Silver-Exchanged Zeolites: Preparation and Applications—A Review
Highlights
- Recent studies on the synthesis, characterization, and applications of silver-exchanged zeolites have been discussed.
- Uses in antimicrobial treatments, water purification, heavy metal removal have been addressed.
- Applications in catalysis, and the separation of inert gases, have also been investigated.
- Silver-exchanged zeolite is a highly promising material for a wide range of applications.
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Zeolites—General Characteristics
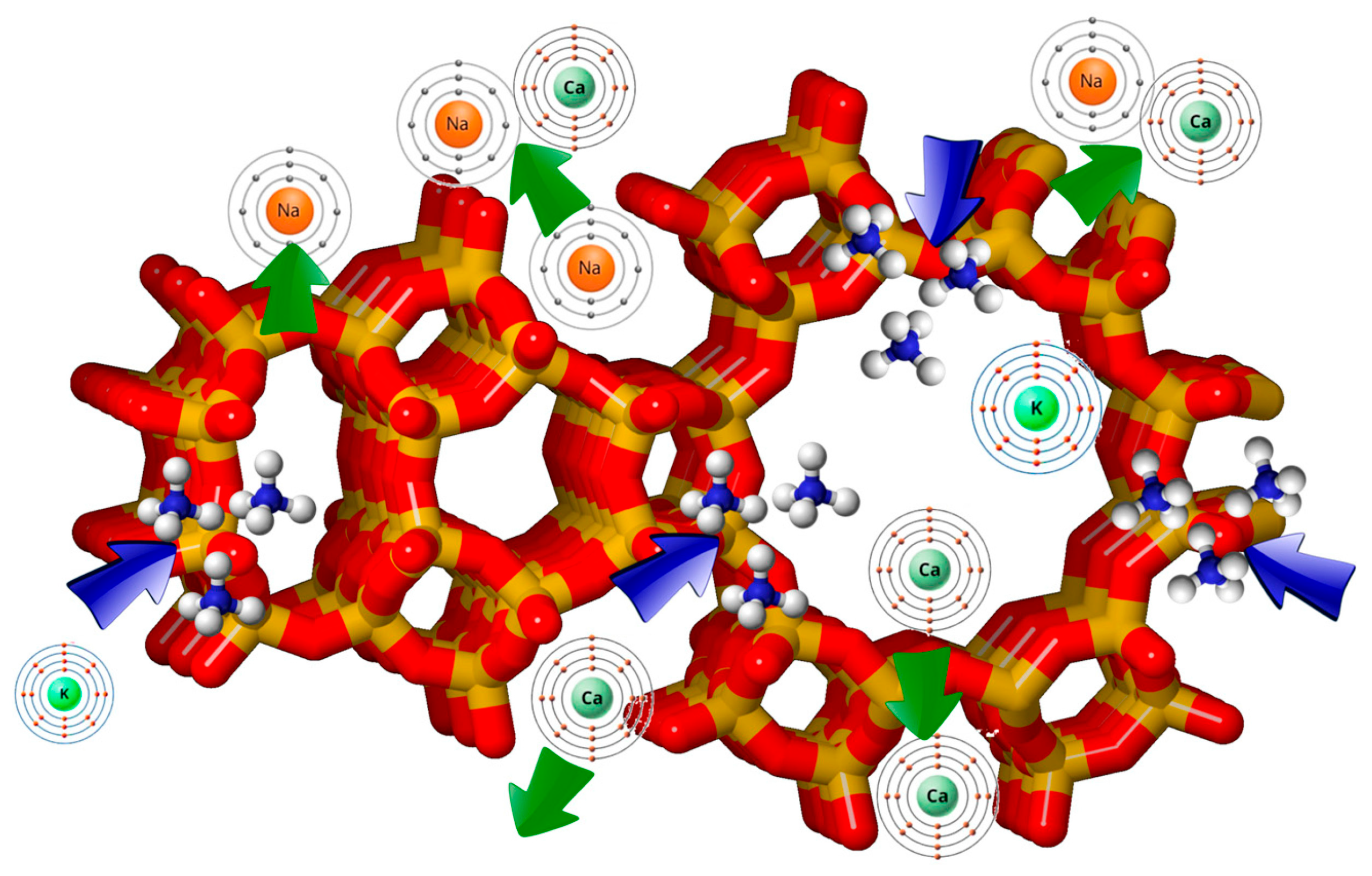
4. Preparation of Silver Exchanged Zeolites
Factors Influencing the Properties of Silver-Exchanged Zeolites
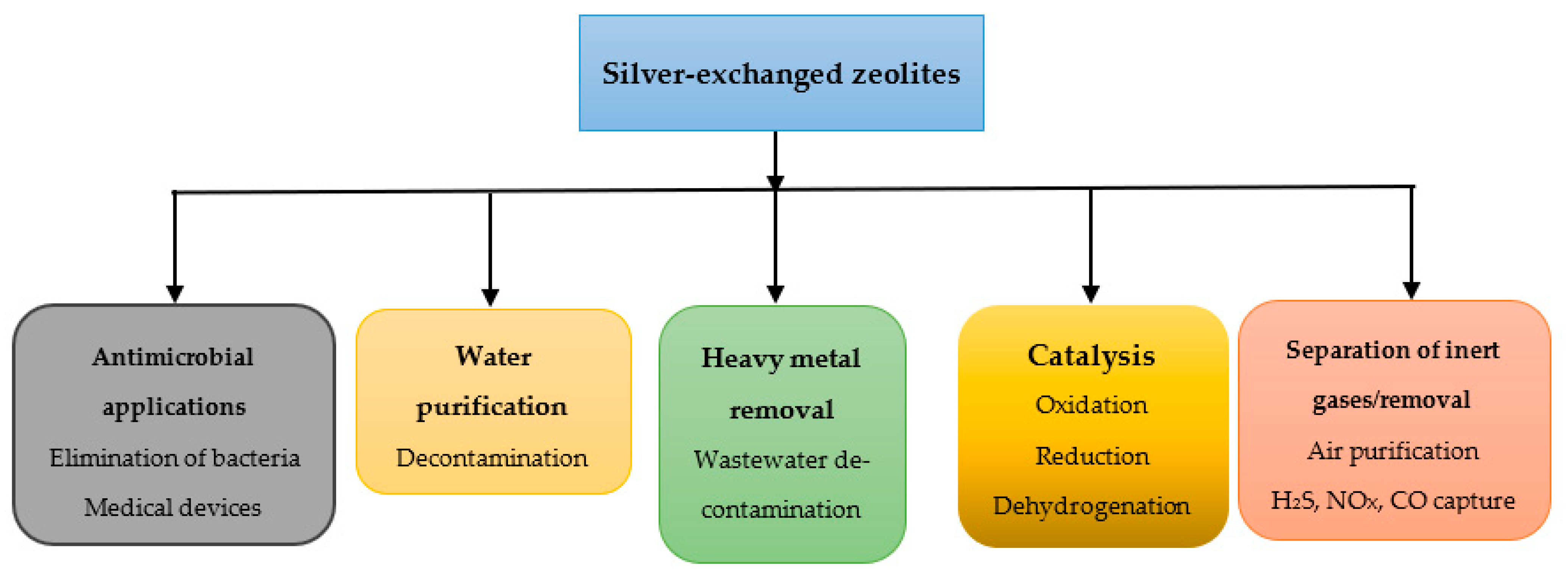
5. Applications of Silver-Exchange Zeolites
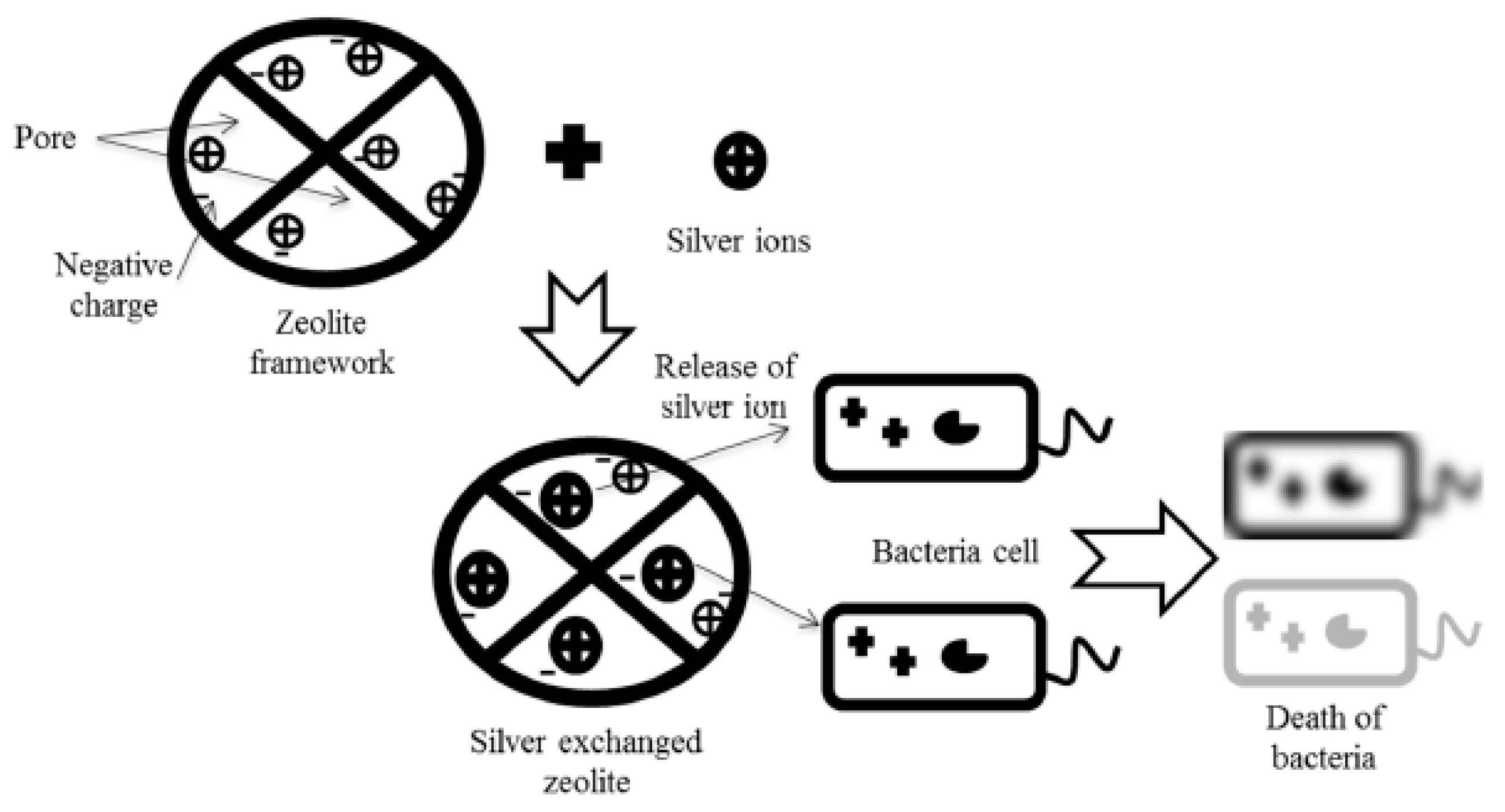
5.1. Antimicrobial Applications of Silver Exchanged Zeolites
5.2. Applications in Water Treatment
5.3. Removal of Metals, Mercury, Iodine
5.4. Applications in Separation of Inert Gases/Adsorption
5.5. Catalysis Reactions
6. Advantages and Limitations
7. Challenges and Future Perspectives
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AgNPs | Silver nanoparticles |
| Ag+ | Silver ions |
| PDADMAC | Poly(diallyldimethylammonium chloride |
| APTES | 3-aminopropyltriethoxysilane |
| ZSM-5 | Zeolite Socony mobil-5 |
| CEC | Cation exchange capacity |
| STI | Stilbite |
| ETS | Tritanosilicates |
| PVA | Polyvinyl alcohol |
| PDA | Polydopamine |
| Ag | Silver |
| Ag0 | Metallic silver |
| MRSA | Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus |
| TIPS | Thermally induced phase separation |
| PFAS | Per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances |
| CTAB | Cetyltrimethylammonium bromide |
| BTEX | Benzene, toluene, and xylene |
| PFAA | Perfluoroalkyl acids |
| GOIZ | Zeolite-impregnated graphite oxide |
| PFOA | Perfluorooctanoic acid |
| PFOS | Perfluorooctane sulfonate |
| Hg | Mercury |
| Hg2+ | Oxidized mercury |
| Hgᵖ | Particulate-bound mercury |
| NP | Nanoparticles |
| CH3I | Volatile methyl iodine |
| DoS | Degree-of-sulfurization |
| FAU | Faujasite |
| FGD | Flue gas desulfurization |
| AA | Acetaldehyde |
| MPV | Meerwein–Ponndorf–Verley |
| VOCs | Volatile organic compounds |
| PS/GR | Polystyrene/graphene |
| CNT | Carbon nanotube |
References
- Noviello, M.; Gattullo, C.E.; Faccia, M.; Paradiso, V.M.; Gambacorta, G. Application of natural and synthetic zeolites in the oenological field. Food Res. Int. 2021, 150, 110737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Senila, M.; Neag, E.; Cadar, O.; Hoaghia, M.A.; Roman, M.; Moldovan, A.; Hosu, A.; Lupas, A.; Kovacs, E.D. Characteristics of Volcanic Tuff from Macicasu (Romania) and Its Capacity to Remove Ammonia from Contaminated Air. Molecules 2022, 27, 3503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jarosz, R.; Szerement, J.; Gondek, K.; Mierzwa-Hersztek, M. The use of zeolites as an addition to fertilisers—A review. Catena 2022, 213, 106125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margeta, K.; Farkaš, A. Introductory Chapter: Zeolites—From Discovery to New Applications on the Global Market. In Zeolites—New Challenges; Margeta, K., Farkaš, A., Eds.; IntechOpen: Rijeka, Croatia, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Senila, M.; Cadar, O.; Begy, R.C.; Tanaselia, C.; Simedru, D.; Roman, C. Silver-Exchanged Clinoptilolite-Rich Natural Zeolite for Radon Removal from Air. Materials 2025, 18, 1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colella, C. Natural zeolites. In Studies in Surface Science and Catalysis; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2005; Volume 157, pp. 13–40. [Google Scholar]
- Senila, M.; Cadar, O.; Senila, L.; Hoaghia, A.; Miu, I. Mercury Determination in Natural Zeolites by Thermal Decomposition Atomic Absorption Spectrometry: Method Validation in Compliance with Requirements for Use as Dietary Supplements. Molecules 2019, 24, 4023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senila, M.; Cadar, O. Modification of natural zeolites and their applications for heavy metal removal from polluted environments: Challenges, recent advances, and perspectives. Heliyon 2024, 10, e25303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdoğan, B.; Şans, B.E.; Esenli, F. A comparative study on the physicochemical and hydrogen adsorption properties of Ag-exchanged Demirci (Türkiye) clinoptilolites. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2025, 145, 1144–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grifasi, N.; Ziantoni, B.; Fino, D.; Piumetti, M. Fundamental properties and sustainable applications of the natural zeolite clinoptilolite. Env. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bish, D.L.; Ming, D.W. Natural Zeolites: Occurrence, Properties, Applications; Walter de Gruyter GmbH & Co KG: Berlin, Germany, 2018; Volume 45, pp. 1–654. [Google Scholar]
- Blatov, V.A.; Blatova, O.A.; Daeyaert, F.; Deem, M.W. Nanoporous materials with predicted zeolite topologies. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 17760–17767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senila, L.; Hoaghia, A.; Moldovan, A.; Torok, I.A.; Kovacs, D.; Simedru, D.; Tomoiag, C.H.; Senila, M. The Potential Application of Natural Clinoptilolite-Rich Zeolite as Support for Bacterial Community Formation for Wastewater Treatment. Materials 2022, 15, 3685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cametti, G.; Scheinost, A.C.; Giordani, M.; Churakov, S.V. Framework Modifications and Dehydration Path of a Ag+-Modified Zeolite with STI Framework Type. J. Phys. Chem. C 2019, 123, 13651–13663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krstić, V. Chapter 14—Role of zeolite adsorbent in water treatment. In Handbook of Nanomaterials for Wastewater Treatment; Bhanvase, B., Sonawane, S., Pawade, V., Pandit, A., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; pp. 417–481. [Google Scholar]
- Millini, R.; Perego, C. The Role of Molecular Mechanics and Dynamics Methods in the Development of Zeolite Catalytic Processes. Top. Catal. 2009, 52, 42–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roth, W.J.; Nachtigall, P.; Morris, R.E.; Cejka, J. Two-dimensional zeolites: Current status and perspectives. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 4807–4837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancinelli, M.; Martucci, A. Exploring the Potential of Zeolites for Sustainable Environmental Applications. Sustain. Chem. 2025, 6, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boles, J. Review of Natural Zeolites: Occurrence, Properties, Applications: Editors: D.L. Bish and D.W. Ming. Reviews in Mineralogy and Geochemistry, Volume 45, Mineralogical Society of America, 1015 Eighteenth Street NW, Suite 601, Washington, D.C. 20036-5274, U.S.A. 2001, 654 p. US $24 for MSA and GS members; US $32 for others. ISBN0-939950-57-X. Can. Mineral.—CAN Mineral. 2002, 40, 1521–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oggiano, G.; Pokimica, B.; Popović, T.; Takić, M. Beneficial properties of zeolite. Ital. J. Food Sci. 2023, 35, 72–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prodinger, S.; Derewinski, M.A. Recent Progress to Understand and Improve Zeolite Stability in the Aqueous Medium. Pet. Chem. 2020, 60, 420–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Peng, Y. Natural zeolites as effective adsorbents in water and wastewater treatment. Chem. Eng. J. 2010, 156, 11–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poorkhalil, A.; Tayefehseyfi, E.; Farrokhzad, H.; Mohsenzadeh, A. Natural and synthetic zeolites for arsenic removal from water: A comprehensive review of mechanisms, performance, and future perspectives. J. Hazard. Mater. Adv. 2025, 19, 100866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Król, M. Natural vs. Synthetic Zeolites. Crystals 2020, 10, 622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javaid, A.; Munir, N.; Abideen, Z.; Siddiqui, Z.S.; Yong, J.W.H. The role of natural and synthetic zeolites as soil amendments for mitigating the negative impacts of abiotic stresses to improve agricultural resilience. Plant Stress. 2024, 14, 100627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes Rocha, M.; Anne Vieira Magalhães Ghiotto, G.; Wernke, G.; Carla Ribeiro, A.; Bergamasco, R.; Guttierres Gomes, R. Development of a new Zeolite-based adsorbent modified with silver nanoparticles for removal of Microcystis aeruginosa. Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manag. 2024, 22, 100981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiraroj, D.; Tungasmita, S.; Tungasmita, D.N. Silver ions and silver nanoparticles in zeolite A composites for antibacterial activity. Powder Technol. 2014, 264, 418–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gicheva, G.; Panayotova, M.; Gemishev, O.; Kulinich, S.A.; Mintcheva, N. Silver Nanoparticles@Zeolite Composites: Preparation, Characterization and Antibacterial Properties. Materials 2025, 18, 3964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlova, E.L.; Nenova, E.P.; Yocheva, L.D.; Ivanova, I.A.; Georgiev, P.A. Antimicrobial and Oxidative Activities of Different Levels of Silver-Exchanged Zeolites X and ZSM-5 and Their Ecotoxicity. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azambre, B.; Chebbi, M.; Ibrahim, N. Structure-Activity Relationships between the State of Silver on Different Supports and Their I(2) and CH(3)I Adsorption Properties. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, L.; Guedes, J.F.; Almeida-Aguiar, C.; Fonseca, A.M.; Neves, I.C. Microbial growth inhibition caused by Zn/Ag-Y zeolite materials with different amounts of silver. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2016, 142, 141–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youssef, H.F.; Abdel-Aziz, M.S.; Fouda, F.K. Evaluation of antimicrobial activity of different silver-exchanged nano and micronized zeolites prepared by microwave technique. J. Porous Mater. 2016, 24, 947–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Popovich, J.; Iannuzo, N.; Haydel, S.E.; Seo, D.K. Silver-Ion-Exchanged Nanostructured Zeolite X as Antibacterial Agent with Superior Ion Release Kinetics and Efficacy against Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 39271–39282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, V.V.; Jurado-Sánchez, B.; Sattayasamitsathit, S.; Orozco, J.; Li, J.; Galarnyk, M.; Fedorak, Y.; Wang, J. Multifunctional Silver-Exchanged Zeolite Micromotors for Catalytic Detoxification of Chemical and Biological Threats. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2015, 25, 2147–2155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, L.; Luo, Y.; Ng, W.J.; Zhao, X.S. Bactericidal activity of silver nanoparticles supported on microporous titanosilicate ETS-10. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2009, 120, 304–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samara, F.; Al Abdel Hamid, A.A.; Gopal, V.; Dronjak, L.; Feghaly, F.; Kanan, S. Modified Zeolites for the Removal of Emerging Bio-Resistive Pollutants in Water Resources. Catalysts 2025, 15, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanan, S.M.; Kanan, M.C.; Patterson, H.H. Silver nanoclusters doped in X and mordenite zeolites as heterogeneous catalysts for the decomposition of carbamate pesticides in solution. Res. Chem. Intermed. 2006, 32, 871–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, P.; Pradeep, T. Potential of silver nanoparticle-coated polyurethane foam as an antibacterial water filter. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2005, 90, 59–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mecha, A.C.; Chollom, M.N.; Babatunde, B.F.; Tetteh, E.K.; Rathilal, S. Versatile Silver-Nanoparticle-Impregnated Membranes for Water Treatment: A Review. Membranes 2023, 13, 432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagy, A.; Harrison, A.; Sabbani, S.; Munson, R.S., Jr.; Dutta, P.K.; Waldman, W.J. Silver nanoparticles embedded in zeolite membranes: Release of silver ions and mechanism of antibacterial action. Int. J. Nanomed. 2011, 6, 1833–1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, C.W.; Martinez-Ortigosa, J.; Góra-Marek, K.; Tarach, K.; Vidal-Moya, J.A.; Palomares, A.E.; Agostini, G.; Blasco, T.; Rey, F. Zeolite-driven Ag species during redox treatments and catalytic implications for SCO of NH3. J. Mater. Chem. A 2021, 9, 27448–27458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancinelli, M.; Martucci, A.; Salani, G.M.; Bianchini, G.; Gigli, L.; Plaisier, J.R.; Colombo, F. High temperature behaviour of Ag-exchanged Y zeolites used for PFAS sequestration from water. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2023, 25, 20066–20075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faryad, S.; Ghorbanpour, M.; Safajou-Jahankhanemlou, M. Effect of silver salt type on the physicochemical properties and antimicrobial activity of solid-state Ag-exchanged zeolites. Int. J. Ceram. Eng. Sci. 2024, 6, e10241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gattucci, F.; Lallukka, M.; Grifasi, N.; Piumetti, M.; Miola, M. Tannic acid-assisted green functionalization of Clinoptilolite: A step-by-step characterization of silver nanoparticles in situ reduction. Ceram. Int. 2025, 51, 13051–13057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reske, G.D.; Pereira, H.A.; Dotto, G.L.; Castilhos, F.D. Enhanced continuous adsorption of silver ions using graphite oxide impregnated with zeolite LTA under high pressure and temperature conditions. J. Mol. Liq. 2025, 426, 127380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambrozova, P.; Kynicky, J.; Urubek, T.; Nguyen, V.D. Synthesis and Modification of Clinoptilolite. Molecules 2017, 22, 1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Znak, Z.O.; Kornii, S.A.; Mashtaler, A.S.; Zin, O.I. Production of Nanoporous Zeolites Modified by Silver Ions with Antibacterial Properties. Mater. Sci. 2021, 56, 536–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, B.; Belkhair, S.; Zaarour, M.; Fisher, L.; Verran, J.; Tosheva, L.; Retoux, R.; Gilson, J.P.; Mintova, S. Silver confined within zeolite EMT nanoparticles: Preparation and antibacterial properties. Nanoscale 2014, 6, 10859–10864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cadar, O.; Vagner, I.; Miu, I.; Scurtu, D.; Senila, M. Preparation, Characterization, and Performance of Natural Zeolites as Alternative Materials for Beer Filtration. Materials 2023, 16, 1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.-K.; Rigolet, S.; Michelin, L.; Paillaud, J.-L.; Mintova, S.; Khoerunnisa, F.; Daou, T.J.; Ng, E.-P. Facile and fast determination of Si/Al ratio of zeolites using FTIR spectroscopy technique. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2021, 311, 110683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misaelides, P. Application of natural zeolites in environmental remediation: A short review. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2011, 144, 15–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osonio, A.P.; Vasquez, M.R. Plasma-assisted reduction of silver ions impregnated into a natural zeolite framework. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 432, 156–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashidvand, A.; Kheirmand, M.; Roozbehani, B.; Hosseini, S.H. Fabrication and characterization of ZSM-5 zeolite modified with silver and assessing its performance in petroleum waste cracking process. Arab. J. Chem. 2023, 16, 105330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gharibshahi, L.; Saion, E.; Gharibshahi, E.; Shaari, A.H.; Matori, K.A. Structural and Optical Properties of Ag Nanoparticles Synthesized by Thermal Treatment Method. Materials 2017, 10, 402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Došić, A.; Obrenović, M.; Obrenović, Z.; Vuković, J.; Savić, I.M. Ion Exchange of Na+ Ions with H+ Ions on ZSM-5 Zeolite Using Acetic Acid. Eng. Proc. 2025, 99, 17. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, T.; Tao, J.; Jia, Y.; Huang, W.; Yao, R.; Xue, X.; Zhou, Y.; Wei, Q. Directly synthesis of H-form ZSM-5 zeolites with n-butylamine in the presence of seed and ethanol. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2024, 370, 113057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haraguchi, N.; Kurosaki, T.; Uchida, S. Small luminescent silver clusters stabilized in porous crystalline solids. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2024, 26, 6512–6523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ul’yanova, N.Y.; Golubeva, O.Y. Zeolites Modified with Silver Nanoparticles and Clusters: Synthesis, Characterization, and Catalytic Performance in H2 and CO Oxidation Reactions. Glass Phys. Chem. 2018, 44, 418–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, L.; Fonseca, A.M.; Botelho, G.; Aguiar, C.A.; Neves, I.C. Antimicrobial activity of faujasite zeolites doped with silver. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2012, 160, 126–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pabalan, R.T.; Bertetti, F.P. Cation-Exchange Properties of Natural Zeolites. Rev. Mineral. Geochem. 2001, 45, 453–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molleman, B.; Hiemstra, T. Time, pH, and size dependency of silver nanoparticle dissolution: The road to equilibrium. Environ. Sci. Nano 2017, 4, 1314–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhigbe, L.; Ouki, S.; Saroj, D.; Lim, X.M. Silver-modified clinoptilolite for the removal of Escherichia coli and heavy metals from aqueous solutions. Env. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2014, 21, 10940–10948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, P.; Wang, B. Zeolite-supported silver as antimicrobial agents. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2019, 383, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancinelli, M.; Stevanin, C.; Ardit, M.; Chenet, T.; Pasti, L.; Martucci, A. PFAS as emerging pollutants in the environment: A challenge with FAU type and silver-FAU exchanged zeolites for their removal from water. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 108026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabbani, S.; Gallego-Perez, D.; Nagy, A.; James Waldman, W.; Hansford, D.; Dutta, P.K. Synthesis of silver-zeolite films on micropatterned porous alumina and its application as an antimicrobial substrate. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2010, 135, 131–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, A.M.; Mekonnen, M.L.; Mekonnen, K.N. Review on nanocomposite materials from cellulose, chitosan, alginate, and lignin for removal and recovery of nutrients from wastewater. Carbohydr. Polym. Technol. Appl. 2023, 6, 100386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salim, M.M.; Malek, N.A.N.N. Review of modified zeolites by surfactant and silver as antibacterial agents. J. Adv. Res. Mater. Sci. 2017, 36, 1–20. [Google Scholar]
- Hagiwara, Z.; Hoshino, S.; Ishino, H.; Nohara, S.; Tagawa, K.; Yamanaka, K. Zeolite Particles Retaining Silver Ions Having Antibacterial Properties. U.S. Patent No. 4911898, 27 March 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Belkhair, S.; Kinninmonth, M.; Fisher, L.; Gasharova, B.; Liauw, C.M.; Verran, J.; Mihailova, B.; Tosheva, L. Silver zeolite-loaded silicone elastomers: A multidisciplinary approach to synthesis and antimicrobial assessment. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 40932–40939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Hutson, N.D.; Reisner, B.A.; Yang, R.T.; Toby, B.H. Silver Ion-Exchanged Zeolites Y, X, and Low-Silica X: Observations of Thermally Induced Cation/Cluster Migration and the Resulting Effects on the Equilibrium Adsorption of Nitrogen. Chem. Mater. 2000, 12, 3020–3031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerrillo, J.L.; Palomares, A.E.; Rey, F.; Valencia, S.; Pérez-Gago, M.B.; Villamón, D.; Palou, L. Functional Ag-Exchanged Zeolites as Biocide Agents. ChemistrySelect 2018, 3, 4676–4682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerrillo, J.L.; Palomares, A.E.; Rey, F. Silver exchanged zeolites as bactericidal additives in polymeric materials. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2020, 305, 110367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, L.; Almeida-Aguiar, C.; Parpot, P.; Fonseca, A.M.; Neves, I.C. Preparation and assessment of antimicrobial properties of bimetallic materials based on NaY zeolite. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 37188–37195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Yu, C.; Li, Q. Novel regenerable antimicrobial nanocomposite membranes: Effect of silver loading and valence state. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 531, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inglezakis, V.J.; Loizidou, M.D.; Grigoropoulou, H.P. Ion exchange of Pb2+, Cu2+, Fe3+, and Cr3+ on natural clinoptilolite: Selectivity determination and influence of acidity on metal uptake. J. Colloid. Interface Sci. 2003, 261, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, S.; Zhong, Y.; Pepe, F.; Zhu, W. Adsorption of Pb2+ and Cu2+ on anionic surfactant-templated amino-functionalized mesoporous silicas. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 189–190, 160–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irannajad, M.; Kamran Haqhighi, H.; Soleimanipour, M. Adsorption of Zn2+, Cd2+ and Cu2+ on zeolites coated by manganese and iron oxides. Physicochem. Probl. Miner. Process. 2016, 52, 894–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y.; Tian, T.; L’Hermitte, A.; Méndez, A.S.J.; Danaci, D.; Platero-Prats, A.E.; Petit, C. Using silver exchange to achieve high uptake and selectivity for propylene/propane separation in zeolite Y. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 446, 137104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darmayanti, R.F.; Muharja, M.; Widjaja, A.; Widiastuti, N.; Rachman, R.A.; Widyanto, A.R.; Halim, A.; Satrio, D.; Piluharto, B. Performance of modified hollow fiber membrane silver nanoparticles-zeolites Na-Y/PVDF composite used in membrane bioreactor for industrial wastewater treatment. Heliyon 2023, 9, e21350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calore, F.; Badetti, E.; Bonetto, A.; Pozzobon, A.; Marcomini, A. Non-conventional sorption materials for the removal of legacy and emerging PFAS from water: A review. Emerg. Contam. 2024, 10, 100303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Cui, J.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, H.; Zhu, J. Kinetic and Thermodynamic Study of Ag+, Cu2+, and Zn2+ Ion Adsorption on LTA for High-Performance Antibacterial Coating. Coatings 2024, 14, 1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czarna, D.; Baran, P.; Kunecki, P.; Panek, R.; Żmuda, R.; Wdowin, M. Synthetic zeolites as potential sorbents of mercury from wastewater occurring during wet FGD processes of flue gas. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 172, 2636–2645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, Y.H.; Ho, K.; Lee, H.C.; Kim, K.M.; Kim, D.W.; Lee, C.H. Understanding silver structural rearrangement on zeolite Y for methyl iodide capture in nuclear safety system. J. Hazard. Mater. 2025, 494, 138520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chebbah, M.; Tarchoun, A.F.; Benaliouche, F.; Abdelaziz, A.; Trache, D. Advancing nitrocellulose thermal stability through the incorporation of ion-exchanged ZSM-5 zeolite for enhanced performance. FirePhysChem 2025, 5, 209–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeghi, M.; Yekta, S.; Ghaedi, H.; Babanezhad, E. Effective removal of radioactive 90Sr by CuO NPs/Ag-clinoptilolite zeolite composite adsorbent from water sample: Isotherm, kinetic and thermodynamic reactions study. Int. J. Ind. Chem. 2016, 7, 315–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmekawy, A.; Quach, Q.; Abdel-Fattah, T.M. Synthesis and Characterization of Silver-Modified Nanoporous Silica Materials for Enhanced Iodine Removal. Nanomaterials 2024, 14, 1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gueibe, C.; Rutten, J.; Camps, J.; Moyaux, D.; Schroeyers, W.; Plenteda, R.; Hermanspahn, N.; Minta, D.; Schreurs, S. Silver-exchanged zeolites for collecting and separating xenon directly from atmospheric air. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2023, 323, 124433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinitz, S.; Mermans, J.; Maertens, D.; Skliarova, H.; Aerts, A.; Cardinaels, T.; Gueibe, C.; Rutten, J.; Ireland, N.; Kuznicki, D.; et al. Adsorption of radon on silver exchanged zeolites at ambient temperatures. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 6811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Zandvoort, I.; van Klink, G.P.M.; de Jong, E.; van der Waal, J.C. Selectivity and stability of zeolites [Ca]A and [Ag]A towards ethylene adsorption and desorption from complex gas mixtures. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2018, 263, 142–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xv, X.; Ye, S.; Pan, L.; Lin, P.; Liao, H.; Wang, D. Tailoring the Luminescence Properties of Silver Clusters Confined in Faujasite Zeolite through Framework Modification. Materials 2022, 15, 7431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, A.; Gupta, V.; Singh, S.; Saini, S.; Gaikwad, K.K. Pine needles lignocellulosic ethylene scavenging paper impregnated with nanozeolite for active packaging applications. Ind. Crops Prod. 2021, 170, 113752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, G.; de Marcos-Galán, A.; Martínez-Ortigosa, J.; Sastre, G.; Jiménez-Ruiz, M.; Rey, F.; Blasco, T. Effects of cage topology on ethylene adsorption mechanism in silver exchanged CHA and RHO zeolites: An Inelastic Neutron Scattering and Density Functional study. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2024, 367, 112982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Chen, Y.; Yang, J.; Li, J.; Li, L. In-situ silver-modification of Silicalite-1 for trace ethylene capture under humid conditions. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2023, 613, 156002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Liao, J.; Chang, L.; Bao, W. Ag modification of SBA-15 and MCM-41 mesoporous materials as sorbents of thiophene. Fuel 2022, 311, 122537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uslamin, E.A.; Saito, H.; Kosinov, N.; Pidko, E.; Sekine, Y.; Hensen, E.J.M. Aromatization of ethylene over zeolite-based catalysts. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2020, 10, 2774–2785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokhtar, A.; Zaiter, K.; Abdelkrim, S.; Sardi, A.; Sassi, M.; Hachemaoui, M.; Boukoussa, B.; Viscusi, G.; Abboud, M. Bimetallic Ag Ni doped LTA zeolite from kaolin: A dual-action catalyst for efficient dye degradation and antibacterial disinfection. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2025, 180, 114943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyriienko, P.I.; Larina, O.V.; Soloviev, S.O.; Orlyk, S.M.; Calers, C.; Dzwigaj, S. Ethanol Conversion into 1,3-Butadiene by the Lebedev Method over MTaSiBEA Zeolites (M = Ag, Cu, Zn). ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 2075–2083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Gao, Y.; Yi, L.; Yang, G.; Wang, L. Simultaneous construction of Zr-β zeolite with high content and high accessibility of framework Zr sites in the conversion of ethanol to 1,3-butadiene: Mechanisms and synergistic effects. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 499, 156298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, R.d.S.; Cavalcante, R.M.; Silva, M.A.P.d. Effects of adding metals to Beta zeolite on ethanol conversion to hydrocarbons. Catal. Today 2025, 445, 115048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phung, T.K.; Radikapratama, R.; Garbarino, G.; Lagazzo, A.; Riani, P.; Busca, G. Tuning of product selectivity in the conversion of ethanol to hydrocarbons over H-ZSM-5 based zeolite catalysts. Fuel Process. Technol. 2015, 137, 290–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palcheva, R.; Kaluza, L.; Shestakova, P.; Moravcik, J.; Lyutskanova, A.; Soukup, K.; Kalvachev, Y.; Tyuliev, G.; Jiratova, K. C-C coupling of 1-butanol over Mg- and Li-doped L-zeolite. Catal. Today 2025, 459, 115436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Vidal-Moya, A.; Hernandez-Garrido, J.C.; Mon, M.; Leyva-Perez, A. Silver-Exchanged Zeolite Y Catalyzes a Selective Insertion of Carbenes into C-H and O-H Bonds. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2023, 145, 24736–24745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngouana Moafor, S.; Macheli, L.; Kabongo, G.L.; Nyongombe, G.; Tsobnang, P.K.; Lambi, J.N.; Jewell, L.L. Supercapacitive performance of cobalt-loaded amorphous zeolite for energy storage applications. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2024, 363, 112784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, J.; Li, H.; Zhuang, S.; Zhang, D.; Yu, D. Recent Advances in g-C3N4 Photocatalysts: A Review of Reaction Parameters, Structure Design and Exfoliation Methods. Catalysts 2023, 13, 1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Z.; Gao, F.; Zhang, J.; Yi, L.; Luo, N.; Yi, H.; Tang, X. Advances in CO catalytic oxidation on typical metal oxide catalysts: Performance, mechanism, and optimization. J. Mater. Chem. A 2025, 13, 26129–26165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stroe, M.; Cristea, M.; Matei, E.; Galatanu, A.; Cotet, L.C.; Pop, L.C.; Baia, M.; Danciu, V.; Anghel, I.; Baia, L.; et al. Optical Properties of Composites Based on Graphene Oxide and Polystyrene. Molecules 2020, 25, 2419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dyachkova, T.P.; Khan, Y.A.; Burakova, E.A.; Galunin, E.V.; Shigabaeva, G.N.; Stolbov, D.N.; Titov, G.A.; Chapaksov, N.A.; Tkachev, A.G. Characteristics of Epoxy Composites Containing Carbon Nanotubes/Graphene Mixtures. Polymers 2023, 15, 1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
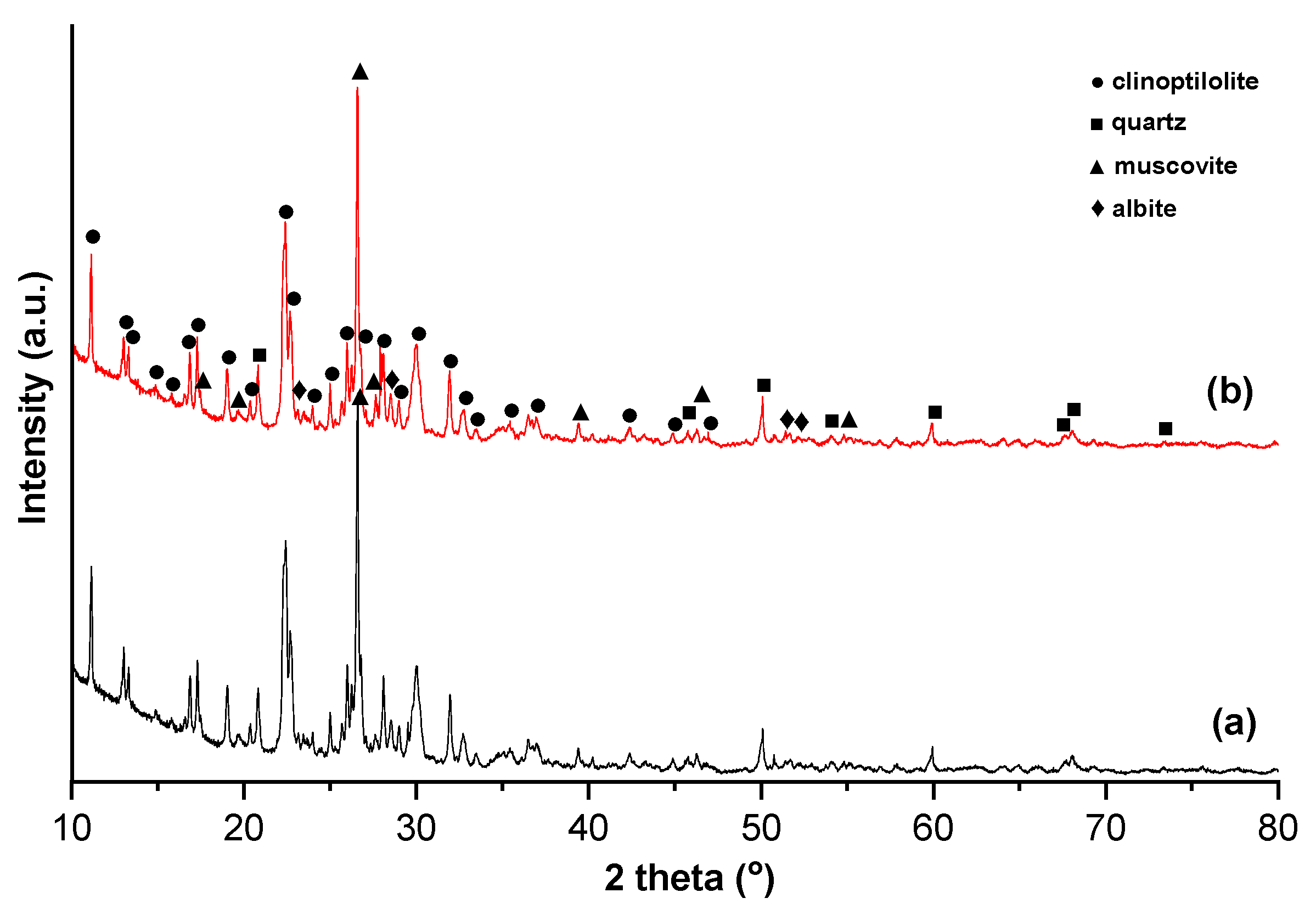
| Zeolite | Chemical Formula | Structure | Used |
|---|---|---|---|
| Clinoptilolite | (K2,Na2,Ca)3Al6Si30O72·21H2O | HEU | Environmental remediation and ion exchange |
| Mordenite | (Na2,Ca)4Al8Si40O96·28H2O | MOR | Strong adsorption properties |
| Chabazite | (Ca,Na2,K2)2Al4Si8O24·12H2O | CHA | CO2 capture and gas separation |
| Heulandite | (Ca,Na)2-3Al3(Al,Si)2Si13O36·12H2O | HEU | Catalysis |
| Phillipsite | K2(Ca,Na2)2Al8Si10O32·12H2O | PHI | Wastewater treatment |
| Scolecite | Ca4Al8Si12O40·12H2O | NAT | Ion exchange and adsorption |
| Stilbite | Na2Ca4Al10Si26O72·30H2O | STI | Catalysis and gas separation |
| Analcime | Na16Al16Si32O96·16H2O | ANA | Ceramics and as a molecular sieve |
| Laumontite | Ca4Al8S16O48·16H2O | LAU | Hydration behavior |
| Zeolite | Framework Type | Idealized Molecular Formula | Typical Si/Al Ratio | Pore Opening |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Natural zeolite | HEU | (Na,K,Ca)6[Al6Si30O72] · 20H2O | 4–5 (Si/Al high) | 3.5 × 7.6 Å & 4.6 × 3.1 Å (10-ring channels) |
| A (Zeolite A) | LTA | Na12[Al12Si12O48] · 27H2O | 1.0 | 4.1 Å × 4.1 Å (8-ring) |
| X (Zeolite X) | FAU | Na86[Al86Si106O384] · 264H2O | 1.2–1.5 | 7.4 Å (12-ring) |
| Y (Zeolite Y) | FAU | Na56[Al56Si136O384] · 250H2O | 2.5–3.0 | 7.4 Å (12-ring) |
| ZSM-5 | MFI | Nan[AlnSi96 − nO192] · 16H2O | 10–1000+ | 5.1 × 5.5 Å & 5.3 × 5.6 Å (10-ring channels) |
| Aspect | Natural Zeolites | Synthetic Zeolites |
|---|---|---|
| Genesis | Formed naturally from volcanic/sedimentary processes. | Manufactured hydrothermally under controlled lab/industrial conditions. |
| Purity | Contain impurities (clays, quartz, feldspar). | High purity, no gangue minerals. |
| Composition | Fixed, limited Si/Al ratios. | Tunable Si/Al ratios |
| Structure Variety | ~50 species, limited pore variety | >200 synthetic zeolite frameworks |
| Pore Size & Shape | Limited range; often irregular due to impurities. | Precisely controlled pore dimensions (molecular sieving at Å-scale). |
| Cation Exchange Capacity (CEC) | Moderate, varies with deposit. | Higher and adjustable |
| Reproducibility | Quality varies between deposits. | Highly reproducible, batch to batch. |
| Availability | Abundant, easily mined. | Requires industrial synthesis |
| Main Applications | Bulk uses: wastewater treatment, soil amendments, animal feed, gas absorption, odor control. | High-tech uses: petrochemical cracking catalysts, detergent builders, molecular sieves, gas separation, fine chemical synthesis. |
| Cost | Low (mined, minimally processed). | Higher (manufactured under controlled conditions). |
| Method | Principle | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ion exchange | Replacement of native cations (Na+, K+, Ca2+, etc.) in zeolite with Ag+ from aqueous solution | Control of Ag content High stability of ionic silver Uniform dispersion of Ag+ at framework sites Maintains crystallinity & pore structure Precise control over Ag loading via exchange conditions | Capacity limited by framework Al content Time-consuming (often multiple cycles) Sensitive to pH/ionic strength (risk of Ag precipitation) Strong Ag binding may hinder later reduction |
| Wet impregnation | Impregnation of zeolite pores with Ag salt solution, followed by drying/calcination | Simple, fast, and scalable Allows higher Ag loadings beyond cation exchange capacity Suitable for nanoparticle formation after calcination | Often non-uniform Ag distribution Risk of surface deposition & pore blockage Silver aggregation/sintering at high temperature Less control of Ag oxidation state |
| Chemical reduction | Introduction of Ag+ (via exchange/impregnation) followed by chemical reduction (e.g., NaBH4, H2) | Enables formation of Ag0 nanoparticles or small Agn clusters inside pores Size/dispersion tunable via reduction conditions Zeolite stabilizes clusters against aggregation | Risk of external nanoparticle deposition Non-uniform size distribution Excessive reduction may block pores or destabilize framework Requires careful handling of reductants |
| Zeolite | Selectivity | Molar Ratio Si/Al |
|---|---|---|
| clinoptilolite | Pb2+ > Ag+ > Cd2+ ~ Zn2+ > Cu2+ | 2.7–5.3 |
| clinoptilolite | Pb2+ > Zn2+ > Cu2+ ~ Ni2+ | 4.9 |
| clinoptilolite | Pb2+ > Cd2+ > Zn2+ ~ Cu2+ | 4.2 |
| clinoptilolite | Pb2+ > Cd2+ > Cu2+ > Co2+ > Cr3+ > Zn2+ > Ni2+ > Hg2+ | - |
| phillipsite | Pb2+ > Cd2+ > Zn2+ > Co2+ | 2.4–2.7 |
| mordenite | Mn2+ > Cu2+ > Co2+ ~ Zn2+ >Ni2+ | 4.4–5.5 |
| scolecite | Cu2+ > Zn2+ > Pb2+ > Ni2+ > Co2+ > Cd2+ | 1.56 |
| chabazite | Pb2+ > Cd2+ > Cu2+ > Zn2+ > Co2+ | 2.2–2.6 |
| Application | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Water treatment | Strong adsorption of heavy metals (Pb2+, Cu2+, Cd2+) and organic pollutants. Can be used in existing water treatment systems. | Risk of Ag+ to leaching into water Limited regeneration in aqueous system Adsorption can be reduced by fouling from natural organic matter. Repeated use may lead to silver nanoparticle agglomeration, reducing efficiency. Silver significantly increases the overall cost. |
| Antimicrobial | Sustained antimicrobial action due to gradual release of Ag+ ions. Broad-spectrum activity against bacteria, fungi, algae, and viruses. High capability of Ag against various bacterial strains Reduces need for harsh chemical disinfectants. Effective at low concentrations, reducing frequent dosing needs. | Potential cytotoxicity with prolonged exposure. Regulatory concerns over silver release. Expensive compared to other antimicrobial agents. Over time, Ag+ release rate may decline, reducing long-term effectiveness. Silver particles may agglomerate, lowering antimicrobial efficiency. Potential cytotoxicity at higher silver concentrations. |
| Catalysis | Active sites for oxidation, hydrogenation and dehydrogenation reactions. Synergistic effects of Ag with zeolite acidity. Useful in environmental catalysis (e.g., VOC oxidation). Catalyst can be regenerated by calcination or reduction treatments. Can replace or reduce use of more expensive noble metals (e.g., Pt, Pd). | Deactivation due to silver sintering or leaching. Requires precise silver loading and dispersion. More expensive than non-precious metal catalysts. Ag nanoparticles can sinter at high temperatures, reducing activity. Selectivity may decrease if silver migrates or agglomerates. Silver still adds significant cost compared to base-metal catalysts. |
| Air purification | Strong affinity for halogens (e.g., iodine, bromine) and sulfur compounds (H2S, SO2). Effective in removing volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and toxic gases. Can operate under a wide temperature range. | Humidity reduces adsorption efficiency. Silver nanoparticles may sinter under high temperatures. Costly compared to activated carbon. |
| Nuclear safety | Strong affinity for I2 and CH3I through Ag–I bond formation for iodine capture High thermal and radiation stability of zeolite framework. Effective even at low iodine concentrations. | Silver restructuring reduces long-term performance. High cost due to silver content. Disposal of radioactive Ag–zeolite waste is challenging. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Senila, M.; Kovacs, E.; Senila, L. Silver-Exchanged Zeolites: Preparation and Applications—A Review. Materials 2025, 18, 4779. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18204779
Senila M, Kovacs E, Senila L. Silver-Exchanged Zeolites: Preparation and Applications—A Review. Materials. 2025; 18(20):4779. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18204779
Chicago/Turabian StyleSenila, Marin, Eniko Kovacs, and Lacrimioara Senila. 2025. "Silver-Exchanged Zeolites: Preparation and Applications—A Review" Materials 18, no. 20: 4779. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18204779
APA StyleSenila, M., Kovacs, E., & Senila, L. (2025). Silver-Exchanged Zeolites: Preparation and Applications—A Review. Materials, 18(20), 4779. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18204779








