Influence and Mechanism of Azodicarbonamide Expansive Agent on the Workability, Mechanical Strength and Plastic Shrinkage of UHPC
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Program
2.1. Raw Materials
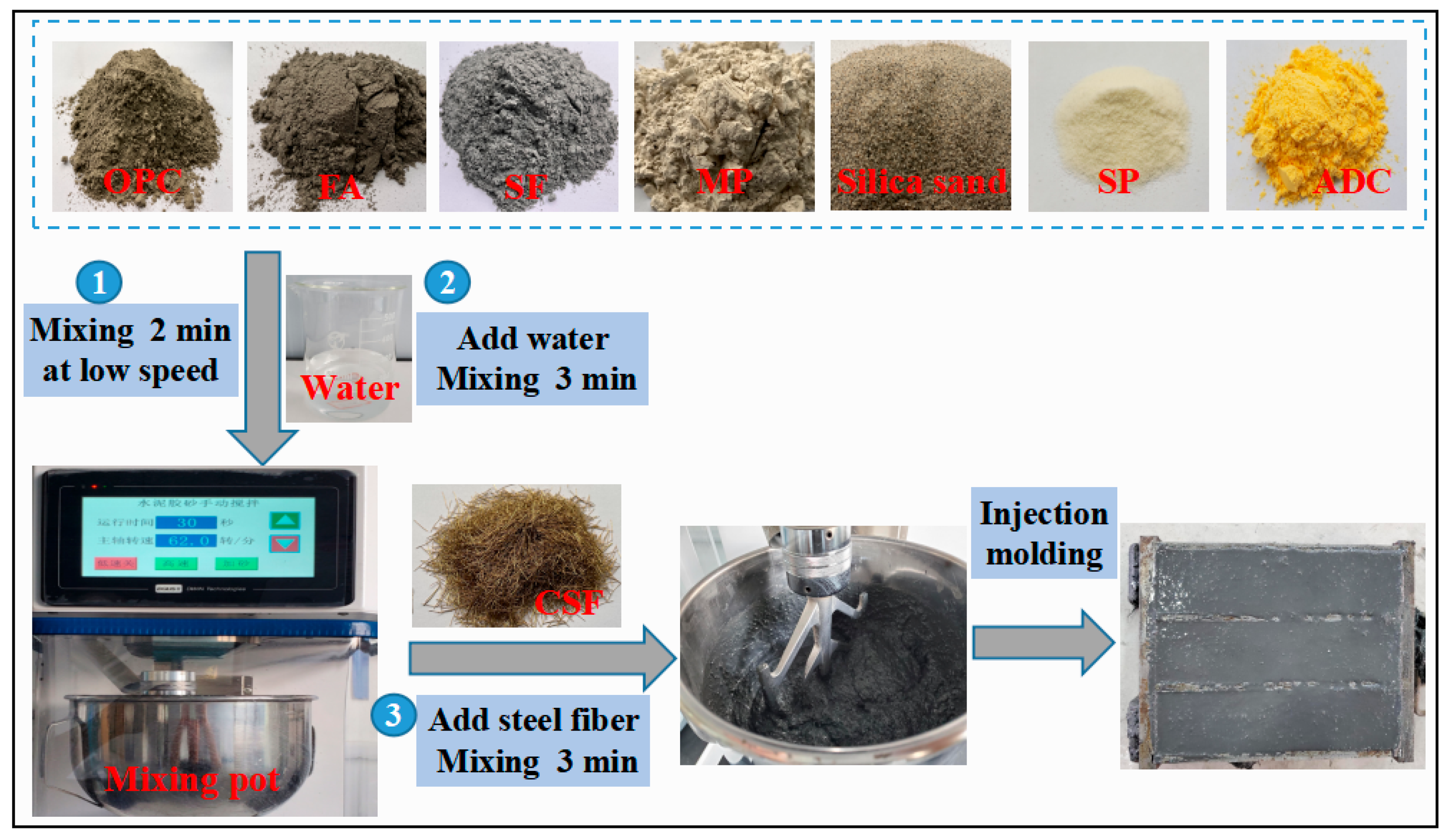
2.2. Mix Proportion and Specimen Preparation
2.3. Testing Method
2.3.1. Workability Tests
2.3.2. Mechanical Properties
2.3.3. Vertical Expansion Rate
2.3.4. Pore Structure Parameters
2.3.5. SEM Analysis
3. Results and Discussions
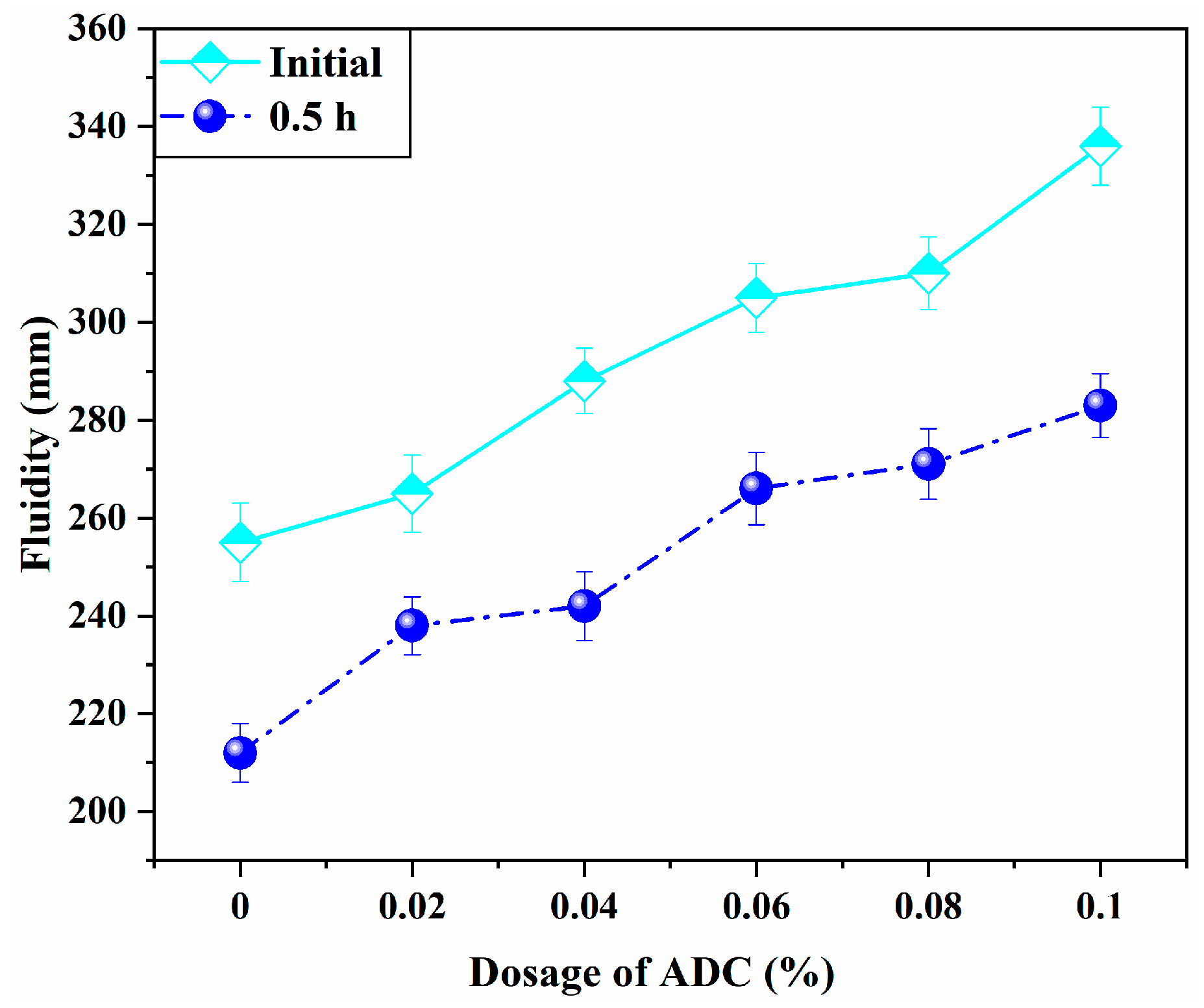
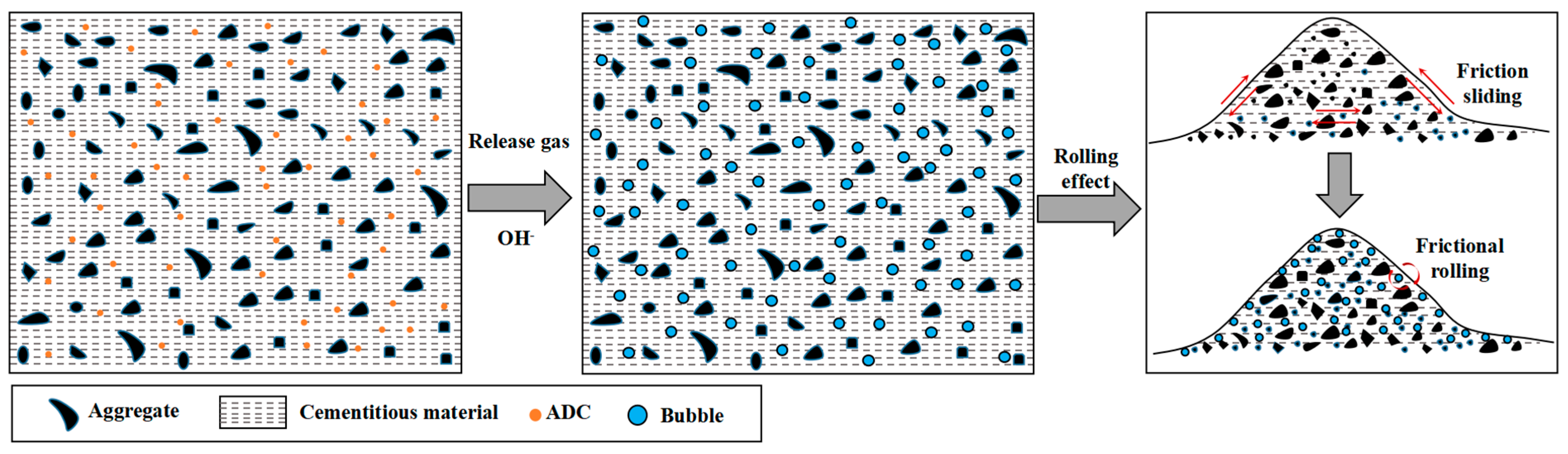
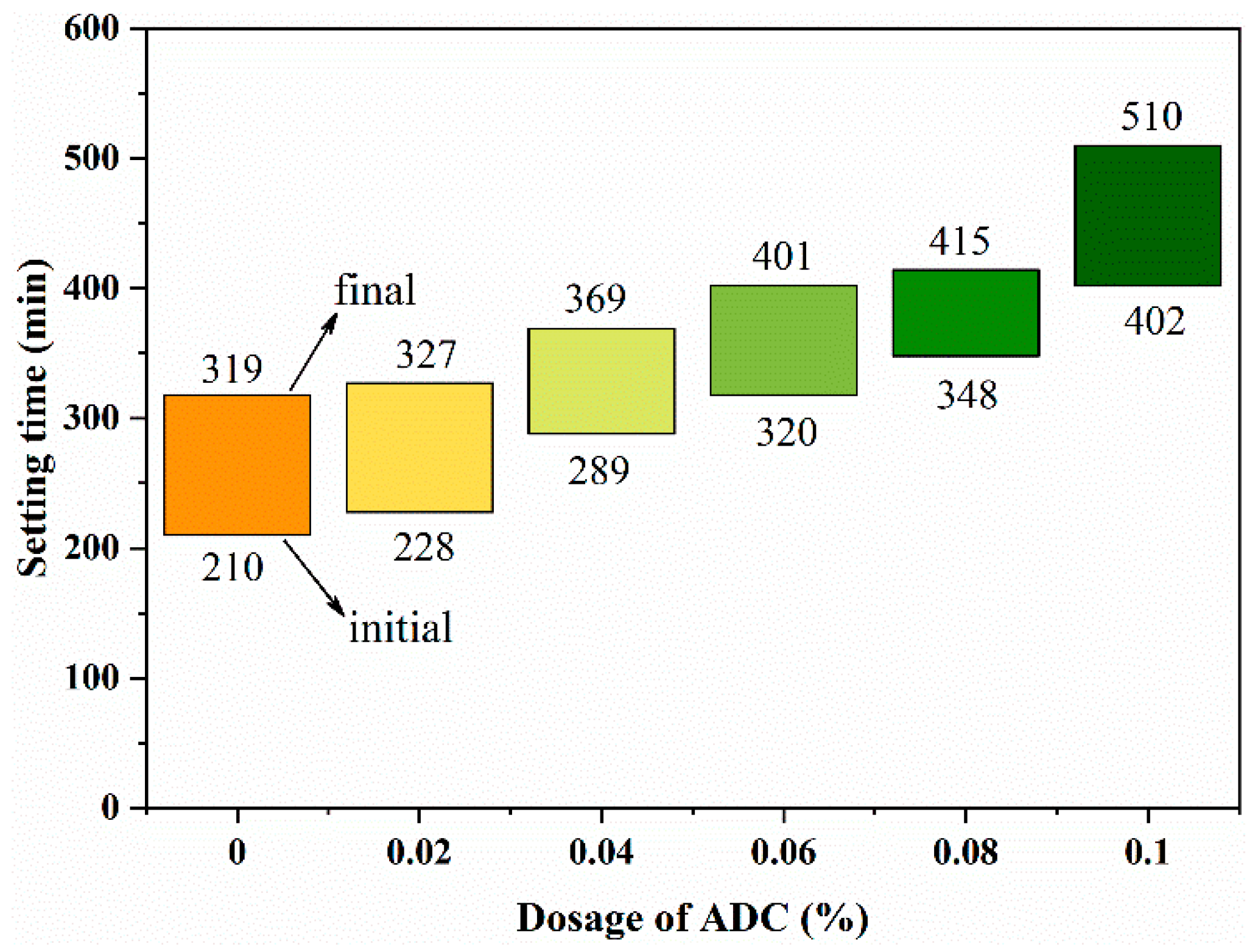
3.1. Effects of ADC on the Fluidity and Setting Time of UHPC
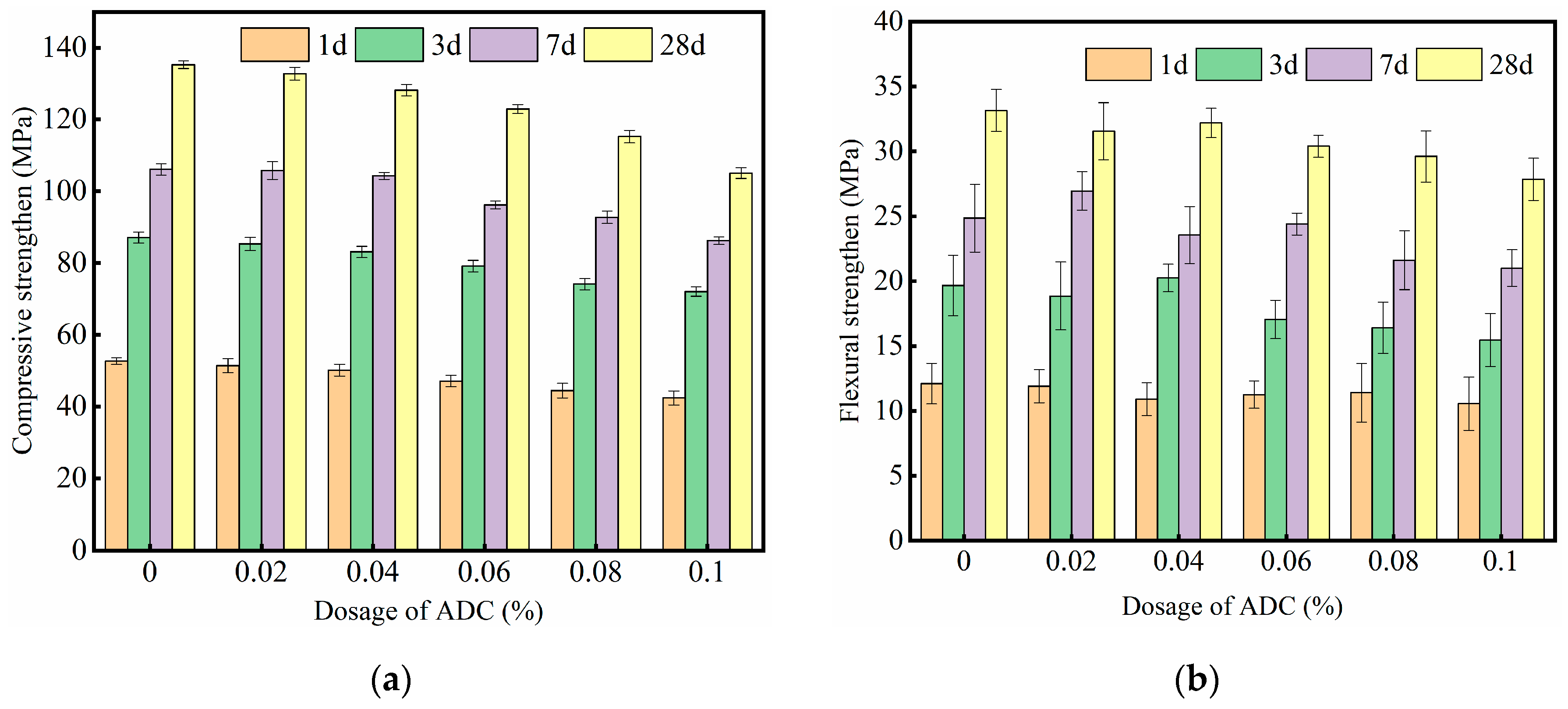
3.2. Effect of ADC on the Mechanical Properties of UHPC
3.3. Effect of ADC on the Vertical Expansion Rate of UHPC
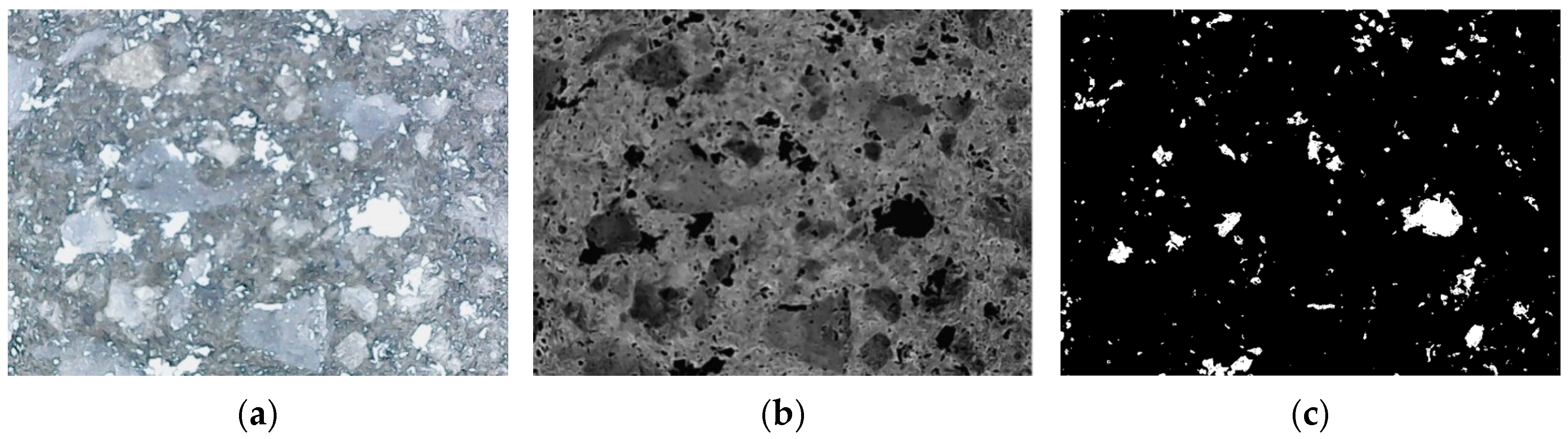
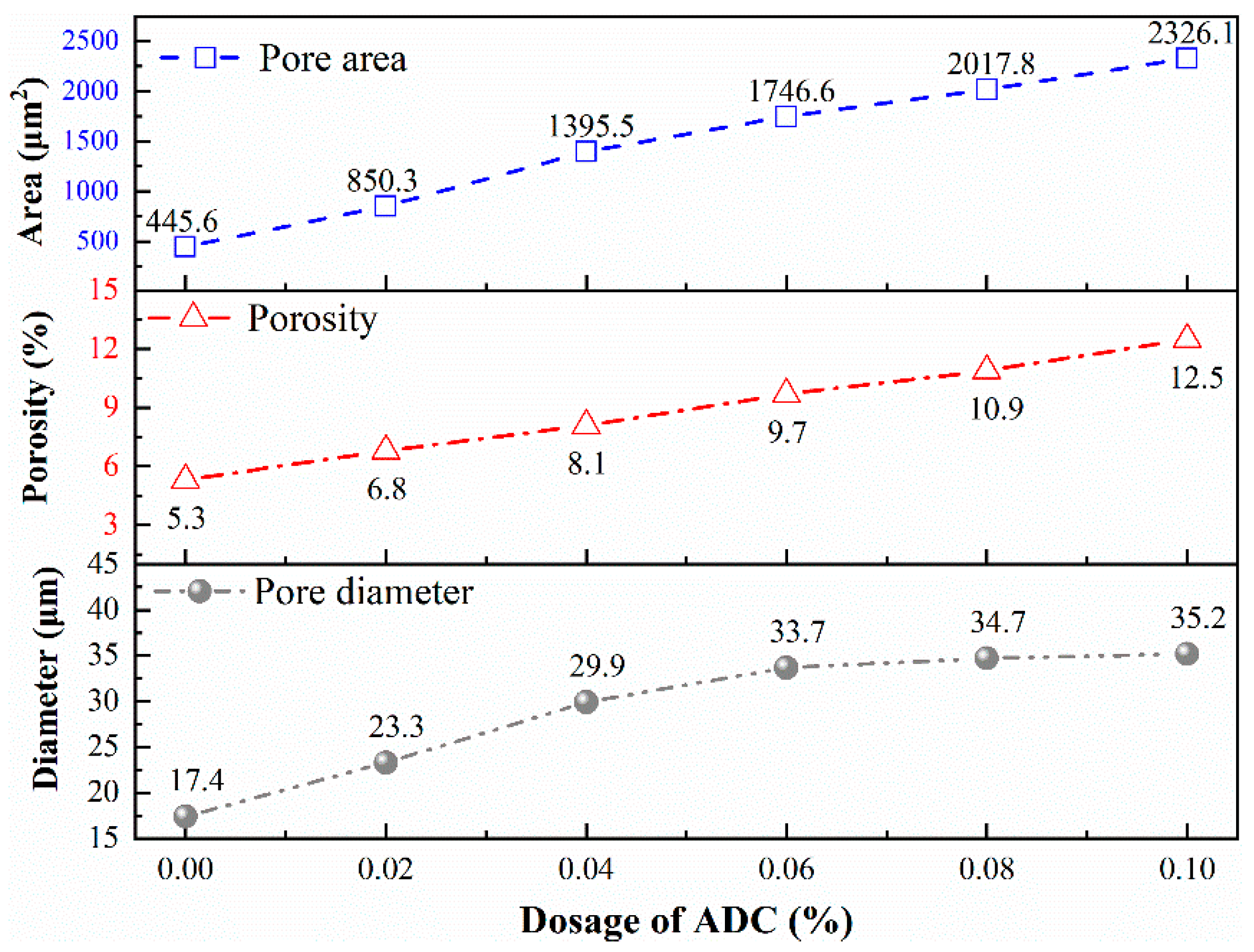
3.4. Effect of ADC on the Pore Structure of UHPC
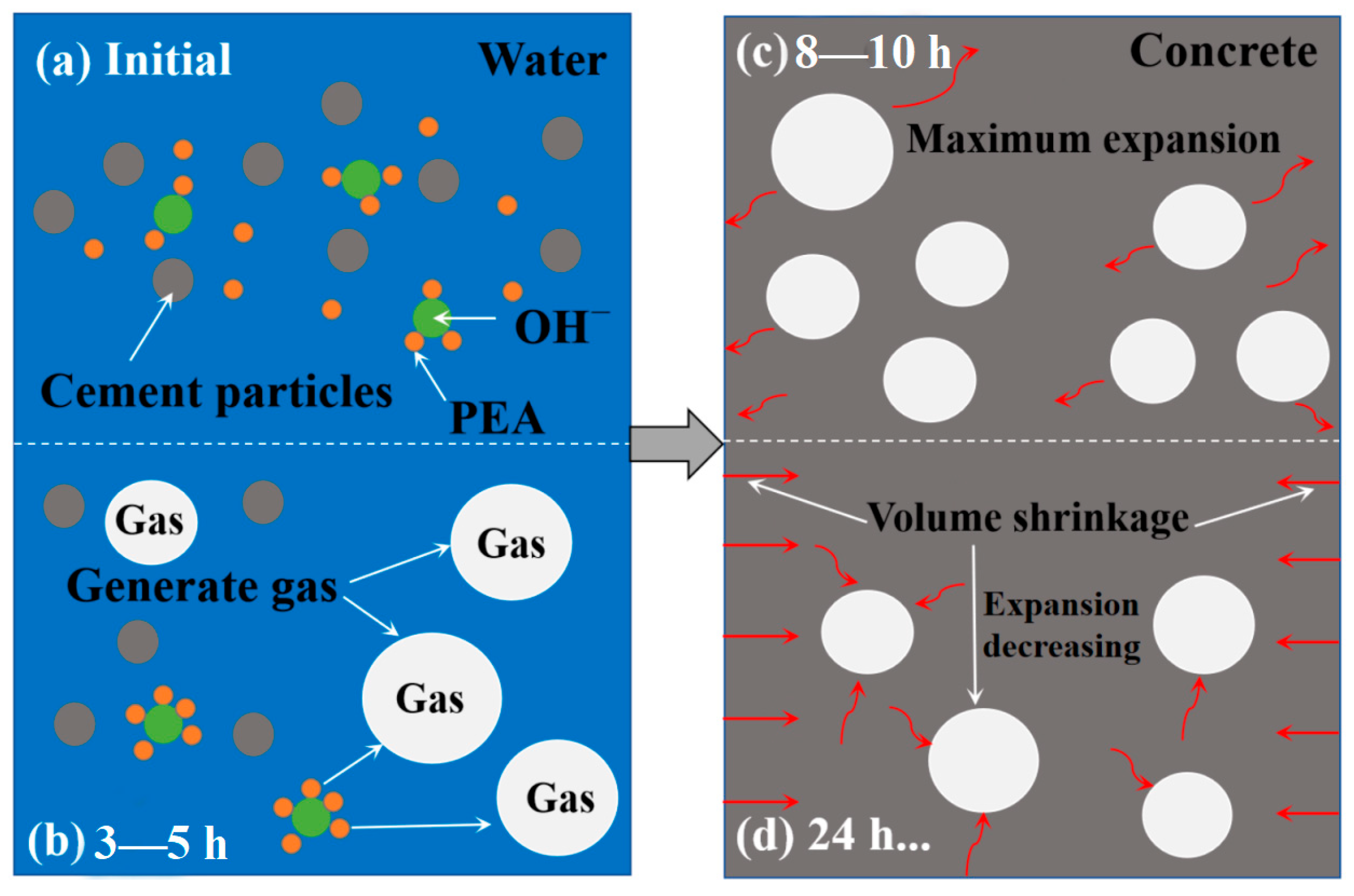
3.5. Effect of ADC on the Microstructure of UHPC
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hooton, R.D. Future directions for design, specification, testing, and construction of durable concrete structures. Cem. Concr. Res. 2019, 124, 105827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.J.; He, X.; Deng, X.; Wu, Y.; Zheng, Z.; Liu, J.; Hui, D. Application of nanomaterials in ultra-high performance concrete: A review. Nanotechnol. Rev. 2020, 9, 1427–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Meng, W.; Khayat, K.H.; Bao, Y.; Guo, P.; Lyu, Z.; Abu-Obeidah, A.; Nassif, H.; Wang, H. New development of ultra-high-performance concrete (UHPC). Compos. Part B-Eng. 2021, 224, 109220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhnoukh, A.K.; Chelsea, B. Ultra-high-performance concrete: Constituents, mechanical properties, applications and current challenges. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2021, 15, e00559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, C.C.; El-Tawil, S.; Chao, S.H. A review of developments and challenges for UHPC in structural engineering: Behavior, analysis, and design. J. Struct. Eng. 2021, 147, 03121001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Hussein, H.H.; Liu, J.; Chen, G. Experimental study and theoretical prediction on shrinkage-induced restrained stresses in UHPC-RC composites under normal curing and steam curing. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2020, 110, 103602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wei, Y.; Ma, L.; Wang, L. Restrained shrinkage behavior of internally-cured UHPC using calcined bauxite aggregate in the ring test and UHPC-concrete composite slab. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2022, 134, 104805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, D.; Xia, C.; Xu, S.; Zhang, C.; Jia, X. Effect of concrete composition on drying shrinkage behavior of ultra-high performance concrete. J. Build. Eng. 2022, 62, 105333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Fang, Z.; Huang, Z.; Wu, Y. Solving shrinkage problem of ultra-high-performance concrete by a combined use of expansive agent, super absorbent polymer, and shrinkage-reducing agent. Compos. Part B-Eng. 2022, 230, 109503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, L.; Teng, L.; Tang, F.; Khayat, K.H.; Chen, G.; Meng, W. Corrosion of steel rebar embedded in UHPC beams with cracked matrix. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 313, 125589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Shi, C.; Wu, Z.; Xiao, J.; Huang, Z.; Fang, Z. A review on ultra high performance concrete: Part II. Hydration, microstructure and properties. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 96, 368–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Ye, G. Examining the “time-zero” of autogenous shrinkage in high/ultra-high performance cement pastes. Cem. Concr. Res. 2017, 97, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Ding, X.; Wang, Q.; Zheng, X. Effective solution for low shrinkage and low permeability of normal strength concrete using calcined zeolite particles. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 160, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Yang, S.; Hang, M.; Yang, T. Optimization design of ultrahigh-performance concrete based on interaction analysis of multiple factors. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2022, 16, e00858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habert, G.; Denarié, E.; Šajna, A.; Rossi, P. Lowering the global warming impact of bridge rehabilitations by using Ultra High Performance Fibre Reinforced Concretes. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2013, 38, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Shi, C.; Wu, Z. Mitigation techniques for autogenous shrinkage of ultra-high-performance concrete—A review. Compos. Part B-Eng. 2019, 178, 107456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soliman, A.M.; Nehdi, M.L. Effect of natural wollastonite microfibers on early-age behavior of UHPC. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2012, 24, 816–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, D.Y.; Banthia, N.; Yoon, Y.S. Effectiveness of shrinkage-reducing admixture in reducing autogenous shrinkage stress of ultra-high-performance fiber-reinforced concrete. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2015, 64, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, W.; Khayat, K. Effects of saturated lightweight sand content on key characteristics of ultra-high-performance concrete. Cem. Concr. Res. 2017, 101, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, D.Y.; Kim, S.; Lee, J.Y.; You, I.; Lee, S.J. Implication of calcium sulfoaluminate-based expansive agent on tensile behavior of ultra-high-performance fiber-reinforced concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 217, 679–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Zhang, X.; Cheng, S.; Li, S.; Bao, M.; Qiao, L. Mechanical properties, hydration behavior and shrinkage deformation of ultra-high performance concrete (UHPC) incorporating MgO expansive agent. J. Build. Eng. 2024, 96, 110529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, D.Y.; Park, J.J.; Kim, S.W.; Yoon, Y.S. Combined effect of expansive and shrinkage-reducing admixtures on the properties of ultra high performance fiber-reinforced concrete. J. Compos. Mater. 2014, 48, 1981–1991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, Q. Engineering performance and expansion mechanism of MgO expansion agent in ultra-high performance concrete (UHPC). J. Build. Eng. 2023, 68, 106079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, P.; Lu, J.X.; Zheng, H.; Lu, L.; Wang, F.; He, Y.; Hu, S. Expansive ultra-high performance concrete for concrete-filled steel tube applications. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2020, 114, 103813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, P.; Lu, L.; He, Y.; Wang, F.; Lu, J.; Zheng, H.; Hu, S. Investigation on expansion effect of the expansive agents in ultra-high performance concrete. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2020, 105, 103425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Huang, Z.; Hu, G.; Duan, W.H.; Shah, S.P. Early-age shrinkage development of ultra-high-performance concrete under heat curing treatment. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 131, 767–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Mo, L.; Deng, M.; Cheng, S. Mitigation on the autogenous shrinkage of ultra-high performance concrete via using MgO expansive agent. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 312, 125422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Li, S.; Cao, Y.Y.Y.; Yu, Q. Enhancing the interfacial bond of steel tube confined ultra-high performance concrete: Synergistic effects of coarse aggregate and expansive agent. J. Build. Eng. 2025, 104, 112228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Tan, X.; Wang, Y.; Bao, Y.; Meng, W. Reducing the cracking potential of ultra-high-performance concrete (UHPC) with the prewet expansive agent. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 431, 136597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, C.; Wang, Y.; Du, Y.; Wang, Q.; Yang, Q. Synergistic effects of multiscale MgO expansion agent and SAP on the mechanical and shrinkage properties of UHPC. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2024, 36, 04023610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matos, A.M.; Nunes, S.; Costa, C.; Barroso-Aguiar, J.L. Spent equilibrium catalyst as internal curing agent in UHPFRC. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2019, 104, 103362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valipour, M.; Khayat, K.H. Coupled effect of shrinkage-mitigating admixtures and saturated lightweight sand on shrinkage of UHPC for overlay applications. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 184, 320–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, H.; Zhang, Y.; Xin, H.; Zhao, J.; Shah, S.Y. Restrained Shrinkage in Ultra-High-Performance Concrete (UHPC)-Normal Strength Concrete Interface. J. Build. Eng. 2025, 111, 113293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soliman, A.M.; Nehdi, M.L. Effect of partially hydrated cementitious materials on early-age shrinkage of ultra-high-performance concrete. Mag. Concr. Res. 2013, 65, 1147–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Long, Y.; Chen, L.; Ling, X.; Yu, R.; Shui, Z.; Fei, S.; Yu, W.; Li, C.; Ge, K. Mechanisms of autogenous shrinkage for Ultra-High Performance Concrete (UHPC) prepared with pre-wet porous fine aggregate (PFA). J. Build. Eng. 2022, 54, 104622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesovik, V.S.; Popov, D.Y.; Fediuk, R.S.; Sabri, M.M.; Vavrenyuk, S.V.; Liseitsev, Y.L. Shrinkage of ultra-high performance concrete with superabsorbent polymers. Mag. Civ. Eng. 2023, 121, 12108. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, W.; Khayat, K.H. Effect of hybrid fibers on fresh properties, mechanical properties, and autogenous shrinkage of cost-effective UHPC. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2018, 30, 04018030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, D.M.; Boshoff, W.P.; Combrinck, R. Utilising super absorbent polymers as alternative method to test plastic shrinkage cracks in concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 248, 118666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Zhong, M.; Magee, B.; Yang, C.; Wang, C.; Zhu, X.; Zhang, Z. Investigation of effects of Portland cement fineness and alkali content on concrete plastic shrinkage cracking. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 144, 279–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Zhang, S.; Qi, C.; Cheng, L.; Yang, L. Effect of calcium sulfoaluminate and MgO expansive agent on the mechanical strength and crack resistance of concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 299, 123833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Qiu, D.; Wang, S.; Wang, P. Effects of plastic expansive agent on the fluidity, mechanical strength, dimensional stability and hydration of high performance cementitious grouts. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 243, 11804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, K.; Ni, G.; Nie, B.; Xu, Y.; Wang, G.; Sun, L.; Liu, Y. Effect of polyvinyl alcohol/aluminum microcapsule expansion agent on porosity and strength of cement-based drilling sealing material. Energy 2021, 224, 119966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Liu, L.; Li, Q.; Peng, W.; Zhang, F.; Cao, J.; Wang, H. Development of cement-based self-stress composite grouting material for reinforcing rock mass and engineering application. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 201, 314–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, P.; Song, X.; Li, B.; Hu, S. Effect of plastic expansion agent on the volume deformation and submicroscopic structure of pre-stressed duct grouting materials. Bull. Chin. Ceram. Soc. 2014, 33, 1329–1335. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, L. Studies on Performance of High-Performance Cementitious Grout for Coupler of Rebar Splicing. Master’s Thesis, Hunan University, Changsha, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Azadi, M.R.; Taghichian, A.; Taheri, A. Optimization of cement-based grouts using chemical additives. J. Rock Mech. Geotech. Eng. 2017, 9, 623–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantaranon, N.; Chirachanchai, S. Polyoxymethylene foam: From an investigation of key factors related to porous morphologies and microstructure to the optimization of foam properties. Polymer 2016, 96, 54–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Hu, Z.; Liu, J. Freeze-thaw resistance of concrete containing azodicarbonamide expansive agent. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 367, 130335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Hu, Z.; Li, H.; Xu, W.; Liu, J. Expansive deformation and mechanical properties of cementitious materials with azodicarbonamide expansive agent: Influencing factors and mechanisms. J. Sustain. Cem.-Based Mater. 2023, 12, 1141–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 50448-2015; Technical Code for Application of Cementitious Grout. China Architecture & Building Press: Beijing, China, 2015. (In Chinese)
- GB/T 50080-2016; Standard for Test Method of Performance on Ordinary Fresh Concrete. China Architecture & Building Press: Beijing, China, 2016. (In Chinese)
- GB/T 17671-2021; Test Method of Cement Mortar Strength. China Standards Press: Beijing, China, 2021. (In Chinese)
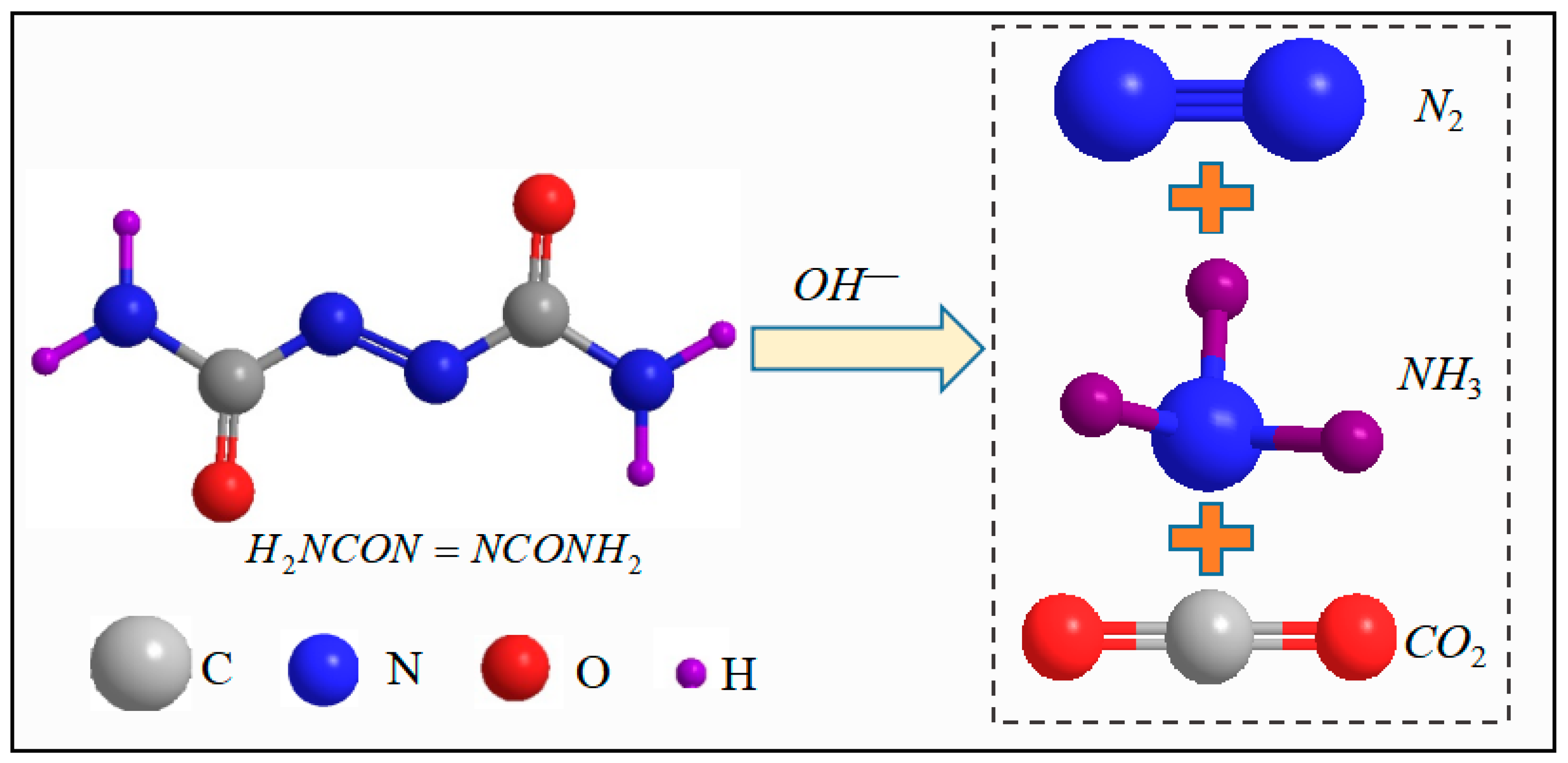


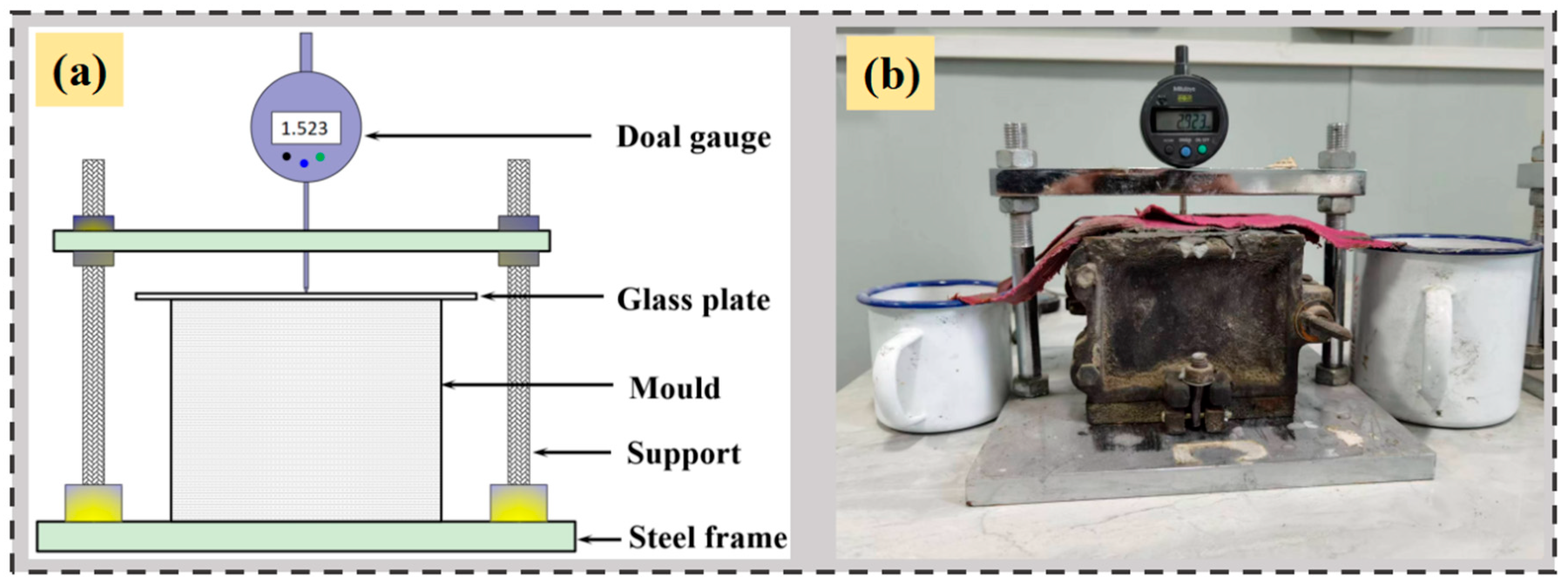


| Materials | Chemical Composition (%) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SiO2 | Al2O3 | CaO | Fe2O3 | SO3 | MgO | K2O | Na2O | |
| OPC | 20.91 | 4.95 | 63.28 | 3.45 | 3.11 | 1.01 | 0.94 | 0.78 |
| MP | 34.21 | 14.15 | 39.11 | 0.82 | 0.12 | 0.32 | 1.95 | 0.58 |
| SF | 91.95 | 1.15 | 0.63 | 0.85 | 0.22 | 1.08 | 1.68 | 0.45 |
| FA | 60.86 | 21.7 | 3.48 | 5.48 | 0.31 | 1.75 | 1.67 | 0.83 |
| Fiber Type | Length (mm) | Diameter (mm) | Tensile Strength (MPa) | Elastic Modulus (GPa) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CSF | 13 | 0.2 | 2800 | 205 |
| Mixture | Materials Dosage/g | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OPC | MP | SF | FA | Sand | ADC | SP | CSF | W/B | |
| ADC-0 | 600 | 150 | 140 | 60 | 1000 | 0 | 6 | 150 | 0.18 |
| ADC-0.02% | 600 | 150 | 140 | 60 | 1000 | 0.2 | 6 | 150 | 0.18 |
| ADC-0.04% | 600 | 150 | 140 | 60 | 1000 | 0.4 | 6 | 150 | 0.18 |
| ADC-0.06% | 600 | 150 | 140 | 60 | 1000 | 0.6 | 6 | 150 | 0.18 |
| ADC-0.08% | 600 | 150 | 140 | 60 | 1000 | 0.8 | 6 | 150 | 0.18 |
| ADC-0.10% | 600 | 150 | 140 | 60 | 1000 | 1 | 6 | 150 | 0.18 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhan, H.; Yang, J.; Guo, H.; Yang, C.; Lu, W.; Yao, Y. Influence and Mechanism of Azodicarbonamide Expansive Agent on the Workability, Mechanical Strength and Plastic Shrinkage of UHPC. Materials 2025, 18, 4656. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18204656
Zhan H, Yang J, Guo H, Yang C, Lu W, Yao Y. Influence and Mechanism of Azodicarbonamide Expansive Agent on the Workability, Mechanical Strength and Plastic Shrinkage of UHPC. Materials. 2025; 18(20):4656. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18204656
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhan, Haowen, Jing Yang, Haoran Guo, Caiqian Yang, Weigang Lu, and Yuan Yao. 2025. "Influence and Mechanism of Azodicarbonamide Expansive Agent on the Workability, Mechanical Strength and Plastic Shrinkage of UHPC" Materials 18, no. 20: 4656. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18204656
APA StyleZhan, H., Yang, J., Guo, H., Yang, C., Lu, W., & Yao, Y. (2025). Influence and Mechanism of Azodicarbonamide Expansive Agent on the Workability, Mechanical Strength and Plastic Shrinkage of UHPC. Materials, 18(20), 4656. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18204656






