Effect of Secondary Aging Conditions on Mechanical Properties and Microstructure of AA7150 Aluminum Alloy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Experimental
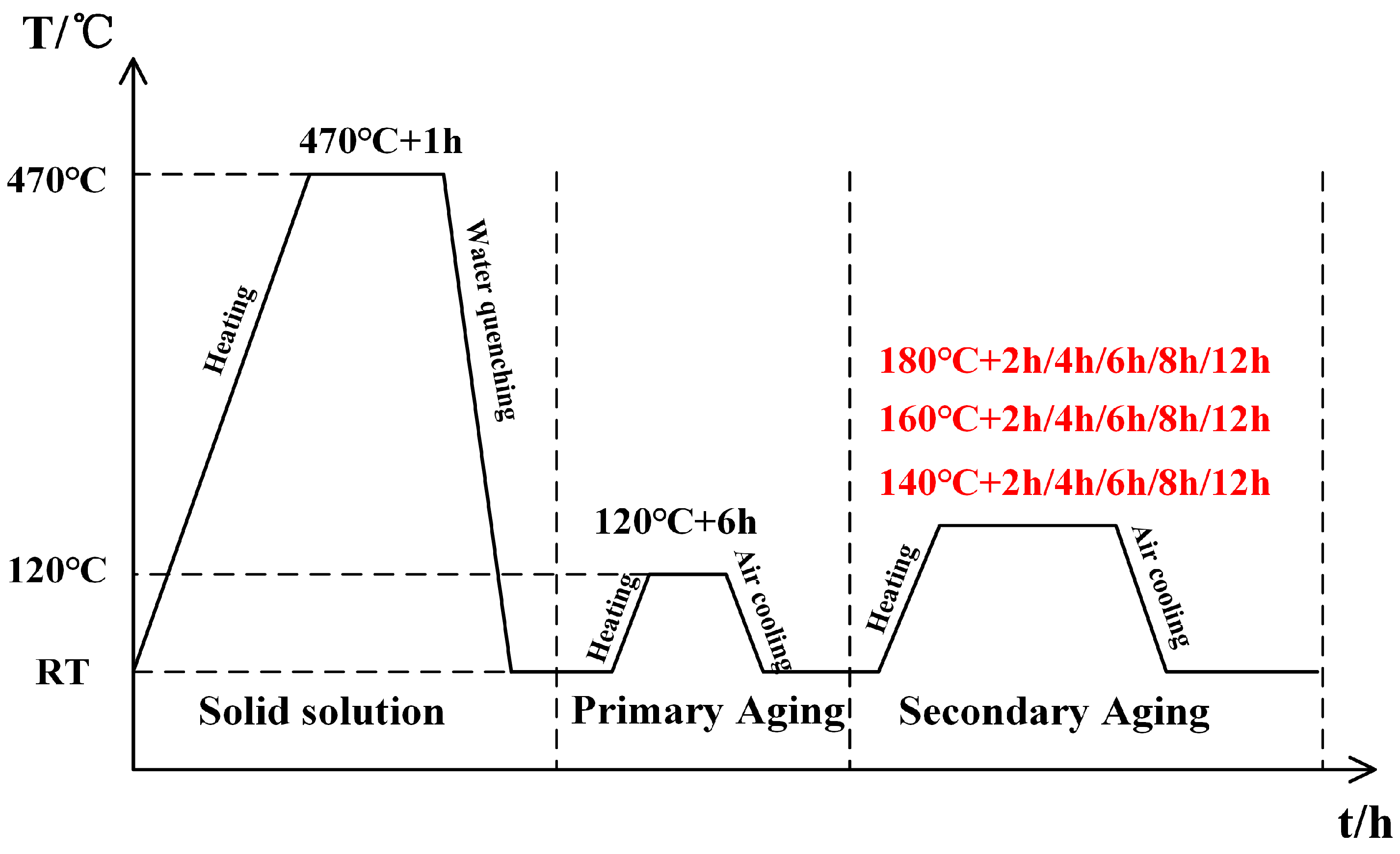
2.1. Materials
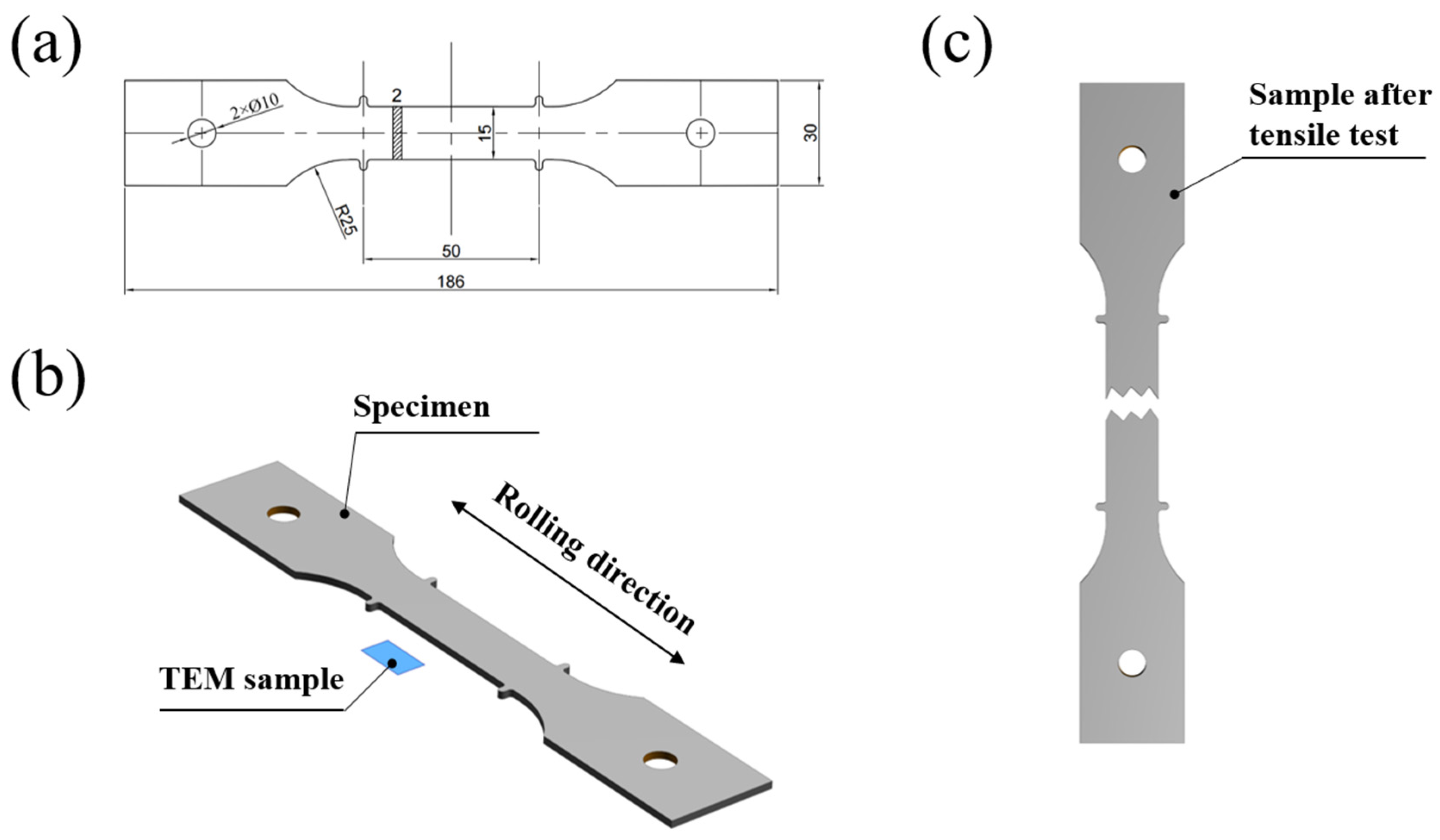
2.2. Mechanical Property Tests
2.3. Microstructure Characterization
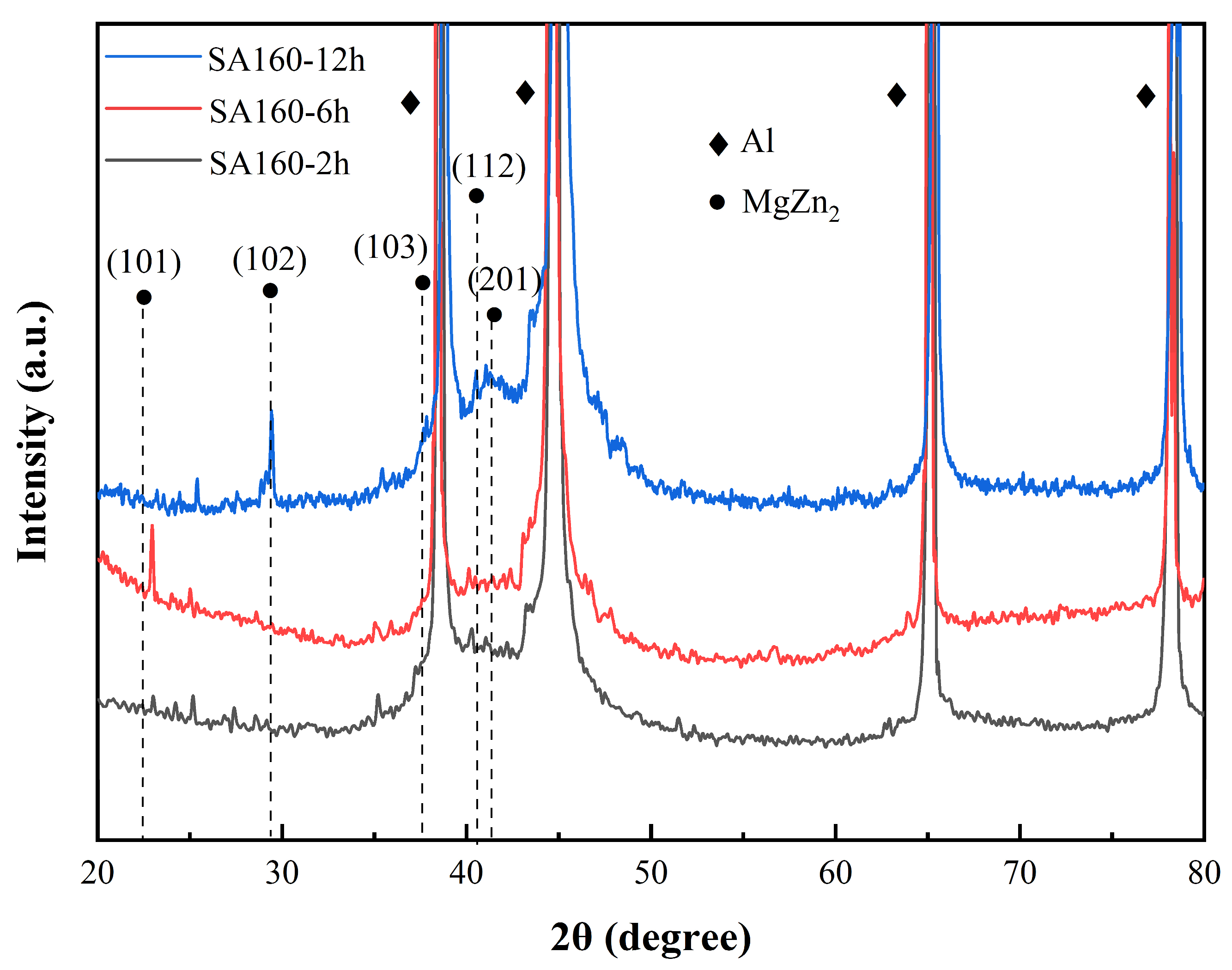
3. Results
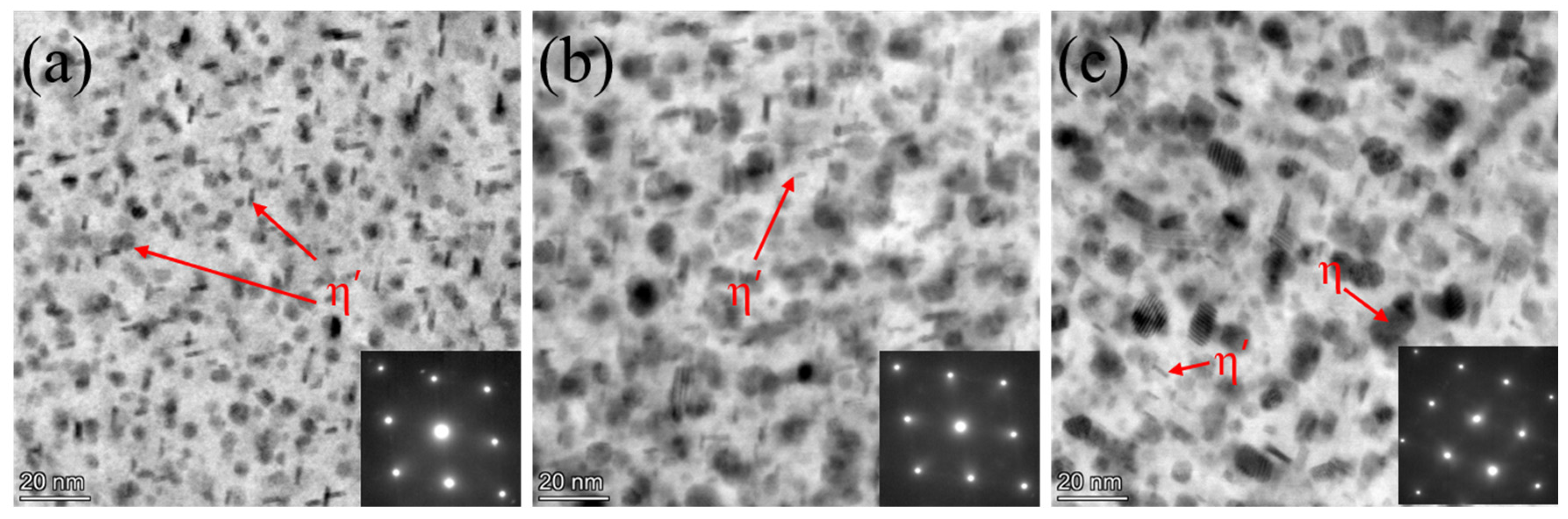
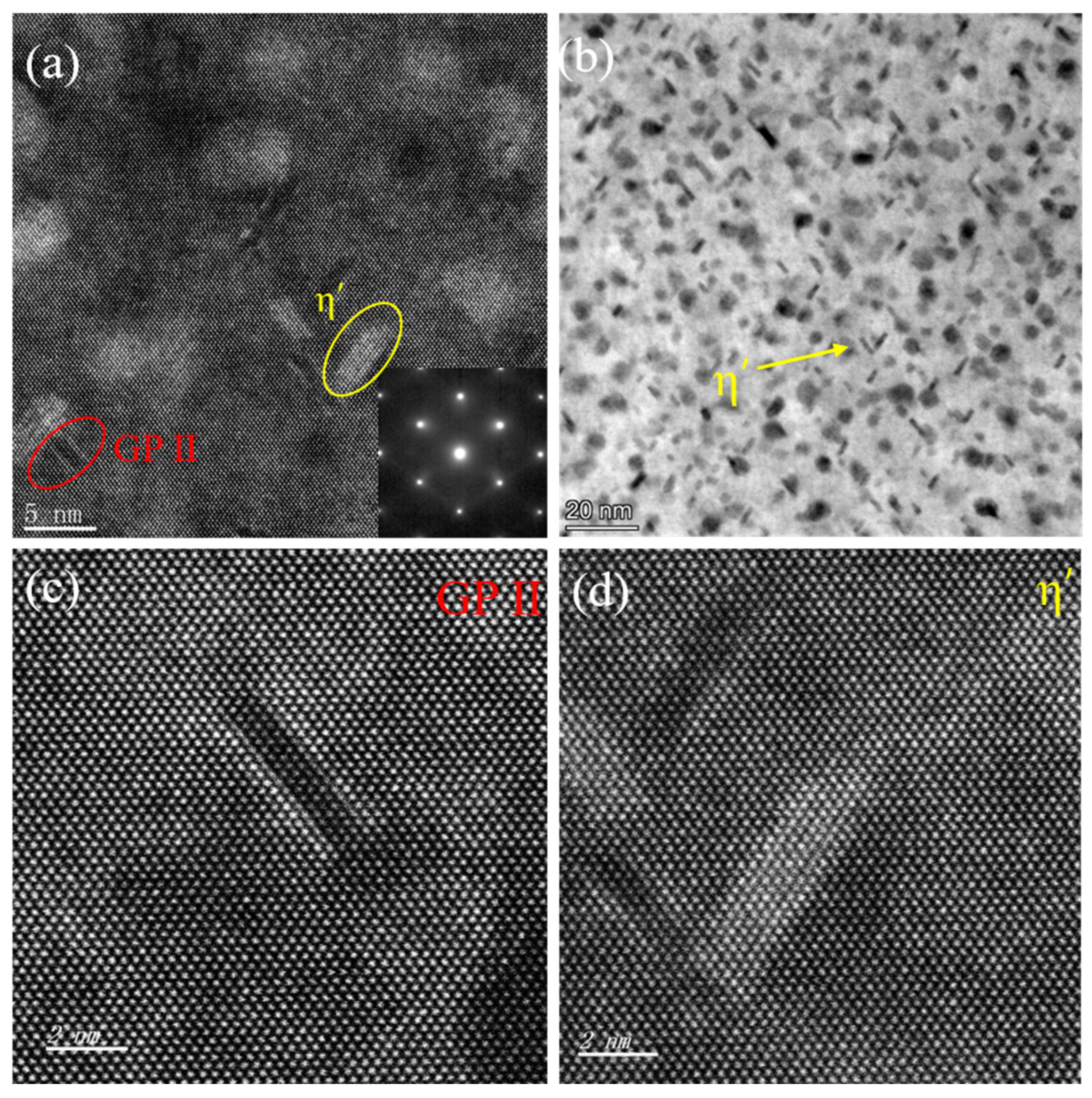
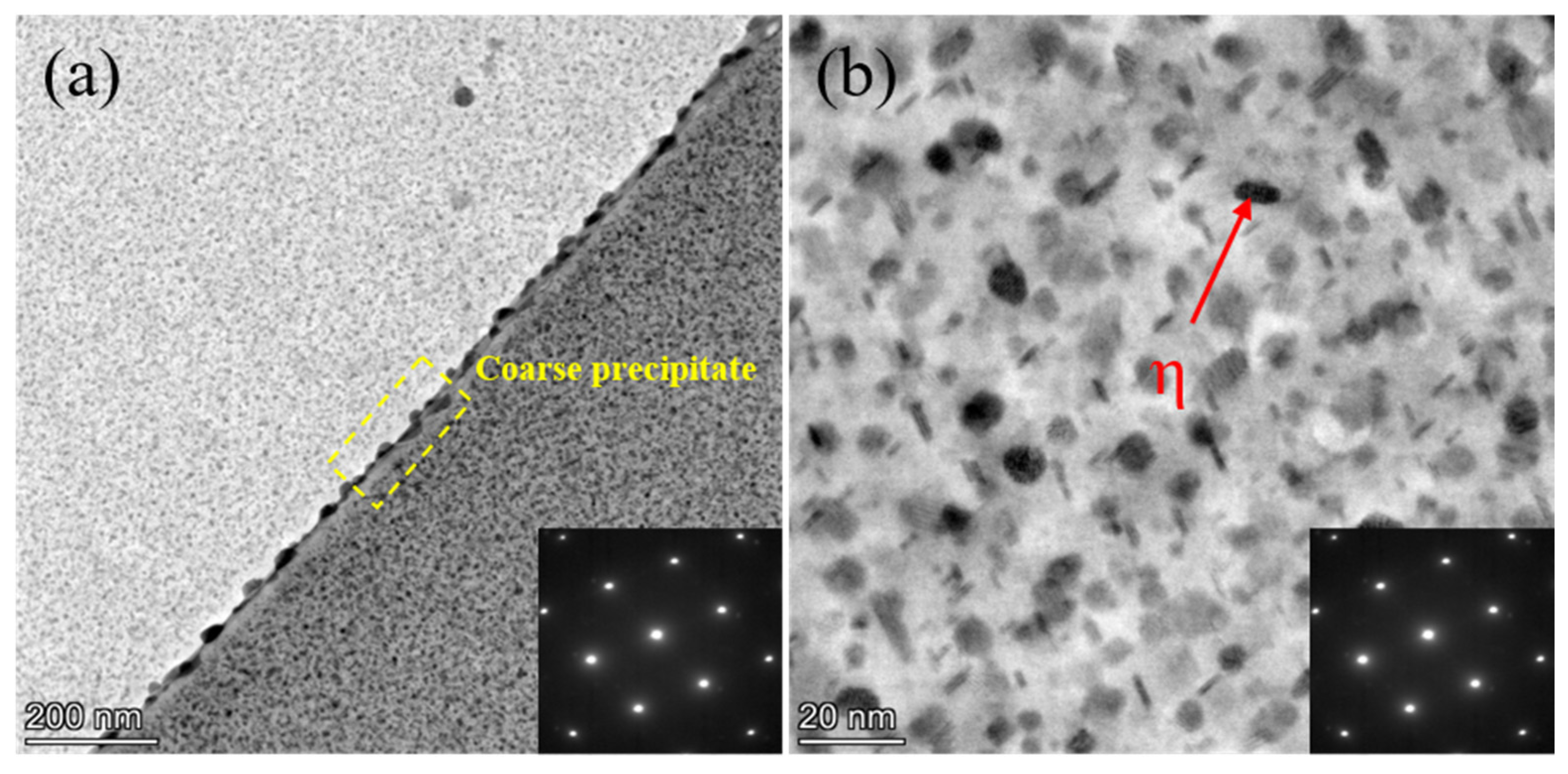
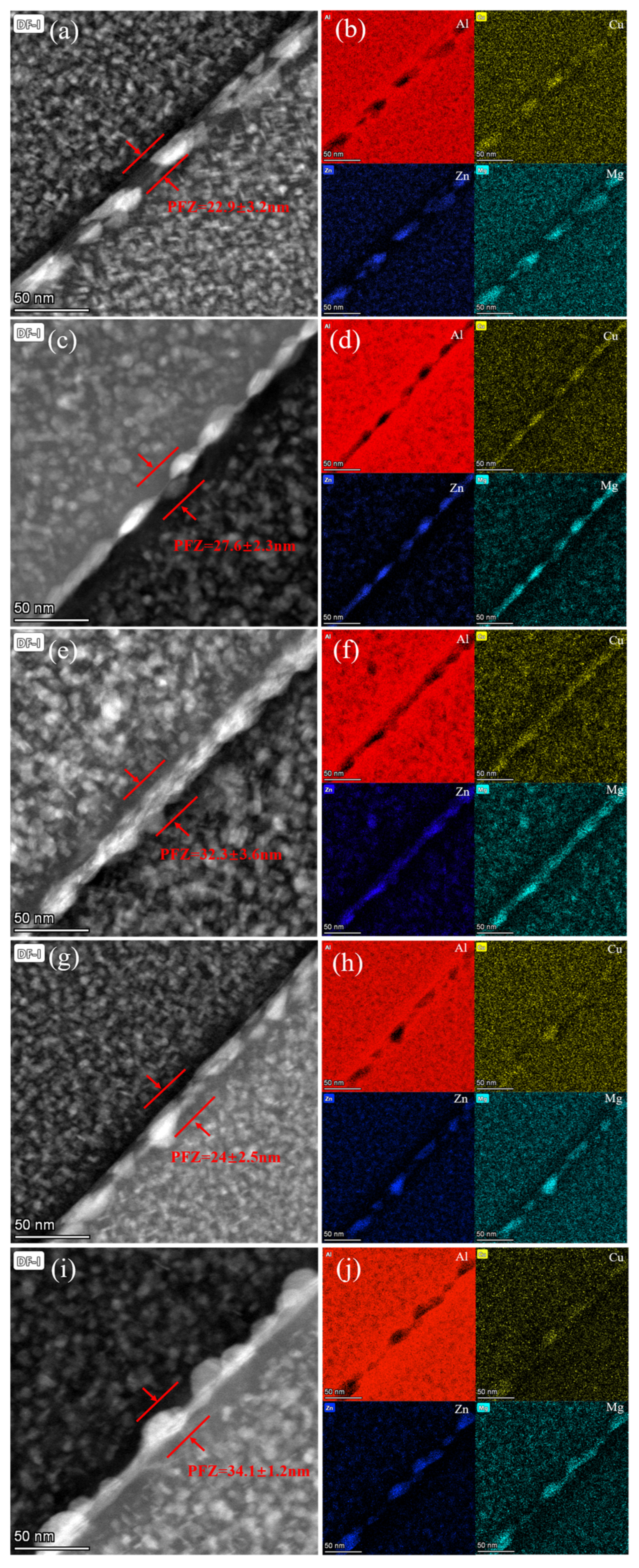
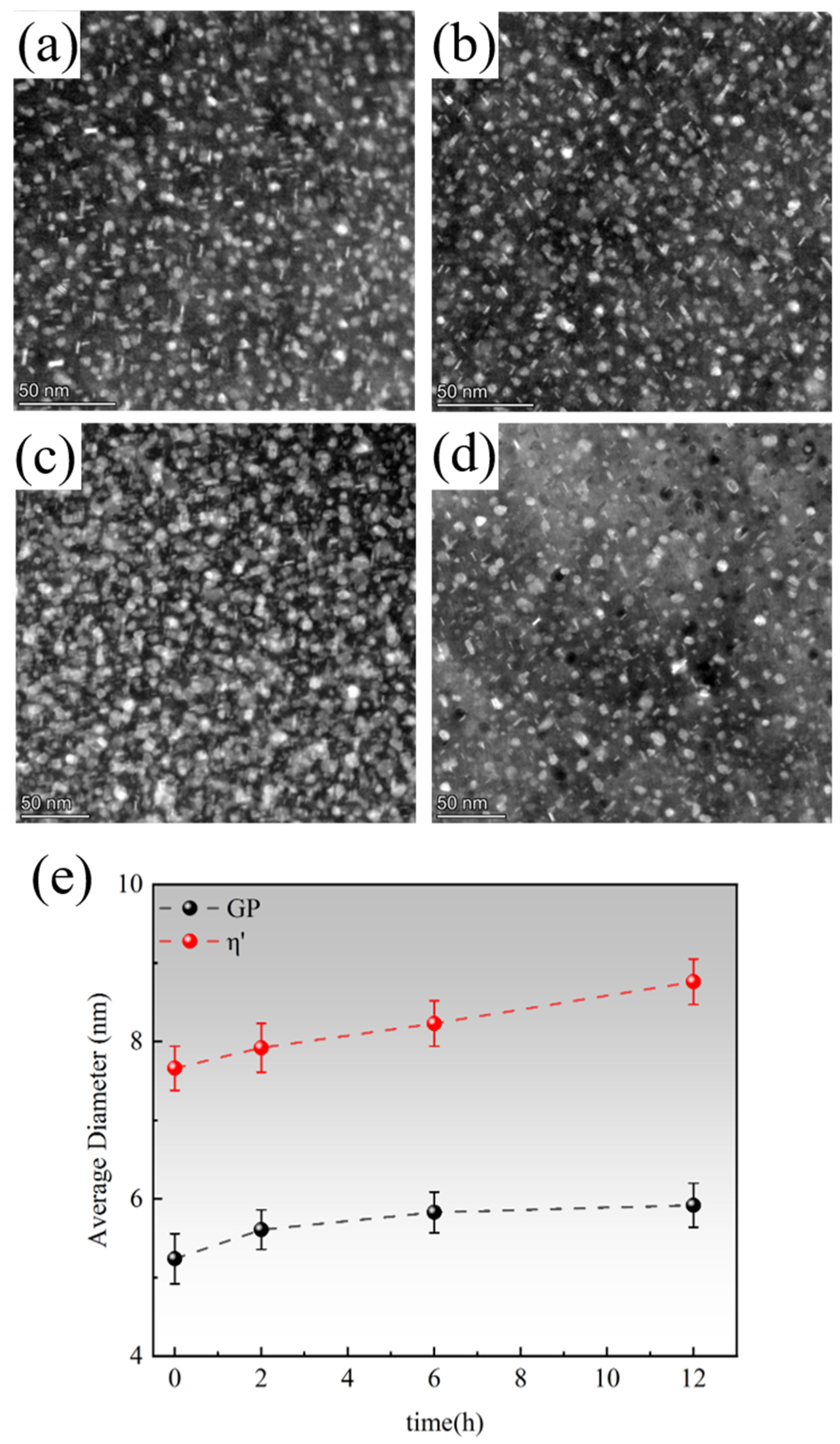
3.1. Microstructure of Two-Step Aging Samples
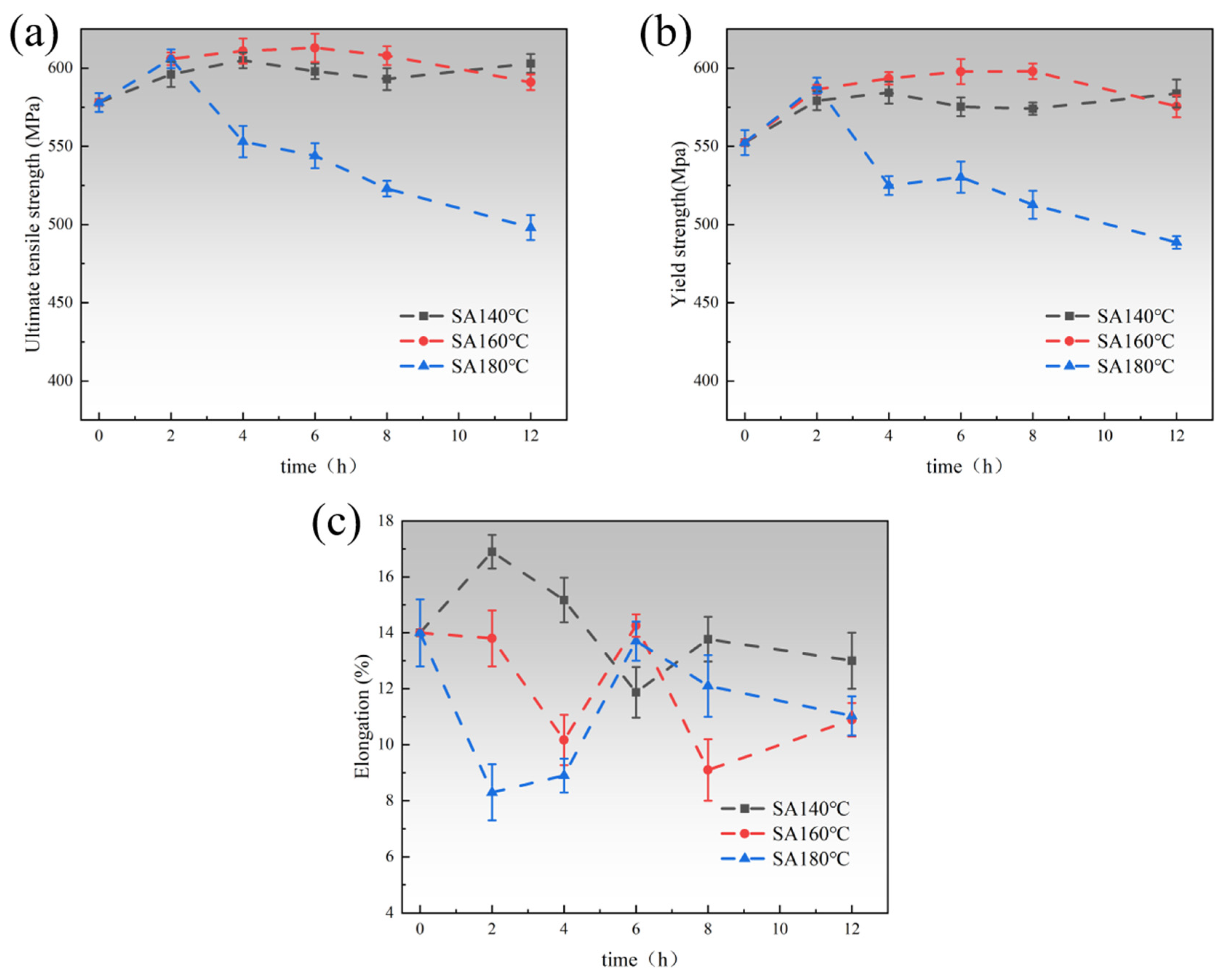
3.2. Mechanical Properties
4. Discussion
4.1. Microstructural Evolution
4.2. Microstructure and Properties
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- After the two-step aging treatment, the precipitates primarily consisted of the metastable η′ phase and the equilibrium η phase, with a relatively uniform distribution. Precipitate strengthening is the primary mechanism for strengthening the alloy, and a precipitation-free zone (PFZ) is clearly observed at the grain boundaries. Additionally, it was found that increasing the secondary aging temperature shortened the time required for the alloy to reach the peak-aging plateau.
- (2)
- Under the regulation of secondary aging temperatures (140 °C, 160 °C, 180 °C), the samples subjected to peak-aging at 160 °C exhibited the optimal overall performance (tensile strength of 613 MPa, yield strength of 589 MPa, and elongation of 14.26%). Additionally, it was observed that with the extension of aging time, the longest duration of the peak plateau period was 6 h at 160 °C, and elongation increased slightly during this period. This indicates that appropriately extending the secondary aging time at this temperature can enhance the plasticity and toughness of the material without a loss in strength.
- (3)
- A relatively short secondary aging time can result in the metastable η′ strengthening phase not having enough time to nucleate and grow, leading to a less pronounced aging strengthening effect. On the other hand, excessive prolongation of the secondary aging time results in the formation of a large number of equilibrium η phases. The larger size of the equilibrium η phase not only fails to strengthen the alloy but also consumes a large amount of zinc and magnesium, restricting the precipitation of the η′ phase during aging. Additionally, the widening of the PFZ around the coarse equilibrium η phases further reduces the mechanical properties of the alloy.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dong, Y.; Ye, L.; Tang, J.; Liu, X.; Sun, Q. The effects of temperature on the creep-aging behavior and mechanical properties of AA2050-T34 alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2020, 796, 140010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khamneh, M.E.; Askari-Paykani, M.; Shahverdi, H.; Hadavi, S.M.M.; Emami, M. Optimization of spring-back in creep age forming process of 7075 Al-Alclad alloy using D-optimal design of experiment method. Measurement 2016, 88, 278–286. [Google Scholar]
- Lam, A.C.L.; Shi, Z.; Lin, J.; Huang, X. Influences of residual stresses and initial distortion on springback prediction of 7B04-T651 aluminium plates in creep-age forming. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2015, 103, 115–126. [Google Scholar]
- Dorward, R.C.; Pritchett, T.R. Advanced aluminium alloys for aircraft and aerospace applications. Mater. Des. 1988, 9, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, J.R. Aluminum and Aluminum Alloys; ASM International: Novelty, OH, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Österreicher, J.A.; Grabner, F.; Tunes, M.A.; Coradini, D.S.R.; Pogatscher, S.; Schlög, C.M. Two step–ageing of 7xxx series alloys with an intermediate warm-forming step. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2021, 12, 1508–1515. [Google Scholar]
- Wolverton, C. Crystal structure and stability of complex precipitate phases in Al–Cu–Mg–(Si) and Al–Zn–Mg alloys. Acta Mater. 2001, 49, 3129–3142. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.F.; Peng, Z.; Li, C.X.; Jia, Z.Q.; Chen, W.J.; Zheng, Z.Q. Mechanical properties, corrosion behaviors and microstructures of 7075 aluminium alloy with various aging treatments. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2008, 18, 755–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Österreicher, J.A.; Tunes, M.A.; Grabner, F.; Arnoldt, A.; Kremmer, T.; Pogatscher, S.; Schlögl, C.M. Warm-forming of pre-aged Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloy sheet. Mater. Des. 2020, 193, 108837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Lei, C.; Tang, H.; Wang, Q. Double-step aging treatment of high strength Al-5 Mg-3Zn-1Cu (wt%) cast alloy. Mater. Lett. 2022, 322, 132514. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Cheng, X.; Ding, L.; Weng, Y.; Yin, J.; Yao, H.; Yu, H. Effect of multi-stage aging on the precipitation strengthening and mechanical properties for an Al-Mg-Si-Ag alloy. Mater. Charact. 2022, 190, 112004. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, J.; Su, R.; Li, G.; Qu, Y. Effect of secondary aging on microstructure and properties of cast Al–Cu–Mg–Ag alloy. Int. J. Met. 2024, 18, 2268–2282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Wang, L.; Ren, Y.; He, B.; Han, S.; Xu, P. Effect of precipitates evolution on mechanical properties of Al 7050 alloy during secondary aging. Mater. Res. Express 2023, 10, 076502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.S.; Koh, D.H.; Kim, H.W.; Ahn, Y.S. Improved bake-hardening response of Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloy through pre-aging treatment. Scr. Mater. 2018, 147, 45–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stemper, L.; Tunes, M.A.; Dumitraschkewitz, P.; Mendez-Martin, F.; Tosone, R.; Marchand, D.; Curtin, W.A.; Uggowitzer, P.J.; Pogatscher, S. Giant hardening response in AlMgZn (Cu) alloys. Acta Mater. 2021, 206, 116617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lumley, R.N.; Polmear, I.J.; Morton, A.J. Temper developments using secondary ageing. Mater. Forum 2004, 28, 85–95. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Y.; Jiang, F.; Zhang, H.; Su, J.; Yuan, W. Residual stress relief in Al–Zn–Mg–Cu alloy by a new multistage interrupted artificial aging treatment. Mater. Des. 2016, 92, 281–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, S.; Wang, R.; Peng, C.; Cai, Z.; Peng, X.; Li, Z.; Wu, Z. Enhancing the strength and ductility of rapidly-solidified 2196 Al-Li alloy through multi-stage ageing treatments. Vacuum 2025, 238, 114235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Liu, K.; Su, R.; Li, G.; Qu, Y. The Effect of Multi-Stage Aging Treatment on the Microstructure and Properties of 7075 Aluminum Alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2025, 1032, 181143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clinch, M.R.; Daval, R.; Harris, S.J.; Hepples, W.; Holroyd, N.J.H.; Lawday, M.J.; Noble, B. A Microstructural Engineering-Based Approach to 7 xxx Series Alloy Optimisation. Mater. Forum 2004, 28, 145–151. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Luo, B.; Bai, Z.; He, C.; Jiang, G. Effect of pre-ageing on nucleating of GP zones and precipitation, strength and stress corrosion properties of 7N01 alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2024, 980, 173681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.H.; Xiong, B.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, B.; Wang, F.; Liu, H. Investigation on strength, toughness and microstructure of an Al–Zn–Mg–Cu alloy pre-stretched thick plates in various ageing tempers. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2009, 209, 2021–2027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.H.; Xiong, B.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, B.; Wang, F.; Liu, H. Effects of the two-step ageing treatment on the microstructure and properties of 7B04 alloy pre-stretched thick plates. Rare Met. 2007, 26, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azarniya, A.; Taheri, A.K.; Taheri, K.K. Recent advances in ageing of 7xxx series aluminum alloys: A physical metallurgy perspective. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 781, 945–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Wei, H.B.; Xu, X.J.; Zhou, Q.; Han, M.N.; Sha, S.H. Microstructure and mechanical properties of a highly alloyed Al–Zn–Mg–Cu–Zr alloy under T6I4 and T6R6I4 agings. Met. Mater. Int. 2024, 30, 857–871. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, Q.; Feng, S.; Chen, F.; Wang, D.; Zhan, L.; Yang, Y.; Tang, L.; Liu, C.; Yan, D. Improving creep-aging behavior and mechanical properties of AA7150 alloy via pre-aging. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2024, 894, 146130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Ji, S.; Wang, M.; Li, Z. Precipitation behaviour of Al–Zn–Mg–Cu alloy and diffraction analysis from η′ precipitates in four variants. J. Alloys Compd. 2014, 610, 623–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sha, G.; Cerezo, A. Early-stage precipitation in Al–Zn–Mg–Cu alloy (7050). Acta Mater. 2004, 52, 4503–4516. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, F.; Qin, Z. Effect of two-stage aging on hardness and electrical conductivity of as-extruded 7075 aAluminum Alloy. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2021, 1885, 042035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Bai, S.; Huang, T.; Wang, J.; Xie, H.; Zeng, D.; Luo, L. Effect of various aging treatment on thermal stability of a novel Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloy for oil drilling. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2021, 803, 140490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.; Cao, L.; Wu, X.; Tang, S.; Guo, M. Synergetic effect of natural ageing and pre-stretching on the ageing behavior in T′/η′ phase-strengthened Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloys. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2023, 146, 240–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Zhen, L.; Yang, S.; Shao, W.; Dai, S. Investigation of precipitation behavior and related hardening in AA 7055 aluminum alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2009, 500, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawabata, T.; Izumi, O. Ductile fracture in the interior of precipitate free zone in an Al-6.0% Zn-2.6% Mg alloy. Acta Metall. 1976, 24, 817–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Du, Z.; Su, J.; Tang, J.; Jiang, F.; Fu, D.; Teng, J.; Zhang, H. Effect of quenching residual stress on precipitation behaviour of 7085 aluminium alloy. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2023, 132, 154–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Xiao, D.; Yuan, S.; Huang, Y.; Li, Z.; Yin, X.; Wang, J.; Huang, L.; Liu, W. Healing the high-temperature-retrogression-caused wide precipitation-free zones in Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloy via strain-aging induced precipitates. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2024, 917, 147398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marceau, R.K.W.; Sha, G.; Lumley, R.N.; Ringer, S.P. Evolution of solute clustering in Al–Cu–Mg alloys during secondary ageing. Acta Mater. 2010, 58, 1795–1805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.W.; Chen, J.H.; Li, J.Y.; Wu, C.L.; Yang, X.B. Effect of pre-deformation on quench-induced inhomogeneity of microstructure and hardness in 7050 aluminum alloy. Mater. Charact. 2019, 158, 110005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Li, H.; Cai, P.; Fu, X.; Feng, Z.; Zhang, L.; Wang, J.; Xiao, N. Effect of aging route on the precipitation behavior and thermal stability of Al–Cu–Mg–Ag alloy. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2023, 23, 2010–2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Li, C.; Liu, S.; Deng, Y.; Zhang, X. Effect of homogenization time on quench sensitivity of 7085 aluminum alloy. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2014, 24, 2275–2281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chobaut, N.; Carron, D.; Arsène, S.; Schloth, P.; Drezet, J.M. Quench induced residual stress prediction in heat treatable 7xxx aluminium alloy thick plates using Gleeble interrupted quench tests. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2015, 222, 373–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steele, D.; Evans, D.; Nolan, P.; Lloyd, D.J. Quantification of grain boundary precipitation and the influence of quench rate in 6XXX aluminum alloys. Mater. Charact. 2007, 58, 40–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afifi, M.A.; Wang, Y.C.; Langdon, T.G. Effect of dynamic plastic deformation on the microstructure and mechanical properties of an Al–Zn–Mg alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2020, 784, 139287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bignon, M.; Ma, Z.; Robson, J.D.; Shanthraj, P. Interactions between plastic deformation and precipitation in Aluminium alloys: A crystal plasticity model. Acta Mater. 2023, 247, 118735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.; Pan, Q.; Liu, B.; Hu, Q.; Qu, L.; Wang, W.; Wang, X. Effects of co-addition of minor Sc and Zr on aging precipitates and mechanical properties of Al–Zn–Mg–Cu alloys. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2023, 22, 2944–2954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.H.; Jung, J.G.; Baik, S.I.; Seidman, D.N.; Kim, M.S.; Lee, Y.K.; Euh, K. Precipitation strengthening in naturally aged Al–Zn–Mg–Cu alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2021, 803, 140719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, H.; Topping, T.D.; Isheim, D.; Seidman, D.N.; Lavernia, E.J. Strengthening mechanisms in a high-strength bulk nanostructured Cu–Zn–Al alloy processed via cryomilling and spark plasma sintering. Acta Mater. 2013, 61, 2769–2782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heo, J.G.; Lee, Y.S.; Kim, M.S.; Kim, H.W.; Kim, Y.D. Effect of pre-aging treatment on bake-hardenability of Al-8.0 Zn-2.5 Mg-2.0 Cu alloy sheet fabricated by twin-roll casting process. Korean J. Met. Mater. 2019, 57, 396–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.H.; Jung, J.G.; Baik, S.I.; Park, S.H.; Kim, M.S.; Lee, Y.K.; Euh, K. Effects of Ti addition on the microstructure and mechanical properties of Al–Zn–Mg–Cu–Zr alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2021, 801, 140437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Hou, H.; Shao, W.; Yang, J.; Wang, Z.; Yang, Q.; LLorca, J. Revisiting the precipitation mechanisms of Guinier-Preston zones, η′, and η precipitates in Al-Zn-Mg alloys. Acta Mater. 2024, 268, 119789. [Google Scholar]
- Xiang, K.; Ding, L.; Jia, Z.; Yang, X.; Liu, Q.; Hao, Z. Phase transition induced by synchroshear in Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloy. Scr. Mater. 2022, 212, 114577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Zhan, L.; Xu, Y.; Ma, B.; Zeng, Q.; Luo, S. Optimizing strength and ductility in 7150 Al alloys via rapid electropulsing cyclic heat treatment. J. Alloys Compd. 2022, 903, 163985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Zhan, L.; Yu, W. Rapidly modifying microstructure and mechanical properties of AA7150 Al alloy processed with electropulsing treatment. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2021, 95, 172–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Zn | Mg | Cu | Mn | Fe | Si | Ni | Cr | Ti | Al |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6.1 | 2.19 | 2.19 | <0.01 | 0.083 | 0.048 | <0.01 | 0.16 | 0.025 | Bal. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, F.; Wang, H.; Jiang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Zeng, Q. Effect of Secondary Aging Conditions on Mechanical Properties and Microstructure of AA7150 Aluminum Alloy. Materials 2025, 18, 4763. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18204763
Chen F, Wang H, Jiang Y, Liu Y, Zhou Q, Zeng Q. Effect of Secondary Aging Conditions on Mechanical Properties and Microstructure of AA7150 Aluminum Alloy. Materials. 2025; 18(20):4763. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18204763
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Fei, Han Wang, Yanan Jiang, Yu Liu, Qiang Zhou, and Quanqing Zeng. 2025. "Effect of Secondary Aging Conditions on Mechanical Properties and Microstructure of AA7150 Aluminum Alloy" Materials 18, no. 20: 4763. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18204763
APA StyleChen, F., Wang, H., Jiang, Y., Liu, Y., Zhou, Q., & Zeng, Q. (2025). Effect of Secondary Aging Conditions on Mechanical Properties and Microstructure of AA7150 Aluminum Alloy. Materials, 18(20), 4763. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18204763






