Al and Cu Effect on the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of HEA Based on the AlCoCuFeNi System
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
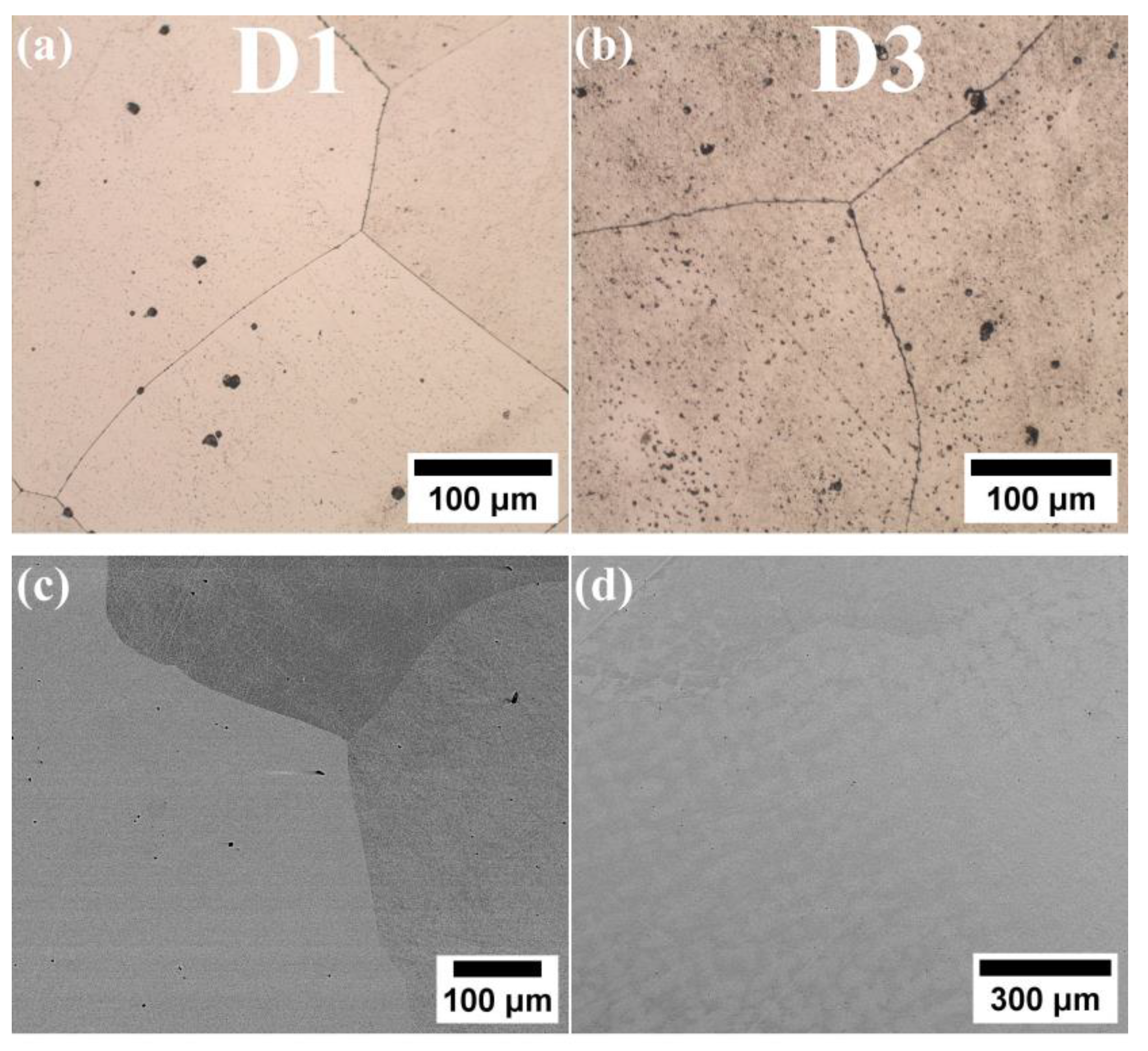
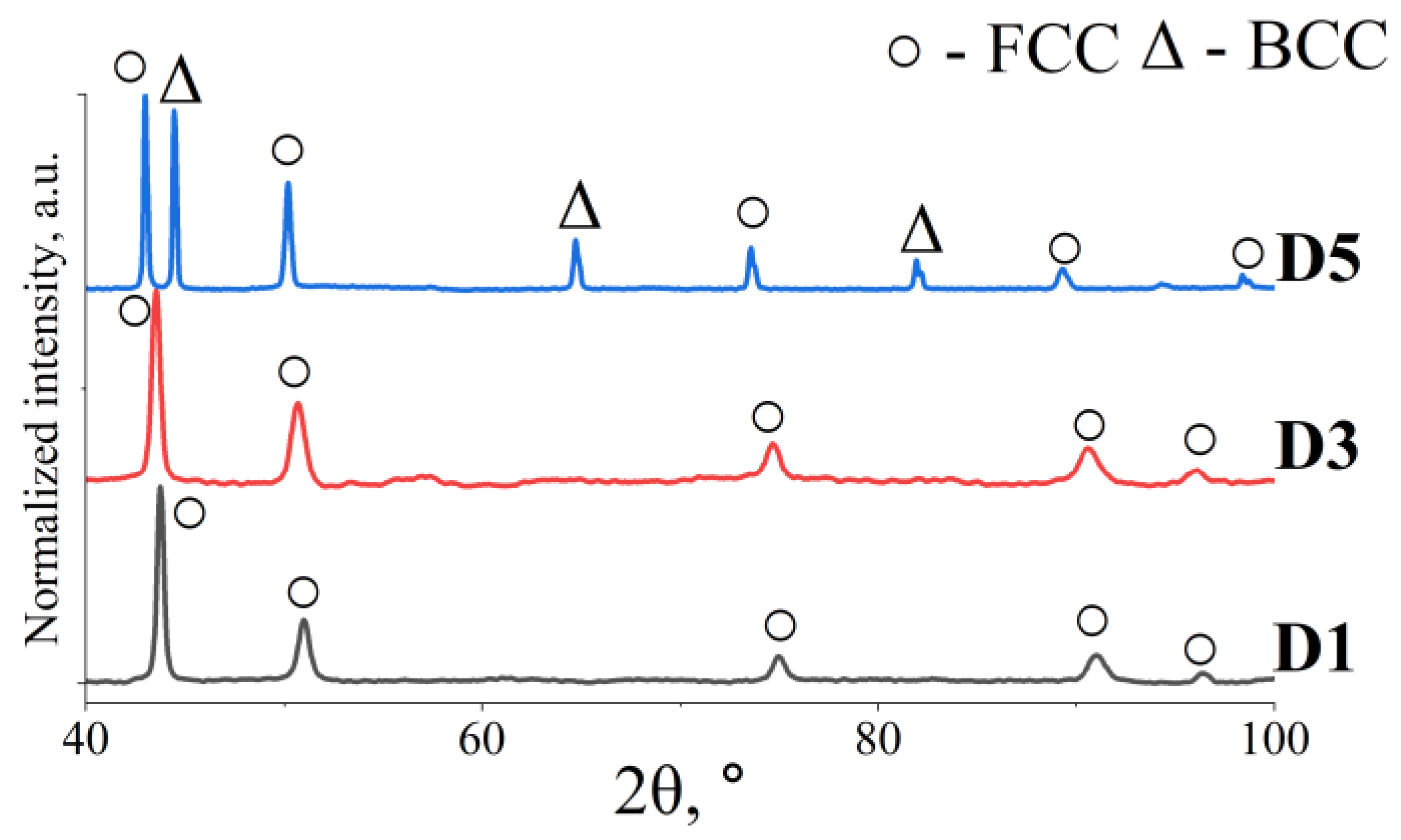
3.1. Microstructure of the Fabricated HEAs
3.2. Mechanical Properties of the High Entropy D1, D3 and D6 Alloys at Room Temperature
3.2.1. Hardness and Tensile Test
3.2.2. Impact Test
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- -
- Variations in Al and Cu content significantly affect the microstructure and mechanical properties of the three HEA from the AlCoCuFeNi group.
- -
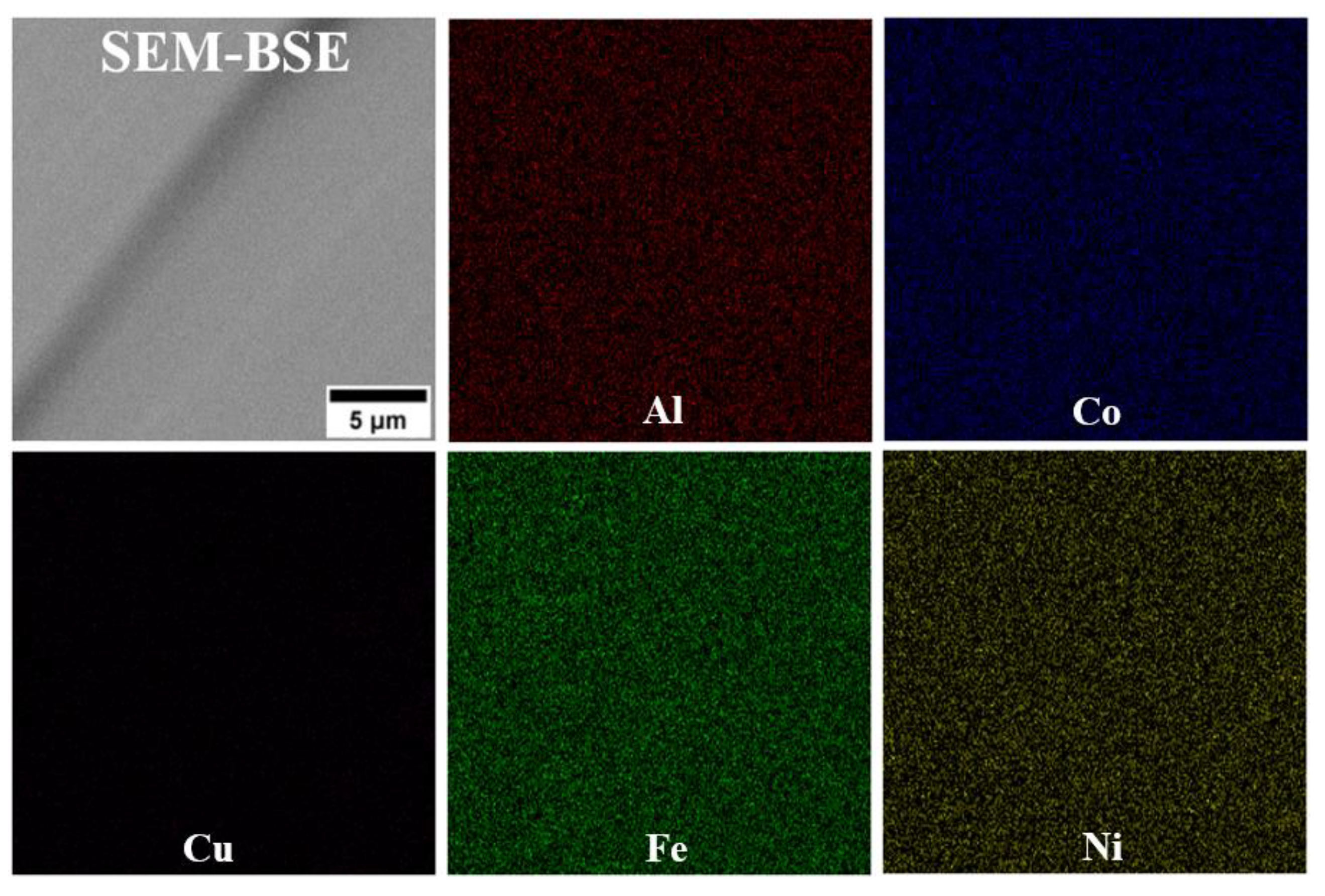
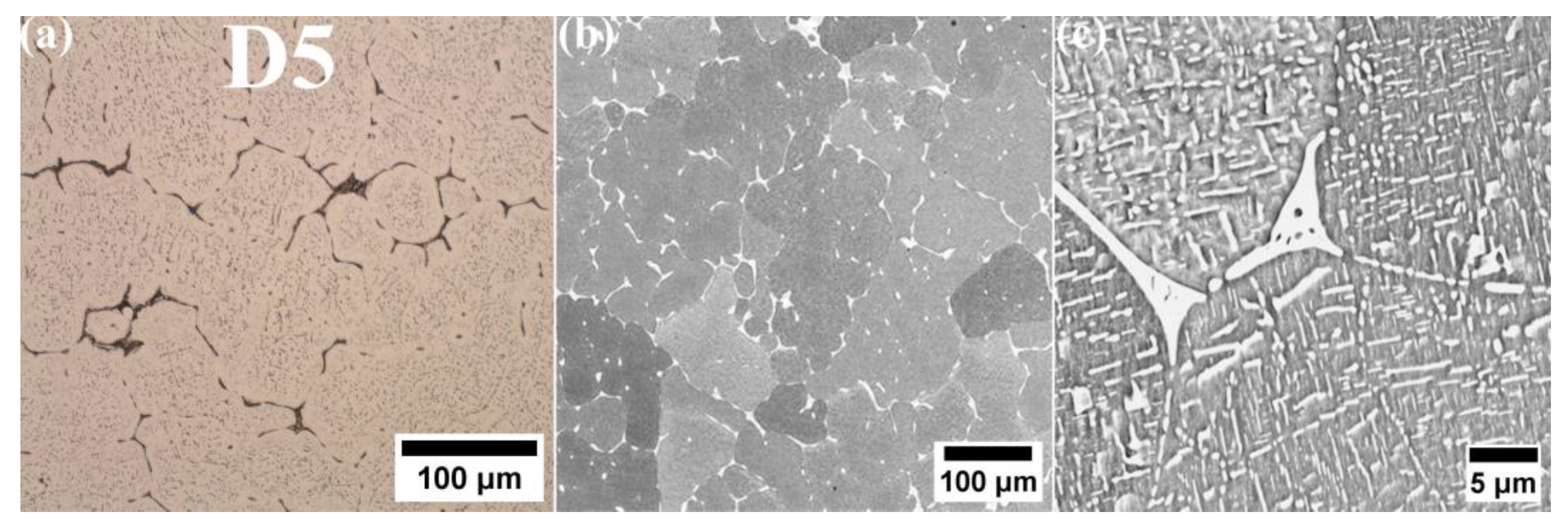
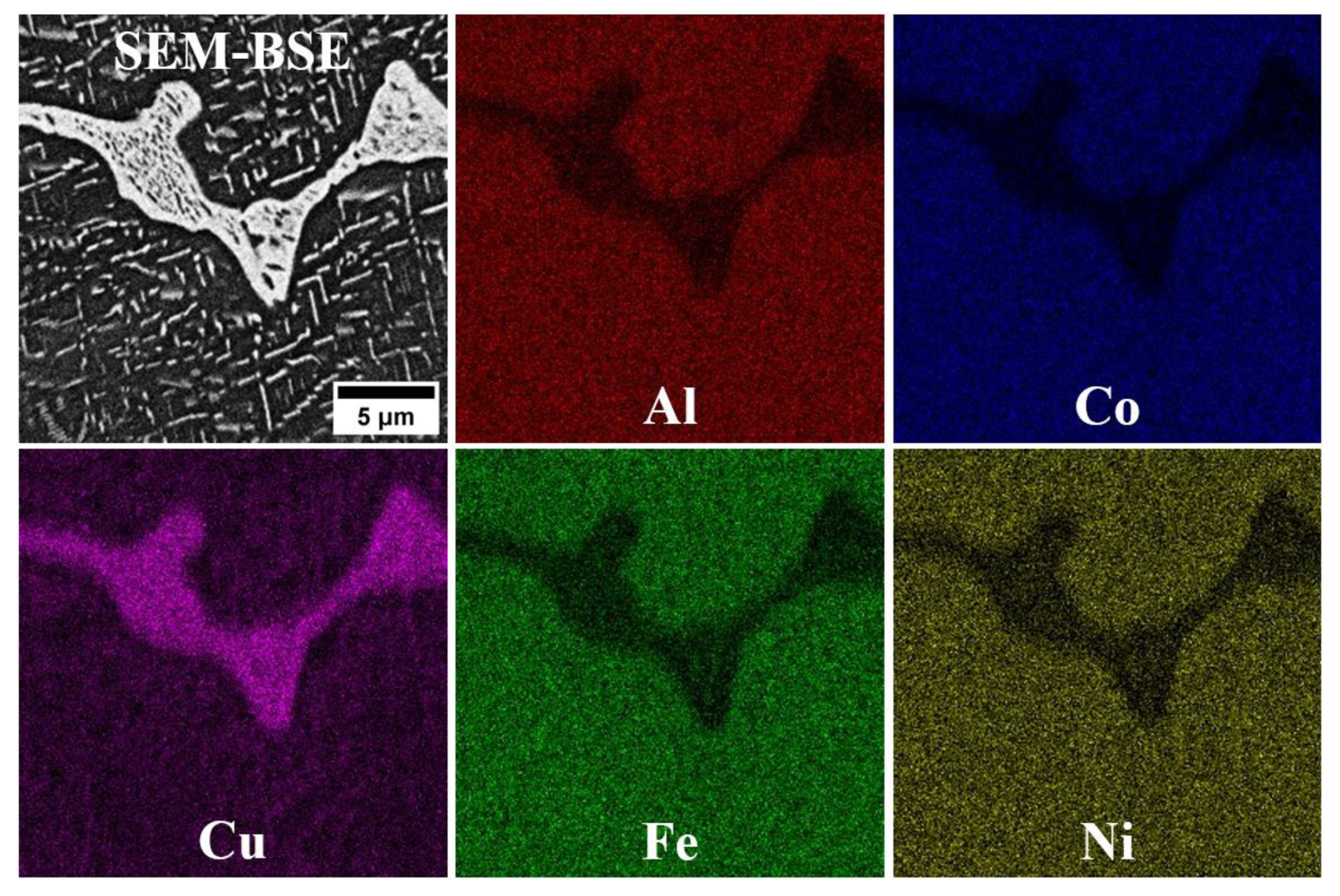
- In the microstructure of the equiatomic D5 alloy, the two phases exhibit distinct chemical compositions and hardness. The SEM-EDS analysis indicates that Al and Cu tend to segregate significantly, whereas Co shows the least susceptibility to segregation.
- -
- In D3 alloy, where the Al content increased to 13.33% while keeping the Cu content comparable to that of the D1 alloy, an enhancement in the mechanical properties was observed when compared to D1 (Rm = 466 MPa and Rp0.2 = 221 MPa). This was achieved while also maintaining satisfactory elongation of 60.6%. However, it was noted that the impact energy of D3 alloy was 20 J lower than that of D1 alloy.
- -
- The equimolar alloy D5 exhibited the lowest strength and impact energy.
- -
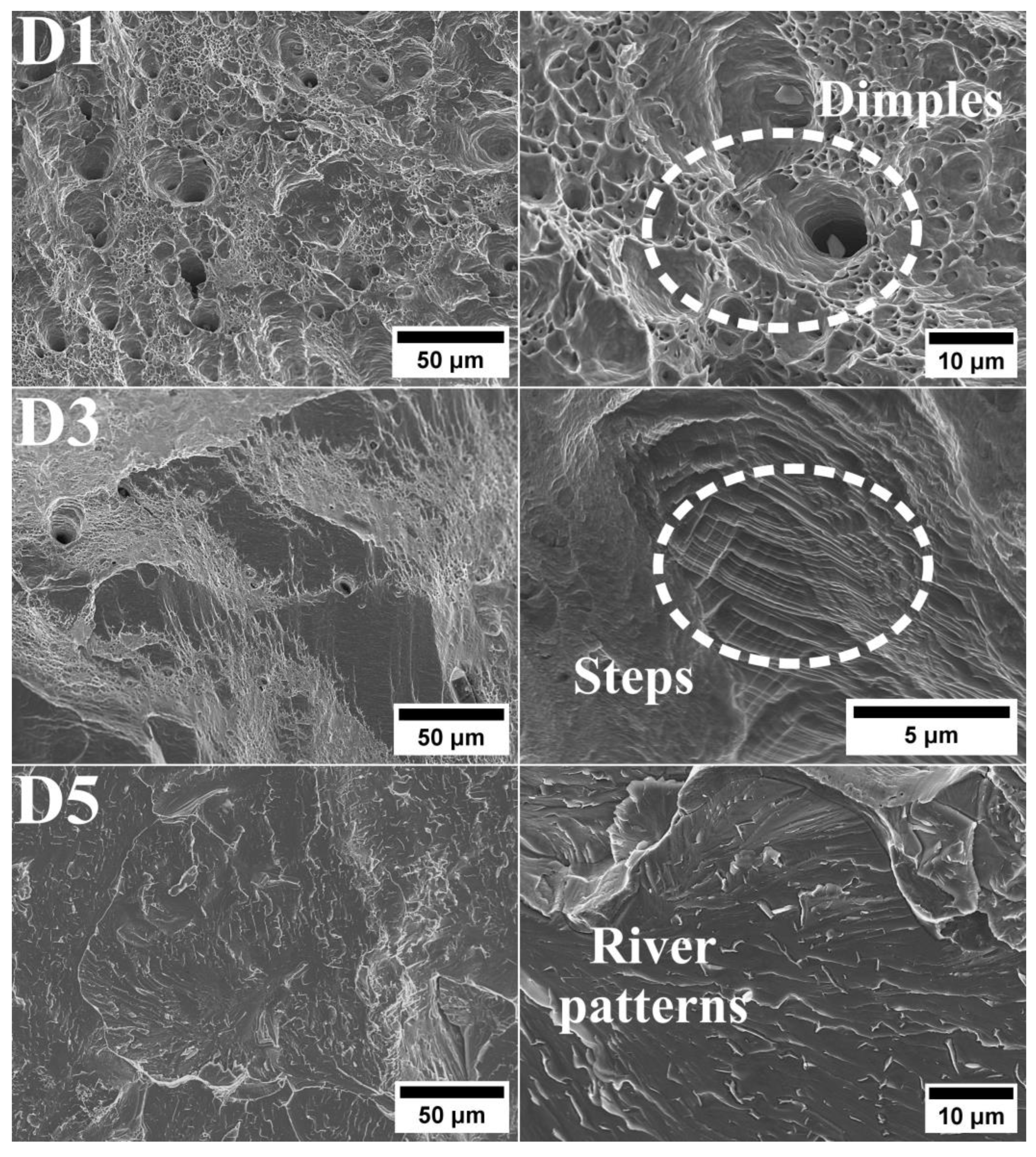
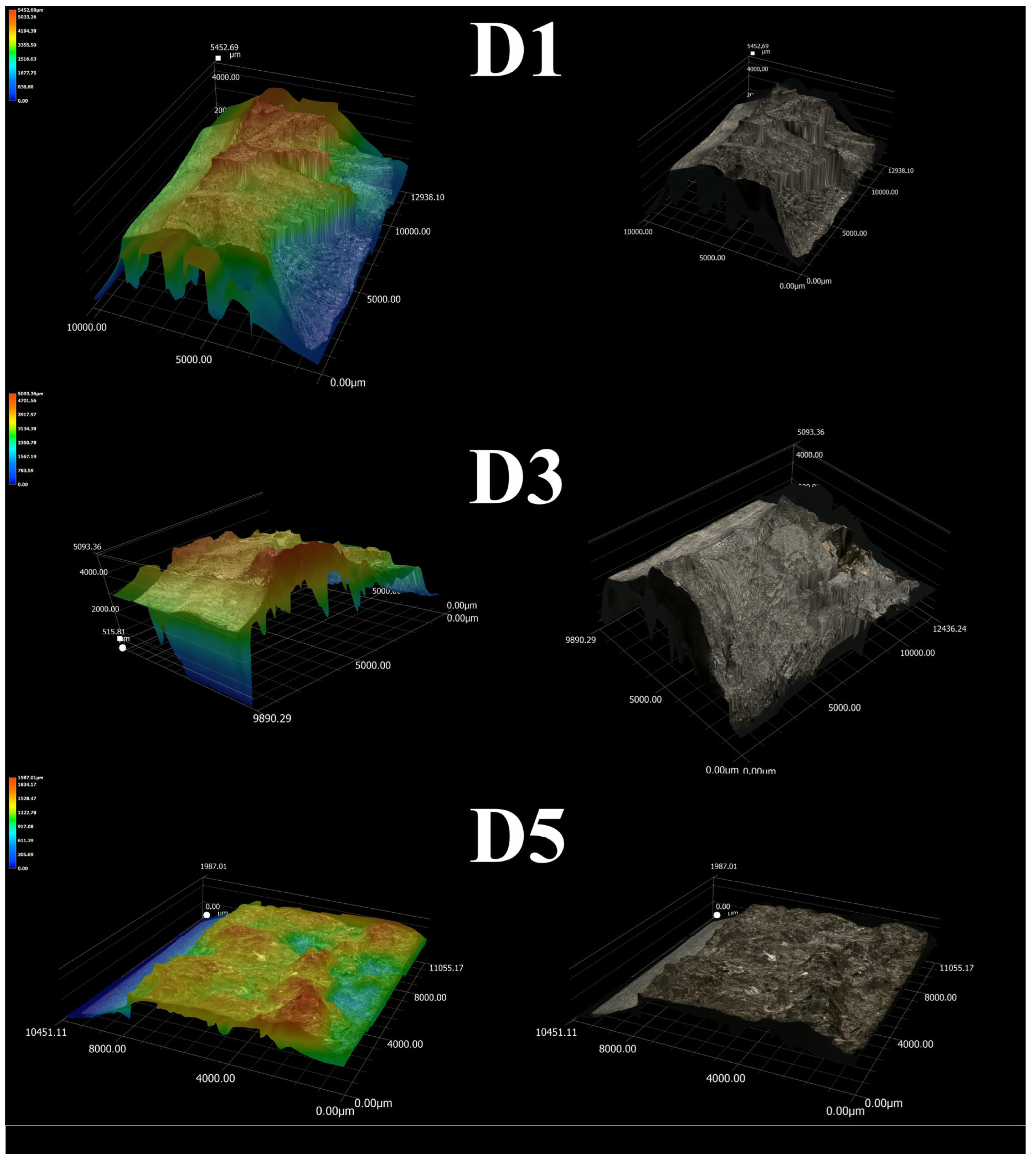
- Fractographic analysis confirmed the brittle nature of the fracture in D5 alloy. In contrast, D1 and D3 alloys exhibited larger areas of ductile fractures characterized by prominent dimples.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yeh, J.W.; Chen, S.K.; Lin, S.J.; Gan, J.Y.; Chin, T.S.; Shun, T.T.; Tsau, C.H.; Chang, S.Y. Nanostructured High-Entropy Alloys with Multiple Principal Elements: Novel Alloy Design Concepts and Outcomes. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2004, 6, 299–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantor, B.; Chang, I.T.H.; Knight, P.; Vincent, A.J.B. Microstructural Development in Equiatomic Multicomponent Alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2004, 375–377, 213–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Y.F.; Wang, Q.; Lu, J.; Liu, C.T.; Yang, Y. High-Entropy Alloy: Challenges and Prospects. Mater. Today 2016, 19, 349–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Zhou, X.; Wang, W.; Liu, B.; Lv, Y.; Yang, W.; Xu, D.; Liu, Y. A Review on Fundamental of High Entropy Alloys with Promising High–Temperature Properties. J. Alloys Compd. 2018, 760, 15–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, M.H.; Yeh, J.W. High-Entropy Alloys: A Critical Review. Mater. Res. Lett. 2014, 2, 107–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.; Yang, Y. On Lattice Distortion in High Entropy Alloys. Front. Mater. 2018, 5, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kucza, W.; Dąbrowa, J.; Cieślak, G.; Berent, K.; Kulik, T.; Danielewski, M. Studies of “Sluggish Diffusion” Effect in Co-Cr-Fe-Mn-Ni, Co-Cr-Fe-Ni and Co-Fe-Mn-Ni High Entropy Alloys; Determination of Tracer Diffusivities by Combinatorial Approach. J. Alloys Compd. 2018, 731, 920–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, B.X.; Wang, C.; Yang, T.; Liu, C.T. Cocktail Effects in Understanding the Stability and Properties of Face-Centered-Cubic High-Entropy Alloys at Ambient and Cryogenic Temperatures. Scr. Mater. 2020, 187, 250–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Fu, L.; Peng, J.; Zheng, H.; Ji, X.; Sun, Y.; Ma, S.; Shan, A. Improving Mechanical Properties of an FCC High-Entropy Alloy by Γ′ and B2 Precipitates Strengthening. Mater. Charact. 2020, 159, 109989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shun, T.T.; Du, Y.C. Microstructure and Tensile Behaviors of FCC Al0.3CoCrFeNi High Entropy Alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2009, 479, 157–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Baker, I. Interstitial Strengthening of a f.c.c. FeNiMnAlCr High Entropy Alloy. Mater. Lett. 2016, 180, 153–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, I. Understanding the Deformation Mechanisms of FeNiMnAlCr High Entropy Alloys; Dartmouth College: Hanover, NH, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, M.; Yang, C.; Kuijer, M.; Baker, I. Enhanced Mechanical Properties of Carbon-Doped FeNiMnAlCr High Entropy Alloy via Hot-Rolling. Mater. Charact. 2019, 158, 109983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Liaw, P.K.; Zhang, Y. Recent Progress with BCC-Structured High-Entropy Alloys. Metals 2022, 12, 501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senkov, O.N.; Wilks, G.B.; Miracle, D.B.; Chuang, C.P.; Liaw, P.K. Refractory High-Entropy Alloys. Intermetallics 2010, 18, 1758–1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, B.; Lee, J.; Ryu, H.J.; Hong, S.H. Ultra-High Strength WNbMoTaV High-Entropy Alloys with Fine Grain Structure Fabricated by Powder Metallurgical Process. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2018, 712, 616–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.; Maiti, S.; Steurer, W.; Spolenak, R. Size-Dependent Plasticity in an Nb25Mo25Ta25W25 Refractory High-Entropy Alloy. Acta Mater. 2014, 65, 85–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Z.; Mo, J.; Shen, B.; Liang, X. Structures and Properties of the (NbMoTaW)100−xCx High-Entropy Composites. J. Alloys Compd. 2021, 889, 161645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raabe, D.; Tasan, C.C.; Springer, H.; Bausch, M. From High-Entropy Alloys to High-Entropy Steels. Steel Res. Int. 2015, 86, 1127–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godoy, C.; Paula E Silva, E.M. Strain Aging: Cribb/Reed-Hill’s Model Applied to the FeMnAlSiC Austenitic System. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2001, 32, 2271–2277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Mayweg, D.; Ponge, D.; Li, Z. Microstructure and Deformation Behavior of Two TWIP/TRIP High Entropy Alloys upon Grain Refinement. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2021, 802, 140661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, D.; Li, X.; Jiang, J.; Heng, W.; Koizumi, Y.; Choi, W.-M.; Lee, B.-J.; Kim, H.S.; Kato, H.; Chiba, A. Novel Co-Rich High Performance Twinning-Induced Plasticity (TWIP) and Transformation-Induced Plasticity (TRIP) High-Entropy Alloys. Scr. Mater. 2019, 165, 39–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Yan, D.; Lu, W.; Li, Z. A TWIP-TRIP Quinary High-Entropy Alloy: Tuning Phase Stability and Microstructure for Enhanced Mechanical Properties. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2021, 801, 140441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayyagari, A.; Hasannaeimi, V.; Grewal, H.S.; Arora, H.; Mukherjee, S. Corrosion, Erosion Andwear Behavior of Complex Concentrated Alloys: A Review. Metals 2018, 8, 603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Q.; Chen, C.; Fan, C.; Liu, Z.; Cai, X.; Lin, S.; Yang, C. AlCoCrFeNi High-Entropy Alloy Coatings Prepared by Gas Tungsten Arc Cladding: Microstructure, Mechanical and Corrosion Properties. Intermetallics 2021, 138, 107337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagy, P.; Rohbeck, N.; Roussely, G.; Sortais, P.; Lábár, J.L.; Gubicza, J.; Michler, J.; Pethö, L. Processing and Characterization of a Multibeam Sputtered Nanocrystalline CoCrFeNi High-Entropy Alloy Film. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2020, 386, 125465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ustinov, A.I.; Demchenkov, S.A.; Melnychenko, T.V.; Skorodzievskii, V.S.; Polishchuk, S.S. Effect of Structure of High Entropy CrFeCoNiCu Alloys Produced by EB PVD on Their Strength and Dissipative Properties. J. Alloys Compd. 2021, 887, 161408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onawale, O.T.; Cobbinah, P.V.; Nzeukou, R.A.; Matizamhuka, W.R. Synthesis Route, Microstructural Evolution, and Mechanical Property Relationship of High-Entropy Alloys (HEAs): A Review. Materials 2021, 14, 3065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, X.-W. Microstructure and Properties of AlCrFeNiCoCu High Entropy Alloy Prepared by Powder Metallurgy. J. Alloys Compd. 2013, 555, 246–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdogan, A.; Günen, A.; Gök, M.S.; Zeytin, S. Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Borided CoCrFeNiAl0.25Ti0.5 High Entropy Alloy Produced by Powder Metallurgy. Vacuum 2021, 183, 109820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Güler, S.; Alkan, E.D.; Alkan, M. Vacuum Arc Melted and Heat Treated AlCoCrFeNiTiX Based High-Entropy Alloys: Thermodynamic and Microstructural Investigations. J. Alloys Compd. 2022, 903, 163901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, J.; Jarvis, T.; Wu, X.; Stanford, N.; Hodgson, P.; Fabijanic, D.M. Comparative Study of the Microstructures and Mechanical Properties of Direct Laser Fabricated and Arc-Melted AlxCoCrFeNi High Entropy Alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2015, 633, 184–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, C.-J.; Chen, Y.-L.; Yeh, J.-W.; Lin, S.-J.; Chen, S.-K.; Shun, T.-T.; Tsau, C.-H.; Chang, S.-Y. Microstructure Characterization of Alx CoCrCuFeNi High-Entropy Alloy System with Multiprincipal Elements. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2005, 36, 881–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nong, Z.; Zhang, Z.-P.; Wang, H.-N.; Deng, X.-G. Microstructure Inhomogeneity of As-Cast High-Entropy Alloy and Heat Treatment Improvement. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2019, 35, 1749–1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Y.F.; Wang, Q.; Zhao, Y.L.; He, Q.F.; Lu, J.; Yang, Y. Elemental Segregation in Solid-Solution High-Entropy Alloys: Experiments and Modeling. J. Alloys Compd. 2016, 681, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Collins, L.; Feng, R.; Zhang, C.; Balke, N.; Liaw, P.K.; Yang, B. Homogenization of AlxCoCrFeNi High-Entropy Alloys with Improved Corrosion Resistance. Corros. Sci. 2018, 133, 120–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jablonski, P.D.; Licavoli, J.J.; Gao, M.C.; Hawk, J.A. Manufacturing of High Entropy Alloys. JOM 2015, 67, 2278–2287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Wu, H.; Liu, B.; Shan, Q.; Guo, S.; Jiao, Z.; Baker, I. A Novel L12-Strengthened AlCoCuFeNi High-Entropy Alloy with Both High Hardness and Good Corrosion Resistance. Mater. Lett. 2023, 331, 133339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chrzan, K.; Kalandyk, B.; Grudzień-Rakoczy, M.; Rakoczy, Ł.; Cichocki, K. Abrasive Wear Resistance of High-Entropy AlCoCuFeNi Alloy in SiC Mixture. Arch. Foundry Eng. 2024, 24, 123–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Alloy Variant | Elements Content, at. % | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Al | Cu | Co | Fe | Ni | |
| D1 | 7.14 | 7.14 | 28.57 | 28.57 | 28.57 |
| D3 | 13.33 | 6.66 | 26.66 | 26.66 | 26.66 |
| D5 | 20.00 | 20.00 | 20.00 | 20.00 | 20.00 |
| Chemical Element | Purity (%) |
|---|---|
| Al | 99.9 |
| Co | 99.95 |
| Cu | 99.99 |
| Fe | 99.9 |
| Ni | 99.95 |
| Alloy | Heating | Cooling | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dissolution of Precipitates | TS | TL | Formation of Precipitates | TS | TL | |
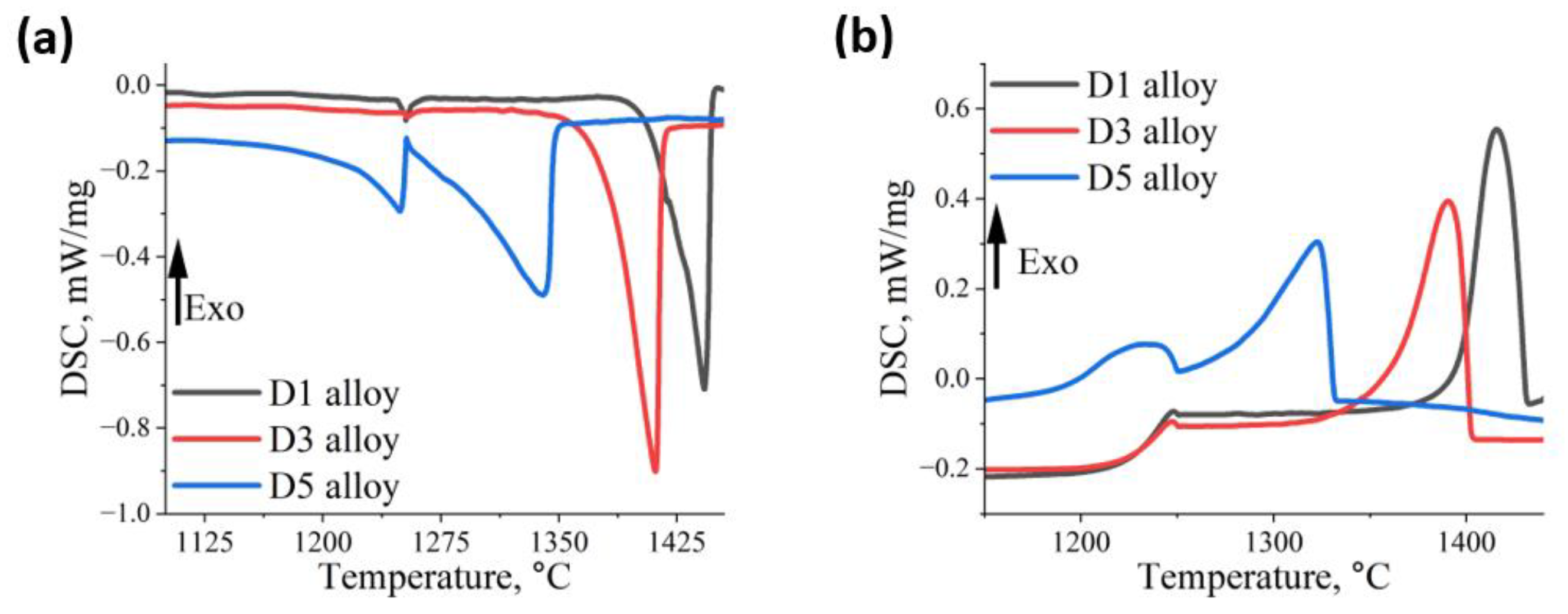
| D1 | 1253 | 1385 | 1442 | 1248 | 1361 | 1415 |
| D3 | 1253 | 1335 | 1411 | 1247 | 1317 | 1390 |
| D5 | 1248 | 1129 | 1340 | 1230 | 1187 | 1322 |
| Element Phase | Al | Co | Cu | Fe | Ni |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bright | 12.3 (±0.3) | 21.9 (±0.1) | 23.7 (±0.3) | 23.5 (±0.1) | 18.5 (±0.1) |
| Dark | 23.5 (±0.2) | 22.4 (±0.1) | 10.6 (±0.1) | 19.4(±0.2) | 24.1 (±0.1) |
| Alloy | Rp0.2, MPa | Rm, MPa | E, GPa | A, % |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| D1 | 171.0 (±30.0) | 369.0 (±24.9) | 184.0 (±1.4) | 49.6 (±11.9) |
| D3 | 271.7 (±13.8) | 465.7 (±17.6) | 120.6 (±8.7) | 60.6 (±6.1) |
| D5 | 25.1 (±10.2) | 27.2 (±9.4) | 28.8 (±8.4) | 0.1 (±0.03) |
| Alloy Variant | D1 | D3 | D5 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Impact energy, [J] | 172.7 (±14.1) | 151.3 (±11.8) | 1.5 (±0.1) |
| Impact toughness, [J/cm2] | 215.9 (±31.7) | 189.1 (±22.5) | 1.9 (±0.1) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chrzan, K.; Kalandyk, B.; Grudzień-Rakoczy, M.; Rakoczy, Ł.; Cichocki, K.; Żuczek, R.; Kateusz, F.; Bętkowska, A.; Polkowska, A.; Kasińska, J. Al and Cu Effect on the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of HEA Based on the AlCoCuFeNi System. Materials 2025, 18, 4564. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18194564
Chrzan K, Kalandyk B, Grudzień-Rakoczy M, Rakoczy Ł, Cichocki K, Żuczek R, Kateusz F, Bętkowska A, Polkowska A, Kasińska J. Al and Cu Effect on the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of HEA Based on the AlCoCuFeNi System. Materials. 2025; 18(19):4564. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18194564
Chicago/Turabian StyleChrzan, Konrad, Barbara Kalandyk, Małgorzata Grudzień-Rakoczy, Łukasz Rakoczy, Kamil Cichocki, Robert Żuczek, Filip Kateusz, Aleksandra Bętkowska, Adelajda Polkowska, and Justyna Kasińska. 2025. "Al and Cu Effect on the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of HEA Based on the AlCoCuFeNi System" Materials 18, no. 19: 4564. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18194564
APA StyleChrzan, K., Kalandyk, B., Grudzień-Rakoczy, M., Rakoczy, Ł., Cichocki, K., Żuczek, R., Kateusz, F., Bętkowska, A., Polkowska, A., & Kasińska, J. (2025). Al and Cu Effect on the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of HEA Based on the AlCoCuFeNi System. Materials, 18(19), 4564. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18194564








