Abstract
Micron-sized near-spherical α-Al2O3 powders are widely used as thermal fillers due to their high thermal conductivity, high packing density, good flowability, and low cost. During the high-temperature calcination, the resulting α-Al2O3 powders often exhibit an aggregated worm-like morphology owing to limitations in solid-state mass transfer. Researchers have employed various mineralizers to regulate the morphology of α-Al2O3 powders; however, the preparation of micron-sized highly spherical α-Al2O3 powders via solid-state calcination is still a great challenge. In this work, micron-sized near-spherical α-Al2O3 powders were synthesized through high-temperature calcination using hydratable alumina (ρ-Al2O3) as precursor with water-soluble mineralizer ammonium fluoroborate (NH4BF4). ρ-Al2O3 can undergo a hydration reaction with water to form AlO(OH) and Al(OH)3 intermediates, serving as an excellent precursor. With the addition of 0.1 wt% NH4BF4, the product exhibits an optimal near-spherical morphology. Excessive addition (>0.2 wt%), however, significantly promotes the transformation of α-Al2O3 from a near-spherical to a plate-like structure. Further studies reveal that the introduction of NH4BF4 not only modulates the crystal morphology but also effectively reduces the content of sodium impurities in the powder through a high-temperature volatilization mechanism, thereby enhancing the thermal conductivity of the powder. It is shown that the thermal conductivity of the micron-sized α-Al2O3/ epoxy resin composites reaches 1.329 ± 0.009 W/(m·K), which is 7.4 times that of pure epoxy resin.
1. Introduction
The relentless pursuit of higher integration density, miniaturization, and performance in modern electronics has elevated effective thermal management to a pivotal challenge, directly impacting the longevity and reliability of these devices [1,2]. Owing to a compelling set of properties—including superior electrical insulation, low density, and ease of fabrication—polymeric thermally conductive materials have found extensive applications in areas ranging from electronic encapsulation to thermal management systems [2,3,4,5]. A fundamental limitation of polymers, however, is their inherently low thermal conductivity (typically < 0.3 W/(m·K)), which falls short of the heat dissipation demands imposed by high-power-density electronic components. Consequently, the strategy of embedding highly thermally conductive fillers into the polymer matrix is indispensable for augmenting the overall thermal transport properties of the composite. These fillers function by creating percolating networks for heat transfer within the insulating polymer, thereby markedly boosting the composite’s effective thermal conductivity. Their type, morphology, size, and content directly determine the final material’s thermal efficiency and processability [6,7,8].
The palette of available thermally conductive fillers is diverse, encompassing several categories: metal oxides (e.g., Al2O3, MgO, and ZnO), nitrides (e.g., AlN and BN), carbon allotropes (e.g., graphene and CNTs), and metallic particles (e.g., Ag and Cu), each presenting a distinct trade-off between performance, cost, and stability [2]. Each type of material has its own advantages and disadvantages in terms of thermal conductivity, cost, processability, and stability. Among these options, aluminum oxide (alumina) has emerged as the predominant filler for commercial applications, particularly in electronics, a status owed to its balanced combination of high thermal performance, electrical insulation, and low cost.
α-Al2O3 is widely valued in critical fields such as refractory materials, electronic packaging, and aerospace due to its exceptional chemical stability (including high corrosion resistance and hardness) and prominent thermophysical properties (such as high melting point and thermal conductivity) [9,10,11,12,13,14]. In α-Al2O3/polymer thermally conductive composites, heat transfer occurs primarily through phonon-mediated mechanisms [15]. Compared to fillers of other morphologies, particles with regular and near-spherical shapes exhibit a smaller specific surface area at the same particle size. This property reduces interparticle contact points and weakens van der Waals forces, thereby effectively suppressing agglomeration and facilitating improved flow and dispersion within the polymer matrix. Furthermore, smooth and geometrically simple interfaces help minimize phonon scattering, significantly reducing interfacial thermal resistance. Owing to their high intrinsic thermal conductivity, low interfacial thermal resistance, and excellent flow and packing characteristics, spherical or near-spherical α-Al2O3 particles have become a preferred choice as high-performance thermal fillers in electronic devices [16,17,18,19].
The common synthesis methods for spherical α-Al2O3 primarily include the sol–gel method, homogeneous precipitation, hydrothermal synthesis, and molten jet spraying. Both the sol–gel and homogeneous precipitation methods enable the preparation of α-Al2O3 powders with controllable particle size, diverse morphology, and high purity at relatively low temperatures by regulating the particle morphology, size, and specific surface area of aluminum-containing precursors [11,20,21,22]. However, the sol–gel method involves high raw material costs, complex processes, and often employs large amounts of organic solvents in the reaction system. Although homogeneous precipitation offers cost advantages, it may generate harmful sulfur-containing by-products during the calcination process. The hydrothermal method can directly synthesize spherical or near-spherical α-Al2O3 at relatively low temperatures (around 450 °C) [23,24]. Nevertheless, this method requires sophisticated equipment, leading to significantly increased capital investment and unit production costs, and demands extremely precise control over reaction parameters such as pH and filling degree. Molten jet spraying typically uses high-purity alumina as a raw material, producing spherical products through high-temperature melting and spray granulation [25,26,27]. As a result, individual spherical α-Al2O3 microbeads are usually polycrystalline and often contain intrinsic defects such as pores and vacancies within the crystal structure. Moreover, due to the extremely high melting point of industrial alumina (>2050 °C), this process imposes stringent requirements on the high-temperature resistance of equipment, resulting in high capital and operating costs. In contrast, near-spherical alumina can be obtained via specific calcination processes and the use of calcination aids [12,13], resulting in single-crystal products with uniform grain size and higher α-phase content. Their regular surface morphology and good fluidity help reduce agglomeration within the matrix and improve dispersion uniformity during processing. By optimizing crystal structure and particle size distribution, high packing density (up to 70 vol% or more) can be achieved, strengthening the thermal conduction pathways and significantly enhancing the thermal conductivity of the composite, thereby meeting the heat dissipation demands of most electronic devices.
ρ-Al2O3 is a transitional alumina phase with high reactivity, capable of undergoing a hydration reaction with water to form a high-strength aluminum hydroxide gel. It is commonly used as a binder in refractories and other related fields [28,29,30]. The hydration products, AlO(OH) and Al(OH)3 [31], can serve as precursors for the preparation of alumina powders via solid-phase calcination. NH4BF4 is a chemical compound widely used in analytical reagents, insecticides, and as a catalyst for resin finishing in the textile industry. In recent years, it has been exploited by researchers for modulating the crystal morphology of alumina [13]. The aqueous gel formed by the hydration of ρ-Al2O3 can dissolve most mineralizers, enabling their uniform dispersion within the hydration products. This enhances the interaction between the mineralizer and the hydration products of ρ-Al2O3, thereby achieving the goal of homogeneous primary crystal formation. This hydration characteristic of ρ-Al2O3 is highly advantageous for implementing strategies to tailor the properties of α-alumina powders, leading to the production of high-quality powders with excellent morphology and performance. NH4BF4 is highly soluble in water, which facilitates better mixing with ρ-Al2O3. Therefore, based on the report by Zhenhao Yang et al. [13], this study used ρ-Al2O3 as the raw material, optimized the selection of precursors, and introduced NH4BF4 as a mineralizer to prepare micron-sized spherical α-Al2O3 powders. The effects of the amount of NH4BF4 addition on the morphology of α-Al2O3 powders and the reduction of sodium impurity content were systematically investigated, and the underlying regulation mechanisms were further analyzed.
2. Experimental
2.1. Preparation of Near-Spherical Alumina Powder of Micron Size
60 g of ρ-Al2O3 powder (supplied by the Aluminum Corporation of China, Chalco, Zhengzhou, China) and 140 g of deionized water were placed in a 500 mL zirconia ball milling jar, giving a solid-to-liquid mass ratio of 3:7. The NH4BF4 mineralizer, which was obtained from Macklin Biochemical Co., Ltd. in Shanghai, China, was added in a predetermined proportion based on the mass fraction of ρ-Al2O3. Then, 120 g of zirconia grinding balls (5 mm in diameter, at a ball-to-powder mass ratio of 2:1) were added to the jar. The mixture was mechanically blended using a KQM-Z/B planetary ball mill (supplied by Xianyang JinHong General Machinery Co., Ltd., Xianyang, China) at 300 r/min for 3 h to ensure a thorough and uniform dispersion of the mineralizer and the precursor.
The ball-milled slurry was transferred into a cylindrical silicone mold (Φ50 mm × 50 mm), covered with a sealing film, and subjected to hydration treatment at 60 °C for 24 h in a constant-temperature drying oven (HWS-150; Shaoxing Huda Machinery Equipment Manufacturing Co., Ltd., Shaoxing, China). After removing the sealing film, drying was continued at the same temperature for another 24 h to obtain a free-standing gel-derived green body. The dried green body was loaded into a 100 mL arc-shaped corundum crucible. The crucible was then covered with its matching arc-shaped lid to ensure a partially sealed environment. It was subsequently transferred to a chamber furnace (KAL-1700X; Hefei Kjing Materials Technology Co., Ltd., Hefei, China) for stepwise calcination: the temperature was first raised to 1100 °C at 5 °C/min, then increased to the target temperature (1300 °C) at 3 °C/min (The heating rate was set to the maximum achievable rate of the chamber furnace within the corresponding temperature range.), and finally held at that temperature for 1–4 h. Micron-scale near-spherical α-Al2O3 powder was obtained after furnace cooling. The cooling process from 1300 °C to 500 °C was controlled by the furnace, with the cooling rate set equal to the heating rate. Upon reaching 500 °C, the program was halted, and the sample was allowed to cool naturally.
2.2. Preparation of α-Al2O3/EP Thermally Conductive Composites
Seventy weight percent (70 wt%) of self-synthesized micron-sized near-spherical α-Al2O3 powder was incorporated into the EP gel (CYDF-170; viscosity: 8000–12,000 mPa·s at 25 °C; thermal conductivity: 0.18 W·m-1·K-1; supplied by Jiangyin Chengyu New Material Technology Co., Ltd., Jiangyin, China)and mixed using a three-roll mill (S100; Shanghai Root Mechanical and Electrical Equipment Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China). All mixing was performed at room temperature. The equipment parameters were set as follows: slow roller speed at 30 r/min, middle roller speed at 70 r/min, and fast roller speed at 150 r/min. The mixture was processed continuously for three cycles, with each cycle lasting 2 h. Afterwards, a curing agent (methyltetrahydrophthalic anhydride supplied by Aladdin Biochemical Technology Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China) was added at a mass ratio of 5:6 and thoroughly mixed by mechanical stirring.
The uniformly mixed material was then degassed for 1 h in a vacuum environment to remove residual internal bubbles and ensure the density of the subsequently molded samples. Following degassing, the α-Al2O3/EP mixture was slowly poured into a mold pre-treated with a release agent. The mold was transferred to a vacuum oven (DZF-6050; Shanghai Yiheng Technical Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China) and cured at 160 °C for 10 h. After curing, the mold was allowed to cool naturally to room temperature before demolding.
2.3. Characterizations
Phase analysis of the powder samples was conducted using an X-ray diffractometer (XRD, Bruker D8 DISCOVER A25, Bruker AXS GmbH, Karlsruhe, Germany) with a scanning range of 10° to 90° and a scanning rate of 5°/min. The microscopic morphology of the powder was observed using a field-emission scanning electron microscope (SEM, JEOL SM-76190F, JEOL Ltd., Tokyo, Japan), with a magnification voltage of 10 kV, and the magnification levels are 1000, 3000, and 5000. The crystal structure of the powder was characterized by transmission electron microscopy (TEM, Thermo Scientific Talos F200X, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) and selected area electron diffraction (SAED). The phase transition behavior of alumina was analyzed using a simultaneous thermal analyzer (STA, Netzsch STA 449 F5, Netzsch-Gerätebau GmbH, Selb, Germany). Powder samples were tested in the temperature range of 30 °C to 1300 °C at a heating rate of 20 °C/min to obtain TG-DSC curves. Grain size distribution was analyzed using a laser diffraction particle size analyzer (LS-POP (9); OMEC Instruments Co., Ltd., Zhuhai, China) and Nanomeasurer 1.2 software (Jade Biomedical Technology Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China). The sodium (Na) content in the sample was determined by inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectrometry (ICP-OES). The thermal conductivity of the composite in the through-plane direction was measured using the laser flash method (LFA 467, NETZSCH-Gerätebau GmbH, Selb, Germany).
3. Results and Discussion
Figure 1 shows the simultaneous thermal analysis (TG-DSC) curve of the product of ρ-Al2O3 hydration for 24 h. Two characteristic endothermic peaks and two exothermic phase transition peaks can be observed in the DSC curve. The endothermic peak observed at 121 °C is attributed to the desorption of physically adsorbed water, while the endothermic effects at 320 °C and 550 °C correspond to the stepwise dehydration of Al(OH)3 (bayerite) and AlO(OH) (boehmite), respectively, leading to the formation of metastable γ-Al2O3. The corresponding TG curve showed continuous weight loss behavior in this temperature range, and the total weight loss rate reached 25%, which was highly consistent with the theoretical dehydration (adsorbed water + structural hydroxyl group removal). The exothermic peak of the DSC curve at 610 °C corresponds to the enthalpy of phase change released by lattice reconstruction during the phase transition of γ-Al2O3 →θ-Al2O3. The strong exothermic peak at 1240 °C is attributed to the irreversible phase transition of θ-Al2O3→α-Al2O3. It is worth noting that the α phase generation peak is fully present before 1300 °C, indicating that the phase transition process can be fully completed at this temperature. Based on this thermodynamic analysis, 1300 °C was selected as the optimal calcination temperature to ensure the high-purity conversion of the α phase.
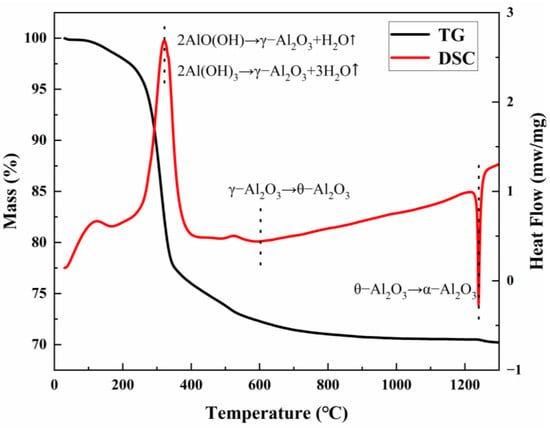
Figure 1.
TG-DSC curve of ρ-Al2O3 after hydration for 24 h.
Figure 2 shows the XRD plots of ρ-Al2O3 feedstock, hydrated 24 h products, and products calcined at 1300 °C for 2 h, and the diffraction peaks of ρ-Al2O3 can be observed as amorphous diffuse peaks, which are consistent with the results reported in the literature [31]. After 24 h of ρ-Al2O3 hydration, the diffraction peak of the product conformed to the PDF cards of Boehmite and Bayerite, indicating that the hydration product was composed of Boehmite and Bayerite. The diffraction peak of the hydration product was consistent with the PDF card of α-Al2O3, and there was no diffraction peak of θ-Al2O3, indicating that the pure phase α-Al2O3 could be obtained after calcination at 1300 °C for 2 h.
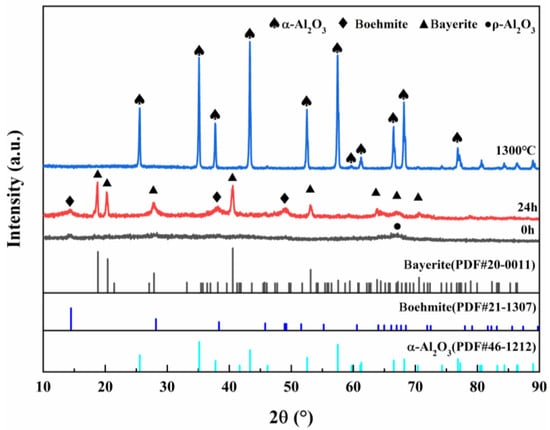
Figure 2.
XRD patterns of ρ-Al2O3 feedstock, hydrated 24 h products, and products calcined at 1300 °C for 2 h.
Figure 3 shows the TEM test results of the sample with 0.1% NH4BF4 addition after calcination at 1300 °C for 2 h. From Figure 3a,b, it can be seen that the sample particles exhibit a near-spherical topography with a particle size between 1 μm and 2 μm. The results are shown in Figure 3c, indicating that the sample has a tripartite phase structure, and the results of the crystal plane index identification corresponding to the diffraction spot are consistent with the tripartite phase. Figure 3d shows the high-resolution HRTEM results, the Fourier transform and the reverse Fourier transform are performed on the red frame area to obtain the lattice fringes of the sample, and the lattice fringe spacing measured at the arrow is 0.342 nm, which is consistent with the spacing of the (012) crystal plane, indicating that the substance is α-Al2O3.
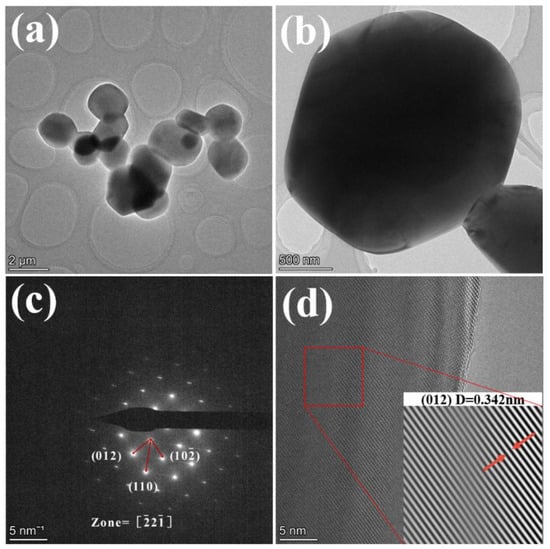
Figure 3.
TEM results of the sample with 0.1% NH4BF4 addition after calcination at 1300 °C for 2 h (a,b) are TEM images at different magnifications (c) SAED (d) HRTEM.
Figure 4 shows the SEM images of ρ-Al2O3, as observed in Figure 4a1,a2, the raw material ρ-Al2O3 exhibits an irregular morphology. The microstructure of the sample after 24 h of hydration of ρ-Al2O3 is shown in Figure 4b1,b2, which is primarily composed of flocculent and particulate matter. The study conducted by R. Salomão et al. [32] provided a detailed investigation into the hydration of ρ-Al2O3, confirming that the flocculent material is AlO(OH) and the particulate matter is Al(OH)3. The hydration product was calcined at 1300 °C for 2 h, and the sample without NH4BF4 was transformed into adherent worm-like α-Al2O3. This is because, without the addition of any mineralizing agent, the mass transfer mode between alumina is solid-phase mass transfer, and the parts that come into contact with each other will form interlocking structures, which in turn will form an adhesion dumbbell-shaped morphology [12]. The samples added with 0.4% NH4BF4 were transformed into flakes and near-spherical α-Al2O3, and the results showed that NH4BF4 could regulate the morphology of alumina.
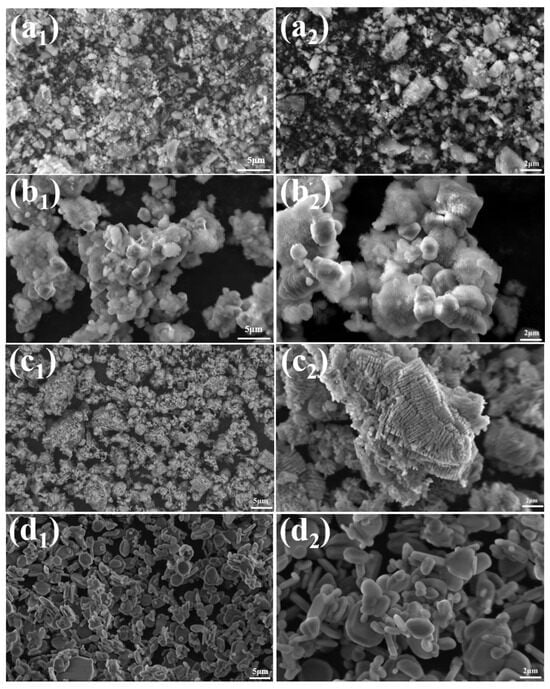
Figure 4.
SEM images of (a1,a2) ρ-Al2O3, (b1,b2) hydration 24 h products, (c1,c2) hydration product was calcined at 1300 °C for 2 h without NH4BF4, (d1,d2) hydration product was calcined at 1300 °C for 2 h with 0.4% NH4BF4.
Figure 5 shows the SEM images of the calcination products of samples with different dosages calcined at 1300 °C for 2 h. As can be seen from Figure 5, 0.1% NH4BF4 was added, the α-Al2O3 grains in the sample exhibited a predominantly near-spherical morphology with high sphericity, good dispersion among grains, and no significant agglomeration. As the amount of NH4BF4 increased, the near-spherical α-Al2O3 grains became progressively flattened with a non-uniform size distribution. When the addition amount was further increased to 0.5%, the morphology of the α-Al2O3 grains almost entirely transitioned to a plate-like shape. These results indicate that under the experimental conditions applied in this study, 0.1% NH4BF4 is the optimal addition amount for obtaining near-spherical α-Al2O3. Excessive addition disrupts the coordination balance during crystal growth, leading to a transition in grain morphology from near-spherical to plate-like.
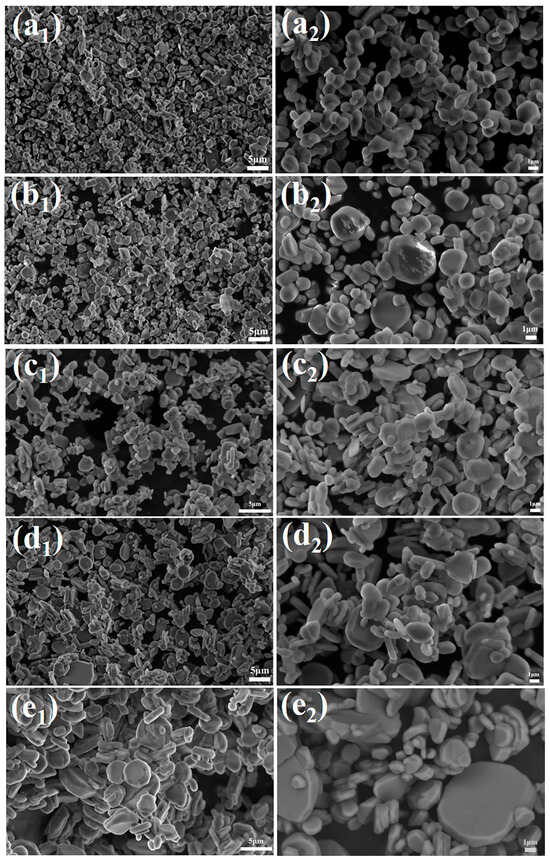
Figure 5.
SEM images of calcination products of samples with different dosages calcined at 1300 °C for 2 h (a1,a2) 0.1%, (b1,b2) 0.2%, (c1,c2) 0.3%, (d1,d2) 0.4%, (e1,e2) 0.5%.
Based on the results from the previous set of experiments, a further experiment was designed to finely adjust the amount of NH4BF4 addition (with fine-tuning in the range of 0.04–0.16%). The morphological evolution was analyzed using its SEM images (as shown in Figure 6), revealing the dynamic regulation mechanism of the α-Al2O3 grain morphology.
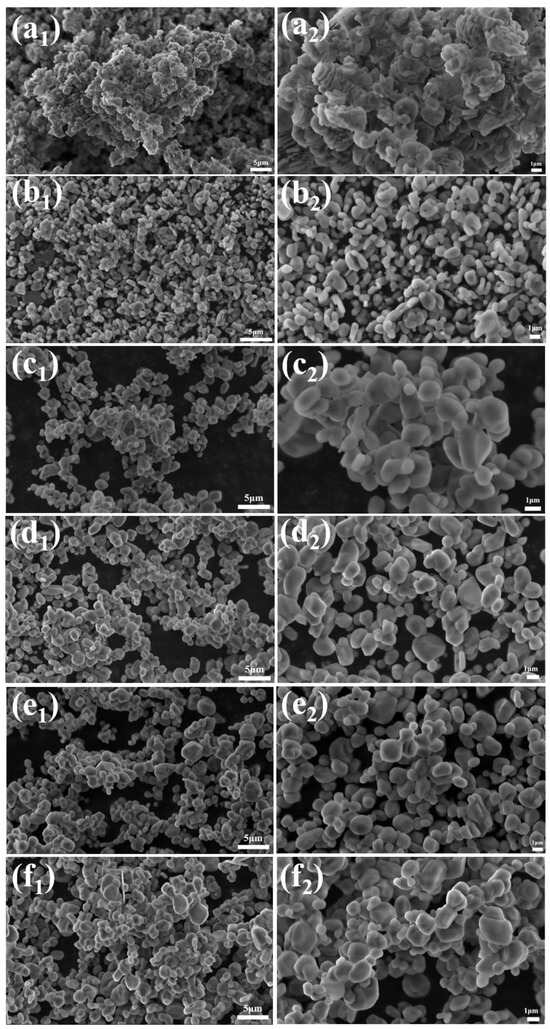
Figure 6.
SEM images of calcination products of samples with different dosages calcined at 1300 °C for 2 h (a1,a2) 0.04%, (b1,b2) 0.06%, (c1,c2) 0.08%, (d1,d2) 0.12%, (e1,e2) 0.14%, and (f1,f2) 0.16%.
In the sample with 0.04% NH4BF4 addition, the α-Al2O3 grains exhibited a highly agglomerated vermicular structure, with lengths ranging from 1 to 4 μm. The grains were interconnected, forming network-like stacked aggregates. This morphology results from the weak regulating effect of BF4− ions on crystal facet growth when the NH4BF4 concentration is insufficient, leading to preferential growth along the (104) crystal plane and mutual adhesion among crystals.
As the amount of NH4BF4 addition increases, the vermicular α-Al2O3 grains gradually disassociate, transforming first into an elliptical shape and then into a near-spherical shape. From Figure 6, it can be observed that in samples with more than 0.1% NH4BF4 addition, the α-Al2O3 grains exhibit a flattened morphology with irregular sizes. Therefore, 0.1% NH4BF4 is identified as the optimal addition amount.
Figure 7 shows the particle size distribution of the calcination product obtained by calcination at 1300 °C for 2 h with 0.1% NH4BF4. Particle size analysis revealed that the D10, D50, and D90 values were 0.81 μm, 1.65 μm, and 3.11 μm, respectively, with a span of 1.39, indicating a moderate dispersion of the particles. Micron-sized particles accounted for 83% of the total. This multi-scale particle size distribution facilitates tighter packing of the fillers within the matrix—wherein larger particles form a primary framework while finer particles fill the interparticle voids—thereby enhancing phonon transport efficiency and contributing to improved thermal conductivity of the composite material. This mechanism is supported by the study of Wang et al. [33], in which an optimized alumina filler system (60 wt% loading, with a particle size ratio of 5.8 μm:2.6 μm:0.5 μm = 7:2:1) exhibited a 23–32% increase in thermal conductivity compared to systems using a single particle size.
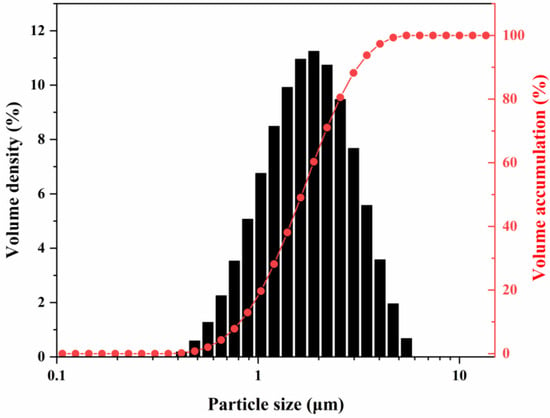
Figure 7.
Particle size distribution of alumina powders calcined at 1300 °C for 2 h with 0.1% NH4BF4.
Since the vast majority of bauxite worldwide is processed using the Bayer process—an alkaline method that utilizes a significant amount of sodium hydroxide solution—industrial-grade Al(OH)3, Al2O3, and other aluminum precursors produced via this method typically contain certain amounts of residual Na impurities [34]. Figure 8 shows the test results of Na content of samples calcined at 1300 °C for 2 h with NH4BF4 addition, and it can be observed from Figure 8 that the addition of NH4BF4 can reduce the content of impurity Na in the calcination products, and the impurity Na content in the sample decreases with the increase of NH4BF4 addition, from the initial 0.24% to 0.03%, as the high-temperature decomposition of NH4BF4 will form intermediate products containing element B and F. The intermediate product containing elements B and F reacts with Na2O to form NaBO2 and NaF, which volatilize at high temperatures, thereby reducing the content of the impurity Na [12].
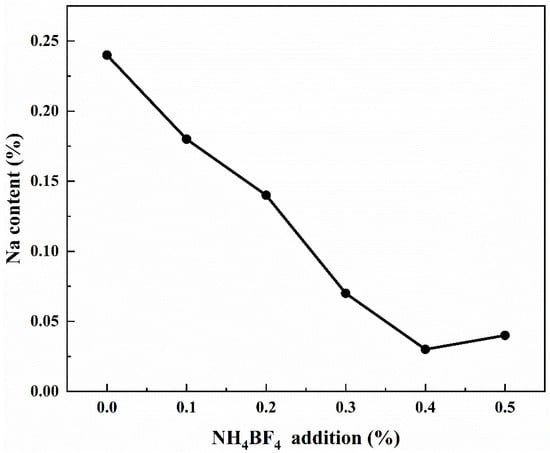
Figure 8.
The Na content of samples calcined at 1300 °C for 2 h with NH4BF4 addition.
Generally speaking, when α-Al2O3 is prepared by high-temperature calcination, the grain size can be increased by extending the holding time to promote the one-time grain growth. Figure 9 shows the SEM images of the samples with 0.1% NH4BF4calcined at 1300 °C for different durations. As can be observed from Figure 9, there is basically no difference in morphology and particle size between the samples obtained at 1300 °C for 1 h and those kept at 1300 °C for 3 h. The results showed that the near-spherical α-Al2O3 powder prepared by adding NH4BF4 was not sensitive to the holding time and had excellent thermal stability.
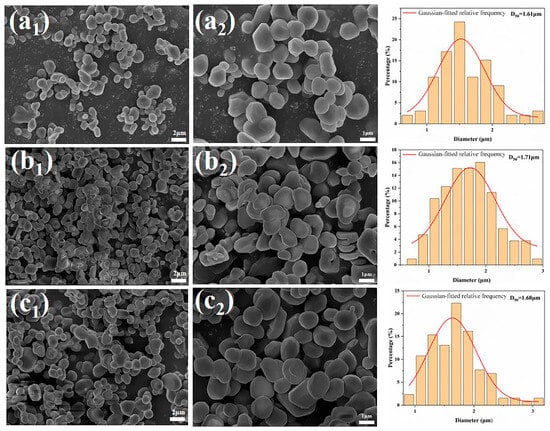
Figure 9.
The SEM images of the samples calcined at 1300 °C for different durations with 0.1% NH4BF4 (a1,a2) 1 h, (b1,b2) 3 h, (c1,c2) 4 h.
NH4BF4 undergoes thermal decomposition at high temperatures, forming gaseous compounds such as HF, NH3, and BF3. The fluorine-containing products further generate gaseous intermediate AlOF during the high-temperature calcination process. The reaction equation is as follows:
Figure 10 illustrates the schematic diagram of the mechanism of NH4BF4 action. Due to the fact that the (0001) crystal plane and its symmetrical equivalents in α-Al2O3 crystals are closely packed planes with relatively low surface free energy and poor adsorption capacity compared to the other six crystal planes, AlOF is preferentially adsorbed onto the other six planes, leading to plate-like growth [12]. However, when H3BO3 is introduced into the system, it may interact with surface hydroxyl groups on the crystals, reducing the growth activation energy and accelerating three-dimensional grain growth. On the other hand, borate ions generated from the decomposition or hydrolysis of H3BO3 at high temperatures may incorporate into the crystal lattice or adsorb at grain boundaries, altering the local ionic environment and further promoting grain growth [35]. As a result, the addition of H3BO3 may cause plate-like grains to thicken and increase in size, driving a morphological transition toward a spherical-like shape.
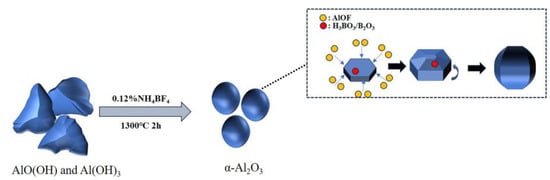
Figure 10.
Schematic diagram of the mechanism of NH4BF4 action.
The mechanism by which NH4BF4 modulates morphology may involve its initial decomposition into gaseous compounds at high temperatures, which subsequently react with water and Al2O3 to form AlF3 and H3BO3. Here, H3BO3 promotes lateral growth and increases particle size, while AlF3 may inhibit the growth of specific crystal planes or alter interfacial energy. Under the synergistic influence of F and B elements, the crystal growth direction is altered, ultimately resulting in the formation of spherical-like alumina particles with increased size.
However, the influence of NH4BF4 on morphology and size is highly dependent on its dosage. When the amount added is low, the insufficient release of gaseous species and low concentration of H3BO3 result in agglomerated worm-like particles with limited size increase. When excessive amounts are added, the increased concentration of AlF3 may suppress growth in the thickness direction, leading to a plate-like morphology. Only at an optimal dosage can the synergistic effects of H3BO3 and AlF3 promote growth to a suitable size and regulate the morphology toward a spherical-like shape.
Micron-sized α-Al2O3 powder, obtained by adding 0.1% NH4BF4 followed by calcination at 1300 °C, was used as the thermal conductive filler to prepare composites with epoxy resin (EP). The thermal conductivity test results of the micron-sized α-Al2O3/EP composites are summarized in Table 1. Four samples from the same batch were tested, and the composite sample exhibited a thermal conductivity of 1.329 W/(m·K). Compared with recently reported polymer composites filled with α-Al2O3, even at higher filler loadings of conventional micron-sized α-Al2O3, the thermal conductivity of such composites mostly falls within the range of 0.5–0.9 W/(m·K) [36], which is significantly lower than the value achieved in this study. This result highlights the remarkable advantage of the filler prepared in this work in enhancing the thermal conductivity of composites.

Table 1.
Test results of thermal conductivity for micron-sized α-Al2O3/EP composites.
4. Conclusions
In this study, micron-scale near-spherical α-Al2O3 powder was synthesized via solid-phase sintering using ρ-Al2O3 as the raw material and NH4BF4 as a mineralizer. The effects of NH4BF4 addition, calcination temperature, and holding time on the morphology and particle size of the resulting α-Al2O3 were systematically investigated. The prepared powder exhibited a median particle size (D50) of 1.65 μm, and the mechanistic role of NH4BF4 appears to be as follows, based on the obtained results:
- (1)
- The addition of NH4BF4 effectively modulates the crystal morphology of α-Al2O3, with a pronounced correlation to the amount added. The underlying mechanism involves the thermal decomposition of NH4BF4 into fluorine-containing (e.g., HF and AlF3) and boron-containing (e.g., H3BO3) intermediates. Fluorine and boron act synergistically to alter the surface energy distribution at the crystal growth interface, thereby suppressing anisotropic growth and promoting equiaxial development, leading to the formation of a near-spherical morphology. Experimental results show that with 0.1% NH4BF4 addition, near-spherical α-Al2O3 powder with D50 = 1.65 μm was obtained. Increasing the addition to 0.5% resulted in a loss of morphological control due to an imbalance in the fluorine-to-boron ratio, yielding a mixture of near-spherical and plate-like α-Al2O3. In contrast, reducing the addition to 0.04% provided insufficient mineralizer concentration, resulting in entirely agglomerated vermicular α-Al2O3 without effective morphology regulation.
- (2)
- NH4BF4 serves as an efficient mineralizer that facilitates the formation of α-Al2O3. Under these conditions, the holding time has minimal influence on the final crystal morphology and particle size. Experiments confirmed that within a 1–4 h holding period, the morphology and size of the α-Al2O3 crystals remained largely unchanged, with no significant agglomeration or abnormal grain growth—markedly superior to the control group without NH4BF4. This behavior is attributed to gaseous products from NH4BF4 decomposition, which regulate grain-boundary diffusion by reducing interfacial energy and suppressing Ostwald ripening, thereby decoupling grain growth rate from holding time.
- (3)
- By introducing 0.1% NH4BF4 and calcining at 1300 °C, near-spherical α-Al2O3 powder with D50= 1.65 μm was successfully prepared. The composite gel formed with epoxy (EP) exhibited a thermal conductivity of 1.329 ± 0.009 W/(m·K). These findings provide a feasible strategy for the industrial production of micron-scale near-spherical α-Al2O3 powder.
Although this study optimized the selection of precursors and utilized NH4BF4 as a mineralizer to modulate morphology, along with an in-depth analysis of the underlying mechanism, conclusive evidence has not yet been established due to experimental constraints. Furthermore, only the thermal conductivity of the prepared composite material was characterized, and its practical applications still require further validation. Therefore, we propose that subsequent research should focus on verifying the proposed mechanism and exploring specific applications of the composite material.
Author Contributions
Methodology, Y.W.; Investigation, Y.W. and J.J.; Resources, J.X. and T.L.; Writing—original draft, Y.W. and J.J.; Writing—review & editing, J.X., T.L. and Z.L.; Supervision, Z.L.; Funding acquisition, J.X. and T.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by Guangxi Industrial Technology Research Project (No. CYY-HT2023-JSJJ-0033), Guangxi Industrial Technology Research Project (No. CYY-HT2023-JSJJ-0034) and Guangxi Science and Technology Plan Project (No. Gui Ke AB22035043).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Acknowledgments
We would like to acknowledge the Analytical and Testing Center of Northwestern Polytechnical University for the XRD, SEM, and other analyses.
Conflicts of Interest
Author Jie Xu is employed by the Shaanxi Shuimu Xusheng New Material Technology Co., Ltd. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
- Zhang, K.; Chai, Y.; Yuen, M.M.F.; Xiao, D.G.W.; Chan, P.C.H. Carbon nanotube thermal interface material for high-brightness light-emitting-diode cooling. Nanotechnology 2008, 19, 215706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, M.; Du, B.X. Review of high thermal conductivity polymer dielectrics for electrical insulation. High Volt. 2016, 1, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Dai, X.; Ruan, K.; Zhang, S.; Shi, X.; Guo, Y.; Cai, H.; Gu, J. Flexible thermally conductive and electrically insulating silicone rubber composite films with BNNS@Al2O3 fillers. Adv. Compos. Hybrid Mater. 2021, 4, 36–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Yang, X.; Li, J.; Shen, Y.; Zhang, L.; Lu, R.; Wang, C.; Zheng, X.; Chen, H.; Zhang, T. Review on polymer composites with high thermal conductivity and low dielectric properties for electronic packaging. Mater. Today Phys. 2022, 22, 100594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, K.; Shi, X.; Guo, Y.; Gu, J. Interfacial thermal resistance in thermally conductive polymer composites: A review. Compos. Commun. 2020, 22, 100518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Chen, W.; Xu, J.; Li, J.; Gan, L.; Chu, X.; Yao, Y.; He, Y.; Li, B.; Kang, F.; et al. Enhanced thermal conductivity by combined fillers in polymer composites. Thermochim. Acta 2019, 676, 198–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, X.; Meng, Y.; Zhou, F.; Ge, C.; Sun, D.; Yang, D.; Jiang, X.; Dai, P.; Wang, X. Enhanced thermal conductivity of polymeric composites with BN@C hybrid fillers. J. Mater. Chem. C 2024, 12, 15965–15974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mumtaz, N.; Li, Y.; Artiaga, R.; Farooq, Z.; Mumtaz, A.; Guo, Q.; Nisa, F.-U. Fillers and methods to improve the effective (out-plane) thermal conductivity of polymeric thermal interface materials—A review. Heliyon 2024, 10, e25381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medvecká, V.; Kováčik, D.; Stupavská, M.; Roch, T.; Kromka, A.; Fajgar, R.; Zahoranová, A.; Černák, M. Preparation and characterization of alumina submicron fibers by plasma assisted calcination. Ceram. Int. 2020, 46, 22774–22780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basha, M.M.; Basha, S.M.; Singh, B.K.; Mandal, N.; Sankar, M.R. A review on synthesis of zirconia toughened alumina (ZTA) for cutting tool applications. Mater. Today Proc. 2020, 26, 534–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shojaie-Bahaabad, M.; Taheri-Nassaj, E. Economical synthesis of nano alumina powder using an aqueous sol–gel method. Mater. Lett. 2008, 62, 3364–3366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ya-Qiang, S.H.E.N.; Dong-Yun, L.I.; Yang, X.U.; Hong-Liang, G.E.; Qiang, X.U.; Hui, Y.A.N.G. Influence mechanism of halide additives on phase conversion, morphology, and purity of alumina powders prepared by solid-phase calcination method. Ceram. Int. 2022, 48, 8403–8408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Liu, G.; Qi, T.; Zhou, Q.; Peng, Z.; Li, X.; Wang, Y.; Shen, L. Influence of NH4BF4 on the alumina phase transition and morphology. Mater. Lett. 2023, 345, 134474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Liu, G.; Qi, T.; Zhou, Q.; Peng, Z.; Shen, L.; Wang, Y.; Li, X. Structural defect and activated alumina of spheric α-Al2O3 improving alumina ceramics density from the industrial coarse gibbsite. Ceram. Int. 2024, 50, 54643–54653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Chen, J.; Zhou, J.; Li, B. Thermal Conductivity of Polymers and Their Nanocomposites. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, e1705544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Li, L.; Wei, X.; Hou, X.; Li, M.; Wu, X.; Li, Y.; Lin, C.-T.; Jiang, N.; Yu, J. Combining Alumina Particles with Three-Dimensional Alumina Foam for High Thermally Conductive Epoxy Composites. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2021, 3, 216–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee Sanchez, W.A.; Huang, C.-Y.; Chen, J.-X.; Soong, Y.-C.; Chan, Y.-N.; Chiou, K.-C.; Lee, T.-M.; Cheng, C.-C.; Chiu, C.-W. Enhanced Thermal Conductivity of Epoxy Composites Filled with Al2O3/Boron Nitride Hybrids for Underfill Encapsulation Materials. Polymers 2021, 13, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akhtar, M.W.; Lee, Y.S.; Yoo, D.J.; Kim, J.S. Alumina-graphene hybrid filled epoxy composite: Quantitative validation and enhanced thermal conductivity. Compos. Part B Eng. 2017, 131, 184–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.; Kim, J. Thermal conductivity of epoxy composites with a binary-particle system of aluminum oxide and aluminum nitride fillers. Compos. Part B Eng. 2013, 51, 140–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, Y.; Yasuda, Y.; Morita, T. Low-temperature synthesis of α-alumina based on sol-gel processes. Adv. Mater. Process. Technol. 2021, 7, 482–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niero, D.F.; Montedo, O.R.K.; Bernardin, A.M. Synthesis and characterization of nano α-alumina by an inorganic sol–gel method. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2022, 280, 115690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhao, D.; Zhou, G.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, P.; Hou, X. Synthesis of nano-sized γ-Al2O3 with controllable size by simple homogeneous precipitation method. Mater. Lett. 2020, 279, 128476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, W.; Qin, F.; Song, Z.; Liu, W. Synthesis of monodisperse spherical nano alumina by hydrothermal method and its mechanism study. Ceram. Int. 2024, 50, 39467–39474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suchanek, W.L. Hydrothermal Synthesis of Alpha Alumina (α-Al2O3) Powders: Study of the Processing Variables and Growth Mechanisms. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. Soc. 2010, 93, 399–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaturvedi, V.; Ananthapadmanabhan, P.V.; Chakravarthy, Y.; Bhandari, S.; Tiwari, N.; Pragatheeswaran, A.; Das, A.K. Thermal plasma spheroidization of aluminum oxide and characterization of the spheroidized alumina powder. Ceram. Int. 2014, 40, 8273–8279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Li, C.; Deng, N.; Sun, H.; Feng, S.; Zhang, Y.; Li, X.; Ci, E.; Li, J. Preparation of high sphericity monodisperse aluminum microspheres by pulsated orifice ejection method. Mater. Today Commun. 2022, 30, 103110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skalon, M.; Hebda, M.; Buzolin, R.; Pottlacher, G.; Mitsche, S.; Sommitsch, C. Preparation Method of Spherical and Monocrystalline Aluminum Powder. Metals 2019, 9, 375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bezerra, B.P.; Luz, A.P.; Pandolfelli, V.C. Novel drying additives and their evaluation for self-flowing refractory castables. Ceram. Int. 2020, 46, 3209–3217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Li, N.; Zhou, W.; Xiong, X.; Gao, S.; Ye, G. Microstructure evolution of hydration products and strength change of hydratable alumina-bonded castables below 1250°C. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2021, 104, 1448–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, L.; Liu, Z.; Tian, C.; Han, L.; Wen, T.; Yu, J.; Hou, X.; Zhu, Q. Synthesis and characterization of mullite-ZrO2 porous fibrous ceramic for highly efficient oil-water separation. Ceram. Int. 2021, 47, 22709–22716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Zhang, B.; Zhong, Z.; Ye, J.; Fang, Z.; Zhang, J.; Ye, F. A simple and efficient hydratable alumina gel-casting method for the fabrication of high-porosity mullite ceramics. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2024, 107, 2067–2080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salomão, R.; Kawamura, M.A.; Souza, A.D.V.; Sakihama, J. Hydratable Alumina-Bonded Suspensions: Evolution of Microstructure and Physical Properties During First Heating. Interceram Int. Ceram. Rev. 2017, 66, 28–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.-Y.; Zhou, X.-N.; Li, Z.-X.; Xu, S.-S.; Hao, L.-C.; Zhao, J.-P.; Wang, B.; Yang, J.-F.; Ishizaki, K. Enhanced thermal conductivity of epoxy composites by constructing thermal conduction networks via adding hybrid alumina filler. Polym. Compos. 2022, 43, 483–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoppert, A.; Valeev, D.; Loginova, I.; Pankratov, D. Low-Temperature Treatment of Boehmitic Bauxite Using the Bayer Reductive Method with the Formation of High-Iron Magnetite Concentrate. Materials 2023, 16, 4678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Z.; Li, J.; Zhao, J. Synthesis of plate-like cordierite using a small amount of H3BO3 flux. Ceram. Int. 2023, 49, 28267–28273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; Sun, Z.; Fu, W.; Lin, Y.-C.; Moon, K.-s.; Wong, C.P. Thermally conductive and electrically insulative alumina/epoxy composites for advanced electronic packaging applications: A comprehensive review of filler morphologies and surface modifications. Mater. Today 2025, 86, 393–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).