Skin-Conformal Hydrogel-Based Electroencephalography Electrodes with Surfactant-Reorganized PEDOT:PSS
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
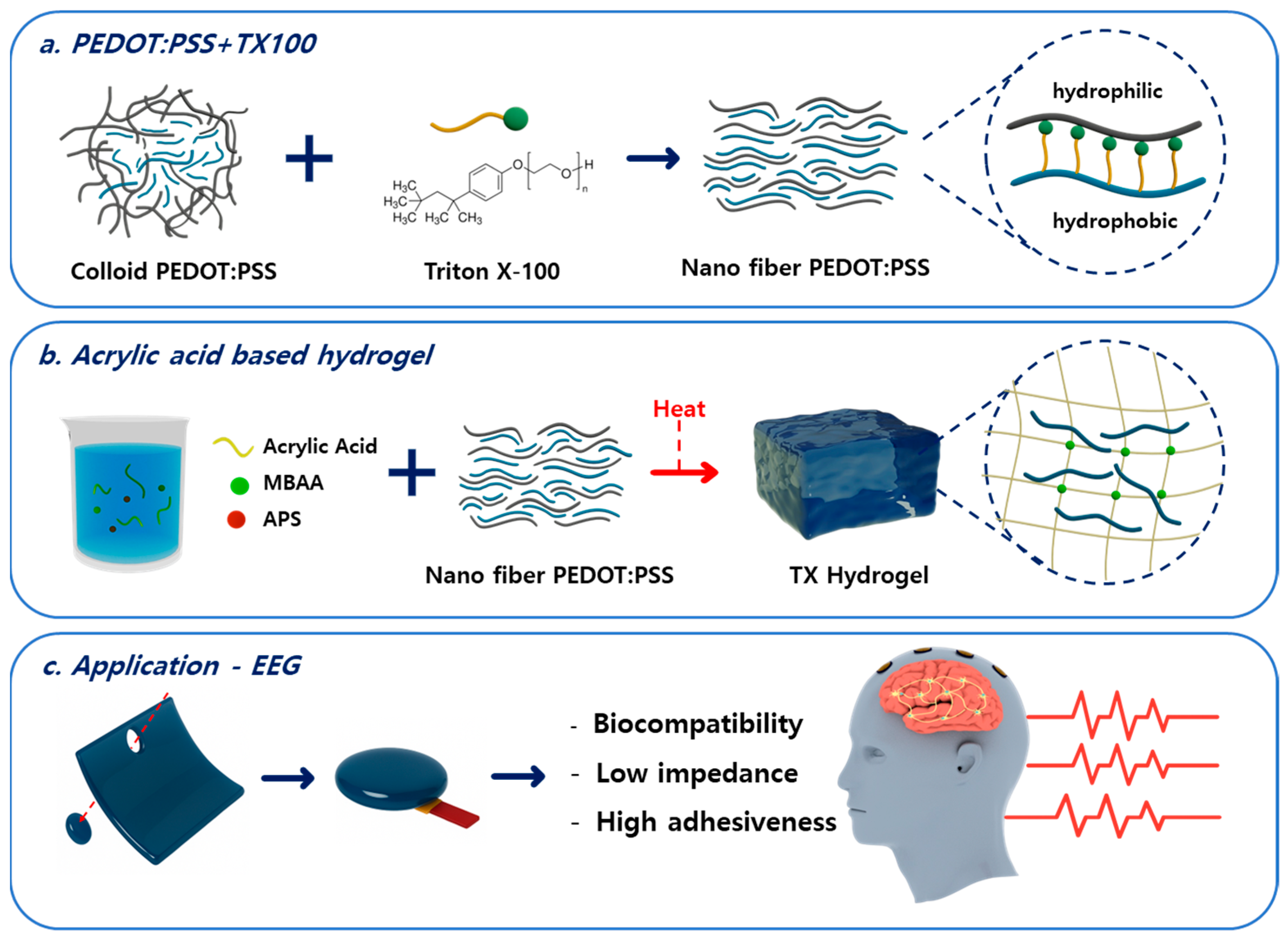
2.2. Preparation of Conductive Filler and Fabrication of Hydrogel EEG Electrodes
2.3. Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
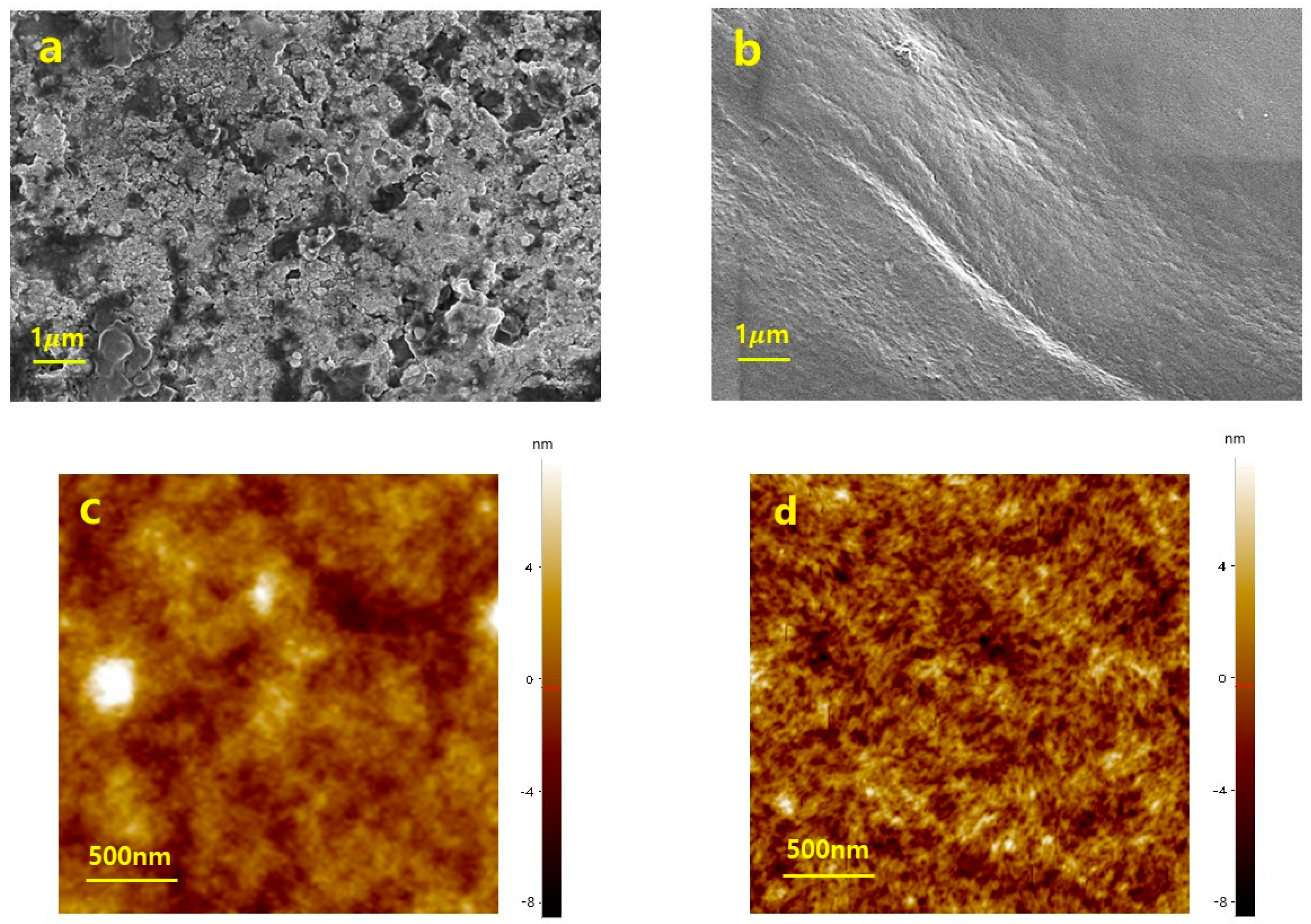
3.1. Morphological Analysis of PEDOT:PSS with Triton X-100
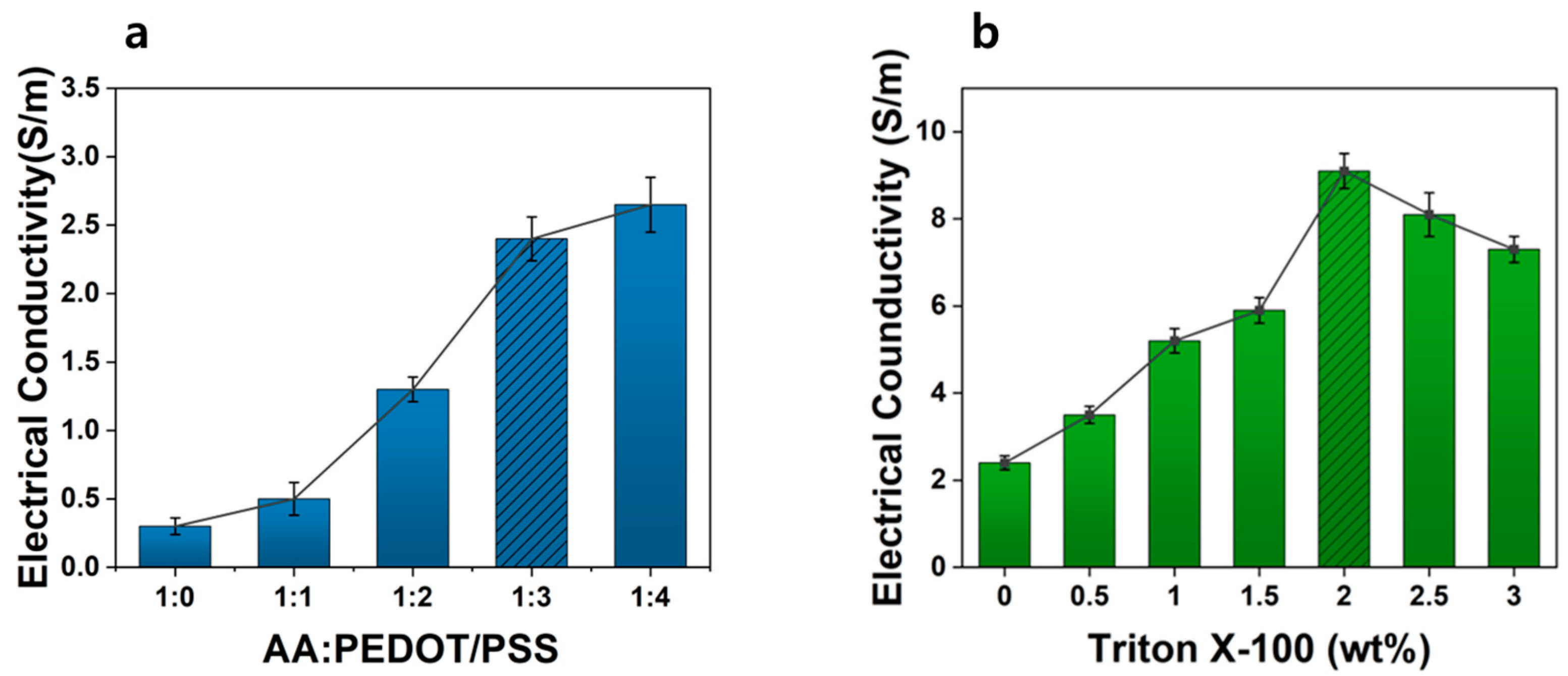
3.2. Optimization of Hydrogel Composition and Electrical Properties
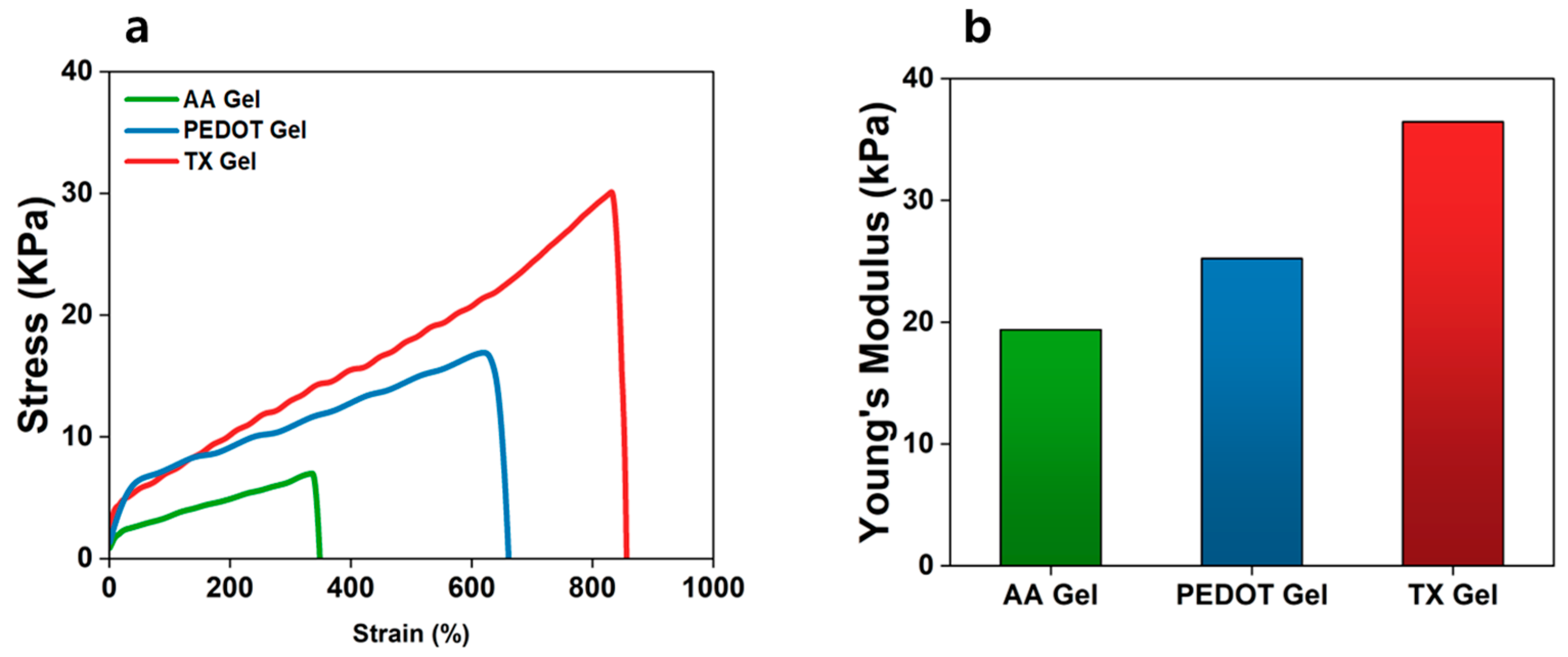
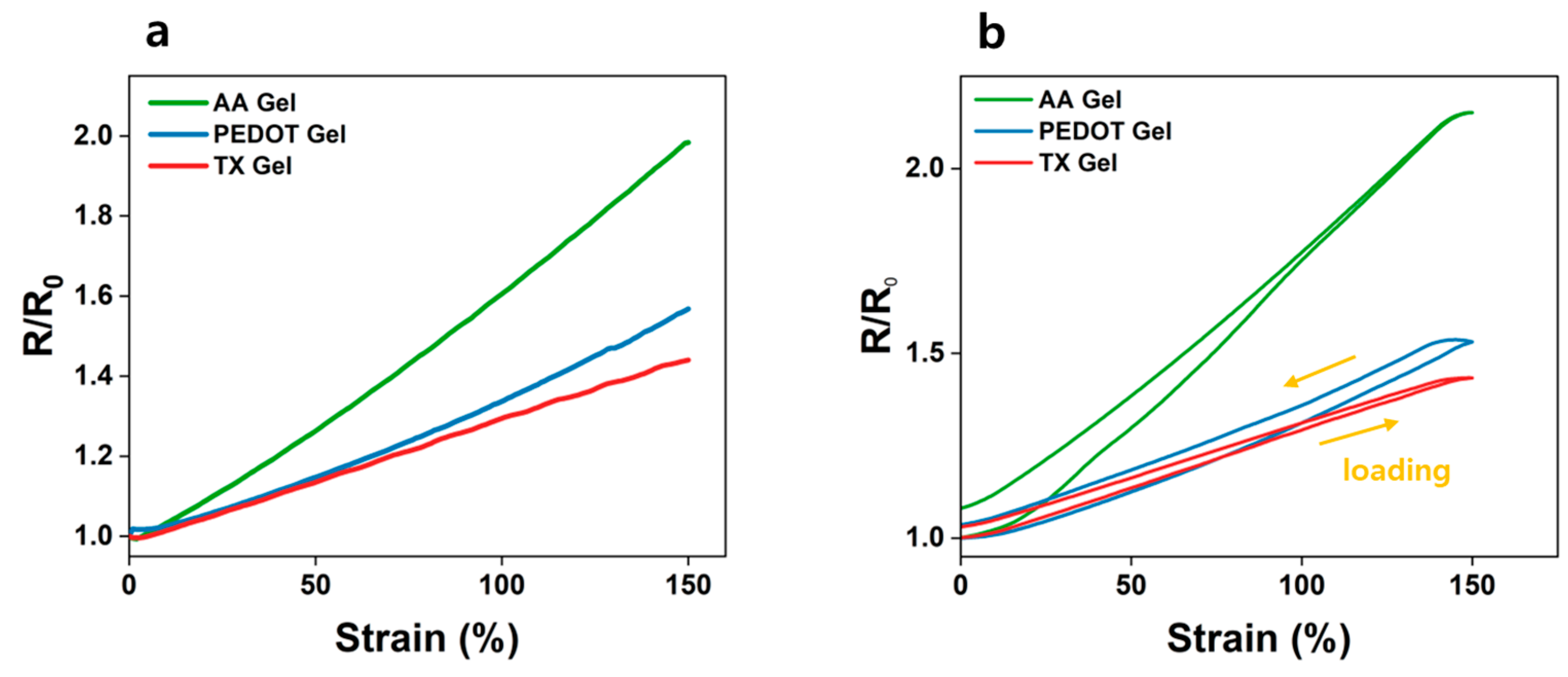
3.3. Mechanical Characterization of AA, PEDOT, and TX Gels
3.4. Evaluating Dynamic Artifacts
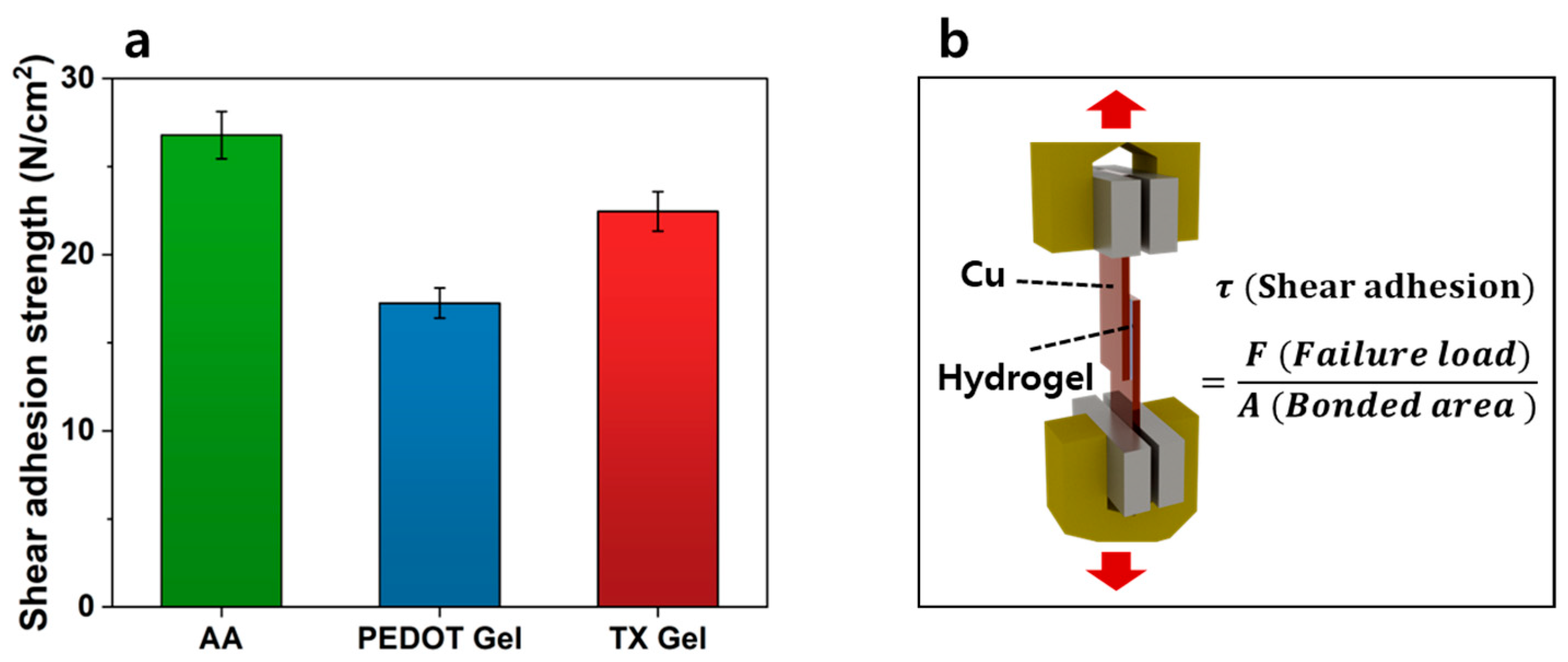
3.5. Evaluation of Adhesion Properties
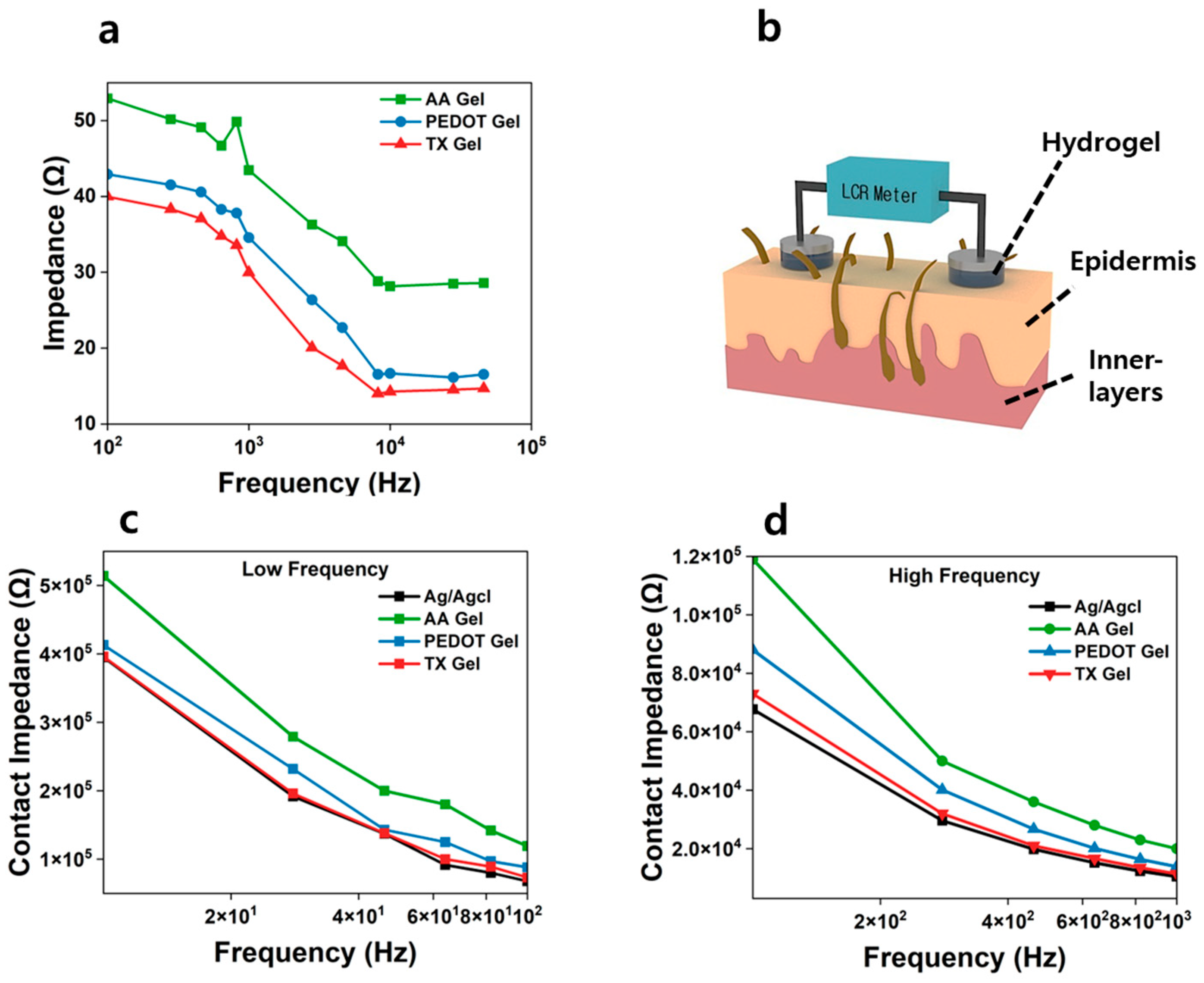
3.6. Evaluation of Impedance Characteristic
3.7. Recording EEG Signals
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Constant, I.; Sabourdin, N. The EEG signal: A window on the cortical brain activity. Pediatr. Anesth. 2012, 22, 539–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brienza, M.; Mecarelli, O. Neurophysiological basis of EEG. In Clinical Electroencephalography; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; pp. 9–21. [Google Scholar]
- da Silva, F.L. Neural mechanisms underlying brain waves: From neural membranes to networks. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. 1991, 79, 81–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaul, N. The fundamental neural mechanisms of electroencephalography. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. 1998, 106, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirschstein, T.; Köhling, R. What is the source of the EEG? Clin. EEG Neurosci. 2009, 40, 146–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McLoughlin, G.; Makeig, S.; Tsuang, M.T. In search of biomarkers in psychiatry: EEG-based measures of brain function. Am. J. Med. Genet. B Neuropsychiatr. Genet. 2013, 165, 111–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeman, W.; Quiroga, R.Q. Imaging Brain Function with EEG: Advanced Temporal and Spatial Analysis of Electroencephalographic Signals; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Darvas, F.; Pantazis, D.; Kucukaltun-Yildirim, E.; Leahy, R.M. Mapping human brain function with MEG and EEG: Methods and validation. NeuroImage 2004, 23, S289–S299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, J. EEG dynamics in patients with Alzheimer’s disease. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2004, 115, 1490–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zerr, I.; Pocchiari, M.; Collins, S.; Brandel, J.-P.; de Pedro Cuesta, J.; Knight, R.S.; Bernheimer, H.; Cardone, F.; Delasnerie-Lauprêtre, N.; Cuadrado Corrales, N.J.N. Analysis of EEG and CSF 14-3-3 proteins as aids to the diagnosis of Creutzfeldt–Jakob disease. Neurology 2000, 55, 811–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patidar, S.; Pachori, R.B.; Upadhyay, A.; Acharya, U.R. An integrated alcoholic index using tunable-Q wavelet transform based features extracted from EEG signals for diagnosis of alcoholism. Appl. Soft Comput. 2017, 50, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miniussi, C.; Thut, G.J. Combining TMS and EEG offers new prospects in cognitive neuroscience. Brain Topogr. 2010, 22, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasan, N. Cognitive neuroscience of creativity: EEG based approaches. Methods 2007, 42, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, D.; Shin, D.; Shin, D. Development of emotion recognition interface using complex EEG/ECG bio-signal for interactive contents. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2017, 76, 11449–11470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Eguren, D.; Azorín, J.M.; Grossman, R.G.; Luu, T.P.; Contreras-Vidal, J.L. Brain–machine interfaces for controlling lower-limb powered robotic systems. J. Neural Eng. 2018, 15, 021004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebedev, M.A.; Nicolelis, M.A. Brain–machine interfaces: Past, present and future. TRENDS Neurosci. 2006, 29, 536–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mota, A.R.; Duarte, L.; Rodrigues, D.; Martins, A.; Machado, A.; Vaz, F.; Fiedler, P.; Haueisen, J.; Nóbrega, J.; Fonseca, C. Development of a quasi-dry electrode for EEG recording. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2013, 199, 310–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Sullivan, M.; Temko, A.; Bocchino, A.; O’Mahony, C.; Boylan, G.; Popovici, E. Analysis of a low-cost EEG monitoring system and dry electrodes toward clinical use in the neonatal ICU. Sensors 2019, 19, 2637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, M.; Sulaiman, N.; PP Abdul Majeed, A.; Musa, R.M.; Ab Nasir, A.F.; Bari, B.S.; Khatun, S. Current status, challenges, and possible solutions of EEG-based brain-computer interface: A comprehensive review. Front. Neurorobot. 2020, 14, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teplan, M.J. Fundamentals of EEG measurement. Meas. Sci. Rev. 2002, 2, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Sazgar, M.; Young, M.G. Overview of EEG, electrode placement, and montages. In Absolute Epilepsy and EEG Rotation Review: Essentials for Trainees; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; pp. 117–125. [Google Scholar]
- Kam, J.W.; Griffin, S.; Shen, A.; Patel, S.; Hinrichs, H.; Heinze, H.-J.; Deouell, L.Y.; Knight, R.T. Systematic comparison between a wireless EEG system with dry electrodes and a wired EEG system with wet electrodes. NeuroImage 2019, 184, 119–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hinrichs, H.; Scholz, M.; Baum, A.K.; Kam, J.W.; Knight, R.T.; Heinze, H.-J. Comparison between a wireless dry electrode EEG system with a conventional wired wet electrode EEG system for clinical applications. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 5218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gargiulo, G.; Calvo, R.A.; Bifulco, P.; Cesarelli, M.; Jin, C.; Mohamed, A.; Van Schaik, A. A new EEG recording system for passive dry electrodes. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2010, 121, 686–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gargiulo, G.; Bifulco, P.; Calvo, R.A.; Cesarelli, M.; Jin, C.; van Schaik, A. A mobile EEG system with dry electrodes. In Proceedings of the 2008 IEEE Biomedical Circuits and Systems Conference, Abu Dhabi, UAE, 16–18 October 2008; pp. 273–276. [Google Scholar]
- Lopez-Gordo, M.A.; Sanchez-Morillo, D.; Valle, F.P. Dry EEG electrodes. Sensors 2014, 14, 12847–12870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arai, M.; Nishinaka, Y.; Miki, N. Electroencephalogram measurement using polymer-based dry microneedle electrode. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2015, 54, 06FP14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, Y.M.; Wang, Y.-T.; Wang, Y.; Maier, C.; Jung, T.-P.; Cauwenberghs, G. Dry and noncontact EEG sensors for mobile brain–computer interfaces. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2011, 20, 228–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, Y.M.; Jung, T.-P.; Cauwenberghs, G. Dry-contact and noncontact biopotential electrodes: Methodological review. IEEE Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2010, 3, 106–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, H.; Wang, D.; Jin, M.; Gao, H.; Wang, X.; Xia, L.; Li, D.a.; Sun, K.; Wang, H.; Dong, X. Hydrogel electrodes with conductive and substrate-adhesive layers for noninvasive long-term EEG acquisition. Microsyst. Nanoeng. 2023, 9, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, G.; Gao, K.; Zhao, N.; Wang, Z.; Jiang, C.; Liu, J. A fully flexible hydrogel electrode for daily EEG monitoring. IEEE Sens. J. 2022, 22, 12522–12529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Offenhäusser, A.; Ingebrandt, S.; Mayer, D. PEDOT: PSS-based bioelectronic devices for recording and modulation of electrophysiological and biochemical cell signals. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2021, 10, 2100061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasaki, R.; Katsuhara, M.; Yoshifuji, K.; Komoriya, Y. Novel dry EEG electrode with composite filler of PEDOT: PSS and carbon particles. In Proceedings of the 2023 45th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine & Biology Society (EMBC), Sydney, Australia, 24–27 July 2023; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Seiti, M.; Giuri, A.; Corcione, C.E.; Ferraris, E. Advancements in tailoring PEDOT: PSS properties for bioelectronic applications: A comprehensive review. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2023, 154, 213655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasha, A.; Roy, A.S.; Murugendrappa, M.; Al-Hartomy, O.A.; Khasim, S. Conductivity and dielectric properties of PEDOT-PSS doped DMSO nano composite thin films. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2016, 27, 8332–8339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lingstedt, L.V.; Ghittorelli, M.; Lu, H.; Koutsouras, D.A.; Marszalek, T.; Torricelli, F.; Crăciun, N.I.; Gkoupidenis, P.; Blom, P.W. Effect of DMSO solvent treatments on the performance of PEDOT: PSS based organic electrochemical transistors. Adv. Electron. Mater. 2019, 5, 1800804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz-Cruz, I.; Reyes-Reyes, M.; Aguilar-Frutis, M.; Rodriguez, A.; López-Sandoval, R. Study of the effect of DMSO concentration on the thickness of the PSS insulating barrier in PEDOT: PSS thin films. Synth. Met. 2010, 160, 1501–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Ruderer, M.A.; Metwalli, E.; Guo, S.; Herzig, E.M.; Perlich, J.; Müller-Buschbaum, P. Effect of methanol addition on the resistivity and morphology of PEDOT: PSS layers on top of carbon nanotubes for use as flexible electrodes. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 8789–8797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almeida, T.P.; Miyazaki, C.M.; Paganin, V.A.; Ferreira, M.; Saeki, M.J.; Perez, J.; Riul, A., Jr. PEDOT: PSS self-assembled films to methanol crossover reduction in Nafion® membranes. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2014, 323, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakunpongpitiporn, P.; Phasuksom, K.; Paradee, N.; Sirivat, A. Facile synthesis of highly conductive PEDOT: PSS via surfactant templates. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 6363–6378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, J.L.; Kelly, C.A.; Marshall, J.E.; Hammond, V.; Goodship, V.; Jenkins, M.J. PEDOT: PSS conductivity enhancement through addition of the surfactant Tween 80. Polymers 2022, 14, 5072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Q.; Li, C.; Wang, M.; Zhu, J.; Gao, C. A low-hysteresis, self-adhesive and conductive PAA/PEDOT: PSS hydrogel enabled body-conformable electronics. J. Mater. Chem. C 2023, 11, 9355–9365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, R.; Yan, X.; Lin, H.; Zhao, Z.; Song, S. Mechanical tough, stretchable, and adhesive PEDOT: PSS-based hydrogel flexible electronics towards multi-modal wearable application. Chem. Eng. J. 2025, 510, 161645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, J.Y.; Shin, M.; Lee, J.B.; Ahn, J.-H.; Baik, H.K.; Jeong, U. Effect of PEDOT nanofibril networks on the conductivity, flexibility, and coatability of PEDOT: PSS films. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 6954–6961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, S.-S.; Khang, D.-Y. Roles of nonionic surfactant additives in PEDOT: PSS thin films. J. Phys. Chem. C 2016, 120, 29525–29532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nardes, A.M.; Kemerink, M.; Janssen, R.A.; Bastiaansen, J.A.; Kiggen, N.M.; Langeveld, B.M.; Van Breemen, A.J.; De Kok, M.M. Microscopic understanding of the anisotropic conductivity of PEDOT: PSS thin films. Adv. Mater. 2007, 19, 1196–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.; Liu, C.; Jiang, Q.; Xu, J. Effective approaches to improve the electrical conductivity of PEDOT: PSS: A review. Adv. Electron. Mater. 2015, 1, 1500017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Q.; Yu, Y.; Kang, L.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, S.; Niu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Di, J.; Li, Q.; et al. Modulus-Tailorable, Stretchable, and Biocompatible Carbonene Fiber for Adaptive Neural Electrode. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022, 32, 2107360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Yi, J.; Lu, R.; Wang, M.; Liao, X.; Cheng, Y.; Zhang, S. Poly (acrylic acid)-derived zwitterionic hydrogel unlocking underwater adhesion and swelling resistance for applications as a tissue patch. Chem. Mater. 2024, 36, 10822–10830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, C.; Shao, C.; Meng, L.; Yang, J. High-strength, self-adhesive, and strain-sensitive chitosan/poly (acrylic acid) double-network nanocomposite hydrogels fabricated by salt-soaking strategy for flexible sensors. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 39228–39237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wan, H.; Lan, W.; Miao, F.; Qin, M.; Wei, Y.; Hu, Y.; Liang, Z.; Huang, D. Fabrication of adhesive hydrogels based on poly (acrylic acid) and modified hyaluronic acid. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2022, 126, 105044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hokajärvi, I.A. Electrode Contact Impedance and Biopotential Signal Quality. Master’s Thesis, Tampere University of Technology, Tampere, Finland, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Bertrand, A.; Mihajlović, V.; Grundlehner, B.; Van Hoof, C.; Moonen, M. Motion artifact reduction in EEG recordings using multi-channel contact impedance measurements. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE Biomedical Circuits and Systems Conference (BioCAS), Rotterdam, The Netherlands, 31 October–2 November 2013; pp. 258–261. [Google Scholar]
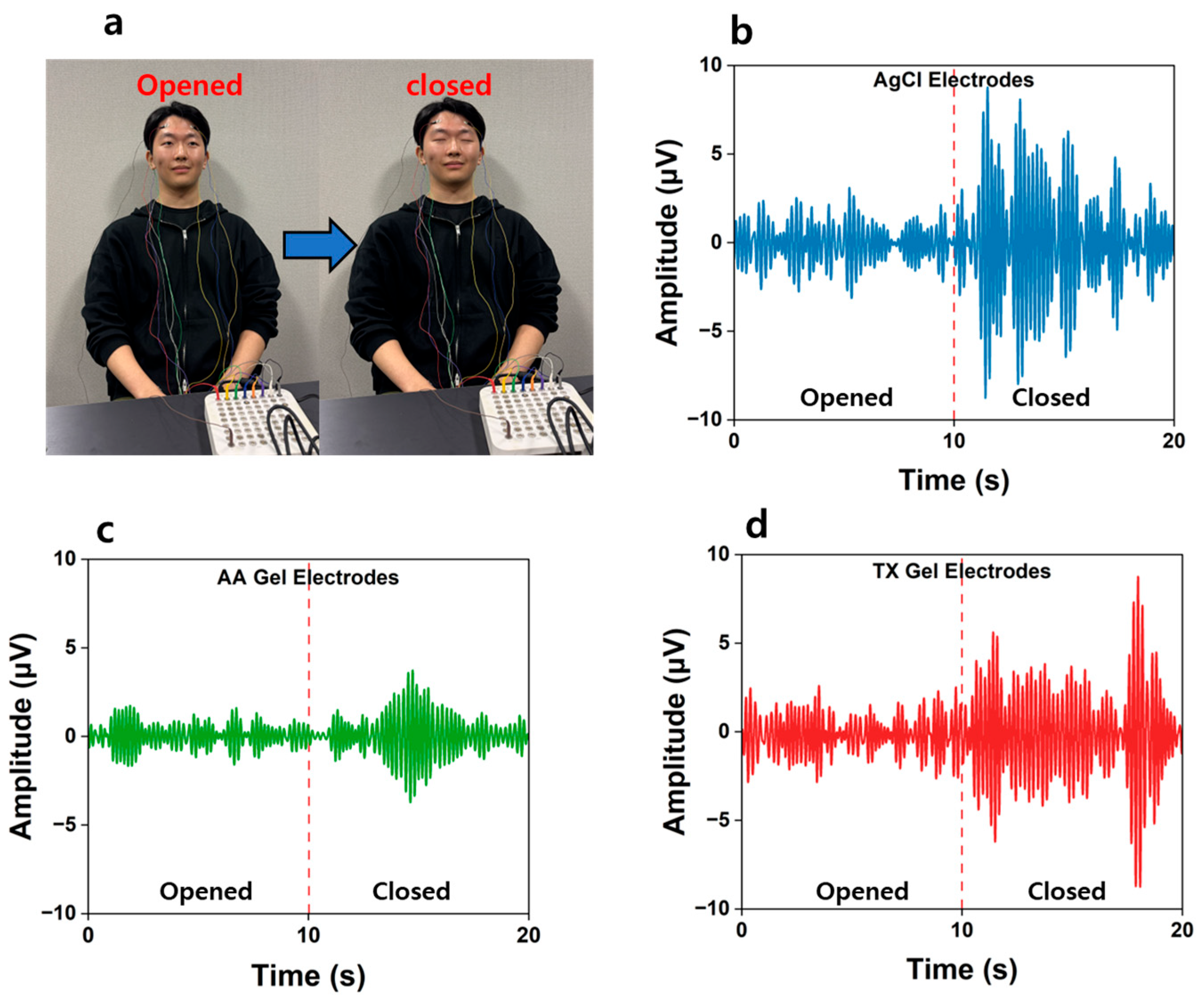

| Electrode Type | Condition | Mean Absolute Amplitude (μV) | Relative Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ag/AgCl | Eyes Opened | 0.8598 | 1 |
| Eyes Closed | 2.1501 | 2.5 | |
| AA Gel | Eyes Opened | 0.2542 | 1 |
| Eyes Closed | 0.4011 | 1.58 | |
| TX Gel | Eyes Opened | 0.8634 | 1 |
| Eyes Closed | 1.9958 | 2.31 |
| Electrode Type | Condition | Mean Power (μV2/Hz) | Relative Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ag/AgCl | Resting | 0.000527556 | 1 |
| Concentration | 0.011846486 | 22.5 | |
| AA Gel | Resting | 0.000216084 | 1 |
| Concentration | 0.003402649 | 15.7 | |
| TX Gel | Resting | 0.000525723 | 1 |
| Concentration | 0.011672563 | 22.2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ahn, J.-Y.; Oh, J.; An, M.-R.; Nam, K.-W.; Kim, J.-W.; Park, S.-H. Skin-Conformal Hydrogel-Based Electroencephalography Electrodes with Surfactant-Reorganized PEDOT:PSS. Materials 2025, 18, 4781. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18204781
Ahn J-Y, Oh J, An M-R, Nam K-W, Kim J-W, Park S-H. Skin-Conformal Hydrogel-Based Electroencephalography Electrodes with Surfactant-Reorganized PEDOT:PSS. Materials. 2025; 18(20):4781. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18204781
Chicago/Turabian StyleAhn, Ji-Yoon, Jihyeon Oh, Mi-Ri An, Kun-Woo Nam, Jin-Whan Kim, and Sung-Hoon Park. 2025. "Skin-Conformal Hydrogel-Based Electroencephalography Electrodes with Surfactant-Reorganized PEDOT:PSS" Materials 18, no. 20: 4781. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18204781
APA StyleAhn, J.-Y., Oh, J., An, M.-R., Nam, K.-W., Kim, J.-W., & Park, S.-H. (2025). Skin-Conformal Hydrogel-Based Electroencephalography Electrodes with Surfactant-Reorganized PEDOT:PSS. Materials, 18(20), 4781. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18204781








