-Guerbet Esters. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 1998, 75, 1861–1866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waykole, C.S.; Mali, S.N.; Mahale, D.D.; Pratap, A.P. Guerbet Alcohol Esters: Practical Synthesis and Applications. J. Indian Chem. Soc. 2022, 99, 100304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veibel, S.; Nielsen, J.I. On the Mechanism of the Guerbet Reaction. Tetrahedron 1967, 23, 1723–1733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burk, P.L.; Pruett, R.L.; Campo, K.S. The Rhodium-Promoted Guerbet Reaction. Part I. Higher Alcohols from Lower Alcohols. J. Mol. Catal. 1985, 33, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burk, P.L.; Pruett, R.L.; Campo, K.S. The Rhodium-Promoted Guerbet Reaction. Part II. Secondary alcohols and methanol as substrates. J. Mol. Catal. 1985, 33, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, F.; Guo, H.; Cui, J.; Hou, B.; Xi, H.; Jia, L.; Li, D. Coupling of Methanol and Ethanol over CuMgAlOx Catalysts: The Roles of Copper Species and Alkalinity. React. Kinet. Mech. Cat. 2019, 126, 119–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birky, T.W.; Kozlowski, J.T.; Davis, R.J. Isotopic Transient Analysis of the Ethanol Coupling Reaction over Magnesia. J. Catal. 2013, 298, 130–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanspal, S.; Young, Z.D.; Shou, H.; Davis, R.J. Multiproduct Steady-State Isotopic Transient Kinetic Analysis of the Ethanol Coupling Reaction over Hydroxyapatite and Magnesia. ACS Catal. 2015, 5, 1737–1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di-Cosimo, J.I.; Apesteguia, C.R.; Gines, M.J.L.; Iglesia, E. Structural Requirements and Reaction Pathways in Condensation Reactions of Alcohols on MgyAlOx Catalysts. J. Catal. 2000, 190, 261–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ordoñez, S.; Díaz, E.; León, M.; Faba, L. Hydrotalcite-Derived Mixed Oxides as Catalysts for Different C–C Bond Formation Reactions from Bioorganic Materials. Catal. Today 2011, 167, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benito, P.; Vaccari, A.; Antonetti, C.; Licursi, D.; Schiarioli, N.; Rodríguez-Castellón, E.; Raspolli Galletti, A.M. Tunable Copper-Hydrotalcite Derived Mixed Oxides for Sustainable Ethanol Condensation to n-Butanol in Liquid Phase. Catal. Today 2016, 167, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messori, A.; Gagliardi, A.; Cesari, C.; Calcagno, F.; Tabanelli, T.; Cavani, F.; Mazzoni, R. Advances in the Homogeneous Catalyzed Alcohols Homologation: The Mild Side of the Guerbet Reaction. A Mini-Review. Catal. Today 2023, 423, 114003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozlowski, J.T.; Davis, R.J. Heterogeneous Catalysts for the Guerbet Coupling of Alcohols. ACS Catal. 2013, 3, 1588–1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaccheria, F.; Scotti, N.; Ravasio, N. The Role of Copper in the Upgrading of Bioalcohols. ChemCatChem 2018, 10, 1526–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, A.M.; Li, Z.Y.; Stephenson, C.R.J.; Szymczak, N.K. Valorization of Ethanol: Ruthenium-Catalyzed Guerbet and Sequential Functionalization Processes. ACS Catal. 2022, 12, 6729–6736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabasi, N.S.; Genç, S.; Gülcemal, D. Tuning the Selectivity in Iridium-Catalyzed Acceptorless Dehydrogenative Coupling of Primary Alcohols. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2022, 20, 6582–6592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olson, E.S.; Sharma, R.K.; Aulich, T.R. Higher-Alcohols Biorefinery: Improvement of Catalyst for Ethanol Conversion. Appl. Biochem. Biotech. 2004, 115, 913–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knothe, G.H. Guerbet Compound. 2011. Available online: https://www.aocs.org/resource/guerbet-compounds/ (accessed on 10 October 2025).
- Noweck, K.; Grafahrend, W. Fatty Alcohols. In Ullmann’s Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry; Wiley-VCH: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2012; Volume 14, pp. 117–141. [Google Scholar]
- ISOFOL C12 to C32. Guerbet Alcohols. Sasol Performance Chemicals. Available online: https://sasoltechdata.com/tds/isofol.pdf (accessed on 10 October 2025).
- Gabriëls, D.; Hernández, W.Y.; Sels, B.; Van Der Voort, P.; Verberckmoes, A. Review of Catalytic Systems and Thermodynamics for the Guerbet Condensation Reaction and Challenges for Biomass Valorization. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2015, 5, 3876–3902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doshi, Y. Guerbet Alcohol Market Analysis and Forecast: 2025–2032. 2025. Available online: https://www.coherentmarketinsights.com/market-insight/guerbet-alcohol-market-3520 (accessed on 10 October 2025).
- Singh, S. Guerbet Alcohol Market Size, Share, and Growth Forecast for 2025–2032. 2025. Available online: https://www.persistencemarketresearch.com/market-research/guerbet-alcohols-market.asp (accessed on 10 October 2025).
- Available online: https://www.basf.com/dam/jcr:cb247fec-3a83-3099-80b6-025f50eb881e/basf/www/mx/documents/2024%20HII%20Product%20Range%20Card.pdf (accessed on 10 October 2025). 117-141.
- Available online: https://chemicals.sasol.com/products/isofol (accessed on 10 October 2025).
- Available online: https://www.nj-chem.co.jp/en/app/products/detail?middle_category_id=4 (accessed on 10 October 2025).
- Available online: https://chemical.kao.com/en/search/result.html?q=alcohol&b.f=Region%3Agl®ion=gl (accessed on 10 October 2025).
- Available online: https://www.kisco-net.com/business/chemicals/fine/index.php (accessed on 10 October 2025).
- Available online: https://www.hai-global.com/product/search?ible-category%5B0%5D=Liquid+higher+fatty+acid+%2F+Liquid+higher+alcohol&ible-category%5B1%5D=Saturated+higher+alcohol&ible-name=&formid=item_list.formgrid1col1-form&page=2 (accessed on 10 October 2025).
- Available online: http://en.dowpol.com/Cosmetic_GA/ (accessed on 10 October 2025).
- Available online: https://www.specialchem.com/cosmetics/supplier/aurorium/jarcol (accessed on 10 October 2025).
- Available online: https://emcochemicals.com/products/ (accessed on 10 October 2025).
- Azzena, U.; Montenero, A.; Carraro, M.; Crisafulli, R.; De Luca, L.; Gaspa, S.; Muzzu, A.; Nuvoli, L.; Polese, R.; Pisano, L.; et al. Recovery, Purification, Analysis and Chemical Modification of a Waste Cooking Oil. Waste Biomass Valori. 2023, 14, 145–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knothe, G. Characterization of Esters of Fatty Acids and Dicarboxylic Acids with Guerbet Alcohols. JAOCS 2001, 78, 537–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, H.S.; Erhan, S.Z. Synthetic Lubricant Basestocks from Epoxidized Soybean Oil and Guerbet Alcohols. Ind. Crops Prod. 2006, 23, 311–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cermak, S.C.; Bredsguard, J.W.; Roth, K.L.; Thompson, T.; Feken, K.A.; Isbell, T.A.; Murraya, R.E. Synthesis and Physical Properties of New Coco-Oleic Estolide Branched Esters. Ind. Crops Prod. 2015, 74, 171–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, S.; Rajurkar, K.; Patil, S.; Pratap, A. Synthesis of Guerbet Esters and its Application in Drilling and Grinding Oil. Tribol. Int. 2023, 177, 107993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://www.specialchem.com/cosmetics (accessed on 10 October 2025).
- Available online: https://www.stearinerie-dubois.com/en/cosmetique/dub-mod/ (accessed on 10 October 2025).
- Regulation (EC) No 1272/2008 of the European Parliament and of the Council. 16 December 2008. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/ES/TXT/?uri=celex:32008R1272 (accessed on 10 October 2025).
- Domínguez de María, P. Biocatalysis, Sustainability, and Industrial Applications: Show Me the Metrics. Curr. Opin. Green Sustain. Chem. 2021, 31, 100514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anastas, P.; Zimmerman, J. Design Through the Twelve Principles of Green Engineering. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2003, 37, 94A–101A. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zappaterra, F.; Presini, F.; Venturi, V.; Lerin, L.A.; Giovannini, P.P.; Costa, S. Biocatalytic Insights for the Synthesis of New Potential Prodrugs: Design of Two Ibuprofen Derivatives. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 9852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roschangar, F.; Sheldon, R.A.; Senanayake, C.H. Overcoming Barriers to Green Chemistry in the Pharmaceutical Industry-The Green Aspiration LevelTM concept. Green Chem. 2015, 17, 752–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Sharma, P.K.; Chaturvedi, S.; Kumar, P.; Nannaware, A.D.; Kalra, A.; Rout, P.K. Biocatalyst for the Synthesis of natural Flavouring Compounds as Food Additives: Bridging the Gap for a More Sustainable Industrial Future. Food Chem. 2024, 435, 137217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Connell, A.; Barry, A.; Burke, A.J.; Hutton, A.E.; Bell, E.L.; Green, A.P.; O’Reilly, E. Biocatalysis: Landmark Discoveries and Applications in Chemical Synthesis. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2024, 53, 2828–2850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, F.; Shah, A.A.; Hameed, A. Industrial Applications of Microbial Lipases. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2006, 39, 235–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barros, M.; Fleuri, L.F.; Macedo, G.A. Seed Lipases: Sources, Applications and Properties-A Review. Braz. J. Chem. Eng. 2010, 27, 15–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaeger, K.E.; Eggert, T. Lipases for Biotechnology. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2002, 13, 390–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuai, W.; Das, R.K.; Naghdi, M.; Brar, S.K.; Verma, M. A Review on the Important Aspects of Lipase Immobilization on Nanomaterials. Biotechnol. Appl. Biochem. 2017, 64, 496–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Remonatto, D.; Oliveira, J.V.; Guisan, J.M.; Oliveira, D.; Ninow, J.; Fernandez-Lorente, G. Immobilization of Eversa Lipases on Hydrophobic Supports for Ethanolysis of Sunflower Oil Solvent-Free. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2022, 194, 2151–2167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gryglewicz, S. Enzyme Catalysed Synthesis of Some Adipic Esters. J. Mol. Catal. B Enzym. 2001, 15, 9–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.L.; Chen, B.Q.; Tan, T.W. Enzymatic Synthesis of 2-Ethylhexyl Esters of Fatty Acids by Immobilized Lipase from Candida sp. 99-125. J. Mol. Catal. B Enzym. 2002, 18, 333–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gryglevicz, S. Lipase Catalysed Synthesis of Sebacic and Phthalic Esters. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2003, 33, 952–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, T.; Chen, B.Q.; Ye, H. Enzymatic Synthesis of 2-Ethylhexyl Palmitate by Lipase Immobilized on Fabric Membranes in the Batch Reactor. Biochem. Eng. J. 2006, 29, 41–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richetti, A.; Leite, S.G.F.; Antunes, O.A.C.; Lerin, L.A.; Dallago, R.M.; Emmerich, D.; Di Luccio, M.; Oliveira, J.V.; Treichel, H.; de Oliveira, D. Assessment of Process Variables on 2-Ethylhexyl Palmitate Production Using Novozym 435 as Catalyst in a Solvent-Free System. Bioprocess Biosyst. Eng. 2010, 33, 331–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brenneis, R.; Baeck, B. Esterification of Fatty Acids Using Candida antarctica Lipase A in Water-Abundant Systems. Biotechnol. Lett. 2012, 34, 1459–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gryglewicz, S.; Muszynski, M.; Nowicki, J. Enzymatic Synthesis of Rapeseed Oil-Based Lubricants. Ind. Crops Prod. 2013, 45, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.; Tao, Y.; Cui, C.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, B.; Tan, T. Synthesis of 2-Ethylhexanol Fatty Acid Esters in a Packed Bed Bioreactor Using a Lipase Immobilized on a Textile Membrane. Biocat. Biotransfor. 2015, 33, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, K.C.; Li, Y.; Kuo, C.H.; Twu, Y.K.; Shieh, C.J. Highly Efficient Synthesis of an Emerging Lipophilic Antioxidant: 2-Ethylhexyl Ferulate. Molecules 2016, 21, 478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Kim, T.; Choi, N.; Kim, B.H.; Oh, S.W.; Kim, I.H. Synthesis of Diethylhexyl Adipate by Candida antarctica Lipase-Catalyzed Esterification. Process Biochem. 2016, 78, 58–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosney, H.; Al-Sakkari, E.G.; Mustafa, A. Kinetics and Gibbs Function Studies on Lipase-Catalyzed Production of Non-Phthalate Plasticizer. J. Oleo Sci. 2020, 69, 727–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gawas, S.; Rathod, V.K. Ultrasound Assisted Green Synthesis of 2-Ethylhexyl Stearate: A Cosmetic Bio-lubricant. J. Oleo Sci. 2020, 69, 1043–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosney, H.; Mustafa, A. Semi-Continuous Production of 2-Ethyl Hexyl Ester in a Packed Bed Reactor: Optimization and Economic Evaluation. J. Oleo Sci. 2020, 69, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez, M.; Murcia, M.D.; Serrano-Arnaldos, M.; Gómez, D.; Gómez, J.L.; Hidalgo, A.M.; Máximo, M.F. Developing the Rate Equations for Two Enzymatic Ping-Pong Reactions in Series: Application to the Bio-Synthesis of Bis(2-ethylhexyl) Azelate. Biochem. Eng. J. 2020, 161, 107691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Ji, H.; Song, Y.; Ma, S.; Xiong, W.; Chen, C.; Chen, B.; Zhang, X. Green Preparation of Branched Biolubricant by Chemically Modifying Waste Cooking Oil with Lipase and Ionic Liquid. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 274, 122918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murcia, M.D.; Serrano-Arnaldos, M.; Ortega-Requena, S.; Máximo, F.; Bastida, J.; Montiel, M.C. Optimization of a Sustainable Biocatalytic Process for the Synthesis of Ethylhexyl Fatty Acids Esters. Catal. Today 2020, 346, 98–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuoko, E.; Papadaki, A.; Papanikolaou, S.; Danezis, G.P.; Georgiou, C.A.; Freire, D.M.G.; Koutinas, A. Enzymatic Production of Isopropyl and 2-Ethylhexyl Esters Using γ-Linolenic Acid Rich Fungal Oil Produced from Spent Sulphite Liquor. Biochem. Eng. J. 2021, 169, 107956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montiel, M.C.; Asensi, M.; Gimeno-Martos, S.; Máximo, F.; Bastida, J. Sustainable Biocatalytic Procedure for Obtaining New Branched Acid Esters. Materials 2021, 14, 6847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, M.V.C.; Rangel, A.B.S.; Rosa, C.M.R.; de Assis, G.P.; Aguiar, L.G.; de Freitas, L. Development of a Magnetically Stabilized Fluidized Bed Bioreactor for Enzymatic Synthesis of 2-Ethylhexyl Oleate. Bioprocess. Biosys. Eng. 2023, 46, 1665–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteiro, R.R.C.; de Melo Neta, M.M.F.; Rocha, W.S.; Soares, J.B.; de Luna, F.M.T.; Fernandez-Lafuente, R.; Vieira, R.S. Optimizing the Enzymatic Production of Biolubricants by the Taguchi Method: Esterification of the Free Fatty Acids from Castor Oil with 2-Ethyl-1-hexanol Catalyzed by Eversa Transform 2.0. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2024, 175, 110409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghandi, N.N.; Sawant, S.B.; Joshi, J.B. Specificity of a Lipase in Ester Synthesis: Effect of Alcohol. Biotechnol. Prog. 1995, 11, 282–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz, C.; Luján Ferreira, M.; Barbosa, O.; dos Santos, J.C.S.; Rodrigues, R.C.; Berenguer-Murcia, A.; Briand, L.E.; Fernandez-Lafuente, R. Novozym 435: The “Perfect” Lipase Immobilized Biocatalyst? Catal. Sci. Technol. 2019, 9, 2380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angulo, B.; Fraile, J.M.; Gil, L.; Herrerías, C.I. Comparison of Chemical and Enzymatic Methods for the Transesterification of Waste Fish Oil Fatty Ethyl Esters with Different Alcohols. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 1479–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montiel, M.C.; Máximo, F.; Gómez, M.; Murcia, M.D.; Ortega-Requena, S.; Bastida, J. Guerbet Alcohols, Ideal Substrates for the Sustainable Production of Branched Esters. Materials 2025, 18, 5129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montiel, M.C.; Máximo, F.; Serrano-Arnaldos, M.; Ortega-Requena, S.; Murcia, M.D.; Bastida, J. Biocatalytic Solutions to Cyclomethicones Problem in Cosmetics. Eng. Life Sci. 2019, 19, 370–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Máximo, F.; Bastida, J.; Montiel, C.; Gómez, M.; Murcia, M.D.; Barqueros, C.; Ortega-Requena, S. Branched Saturated Esters and Diesters: Sustainable Synthesis of Excellent Biolubricants. Catal. Today 2024, 429, 1145509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montiel, M.C.; Gómez, M.; Murcia, M.D.; Ortega-Requena, S.; Máximo, F.; Bastida, J. Sustainable Biocatalytic Synthesis of a Second-Generation Biolubricant. Sustainability 2024, 16, 1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nogales-Delgado, S.; Encinar, J.M.; González, J.F. A Review on Biolubricants Based on Vegetable Oils through Transesterification and the Role of Catalysts: Current Status and Future Trends. Catalysts 2023, 13, 1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanciu, I. Viscosity Index for Oil Used as Biodegradable Lubricant. Indian J. Sci. Technol. 2020, 13, 352–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obanla, O.R.; Mohammed, F.U.; Alebiosu, O.S.; Ojewumi, M.E.; Oladimeji, T.E.; Babatunde, D.E. Study on the Lubricating Properties of Castor (Ricinus communis) and Hydroxylated Rubber (Hevea brasiliensis) Seed Oil. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 28471–28476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Guerbet Alcohol | Formula | Melting Point (°C) | Boiling Point (°C) (p, kPa) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2-Methyl-1-pentanol | C6H14O | 147.9 (101.3) | [27] | |
| 2-Ethyl-1-hexanol | C8H18O | <−76/−70 | 118 (10.7) | [26,27] |
| 2-Propyl-1-heptanol | C10H22O | 117 (2.7) | [27] | |
| 2-Butyl-1-octanol | C12H26O | ≈−30 | 126–128 (1.5) | [27,28] |
| 2-Pentyl-1-nonanol | C14H30O | ≈−25 | 154 (1.7) | [27,28] |
| 2-Hexyl-1-decanol | C16H34O | −30 to −26 | 175 (1.5) | [27] |
| 2-Heptyl-1-undecanol | C18H38O | −26 | 198 (2) | [27] |
| 2-Octyl-1-dodecanol | C20H42O | −20 | 135–137 (0.007) | [27] |
| 2-Nonyl-1-tridecanol | C22H46O | ≈10 | 164–167 (0.013) | [27,28] |
| 2-Decyl-1-tetradecanol | C24H50O | ≈18 | 173–175 (0.007) | [27,28] |
| 2-Undecyl-1-pentadecanol | C26H54O | |||
| 2-Dodecyl-1-hexadecanol | C28H58O | 32–39 | 203–207 (0.007) | [27,28] |
| 2-Tridecyl-1-heptadecanol | C30H62O | |||
| 2-Tetradecyl-1-octadecanol | C32H66O | 38–39 | 308–310 (2.0) | [26,27,28] |
| 2-Pentadecyl-1-nonadecanol | C34H70O | |||
| 2-Hexadecyl-1-eicosanol | C36H74O | 43–45 | 270–280 (0.013) | [26,27] |
| 2-Heptadecyl-1-heneicosanol | C38H78O | |||
| 2-Octadecyl-1-docosanol | C40H82O | |||
| 2-Nonadecyl-1-tricosanol | C42H86O | |||
| 2-Eicosyl-1-tetracosanol | C44H90O |
| Key Companies in the Market | Trade Name | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| BASF SE | Lutensol® XL (40, 50, 70, 79, 80, 90, 100) Lutensol® XP (30, 40, 50, 70, 79, 80, 89, 90) (ethers based on C10 Guerbet alcohol) | [32] |
| Sasol Ltd. | ISOFOL 12 (2-butyl-1-octanol) ISOFOL 16 (2-hexyl-1-decanol) ISOFOL 18T (2-octyl-1-decanol) ISOFOL 18E (2-octyl-1-decanol) ISOFOL 20 (2-octyl-1-dodecanol) ISOFOL 24 (2-decyl-1-tetradecanol) ISOFOL 2426S (C24 and C26) ISOFOL 28 (2-dodecyl-1-hexadecanol) ISOFOL 32 (2-tetradecyl-1-octadecanol) | [33] |
| New Japan Chemical Co., Ltd. | NJCOL 160BR (2-hexyl-1-decanol) NJCOL 200A (2-octyl-1-dodecanol) NJCOL 240A (2-decyl-1-tetradecanol) | [34] |
| Kao Corporation | FINDET LI/1990 FINDET LR4/2585 (Polyoxyethylene fatty branched alcohol) | [35] |
| Kisco Ltd. | 2-Butyl-1-octanol 2-Octyl-1-dodecanol | [36] |
| Kokyu Alcohol Kogyo Co., Ltd. | RISONOL 24SP (2-decyl-1-tetradecanol) | [37] |
| DowPol Corporation | Guerbet Alcohol G 16 (2-hexyl-1-decanol) Guerbet Alcohol G 20 (2-octyl-1-dodecanol) | [38] |
| Aurorium (formerly Vertellus. The company acquired Jarchem Industries in 2021) | Jarcol ™ I-12 (2-butyl-1-octadecanol) Jarcol ™ I-16CG (2-hexyl-1-decanol) Jarcol ™ I-20H (2-octyl-1-dodecanol) Jarcol ™ I-20P (2-octyl-1-dodecanol) Jarcol ™ I-20N (2-octyl-1-dodecanol) Jarcol ™ I-24 (2-decyl-1-teradecanol) Jarcol ™ I-28CG (2-dodecyl-1-hexadecanol) Jarcol ™ I-28 (2-dodecyl-1-hexadecanol) | [39] |
| Emco Dyestuff P. Ltd. | XL (140, 100, 90, 80, 70, 60, 50) (ethers based on C10 Guerbet alcohol) | [40] |
| Guerbet Alcohol | Acid | Application | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2-Butyl-1-octanol (C12) | Waste cooking oil | Biolubricant for drilling fluids | [41] |
| C18 Guerbet acid C24 Guerbet acid | Lubricant | [9] | |
| Glutaric acid 2,2-Diglutaric acid Adipic acid Suberic acid Palmitic acid Stearic acid Oleic acid | Biodiesel additive | [42] | |
| Epoxidized soybean oil | Lubricant | [43] | |
| Coco-oleic estolide | Lubricant | [44] | |
| 2-Pentyl-1-nonanol (C14) | C18 Guerbet acid | Lubricant | [9] |
| Epoxidized soybean oil | Lubricant | [43] | |
| 2-Hexyl-1-decanol (C16) | C18 Guerbet acid | Lubricant | [9] |
| Adipic acid Sebacic acid | Lubricant | [5] | |
| Glutaric acid 2,2-Diglutaric acid Adipic acid Suberic acid Sebacic acid Palmitic acid Stearic acid Oleic acid | Biodiesel additive | [42] | |
| Epoxidized soybean oil | Lubricant | [43] | |
| Coco-oleic estolide | Lubricant | [44] | |
| 2-Heptyl-1-decanol (C17) | Oleic acid Erucic acid Adipic acid Sebacic acid | Lubricant | [10] |
| 2-Heptyl-1-undecanol (C18) | C12 Guerbet acid C16 Guerbet acid C18 Guerbet acid | Lubricant | [9] |
| Oleic acid Erucic acid Adipic acid Sebacic acid | Lubricant | [10] | |
| Epoxidized soybean oil | Lubricant | [43] | |
| 2-Octyl-1-dodecanol (C20) | C18 Guerbet acid C24 Guerbet acid | Lubricant | [9] |
| Adipic acid Sebacic acid | Lubricant | [5] | |
| Eicosanoic acid C20 Guerbet acid | Surfactant | [4] | |
| Coco-oleic estolide | Lubricant | [44] | |
| 2-Decyl-1-tetradecanol (C24) | C18 Guerbet acid | Lubricant | [9] |
| Butyric acid Lauric acid Stearic acid | Metalworking fluids | [44] | |
| Adipic acid Sebacic acid | Lubricant | [5] |
| Alcohol | Guerbet Alcohol Ester | Number of Cosmetic Ingredients |
|---|---|---|
| 2-Butyl-1-octanol (C12) | Butyloctyl salicylate | 17 |
| 2-Hexyl-1-decanol (C16) | Hexyldecyl laurate | 4 |
| Hexyldecyl stearate | 1 | |
| Hexyldecyl ethylhexanoate | 3 | |
| Hexyldecyl isostearate | 2 | |
| 2-Octyl-1-dodecanol (C20) | Octyldodecyl stearoyl stearate | 14 |
| Octyldodecyl myristate | 27 | |
| Octyldodecyl neopentanoate | 5 | |
| Octyldodecyl PCA | 4 | |
| Octyldodecyl stearate | 4 | |
| Octyldodecyl xyloside | 3 | |
| Octyldodecyl oleate | 5 | |
| Octyldodecyl citrate | 1 | |
| Octyldodecyl lactate | 4 | |
| Octyldodecyl olivate | 1 | |
| Octyldodecyl ricinoleate | 3 | |
| Octyldodecyl isostearate | 5 | |
| Octyldodecyl lanolate | 2 | |
| Octyldodecyl/lauroyl glutamate | 11 | |
| Octyldodecyl hydroxystearate | 1 | |
| Octyldodecyl erucate | 3 | |
| Octyldodecyl neodecanoate | 1 | |
| Octyldodecyl benzoate | 1 | |
| Octyldodecyl behenate | 1 | |
| 2-Decyl-1-tetradecanol (C24) | Decyltetradecyl myristoyl methyl beta-alaninate | 1 |
| Ester | Lipase | Application | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Di-2-ethylhexyl adipate | Novozym® 435 Lipozyme® IM | Synthetic lubricant | [60] |
| 2-Ethylhexyl palmitate | Candida sp. 99-125 lipase | Cosmetics, pharmaceutics, and food and chemical industries | [61] |
| Di-2-ethylhexyl sebacate | Novozym® 435 Lipozyme® IM Porcine pancreas lipase | - | [62] |
| 2-Ethylhexyl palmitate | Candida sp. 99-125 lipase | Cosmetic, pharmaceutic, food and chemical industries | [63] |
| 2-Ethylhexyl palmitate | Novozym® 435 | Lubricant and plasticizer | [64] |
| 2-Ethyl-1-hexyl palmitate | Candida antarctica (CAL A) | - | [65] |
| 2-Ethylhexyl esters of fatty acids of rapeseed oil | Candida antarctica lipase Pseudomonas cepacia lipase Rhizomucor miehei lipase | Lubricant | [66] |
| 2-Ethylhexyl palmitate | Candida sp. 99-125 lipase | Cosmetic, pharmaceutical, food, and chemical industries | [67] |
| 2-Ethylhexyl ferulate | Novozym® 435 | Antioxidant in pharmaceutical, cosmetic and food industries | [68] |
| Diethylhexyl adipate | Novozym® 435 | Paint stripper, fragrance, perfume, lubricant, food packaging, and plasticizer | [69] |
| 2-Ethylhexyl oleate | Novozym® 435 | Green plasticizer | [70] |
| 2-Ethylhexyl stearate | Fermase CALB 10000 | Cosmetic biolubricant | [71] |
| 2-Ethylhexyl oleate | Novozym® 435 | Emollient | [72] |
| Bis(2-ethylhexyl) azelate | Novozym® 435 | Lubricant | [73] |
| Ethylhexyl ester of waste cooking oil | Novozym® 435 | Lubricant | [74] |
| 2-Ethylhexyl palmitate 2-Ethylhexyl stearate | Novozym® 435 Novozym® 40086 | Natural alternatives of cyclomethicone in cosmetics | [75] |
| Ethylhexyl ester of γ-linolenic acid | Novozym® 435 | Cosmetic ingredient | [76] |
| 2-Ethylhexyl 2-methylhexanoate | Novozym® 435 | Cosmetic ingredient | [77] |
| 2-Ethylhexyl oleate | Candida antarctica lipase | Pharmaceutical, food, cosmetics, and chemical industries | [78] |
| 2-Ethylhexyl esters of castor oil fatty acids | Eversa Transform 2.0 lipase Candida antarctica CAL A Candida antarctica CAL B Rhizomucor miehei lipase Thermomyces lanuginosus lipase | Biolubricant | [79] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Montiel, M.C.; Ortega-Requena, S.; Gómez, M.; Murcia, M.D.; Máximo, F.; Bastida, J. A Review of Guerbet Alcohols and Their Esters: Synthesis, Applications, and Future Perspectives. Materials 2025, 18, 5180. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18225180
Montiel MC, Ortega-Requena S, Gómez M, Murcia MD, Máximo F, Bastida J. A Review of Guerbet Alcohols and Their Esters: Synthesis, Applications, and Future Perspectives. Materials. 2025; 18(22):5180. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18225180
Chicago/Turabian StyleMontiel, María Claudia, Salvadora Ortega-Requena, María Gómez, María Dolores Murcia, Fuensanta Máximo, and Josefa Bastida. 2025. "A Review of Guerbet Alcohols and Their Esters: Synthesis, Applications, and Future Perspectives" Materials 18, no. 22: 5180. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18225180
APA StyleMontiel, M. C., Ortega-Requena, S., Gómez, M., Murcia, M. D., Máximo, F., & Bastida, J. (2025). A Review of Guerbet Alcohols and Their Esters: Synthesis, Applications, and Future Perspectives. Materials, 18(22), 5180. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18225180








