Abstract
High-temperature sintering for ceramsite preparation is a safe and effective approach to recycle solid waste. Flux components are critical in ceramsite sintering, as they can reduce sintering temperature, modulate the viscosity and content of the liquid phase, and ultimately optimize ceramsite performance. However, existing studies on lead–zinc tailings (LZTs) and coal gangue (CG)-based ceramsite lack systematic exploration of key fluxes (Na2O, MgO, CaO, Fe2O3), limiting the high-value utilization of these wastes. Under fixed sintering conditions (preheating at 400 °C for 30 min, sintering at 1250 °C for 30 min, heating rate of 10 °C/min), this work systematically investigated the effects of these fluxes (in the forms of carbonates, except for Fe2O3) on LZTs-CG ceramsite. The mechanical properties, mineral composition, microstructure and heavy metal leaching of samples were analyzed using various methods, including uniaxial compression, X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), and inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectrometry (ICP-OES). Results showed that, while Fe2O3 exerted a non-monotonic influence, Na2O, MgO, and CaO improved apparent density and compressive strength, concurrently reducing water absorption, with these effects enhancing in a dose-dependent manner. Na2O, MgO and Fe2O3 facilitated the formation of labradorite, cordierite and hematite, respectively. All fluxes weakened the diffraction peaks of quartz and mullite. ICP-OES results indicated that the fluxes slightly increased Pb and Zn leaching, yet the highest values (0.1975 mg/L for Pb, 0.0485 mg/L for Zn) were well below the limits specified in the Chinese national standard GB 5086.2-1997 (Leaching Toxicity of Solid Waste—Horizontal Vibration Extraction Procedure). This work shows optimized flux composition enables high-performance, eco-safe LZTs-CG ceramsite, supporting LZTs and CG high-value utilization and sustainable development.
1. Introduction
Accelerated industrialization has driven a surge in global mineral resource exploration and production, leading to substantial mining waste issues [1,2]. Lead–zinc tailings (LZTs) are residual solid wastes from lead–zinc ore crushing and flotation [3]. As a major global producer of these ores, China accounts for 47% and 35% of global lead and zinc output, respectively [4,5], generating over 10 million tons of LZTs annually with a utilization rate of only ~7% [6]. Most LZTs are openly stockpiled, occupying vast land and causing gradual heightening of tailings dams via continuous accumulation, which elevates dam safety risks [7,8]. They also contain lead, zinc, and other toxic heavy metals that migrate into surrounding ecosystems, markedly increasing environmental contamination risks [9]. Similarly, coal gangue (CG), a major solid waste from coal mining and washing and one of the most abundant industrial residues in the global coal industry, has a global annual discharge exceeding 1 billion tons, with China alone producing over 300 million tons yearly. This volume is predominantly openly stockpiled, resulting in extremely low utilization efficiency [10,11]. Like LZTs, CG poses prominent environmental and resource challenges, particularly land occupation and pollution [12,13], making the investigation of efficient treatment and recycling approaches for LZTs and CG a prominent research focus in this field.
Ceramsite, an artificial lightweight aggregate with excellent properties (e.g., low bulk density, high compressive strength), is conventionally fabricated from clay, shale, or natural expandable minerals via high-temperature sintering [14,15]. However, as non-renewable resources, clay and shale are being depleted due to over-exploitation, prompting the adoption of industrial solid wastes as alternative raw materials for ceramsite production [16,17,18]. Numerous bulk solid wastes (e.g., fly ash, red mud, iron tailings) have been validated as viable ceramsite feedstocks [19,20,21,22]. Notably, CG is widely employed as a primary raw material for sintered ceramsite, owing to its high silica and alumina content that enhances sintering stability [23]. Similarly, LZTs offer distinct advantages: their alkali metals act as sintering aids to reduce energy consumption, while gaseous products generated during sintering induce a foaming effect favorable for forming a porous ceramsite structure [24]. Thus, building on the aforementioned advantages of CG and LZTs, utilizing LZTs in combination with CG for ceramsite production is highly feasible, thereby facilitating the efficient utilization and resource recycling of these two industrial solid wastes.
Numerous studies confirm that raw material composition and sintering regime are the two core factors governing ceramsite’s sintering quality and performance [17,22,25,26]. Functionally, ceramsite feedstocks comprise three indispensable categories (structural components, gas-generating components, and flux components), with flux components being particularly critical for regulating the sintering process [27]. As validated in previous research, alkali and alkaline earth metal oxides (e.g., Na2O, CaO, MgO, and Fe2O3) act as effective fluxes, reducing sintering temperature and modulating liquid phase viscosity to optimize sintering efficiency [28]. Specifically, for solid waste-based ceramsite, extensive studies have explored the impacts of these oxides as fluxes on sintering performance. For instance, Zou et al. [29] investigated the influences of Fe2O3, CaO, and MgO on ceramsite synthesized from wastewater and drinking-water treatment sludge, revealing that increasing Fe2O3 content promoted the formation of complex crystalline phases, reduced pore volume, and thereby enhanced compressive strength. In contrast, higher CaO content increased porosity, while MgO exerted a negligible influence on overall performance. Similarly, Cao et al. [30] prepared ceramsite using municipal solid waste incineration bottom ash sludge (MSWI-BAS) as the main raw material, demonstrating that adjusting the contents of SiO2 and CaO improved product performance, whereas excessive Al2O3 inhibited internal crystallization, resulting in increased porosity and decreased compressive strength. Li et al. [31] evaluated the effects of Na2O, MgO, CaO, and Fe2O3 on the preparation of lightweight aggregate (LWA) and the solidification of chromium (Cr), reporting that Na2O significantly promoted both LWA formation and Cr solidification, while CaO, MgO, and Fe2O3 had only minor regulatory effects.
Notably, these existing studies focus on specific solid waste systems (e.g., sludge, MSWI-BAS), yet lead–zinc tailings (LZTs) and coal gangue (CG)—two of the most abundant industrial solid wastes with substantial resource utilization potential—remain underexplored. Specifically, there is a critical lack of systematic research on how key flux components (Na2O, MgO, CaO, Fe2O3) influence the characteristics of LZTs-CG-based ceramsite. Furthermore, while our previous work [32] has validated the feasibility of preparing high-performance LZTs-CG-based ceramsite (laying the foundation for their large-scale recycling), the underlying mechanisms by which these fluxes regulate sintering behavior, mechanical/physical properties, and heavy metal (Pb, Zn) leaching behavior of the product remain unclear. Given that flux effects are highly dependent on the parent solid waste matrix, this dual knowledge gap not only hinders the rational design of flux compositions for optimizing LZTs-CG ceramsite performance but also limits the practical application of this resource recycling technology. Thus, investigating the roles of Na2O, MgO, CaO, and Fe2O3 in LZTs-CG-based ceramsite is both novel and necessary, as it can fill the existing research void, enable targeted performance optimization, and ultimately facilitate the efficient resource utilization of these two massive industrial solid wastes.
Specifically, this study aims to address the aforementioned knowledge gaps through three core objectives: (i) systematically investigate the effects of Na2O, MgO, CaO, and Fe2O3 on the key properties of LZTs-CG-based ceramsite (including apparent density, compressive strength, and water absorption) under a fixed sintering regime (preheating at 400 °C for 30 min, sintering at 1250 °C for 30 min, heating rate of 10 °C/min); (ii) quantitatively evaluate the leaching behavior of Pb and Zn from the sintered ceramsite to assess its environmental safety; (iii) comprehensively analyze the effects of flux components on the mineral composition and microstructure of ceramsite using scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and X-ray diffraction (XRD). The findings of this study are expected to enrich the theoretical framework for the preparation and performance optimization of LZTs-CG-based ceramsite, while providing targeted technical support for the high-value recycling of LZTs and CG, ultimately contributing to sustainable development in the mining and construction sectors, as well as the alleviation of environmental contamination caused by industrial solid wastes.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
In this study, LZTs, CG, and SiC (serving as the foaming agent) were employed as the raw materials for ceramsite preparation. Specifically, LZTs were sourced from Zhongjin Lingnan Mining Co., Ltd., Nanning, China, while CG was procured from Lixin Coal Mine, Tongling, China. The foaming agent SiC was obtained from a commercial supplier. Furthermore, LZTs and CG were ball-milled for 15 min using an SM-500 ball mill, dried to constant weight at 105 ± 5 °C, and passed through a 0.074 mm sieve. Notably, CG was subjected to additional desulfurization and decarbonization pretreatment before use, aiming to eliminate adverse effects of residual sulfur and carbon on the sintering behavior and mechanical properties of the final ceramsite. The detailed pretreatment procedure for CG was as follows: the sieved CG powder was placed in a muffle furnace, heated from room temperature to 700 °C at a rate of 10 °C/min under air atmosphere, held at 700 °C for 90 min for oxidative decomposition of sulfur-containing and carbonaceous components, and then cooled to room temperature along with the furnace to obtain pretreated CG with significantly reduced sulfur and carbon contents.
The chemical compositions of pretreated LZTs and CG are presented in Table 1, and the corresponding test methods are detailed in the subsequent Section 2.3.1.

Table 1.
Chemical compositions of raw material (wt. %).
The flux components employed in this study included Na2O, MgO, CaO, and Fe2O3. These oxides were introduced via their respective carbonate or oxide precursors to ensure uniform dispersion in the raw material matrix: specifically, Na2O was incorporated as sodium carbonate (Na2CO3), MgO as magnesium carbonate (MgCO3), CaO as calcium carbonate (CaCO3), and Fe2O3 as analytical-grade iron oxide powder. All chemical reagents (Na2CO3, MgCO3, CaCO3, and Fe2O3) were of analytical grade and purchased from Sinopharm Chemical Reagent Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China.
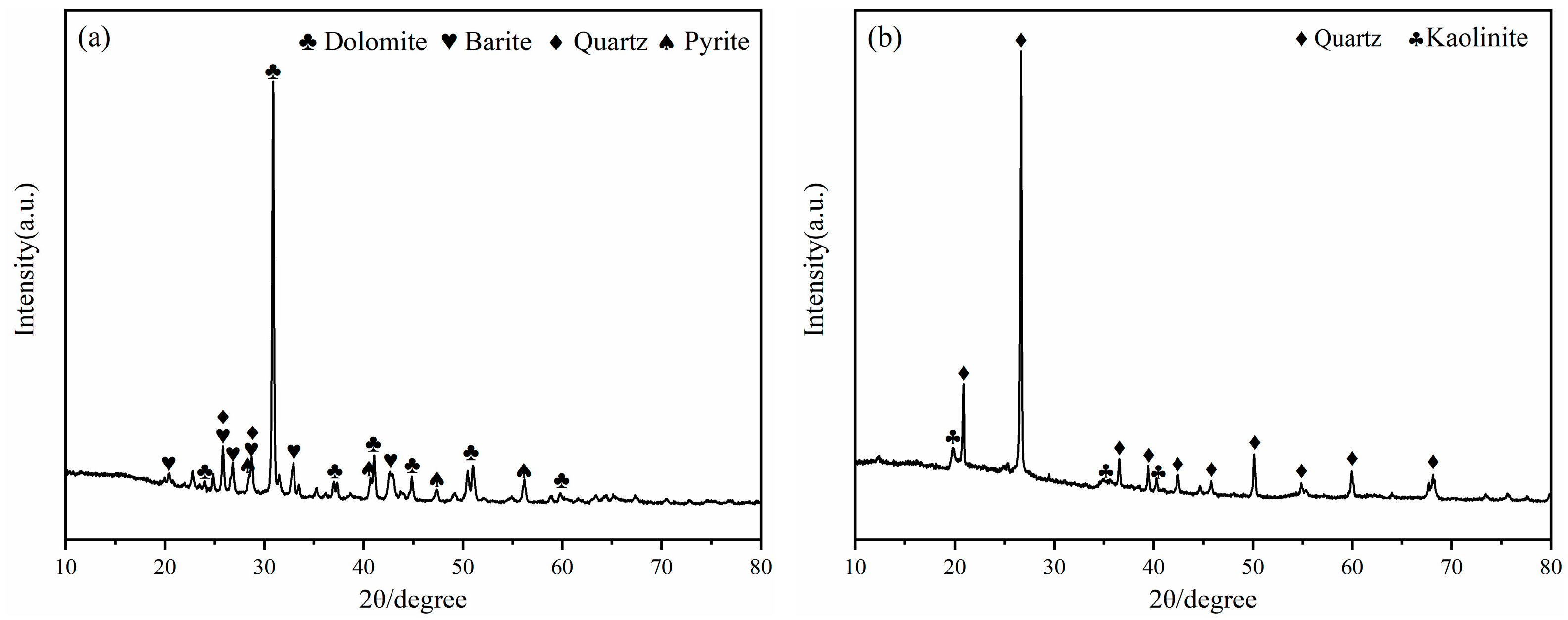
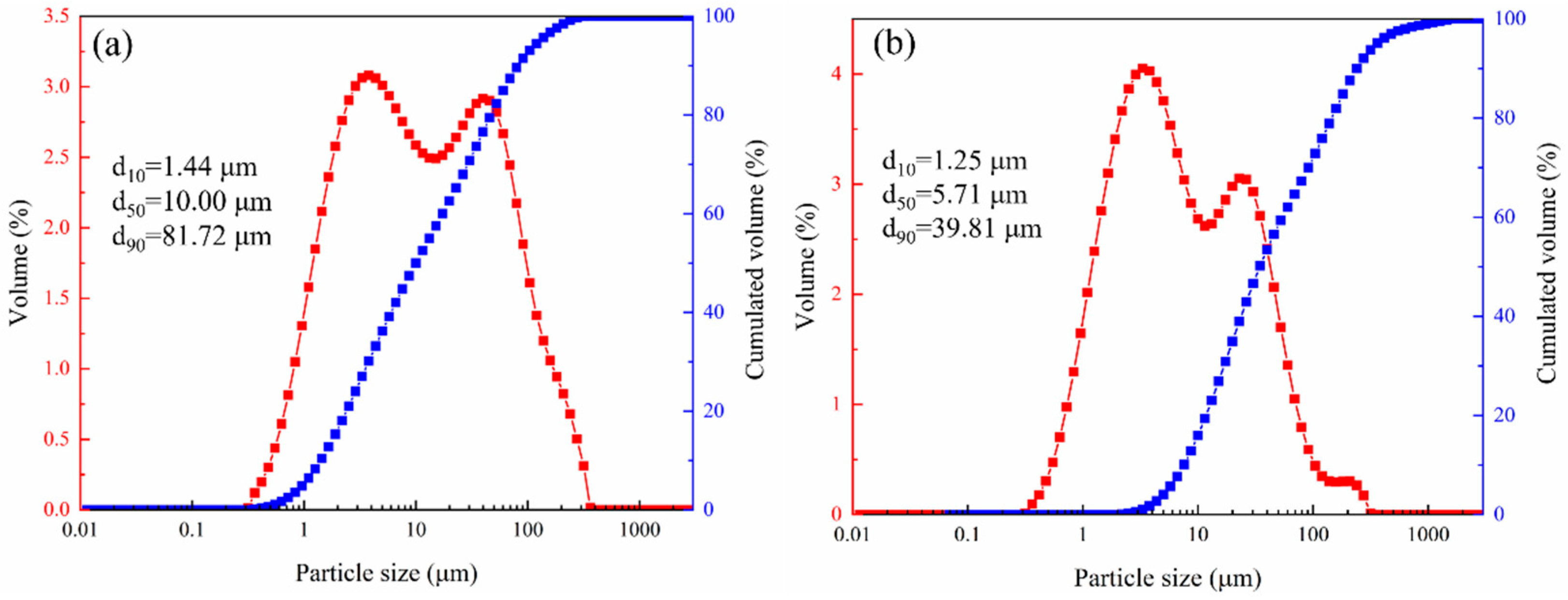
The mineral composition of LZTs and CG was analyzed by XRD, and the results are presented in Figure 1. The minerals in LZTs were primarily dolomite (CaMg(CO3)2, PDF #36-0426), barite (BaSO4, PDF #80-0512), quartz (SiO2, PDF #46-1045) and pyrite (FeS2, PDF #71-2219), while the minerals in CG were mainly quartz (SiO2, PDF #46-1045) and Kaolinite (Al2Si2O5(OH)4, PDF #78-2109). Meanwhile, the particle size distribution of LZTs and CG were tested using a laser particle size analyzer, as shown in Figure 2. The median particle size of LZTs and CG was 10.00 μm and 5.71 μm, respectively.
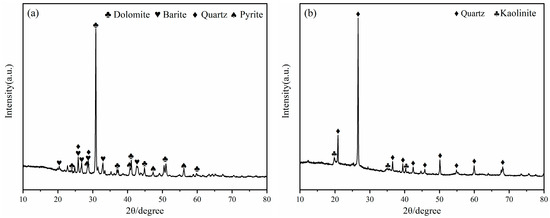
Figure 1.
XRD patterns of LZTs (a) and CG (b).
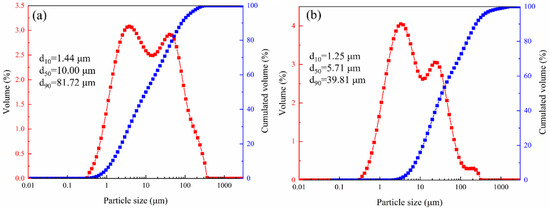
Figure 2.
The particle size distribution of LZTs (a) and CG (b).
2.2. Sample Preparation
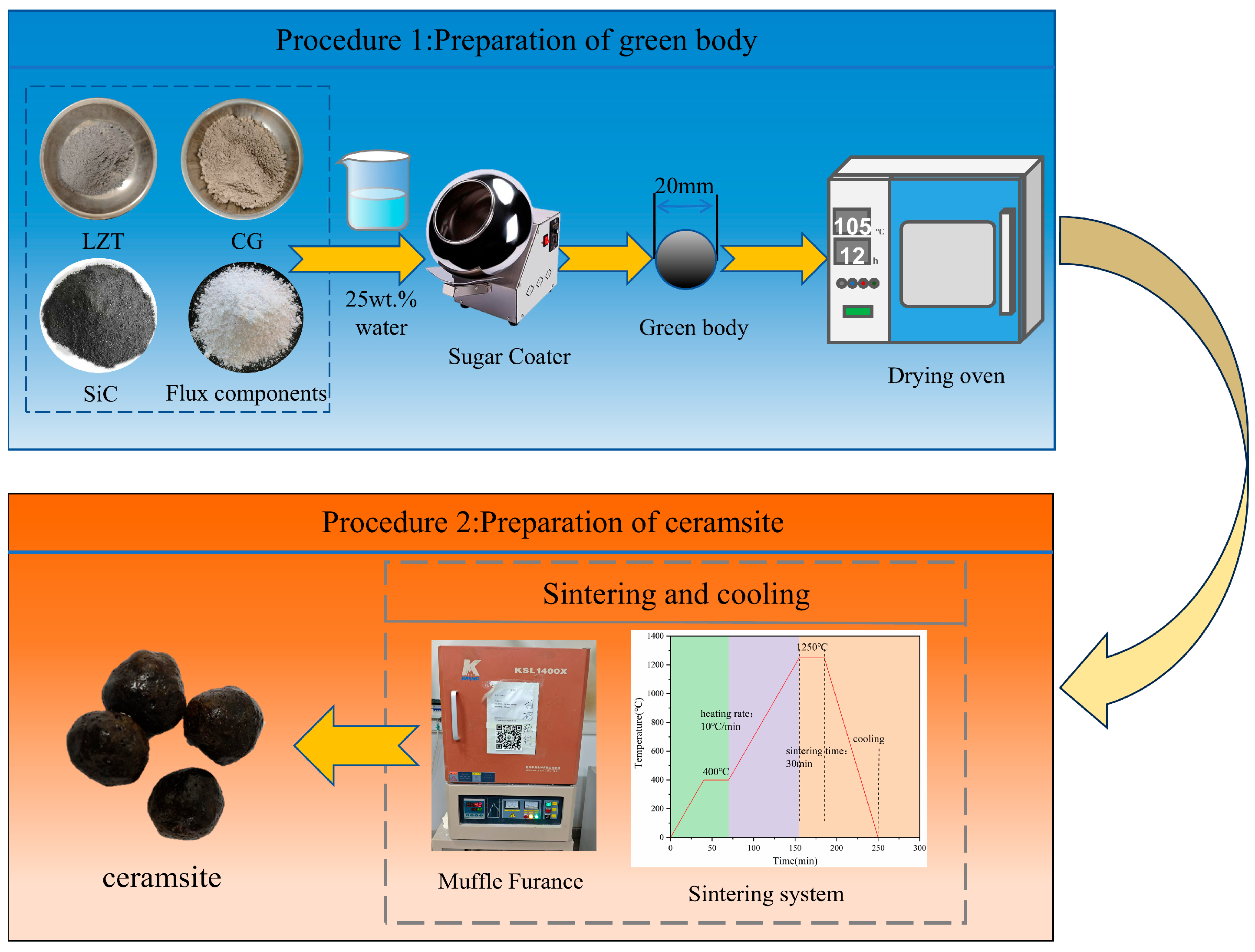
Several experimental parameters were determined based on our prior research [32]. For instance, an LZTs:CG mass ratio of 2:8 was selected as the matrix ratio for ceramsite preparation, with the same preparation process as reported previously employed. In the present study, the preparation experiments were conducted under a fixed sintering regime: preheating at 400 °C for 30 min, sintering at 1250 °C for 30 min, and a heating rate of 10 °C/min. The remaining detailed experimental procedures are presented in Figure 3.
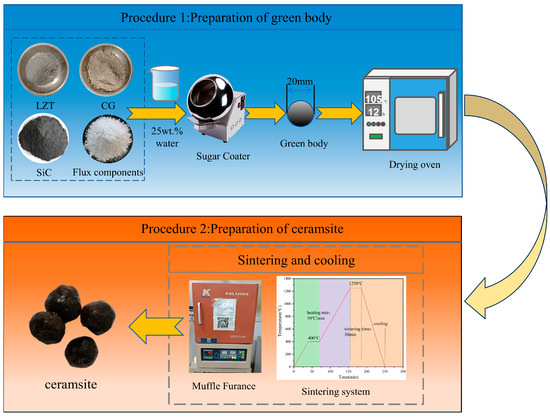
Figure 3.
The preparation procedures of the ceramsite in this study.
The mass ratios of the four flux components (Na2O, MgO, CaO, Fe2O3) to the LZTs-CG ceramsite base matrix are presented in Table 2. Notably, in the ceramsite preparation process, the dosages of these flux components were calculated on an oxide basis (hereafter consistently applied for all subsequent flux dosage calculations). All flux components were incorporated as external admixtures—i.e., added separately to the preblended LZTs-CG base matrix.

Table 2.
Formulations of ceramsite (wt.%).
The specific addition levels of each flux component (by mass of the total base matrix) were as follows: Na2O and MgO were each tested at 1%, 2%, and 5%; CaO and Fe2O3 were tested at 1%, 2%, 5%, and an additional 10%. This differential design for CaO and Fe2O3 was based on two key considerations [25,29]: (i) CaO acts as a flux that can promote liquid phase formation during sintering—exploring a 10% high addition level helps clarify the threshold at which excessive CaO may induce over-sintering; (ii) Fe2O3 not only modulates sintering behavior but also influences ceramsite performance—adding a 10% level enables investigation of its dual effects on composition, microstructure and mechanical properties under high-concentration conditions. This expanded testing range ensures comprehensive coverage of both moderate and high flux dosages, which is critical for optimizing flux addition and avoiding performance degradation in LZTs-CG based ceramsite.
2.3. Characterization
2.3.1. Chemical Composition Analysis
X-ray fluorescence spectroscopy (XRF, PANalytical B.V., Almelo, The Netherlands) was used to determine the chemical compositions of pretreated LZTs and CG. Calibration was performed using silicate-matched certified reference materials (CRMs, GBW 07405), which cover both main elements (Si, Al, Fe, Ca) and characteristic elements (Pb, Zn, S) of the samples. The calibration curve exhibited a fitting degree (R2) ≥ 0.995. Loss on ignition (LOI) was measured to correct the XRF results. Briefly, 2.0000 g of dried sample was placed in a pre-weighed platinum crucible, heated to 550 °C for organic matter removal, then further heated to 950 °C for carbonate and crystal water decomposition. After cooling to room temperature in a desiccator, LOI was calculated from the mass loss.
2.3.2. Apparent Density Test
According to the Chinese national standard GB/T 17431.2-2010 (Lightweight Aggregates and Its Test Methods—Part 2: Test Methods) [33], the apparent density (ρ) of ceramsite was determined by the water flooding method. Its numerical calculation is carried out using Equation (1):
where m was the weight of ceramsite (g), V1 and V2 were the volume of water before and after the ceramsite sample was immersed in water, respectively (mL).
2.3.3. Compressive Strength Test
As in previous studies [34,35], the compressive strength of individual ceramsites was evaluated by averaging the individual compressive strengths of five ceramsites in the test. In this study, individual ceramsite specimens were subjected to compressive loading using a computer-controlled compression testing machine (WHY-300/10, Jinan Shijin Group Co., Ltd., Shandong, China) until rupture. The force values at rupture were recorded, and the individual compressive strength was calculated using Equation (2).
where P was the compressive strength of ceramsite single grain (MPa), FC was the fracture load (N), and d was the diameter of ceramsite (mm).
2.3.4. Water Absorption Test
The water absorption of ceramsite was also tested according to the Chinese national standard GB/T 17431.2-2010, and the value was characterized by the average value of the 1 h water absorption of ceramsite in three measurements in the test. The water absorption of the ceramsite was calculated according to Equation (3).
where W was the water absorption of ceramsite (%), m1 and m2 were the mass of ceramsite in dry state and saturated surface dry state (g), respectively.
2.3.5. Heavy Metals Leaching Test
The leaching test for heavy metals in ceramsite was conducted in accordance with the Chinese national standard GB 5086.2-1997 (Leaching Toxicity of Solid Waste—Horizontal Vibration Extraction Procedure) [36], and the leaching concentrations of target heavy metals were determined using an inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectrometer (ICP-OES, ICPE-9820, Shimadzu Corporation, Kyoto, Japan). Before the test, the leachate was filtered through a 0.45 μm filter membrane, and the detection limit of the instrument was ≤0.01 mg/L. During the test, the ceramsite sample is ground into powder and mixed with deionized water at a ratio of 1:200. After stirring at 3000 rpm for 120 min, the clarified supernatant is filtered and the well solution to be tested is separated.
2.3.6. X-Ray Diffraction (XRD) Analysis
The mineral composition of the ceramsite samples was analyzed using a D8 Advance X-ray diffractometer (XRD, Bruker Optics, Karlsruhe, Germany) with CuKα1,2 radiation (λ = 0.15418 nm). The diffractometer was operated at 40 kV (voltage) and 40 mA (current), with a scanning rate of 4°/min, a 2θ scanning range of 10°−80°, and a step size of 0.02°. The obtained XRD patterns were analyzed using Jade Software Version 6.5.
2.3.7. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) Analysis
The ceramsite was crushed into small fragments. The microscopic morphology of the ceramsite samples was observed using a scanning electron microscope (Gemini SEM 300, Carl Zeiss AG, Jena, Germany). Before the test, the sample was subjected to gold spraying treatment (gold spraying thickness 5-10 nm), with an acceleration voltage of 15 kV.
3. Results
3.1. Apparent Density and Compressive Strength
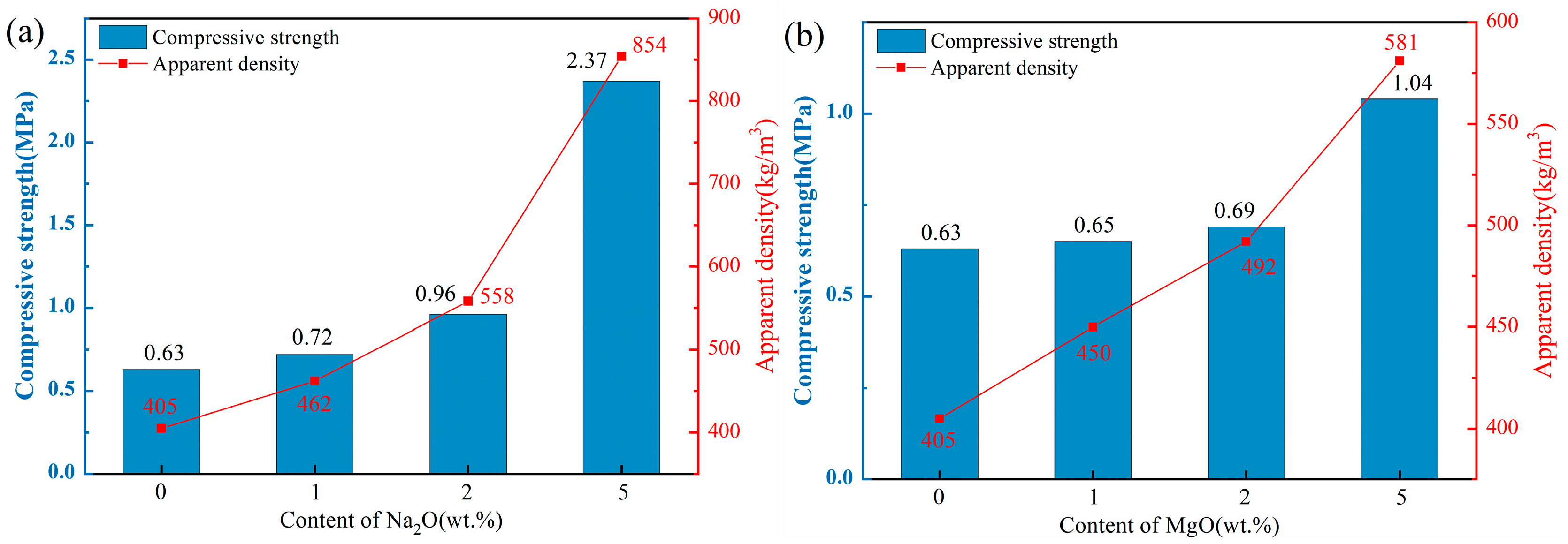
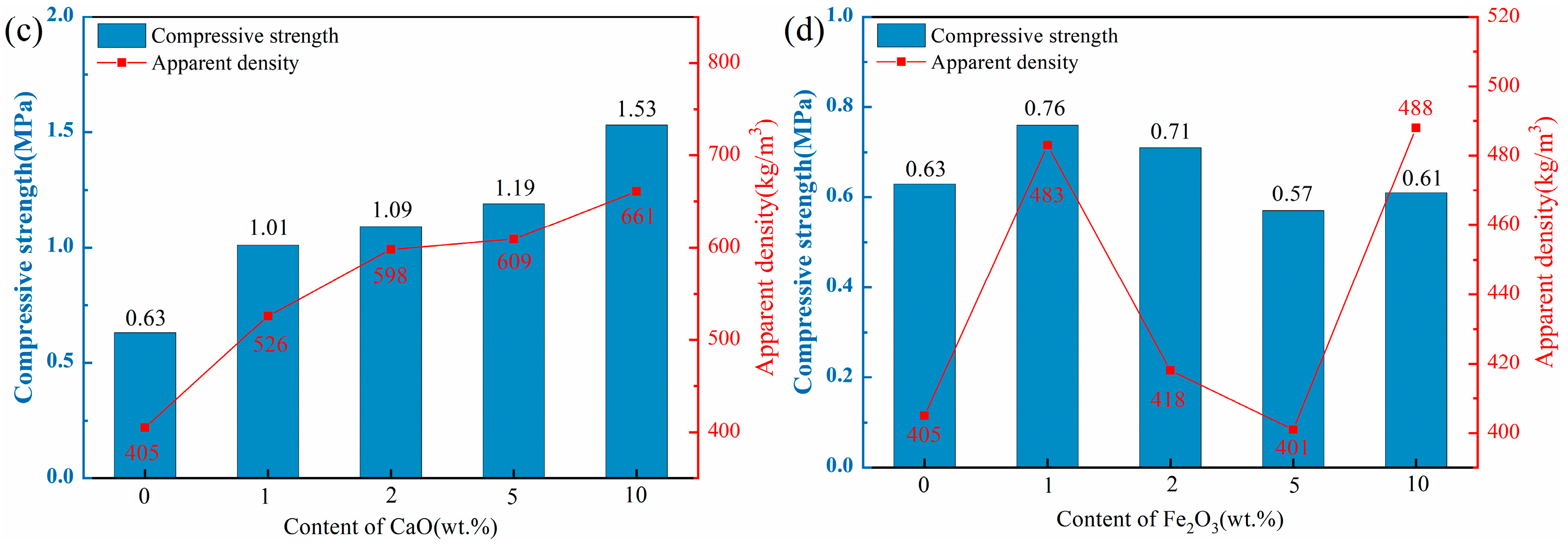
Figure 4 illustrates the apparent density and compressive strength of ceramsite doped with varying contents of flux components. The apparent densities of all ceramsite groups ranged from 401 to 854 kg/m3, below the standard limit of 2000 kg/m3. Consequently, each sample group met the basic ceramsite criteria.
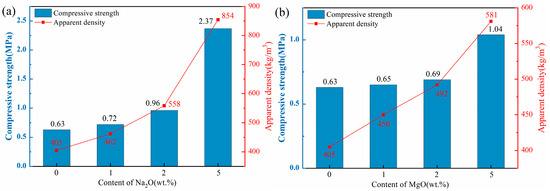
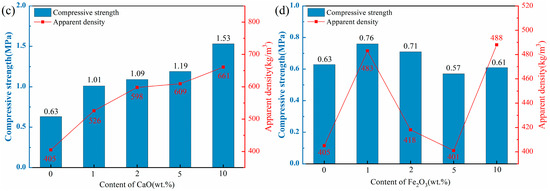
Figure 4.
Effect of different flux components on apparent density and compressive strength of ceramsite, (a): Na2O; (b) MgO; (c) CaO; (d) Fe2O3.
As depicted in Figure 4a,b, the apparent density and compressive strength of the ceramsite substantially rose with higher Na2O and MgO component levels. Notably, the apparent density and compressive strength of the Na1 sample increased by 14% compared to the control. However, with a Na2O content increase to 5 wt.%, these two indexes of the Na5 sample surged by 111% and 276%, respectively, in comparison with the control. The observed enhancement trends could be attributed to the addition of alkali flux Na2O that lowered the sintering temperature and widened the sintering temperature range, thus providing a substantial quantity of high-temperature liquid phase. This significantly reduced the number of pores [37]. Furthermore, the incorporation of the CaO component, as depicted in Figure 4c, demonstrated a consistent trend with the aforementioned Na2O and MgO. The apparent density and compressive strength of the samples escalated in conjunction with the increment in CaO content. Notably, the Ca10 sample exhibited a remarkable enhancement of 63% and 143% in apparent density and compressive strength, respectively, when compared to the control. The incorporation of CaO could facilitate the formation of the crystalline phase by the excess Ca with the Si-Al system, thereby enhancing the structural integrity of the ceramsite [38,39], which was confirmed by the subsequent XRD and SEM analyses.
In contrast to other flux components, the influence of Fe2O3 on ceramsite properties was more complex. As shown in Figure 4d, with increasing Fe2O3 content, the compressive strength of ceramsite exhibited a non-monotonic trend: initial increase, subsequent decrease, and final recovery. Specifically, at 1 wt.% Fe2O3, the apparent density and compressive strength of the samples were higher than those of the control group. When Fe2O3 content increased to 5 wt.%, both indexes decreased. Further increasing Fe2O3 to 10 wt.% led to the recovery of apparent density and compressive strength. This complex variation can be closely associated with the dual role of Fe2O3 in the sintering process: (i) Redox-induced pore evolution: At high sintering temperatures, Fe3+ in Fe2O3 underwent stepwise reduction (Fe2O3→FeO), releasing trace oxygen. At 1 wt.% Fe2O3, the released oxygen generated small, uniformly distributed pores, while the moderate liquid phase (promoted by Fe2O3 as a flux) enhanced structural compactness—collectively improving strength and density. At 5 wt.% Fe2O3, excessive oxygen release leaded to pore coarsening and uneven distribution, and the liquid phase was insufficient to fill these large pores, resulting in decreased strength and density. (ii) Liquid phase regulation: When Fe2O3 content reached 10 wt.%, its strong fluxing effect significantly promoted a substantial amount of liquid phase to fill partial pores and densify the structure—thus reversing the downward trend of apparent density and compressive strength. This mechanism was consistent with the findings of [40,41], which confirmed that high Fe2O3 content could mitigate pore-induced performance degradation by optimizing liquid phase behavior.
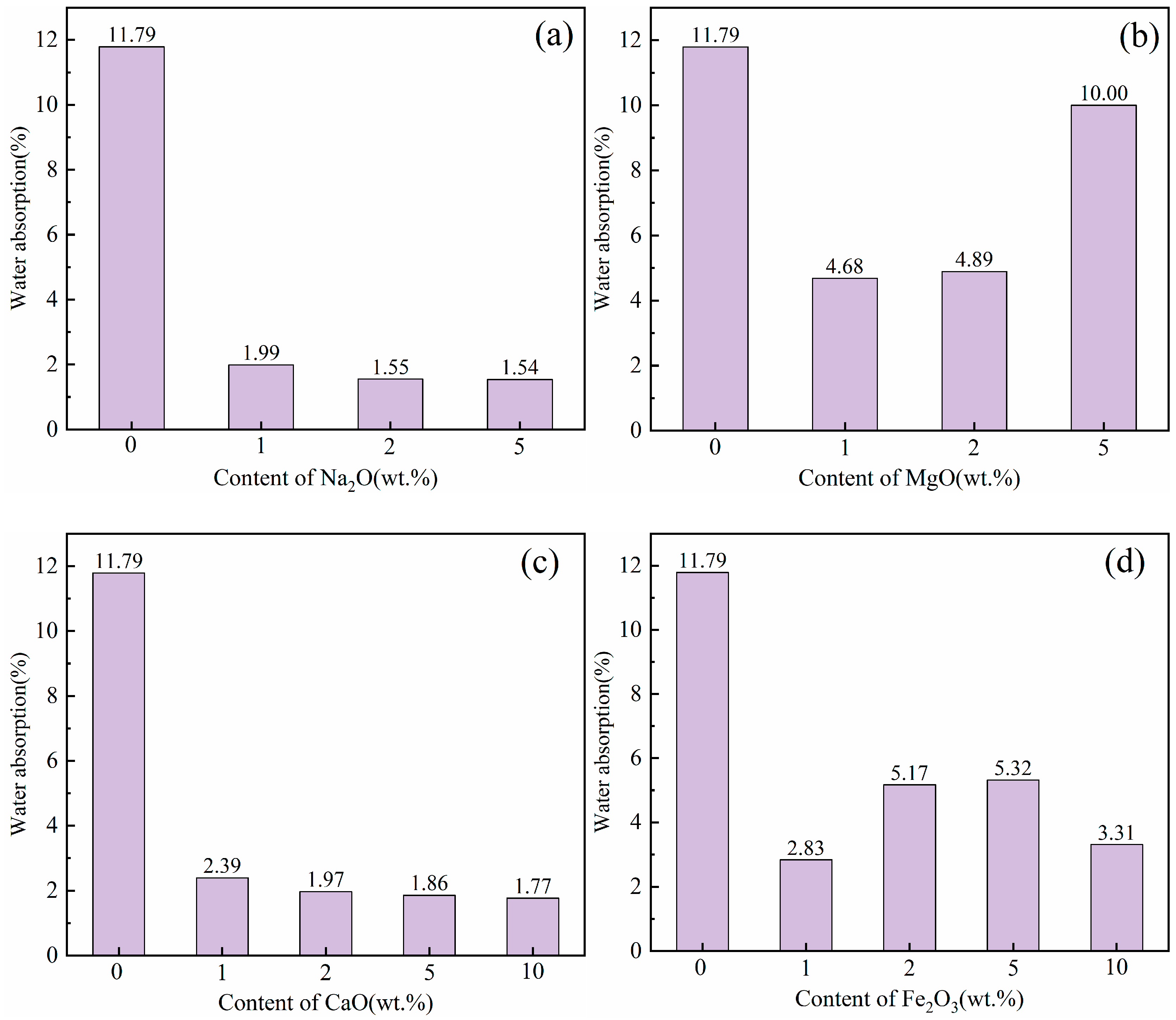
3.2. Water Absorption
Figure 5 illustrates the water absorption of ceramsite mixed with varying flux component contents. The water absorption of the control group was 11.79%, while all experimental groups exhibited a reduction (the maximum decrease was 87%), indicating that the flux components exert a more pronounced influence on the water absorption of ceramsite.
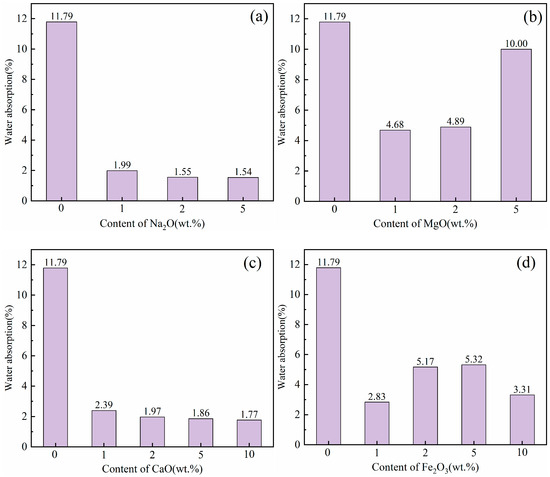
Figure 5.
Effect of different flux components on water absorption of ceramsite, (a): Na2O; (b) MgO; (c) CaO; (d) Fe2O3.
The introduction of the Na2O component significantly reduced the water absorption of the ceramsite. With the addition of 1 wt.% Na2O, water absorption decreased from 11.79% (control) to 1.99%. When the Na2O addition further increased to 5 wt.%, water absorption was further reduced to 1.54%. The observed decline in water absorption was mainly attributed to the addition of Na2O, which leaded to an increase in the amount of liquid phase, thereby enhancing the densification of the ceramsite matrix [42]. The addition of the MgO component similarly reduced the water absorption of ceramsite. However, the highest water absorption of 10.00% was achieved when the MgO content reached 5 wt.%, although it was still lower than that of the control. This occurrence deviated from the typical trend of reduced water absorption as apparent density and compressive strength increased. This anomaly could be attributed to the heterogeneity in raw material mixing, thereby causing an abnormal increase in water absorption. The incorporation of the CaO component consistently reduced the water absorption of the ceramsite, decreasing from 11.79% (control) to 1.77% as the CaO content continuously increased to 10 wt.%. Notably, this reduction in water absorption shows a positive correlation with increasing CaO content. Specifically, the incorporation of CaO facilitates the formation of more dense crystalline phases, thereby enhancing the structural integrity of the ceramsite (see the following analysis of mineral composition and microstructure). The influence of the Fe2O3 component on the water absorption of ceramsite was complex. The water absorption for the sample of 1 wt.% Fe2O3 was 2.83%, increasing to 5.17% and 5.32% as the Fe2O3 content was raised to 2 wt.% and 5 wt.%, respectively, yet both values remained below that of the control. Then, water absorption decreased again to 3.31% when Fe2O3 addition was further increased to 10 wt.%. The incorporation of Fe2O3 might have resulted in a reduction in the number of open pores on the surface and a shift in the ratio of open to closed pores, which consequently led to a decrease in water absorption.
3.3. Heavy Metals Leaching Test
Table 3 presents the leaching concentrations of Pb and Zn from the LZTs-CG based ceramsite samples with different flux component additions. All leaching tests were conducted in accordance with the Chinese national standard GB 5086.2-1997, which specifies the maximum allowable leachate concentrations of 5 mg/L for Pb and 100 mg/L for Zn.

Table 3.
Leaching concentrations of Pb and Zn in ceramsite with different flux component contents.
Compared to the control sample, the ceramsite samples with flux additions exhibited slightly elevated Pb and Zn leaching concentrations. However, all detected values remained at extremely low levels. Specifically, the highest Pb leaching concentration (0.1975 mg/L) was observed in the Mg5 sample (5 wt.% MgO addition), while the highest Zn leaching concentration (0.0485 mg/L) was detected in the Ca10 sample (10 wt.% CaO addition).
Notably, all measured Pb and Zn leaching concentrations were far below the respective limits specified in GB 5086.2-1997 (Pb: 5 mg/L; Zn: 100 mg/L). This result confirms that the flux-modified LZTs-CG based ceramsite complies with environmental safety standards, verifying its feasibility for practical engineering application from the perspective of heavy metal pollution risk.
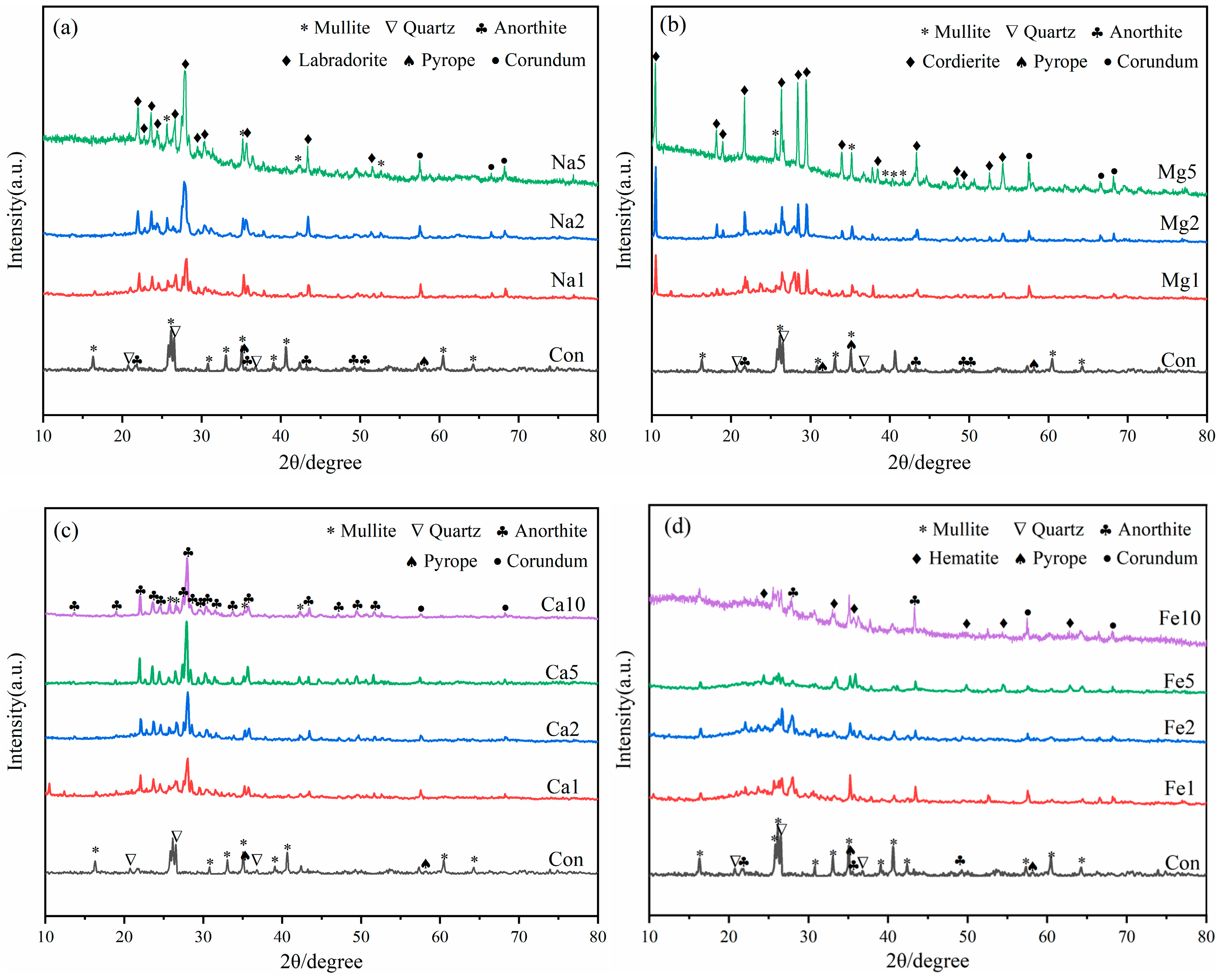
3.4. XRD Analysis
The effect of different flux component additions on the mineral composition of LZTs-CG based ceramsite was investigated using XRD, with the results presented in Figure 6. Notably, no Pb- or Zn-bearing minerals were detected in any sample. which indicates that Pb and Zn ions existed as solid solution ions in other aluminosilicate phases or in molten amorphous phases during ceramsite sintering, and this is also the primary reason for the extremely low leaching concentrations of these heavy metals (see Section 3.3).
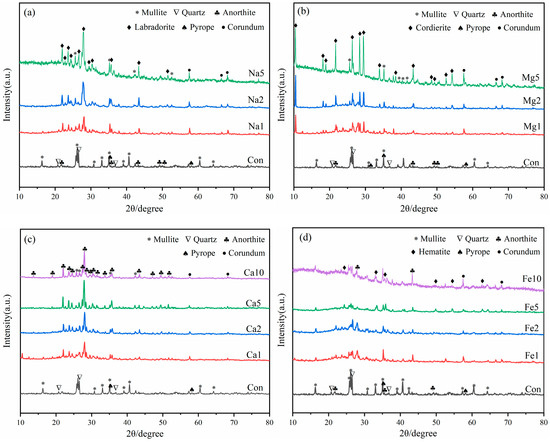
Figure 6.
XRD patterns of ceramsite samples with different flux components, (a): Na2O; (b) MgO; (c) CaO; (d) Fe2O3.
First, as observed in Figure 6, the sintered control sample contained newly formed minerals including mullite (Al6Si2O13, PDF #79-1275), anorthite (CaAl2Si2O8, PDF #89-1459), and pyrope (Mg3Al2Si3O12, PDF #73-2366), along with residual quartz. Notably, the dolomite, barite, pyrite, and kaolinite minerals presented in the original LZTs and CG raw materials disappeared, indicating that these minerals have undergone transformation reactions during sintering. Furthermore, it is noteworthy that diffraction peaks of corundum (Al2O3, PDF #74-1081) were detected in all flux-added ceramsite samples. This is presumably attributed to the fact that flux addition reduced the decomposition temperature of mullite to varying degrees. Specifically, the Si sources released from mullite decomposition were preferentially consumed in other reactions, leading to the enrichment of Al sources and subsequent formation of corundum [43,44].
As shown in Figure 6a, With the incorporation of Na2O, a new mineral labradorite ((Ca, Na)(Si, Al)4O8, PDF #78-0433) formed and its diffraction peak intensity increased with increasing Na2O dosage. This is presumably because the addition of Na2O enabled Na+ ions to incorporate into the aluminosilicate framework alongside the pre-existing Ca2+ ions, thereby forming labradorite with a mixed Ca-Na composition. Additionally, the diffraction intensities of mullite and quartz obviously decreased with higher Na2O addition, accompanied by the growing prominence of diffuse peaks in the 20–35° range. This phenomenon is attributed to the prominent fluxing effect of alkali flux Na2O, which specifically lowered the eutectic temperature of the LZTs-CG system, thereby facilitating the dissolution and melting of crystalline mullite and quartz [42,45].
For samples with MgO addition (Figure 6b), the diffraction peaks of mullite and quartz weakened as MgO content increased. Simultaneously, a new mineral cordierite (Mg2Al4Si5O18, PDF #84-1219) emerged, and its diffraction peak intensity increased with increasing MgO dosage. This cordierite formation was attributed to the increased Mg2+ concentration, which promoted the reaction between mullite, quartz and Mg2+ ions during high-temperature sintering, thus facilitating the synthesis of Mg-rich cordierite [46,47]. Additionally, diffuse peaks also gradually became prominent in the 20–35° range with increasing MgO dosage, indicating that the incorporation of MgO also facilitated the transformation of crystalline phases into the molten phase to a certain extent.
In the CaO-added samples (Figure 6c), the main minerals remained consistent with the control group (mullite, quartz, anorthite, and pyrope), but their peak intensities varied with CaO dosage, with anorthite diffraction peaks strengthening and those of mullite and quartz weakening. Pyrope diffraction peaks remained essentially unchanged. This suggests that most of the added CaO presumably participated in the formation of anorthite by promoting the reaction between mullite, quartz and Ca2+ [48]. This phase evolution was consistent with the reduced water absorption of CaO-modified samples (Section 3.2), as the enhanced anorthite formation (a dense crystalline phase) reduces the number of open pores on the ceramsite surface [39].
For samples with Fe2O3 addition (Figure 6d), diffraction peaks of hematite (Fe2O3, PDF #85-0987) were observed, with their intensities increasing as Fe2O3 dosage increased. This indicates that a fraction of the added Fe2O3 remained unreacted during high-temperature sintering. The other fraction of Fe2O3 presumably exerted fluxing effects that promoted the melting of crystalline phases, which could be confirmed by the emergence of diffuse peaks in the 20–35° range.
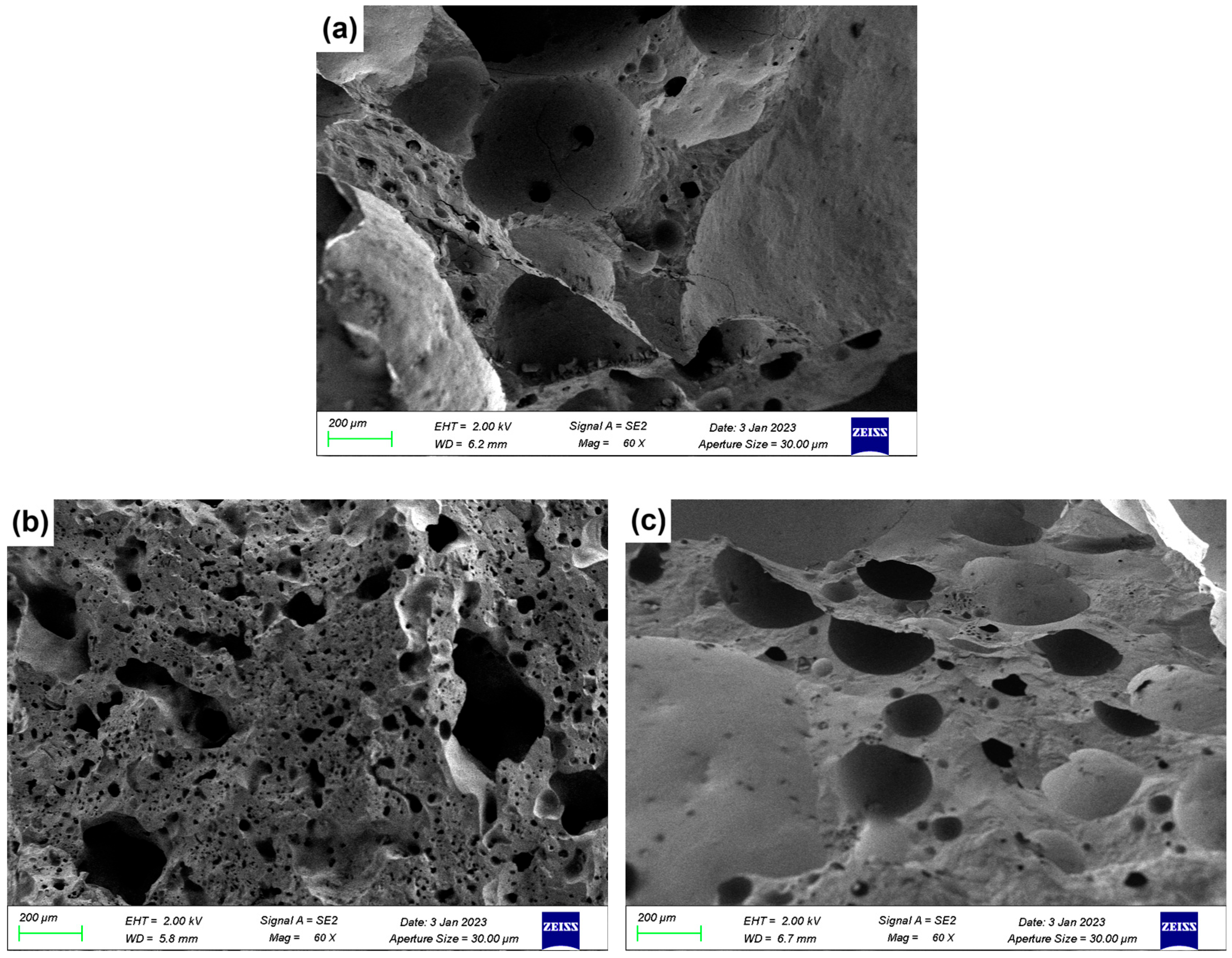
3.5. SEM Analysis
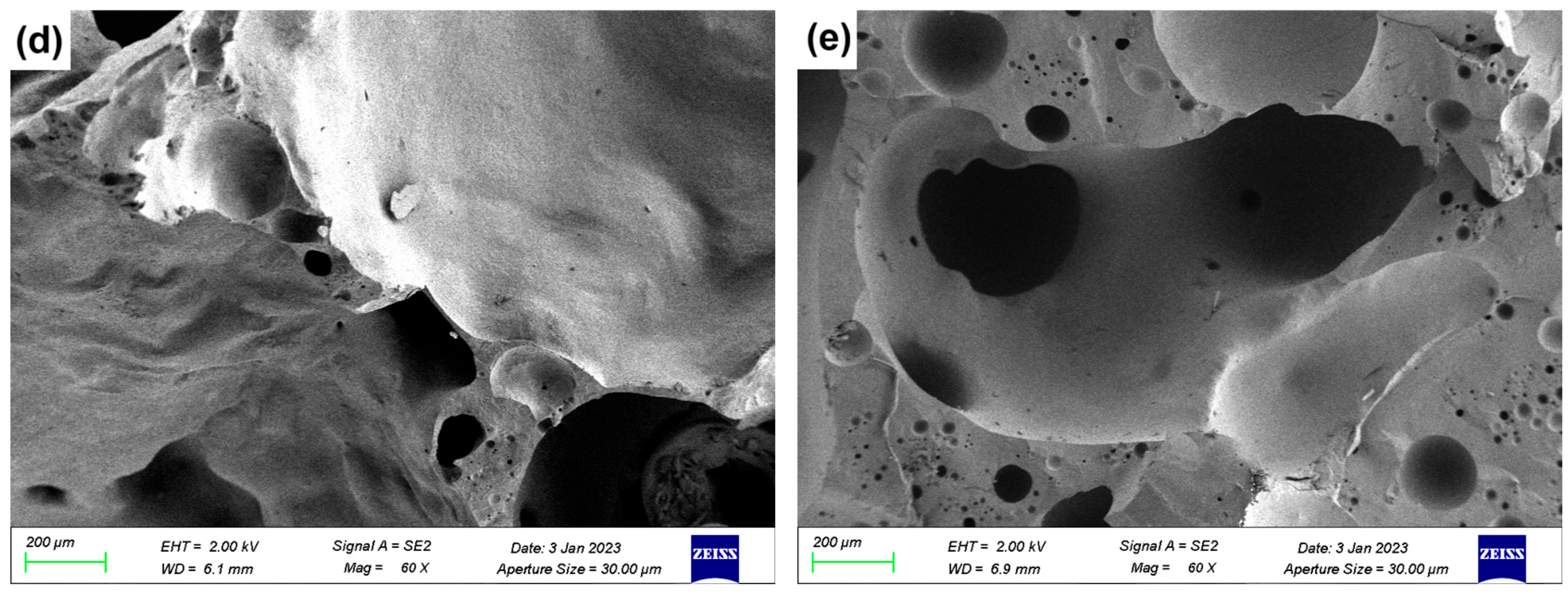
Figure 7 presents the SEM micrographs of LZTs-CG based ceramsite samples with different flux component additions, revealing the evolution of pore structure and matrix densification.
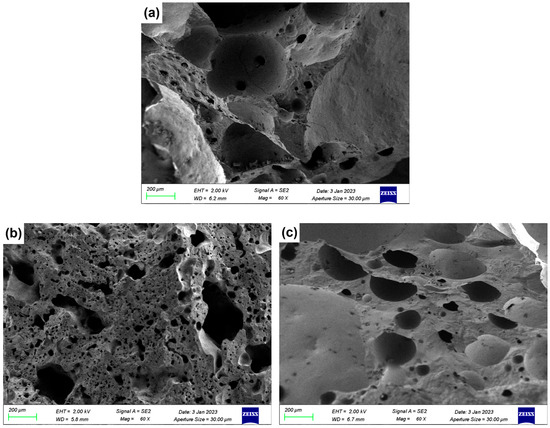

Figure 7.
SEM images of ceramsite with different flux components added: (a) Con; (b) Na5; (c) Mg5; (d) Ca5; (e) Fe5.
As shown in Figure 7a (control sample, no flux addition), the cross-section exhibited numerous irregularly shaped pores with non-uniform size distribution and incomplete pore wall densification. This porous was attributed to the limited liquid phase formation in the unmodified LZTs-CG system, which failed to effectively coat and bond solid particles, which was consistent with the control sample’s relatively low compressive strength (Section 3.1).
Figure 7b shows the micrograph of the 5 wt.% Na2O-added sample (Na5 sample). Compared to the control, the Na5 sample exhibited distinct melting behavior: the solid particles were effectively bonded together, the number of macropores was significantly reduced and replaced by the formation of micropores, resulting in a remarkable improvement in the overall densification of the ceramsite matrix. This phenomenon could be explained by the fluxing effect of Na2O: as a strong alkali flux, Na2O lowered the sintering temperature of the LZTs-CG system and facilitated the generation of a substantial amount of liquid phase. As observed in the 5 wt.% MgO-added sample (Mg5) and presented in Figure 7c, the pore size decreased compared to the control sample, and adhesion of molten substances was observed on its fracture surface. This phenomenon is associated with MgO’s dual role: on one hand, it promoted cordierite formation (confirmed by XRD in Figure 6b), enhancing matrix bonding. On the other hand, its incorporation induced liquid phase formation, further strengthening bonding and thus improving ceramsite matrix densification.
For the CaO-added samples, Figure 7d (5 wt.% CaO-added sample, Ca5) exhibits significant integrity and smoothness of the fracture surface with a more stable ceramsite matrix compared to the control sample. This observation was consistent with the XRD result that most CaO converts to anorthite (CaAl2Si2O8): the formation of this dense crystalline phase strengthened the matrix directly contributing to the reduced water absorption and increased compressive strength of CaO-modified samples.
In the Fe2O3-added sample (Figure 7e, 5 wt.% Fe2O3-added sample, Fe5), there are obvious interconnected pores. This was primarily due to the local reducing atmosphere generated by trace organic matter in LZTs and CG, under which Fe2O3 underwent redox reactions, increasing gas yield [40,41]. The excess gas aggregated and percolated to form interconnected pores when the liquid phase could not fully encapsulate the gas.
4. Conclusions
This study systematically investigated the effects of four flux components (Na2O, MgO, CaO, Fe2O3) on the performance, heavy metal solidification, mineral composition, and microstructure of ceramsite prepared from LZTs and CG. The key findings are as follows:
- (1)
- Performance: Na2O, MgO, and CaO enhanced apparent density/compressive strength and reduced water absorption with higher dosage. 5 wt.% Na2O (Na5) achieved the most significant improvement—apparent density increased by approximately 111% to 854 kg/m3 and compressive strength by approximately 276% to 2.37 MPa compared to the control (405 kg/m3, 0.63 MPa). This superiority stems from the melting-liquid phase effect induced by the alkali flux Na2O, which optimized the pore structure and strengthened the matrix. Fe2O3 exhibited a non-monotonic effect (increase → decrease → recovery): 5 wt.% Fe2O3 caused pore coarsening and interconnection (minimum density 401 kg/m3, strength 0.57 MPa), while 10 wt.% reversed degradation via liquid phase densification, providing guidance for sintering dosage control. All fluxes reduced water absorption, with 5 wt.% Na2O achieving a maximum reduction of 87% (compared to the control sample, 11.79% water absorption).
- (2)
- Environmental safety: Fluxes slightly increased Pb/Zn leaching (undetected in control), but all values (max Pb 0.1975 mg/L, max Zn 0.0485 mg/L) were far below the Chinese national standard GB 5086.2-1997 limits (Pb 5 mg/L, Zn 100 mg/L). The low leaching was primarily attributed to Pb and Zn ions being solidified into the aluminosilicate matrix (either lattice incorporation or amorphous encapsulation), confirming eco-safety.
- (3)
- Mineral evolution: Control ceramsite was dominated by mullite, quartz, anorthite, and pyrope. Corundum emerged in all flux-added samples, attributed to fluxes promoting mullite decomposition—released silicon sources were preferentially consumed in other reactions, leading to aluminum source enrichment and subsequent corundum formation. Specifically, Na2O facilitated labradorite formation, MgO promoted cordierite, and Fe2O3 induced hematite. All fluxes weakened the diffraction peaks of quartz and mullite.
- (4)
- Microstructure: Flux type significantly modified LZTs-CG ceramsite microstructure. The control sample had irregular, uneven pores and incomplete pore wall densification (limited liquid phase). 5 wt.% alkali flux Na2O enhanced densification via abundant liquid phase (melting behavior, macropore reduction). 5 wt.% alkaline earth flux MgO reduced pore size and strengthened bonding (cordierite & liquid phase). 5 wt.% alkaline earth flux CaO yielded a smooth, stable matrix (anorthite formation). 5 wt.% Fe2O3 induced interconnected pores (redox gas generation).
Collectively, this study demonstrates that rational flux regulation enabled the preparation of high-performance, environmentally safe LZTs-CG ceramsite, providing technical support for the high-value recycling of these two industrial solid wastes.
Author Contributions
Writing—original draft preparation, Q.Z.; writing—review and editing, L.L.; project administration, X.L.; funding acquisition, Z.L.; Conceptualization, M.Z. and X.W.; formal analysis, J.G.; validation, L.L., X.L. and Z.L.; supervision, J.Y. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 52374416 and 52402037); the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (Grant No. 2025M770083); the Science and Technical Development Program of Henan Province (Grant No. 252102231004); the Key Research and Development Program of Henan Province (Grant No. 251111230100).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Conflicts of Interest
Authors Maoliang Zhang and Xindi Wan were employed by the company Henan Building Materials Research and Design Institute Co., Ltd. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
- Owen, J.R.; Kemp, D.; Lechner, A.M.; Ern, M.A.L.; Lèbre, E.; Mudd, G.M.; Macklin, M.G.; Saputra, M.R.U.; Witra, T.; Bebbington, A. Increasing mine waste will induce land cover change that results in ecological degradation and human displacement. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 351, 119691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Yang, L. Mineral resource extraction and resource sustainability: Policy initiatives for agriculture, economy, energy, and the environment. Resour. Policy 2024, 89, 104657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Z.; Ge, M.; Ou, J.; Liu, X.; Mu, Y.; Zhang, W.; Ye, J.; Zhang, M.; Gao, M.; Yang, Y.; et al. Precalcination-modified lead-zinc tailings for supersulfated cement production: Insights into phase assemblages, microstructure, and mechanical properties. Constr. Build. Mater. 2025, 473, 141076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Zhang, G.; Wang, M.; Zhen, S. Preparation of high-purity vaterite CaCO3 from lead-zinc tailings. Sustain. Chem. Pharm. 2022, 29, 100835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, M.; Zhang, X.; Wang, S.; Cao, W.; Jiang, Y. Life cycle assessment on lead-zinc ore mining and beneficiation in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 237, 117833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wang, J.; Deng, R.; Xing, D.; Chen, Q. Research status and significance of comprehensive utilization of lead-zinc tailings in China. Geol. Explor. 2024, 60, 724–734. [Google Scholar]
- Hudson-Edwards, K.A.; Kemp, D.; Torres-Cruz, L.A.; Macklin, M.G.; Brewer, P.A.; Owen, J.R.; Franks, D.M.; Marquis, E.; Thomas, C.J. Tailings storage facilities, failures and disaster risk. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2024, 5, 612–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Yin, Z.; Lin, H. Research status and prospects for the utilization of lead-zinc tailings as building materials. Buildings 2023, 13, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Zhao, B.; Jin, M.; Hu, L.; Zhong, H.; He, Z. A comprehensive survey on the horizontal and vertical distribution of heavy metals and microorganisms in soils of a Pb/Zn smelter. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 400, 123255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Jiang, W.; Zhang, C.; Li, J.; Wu, S.; Wang, X.; Xu, Y.; Wang, W.; Feng, M. Preparation of solid-waste-based pervious concrete for pavement: A two-stage utilization approach of coal gangue. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 319, 125962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wang, J. Comprehensive utilization and environmental risks of coal gangue: A review. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 239, 117946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, D.; Wang, C.; Bai, D.; Huang, D. Representative coal gangue in China: Physical and chemical properties, heavy metal coupling mechanism and risk assessment. Sustain. Chem. Pharm. 2024, 37, 101402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Liu, Z.; Han, L.; Zhang, Y.; Li, L.; Zhu, S.; Peng, Z.; Li, J.; Wang, D. Synthesis of coal-analcime composite from coal gangue and its adsorption performance on heavy metal ions. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 423, 127027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ducman, V.; Mirtic, B. The applicability of different waste materials for the production of lightweight aggregates. Waste Manag. 2009, 29, 2361–2368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, J.; Pan, X.; Qi, Y.; Yu, H.; Tu, G. Preparation and characterization of ultra-lightweight ceramsite using non-expanded clay and waste sawdust. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 346, 128410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, Y.; Hu, W.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Peng, J.; An, S. Process and property optimization of ceramsite preparation by Bayan Obo tailings and blast furnace slag. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 2023, 30, 1381–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mi, H.; Yi, L.; Wu, Q.; Xia, J.; Zhang, B. Preparation of high-strength ceramsite from red mud, fly ash, and bentonite. Ceram. Int. 2021, 47, 18218–18229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, T.; Fan, X.; Zhou, C.; Wang, H.; Wu, K.; Zhou, H. Preparation of ultra-lightweight ceramsite from waste materials: Using phosphate tailings as pore-forming agent. Ceram. Int. 2024, 50, 15218–15229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Zhang, Y.; Yan, J.; Chen, Z.; Wei, Q.; Wang, H.; Lu, Y. Microstructure and properties of high-strength lightweight ceramsites customised with ultra-fine copper tailings. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 429, 136433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, J.; Pan, X.; Qi, Y.; Yu, H.; Tu, G. Preparation of ultra-lightweight ceramsite from red mud and immobilization of hazardous elements. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 108157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, S.; Wu, D.; Wu, J.; Li, S.; Liu, G.; Pei, D. Characterization of the physical chemistry properties of iron-tailing-based ceramsite. Molecules 2023, 28, 2258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Tian, H.; Lei, W.; Dai, N.; Wang, H. Development of high-strength ceramsite via sintering of iron ore tailings: Process optimization and properties. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 457, 139440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.; Zhang, S.; Yang, H.; Ni, W.; Li, J.; Zhang, G.; Teng, G. Influence on fine lead-zinc tailings solidified/stabilised by clinker-free slag-based binder. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 108692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Tang, Y.; Li, Z.; Wu, T.; Lu, A. Red mud and fly ash incorporation for lightweight foamed ceramics using lead-zinc mine tailings as foaming agent. Mater. Lett. 2016, 183, 362–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Qin, Y.; Okeke, I.; He, C.; Li, X.; Wei, Y.; Yuan, J. Revealing the intrinsic sintering mechanism of high-strength ceramsite from CFB fly ash: Focus on the role of CaO. Ceram. Int. 2024, 50, 24281–24292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Duan, X.; Li, Y. Effect of temperature and pyrolysis atmosphere on pore structure of sintered coal gangue ceramsites. Materials 2025, 18, 3386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, L.; Ji, J.; Yang, J.; Qian, X.; Li, X.; Wang, H.; Zhou, S.; Wu, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Yuan, X. Sludge-based ceramsite for environmental remediation and architecture ingredients. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 448, 141556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molineux, C.J.; Newport, D.J.; Ayati, B.; Wang, C.; Connop, S.P.; Green, J.E. Bauxite residue (red mud) as a pulverised fuel ash substitute in the manufacture of lightweight aggregate. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 112, 401–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, J.L.; Xu, G.R.; Li, G.B. Ceramsite obtained from water and wastewater sludge and its characteristics affected by Fe2O3, CaO, and MgO. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 165, 995–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Liu, R.; Xu, Y.; Ye, F.; Xu, R.; Han, Y. Effect of SiO2, Al2O3 and CaO on characteristics of lightweight aggregates produced from MSWI bottom ash sludge (MSWI-BAS). Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 205, 368–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Jian, S.; Zhu, J.; Yu, H.; Wu, R.; Gao, W.; Tan, H. Effect of flux components of lightweight aggregate on physical properties and heavy metal solidification performance. Waste Manag. 2020, 118, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Z.; Guo, J.; Liu, X.; Mu, Y.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, M.; Tian, C.; Ou, J.; Mi, J. Preparation of ceramsite from lead-zinc tailings and coal gangue: Physical properties and solidification of heavy metals. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 368, 130426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 17431.2-2010; Lightweight Aggregates and Its Test Methods—Part 2: Test Methods. Standardization Administration of China: Beijing, China, 2010.
- Yashima, S.; Kanda, Y.; Sano, S. Relationships between particle-size and fracture energy or impact velocity required to fracture as estimated from single-particle crushing. Powder Technol. 1987, 51, 277–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wu, D.; Zhang, J.; Chang, L.; Wu, D.; Fang, Z.; Shi, Y. Measurement and statistics of single pellet mechanical strength of differently shaped catalysts. Powder Technol. 2000, 113, 176–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB 5086.2-1997; Leaching Toxicity of Solid Waste—Horizontal Vibration Extraction Procedure. Standardization Administration of China: Beijing, China, 1997.
- Goltsman, B.M.; Yatsenko, E.A. Modern fluxing materials and analysis of their impact on silicate structures: A review. Open Ceram. 2024, 17, 100540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, J.; Pan, X.; Wang, Y.; Lv, Z.; Yu, H.; Tu, G. Effects of alkali and alkaline-earth oxides on preparation of red mud based ultra-lightweight ceramsite. Ceram. Int. 2023, 49, 18379–18387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, D.; Li, Y.; Hua, S.; Li, S.; Jiang, F.; Yao, J. In situ XRD study on function mechanism of pyroxene and anorthite in Si-Ca ceramics from ferronickel slag. Mater. Lett. 2021, 305, 130839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, D.; Ren, Q.; Ru, H.; Wang, W.; Jiang, Y.; Ren, S.; Ye, C.; Zhang, C.; Wang, S. Pressureless sintering behaviour and mechanical properties of Fe2O3-containing SiC ceramics. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 790, 134–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Luo, L.; Sun, H.; Peng, T.; Lei, J.; Wu, M.; Wang, C.; Huang, S. Effect and mechanism of Fe2O3 decomposition in the preparation of foaming ceramics from industrial solid waste. Int. J. Appl. Ceram. Technol. 2024, 21, 934–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Xiao, T.; Hu, X.; Pan, Z.; Fan, X.; Zhou, H. Preparation of lightweight ceramsite from weathered granite washing sludge: Reinforcing roles of MgO and Na2O and thermal analysis. Chem. Eng. J. 2025, 521, 166694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Du, M.; Zhang, Z.; Guan, R.; Chen, Y.; Liu, T. Selection of fluxing agent for coal ash and investigation of fusion mechanism: A first-principles study. Energy Fuels 2009, 23, 704–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, K.; Guo, Y.; Liu, D.; Ma, Z.; Cheng, F. Thermal decomposition and transformation mechanism of mullite with the action of sodium carbonate. J. Solid State Chem. 2018, 265, 326–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Wen, G.; Sun, Q.; Tang, P.; Liu, Q. The Influence of Na2O on the solidification and crystallization behavior of CaO-SiO2-Al2O3-based mold flux. Metall. Mater. Trans. B-Proc. Metall. Mater. Proc. Sci. 2015, 46, 1850–1859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Lu, C.; Xu, X.; Wang, D.; Sang, Y.; Zhang, C. Influence of silica phase transformation on synthesis of cordierite ceramic. J. Aust. Ceram. Soc. 2017, 53, 499–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ariyajinno, N.; Thiansem, S. Characterization and properties of cordierite—Mullite refractories from raw materials and Narathiwat clay (in Thailand). Mater. Today Proc. 2018, 5, 13948–13953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harabi, A.; Zaiou, S.; Guechi, A.; Foughali, L.; Harabi, E.; Karboua, N.E.; Zouai, S.; Mezahi, F.Z.; Guerfa, F. Mechanical properties of anorthite based ceramics prepared from kaolin DD2 and calcite. Cerâmica 2017, 63, 311–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).