Comprehensive Characterization of Carbonaceous Material Derived from Rice Husk Pyrolysis and Its Potential for CO2 Adsorption
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Obtaining Process of the Materials
2.2. Characterization
2.3. CO2 Adsorption Tests
3. Results and Discussion
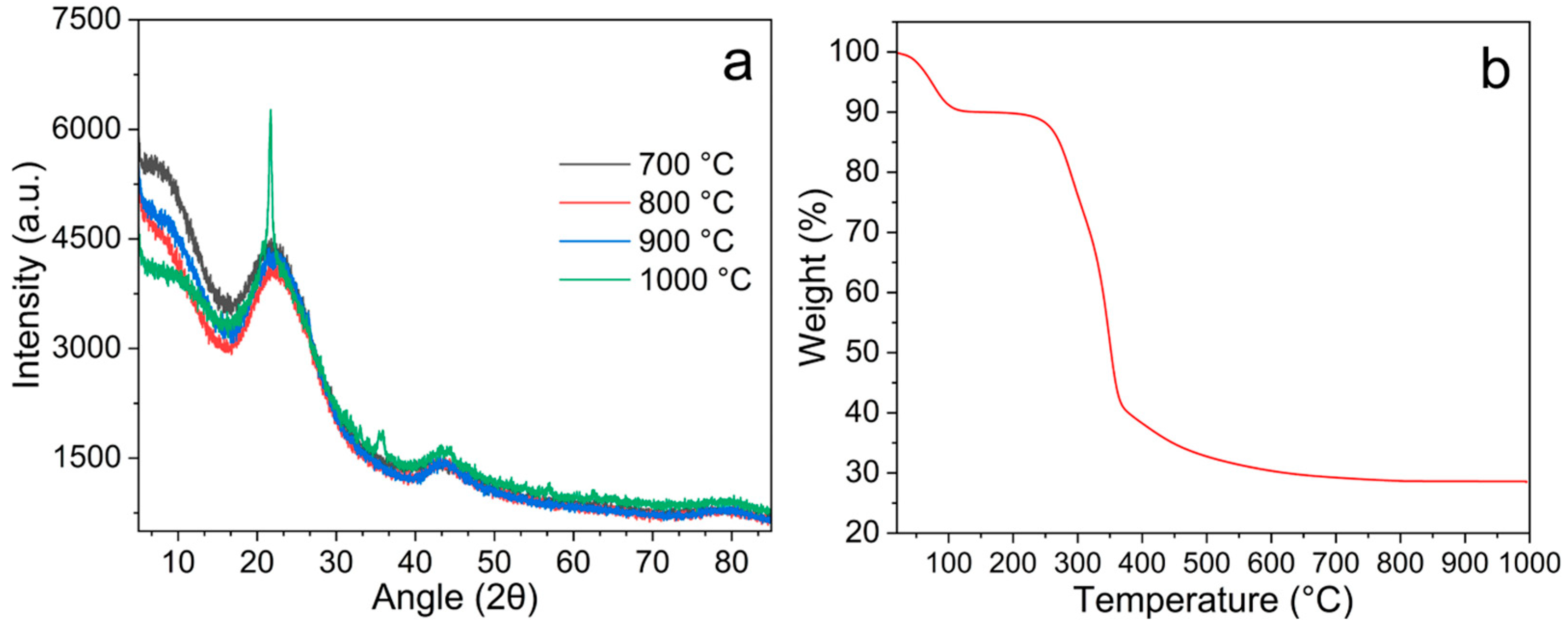
3.1. X-Ray Diffraction and TGA
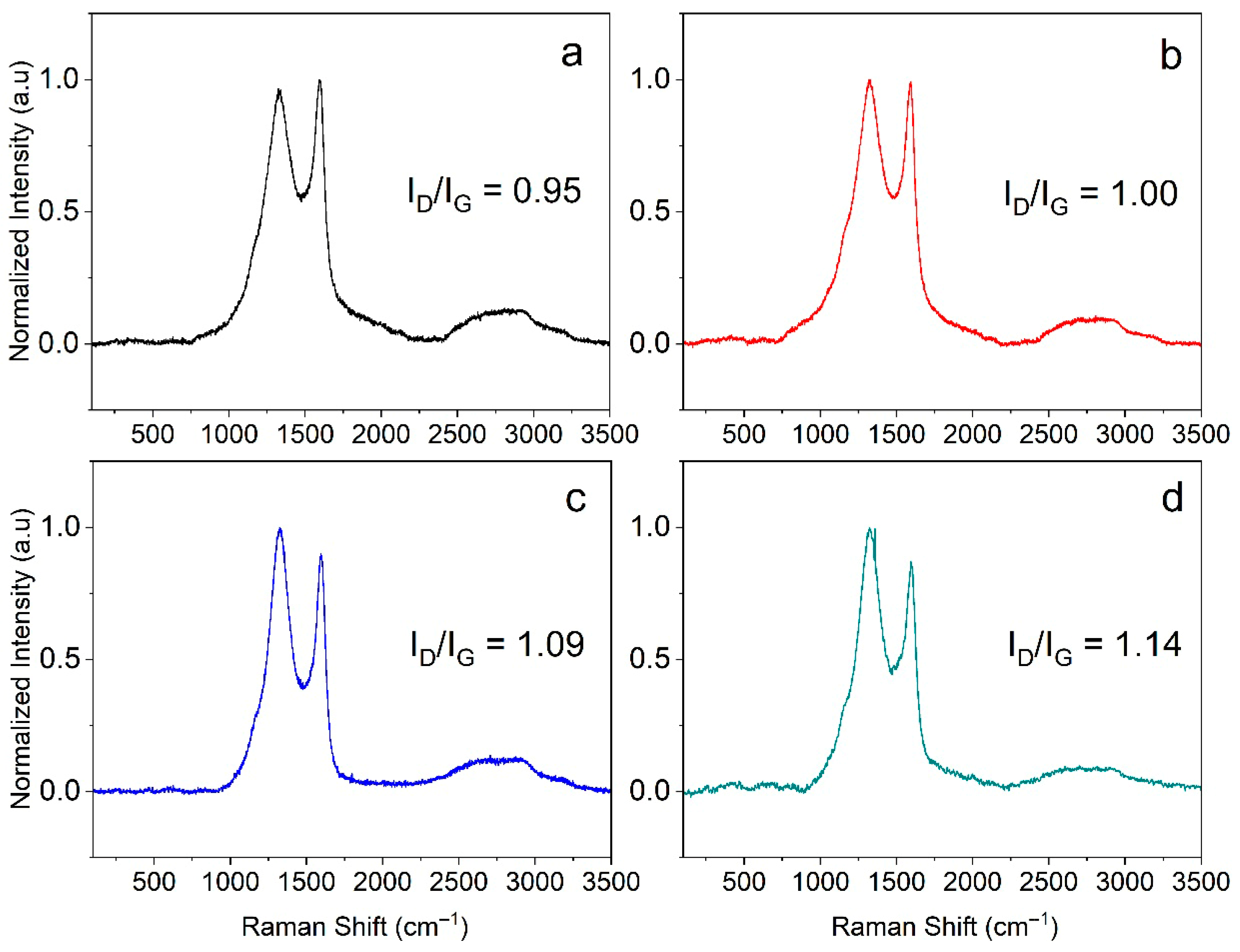
3.2. Raman Analysis
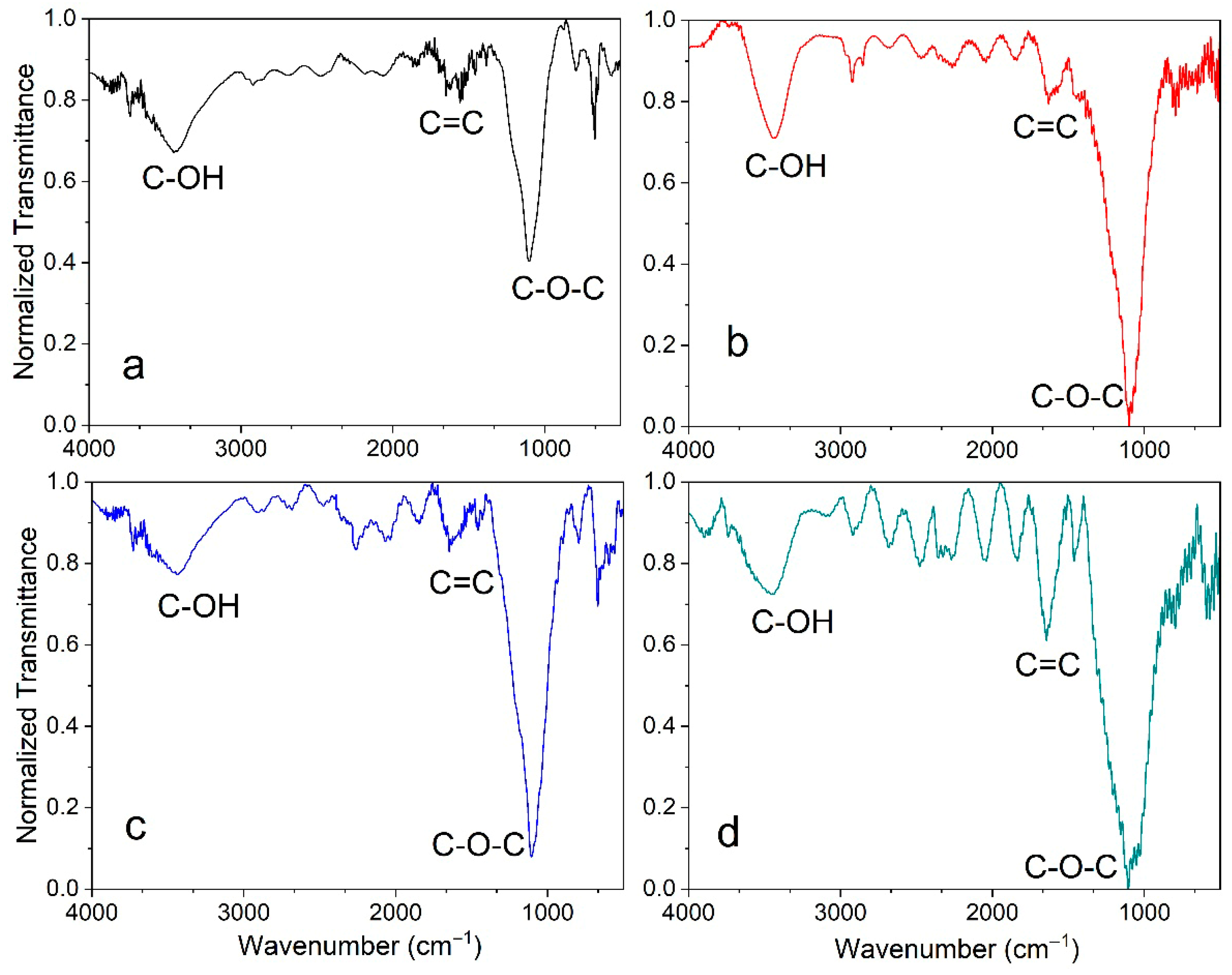
3.3. FTIR Analysis
3.4. Textural Characterization
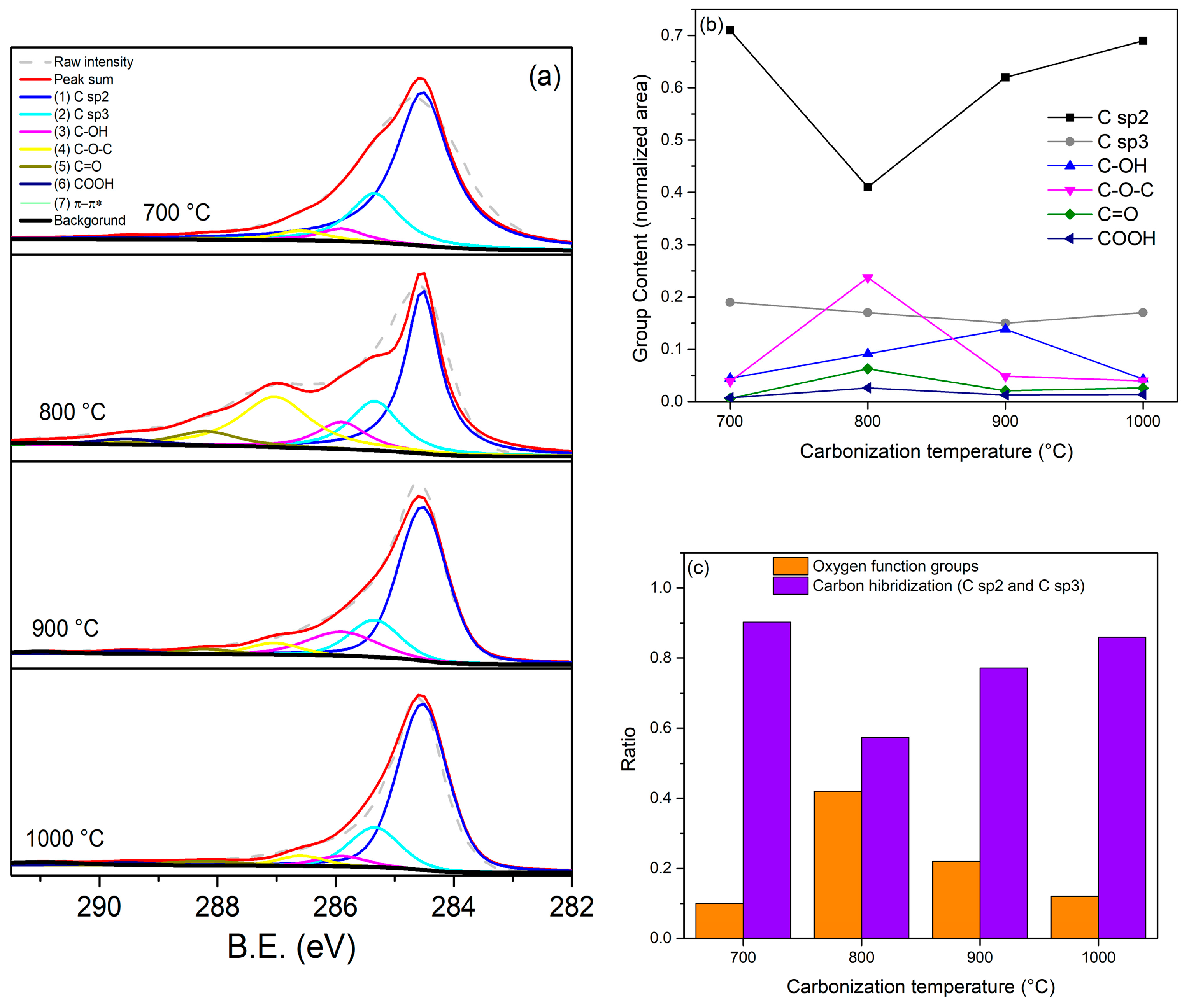
3.5. XPS Analysis
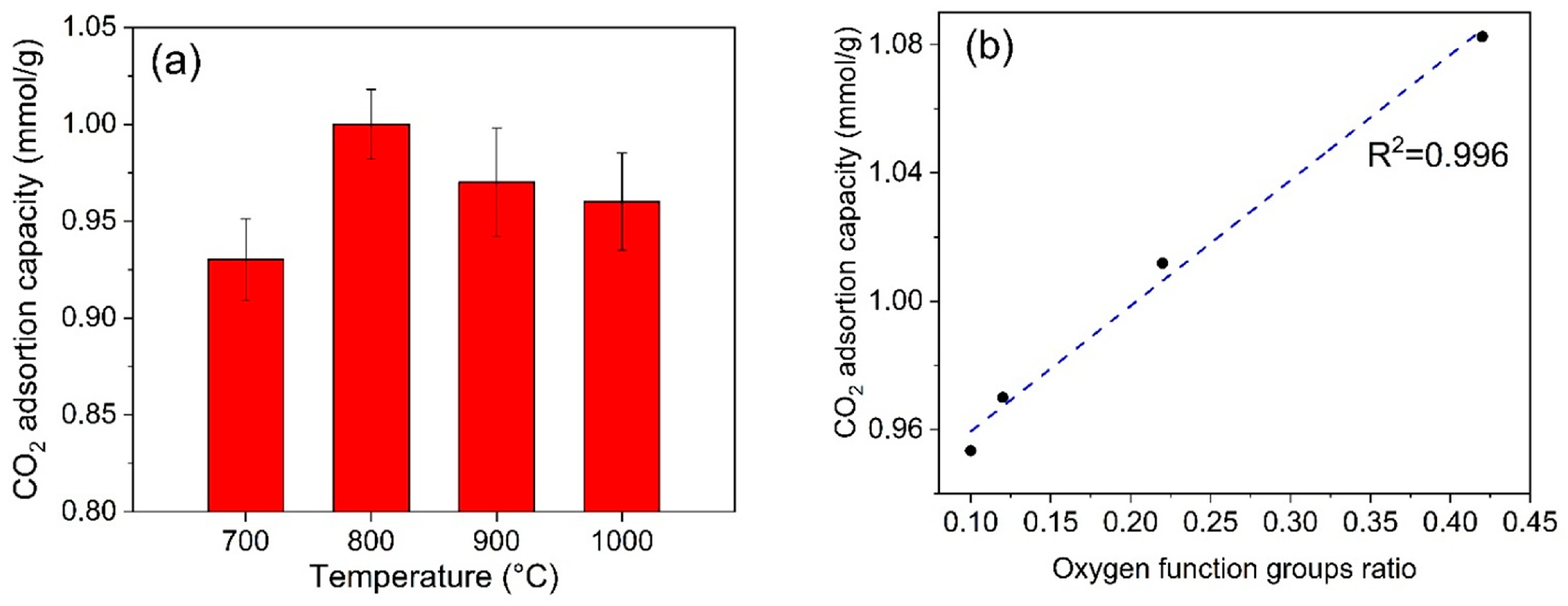
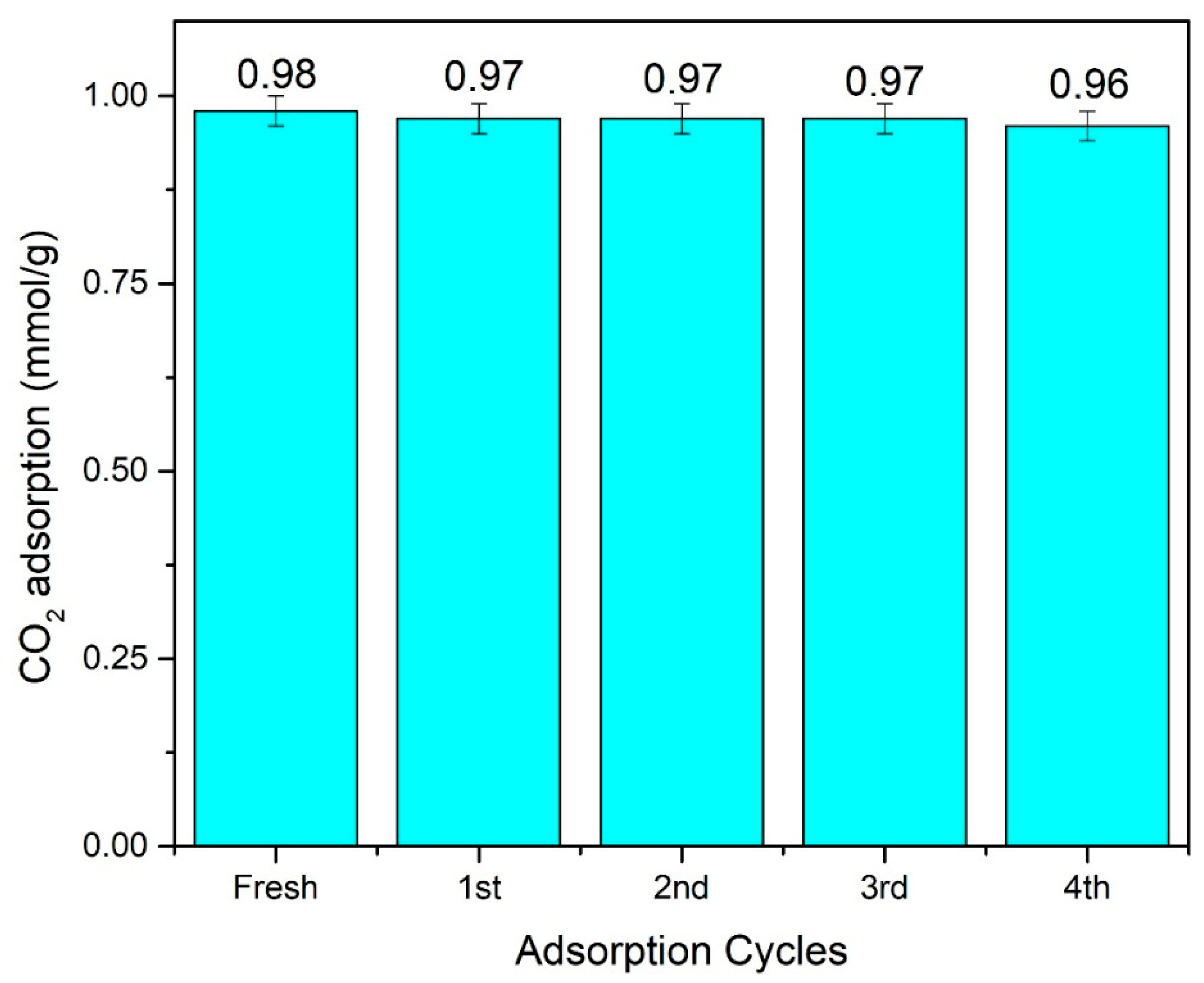
3.6. CO2 Adsorption Test
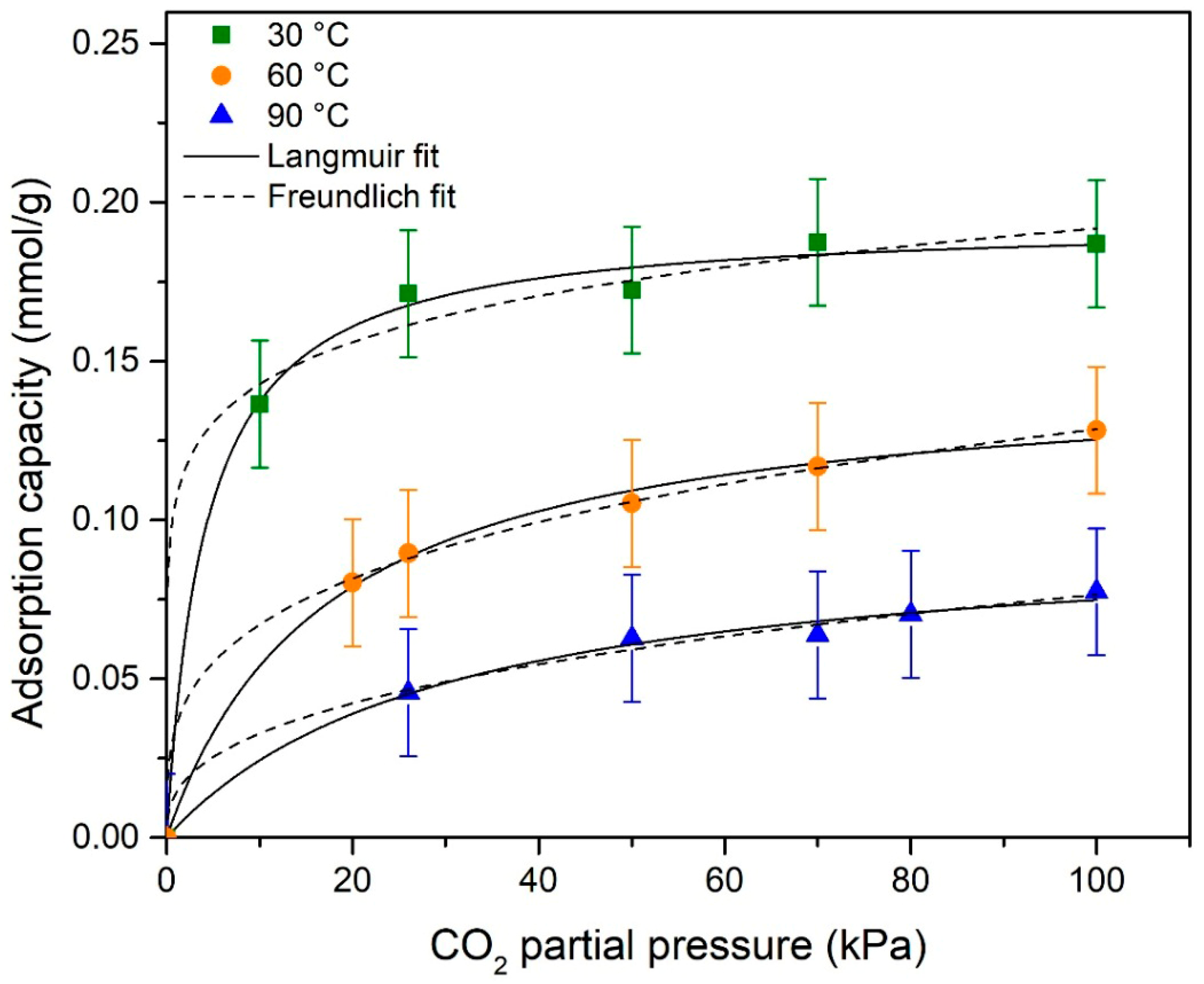
3.7. Adsorption Isotherms
3.8. Adsorption Thermodynamics
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liou, T.-H.; Wang, P.-Y. Utilization of rice husk wastes in synthesis of graphene oxide-based carbonaceous nanocomposites. Waste Manag. 2020, 108, 51–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kordi, M.; Farrokhi, N.; Pech-Canul, M.I.; Ahmadikhah, A. Rice Husk at a Glance: From Agro-Industrial to Modern Applications. Rice Sci. 2024, 31, 14–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, S.S.; Chava, R.; Appari, S.; A, B.; Kuncharam, B.V.R. Sustainable use of rice husk for the cleaner production of value-added products. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 106899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.-G.; Park, D.-G.; Lee, J.-Y.; Choi, J.; Kim, J.-H.; Kim, J.-H.; Yun, Y.-U.; Oh, T.-K. Ammonium capture Kinetic, Capacity, and Prospect of Rice Husk Biochar produced by different pyrolysis conditions. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 29910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, T.T.V.; Viet, N.M.; Quan, V.T.; Huong, N.T.L. Novel Fe3O4-modified biochar generated from rice husk: A sustainable strategy for strengthening lead absorption in wastewater. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2024, 21, 9677–9686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, T.; Batool, F.; Iqbal, S. Exploration of haematite-loaded rice husk biochar as a low-cost nanosorbent to remove Cr (III) from the aqueous media. Chem. Ecol. 2023, 39, 404–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che Othman, F.E.; Ismail, M.S.; Yusof, N.; Samitsu, S.; Yusop, M.Z.; Arifin, N.F.T.; Alias, N.H.; Jaafar, J.; Aziz, F.; Salleh, W.N.W.; et al. Methane adsorption by porous graphene derived from rice husk ashes under various stabilization temperatures. Carbon Lett. 2020, 30, 535–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chithra, A.; Rajeev, R.; Prabhakaran, K. C/SiO2 and C/SiC composite foam monoliths from rice husk for thermal insulation and EMI shielding. Carbon Lett. 2022, 32, 639–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Lin, H.; Li, Y.; Shen, J.; Yang, C.; Wang, K. Carbon Sequestration of Silica-Rich Biochar in Cement Accompanied by the Pozzolanic Effect. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 13826–13839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dien, L.X.; Luque, R. Rice Husk Valorization into NiO@SiO2/Carbon Nanocomposites for Low-Temperature CO Oxidation: Effect of Surface Area and Ni3+ Cations. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 13681–13685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Shi, J.; Wu, Y.; Liu, H.; Liu, Z.; You, Q.; Li, X.; Cong, L.; Liu, D.; Liu, F.; et al. Heterostructure CoFe@(Co0.5Fe0.5)S@NCNT anchored on rice husk-based hierarchical porous carbon as a bifunctional cathode catalyst for Zn–air batteries. J. Mater. Chem. A 2024, 12, 11907–11919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paramitha, T.; Munika, A.D.; Saputra, D.R.; Nisa, S.S.; Purwanto, A.; Supriyanto, A.; Widiyandari, H.; Aliwarga, H.K. Application of rice husk as a carbon source for substitution of sensitizer and counter electrode material in dye-sensitized solar cells. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2024, 2696, 012010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajamani, S.; Kolla, S.S.N.; Gudivada, R.; Raghunath, R.; Ramesh, K.; Jadhav, S.A. Valorization of Rice Husk to Value-Added Chemicals and Functional Materials. Int. J. Environ. Res. 2023, 17, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwuozor, K.O.; Emenike, E.C.; Bakare, B.F.; Eleregbe, F.O.; Aransiola, F.T.; Omonayin, E.; Owolabi, O.O.; Ogundana, M.R.; Adeniyi, A.G. A review on the conversion of plant husk-based biomass into biochar. Biofuels 2024, 15, 1331–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafiei, N.; Nasrollahzadeh, M.; Iravani, S. Green Synthesis of Silica and Silicon Nanoparticles and Their Biomedical and Catalytic Applications. Comments Inorg. Chem. 2021, 41, 317–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar Das, S.; Adediran, A.; Rodrigue Kaze, C.; Mohammed Mustakim, S.; Leklou, N. Production, characteristics, and utilization of rice husk ash in alkali activated materials: An overview of fresh and hardened state properties. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 345, 128341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peralta, Y.M.; Molina, R.; Moreno, S. Chemical and structural properties of silica obtained from rice husk and its potential as a catalytic support. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 112370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, S.S.; Mathur, L.; Roy, P.K. Rice husk/rice husk ash as an alternative source of silica in ceramics: A review. J. Asian Ceram. Soc. 2018, 6, 299–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Othman, F.E.C.; Nordin, N.A.H.M.; Ismail, N.; Zakria, H.S.; Junoh, H.; Aziz, M.H.A. A review on sustainable graphene production from rice husks: Strategies and key considerations. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 497, 154408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nandi, R.; Jha, M.K.; Guchhait, S.K.; Sutradhar, D.; Yadav, S. Impact of KOH Activation on Rice Husk Derived Porous Activated Carbon for Carbon Capture at Flue Gas alike Temperatures with High CO2/N2 Selectivity. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 4802–4812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gargiulo, V.; Alfè, M.; Raganati, F.; Zhumagaliyeva, A.; Doszhanov, Y.; Ammendola, P.; Chirone, R. CO2 Adsorption under Dynamic Conditions: An Overview on Rice Husk-Derived Sorbents and Other Materials. Combust. Sci. Technol. 2019, 191, 1484–1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Du, T.; Jia, H.; Qiu, Z.; Song, Y. Synthesis, characterization and CO2 adsorption of NaA, NaX and NaZSM-5 from rice husk ash. Solid State Sci. 2018, 86, 24–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granados-Correa, F.; Gutiérrez-Bonılla, E.; Jiménez-Reyes, M.; Roa-Morales, G.; Balderas-Hernández, P. CO2 adsorption behavior of a highly-microporous KOH-activated carbon obtained from rice husk waste: Kinetic and equilibrium studies. Int. J. Chem. React. Eng. 2024, 22, 181–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Yan, W.; Liu, X.; Hu, T.; Xiong, Y.; Tian, S.; Feng, J.; Huang, Z.; Zhao, Z. Rice husk waste-derived super-biochar with the max surface area and Philic-CO2 textural structure: Boosting effect and mechanism of post-desilication. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 490, 151583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Li, M.; Xie, X.; Li, C.; Liu, D. Pyrolysis of rice husk in molten lithium chloride: Biochar structure evolution and CO2 adsorption. J. Energy Inst. 2024, 113, 101526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanif, A.; Aziz, A.; Helal, A.; Abdelnaby, M.M.; Khan, A.; Theravalappil, R.; Khan, M.Y. CO2 Adsorption on Biomass-Derived Carbons from Albizia procera Leaves: Effects of Synthesis Strategies. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 36228–36236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, K.K.; Omal, N.M.; Sharma, V.K.; Kandy, S.B.; Ağbulut, Ü. CO2 storage behavior of rice husk biochar–bitumen mixture at different pressures and temperatures: A detailed experimental investigation. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2025, 150, 4599–4616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoang, T.-D.; Liu, Y.; Le, M.T. Synthesis and Characterization of Biochars and Activated Carbons Derived from Various Biomasses. Sustainability 2024, 16, 5495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Liu, C.; Ouyang, J.; Xue, B.; Xu, J.; Zhai, J.; Xiao, R. Porous carbon materials derived from rice husk pyrolysis with NaCl/Na2CO3 binary molten salt for CO2 capture. Ind. Crops Prod. 2025, 227, 120808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barakat, N.A.M.; Mahmoud, M.S.; Moustafa, H.M. Comparing specific capacitance in rice husk-derived activated carbon through phosphoric acid and potassium hydroxide activation order variations. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, A.; Singh, R.K.; Kumar, N.; Kumari, R.; Monalisa; Sharma, S. Green synthesis and physical properties of crystalline silica engineering nanomaterial from rice husk (agriculture waste) at different annealing temperatures for its varied applications. J. Indian Chem. Soc. 2023, 100, 100982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hidayat; Rahmat, A.; Nissa, R.C.; Sukamto; Nuraini, L.; Nurtanto, M.; Ramadhani, W.S. Analysis of rice husk biochar characteristics under different pyrolysis temperature. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2023, 1201, 012095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wazir, A.H.; Wazir, I.U.; Wazir, A.M. Preparation and characterization of rice husk based physical activated carbon. Energy Sources Part A Recover. Util. Environ. Eff. 2020, 46, 4875–4885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genieva, S.D.; Turmanova, S.C.; Dimitrova, A.S.; Vlaev, L.T. Characterization of rice husks and the products of its thermal degradation in air or nitrogen atmosphere. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2008, 93, 387–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Lin, Y.; Hagio, T.; Hu, Y.H. Surface-microporous graphene for CO2 adsorption. Catal. Today 2020, 356, 514–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, M.S.; Yusof, N.; Yusop, M.Z.M.; Ismail, A.F.; Jaafar, J.; Aziz, F.; Karim, Z.A. Synthesis and characterization of graphene derived from rice husks. Malays. J. Fundam. Appl. Sci. 2019, 15, 516–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro-Ladino, J.R.; Cuy-Hoyos, C.A.; Prías-Barragán, J.J. Basic physical properties and potential application of graphene oxide fibers synthesized from rice husk. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 17967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jha, R.K.; Bhunia, H.; Basu, S. Enhancing CO2 capture through innovating monolithic graphene oxide frameworks. Environ. Res. 2024, 249, 118426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Yang, Y.; Wu, Q.; Liu, B.; Li, D.; Chen, R.; Wang, C.; Li, H.; Zeng, Z.; Li, L. Underlying mechanism of CO2 uptake onto biomass-based porous carbons: Do adsorbents capture CO2 chiefly through narrow micropores? Fuel 2020, 282, 118727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mochizuki, Y.; Bud, J.; Byambajav, E.; Tsubouchi, N. Pore properties and CO2 adsorption performance of activated carbon prepared from various carbonaceous materials. Carbon Resour. Convers. 2025, 8, 100237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-García, S.; Santiago, R.; López-Díaz, D.; Merchán, M.D.; Velázquez, M.M.; Fierro, J.L.G.; Palomar, J. Role of the Structure of Graphene Oxide Sheets on the CO2 Adsorption Properties of Nanocomposites Based on Graphene Oxide and Polyaniline or Fe3O4-Nanoparticles. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 12464–12473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Y.; Vega Martín, L.; Sánchez Montero, M.J.; López-Díaz, D.; Velázquez, M.M.; Merchán, M.D. Optimizing the Properties of Hybrids Based on Graphene Oxide for Carbon Dioxide Capture. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2022, 61, 1332–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liou, T.-H.; Tseng, Y.-K.; Zhang, T.-Y.; Liu, Z.-S.; Chen, J.-Y. Rice husk char as a sustainable material for the preparation of graphene oxide-supported biocarbons with mesoporous structure: A characterization and adsorption study. Fuel 2023, 344, 128042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junkermeier, C.E.; Larmand, E.; Morais, J.-C.; Kobebel, J.; Lavarez, K.; Adra, R.M.; Yang, J.; Diaz, V.A.; Paupitz, R.; Psofogiannakis, G. Functionalized carbophenes as high-capacity versatile gas adsorbents: An ab initio study. Comput. Mater. Sci. 2024, 232, 112665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, D.; Bhunia, H.; Bajpai, P.K. Epoxy based oxygen enriched porous carbons for CO2 capture. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 414, 380–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Autthawong, T.; Namsar, O.; Yu, A.; Sarakonsri, T. Cost-effective production of SiO2/C and Si/C composites derived from rice husk for advanced lithium-ion battery anodes. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2020, 31, 9126–9132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Botella, E.; Valencia, S.; Rey, F. Zeolites in Adsorption Processes: State of the Art and Future Prospects. Chem. Rev. 2022, 122, 17647–17695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, F.; Wang, Y.; Li, L.; Zhang, K.; Smith, R.L.; Qi, X. Porous carbonaceous materials from hydrothermal carbonization and KOH activation of corn stover for highly efficient CO2 capture. Chem. Eng. Commun. 2018, 205, 423–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Yin, Y.; Liu, X.; Liu, Y.; Xiao, Q.; Zhao, L.; Demir, M.; Çolak, M.Ö.A.; Wang, L.; Hu, X. Potassium metaborate-activated boron-doped porous carbons for selective CO2 adsorption. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2025, 376, 134079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, J.; Basu, S.; Bhunia, H. Dynamic CO2 adsorption on activated carbon adsorbents synthesized from polyacrylonitrile (PAN): Kinetic and isotherm studies. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2019, 280, 357–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jedli, H.; Almoneef, M.M.; Mbarek, M.; Jbara, A.; Slimi, K. Adsorption of CO2 onto zeolite ZSM-5: Kinetic, equilibrium and thermodynamic studies. Fuel 2022, 321, 124097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, B.; Mondal, N.K.; Bhaumik, R.; Roy, P. Insight into adsorption equilibrium, kinetics and thermodynamics of lead onto alluvial soil. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 11, 1101–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, R.; Ahmad, W.; Ahmad, I.; Khan, M.; Iqbal Khattak, M.; Hussain, F. Adsorption and recovery of hexavalent chromium from tannery wastewater over magnetic max phase composite. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2021, 56, 439–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
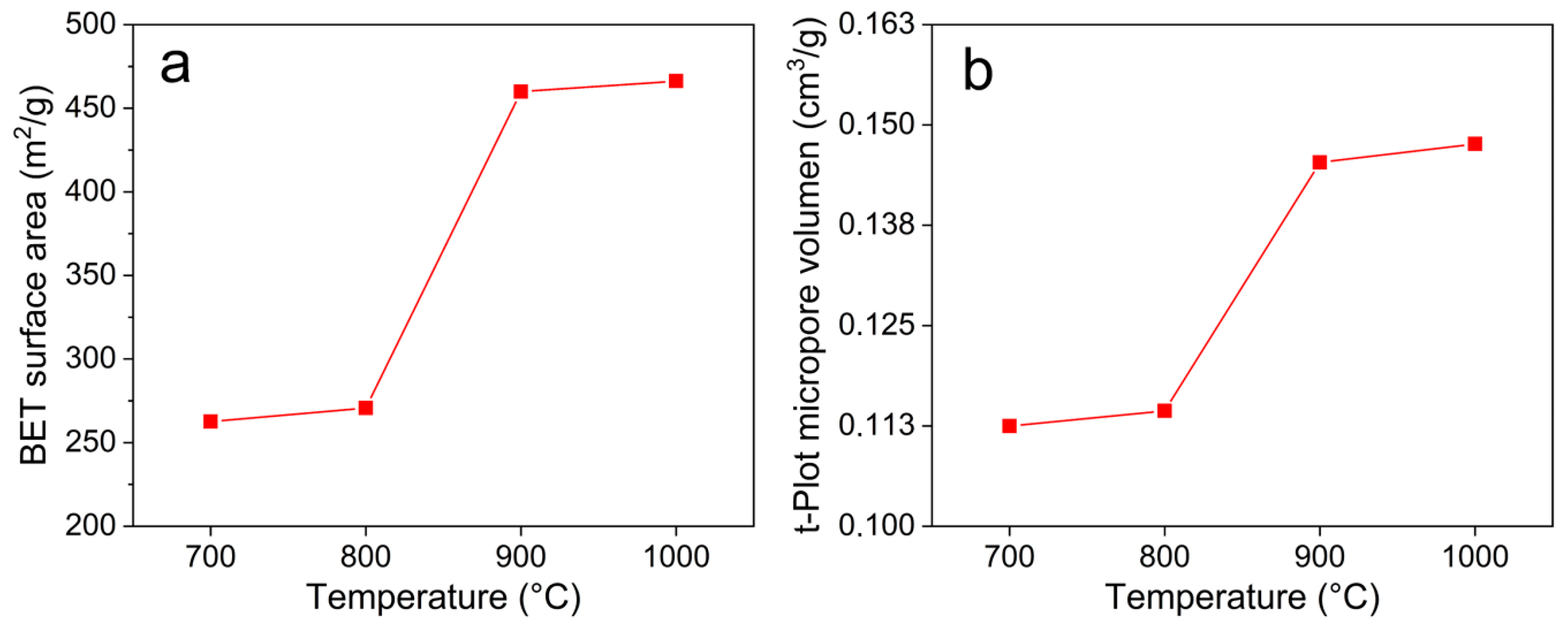
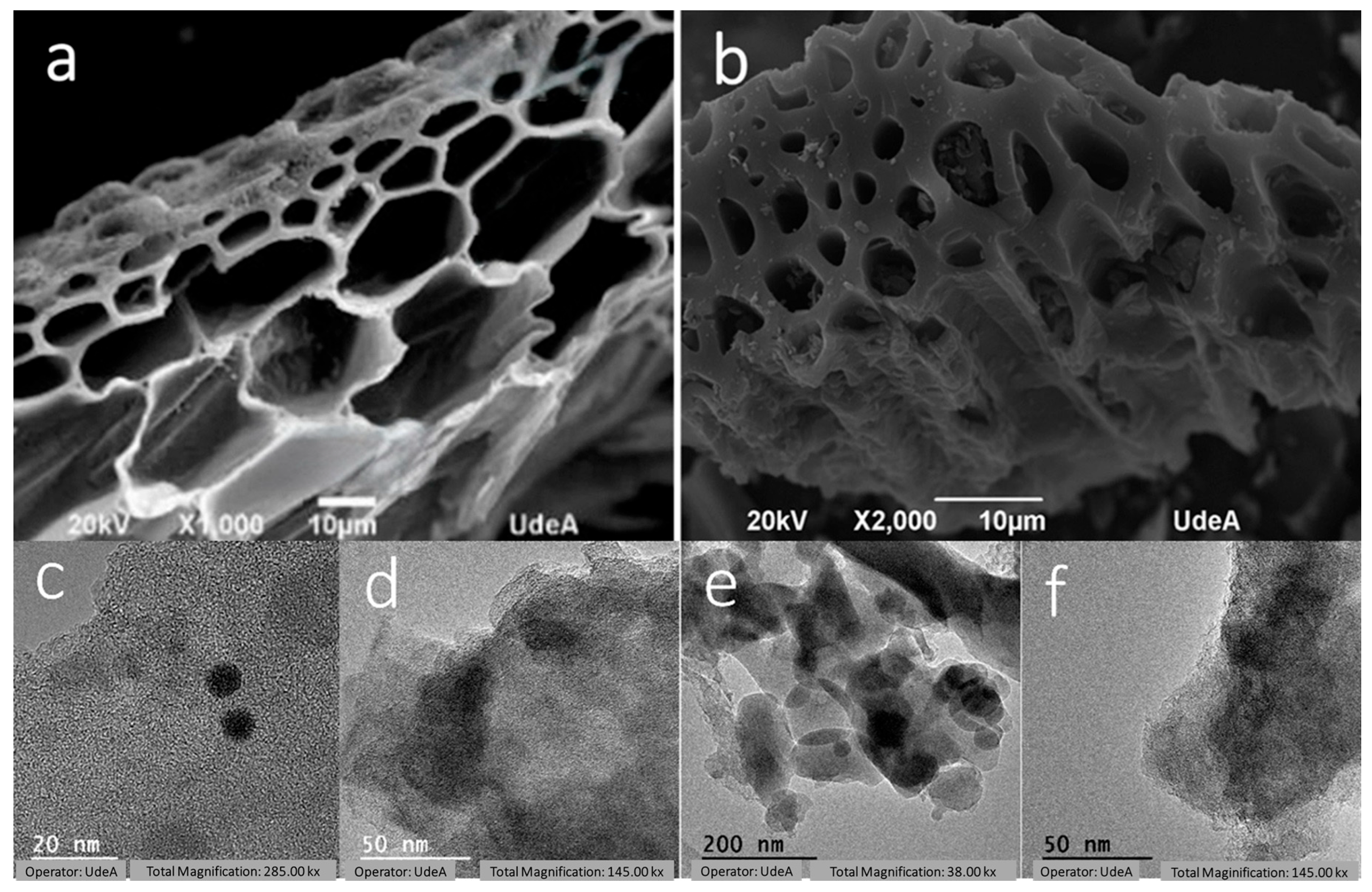
| Sample (°C) | SBET a | Smicro b | Sext c | Vtotal d | Vmicro e |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 700 | 263 | 222 | 40.64 | 0.112 | 0.112 |
| 800 | 271 | 226 | 44.86 | 0.114 | 0.114 |
| 900 | 457 | 377 | 80.07 | 0.220 | 0.144 |
| 1000 | 468 | 293 | 72.03 | 0.227 | 0.149 |
| Sample | Pretreatment | T, P * | Surface Area (m2/g) | CO2 Adsorption (mmol/g) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carbonaceous material from rice husk (800 °C) | Without activation | 30 °C, 1 bar | 271 | 1.0 | Present work |
| Corn stover-derived porous carbon (AC800-2-2) | KOH activation | 0 °C, 1 bar | 2442 | 7.14 | [48] |
| Corn stover-hydrothermal carbonization (HC) | Without activation | 0 °C, 1 bar | 11 | 0.71 | |
| Albizia procera leaves-derived nitrogen-doped carbons (NDCs) | NaHCO3 activation | 0 °C, 1 bar | 426 | 2.54 | [26] |
| Water chestnut shell | KBO2 activated | 0 °C, 1 bar 25 °C, 1 bar | 683 | 4.22 3.15 | [49] |
| Rice husk-derived porous activated carbon | KOH activation | 0 °C, 1 bar | 755.73 | 3.13 | [20] |
| 25 °C, 1 bar | 2.24 | ||||
| 50 °C, 1 bar | 1.55 | ||||
| W/O activation | 0 °C, 1 bar | 9.77 | 1.39 | ||
| 25 °C, 1 bar | 1.06 | ||||
| 50 °C, 1 bar | 0.74 | ||||
| Rice husk biochar | KOH activation | 25 °C, 1 bar | 2492.9 | 3.10 | [27] |
| Model | Parameter | Temperature (°C) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 30 | 60 | 90 | ||
| Langmuir | qm (mmol/g) | 0.194 | 0.147 | 0.097 |
| KL (kPa−1) | 0.240 | 0.058 | 0.033 | |
| R2 | 0.996 | 0.997 | 0.990 | |
| Freundlich | KF | 0.106 | 0.035 | 0.014 |
| n | 7.805 | 3.539 | 2.717 | |
| R2 | 0.854 | 0.995 | 0.942 | |
| Temperature (°C) | ∆G0 (kJ/mol) | ∆H0 (kJ/mol) | ∆S0 (kJ/mol K) | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 30 (303.15 K) | 3.85 | −30.58 | −0.11 | 0.964 |
| 60 (333.15 K) | 7.26 | |||
| 90 (363.15 K) | 10.67 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mesa, S.; Castro-Ladino, J.R.; Amaya, S.L.; Manrique, C.; Echavarría, A.; Hoyos-Ayala, D.A.; Uran, L. Comprehensive Characterization of Carbonaceous Material Derived from Rice Husk Pyrolysis and Its Potential for CO2 Adsorption. Materials 2025, 18, 5151. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18225151
Mesa S, Castro-Ladino JR, Amaya SL, Manrique C, Echavarría A, Hoyos-Ayala DA, Uran L. Comprehensive Characterization of Carbonaceous Material Derived from Rice Husk Pyrolysis and Its Potential for CO2 Adsorption. Materials. 2025; 18(22):5151. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18225151
Chicago/Turabian StyleMesa, Santiago, Javier Ricardo Castro-Ladino, Sandra Liliana Amaya, Cecilia Manrique, Adriana Echavarría, Dora A. Hoyos-Ayala, and Laura Uran. 2025. "Comprehensive Characterization of Carbonaceous Material Derived from Rice Husk Pyrolysis and Its Potential for CO2 Adsorption" Materials 18, no. 22: 5151. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18225151
APA StyleMesa, S., Castro-Ladino, J. R., Amaya, S. L., Manrique, C., Echavarría, A., Hoyos-Ayala, D. A., & Uran, L. (2025). Comprehensive Characterization of Carbonaceous Material Derived from Rice Husk Pyrolysis and Its Potential for CO2 Adsorption. Materials, 18(22), 5151. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18225151







